Pacific Southwest, Region 9
Serving: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Pacific Islands, 148 Tribes
Tribal Successes in 2003
Note: EPA no longer updates this information, but it may be useful as a reference or resource.

Tribes take the lead
2003 marked the 10-year anniversary of EPA's Indian Environmental General Assistance Program (GAP). Ninety percent of the Pacific Southwest Region's 146 tribes receive GAP grants, and more than half have EPA-approved authority, equivalent to that of a state, to carry out one or more federal environmental programs. Work funded by 527 GAP grants, totaling over $111 million, was underway in the region in 2004.
Where the tribes' environmental programs are not yet sufficiently developed, EPA retains primary responsibility. Working as partners, the tribes and EPA have made significant progress in protecting tribal lands, waters, and cultural resources (see links below). The tribes have also forged productive partnerships with other agencies and neighboring communities.

- Solid Waste Management
Tribes closed and cleaned up open dumps, abandoned cars
- Hazardous Waste Cleanup
Tribes, EPA oversaw over 100 underground tank cleanups; progress at five Superfund sites
- Safe Drinking Water, Clean Waterways
Tribes used EPA grants to build and maintain safe drinking water, wastewater treatment facilities - Air Quality
Tribes used EPA grants to assess air quality
- Pesticides and Toxics Regulation
Twenty-three tribes regulate pesticides on over 22 million acres of land - Natural and Cultural Resource Successes
Tribes' achievements in cultural preservation, environmental education, and outreach
Plan for 2004
Every year, EPA's Pacific Southwest Tribal Program designs a plan (called an "operating plan") for the upcoming year. Highlights of the plan are viewable at the bottom of each "Tribal Successes" Web page.
- EPA will help 131 tribes in the Pacific Southwest build and maintain tribal environmental programs.
- More than one-third of the homes on reservations in the Pacific Southwest are at or below the poverty level.
- 27% of tribal homes in the region lack complete plumbing.
- Nearly one-half of tribal drinking water systems in the region fail to meet Safe Drinking Water Act requirements.
- There are more than 700 open dumps on reservation lands in the region.
- Over one-third of the region's tribes breathe air that does not meet national health standards.
Tribes in the Pacific Southwest
Of the 146 Indian tribes in the Pacific Southwest Region, more than 130 are now working with EPA to meet the unique challenges of environmental protection in Indian Country. Indian lands account for 11% of the region's land area and are home to about 400,000 people.
The tribes range from the Navajo Nation, largest in the U.S., with over 200,000 members and over 27,000 square miles, to tribes with less than a thousand members and under 50 acres.
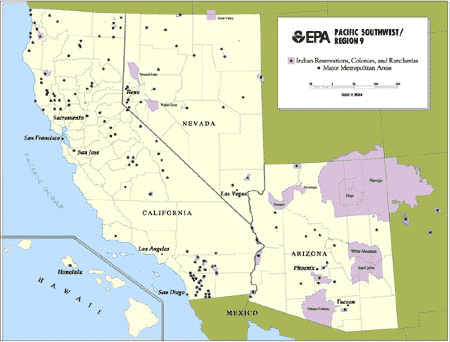
EPA's Pacific Southwest Region includes the States of Arizona, California, Hawaii and Nevada; 146 tribal nations and communities; and Pacific islands such as American Samoa, Guam, and the Northern Mariana Islands. Map shows boundaries of states, counties and tribal lands.
Information archive
| Pacific Southwest NewsroomPacific Southwest Programs | Grants & FundingUS-Mexico Border | Media Center Careers | About EPA Region 9 (Pacific Southwest)A-Z Index |