ReefLink Database

Security & Public Administration Policies
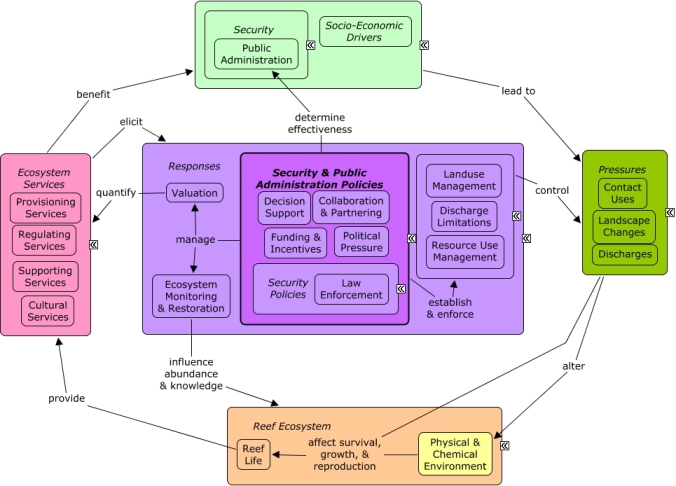
Security and public administration policies are responses to improve the decision-making and enforcement abilities of governmental institutions. Examples include collaborations and partnering with academic scientists or local stakeholders, developing management plans, conducting environmental assessments, using decision support tools, political pressure, and law enforcement.
CMap
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses from public administration to manage and reduce stressors on the reef ecosystem for the benefit of society. Governmental agencies can request addition funding or provide incentives for research, monitoring, education , or outreach that are particularly relevant for research goals. Collaboration and partnering can improve the effectiveness of management by integrating the efforts of academic and government institutions, or incorporating the knowledge and support of local stakeholders. Decision support activities, including development of management plans, conducting environmental assessments, utilizing decision support tools, managing data, or acquiring additional personnel can improve the effectiveness of decisions. Political pressure can influence the activities of public administration to target particular management concerns. Law enforcement, including surveillance or penalties, can also improve the effectiveness of regulations and laws.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ananthasubramaniam, B; Nisbet, RM; Morse, DE; Doyle, FJ. 2011. Integrate-and-fire models of insolation-driven entrainment of broadcast spawning in corals. Theoretical Ecology 4:69-85. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Ang, TZ; Manica, A. 2011. Effect of the Presence of Subordinates on Dominant Female Behaviour and Fitness in Hierarchies of the Dwarf Angelfish Centropyge bicolor. Ethology 117:1111-1119. | 2011 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Funding & Incentives; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Atkins, J. P., D. Burdon, M. Elliott, and A. J. Gregory. 2011. Management of the marine environment: Integrating ecosystem services and societal benefits with the DPSIR framework in a systems approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:215-226. | 2011 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Bellchambers, LM; Meeuwig, JJ; Evans, SN; Legendre, P. 2011. Modelling habitat associations of the common spider conch in the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. Marine Ecology Progress Series 432:83-90. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral | |
| Brodie, JE; Devlin, M; Haynes, D; Waterhouse, J. 2011. Assessment of the eutrophication status of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon (Australia). Biogeochemistry 106:281-302. | 2011 | Australia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Burke, L., K. Reytar, M. Spalding, and A. Perry. 2011. Reefs at Risk Revisited. World Research Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Panama; Tanzania; Indonesia | Biomedical Research Policies; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Cetina-Heredia, P; Connolly, SR. 2011. A simple approximation for larval retention around reefs. Coral Reefs 30:593-605. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Chen, CP; Tseng, CH; Chen, CA; Tang, SL. 2011. The dynamics of microbial partnerships in the coral Isopora palifera. ISME Journal 5:728-740. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Christensen, V., J. Steenbeek, and P. Failler. 2011. A combined ecosystem and value chain modeling approach for evaluating societal cost and benefit of fishing. Ecological Modelling 222:857-864. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting | |
| Cruz-Trinidad, A; Geronimo, RC; Cabral, RB; Alino, PM. 2011. How much are the Bolinao-Anda coral reefs worth? Ocean and Coastal Management 54:696-705. | 2011 | Philippines | Model; Index or Indicator | Aquaculture; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Dale, JJ; Stankus, AM; Burns, MS; Meyer, CG. 2011. The Shark Assemblage at French Frigate Shoals Atoll, Hawai'i: Species Composition, Abundance and Habitat Use. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest |
| Dunstan, A; Bradshaw, CJA; Marshall, J. 2011. Nautilus at Risk - Estimating Population Size and Demography of Nautilus pompilius. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Australia; Palau; Fiji | Model | Octopus & Squid |
| Edwards, HJ; Elliott, IA; Eakin, CM; Irikawa, A; Madin, JS; McField, M; Morgan, JA; van Woesik, R; Mumby, PJ. 2011. How much time can herbivore protection buy for coral reefs under realistic regimes of hurricanes and coral bleaching? Global Change Biology 17:2033-2048. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; Bahamas; Belize; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Ocean Acidity; Resource Use Management; Sea Temperatures; Sea Urchins; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Elfman, L; Tooke, NE; Patring, JDM. 2011. Detection of pesticides used in rice cultivation in streams on the island of Leyte in the Philippines. Agricultural Water Management 101:81-87. | 2011 | Global; Southeast Asia; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mangroves; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges |
| Evans, LS; Brown, K; Allison, EH. 2011. Factors Influencing Adaptive Marine Governance in a Developing Country Context: a Case Study of Southern Kenya. Ecology and Society 16. | 2011 | Kenya; Oman | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Fablet, R; Pecquerie, L; de Pontual, H; Hoie, H; Millner, R; Mosegaard, H; Kooijman, SALM. 2011. Shedding Light on Fish Otolith Biomineralization Using a Bioenergetic Approach. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Bivalves; Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Ocean Acidity | |
| Figueiredo, J; Pereira, HM. 2011. Regime shifts in a socio-ecological model of farmland abandonment. Landscape Ecology 26:737-749. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Nutrients | |
| Francis, T. B., P. S. Levin, and C. J.Harvey. 2011. The perils and promise of futures analysis in marine ecosystem-based management. Marine Policy 35:675-681. | 2011 | Review; Model | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Game, ET; Lipsett-Moore, G; Hamilton, R; Peterson, N; Kereseka, J; Atu, W; Watts, M; Possingham, H. 2011. Informed opportunism for conservation planning in the Solomon Islands. Conservation Letters 4:38-46. | 2011 | Solomon Islands | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas |
| Goater, S; Derne, B; Weinstein, P. 2011. Critical Issues in the Development of Health Information Systems in Supporting Environmental Health: A Case Study of Ciguatera. Environmental Health Perspectives 119:585-590. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Health Policies; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hart, MK; Shenoy, K; Crowley, PH. 2011. Sexual conflicts along gradients of density and predation risk: insights from an egg-trading fish. Evolutionary Ecology 25:1081-1105. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Marine Worms; Planktivorous Fish |
| Kellner, JB; Sanchirico, JN; Hastings, A; Mumby, PJ. 2011. Optimizing for multiple species and multiple values: tradeoffs inherent in ecosystem-based fisheries management. Conservation Letters 4:21-30. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector |
| Kragt, M. E., L. T. H. Newham, J. Bennett, and A. J. Jakeman. 2011. An integrated approach to linking economic valuation and catchment modelling. Environmental Modelling & Software 26:92-102. | 2011 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation |
| Kushner, B., P. Edwards, L. Burke, and E. Cooper. 2011. Coastal Capital: Jamaica - Coral Reefs, Beach Erosion and Impacts to Tourism in Jamaica. Working Paper, World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Jamaica | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Social Organizations; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation |
| Lamb, JB; Willis, BL. 2011. Using Coral Disease Prevalence to Assess the Effects of Concentrating Tourism Activities on Offshore Reefs in a Tropical Marine Park. Conservation Biology 25:1044-1052. | 2011 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Leis, JM; Van Herwerden, L; Patterson, HM. 2011. Estimating Connectivity In Marine Fish Populations: What Works Best? Oceanography and Marine Biology: Annual Review 49:193-234. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Lowe, PK; Bruno, JF; Selig, ER; Spencer, M. 2011. Empirical Models of Transitions between Coral Reef States: Effects of Region, Protection, and Environmental Change. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Marine Protected Areas |
| Maljkovic, A; Cote, IM. 2011. Effects of tourism-related provisioning on the trophic signatures and movement patterns of an apex predator, the Caribbean reef shark. Biological Conservation 144:859-865. | 2011 | South & Central America; Bahamas; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Funding & Incentives; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Maxam, A., P. Lyew-Ayee, and K. McIntyre. 2011. A Classification of the Protection Provided by Coral Reef Systems in Jamaica - Utilizing GIS and Oceanographic Methods of Analysis. Mona Geoinformatics Institute, St. Andrew (Jamaica). | 2011 | South & Central America; Dominican Republic; Jamaica; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Belize; Caribbean | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Maynard, JA; Anthony, KRN; Harvell, CD; Burgman, MA; Beeden, R; Sweatman, H; Heron, SF; Lamb, JB; Willis, BL. 2011. Predicting outbreaks of a climate-driven coral disease in the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 30:485-495. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Pathogens; Sea Temperatures |
| McClanahan, TR. 2011. Human and coral reef use interactions: From impacts to solutions? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 408:3-10. | 2011 | Review | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | |
| McCloskey, J. T., R. J. Lilieholm, and C. Cronan. 2011. Using Bayesian belief networks to identify potential compatibilities and conflicts between development and landscape conservation. Landscape and Urban Planning 101:190-203. | 2011 | Model; GIS & Maps | Economic Markets & Policies; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Meadows, A. 2011. Wildlife Conservation Education And International Programmes. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences 21:305-316. | 2011 | Global | Review; Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Invasive Species; Mangroves |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J., C. R. Johnson, T. Fung, R. M. Seymour, L. M. Cherubin, J. E. Arias-Gonzalez, and E. A. Fulton. 2011. Regional-scale scenario modeling for coral reefs: a decision support tool to inform management of a complex system. Ecological Applications 21:1380-1398. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Physical Damage; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J., C.R. Johnson, P.M. Ali�o, R.C. Geronimo, C.L. Villanoy, and G.G. Gurney. 2011. A multi-scale biophysical model to inform regional management of coral reefs in the western Philippines and South China Sea. Environmental Modelling & Software 26:66-82. | 2011 | China; Philippines | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fish; Mitigation |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Alino, PM; Geronimo, RC; Villanoy, CL; Gurney, GG. 2011. A multi-scale biophysical model to inform regional management of coral reefs in the western Philippines and South China Sea. Environmental Modelling & Software 26:66-82. | 2011 | China; Philippines | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Mitigation; Nutrients; Sea Urchins |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Fulton, EA. 2011. Regional-scale scenario analysis for the Meso-American Reef system: Modelling coral reef futures under multiple stressors. Ecological Modelling 222:1756-1770. | 2011 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Fung, T; Seymour, RM; Cherubin, LM; Arias-Gonzalez, JE; Fulton, EA. 2011. Regional-scale scenario modeling for coral reefs: a decision support tool to inform management of a complex system. Ecological Applications 21:1380-1398. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fish; Nutrients; Physical Damage; Sea Urchins; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Perez, P; Eustache, J; Fulton, EA; Cleland, D. 2011. Coupling Biophysical and Socioeconomic Models for Coral Reef Systems in Quintana Roo, Mexican Caribbean. Ecology and Society 16. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Tourism & Recreation |
| Mills, M; Jupiter, SD; Pressey, RL; Ban, NC; Comley, J. 2011. Incorporating Effectiveness of Community-Based Management in a National Marine Gap Analysis for Fiji. Conservation Biology 25:1155-1164. | 2011 | Fiji; Philippines | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Muallil, RN; Geronimo, RC; Cleland, D; Cabral, RB; Doctor, MV; Cruz-Trinidad, A; Alino, PM. 2011. Willingness to exit the artisanal fishery as a response to scenarios of declining catch or increasing monetary incentives. Fisheries Research 111:74-81. | 2011 | China; Philippines | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Monetary Valuation | |
| Munoz, PD; Murillo, FJ; Sayago-Gil, M; Serrano, A; Laporta, M; Otero, I; Gomez, C. 2011. Effects of deep-sea bottom longlining on the Hatton Bank fish communities and benthic ecosystem, north-east Atlantic. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 91:939-952. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Littering; Marine Birds; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Pittman, S. J. and K. A. Brown. 2011. Multi-Scale Approach for Predicting Fish Species Distributions across Coral Reef Seascapes. PLoS One 3:1-12. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas |
| Pittman, SJ; Brown, KA. 2011. Multi-Scale Approach for Predicting Fish Species Distributions across Coral Reef Seascapes. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas |
| Richard Newton. 2011. Continental Marsh Preserve: Baseline Documentation File / Property Management Plan. | 2011 | |||
| Rohr, JR; Dobson, AP; Johnson, PTJ; Kilpatrick, AM; Paull, SH; Raffel, TR; Ruiz-Moreno, D; Thomas, MB. 2011. Frontiers in climate change-disease research. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 26:270-277. | 2011 | Review; Model | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Pathogens | |
| Rolfe, J; Windle, J. 2011. Assessing community values for reducing agricultural emissions to improve water quality and protect coral health in the Great Barrier Reef. Water Resources Research 47. | 2011 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Monetary Valuation; Non-point Source Runoff |
| Rosic, NN; Pernice, M; Dove, S; Dunn, S; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 2011. Gene expression profiles of cytosolic heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp90 from symbiotic dinoflagellates in response to thermal stress: possible implications for coral bleaching. Cell Stress & Chaperones 16:69-80. | 2011 | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Sea Temperatures; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | ||
| Rouphael, AB; Abdulla, A; Said, Y. 2011. A framework for practical and rigorous impact monitoring by field managers of marine protected areas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 180:557-572. | 2011 | Australia; Egypt | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Pathogens |
| Ryu, J., T. M. Leschine, J. Namb, W. K. Chang, and K. Dyson. 2011. A resilience-based approach for comparing expert preferences across two large-scale coastal management programs. Journal of Environmental Management 92:92-101. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Salmela, L; Schroder, J. 2011. Correcting errors in short reads by multiple alignments. Bioinformatics 27:1455-1461. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Samy, M; Lizaso, JLS; Forcada, A. 2011. Status of marine protected areas in Egypt. Pages 165-177 in Conference on SIEBM 2010. BARCELONA. | 2011 | Egypt | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Santos, MN; Leitao, F; Moura, A; Cerqueira, M; Monteiro, CC. 2011. Diplodus spp. on artificial reefs of different ages: influence of the associated macrobenthic community. ICES Journal of Marine Science 68:87-97. | 2011 | Artificial Habitat; Fish | ||
| Soares, MC; Oliveira, RF; Ros, AFH; Grutter, AS; Bshary, R. 2011. Tactile stimulation lowers stress in fish. Nature Communications 2. | 2011 | Model | Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Souter, P; Bay, LK; Andreakis, N; Csaszar, N; Seneca, FO; van Oppen, MJH. 2011. A multilocus, temperature stress-related gene expression profile assay in Acropora millepora, a dominant reef-building coral. Molecular Ecology Resources 11:328-334. | 2011 | Lab Study; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Stony Coral | |
| Spillman, CM. 2011. Operational real-time seasonal forecasts for coral reef management. Journal Of Operational Oceanography 4:13-22. | 2011 | Global; Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Sea Temperatures |
