ReefLink Database
ReefLink Database
A Decision Support Tool for Linking Coral Reefs and Society through Systems Thinking
This scientific and management information database utilizes systems thinking to describe the linkages between decisions, human activities, and provisioning of reef ecosystem goods and services. This database provides:
- Hierarchy of related topics - Click on topics below to navigate to sub-topics or related topics
- Four kinds of information for each topic - Concept maps, scientific citations, management options, and laws
- Three ways of searching for topics - Navigate through individual concept maps below, or see the Whole systems model or search for keywords from a Topic list.
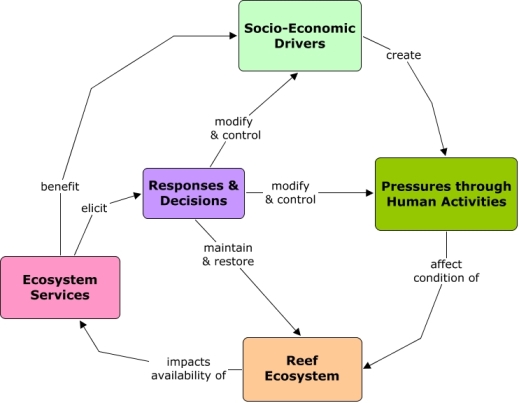
Concept Map
Concept maps (Cmaps) visually represent relationships between concepts.
- Identify which Socio-Economic Drivers create Pressures on the reef through human activities.
- Understand how Reef Ecosystem condition may impact Ecosystem Goods and Services which benefit society.
- Identify potential management or regulatory Responses to reduce impacts on environmental resources.
- Select sub-topics or related topics to expand the Cmap and see more detailed information.
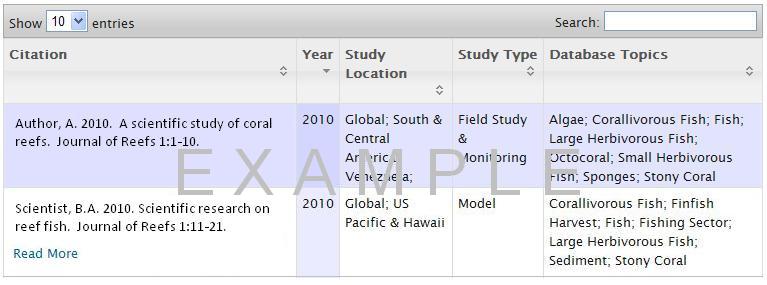
Citations
The Citations database gives scientific journal articles, reports, and books associated with each topic keyword.
- Identify scientific information and research related to each topic.
- Identify the study location, type of study, and related database topics covered in each scientific article.
- Search the database by keywords to look for particular citations.
- Go to the Cmap tab to choose a keyword topic, or select from the Whole Systems Model or Topic List & Glossary.
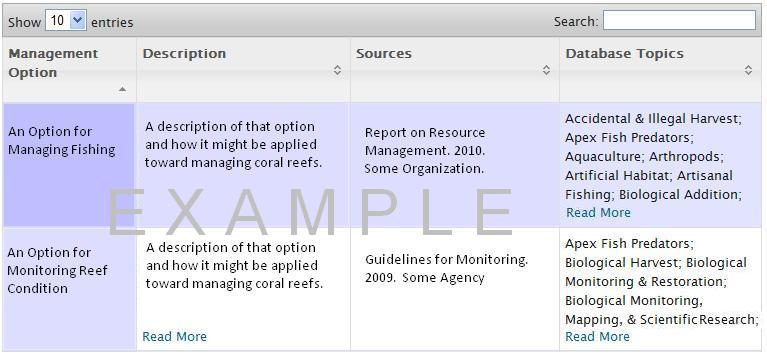
Management Options
The Management Options database provides a list of potential actions managers could inact to respond to a given keyword topic.
- Identify potential management actions from existing sources such as management plans and best practices.
- Identify related database topics which may be address by each management option.
- Search the database by keywords to look for particular management options.
- Go to the Cmap tab to choose a keyword topic, or select from the Whole Systems Model or Topic List & Glossary.
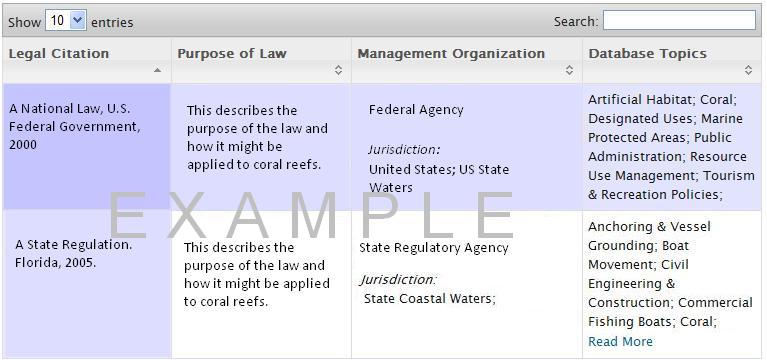
Laws
The Laws database provides a list of laws, policies, and regulations which may be relevant for a given keyword topic.
- Identify potential legal options for protecting environmental resources.
- Identify the management organization responsible for implementation and the relevant jurisdiction.
- Identify related database topics which may be addressed by each legislative option.
- Search the database by keywords to look for particular laws or regulations.
- Go to the Cmap tab to choose a keyword topic, or select from the Whole Systems Model or Topic List & Glossary.