Midwest - EDT
Environmental Decision Toolkit
- EDT Projects
- National
- Regional
- Place Based
Introduction
The Midwest Environment Data Toolkit (MW-EDT) is under development and will ultimately be a user-friendly and interactive web-based software application that informs the user about the environmental and socioeconomic condition of a specific watershed or group of watersheds within the region.
The application will also place a user selected watershed into the larger context of the region to allow the user to simply and easily compare indicators across the region.
Objectives
The MW-EDT is being designed according to client input regarding key assessment questions and issues in the Midwest and Great Lakes Basin. The goal is to statistically integrate data on environmental condition, sensitivity, and risk of future impacts from multiple stresses and translate this information into measures of relative vulnerability across the geographic region.
The integration techniques will involve combinations of fuzzy set theory, multivariate statistics, and hierarchical decision theory, along with possible others. There is a need to illustrate these techniques visually and in written text oriented for an informed lay audience (e.g. biologists, environmental decision makers) to facilitate understanding and acceptance of a suite of techniques that are being developed, evaluated, and demonstrated through this research program.
To accomplish these goals the objectives of MW-EDT are to:
- The MW-EDT is largely a form of outreach and envisions three types of users:
- Public
- Management
- Technical
- Develop a tool to support policy and interagency strategic planning at the regional management level.
- Design a tool for management use which would address comprehensive planning efforts, particularly as they pertain to the Wisconsin comprehensive planning law.
Data & Methods
Public
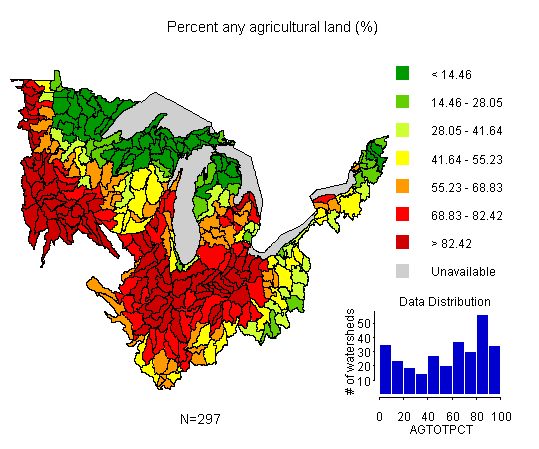 In its final form, the public will be able to query the MW-EDT and view various indicators over the entire region - in this case percent agricultural land.
In its final form, the public will be able to query the MW-EDT and view various indicators over the entire region - in this case percent agricultural land.The public user will be able to view various indicators and indices of water quality, air quality, biological diversity, and quality of life at both the 8-digit and possibly the 12-digit hydrologic unit code (HUC) scale (see figure to the right). In addition, the user will have access to basic descriptive statistics about a reporting unit (e.g., the distribution of land cover types). The desired outcome is increased public awareness and ultimately, increased involvement in activities that improve the condition of a watershed or group of watersheds in the Midwest region.
Management
A second group of users encompasses employees within state and federal agencies such as the EPA, the International Joint Commission (IJC), and the Great Lakes Commission (GLC). To support multiple users, multiple objectives and several key capabilities were identified as important for the management end user portion of the Midwest EDT. The ability to track the performance of various activities such as restoration actions and Best Management Practices (BMPs) implementation was identified as a critical goal. "What-if" scenarios (for an example see scenarios developed for the MAIA-EDT) could be an integral component in supporting regional decision-making by enabling decision-makers to see the potential impacts of various actions such as reducing agriculture on steep slopes and increasing riparian buffers. Specifically, users could assess the allocation of resources among watersheds and the affects of urban sprawl on water quality and habitat (e.g., L-THIA modeling). Finally, clients identified a "sister watershed" approach in which management users would have the ability to identify reporting units with similar issues and problems in order to facilitate cooperative problem-solving and information sharing among different organizations.
Technical
The third user group is comprised of technical users such as data analysts, programmers, and database managers. The key functionality of the EDT as pertains to these users is the interoperability of the EDT with proposed web services including online versions of EPA's landscape analysis tool called Analytical Tools Interface for Landscape Assessments (ATtILA) and the Digital Watershed. In addition, the technical user should have the ability to upload his/her own data and take advantage of ReVA’s robust statistical integration methods. Further, the technical user is expected to be knowledgeable in the creation of new indices as well as the exploration of interactions among individual indicators.
Partners
EPA Region 5 (EPA R5), Great Lakes National Program Office (GLNPO), the International Joint Commission (IJC ![]() ), and the Great Lakes Commission (GLC
), and the Great Lakes Commission (GLC ![]() ).
).
![[logo] US EPA](../gif/logo_epaseal.gif)