| Strubin, C; Steinegger, M; Bshary, R. 2011. On Group Living and Collaborative Hunting in the Yellow Saddle Goatfish (Parupeneus cyclostomus). Ethology 117:961-969. | 2011 | Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Tallis, H., T. Ricketts, A.D Guerry, E. Nelson, D. Ennaanay, S. Wolny, N. Olswero, K. Vigerstol, D. Pennington, G. Mendoza, J. Aukema, J. Foster, J. Forrest, D. Cameron, E. Lonsdorf, C. Kennedy, G. Verutes, C. K. Kim, G. Guannel, M. Papenfus, et al., editor. 2011. InVEST 2.0 Beta User�s Guide: Integrated Valuation of Ecosystem Services and Tradeoffs - A modeling suite developed by the Natural Capital Project to support environmental decision-making. The National Project, Stanford, Palo Alto, (CA, USA). | 2011 | Model | Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Teixido, N; Albajes-Eizagirre, A; Bolbo, D; Le Hir, E; Demestre, M; Garrabou, J; Guigues, L; Gili, JM; Piera, J; Prelot, T; Soria-Frisch, A. 2011. Hierarchical segmentation-based software for cover classification analyses of seabed images (Seascape). Marine Ecology Progress Series 431:45+. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Thieblemont, C; Briere, J; Mounier, N; Voelker, HU; Cuccuini, W; Hirchaud, E; Rosenwald, A; Jack, A; Sundstrom, C; Cogliatti, S; Trougouboff, P; Boudova, L; Ysebaert, L; Soulier, J; Chevalier, C; Bron, D; Schmitz, N; Gaulard, P; Houlgatte, R; Gisselbrecht. 2011. The Germinal Center/Activated B-Cell Subclassification Has a Prognostic Impact for Response to Salvage Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bio-CORAL Study. Journal Of Clinical Oncology 29:4079-4087. | 2011 | Model; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Toropova, AP; Toropov, AA; Benfenati, E; Gini, G. 2011. QSAR modelling toxicity toward rats of inorganic substances by means of CORAL. Central European Journal Of Chemistry 9:75-85. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Internet & Telecommunications | |
| Toropova, AP; Toropov, AA; Diaza, RG; Benfenati, E; Gini, G. 2011. Analysis of the co-evolutions of correlations as a tool for QSAR-modeling of carcinogenicity: an unexpected good prediction based on a model that seems untrustworthy. Central European Journal Of Chemistry 9:165-174. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Wang, Y; Pan, Y; Price, A; Martin, LJ. 2011. Generation and characterization of transgenic mice expressing mitochondrial targeted red fluorescent protein selectively in neurons: modeling mitochondriopathy in excitotoxicity and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Molecular Neurodegeneration 6. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pathogens | |
| Webster, NS; Botte, ES; Soo, RM; Whalan, S. 2011. The larval sponge holobiont exhibits high thermal tolerance. Environmental Microbiology Reports 3:756-762. | 2011 | Global; Australia | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Sponges | |
| Whitall, D. R., B. M. Costa, L. J. Bauer, A. Dieppa, and S. D. Hile, editors. 2011. A Baseline Assessment of the Ecological Resources of Jobos Bay, Puerto Rico. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 133, NOAA, Silver Spring, (MD, USA). | 2011 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics |
| Adams, E. W. and C. A. Hasler. 2010. The intrinsic effect of shape on the retrogradation motif and timing of drowning of carbonate patch reef systems (Lower Frasnian, Bugle Gap, Canning Basin, Western Australia). Sedimentology 57:956-984. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment |
| Albouy, C., D. Mouillot, D. Rocklin, J. M. Culioli, and F. Le Loc'h. 2010. Simulation of the combined effects of artisanal and recreational fisheries on a Mediterranean MPA ecosystem using a trophic model. Marine Ecology Progress Series 412:207-221. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Almany, G. R., R. J. Hamilton, D. H. Williamson, R. D. Evans, G. P. Jones, M. Matawai, T. Potuku, K. L. Rhodes, G. R. Russ, and B. Sawynok. 2010. Research partnerships with local communities: two case studies from Papua New Guinea and Australia. Coral Reefs 29:567-576. | 2010 | Australia; Papua New Guinea | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Anton, C., J. Young, P. A. Harrison, M. Musche, G. Bela, C. K. Feld, R. Harrington, J. R. Haslett, G. Pataki, M. D. A. Rounsevell, M. Skourtos, J. P. Sousa, M. T. Sykes, R. Tinch, M. Vandewalle, A. Watt, and J. Settele. 2010. Research needs for incorporating the ecosystem service approach into EU biodiversity conservation policy. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2979-2994. | 2010 | Review; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation | |
| Armsworth, P. R. and J. E. Roughgarden. 2010. The economic value of ecological stability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 100:7147-7151. | 2010 | Model | Monetary Valuation | |
| Beger, M., S. Linke, M. Watts, E. Game, E. Treml, I. Ball, and H. P. Possingham. 2010. Incorporating asymmetric connectivity into spatial decision making for conservation. Conservation Letters 3:359-368. | 2010 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bejarano, S., P. J. Mumby, J. D. Hedley, and I. Sotheran. 2010. Combining optical and acoustic data to enhance the detection of Caribbean forereef habitats. Remote Sensing of Environment 114:2768-2778. | 2010 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Bischof, B. G. 2010. Negotiating uncertainty Framing attitudes, prioritizing issues, and finding consensus in the coral reef environment management "crisis". Ocean and Coastal Management 53:597-614. | 2010 | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Mitigation | |
| Bohnet, I. C. 2010. Integrating social and ecological knowledge for planning sustainable land- and sea-scapes: experiences from the Great Barrier Reef region, Australia. Landscape Ecology 25:1201-1218. | 2010 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Valuation |
| Bordalo, P., N. Gennaioli, and A. Shleifer. 2010. Salience theory of choice under risk. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA. | 2010 | Model | ||
| Boudali, H., P. Crouzen, and M. Stoelinga. 2010. A Rigorous, Compositional, and Extensible Framework for Dynamic Fault Tree Analysis. Ieee Transactions On Dependable And Secure Computing 7:128-143. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Campbell, R. J., N. Ledesma, G. Zill, J. C. Herrera, and J. Leon. 2010. Collecting Pouterias (Pouteria spp.), Sapodilla (Manilkara zapota) and Caimito (Chrysophyllum cainito) for the Creation of New Markets. Journal Of The American Pomological Society 64:24-27. | 2010 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Nicaragua; Costa Rica | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Collaboration & Partnering; Landscaping & Household Services | |
| Chou, L. M., D. W. Huang, K. P. P. Tun, J. T. B. Kwik, Y. C. Tay, and A. L. Seow. 2010. Temporal Changes in Reef Community Structure at Bintan Island (Indonesia) Suggest Need for Integrated Management. Pacific Science 64:99-111. | 2010 | Southeast Asia; Indonesia | Fish; Hotel & Food Services; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Cisneros-Montemayor, A. M., U. R. Sumaila, K. Kaschner, and D. Pauly. 2010. The global potential for whale watching. Marine Policy [inpress]. | 2010 | Global | Funding & Incentives; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Clarke, P. and S. D. Jupiter. 2010. Law, custom and community-based natural resource management in Kubulau District (Fiji). Environmental Conservation 37:98-106. | 2010 | Fiji | Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Colton, M. A. and S. E. Swearer. 2010. A comparison of two survey methods: differences between underwater visual census and baited remote underwater video. Marine Ecology Progress Series 400:19-36. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish |
| Crawford, B., M. D. Herrera, N. Hernandez, C. R. Leclair, N. Jiddawi, S. Masumbuko, and M. Haws. 2010. Small Scale Fisheries Management: Lessons from Cockle Harvesters in Nicaragua and Tanzania. Coastal Management 38:195-215. | 2010 | Nicaragua; Tanzania; Fiji | Model | Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector |
| Croquer, A., D. Debrot, E. Klein, M. Kurten, S. Rodriguez, and C. Bastidas. 2010. What can two years of monitoring tell us about Venezuelan coral reefs? The Southern Tropical America node of the Global Coral Reef Monitoring Network (STA-GCRMN). Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:51-65. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Venezuela; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Sponges; Stony Coral |
| Dalton, S. J., S. Godwin, S. D. A. Smith, and L. Pereg. 2010. Australian subtropical white syndrome: a transmissible, temperature-dependent coral disease. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:342-350. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Marine Protected Areas; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| DeSalvo, M. K., S. Sunagawa, P. L. Fisher, C. R. Voolstra, R. Iglesias-Prieto, and M. Medina. 2010. Coral host transcriptomic states are correlated with Symbiodinium genotypes. Molecular Ecology 19:1174-1186. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| dos Santos, L. N., D. S. Brotto, and I. R. Zalmon. 2010. Fish responses to increasing distance from artificial reefs on the Southeastern Brazilian Coast. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 386:54-60. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Dunne, R. P. 2010. Synergy or antagonism-interactions between stressors on coral reefs. Coral Reefs 29:145-152. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Eakin, C. M., J. A. Morgan, S. F. Heron, T. B. Smith, G. Liu, L. Alvarez-Filip, B. Baca, E. Bartels, C. Bastidas, C. Bouchon, M. Brandt, A. W. Bruckner, L. Bunkley-Williams, A. Cameron, B. D. Causey, M. Chiappone, T. R. L. Christensen, M. J. C. Crabbe, O. Day, and de la Guardia. 2010. Caribbean Corals in Crisis: Record Thermal Stress, Bleaching, and Mortality in 2005. PLoS One 5:e13969. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Sea Temperatures |
| Faure, V., C. Pinazo, J. P. Torreton, and P. Douillet. 2010. Modelling the spatial and temporal variability of the SW lagoon of New Caledonia II: Realistic 3D simulations compared with in situ data. Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:480-502. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ferse, S. C. A., M. M. Costa, K. S. Manez, D. S. Adhuri, and M. Glaser. 2010. Allies, not aliens: increasing the role of local communities in marine protected area implementation. Environmental Conservation 37:23-34. | 2010 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management | |
| Frank, D. M. and S. Sarkar. 2010. Group Decisions in Biodiversity Conservation: Implications from Game Theory. PLoS One 5:e10688. | 2010 | Philippines; South Africa; United Kingdom | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Funding & Incentives |
| Fujita, R. M., K. T. Honey, A. Morris, J. R. Wilson, and H. Russell. 2010. Cooperative Strategies In Fisheries Management: Integrating Across Scales. Bulletin of Marine Science 86:251-271. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives | |
| Galindo, H. M., A. S. Pfeiffer-Herbert, M. A. McManus, Y. Chao, F. Chai, and S. R. Palumbi. 2010. Seascape genetics along a steep cline: using genetic patterns to test predictions of marine larval dispersal. Molecular Ecology 19:3692-3707. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Gavin, M. C., J. N. Solomon, and S. G. Blank. 2010. Measuring and Monitoring Illegal Use of Natural Resources. Conservation Biology 24:89-100. | 2010 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Funding & Incentives |
| Gleason, M., S. McCreary, M. Miller-Henson, J. Ugoretz, E. Fox, M. Merrifield, W. McClintock, P. Serpa, and K. Hoffman. 2010. Science-based and stakeholder-driven marine protected area network planning: A successful case study from north central California. Ocean and Coastal Management 53:52-68. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Harper, S. J. M., C. R. Bates, H. M. Guzman, and J. M. Mair. 2010. Acoustic mapping of fish aggregation areas to improve fisheries management in Las Perlas Archipelago, Pacific Panama. Ocean and Coastal Management 53:615-623. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Panama | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management |
| Harrington, R., C. Anton, T. P. Dawson, F. de Bello, C. K. Feld, J. R. Haslett, T. Kluvankova-Oravska, A. Kontogianni, S. Lavorel, G. W. Luck, M. D. A. Rounsevell, M. J. Samways, J. Settele, M. Skourtos, J. H. Spangenberg, M. Vandewalle, M. Zobel, and P. A. Harrison. 2010. Ecosystem services and biodiversity conservation: concepts and a glossary. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2773-2790. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Valuation | |
| Hayes, M. L., R. I. Eytan, and M. E. Hellberg. 2010. High amino acid diversity and positive selection at a putative coral immunity gene (tachylectin-2). BMC Evolutionary Biology 10:150. | 2010 | Japan | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Hill, N. A., A. R. Pepper, M. L. Puotinen, M. G. Hughes, G. J. Edgar, N. S. Barrett, R. D. Stuart-Smith, and R. Leaper. 2010. Quantifying wave exposure in shallow temperate reef systems: applicability of fetch models for predicting algal biodiversity. Marine Ecology Progress Series 417:83-U100. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae |
| Holmes, G. and R. W. Johnstone. 2010. Modelling coral reef ecosystems with limited observational data. Ecological Modelling 221:1173-1183. | 2010 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral |
| Ikmi, A. and M. C. Gibson. 2010. Identification and In Vivo Characterization of NvFP-7R, a Developmentally Regulated Red Fluorescent Protein of Nematostella vectensis. PLoS One 5:e11807. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anemones & Zooanthids | |
| Ilagan, R. P., E. Rhoades, D. F. Gruber, H. T. Kao, V. A. Pieribone, and L. Regan. 2010. A new bright green-emitting fluorescent protein - engineered monomeric and dimeric forms. FEBS Journal 277:1967-1978. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Jenkins, A. P., S. D. Jupiter, I. Qauqau, and J. Atherton. 2010. The importance of ecosystem-based management for conserving aquatic migratory pathways on tropical high islands: a case study from Fiji. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:224-238. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Fiji; Papua New Guinea | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Kaplan, D. M., S. Planes, C. Fauvelot, T. Brochier, C. Lett, N. Bodin, F. Le Loc'h, Y. Tremblay, and J. Y. Georges. 2010. New tools for the spatial management of living marine resources. Current Opinion In Environmental Sustainability 2:88-93. | 2010 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Kirkby, C. A., R. Giudice-Granados, B. Day, K. Turner, L. M. Velarde- Andrade, A. Duenas-Duenas, J. C. Lara-Rivas, and D. W. Yu. 2010. The Market Triumph of Ecotourism: An Economic Investigation of the Private and Social Benefits of Competing Land Uses in the Peruvian Amazon. PLoS One 5:1-14. | 2010 | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Funding & Incentives; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Klein, C. J., N. C. Ban, B. S. Halpern, M. Beger, E. T. Game, H. S. Grantham, A. Green, T. J. Klein, S. Kininmonth, E. Treml, K. Wilson, and H. P. Possingham. 2010. Prioritizing Land and Sea Conservation Investments to Protect Coral Reefs. PLoS One 5:e12431. | 2010 | Global | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Ocean Acidity | |
| Knudby, A., A. Brenning, and E. LeDrew. 2010. New approaches to modelling fish�habitat relationships. Ecological Modelling 221:503-211. | 2010 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Knudby, A., A. Brenning, and E. LeDrew. 2010. New approaches to modelling fish-habitat relationships. Ecological Modelling 221:503-511. | 2010 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| LaJeunesse, T. C., R. Smith, M. Walther, J. Pinzon, D. T. Pettay, M. McGinley, M. Aschaffenburg, P. Medina-Rosas, A. L. Cupul-Magana, A. L. Perez, H. Reyes-Bonilla, and M. E. Warner. 2010. Host-symbiont recombination versus natural selection in the response of coral-dinoflagellate symbioses to environmental disturbance. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 277:2925-2934. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Mexico | Anemones & Zooanthids; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| Launio, C. C., Y. Morooka, H. Aizaki, and Y. Iiguni. 2010. Perceptions of small-scale fishermen on the value of marine resources and protected areas: case of Claveria, Northern Philippines. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 17:401-409. | 2010 | Philippines | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Housing; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management |
| Lauzon-Guay, J. S. and R. E. Scheibling. 2010. Spatial dynamics, ecological thresholds and phase shifts: modelling grazer aggregation and gap formation in kelp beds. Marine Ecology Progress Series 403:29-41. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Sea Urchins |
| Linan-Cabello, M. A., L. A. Flores-Ramirez, J. F. Cobo-Diaz, T. Zenteno-Savin, N. O. Olguin-Monroy, A. Olivos-Ortiz, and A. Tintos-Gomez. 2010. Response to short term ultraviolet stress in the reef-building coral Pocillopora capitata (Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:103-118. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Lynam, T., J. Drewry, W. Higham, and C. Mitchell. 2010. Adaptive modelling for adaptive water quality management in the Great Barrier Reef region, Australia. Environmental Modelling & Software 25:1291-1301. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| Malcolm, H. A. and S. D. A. Smith. 2010. Objective selection of surrogate families to describe reef fish assemblages in a subtropical marine park. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:3611-3618. | 2010 | Australia | Fish; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Maynard, J. A., K. R. N. Anthony, S. Afatta, N. Dahl-Tacconi, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2010. Making a Model Meaningful to Coral Reef Managers in a Developing Nation: a Case Study of Overfishing and Rock Anchoring in Indonesia. Conservation Biology 24:1316-1326. | 2010 | Indonesia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| McClanahan, T. R. 2010. Effects of Fisheries Closures and Gear Restrictions on Fishing Income in a Kenyan Coral Reef. Conservation Biology 24:1519-1528. | 2010 | Indian Ocean; Kenya; India | Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Special Use Permitting; Valuation | |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J. 2010. CORSET documentation: how to access and use the Coral Reef Scenario Evaluation Tool via the reef scenarios portal. Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Australia. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support | |
