ReefLink Database

Shoreline Protection
Shoreline Protection is the attenuation of wave energy by reefs that protects coastal communities against shoreline erosion and flooding during storms, hurricanes, and tsunamis that can cause property damage and loss of life.
CMap
CMap Description
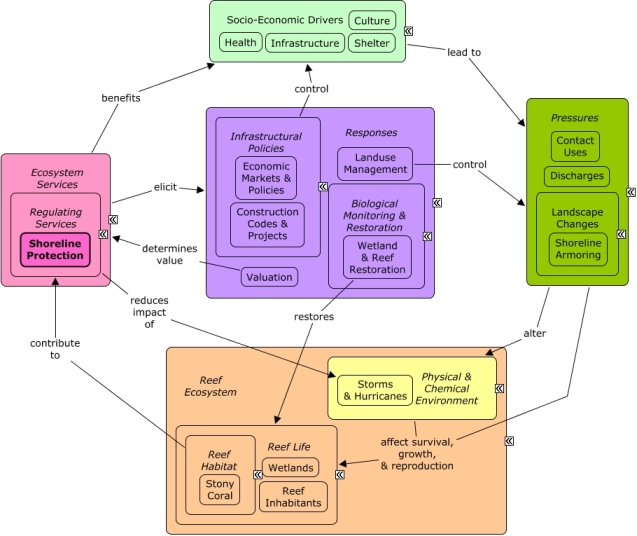
Waves encountering reefs experience significant reductions in wave height and wave energy. Wave attenuation benefits coastal communities by reducing erosion of beaches, and reducing potential damage to property and loss of life during natural hazards, such as storms, hurricanes, or tsunamis. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that benefit from shoreline protection also create pressures on the reef through coastal development, pollution, and harvesting. Valuation methods and finance and insurance policies can be used to determine the value of shoreline protection in the presence of reefs. Landuse management, including zoning and construction codes, can reduce the risk of damage from flooding events and the dependence on shoreline protection. Artificial breakwaters can be constructed to replace or supplement natural reefs.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitor & Research: Research Global Change | This management option involves research to examine the effects of stresses associated with global change on the ecosystem. Stresses can include changes in temperature, hydrology, salinity, frequency and intensity of storms, turbidity, sea level change, and ultra violet and visible radiation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Regulating Services; Salinity; Sea Temperatures; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Research and Monitor Wetlands | This management option involves monitoring and research of mangroves, both for biotic and abiotic factors. Some biotic factors include disease, species, invasive species, abundance, age and leaf litter. Important abiotic factors include sedimentation rates, types and causes of turbidity, and soil chemistry. The activity would document changes to the extent of mangrove vegetation by using historical aerial photography and other records. Wetland nutrient and contaminant processing productivity depends on maintaining a balance and not exceeding thresholds. There remain many unknowns in wetland restoration as to optimal capacity and how to achieve this. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Primary Production; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Restoration: Beach Renourishment and Nourishment | Beaches are subject to natural accretion and erosion. Tourism is often best supported by wide, accessible, public sandy beaches. Beaches can be restored to counteract natural erosion by transporting large quantities of sand onto the beach. This sand often comes from nearby dredging. Caution should be used when restoring long sections of beaches, as often the area above the mean high tide line is littoral, or privately owned, and restoration of these beaches can impact these property rights, see "Stop the Beach Renourishment, Inc. v. Florida Department of Environmental Protection (2010) U.S. Supreme Court decision." Beach protection or nourishment offers an alternative to this often expensive and abrupt type of renourishment, nourishment involves practices which encourage coastal accretion and discourage erosional forces. See "Florida's Beach and Shore Preservation Act" for some restrictions on this. | NOAA Coastal Services Center. Beach Nourishment: A Guide for Local Government Officials. Coastal Services Center Accessed 6/17/2011. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Culture; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Recreational Opportunities; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chapter 3: Trees and vegetation next to waterways, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Establishes buffer zone for protecting natural watercourses from vegetation clearing. The buffer zone either 30 feet from the center of the natural watercourse, or 25 feet from its edge, whichever is greater. Application to Coral Reefs:Assists in erosion control and can protect reefs from harmful sedimentation, if the stream or river sediment is capable of reaching the coral reef. Vegetation along river and stream banks will remove nutrients and assist in preventing eutrophocation of waters that can reach coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Enforcement is by conservation officers with assistance from local police when required. Penalties are fines of not more than $100, or 180 days in jail, or both Comments:Permits can be obtained if the purpose of clearing is for development. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management; Shoreline Protection; Wetlands |
| Conceptual Agency Review, 62-029 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter is limited in application to dredge and fill permit applications for projects in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District which, pursuant to Section 373.4145, F.S., are to be reviewed and processed under the rules authorized and adopted under Sections 403.91-.929, F.S. (1984 Supp.), as amended.
