Water Energy

If you've ever stood in a fast–moving stream, under a waterfall, or on the ocean shore as waves come crashing in, then you've felt the power of the water. The energy from moving water can be used to create electricity in several different ways. For example:
- A hydroelectric dam captures energy from the movement of a river. Dam operators control the flow of water and the amount of electricity produced. Dams create reservoirs (large bodies of calm water) behind them, which can be used for recreation, wildlife sanctuaries, and sources of drinking water.
- Wave power captures energy from waves on the surface of the ocean using a special buoy or other floating device.
- Tidal power captures the energy of flowing waters with the help of turbines as tides rush in and out of coastal areas.
How It Works
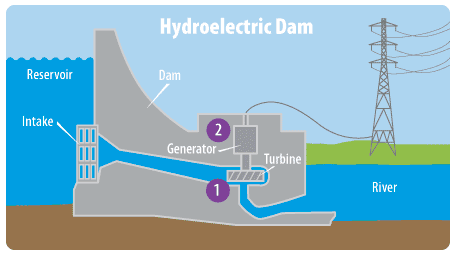
- Flowing water turns a water wheel or turbine.
- A generator attached to the turbine produces electricity.
Cool Facts
- A natural wonder! Did you know that one of the world's great natural wonders has been generating electricity for more than 100 years? Today, Niagara Falls is the biggest electricity producer in New York State, generating enough electricity to light 24 million 100–watt bulbs at once!
- Leading the way. Hydropower is the leading renewable energy source used to generate electricity in the United States.
- Wave of the future. The first commercial U.S. power station using ocean waves to generate electricity is in the works in Oregon. When finished, 10 “powerbuoys” in the ocean will generate enough electricity to power 1,000 homes.