| Miller, T. L., R. D. Adlard, R. A. Bray, J. L. Justine, and T. H. Cribb. 2010. Cryptic species of Euryakaina n. g. (Digenea: Cryptogonimidae) from sympatric lutjanids in the Indo-West Pacific. Systematic Parasitology 77:185-204. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Maldives; New Caledonia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Docks & Marinas |
| Molina, J. L., J. Bromley, J.L. Garcia-Arostegui, C. Sullivan, J. Benavente. 2010. Integrated water resources management of overexploited hydrogeological systems using Object-Oriented Bayesian Networks. Environmental Modelling & Software 25:383-397. | 2010 | Spain | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Moussa, R. M. 2010. Estimation of the size of lagoon fish sold at the roadside as tui on Moorea Island (French Polynesia) by analysis of digital images. Cybium 34:73-82. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Oran. C. and C. Marriott. 2010. Using Adaptive Management to Resolve Uncertainties for Wave and Tidal Energy Projects. Oceanography 23:92-97. | 2010 | Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Oren, M., K. O. Amar, J. Douek, T. Rosenzweig, G. Paz, and B. Rinkevich. 2010. Assembled catalog of immune-related genes from allogeneic challenged corals that unveils the participation of vWF-like transcript. Developmental and Comparative Immunology 34:630-637. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Patrick, W. S., P. Spencer, J. Link, J. Cope, J. Field, D. Kobayashi, P. Lawson, T. Gedamke, E. Cortes, O. Ormseth, K. Bigelow, and W. Overholtz. 2010. Using productivity and susceptibility indices to assess the vulnerability of United States fish stocks to overfishing. Fishery Bulletin 108:305-322. | 2010 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Pert, P. L., J. R. A. Butler, J. E. Brodie, C. Bruce, M. Honzak, F. J. Kroon, D. Metcalfe, D. Mitchell, and G. Wong. 2010. A catchment-based approach to mapping hydrological ecosystem services using riparian habitat: A case study from the Wet Tropics, Australia. Ecological Complexity 7:378-388. | 2010 | Australia | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Peterson, M. J., D. M. Hall, A. M. Feldpausch-Paker, and T. R. Peterson. 2010. Obscuring ecosystem function with application of the ecosystem services concept. Conservation Biology 21:113-119. | 2010 | Global | Valuation | |
| Pittman, S. J., C. F. G. Jeffrey, R. Clark, K. Woody, B. D. Herlach, C. Caldow, M. E. Monaco, and R. Appledoorn. 2010. Coral reef ecosystems of Reserva Natural de La Parguera (Puerto Rico): spatial and temporal patterns in fish and benthic communities (2001-2007). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring, MD. | 2010 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation |
| Roelfsema, C. and S. Phinn. 2010. Integrating field data with high spatial resolution multispectral satellite imagery for calibration and validation of coral reef benthic community maps. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 4:43527. | 2010 | Fiji | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Seagrasses |
| Rogers, C. S. 2010. Words matter: recommendations for clarifying coral disease nomenclature and terminology. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 91:167-175. | 2010 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Pathogens |
| Rounsevell, M. D. A., T. P. Dawson, and P. A. Harrison. 2010. A conceptual framework to assess the effects of environmental change on ecosystem services. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2823-2842. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mitigation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation | |
| Ryan, J. C., J. S. Morey, M. Y. D. Bottein, J. S. Ramsdell, and F. M. Van Dolah. 2010. Gene expression profiling in brain of mice exposed to the marine neurotoxin ciguatoxin reveals an acute anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective response. Bmc Neuroscience 11:107. | 2010 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish |
| Sagoff, M. 2010. The quantification and valuation of ecosystem services. Ecological Economics [inpress]. | 2010 | Collaboration & Partnering; Valuation | ||
| Samhouri, J. F., P. S. Levin, and C. H. Ainsworth. 2010. Identifying Thresholds for Ecosystem-Based Management. PLoS One 5:e8907. | 2010 | Columbia | Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest |
| Samonte, G., L. Karrer, and M. Orbach. 2010. People and oceans. Science and Knowledge Division, Conservation International, Arlington, VA. | 2010 | Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation | ||
| Sarkis, S., P. J. H. VanBeukering, and E. McKenzie, editors. 2010. TOTAL ECONOMIC VALUE OF BERMUDA�S CORAL REEFS: Valuation of Ecosystem Services. Department of Conservation Services, Bermuda. | 2010 | Bermuda | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Scharron, C. E. R. 2010. Sediment production from unpaved roads in a sub-tropical dry setting - Southwestern Puerto Rico. Catena 82:146-158. | 2010 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Development; Mitigation; Sediment; Transportation Policies |
| Schreck, C. B. 2010. Stress and fish reproduction: The roles of allostasis and hormesis. General and Comparative Endocrinology 165:549-556. | 2010 | Review | Fish; Security Policies | |
| Scopelitis, J., S. Andrefouet, S. Phinn, L. Arroyo, M. Dalleau, A. Cros, and P. Chabanet. 2010. The next step in shallow coral reef monitoring: Combining remote sensing and in situ approaches. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1956-1968. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Selig, E. R. and J. F. Bruno. 2010. A global analysis of the effectiveness of marine protected areas in preventing coral loss. PLoS One 5:e9278. | 2010 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Stony Coral |
| Semmens, B. X., P. J. Auster, M. J. Paddack. 2010. Using ecological null models to assess the potential for marine protected area networks to protect biodiversity. PLoS Biology 5:e8895.doi:10.1371/jourl.pone.0008895. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Shank, T. M. 2010. Seamounts Deep-Ocean Laboratories of Faunal Connectivity, Evolution, and Endemism. Oceanography 23:108-122. | 2010 | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector | ||
| Shenton, W., B. T. Hart, and J. Brodie. 2010. A Bayesian network model linking nutrient management actions in the Tully catchment (northern Queensland) with Great Barrier Reef condition. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:587-595. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Algae; Decision Support; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Sheppard, C., M. Al-Husiani, F. Al-Jamali, F. Al-Yamani, R. Baldwin, J. Bishop, F. Benzoni, E. Dutrieux, N. K. Dulvy, S. R. V. Durvasula, D. A. Jones, R. Loughland, D. Medio, M. Nithyanandan, G. M. Pilling, I. Polikarpov, A. R. G. Price, S. Purkis, B. Riegl, and M. Saburova. 2010. The Gulf: A young sea in decline. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:13-38. | 2010 | Review | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Springer, Y. P., C. G. Hays, M. H. Carr, and M. R. Mackey. 2010. Toward Ecosystem-Based Management Of Marine Macroalgae-The Bull Kelp, Nereocystis Luetkeana. Pages 1-41 Oceanography And Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol 48. | 2010 | Review | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Steiner, S. C. C. and D. A. Willette. 2010. Distribution and size of benthic marine habitats in Dominica, Lesser Antilles. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:589-602. | 2010 | Antilles | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Ports & Harbors; Seagrasses |
| STEWART-KOSTER, B., S. E. BUNN, S. J . MACKAY, N. L. POFF, R. J. NAIMAN, AND P. S. LAKE. 2010. The use of Bayesian networks to guide investments in flow and catchment restoration for impaired river ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 55:243-260. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Seawater Flow; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| TEEB. 2010. Integrating the ecological and economic dimensions in biodiversity and ecosystem service valuation. in Kumar, P., editor. The economics of ecosystems and biodiversity: ecological and economic foundations. Earthscan, United Kingdom. | 2010 | Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives | ||
| TEEB. 2010. Socio-cultural context of ecosystem and biodiversity valuation. in P. Kumar, editor. The economics of ecosystems and biodiversity: ecological and economic foundations. Earthscan, United Kingdom. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Existence Value & Sense of Place; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Valuation | |
| Teske, P. R., F. R. G. Forget, P. D. Cowley, S. von der Heyden, and L. B. Beheregaray. 2010. Connectivity between marine reserves and exploited areas in the philopatric reef fish Chrysoblephus laticeps (Teleostei: Sparidae). Marine Biology 157:2029-2042. | 2010 | Oman; South Africa | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| van Beukering, P. J. H., S. Sarkis, E. McKenzie, S. Hess, L. Brander, M. Roelfsema, L. Looijenstijn-van der Putten, and T. Bervoets. 2010. Total Economic Value of Bermuda�s Coral Reefs Valuation of Ecosystem Services. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Bermuda; Caribbean | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Fish; Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| van Beukering, P. J. H., S. Sarkis, E. McKenzie, S. Hess, L. Brander, M. Roelfsema, L. Looijenstijn-van der Putten, and T. Bervoets. 2010. Total economic value of bermuda�s coral reefs: valuation of ecosystem services. Van Beukering Consulting, Amsterdam, NL. | 2010 | Bermuda | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Vignon, M. and P. Sasal. 2010. Multiscale determinants of parasite abundance: A quantitative hierarchical approach for coral reef fishes. International Journal for Parasitology 40:443-451. | 2010 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Voinov, A. and F. Bousquet. 2010. Modelling with stakeholders. Environmental Modelling & Software 25:1268-1281. | 2010 | Oman | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Special Use Permitting |
| Walker, S. P. W., L. Thibaut, and M. I. McCormick. 2010. Density-Dependent Sex Ratio Adjustment and the Allee Effect: A Model and a Test Using a Sex-Changing Fish. American Naturalist 176:312-321. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Invertebrates | |
| Ward-Paige, C., J. M. Flemming, and H. K. Lotze. 2010. Overestimating Fish Counts by Non-Instantaneous Visual Censuses: Consequences for Population and Community Descriptions. PLoS One 5:e11722. | 2010 | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Fish | |
| Water Stewardship Inc. 2010. Beta Test Report: Process Development & Description of Findings. | 2010 | Agriculture; Nutrients | ||
| Westerberg, V. H., R. Lifran, and S. B. Olsen. 2010. To restore or not? A valuation of social and ecological functions of the Marais des Baux wetland in Southern France. Ecological Economics 69:2383-2393. | 2010 | France | Model | Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Wicks, L. C., E. Sampayo, J. P. A. Gardner, and S. K. Davy. 2010. Local endemicity and high diversity characterise high-latitude coral-Symbiodinium partnerships. Coral Reefs 29:989-1003. | 2010 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Octocoral | |
| Wielgus, J., A. Balmford, T. B. Lewis, C. Mora, and L. R. Gerber. 2010. Coral reef quality and recreation fees in marine protected areas. Conservation Letters 3:38-44. | 2010 | Global; Cuba | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Wilson, S. K., M. Adjeroud, D. R. Bellwood, M. L. Berumen, D. Booth, Y. M. Bozec, P. Chabanet, A. Cheal, J. Cinner, M. Depczynski, D. A. Feary, M. Gagliano, N. A. J. Graham, A. R. Halford, B. S. Halpern, A. R. Harborne, A. S. Hoey, S. J. Holbrook, G. P. Jones, M. Kulbiki, and Letourneu. 2010. Crucial knowledge gaps in current understanding of climate change impacts on coral reef fishes. Journal of Experimental Biology 213:894-900. | 2010 | Global | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing Sector; Ocean Acidity | |
| Yasue, M., L. Kaufman, and A. C. J. Vincent. 2010. Assessing ecological changes in and around marine reserves using community perceptions and biological surveys. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:407-418. | 2010 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Yender, R. A. and J. Michel, editors. 2010. Oil Spills in Coral Reefs: Planning & Respoinse Considerations, Second Edition. U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Washington, D.C. | 2010 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Petroleum Spills | |
| 2009. Federal Expenditures for U.S. Coral Reef Task Force Conservation Activities (2002-2004). Appendix A, NOAA. | 2009 | Global | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Aburto-Oropeza, O., I. Dominguez-Guerrero, J. Cota-Nieto, and T. Plomozo-Lugo. 2009. Recruitment and ontogenetic habitat shifts of the yellow snapper (Lutjanus argentiventris) in the Gulf of California. Marine Biology 156:2461-2472. | 2009 | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Piscivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Aguilar-Perera, A., C. Gonzalez-Salas, A. Tuz-Sulub, and H. Villegas-Hernandez. 2009. Fishery of the Goliath grouper, Epinephelus itajara (Teleostei: Epinephelidae) based on local ecological knowledge and fishery records in Yucatan, Mexico. Revista de Biologia Tropical 57:557-566. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Piscivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Albanez-Lucero, M. O. and F. Arreguin-Sanchez. 2009. Modelling the spatial distribution of red grouper (Epinephelus morio) at Campeche Bank, Mexico, with respect substrate. Ecological Modelling 220:2744-2750. | 2009 | South & Central America; Cuba; Mexico | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Piscivorous Fish; Substrate |
| Armada, N., A. T. White, and P. Christie. 2009. Managing Fisheries Resources in Danajon Bank, Bohol, Philippines: An Ecosystem-Based Approach. Coastal Management 37:308-330. | 2009 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management |
| Armstrong, C. W., A. J. Grehan, V. Kahui, E. Mikkelsen, S. Reithe, and S. van den Hove. 2009. Bioeconomic Modeling and the Management of Cold-Water Coral Resources. Oceanography 22:86-91. | 2009 | Model | Funding & Incentives | |
| Ban, N. C., G. J. A. Hansen, M. Jones, and A. C. J. Vincent. 2009. Systematic marine conservation planning in data-poor regions: Socioeconomic data is essential. Marine Policy 33:794-800. | 2009 | Philippines | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas |
| Barber, J. S., D. M. Chosid, R. P. Glenn, and K. A. Whitmore. 2009. A systematic model for artificial reef site selection. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 43:283-297. | 2009 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mitigation; Substrate | |
| Baron, J. S., L. Gunderson, C. D. Allen, E. Fleishman, D. McKenzie, L. A. Meyerson, J. Oropeza, and N. Stephenson. 2009. Options for National Parks and Reserves for Adapting to Climate Change. Environmental Management 44:1033-1042. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management | |
| Bartlett, C. Y., K. Pakoa, and C. Manua. 2009. Marine reserve phenomenon in the Pacific islands. Marine Policy 33:673-678. | 2009 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Vanuatu | Marine Protected Areas | |
| Binimelis, R., I. Monterroso, and B. Rodriguez-Labajos. 2009. Catalan agriculture and genetically modified organisms (GMOs) � An application of DPSIR model. Ecological Economics 69:55-62. | 2009 | Europe; Spain | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture |
| Blanco, E., J. Lozano, J. Rey-Maquieira. 2009. A dynamic approach to voluntary environmental contributions in tourism. Ecological Economics 69:104-114. | 2009 | Model | Funding & Incentives; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Bohnet, I. C. and C. Kinjun. 2009. Community uses and values of water informing water quality improvement planning: a study from the Great Barrier Reef region, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1176-1182. | 2009 | Australia | Valuation | |
| Botsford, L. W., J. W. White, A. Coffroth M.-, C. B. Paris, S. Planes, T. L. Shearer, S. R. Thorrold, and G. P. Jones. 2009. Connectivity and resilience of coral reef metapopulations in marine protected areas: matching empirical efforts to predictive needs. Coral Reefs 11-Jan. | 2009 | Model | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Bourne, D. G., M. Garren, T. M. Work, E. Rosenberg, G. W. Smith, and C. D. Harvell. 2009. Microbial disease and the coral holobiont. Trends in Microbiology 17:554-562. | 2009 | Global | Review | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics |
| Brandt, M. E. and J. W. McManus. 2009. Dynamics and impact of the coral disease white plague: insights from a simulation model. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 87:117-133. | 2009 | Cayman Islands | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pathogens |
| Butardo-Toribio, M. Z., P. M. Alino, and E. S. Guiang. 2009. Cost-Benefit Study of Marine Protected Areas: Implications on Financing and Institutional Needs. Philippine Agricultural Scientist 92:153-169. | 2009 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Social Organizations |
| Callaway, A., J. Smyth, C. J. Brown, R. Quinn, M. Service, and D. Long. 2009. The impact of scour processes on a smothered reef system in the Irish Sea. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84:409-418. | 2009 | Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Sediment | ||
