Pacific Southwest, Region 9
Serving: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Pacific Islands, 148 Tribes
Tribal Successes and Challenges: Air Quality
Note: EPA no longer updates this information, but it may be useful as a reference or resource.

Smoke from forest fire, Hoopa Valley
Reservation
Tribes set up air monitoring stations to measure pollution
As of late 2002, twenty-six tribes received EPA funding for air quality programs. There were 42 air monitoring stations at 23 tribal sites.
- EPA and the Navajo Nation took enforcement action against a major oil company for Clean Air Act, Oil Pollution Act, and Community Right-to-Know violations at the Aneth Oil Field on the Navajo Nation. The company paid over $600,000 in penalties and over $500,000 to improve drinking water and sanitation facilities and buy emergency response equipment for the Navajo Nation.
- The Yurok Tribe of northwestern California used EPA funds and equipment from EPA’s lab in Las Vegas, Nev., to build a weather station.
Remaining Challenges
- Of the 147 tribes in the Pacific Southwest, 58 live in areas that do not meet federal clean air standards.
- Most major air pollution sources in these areas are off-reservation and not subject to tribal jurisdiction.
- Many tribes still lack air monitoring data and trained air quality staff.
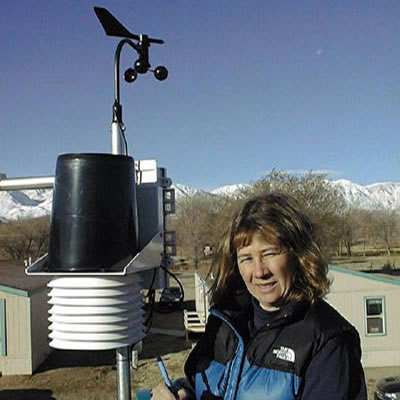 Bishop Paiute Tribe air monitoring
station
Bishop Paiute Tribe air monitoring
station| Pacific Southwest NewsroomPacific Southwest Programs | Grants & FundingUS-Mexico Border | Media Center Careers | About EPA Region 9 (Pacific Southwest)A-Z Index |