(1) The purpose of this rule is to establish those procedures applicable to review of requests for conceptual agency review pursuant to Section 380.06(9), F.S., for projects that undergo development of regional impact review (DRIs).
(2) Conceptual agency review is a licensing action and approval or denial shall constitute final agency action.
(3) Under this rule, applicants who must obtain construction or operation permits for potential sources of water pollution or for dredging and filling activities may apply for conceptual agency review of certain aspects of a proposed development, including the location, densities, intensity of use, character and major design features. Application to Coral Reefs:Limited to projects in Northwest Florida. Legislative Actions:The legislation applies only to dredge and fill projects in the area of the Northwest Florida Water Mkanagement District. Comments:The purpose of this rule is to establish those procedures for dredge and fill permit applications for projects in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District that require conceptual agency review of certain aspects of a proposed development, including the location, densities, intensity of use, character and major design features. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Joint Coastal Permits and Concurrent Processing of Proprietary Authorizations, 62B-049 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. In the event that there is a conflict between the procedural requirements of this chapter and other procedural rules promulgated pursuant to the referenced statutes, then this chapter shall govern. The standards and criteria for issuance of joint coastal permits include the criteria for environmental resource or wetland resource permits pursuant to Chapter 62-312, F.A.C., and the rules adopted under Chapter 62-330, F.A.C., the coastal construction criteria pursuant to Chapter 62B-41, F.A.C., and any specific criteria for issuance of a joint coastal permit listed in this chapter. The criteria for the associated proprietary authorizations are found in Chapters 18-18, 18-20, 18-21, F.A.C.
Specific Authority 161.055, 373.427 FS. Law Implemented 161.041, 161.055, 373.427 FS. History�New 10-12-95, Amended 2-19-98, 5-17-07. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring a permit with regulatory review of the construction project, in a joint review of wetland and submerged land issues, will assist in minimizing potential adverse environmental impacts from the work and such potential detrimental portions of the project (e.g. sedimentation) will not enter the marine environment resulting in ecosystem damage. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection |
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 include (1) Coastal Barrier Improvement Act of 1990, (2) Coastal Barrier Resources Reauthorization Act of 2000, (3) Coastal Barriers Resources Reauthorization Act of 2005,. | (1) Added additional areas along the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, the Florida Keys and the Virgin Islands and established "Otherwise Protected Areas OPAs); (2) amended the guidelines for making recommendations regarding additions to the CBRS and reqired a pilot digital mapping project; (3) reauthorized CBRA and required the submission of the final digital mapping pilot project. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restricted most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Forestry; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection |
| Sovereign submerged lands management, 18-21 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | To manage, protect, and enhance sovereignty lands so that the public may continue to enjoy traditional uses, including, but not limited to, navigation, fishing and swimming, public drinking water supply, shellfish harvesting, public recreation, and fish and wildlife propagation and management. Application to Coral Reefs:Permitting activities on submerged lands owned by Florida will improve water quality which will indirectly protect reef systems. Legislative Actions:These rules are to implement the administration and management responsibilities of the board and department regarding sovereign submerged lands. Responsibility for environmental permitting of activities and water quality protection on sovereign lands is vested with the Department of Environmental Protection. These rules are considered cumulative. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Energy Policy & Development; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary and Protection Act, Public Law 101-605 (H.R. 5909 United States Code (1990). | To protect the resources of the area delineated in section 5(b) of the Act, to educate and interpret for the public regarding the Florida Keys marine environment, and to manage such human uses of the Sanctuary consistent with the Act. Nothing in the Act is intended to restrict activities that do not cause adverse effects to the resources or property of the Sanctuary or that do not pose harm to the users of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the thrid largest coral reef barrier in the world. Included in the FKNMS are Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 squared nautical miles of coral reefs.The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive in the Sanctuary. From Miami to the Marquesas Keys there are over 6000 patch reefs. The Act also protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, futher protecting mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act required the preparation of a comprehensive mangement plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:Large vessel groundings on coral reefs in the Florida Keys was a major driver for the designation of the Sanctuary. In 1989, there were three groundings of large commercial vessels on the coral reef tract within an eighteen day period. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as lead agency and Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Florida Fish and Wildlife Commission, and Monroe County as Co-Trustees Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Transportation |