| Calo, C. F. F., A. Schiavetti, and M. Cetra. 2009. Local ecological and taxonomic knowledge of snapper fish (Teleostei: Actinopterygii) held by fishermen in Ilheus, Bahia, Brazil. Neotropical Ichthyology 7:403-414. | 2009 | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Camargo, C., J. H. Maldonado, E. Alvarado, R. Moreno-Sanchez, S. Mendoza, N. Manrique, A. Mogollon, J. D. Osorio, A. Grajales, and J. A. Sanchez. 2009. Community involvement in management for maintaining coral reef resilience and biodiversity in southern Caribbean marine protected areas. Biodiversity and Conservation 18:935-956. | 2009 | South & Central America; Oman; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Caras, T. and Z. Pasternak. 2009. Long-term environmental impact of coral mining at the Wakatobi marine park, Indonesia. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:539-544. | 2009 | Indonesia | Algae; Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas; Octocoral; Skeletal Coral; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Chai, H., N. Li, C. Xiao, X. Liu, D. Li, C. Wang, and D. Wu. 2009. Automatic discrimination of sedimentary facies and lithologies in reef-bank reservoirs using borehole image logs. Applied Geophysics 6:17-29. | 2009 | China | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment |
| Church, R. A., D. J. Warren, and J. B. Irion. 2009. Analysis of Deepwater Shipwrecks in the Gulf of Mexico: Artificial Reef Effect of Six World War II Shipwrecks. Oceanography 22:50-63. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering; Invertebrates; Marine Vertebrates; Schools & Colleges; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Clifton, J. 2009. Science, funding and participation: key issues for marine protected area networks and the Coral Triangle Initiative. Environmental Conservation 36:91-96. | 2009 | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | ||
| Collen, J. D., J. P. A. Gardner, and D. W. Garton. 2009. Application of the littoral cell concept to managing a protected atoll: Palmyra Atoll National Wildlife Refuge. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:628-635. | 2009 | Palmyra Atoll | Sediment | |
| Contamin, R. and A. M. Ellison. 2009. Indicators of regime shifts in ecological systems: What do we need to know and when do we need to know it? Ecological Applications 19:799-816. | 2009 | Model; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Costa, C., M. Scardi, V. Vitalini, and S. Cataudella. 2009. A dual camera system for counting and sizing Northern Bluefin Tuna (Thunnus thynnus; Linnaeus, 1758) stock, during transfer to aquaculture cages, with a semi automatic Artificial Neural Network tool. Aquaculture 291:161-167. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Finfish Harvest; Fish | |
| Cragg, G. M. and D. J. Newman. 2009. Nature: a vital source of leads for anticancer drug development. Phytochemistry Reviews 8:313-331. | 2009 | Review; Model | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Cruz-Trinidad, A., R. C. Geronimo, and P. M. Alino. 2009. Development trajectories and impacts on coral reef use in Lingayen Gulf, Philippines. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:173-180. | 2009 | Philippines | Index or Indicator | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Housing; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Cudney-Bueno, R., M.F. Lavin, S.G. Marinone, P.T. Raimondi, W.W. Shaw. 2009. Rapid Effects of Marine Reserves via Larval Dispersal. PLoS One 4:e4140. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Molluscs; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Daily, G.C., S. Polasky, J. Goldstein, P.M. Kareiva, H.A. Mooney, L. Pejchar, T.H. Ricketts, J. Salzman, and R. Shallenberger. 2009. Ecosystem services in decision making: time to deliver. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:21-28. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| deGroot, R. S., R. Alkemade, L. Braat, L. Hein, and L. Willemen. 2009. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecological Complexity (inpress). | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Valuation | |
| Deng, W. F., G. J. Wei, X. H. Li, K. F. Yu, J. X. Zhao, W. D. Sun, and Y. Liu. 2009. Paleoprecipitation record from coral Sr/Ca and delta O-18 during the mid Holocene in the northern South China Sea. Holocene 19:811-821. | 2009 | China | Model; Index or Indicator | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Salinity |
| Dikou, A., C. Ackerman, C. Banks, A. Dempsey, M. Fox, M. Gins, P. Hester, A. Parnes, S. Roach, J. Rohde, C. Spital, M. Tapleshay, and L. Thomas. 2009. Ecological assessment to detect imminent change in coral reefs of Admiral Cockburn Land and Sea National Park, Turks and Caicos Islands. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 30:425-436. | 2009 | South & Central America; Turks and Caicos; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation; Turf Algae |
| Dung, L. D. 2009. Nha Trang Bay marine protected area, Vietnam: Initial trends in coral structure and some preliminary linkages between these trends and human activities (2002-2005). Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management 12:249-257. | 2009 | Vietnam | Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Eberhard, R., C. J. Robinson, J. Waterhouse, J. Parslow, B. Hart, R. Grayson, and B. Taylor. 2009. Adaptive management for water quality planning - from theory to practice. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1189-1195. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management |
| Edgar, G. J., N. S. Barrett, and R. D. Stuart-Smith. 2009. Exploited reefs protected from fishing transform over decades into conservation features otherwise absent from seascapes. Ecological Applications 19:1967-1974. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Political Pressure; Sea Urchins |
| Edwards, P. E. T. 2009. Sustainable financing for ocean and coastal management in Jamaica: The potential for revenues from tourist user fees. Marine Policy 33:376-385. | 2009 | Jamaica | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. | 2009 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Cultural Policies; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Mitigation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies | |
| Erbe, C. and A. R. King. 2009. Modeling cumulative sound exposure around marine seismic surveys. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America 125:2443-2451. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Fancy, S. G., J. E. Gross, and S. L. Carter. 2009. Monitoring the condition of natural resources in US national parks. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 151:161-174. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Fernandes, L., J. Day, B. Kerrigan, D. Breen, G. De'ath, B. Mapstone, R. Coles, T. Done, H. Marsh, I. Poiner, T. Ward, D. Williams, and R. Kenchington. 2009. A process to design a network of marine no-take areas: Lessons from the Great Barrier Reef. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:439-447. | 2009 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Fisher, B., R. K. Turner, and P. Morling. 2009. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecological Economics 68:643-653. | 2009 | Model | ||
| Green, A., S. E. Smith, G. Lipsett-Moore, C. Groves, N. Peterson, S. Sheppard, P. Lokani, R. Hamilton, J. Almany, J. Aitsi, and L. Bualia. 2009. Designing a resilient network of marine protected areas for Kimbe Bay, Papua New Guinea. ORYX 43:488-498. | 2009 | Papua New Guinea | Climate; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation | |
| Green, B. S. and C. Gardner. 2009. Surviving a sea-change: survival of southern rock lobster (Jasus edwardsii) translocated to a site of fast growth. ICES Journal of Marine Science 66:656-664. | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Greiner, R., L. Patterson, and O. Miller. 2009. Motivations, risk perceptions and adoption of conservation practices by farmers. Agricultural Systems 99:86-104. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Guo, W., S. H. Li, and D. K. Zhu. 2009. The application of geographic information technology to coastal geomorphology. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 28:49-57. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing | Ports & Harbors | |
| Gutierrez-Rodriguez, C., M. S. Barbeitos, J. A. Sanchez, and H. R. Lasker. 2009. Phylogeography and morphological variation of the branching octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 50:1-15. | 2009 | South & Central America; Florida; Bahamas; Caribbean | Octocoral | |
| Gutierrez-Rodriguez, C., M. S. Barbeitos, J. A. Sanchez, and H. R. Lasker. 2009. Phylogeography and morphological variation of the branching octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 50:15-Jan. | 2009 | South & Central America; Florida; Bahamas; Caribbean | Octocoral | |
| Halpern, B. S., S. E. Lester, and J. B. Kellner. 2009. Spillover from marine reserves and the replenishment of fished stocks. Environmental Conservation 36:268-276. | 2009 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Hattori, A. and M. Kobayashi. 2009. Incorporating fine-scale seascape composition in an assessment of habitat quality for the giant sea anemone Stichodactyla gigantea in a coral reef shore zone. Ecological Research 24:415-422. | 2009 | Japan | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Seagrasses |
| Hourigan, T. F. 2009. Managing fishery impacts on deep-water coral ecosystems of the USA: emerging best practices. Marine Ecology Progress Series 397:333-340. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Sponges; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| ILM Secretariat (Environment Canada), GeoConnections and International Institute for Sustainable Development. 2009. Integrated management and geospatial information network for the environment - building a shared vision: workshop report. Ottawa, ON, Canada. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landuse Management | |
| Johnson, C. R. 2009. Natural Length Scales of Ecological Systems: Applications at Community and Ecosystem Levels. Ecology and Society 14:7. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Kendall, M. S., L. J. Bauer, and C. F. G. Jeffrey. 2009. Influence Of Hard Bottom Morphology On Fish Assemblages Of The Continental Shelf Off Georgia, Southeastern Usa. Bulletin of Marine Science 84:265-286. | 2009 | Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates | ||
| Kroon, F. J., C. J. Robinson, and A. P. Dale. 2009. Integrating knowledge to inform water quality planning in the Tully-Murray basin, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1183-1188. | 2009 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Kuldna, P., K. Peterson, H. Poltimae, and Jaan Luig. 2009. An application of DPSIR framework to identify issues of pollinator loss. Ecological Economics 69:32-42. | 2009 | Europe | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies |
| Lane, M. B. and C. J. Robinson. 2009. Institutional complexity and environmental management: The challenge of integration and the promise of large-scale collaboration. Australasian Journal of Environmental Management 16:16-24. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research |
| Luo, J. G., J. E. Serafy, S. Sponaugle, P. B. Teare, and D. Kieckbusch. 2009. Movement of gray snapper Lutjanus griseus among subtropical seagrass, mangrove, and coral reef habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380:255-269. | 2009 | Florida | Complex Habitat & Resources; Mangroves; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Luo, J., J. E. Serafy, S. Sponaugle, P. B. Teare, and D. Kieckbusch. 2009. Movement of gray snapper Lutjanus griseus among subtropical seagrass, mangrove, and coral reef habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380:255-269. | 2009 | Florida | Complex Habitat & Resources; Mangroves; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Macpherson, A. J., P. P. Principe, and E. R. Smith. 2009. A production function approach to regional environmental-economic assessments. US Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, (NC, USA). | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model; Index or Indicator | |
| Maeno, S., L. G. Bierawski, W. Magda, and M. Ogawa. 2009. Vof-Dem-Fem Combined Model Of The Reef Breakwater Collapse. Coastal Engineering Journal 51:223-242. | 2009 | Lab Study; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Shoreline Protection; Skeletal Coral | |
| Maxim, L. and J. H. Spangenberg. 2009. Driving forces of chemical risks for the European biodiversity. Ecological Economics 69:43-54. | 2009 | Europe | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Special Use Permitting |
| Maxim, L., J. H. Spangenberg, and M. O'Connor. 2009. An analysis of risks for biodiversity under the DPSIR framework. Ecological Economics 69:12-23. | 2009 | Europe | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| McAdoo, B. G., A. Moore, and J. Baumwoll. 2009. Indigenous knowledge and the near field population response during the 2007 Solomon Islands tsunami. Natural Hazards 48:73-82. | 2009 | Solomon Islands | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Housing; Mitigation; Shoreline Protection |
| McClinktock, W., M. Merrifield, and C. Steinback. 2009. MarineMap: Decision Support for Marine Spatial Planning. UC Santa Barbara, Ecotrust, and The Nature Conservancy. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support | |
| Metaxas, A. and M. Saunders. 2009. Quantifying the "bio-" components in biophysical models of larval transport in marine benthic invertebrates: advances and pitfalls. Biological Bulletin 216:257-272. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Invertebrates | |
| Moses, C. S., S. Andrefouet, C. J. Kranenburg, and F. E. Muller-Karger. 2009. Regional estimates of reef carbonate dynamics and productivity Using Landsat 7 ETM+, and potential impacts from ocean acidification. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380:103-115. | 2009 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Ocean Acidity; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Nelson, D.M., T. Haverland, and E. Finnen. 2009. EcoGIS - GIS Tools for Ecosystem Approaches to Fisheries Management. Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 75, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring (MD, USA). | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Nelson, E., G. Mendoza, J. Regetz, S. Polasky, H. Tallis, D. R. Cameron, K. M. A. Chan, G. C. Daily, J. Goldstein, P. M. Kareiva, E. Lonsdorf, R. Naidoo, T. H. Ricketts, and M. R. Shaw. 2009. Modeling multiple ecosystem services, biodiversity conservation, commodity production, and tradeoffs at landscape scales. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:4-11. | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Resource Use Management; Valuation | |
| Nguyen, H. Y. T., O. Pedersen, K. Ikejima, K. Sunada, and S. Oishi. 2009. Using reefcheck monitoring database to develop the coral reef index of biological integrity. Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Science 4:90-102. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Skeletal Coral; Small Boats; Stony Coral | |
| Nunn, P. D. 2009. Responding to the challenges of climate change in the Pacific Islands: management and technological imperatives. Climate Research 40:211-231. | 2009 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Cultural Policies; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Nursey-Bray, M. 2009. A Guugu Yimmithir Bam Wii: Ngawiya and Girrbithi: Hunting, planning and management along the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Geoforum 40:442-453. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Resource Use Management |
| Ojeda-Martinez, C., F. G. Casalduero, J. T. Bayle-Sempere, C. B. Cebrian, C. Valle, J. L. Sanchez-Lizaso, A. Forcada, P. Sanchez-Jerez, P. Martin-Sosa, J. M. Falcon, F. Salas, M. Graziano, R. Chemello, B. Stobart, P. Cartagena, A. Perez-Ruzafa, F. Vandeperre, E. Rochel, S. Planes, and A. Brito. 2009. A conceptual framework for the integral management of marine protected areas. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:89-101. | 2009 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Marine Protected Areas; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Omann, I., A. Stocker, and J. Jager. 2009. Climate change as a threat to biodiversity: an application of the DPSIR approach. Ecological Economics 69:24-31. | 2009 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mitigation; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Ortiz-Lozano, L., A. Granados-Barba, and I. Espejel. 2009. Ecosystemic zonification as a management tool for marine protected areas in the coastal zone: Applications for the Sistema Arrecifal Veracruzano National Park, Mexico. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:317-323. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Marine Protected Areas |
| Parks, N. 2009. Is regulation on ocean acidification on the horizon? Environmental Science and Technology 6118-6119. | 2009 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; CO2; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Ocean Acidity; Special Use Permitting |
| Pedersen, S. A., H. Fock, J. Krause, C. Pusch, A. L. Sell, U. Bottcher, S. I. Rogers, M. Skold, H. Skov, M. Podolska, G. J. Piet, and J. C. Rice. 2009. Natura 2000 sites and fisheries in German offshore waters. ICES Journal of Marine Science 66:155-169. | 2009 | Designate Protected Species; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Pellegrini, J. A. C., M. L. G. Soares, F. O. Chaves, G. C. D. Estrada, and V. F. Cavalcanti. 2009. A Method for the Classification of Mangrove Forests and Sensitivity/Vulnerability Analysis. Journal of Coastal Research 443-447. | 2009 | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Industry; Petroleum Spills | |
| Peters, H. and J. P. Hawkins. 2009. Access to marine parks: A comparative study in willingness to pay. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:219-228. | 2009 | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Puig, V., G. Cembrano, J. Romera, J. Quevedo, B. Aznar, G. Ramon, and J. Cabot. 2009. Predictive optimal control of sewer networks using CORAL tool: application to Riera Blanca catchment in Barcelona. Water Science and Technology 60:869-878. | 2009 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support |
| Puillandre, N., E. E. Strong, P. Bouchet, M. C. Boisselier, A. Couloux, and S. Samadi. 2009. Identifying gastropod spawn from DNA barcodes: possible but not yet practicable. Molecular Ecology Resources 9:1311-1321. | 2009 | New Caledonia; Philippines | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Molluscs |
| Reid-Grant, K. and M. G. Bhat. 2009. Financing marine protected areas in Jamaica: An exploratory study. Marine Policy 33:128-136. | 2009 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Rodriguez-Labajos, B., R. Binimelis, and I. Monterroso. 2009. Multi-level driving forces of biological invasions. Ecological Economics 69:63-75. | 2009 | Review; Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Roseman, E. F., J. S. Schaeffer, and P. J. Steen. 2009. Review of fish diversity in the Lake Huron basin. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 12:22-Nov. | 2009 | Review | Climate; Fish; Fishing Sector; Remediation; Schools & Colleges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Russell, B. D., J. A. I. Thompson, L. J. Falkenberg, and S. D. Connell. 2009. Synergistic effects of climate change and local stressors: CO2 and nutrient-driven change in subtidal rocky habitats. Global Change Biology 15:2153-2162. | 2009 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Coralline Algae; Economic Markets & Policies; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Sanchirico, J. N. and P. Mumby. 2009. Mapping ecosystem functions to the valuation of ecosystem services: Implications of species-habitat associations for coastal land-use decisions. Theoretical Ecology 2:67-77. | 2009 | Model; GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Valuation | |
| Santos, R. S., S. Christiansen, B. Christiansen, and S. Gubbay. 2009. Toward the conservation and management of Sedlo Seamount: A case study. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 56:2720-2730. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Sashidhara, K. V., K. N. White, and P. Crews. 2009. A selective account of effective paradigms and significant outcomes in the discovery of inspirational marine natural products. Journal of Natural Products 72:588-603. | 2009 | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Scarfe, B. E., T. R. Healy, and H. G. Rennie. 2009. Research-Based Surfing Literature for Coastal Management and the Science of Surfing-A Review. Journal of Coastal Research 25:539-557. | 2009 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. | 2009 | Southeast Asia; Europe | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Special Use Permitting; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Semeniuk, C. A. D., W. Haider, B. Beardmore, and K. D. Rothley. 2009. A multi-attribute trade-off approach for advancing the management of marine wildlife tourism: a quantitative assessment of heterogeneous visitor preferences. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 19:194-208. | 2009 | Cayman Islands | Model | Tourism & Recreation |
| Sibuet, M. and A. Vangriesheim. 2009. Deep-sea environment and biodiversity of the West African Equatorial margin. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 56:2156-2168. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Smajgl, A., S. Morris, and S. Heckbert. 2009. Water policy impact assessment - combining modelling techniques in the Great Barrier Reef region. Water Policy 11:191-202. | 2009 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support |
| Smith, R. T., J. H. Pinzon, and T. C. LaJeunesse. 2009. Symbiodinium (Dinophyta) Diversity And Stability In Aquarium Corals. Journal of Phycology 45:1030-1036. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Collaboration & Partnering; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Som, S. K., V. Shivgotra, and A. Saha. 2009. Coral microatoll as geodetic tool in North Andaman and Little Andaman, India. Journal of Earth System Science 118:157-162. | 2009 | Global; India | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Spangenberg, J. H., J. Martinez-Alier, I. Omann, I. Monterroso, and R. Binimelis. 2009. The DPSIR scheme for analysing biodiversity loss and developing preservation strategies. Ecological Economics 69:9-11. | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Spillman, C. M. and O. Alves. 2009. Dynamical seasonal prediction of summer sea surface temperatures in the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 28:197-206. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Stone, R., D. White, R. Guest, and B. Francis. 2009. The Virtual Scylla: An exploration of \serious games\", artificial life and simulation complexity". Virtual Reality 13:13-25. | 2009 | Europe; England | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Climate; Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Military; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Sunagawa, S., E. C. Wilson, M. Thaler, M. L. Smith, C. Caruso, J. R. Pringle, V. M. Weis, M. Medina, and J. A. Schwarz. 2009. Generation and analysis of transcriptomic resources for a model system on the rise: the sea anemone Aiptasia pallida and its dinoflagellate endosymbiont. BMC Genomics 10:258. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Sutton, S. G. and R. C. Tobin. 2009. Recreational fishers' attitudes towards the 2004 rezoning of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Environmental Conservation 36:245-252. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Tallis, H., R. Goldman, M. Uhl, and B. Brosi. 2009. Integrating conservation and development in the field: implementing ecosystem service projects. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:12�20. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Teh, L. C. L., L. S. L. Teh, B. Starkhouse, and U. Rashid Sumaila. 2009. An overview of socio-economic and ecological perspectives of Fiji's inshore reef fisheries. Marine Policy 33:807-817. | 2009 | Fiji | Review | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector |
| Tissot, B. N., W. J. Walsh, and M. A. Hixon. 2009. Hawaiian Islands Marine Ecosystem Case Study: Ecosystem- and Community-Based Management in Hawaii. Coastal Management 37:255-273. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Tittensor, D. P., A. R. Baco, P. E. Brewin, M. R. Clark, M. Consalvey, J. Hall-Spencer, A. A. Rowden, T. Schlacher, K. I. Stocks, and A. D. Rogers. 2009. Predicting global habitat suitability for stony corals on seamounts. Journal of Biogeography 36:1111-1128. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Complex Habitat & Resources; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Truscan, D., T. Lundkvist, M. Alanen, K. Sandstrom, I. Porres, and J. Lilius. 2009. MDE for SoC design. Pages 49-64 in Innovations in Systems and Software Engineering. | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Tweedie, J. 2009. Always finding a \better way of doing things\"". Geodrilling International 151:20-21. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration |
| U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2009. Federal Member Coral Profiles. Department of the Interior, Washington, DC. | 2009 | Agriculture; Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| UNCWI. 2009. Healthy Watersheds through Healthy Forests. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Drinking Water Supply; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Van Herwerden, L., J. H. Choat, S. J. Newman, M. Leray, and G. Hillersoy. 2009. Complex patterns of population structure and recruitment of Plectropomus leopardus (Pisces: Epinephelidae) in the Indo-West Pacific: implications for fisheries management. Marine Biology 156:1595-1607. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Taiwan | Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Van Herwerden, L., J. Howard Choat, S. J. Newman, M. Leray, and G. Hillersoy. 2009. Complex patterns of population structure and recruitment of Plectropomus leopardus (Pisces: Epinephelidae) in the Indo-West Pacific: implications for fisheries management. Marine Biology 13-Jan. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Taiwan | Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| van Hooidonk, R. and M. Huber. 2009. Quantifying the quality of coral bleaching predictions. Coral Reefs 28:579-587. | 2009 | Global | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sea Temperatures |
| van Hooidonk, R. and M. Huber. 2009. Quantifying the quality of coral bleaching predictions. Coral Reefs 9-Jan. | 2009 | Global | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sea Temperatures |
| Vignon, M., P. Sasal, M. C. Rigby, and R. Galzin. 2009. Multiple parasite introduction and host management plan: case study of lutjanid fish in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 85:133-145. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Worms; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Villa, F., M. Ceroni, K. Bagstad, G. Johnson, and S. Krivov. 2009. ARIES (ARtificial Intelligence for Ecosystem Services): a new tool for ecosystem services assessment, planning, and valuation. in Proceedings of the 11th Annual BIOECON Conference on Economic Instruments to Enhance the Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biodiversity. Venice, Italy, September, 2000. | 2009 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| von Winterfeldt, D. and B. Fasolo. 2009. Structuring decision problems: A case study and reflections for practitioners. European Journal of Operational Research 199:857-866. | 2009 | Review; Model | Natural Gas & Electric Power | |
| Walton, R. S. and H. M. Hunter. 2009. Isolating the water quality responses of multiple land uses from stream monitoring data through model calibration. Journal of Hydrology 378:29-45. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ward, R. D., R. Hanner, and P. D. N. Hebert. 2009. The campaign to DNA barcode all fishes, FISH-BOL. Journal of Fish Biology 74:329-356. | 2009 | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish | ||
| Watts, M. E., I. R. Ball, R. S. Stewart, C. J. Klein, K. Wilson, C. Steinback, R. Lourival, L. Kircher, and H. P. Possingham. 2009. Marxan with Zones: Software for optimal conservation based land- and sea-use zoning. Environmental Modelling & Software 24:1513-1521. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management |
| Weir, C. R. 2009. Distribution, behaviour and photo-identification of Atlantic humpback dolphins Sousa teuszii off Flamingos, Angola. African Journal of Marine Science 31:319-331. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Housing; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| Wooldridge, S. A. and T. J. Done. 2009. Improved water quality can ameliorate effects of climate change on corals. Ecological Applications 19:1492-1499. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Climate; CO2; Collaboration & Partnering; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures | |
| World Resources Institute. 2009. Value of coral reefs & mangroves in the caribbean: economic valuation methodology v3.0. | 2009 | South & Central America; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Belize; Caribbean | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Cruise Ships; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Yadav, S. P., D. N. Singh, A. K. Singh, and R. Prasad. 2009. Electrical resistivity imaging for the study of quartz reef using inverse slope method. Current Science 96:1521-1527. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Yokoo, T., T. Sakamoto, K. Kanou, M. Moteki, H. Kohno, P. Tongnunui, and H. Kurokura. 2009. Morphological characters and occurrence patterns of juveniles of two estuarine gobies, Acentrogobius kranjiensis and Acentrogobius malayanus, verified by molecular identification. Journal of Fish Biology 75:2805-2819. | 2009 | Thailand | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Mangroves; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Zorrilla, P., G. Carmona, A. De la Hera, C. Varela-Ortega, P. Martinez-Santos, J. Bromley, and H. Jorgen Henriksen. 2009. Evaluation of Bayesian Networks in Participatory Water Resources Management, Upper Guadiana Basin, Spain. Ecology and Society 15. | 2009 | Spain | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| [No author name available]. 2008. Bucking bindery trends. Printing Impressions 50:58. | 2008 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| 2008. Coral Bay Watershed Management Plan A Pilot Project for Watershed Planning in the USVI. Center for Watershed Protection, Wllicott City,(Maryland, USA). | 2008 | |||
| Alkendi, M. Y. and M. Chandler. 2008. A successful stakeholder partnership - The Dolphin Energy experience coral reef habitats of the Arabian Gulf. Pages 2039-2047 in Society of Petroleum Engineers - 9th International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production 2008 - \In Search of Sustainable Excellence\"". | 2008 | Global; Qatar | GIS & Maps | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cultural Policies; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins |
| Andrefouet, S. 2008. Coral reef habitat mapping using remote sensing: A user vs producer perspective. Implications for research, management and capacity building. Journal of Spatial Science 53:113-129. | 2008 | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Arentze, T. A., B. G. C. Dellaert, H. J. P. Timmermans. 2008. Modeling and Measuring Individuals� Mental Representations of Complex Spatio-Temporal Decision Problems. Environment and Behavior 40:843-869. | 2008 | Model; GIS & Maps | ||
| Aydin, N. 2008. The need for tourism satellite account: a florida case study: more basic estimating methods reach only the tip of the iceberg. Applied Research in Economic Development 5:37-47. | 2008 | Florida | Model | Tourism & Recreation |
| Barton, D. N., T. Saloranta, S.J. Moe, H.O. Eggestad, and S. Kuikka. 2008. Bayesian belief networks as a meta-modelling tool in integrated river basin management Pros and cons in evaluating nutrient abatement decisions under uncertainty in a Norwegian river basin. Ecological Economics 66:91-104. | 2008 | Norway | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Recreational Opportunities; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation |
| Baums, I. B. 2008. A restoration genetics guide for coral reef conservation. Molecular Ecology 17:2796-2811. | 2008 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bay, L. K., M. J. M. Caley, and R. H. Crozier. 2008. Meta-population structure in a coral reef fish demonstrated by genetic data on patterns of migration, extinction and re-colonisation. BMC Evolutionary Biology 8. | 2008 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish |
| Beech, T., M. Dowd, C. Field, B. Hatcher, and S. Andrefouet. 2008. A stochastic approach to marine reserve design: Incorporating data uncertainty. Ecological Informatics 3:321-333. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Marine Protected Areas |
| Ben-Tzvi, O., M. Kiflawi, S. D. Gaines, M. Al-Zibdah, M. S. Sheeny, G. L. Paradis, and A. Abelson. 2008. Tracking recruitment pathways of Chromis viridis in the Gulf of Aqaba using otolith chemistry. Marine Ecology Progress Series 359:229-238. | 2008 | Egypt | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Bokma, B. H., E. P. J. Gibbs, A. A. Aguirre, and B. Kaplan. 2008. A resolution by the Society for Tropical Veterinary Medicine in support of \One Health\"". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1149:8-Apr. | 2008 | Collaboration & Partnering; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics | ||
| Bradley, P., W. Davis, W. Fisher, H. Bell, V. Chan, C. LoBue, and W. Wiltse. 2008. Biological criteria for protection of U.S. coral reefs. Pages 1078-1082 in Proceedings of the 11th International Coral Reef Symposium. Ft. Lauderdale, Florida. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria | |
| Bradshaw, C. J. A., B. M. Fitzpatrick, C. C. Steinberg, B. W. Brook, and M. G. Meekan. 2008. Decline in whale shark size and abundance at Ningaloo Reef over the past decade: The world's largest fish is getting smaller. Biological Conservation 141:1894-1905. | 2008 | Australia | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Tourism & Recreation |
| Buddemeier, R. W., P. L. Jokiel, K. M. Zimmerman, D. R. Lane, J. M. Carey, G. C. Bohling, and J. A. Martinich. 2008. A modeling tool to evaluate regional coral reef responses to changes in climate and ocean chemistry. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 6:395-411. | 2008 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; CO2 |
| Cardona-Maldonado, M. A. 2008. Assessment of coral reef community structure using water optical properties. Masters Thesis. University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez (Puerto Rico). | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Sediment; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. | 2008 | Puerto Rico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Improved Technology; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chang, Y.C., F.W. Hong, and M.T. Lee. 2008. A system dynamic based DSS for sustainable coral reef management in Kenting coastal zone, Taiwan. Ecological Modelling 211:153-168. | 2008 | Taiwan | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fish; Sewage Treatment; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chang, Y.-C., M.-T. Lee, and K.-C. Lai. 2008. Web-based information management system for the Long Term Ecological Research program in kenting, Taiwan. Journal of Marine Science and Technology 16:174-181. | 2008 | Taiwan | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Housing; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Clemencic, M. 2008. LHCb distributed conditions database. in Journal of Physics: Conference Series. | 2008 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Conroy, M. J., R. J. Baker, P. W. Dillingham, D. Fletcher, A. M. Gormley, and I. M. Westbrooke. 2008. Application of decision theory to conservation management: recovery of Hector�s dolphin. Wildlife Research 35:93-102. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Crabbe, J.C. 2008. Climate change, global warming and coral reefs: Modelling the effects of temperature. Computational Biology and Chemistry | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Internet & Telecommunications; Stony Coral |
| Daily, G. C. and P. A. Matson. 2008. Ecosystem services: from theory to implementation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105:9455-9456. | 2008 | GIS & Maps | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives | |
| Davies, A. J., M. Wisshak, J. C. Orr, and J. Murray Roberts. 2008. Predicting suitable habitat for the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia). Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 55:1048-1062. | 2008 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Salinity; Stony Coral |
| deJongh Jr., J. P., editor. 2008. United States Virgin Islands comprehensive economic development strategy. USVI Bureau of Economic Research, Unites States Virgin Islands. | 2008 | US Virgin Islands | Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Housing | |
| D'Entremont, A., J. Kaariainen, and K. Baker. 2008. SERPENT of the Deep - Research, monitoring and partnerships for a deepwater well off atlantic canada. Pages 1493-1500 in Society of Petroleum Engineers - 9th International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production 2008 - \In Search of Sustainable Excellence\"". | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Schools & Colleges; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Drew, C. A. and D. B. Eggleston. 2008. Juvenile fish densities in Florida Keys mangroves correlate with landscape characteristics. Marine Ecology Progress Series 362:233-243. | 2008 | Florida | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves |
| Dryden, J., A. Grech, J. Moloney, and M. Hamann. 2008. Rezoning of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area: Does it afford greater protection for marine turtles? Wildlife Research 35:477-485. | 2008 | Australia | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Duarte, C. M., W. C. Dennison, R. J. W. Orth, and T. J. B. Carruthers. 2008. The charisma of coastal ecosystems: Addressing the imbalance. Estuaries and Coasts 31:233-238. | 2008 | Collaboration & Partnering; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Seagrasses | ||
| Fisher, J. B., R. Nawaz, R. Fauzi, F. Nawaz, E. S. Said Md. Sadek, Z. Abd. Latif, and M. Blackett. 2008. Balancing water, religion and tourism on Redang Island, Malaysia. Environmental Research Letters 3:1-6. | 2008 | Malaysia | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Schools & Colleges; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Forest Trends, The Katoomba Group, and UNEP. 2008. Payments for ecosystem services: getting started a primer. | 2008 | Review | ||
| Francini-Filho, R. B. and R. L. Moura. 2008. Evidence for spillover of reef fishes from a no-take marine reserve: An evaluation using the before-after control-impact (BACI) approach. Fisheries Research 93:346-356. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Gangai, J. W., R. Lenaburg, B. Batten, E. Drei-Horgan, N. Sheffner, D. Hamilton, M. Rezakhani, and P. Shrestha. 2008. Hurricane Flood Insurance study for the Hawaiian Islands. Pages 432-443 in Solutions to Coastal Disasters Congress 2008 - Proceedings of the Solutions to Coastal Disasters Congress 2008. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Insurance; Military; Security Policies; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Goodman, J. A., M. Velez-Reyes, and S. Rosario-Torres. 2008. An update on SeaBED: A TesBED for validating subsurface aquatic hyperspectral remote sensing algorithms. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 7105. | 2008 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Infrastructure; Seagrasses |
| Granek, E. F., E. M. P. Madin, M. A. Brown, W. Figueira, D. S. Cameron, Z. Hogan, G. Kristianson, P. De Villiers, J. E. Williams, J. Post, S. Zahn, and R. Arlinghaus. 2008. Engaging recreational fishers in management and conservation: Global case studies. Conservation Biology 22:1125-1134. | 2008 | Global; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Grech, A. and H. Marsh. 2008. Rapid assessment of risks to a mobile marine mammal in an ecosystem-scale marine protected area. Conservation Biology 22:711-720. | 2008 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Whales & Dolphins |
| Greiner, R. and O. Miller. 2008. Reducing diffuse water pollution by tailoring incentives to region specific requirements: Empirical study for the Burdekin River basin (Australia). Pages 31-42 in WIT Transactions on Ecology and the Environment. | 2008 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges |
| Greiner-Wronowa, E. 2008. Glass decoration elements - History and technology. Pages 505-510 in Advanced Materials Research. | 2008 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Guzy, M. R., C. L. Smith, J. P. Bolte, D. W. Hulse and S. V. Gregory. 2008. Policy research using agent-based modeling to assess future impacts of urban expansion into farmlands and forests. | 2008 | Model | Agriculture; Fish; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hajkowicz, S. A. 2008. Supporting multi-stakeholder environmental decisions. Journal of Environmental Management 88:607-614. | 2008 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Primary Production |
| Halpern, B. S., S. Walbridge, K. A. Selkoe, C. V. Kappel, F. Micheli, C. D�Agrosa, J. F. Bruno, K. S. Casey, C. Ebert, H. E. Fox, R. Fujita, D. Heinemann, H. S. Lenihan, E. M. P. Madin, M. T. Perry, E. R. Selig, M. Spalding, R. Steneck, and R. Watson. 2008. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 319:948-952. | 2008 | Global | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hennige, S. 2008. Harvesting light. Planet Earth 18-19. | 2008 | Algae; Collaboration & Partnering; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Henriques, S., M. P. Pais, M. J. Costa, and H. Cabral. 2008. Development of a fish-based multimetric index to assess the ecological quality of marine habitats: the Marine Fish Community Index. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:1913-1934. | 2008 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Holmberg, J., B. Norman, and Z. Arzoumanian. 2008. Robust, comparable population metrics through collaborative photo-monitoring of whale sharks Rhincodon typus. Ecological Applications 18:222-233. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Irion, J. B., D. Ball, and C. E. Horrell. 2008. The US government's role in deepwater archaeology: The deep gulf Wrecks project. International Journal of Historical Archaeology 12:75-81. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Remote Sensing | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration |
| Lloret, J. and V. Riera. 2008. Evolution of a mediterranean coastal zone: Human impacts on the marine environment of cape creus. Environmental Management 42:977-988. | 2008 | Cuba | Boating Activities; Climate; Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Lundquist, C. J. and M. H. Pinkerton. 2008. Collation of data for ecosystem modelling of Te Tapuwae o Rongokako Marine Reserve. Science for Conservation 1-103. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Maina, J., V. Venus, T. R. McClanahan, and M. Ateweberhan. 2008. Modelling susceptibility of coral reefs to environmental stress using remote sensing data and GIS models. Ecological Modelling 212:180-199. | 2008 | Indian Ocean; Madagascar; India | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Light; Marine Protected Areas |
| Metcalf, S. J., J. M. Dambacher, A. J. Hobday, and J. M. Lyle. 2008. Importance of trophic information, simplification and aggregation error in ecosystem models. Marine Ecology Progress Series 360:25-36. | 2008 | Model | Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Metzger, M.J., D. Schroter, R. Leemans, W. Cramer. 2008. A spatially explicit and quantitative vulnerability assessment of ecosystem service change in Europe. Regional Environmental Change 3:91-107. | 2008 | Global; Europe | Model; Index or Indicator | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering |
| Moltu, U. E. and L. Pinturier. 2008. Zero harmful impact from drilling discharges: Where are the limits? Pages 988-1002 in Society of Petroleum Engineers - 9th International Conference on Health, Safety and Environment in Oil and Gas Exploration and Production 2008 - \In Search of Sustainable Excellence\"". | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Corporate Responses; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Sediment; Toxics | |
| Montagna, P., S. Silenzi, S. Devoti, C. Mazzoli, M. McCulloch, G. Scicchitano, and M. Taviani. 2008. Climate reconstructions and monitoring in the Mediterranean Sea: A review on some recently discovered high-resolution marine archives. Rendiconti Lincei 19:121-140. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Salinity | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Chapter 13, Part 650. Wetland Restoration, Enhancement or Creation. Engineering Field Handbook. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Military; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands | |
| NOAA; The Nature Conservancy. 2008. Creosote Assessment in Puget Sound Beaches. NOAA. | 2008 | Beaches & Nature Parks; Collaboration & Partnering; Docks & Marinas; Sediment | ||
| Pelletier, D., J. Claudet, J. Ferraris, L. Benedetti-Cecchi, and J. Antonio Garc�a-Charton. 2008. Models and indicators for assessing conservation and fisheries-related effects of marine protected areas. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 65:765-779. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Pittman, S. J., S. D. Hile, C. F. G. Jeffrey, C. Caldow, M. S. Kendall, M. E. Monaco, and Z. Hillis-Starr. 2008. Fish assemblages and benthic habitats of Buck Island Reef National Monument (St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands) and the surrounding seascape: a characterization of spatial and temporal patterns. NOAA, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Seagrasses |
| Prince, J. D., H. Peeters, H. Gorfine, and R. W. Day. 2008. The novel use of harvest policies and rapid visual assessment to manage spatially complex abalone resources (Genus Haliotis). Fisheries Research 94:330-338. | 2008 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Corporate Responses; Fishing Sector |
| Ridgway, T., C. Riginos, J. Davis, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2008. Genetic connectivity patterns of Pocillopora verrucosa in southern African Marine Protected Areas. Marine Ecology Progress Series 354:161-168. | 2008 | Mozambique; South Africa | Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral | |
| Rodriguez-Martinez, R. E. 2008. Community involvement in marine protected areas: The case of Puerto Morelos reef, Mexico. Journal of Environmental Management 88:1151-1160. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Roelfsema, C. and S. Phinn. 2008. Evaluating eight field and remote sensing approaches for mapping the benthos of three different coral reef environments in Fiji. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 7150. | 2008 | Fiji | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Seagrasses |
| Sammarco, P. W. 2008. Crises on coral reefs and in coral reef science in the 21st century: The need for a new peer-review system. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8:109-119. | 2008 | Global | Review; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Pathogens |
| Shivlani, M., V. R. Leeworthy, T. J. Murray, D. O. Suman, and F. Tonioli. 2008. Knowledge, attitudes and perceptions of management strategies and regulations of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuaries by commercial fishers, dive operators, and environmental group members: a baseline characterization and 10-year comparison. U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Office of National Marine Sanctuaries, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | Florida | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Commercial Fisheries; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Sonak, S., P. Pangam, and A. Giriyan. 2008. Green reconstruction of the tsunami-affected areas in India using the integrated coastal zone management concept. Journal of Environmental Management 89:14-23. | 2008 | Global; Sri Lanka; India; Thailand; Malaysia; Indonesia | Collaboration & Partnering; Infrastructure | |
| Spencer, M. and J. E. Tanner. 2008. Lotka-Volterra competition models for sessile organisms. Ecology 89:1134-1143. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Stelzenmuller, V., F. Maynou, G. Bernard, G. Cadiou, M. Camilleri, R. Crec�hriou, G. Criquet, M. Dimech, O. Esparza, R. Higgins, P. Lenfant, and A. P�rez-Ruzafa. 2008. Spatial assessment of fishing effort around European marine reserves: Implications for successful fisheries management. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:2018-2026. | 2008 | Europe; Spain; France | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Teh, L. C. L., L. S. L. Teh, and F. C. Chung. 2008. A private management approach to coral reef conservation in Sabah, Malaysia. Biodiversity and Conservation 17:3061-3077. | 2008 | Malaysia | Field Study & Monitoring | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Tessier, E., L. Bigot, C. Cadet, B. Cauvin, P. Chabanet, C. Conand, J.-B. Nicet, and J.-P. Quod. 2008. Coral reefs of Reunion Island in 2007: Status report and monitoring network [Les recifs coralliens de la Reunion en 2007: etat des lieux et reseau de suivi]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:85-102. | 2008 | Global; Indian Ocean; Reunion; India; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Thangaradjou, T., R. Sridhar, S. Senthilkumar, and S. Kannan. 2008. Seagrass resource assessment in the Mandapam coast of the Gulf of Mannar biosphere reserve, India. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research 6:139-146. | 2008 | India | Remote Sensing | Seagrasses |
| Torrents, O., E. Tambutte, N. Caminiti, and J. Garrabou. 2008. Upper thermal thresholds of shallow vs. deep populations of the precious Mediterranean red coral Corallium rubrum (L.): Assessing the potential effects of warming in the NW Mediterranean. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 357:19-Jul. | 2008 | Global; France | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate |
| US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. | 2008 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Energy Policy & Development; Food & Energy Policies; Transportation Policies | |
| Valassi, A., R. Basset, M. Clemencic, G. Pucciani, S. A. Schmidt, and M. Wache. 2008. Cool, LCG conditions database for the IHC experiments: Development and deployment status. Pages 3021-3028 in IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record. | 2008 | Europe | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering |
| Venkatachalam, L. 2008. Behavioral economics for environmental policy. Ecological Economics 67:640-645. | 2008 | Global | Model | |
| Vicente, M., M. Falcao, M. N. Santos, M. Caetano, D. Serpa, C. Vale, and C. Monteiro. 2008. Environmental assessment of two artificial reef systems off southern Portugal (Faro and Olhão): A question of location. Continental Shelf Research 28:839-847. | 2008 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Waddell, J. E. and A. M. Clarke, editors. 2008. The state of coral reef ecosystems of the United States and Pacific Freely Associated States: 2008. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 73. NOS NCCOS 73, NOAA/NCCOS Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment�s Biogeography Team, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Internet & Telecommunications |
| Wantiez, L. 2008. Coral reefs of New Caledonia in 2006: Status report and monitoring network [Les recifs coralliens de nouvelle-caledonie en 2006: etat des lieux et reseau de suivi]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:117-132. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Cruise Ships; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Mining; Mining Policies; Seastars; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| Wase, N. V. and P. C. Wright. 2008. Systems biology of cyanobacterial secondary metabolite production and its role in drug discovery. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery 3:903-929. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| White, I., T. Falkland, T. Metutera, M. Katatia, T. Abete-Reema, M. Overmars, P. Perez, and A. Dray. 2008. Safe water for people in low, small Island Pacific Nations: The rural-urban dilemma. Development 51:282-287. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Water |
| Whiteley, R. J. and S. B. Stewart. 2008. Case studies of shallow marine investigations in Australia with advanced underwater seismic refraction (USR). Exploration Geophysics 39:34-40. | 2008 | Australia | Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Pipelines; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Work, T. M., L. L. Richardson, T. L. Reynolds, and B. L. Willis. 2008. Biomedical and veterinary science can increase our understanding of coral disease. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 362:63-70. | 2008 | Global | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Iran; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Wulff, J. L. 2008. Collaboration among sponge species increases sponge diversity and abundance in a seagrass meadow. Marine Ecology 29:193-204. | 2008 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Collaboration & Partnering; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Yee, S. H., D. L. Santavy, and M. G. Barron. 2008. Comparing environmental influences on coral bleaching across and within species using clustered binomial regression. Ecological Modelling 218:162-174. | 2008 | Florida | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Light; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Yost, R. W. and E. L. F. Gonzalez. 2008. A coral reef as an analogical model to promote collaborative learning on cultural & ethnic diversity in science. American Biology Teacher 70:39-43. | 2008 | Model | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Zoraja, I., I. Zulim, and M. Stula. 2008. CORAL - Online monitoring in distributed applications: Issues and solutions. WSEAS Transactions on Computers 7:113-118. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| [No author name available]. 2007. Alien invaders - Nowhere to hide. Pages 31-33 MER - Marine Engineers Review. | 2007 | Review | Ballast Discharge; Collaboration & Partnering; Cruise Ships | |
| Aswani, S., S. Albert, A. Sabetian, and T. Furusawa. 2007. Customary management as precautionary and adaptive principles for protecting coral reefs in Oceania. Coral Reefs 26:1009-1021. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management | |
| Bannister, R. J., R. Brinkman, C. Wolff, C. Battershill, and R. De Nys. 2007. The distribution and abundance of dictyoceratid sponges in relation to hydrodynamic features: Identifying candidates and environmental conditions for sponge aquaculture. Marine and Freshwater Research 58:624-633. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Aquaculture; Sponges |
| Beaman, R. J. and P. T. Harris. 2007. Geophysical variables as predictors of megabenthos assemblages from the Northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Special Paper - Geological Association of Canada 247-263. | 2007 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Physical Variables; Sediment; Substrate |
| Brander L.M., Van Beukering P., Cesar H.S.J. 2007. The recreational value of coral reefs: a meta-analysis. Ecological Economics 63:209-218. | 2007 | Model | Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Busing, R. T. 2007. A spatial landscape model of forest patch dynamics and climate change. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate | |
| Chakalall, B., R. Mahon, P. McConney, L. Nurse, and D. Oderson. 2007. Governance of fisheries and other living marine resources in the Wider Caribbean. Fisheries Research 87:92-99. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Tourism & Recreation |
| Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Mitigation; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Ding, H., A. Ruijs, and E. C. van Ierland. 2007. Designing a Decision Support System for Marine Reserves Management: An Economic Analysis for the Dutch North Sea. FEEM Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei Research Paper Series 23, Italy. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Dytham, C. and S. D. Simpson. 2007. Elevated mortality of fish larvae on coral reefs drives the evolution of larval movement patterns. Marine Ecology Progress Series 346:255-264. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish | |
| Erlandson, J. M., M. H. Graham, B. J. Bourque, D. Corbett, J. A. Estes, and R. S. Steneck. 2007. The kelp highway hypothesis: Marine ecology, the coastal migration theory, and the peopling of the Americas. Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology 2:161-174. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Fenton, N., m. Neil, W. Marsh, P. Hearty, D. Marquez, P. Krause, and R. Mishra. 2007. Predicting software defects in varying development lifecycles using Bayesian nets. Information and Software Technology 49:32-43. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support | |
| Fisher, W.S. 2007. Stony soral rapid bioassessment protocol. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Biocriteria; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Stony Coral; Valuation | |
| Goodman, J. A. and S. L. Ustin. 2007. Classification of benthic composition in a coral reef environment using spectral unmixing. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 1. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Substrate |
| Greenwood, M. A. 2007. Watery laboratory whets interest. Photonics Spectra 41:148. | 2007 | Florida | Lab Study | Collaboration & Partnering; Sponges |
| Hagan, A. B., R. Foster, N. Perera, C. A. Gunawan, I. Silaban, Y. Yaha, Y. Manuputty, I. Hazam, and G. Hodgson. 2007. Tsunami impacts in Aceh Province and North Sumatra, Indonesia. Atoll Research Bulletin 37-54. | 2007 | Indian Ocean; India; Thailand; Indonesia | Collaboration & Partnering; Social Organizations | |
| Halpern, B. S., K. A. Selkoe, F. Micheli, and C. V. Kappel. 2007. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conservation Biology 21:1301-1315. | 2007 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Point Source Discharges; Sea Temperatures | |
| Heck Jr., K. L. and J. F. Valentine. 2007. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 30:371-381. | 2007 | Review | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Henriksen, H. J., P. Rasmussen, G. Brandt, D. von Bulow, and F. V. Jensen. 2007. Public participation modelling using Bayesian Networks in management of groundwater contamination. Environmental Modelling & Software 22:1101-1113. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Chemical Use Regulations; Decision Support; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Herr, A. and P. M. Kuhnert. 2007. Assesment of uncertainty in Great Barrier Reef catchment models. Water Science and Technology 56:181-188. | 2007 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| Jenkin, M., A. Hogue, A. Germam, S. Gill, A. Topol, and S. Wilson. 2007. Underwater surface recovery and segmentation. Pages 373-380 in Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Conference on Cognitive Informatics, ICCI 2007. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Jones, A., S. J. Slade, A. J. Williams, B. D. Mapstone, and K. J. Kane. 2007. Pitfalls and benefits of involving industry in fisheries research: A case study of the live reef fish industry in Queensland, Australia. Ocean and Coastal Management 50:428-442. | 2007 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Kuffner, I. B., J. C. Brock, R. Grober-Dunsmore, V. E. Bonito, T. D. Hickey, and C. W. Wright. 2007. Relationships between reef fish communities and remotely sensed rugosity measurements in Biscayne National Park, Florida, USA. 78:71-82. | 2007 | Florida | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Physical Variables |
| Little, L. R., A. E. Punt, B. D. Mapstone, F. Pantus, A. D. M. Smith, C. R. Davies, and A. D. McDonald. 2007. ELFSim-A model for evaluating management options for spatially structured reef fish populations: An illustration of the \larval subsidy\" effect". Ecological Modelling 205:381-396. | 2007 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation |
| Lund, K. and A. R. Wilbur. 2007. Habitat classification feasibility study for coastal and marine environments in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management, Boston, MA. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Wetlands | |
| Mangi, S. C., C. M. Roberts, and L. D. Rodwell. 2007. Reef fisheries management in Kenya: Preliminary approach using the driver-pressure-state-impacts-response (DPSIR) scheme of indicators. Ocean and Coastal Management 50:463-480. | 2007 | Kenya | Review; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Mellin, C., S. Andrefouet, and D. Ponton. 2007. Spatial predictability of juvenile fish species richness and abundance in a coral reef environment. Coral Reefs 26:895-907. | 2007 | New Caledonia | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Seagrasses |
| Mohamed, M. 2007. ECONOMIC VALUATION OF CORAL REEFS: A CASE STUDY OF THE COSTS AND BENEFITS OF IMPROVED MANAGEMENT OF DHIGALI HAA, A MARINE PROTECTED AREA IN BAA ATOLL, MALDIVES. Masters Thesis. University of Canterbury, (Christchurch, New Zealand). | 2007 | Maldives | Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation | |
| Nassiri, N. 2007. Materials: Coral bone substitute proves able to heal bone fast and effectively. Pages 3-Jan Biomedical Materials. | 2007 | Europe; France | Collaboration & Partnering; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Military; Mitigation; Schools & Colleges | |
| Neigel, J., A. Domingo, and J. Stake. 2007. DNA barcoding as a tool for coral reef conservation. Coral Reefs 26:487-499. | 2007 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish |
| NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | |
| Pimentel, J. C. L., R. Monroy, and D. Hutter. 2007. A Method for Patching Interleaving-Replay Attacks in Faulty Security Protocols. Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 174:117-130. | 2007 | Europe; Germany; Norway | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Pittman, S. J., J. D. Christensen, C. Caldow, C. Menza, and M. E. Monaco. 2007. Predictive mapping of fish species richness across shallow-water seascapes in the Caribbean. Ecological Modelling 204:9-21. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Seagrasses; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Ramos, J., M. N. Santos, D. Whitmarsh, and C. C. Monteiro. 2007. Stakeholder perceptions regarding the environmental and socio-economic impacts of the Algarve artificial reefs. Hydrobiologia 580:181-191. | 2007 | Europe | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives |
| Ramos-Scharron, C. E. 2007. Sediment Production From Natural And Disturbed Surfaces In Dry Tropical Areas Of La Parguera-Pr, 2003-2005. Pages 1-5 in SEVENTH CARIBBEAN ISLANDS WATER RESOURCES CONGRESS. | 2007 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Model; GIS & Maps | Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Transportation Policies |
| Ramos-Scharron, C. E. and L. H. MacDonald. 2007. Development and application of a GIS-based sediment budget model. Journal of Environmental Management 84:157-172. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fish; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies |
| Reichert, P., M. Borsuk, M. Hostmann, S. Schweizer, C. Sporri, K. Tockner, and B. Truffer. 2007. Concepts of decision support for river rehabilitation. Environmental Modelling & Software 22:188-201. | 2007 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Relini, G., M. Relini, G. Palandri, S. Merello, and E. Beccornia. 2007. History, ecology and trends for artificial reefs of the Ligurian sea, Italy. Hydrobiologia 580:193-217. | 2007 | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Rhodes, K. L. and M. H. Tupper. 2007. A preliminary market-based analysis of the Pohnpei, Micronesia, grouper (Serranidae: Epinephelinae) fishery reveals unsustainable fishing practices. Coral Reefs 26:335-344. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Micronesia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish |
| Roiser, S. and A. Pfeiffer. 2007. Configuration, build and distribution of LCG applications area software for the LHC experiments. Pages 1918-1922 in IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record. | 2007 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure | |
| Sammarco, P. W., P. Hallock, J. C. Lang, and R. S. Legore. 2007. Roundtable discussion groups summary papers: Environmental bio-indicators in coral reef ecosystems: The need to align research, monitoring, and environmental regulation. Environmental Bioindicators 2:35-46. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Toxics | |
| Santangelo, G., L. Bramanti, and M. Iannelli. 2007. Population dynamics and conservation biology of the over-exploited Mediterranean red coral. Journal of Theoretical Biology 244:416-423. | 2007 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Octocoral |
| Santos, M. N. and C. C. Monteiro. 2007. A fourteen-year overview of the fish assemblages and yield of the two oldest Algarve artificial reefs (southern Portugal). Hydrobiologia 580:225-231. | 2007 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Scopelitis, J., S. Andrefouet, and C. Largouet. 2007. Modelling coral reef habitat trajectories: evaluation of an integrated timed automata and remote sensing approach. Ecological Modelling 205:59-80. | 2007 | New Caledonia | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Seastars; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Seijo, J. C. 2007. Considerations for management of metapopulations in small-scale fisheries of the Mesoamerican barrier reef ecosystem. Fisheries Research 87:86-91. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Monetary Valuation |
| Shephard, S., P. Connolly, N.-R. Hareide, and E. Rogan. 2007. Establishing stakeholder connections for management of the Irish orange roughy fishery. ICES Journal of Marine Science 64:841-845. | 2007 | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector | ||
| Sherman, B. S., J. Brodie, L. Cogle, and C. Carroll. 2007. Appropriate use of catchment models for water-quality target setting and land-use management. IAHS-AISH Publication 239-250. | 2007 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps | Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Simpson, B. W. 2007. Lessons for achieving effective management from field research on agrochemicals. Pages 338-359 in ACS Symposium Series. | 2007 | Australia; Mauritius | Field Study & Monitoring | Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Smajgl, A. and P. C. Gehrke. 2007. Integrating economic and ecological modelling in the great barrier reef catchments. IAHS-AISH Publication 107-115. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Climate; Funding & Incentives; Non-point Source Runoff |
| Starr, R. M., E. Sala, E. Ballesteros, and M. Zabala. 2007. Spatial dynamics of the Nassau grouper Epinephelus striatus in a Caribbean atoll. Marine Ecology Progress Series 343:239-249. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Stolk, P., K. Markwell, and J. M. Jenkins. 2007. Artificial reefs as recreational scuba diving resources: A critical review of research. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 15:331-350. | 2007 | Cuba | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Svarstad, H., L. K. Petersen, D. Rothman, H. Siepel, and F. Watzold. 2007. Discursive biases of the environmental research framework DPSIR. Land Use Policy [inpress]. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Taghavi, A. A., A. Mork, and E. Kazemzadeh. 2007. Flow unit classification for geological modelling of a heterogeneous carbonate reservoir: Cretaceous sarvak formation, Dehluran field, SW Iran. Journal of Petroleum Geology 30:129-146. | 2007 | Iran | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Toxics |
| Tarrant, A. M. 2007. Hormonal signaling in cnidarians: Do we understand the pathways well enough to know whether they are being disrupted? Ecotoxicology 16:13-May. | 2007 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Special Use Permitting | |
| Thiel, M., E. C. Macaya, E. Acuna, W. E. Arntz, H. Bastias, K. Brokordt, P. A. Camus, J. C. Castilla, L. R. Castro, M. Cortes, C. P. Dumont, R. Escribano, M. Fernandez, J. A. Gajardo, C. F. Gaymer, I. Gomez, A. E. Gonzalez, H. E. Gonzalez, P. A. Haye, and J.-E. Illanes. 2007. The Humboldt Current System of northern and central Chile - Oceanographic processes, ecological interactions and socioeconomic feedback. Oceanography and Marine Biology 45:195-344. | 2007 | South & Central America | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| Thomas, F. R. 2007. The behavioral ecology of shellfish gathering in Western Kiribati, Micronesia 1: Prey choice. Human Ecology 35:179-194. | 2007 | Micronesia; Kiribati | Model | Invertebrates |
| Vega-Zepeda, A., H. Hernandez-Arana, and J. P. Carricart-Ganivet. 2007. Spatial and size-frequency distribution of Acropora (Cnidaria: Scleractinia) species in Chinchorro Bank, Mexican Caribbean: Implications for management. Coral Reefs 26:671-676. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral |
| White, S. 2007. Utilization of LIDAR and NOAA's vertical datum transformation tool (VDatum) for shoreline delineation. in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Wilson, A. 2007. Nonwoven support - From Boscombe Pier to Palm Jumeirah. Technical Textiles International 16:25-28. | 2007 | Global; United Arab Emirates; Europe | Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Road Construction & Maintenance; Shoreline Protection | |
| Yang, S., L. Li, and C. Shi. 2007. Decision-making support system for vessel automatic anti-grounding and anti-reef. Pages 2356-2361 in International Conference on Transportation Engineering 2007, ICTE 2007. | 2007 | Model | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Yang, S., N. Li, Y. Suo, and G. Chen. 2007. Study on construction of simulation platform for vessel automatic anti-collision and its test method. Pages 2414-2419 in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, ICAL 2007. | 2007 | Model | ||
| 2006. NOAA Essential Fish Habitat Research Implementation Plan for Alaska for FY 2007 - 2011. NOAA. | 2006 | GIS & Maps | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sponges; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Adams, A. J., C. P. Dahlgren, G. T. Kellison, M. S. Kendall, C. A. Layman, J. A. Ley, I. Nagelkerken, and J. E. Serafy. 2006. Nursery function of tropical back-reef systems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 318:287-301. | 2006 | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Seagrasses | |
| Ando, A. W. and M. Getzner. 2006. The roles of ownership, ecology, and economics in public wetland-conservation decisions. Ecological Economics 58:287-303. | 2006 | Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Political Pressure; Wetlands | ||
| Babinsky, H., L. Cattafesta, and G. Abate. 2006. Design considerations for a micro aerial vehicle aerodynamic characterization facility at the University of Florida research and engineering education facility. Pages 713-722 in Collection of Technical Papers - 25th AIAA Aerodynamic Measurement Technology and Ground Testing Conference. | 2006 | Florida | Lab Study | Collaboration & Partnering; Military |
| Balaram, V., M. L. Patil, A. K. Agrawal, D. V. Subba Rao, S. N. Charan, M. Satyanarayanan, R. Mathur, K. Kapilavastu, D. S. Sarma, M. Sankara Gowda, S. L. Ramesh, P. Sangurmath, K. V. Anjaiah, B. Dasaram, R. K. Saxena, and Z. Begum. 2006. Preparation and certification of high-grade gold geochemical reference material. Accreditation and Quality Assurance 11:329-335. | 2006 | Tanzania; India; China | Lab Study | Collaboration & Partnering; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining |
| Beaver, C. R., W. C. Jaap, M. K. Callahan, J. Kidney, S. Slade, S. Kupfner, S. Wade, J. W. Porter, K. Sutherland, C. Torres, C. Tsokos, and G. Yanev. 2006. U.S. EPA / FKNMS coral reef evaluation and monitoring project. | 2006 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Pathogens; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Beecham, B. 2006. 'Eclipse' - A New Wave dive catamaran for the Great Barrier Reef. Work Boat World 25:30. | 2006 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Bello-Pineda, J., R. Ponce-Hernandez, and M. A. Liceaga-Correa. 2006. Incorporating GIS and MCE for suitability assessment modelling of coral reef resources. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 114:225-256. | 2006 | Model; GIS & Maps | ||
| Berman, D. J. 2006. Recycling from rhodes to reefs. Public Roads 70. | 2006 | Artificial Habitat; Solid Waste Disposal | ||
| Bortone, S. A. 2006. A perspective of artificial reef research: The past, present, and future. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:8-Jan. | 2006 | Artificial Habitat; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Brown, C. J. and C. Harper. 2006. Mapping of the loch linnhe artificial reef complex. Sea Technology 47:31-35. | 2006 | GIS & Maps | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Burke, L. and Z. Sugg. 2006. Hydrologic Modeling of Watersheds Discharging Adjacent to the Mesoamerican Reef. World Resource Institute. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Campbell, G. 2006. High resolution aeromagnetic mapping of \loss-of-ground\" features at platinum and coal mines in South Africa". South African Journal of Geology 109:439-458. | 2006 | South Africa | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coal Mining; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining |
| CERP Committee. 2006. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan Adaptive Management Strategy. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Military | |
| Chatterjea, S., S. Kininmonth, and P. J. M. Havinga. 2006. Sensor networks. GEO: connexion 5:20-22. | 2006 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Energy Policy & Development | |
| Claudet, J., D. Pelletier, J.-Y. Jouvenel, F. Bachet, and R. Galzin. 2006. Assessing the effects of marine protected area (MPA) on a reef fish assemblage in a northwestern Mediterranean marine reserve: Identifying community-based indicators. Biological Conservation 130:349-369. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Coppe, A., G. A. Danieli, and S. Bortoluzzi. 2006. REEF: Searching regionally enriched features in genomes. BMC Bioinformatics 7. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Special Use Permitting | |
| Cowell, P. J., B. G. Thom, R. A. Jones, C. H. Everts, and D. Simanovic. 2006. Management of uncertainty in predicting climate-change impacts on beaches. Journal of Coastal Research 22:232-245. | 2006 | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Crueger, T., H. Kuhnert, J. Patzold, and E. Zorita. 2006. Calibrations of Bermuda corals against large-scale sea surface temperature and sea level pressure pattern time series and implications for climate reconstructions. Journal of Geophysical Research D: Atmospheres 111. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Dearden, P., M. Bennett, and R. Rollins. 2006. Implications for coral reef conservation of diver specialization. Environmental Conservation 33:353-363. | 2006 | Cuba; Thailand | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Incentives; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation |
| Dirhamsyah, D. 2006. Indonesian legislative framework for coastal resources management: A critical review and recommendation. Ocean and Coastal Management 49:68-92. | 2006 | Indonesia | Review | Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting |
| Galindo, H. M., D. B. Olson, and S. R. Palumbi. 2006. Seascape Genetics: A Coupled Oceanographic-Genetic Model Predicts Population Structure of Caribbean Corals. Current Biology 16:1622-1626. | 2006 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Bahamas; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Goffredo, S. and H. R. Lasker. 2006. Modular growth of a gorgonian coral can generate predictable patterns of colony growth. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 336:221-229. | 2006 | South & Central America; Bahamas; Caribbean | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Octocoral; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Gomez, E. D. and S. S. Mingoa-Licuanan. 2006. Achievements and lessons learned in restocking giant clams in the Philippines. Fisheries Research 80:46-52. | 2006 | Philippines | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Bivalves; Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Goodman, J. A., M. Velez-Reyes, S. Hunt, and R. Armstrong. 2006. Development of a field test environment for the validation of coastal remote sensing algorithms: Enrique Reef, Puerto Rico. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 6360. | 2006 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Seagrasses; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Grimaccia, F., A. Gandelli, R. W. Johnstone, T. Chiffings, and R. E. Zich. 2006. Smart integrated sensor networks for the marine environment. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 6035. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Salinity; Substrate | |
| Halls, A. S., R. L. Welcomme, and R. W. Burn. 2006. The relationship between multi-species catch and effort: Among fishery comparisons. Fisheries Research 77:78-83. | 2006 | South & Central America | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Howell, B. and S. Wood. 2006. Kamikaze: Investigational autonomous underwater vehicle for collaborative research and undergraduate education and training. in ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings. | 2006 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering |
| Huang, H., J. Lian, X. Huang, L. Huang, R. Zou, and D. Wang. 2006. Coral cover as a proxy of disturbance: A case study of the biodiversity of the hermatypic corals in Yongxing Island, Xisha Islands in the South China Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin 51:129-135. | 2006 | China | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Hviding, E. 2006. Knowing and managing biodiversity in the Pacific Islands: Challenges of environmentalism in Marovo Lagoon. International Social Science Journal 58:69-85. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Solomon Islands | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Forestry; Landscape Conservation & Restoration |
| Jones, A. T., M. Thankappan, G. A. Logan, J. M. Kennard, C. J. Smith, A. K. Williams, and G. M. Lawrence. 2006. Coral spawn and bathymetric slicks in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data from the Timor Sea, north-west Australia. International Journal of Remote Sensing 27:2063-2069. | 2006 | Australia | Remote Sensing | |
| Kaiser, M. J. 2006. The Louisiana artificial reef program. Marine Policy 30:605-623. | 2006 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Construction Codes & Projects; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Kirkman, H. 2006. The east Asian seas UNEP regional seas programme. International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics 6:305-316. | 2006 | Global; China | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Kodati, P. and X. Deng. 2006. Towards the body shape design of a hydrodynamically stable robotic boxfish. Pages 5412-5417 in IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Kutser, T., I. Miller, and D. L. B. Jupp. 2006. Mapping coral reef benthic substrates using hyperspectral space-borne images and spectral libraries. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 70:449-460. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Lan, C.-H. and C.-Y. Hsui. 2006. The deployment of artificial reef ecosystem: Modelling, simulation and application. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 14:663-675. | 2006 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Decision Support; Waste Management Policies | |
| Lang, J. C. and R. N. Ginsburg. 2006. A vision for regular, rapid assessments of the tropical northwestern Atlantic's coral reefs. Revista de Biologia Tropical 54:23-29. | 2006 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish |
| Lemon, N., M. Alimchandani, and W. Hoban. 2006. LADS passage and fairway channel. Hydro International 10:27-29. | 2006 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing | |
| Liu, T.-L., S.-Y. Liou, D.-T. Su, and D.-W. Chen. 2006. Numerical flow simulation for the deployment analysis of artificial reefs. Pages 533-537 in Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat | |
| Martin, C., H. G. Deters, and T. W. Nattkemper. 2006. Fusing biomedical multi-modal data for exploratory data analysis. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 798-807. | 2006 | GIS & Maps | Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| McClanahan, T. R., E. Verheij, and J. Maina. 2006. Comparing the management effectiveness of a marine park and a multiple-use collaborative fisheries management area in East Africa. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16:147-165. | 2006 | Kenya; Tanzania | Algae; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | |
| Mellin, C., J. Ferraris, R. Galzin, M. Kulbicki, D. Ponton. 2006. Diversity of coral reef fish assemblages: Modelling of the species richness spectra from multi-scale environmental variables in the Tuamotu Archipelago (French Polynesia). Ecological Modelling 198:409-425. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish |
| Menza, C., J. Ault, J. Beets, J. Bohnsack, C. Caldow, J. Christensen, A. Friedlander, C. Jeffrey, M. Kendall, J. Luo, M. Monaco, S. Smith, and K. Woody. 2006. A guide to monitoring reef fish in the National Park Service�s South Florida/Caribbean Network. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 39. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. | 2006 | South & Central America; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Miller, J. E., S. Vogt, R. Hoeke, S. Ferguson, B. Appelgate, J. R. Smith, and M. Parke. 2006. Bathymetric atlas and website for the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Atoll Research Bulletin 409-422. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish |
| Morgan, S. K. and S. A. Lourie. 2006. Threatened fishes of the world: Hippocampus comes cantor 1850 (Syngnathidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 75:311-313. | 2006 | Global; Thailand; Malaysia; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biomedical Research Policies; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Seagrasses; Sponges; Stony Coral; Substrate |
| Mumby, P. J. 2006. Connectivity of reef fish between mangroves and coral reefs: algorithms for the design of marine reserves at seascape scales. Biological Conservation 128:215-222. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Mangroves; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses | |
| Poulsen, A., K. Burns, J. Lough, D. Brinkman, and S. Delean. 2006. Trace analysis of hydrocarbons in coral cores from Saudi Arabia. Organic Geochemistry 37:1913-1930. | 2006 | Australia; Saudi Arabia; Iran | Petroleum Spills; Stony Coral | |
| Ranasinghe, R., I. L. Turner, and G. Symonds. 2006. Shoreline response to multi-functional artificial surfing reefs: A numerical and physical modelling study. Coastal Engineering 53:589-611. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Shoreline Protection | |
| Saez, J. M., A. Hogue, F. Escolano, and M. Jenkin. 2006. Underwater 3D SLAM through entropy minimization. Pages 3562-3567 in Proceedings - IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. | 2006 | Global | GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Pipelines |
| Santavy, D.L., J. Campbell, R.L. Quarles, J.M. Patrick, L.M. Harwell, M. Parsons, L. MacLaughlin, J. Halas, E. Mueller, E.C. Peters, and J. Hawkridge. 2006. The Epizootiology of Coral Diseases in South Florida. EPA/600/R-05/146, US Environmental Protection Agency, Gulf Breeze, (Florida, USA). | 2006 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Collaboration & Partnering; Octocoral; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Santos, M. N., P. G. Lino, P. Pousao-Ferreira, and C. C. Monteiro. 2006. Preliminary results of hatchery-reared seabreams released at artificial reefs off the algarve coast (Southern Portugal): A pilot study. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:177-184. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Silvano, R. A. M., P. F. L. MacCord, R. V. Lima, and A. Begossi. 2006. When does this fish spawn? Fishermen's local knowledge of migration and reproduction of Brazilian coastal fishes. Environmental Biology of Fishes 76:371-386. | 2006 | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Sinclair, D. J. and M. J. Risk. 2006. A numerical model of trace-element coprecipitation in a physicochemical calcification system: Application to coral biomineralization and trace-element 'vital effects'. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70:3855-3868. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | |
| Steel, G. and A. Bundy. 2006. Attacking group protocols by refuting incorrect inductive conjectures. Pages 149-176 in Journal of Automated Reasoning. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Stewart, L. K., P. B. Charlesworth, K. L. Bristow, and P. J. Thorburn. 2006. Estimating deep drainage and nitrate leaching from the root zone under sugarcane using APSIM-SWIM. Agricultural Water Management 81:315-334. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Teeter, A. M. and B. H. Johnson. 2006. Sediment and fluid mud modeling of atchafalaya pro-delta channel. Pages 714-733 in Proceedings of the International Conference on Estuarine and Coastal Modeling. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| The Coastal Theme Team, editor. 2006. IGOS Coastal Theme Report: For the monitoring of our environment from space and from earth. Integrated Global Observing Strategy. | 2006 | Global; Florida; China; France | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives |
| Theberge, M. and G. Dudek. 2006. Gone Swimmin'. IEEE Spectrum 43:38-43. | 2006 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| van Dongen-Vogels, V. and J. Mallefet. 2006. Fragment growth-rates of six cultivated coral species: A reference framework for coral transplantation. Mer 44:99-107. | 2006 | Stony Coral | ||
| Watanuki, N. and B. J. Gonzales. 2006. The potential of artificial reefs as fisheries management tools in developing countries. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:19-Sep. | 2006 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish |
| Welpa, M., A. de la Vega-Leinerta, S. Stoll-Kleemannb, and C. C. Jaegera. 2006. Science-based stakeholder dialogues: Theories and tools. Global Environmental Change 16:170-181. | 2006 | Global; Europe | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate |
| Yu, Y., M. Breitbart, P. McNairnie, and F. Rohwer. 2006. FastGroupII: A web-based bioinformatics platform for analyses of large 16S rDNA libraries. BMC Bioinformatics 7. | 2006 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Microorganisms; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| [No author name available]. 2005. News: Mock ship grounding and oil spill in Florida keys National Marine Sanctuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50. | 2005 | Florida | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Complex Habitat & Resources; Petroleum Spills; Security Policies | |
| Ahlen, J., D. Sundgren, and E. Bengtsson. 2005. Pre-processing of underwater images taken in shallow water for color reconstruction purposes. Pages 560-564 in Proceedings of the Seventh IASTED International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, SIP 2005. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Amaral, A. C. Z. and S. Jablonski. 2005. Conservation of marine and coastal biodiversity in Brazil. Conservation Biology 19:625-631. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Arvidson, R. and S. Jones. 2005. Ice detection and avoidance. Pages 9570-9573 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Columbia | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Auble, G. T., M. L. Scott, and J. M. Friedman. 2005. Use of individualistic streamflow-vegetation relations along the Fremont River, Utah, USA to assess impacts of flow alteration on Wetland and riparian areas. Wetlands 25:143-154. | 2005 | Model; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Beegle-Krause, C. J., M. Fonseca, and G. Shigenaka. 2005. Noaa habitat recovery models using cellular automata techniques. Pages 10645-10651 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Coralline Algae; Monetary Valuation; Petroleum Spills; Seagrasses | |
| Bell, R., R. Buchsbaum, C. Roman, and M. Chandler. 2005. Inventory of intertidal marine habitats, Boston Harbor Islands national park area. Northeastern Naturalist 12:169-200. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Algae; Invertebrates; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Bello, P. J., L. V. Rios, C. M. A. Liceaga, M. C. Zetina, C. K. Cervera, B. P. Arceo, and N. H. Hernandez. 2005. Incorporating spatial analysis of habitat into spiny lobster (Panulirus argus) stock assessment at Alacranes reef, Yucatan, Mexico. Fisheries Research 73:37-47. | 2005 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| Bello-Pineda, J., M. A. Liceaga-Correa, H. Hernandez-Nunez, and R. Ponce-Hernandez. 2005. Using aerial video to train the supervised classification of Landsat TM imagery for coral reef habitats mapping. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 105:145-164. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources | |
| Bennett, J., P. Lawrence, R. Johnstone, R. Shaw. 2005. Adaptive management and its role in managing Great Barrier Reef water quality. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:70-75. | 2005 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering |
| Bodnar, J. L. 2005. The information technology of SHIELDS - NOAA'S Sanctuaries Hazardous Incident Emergency Logistics Database System. Pages 11312-11316 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Internet & Telecommunications; Petroleum Spills | |
| Boling, E. A. 2005. Environmental Management Systems and NEPA: A Framework for Productive Harmony. Environmental Law Reporter 35:10022-10031. | 2005 | Review | ||
| Bosman, C., R. Uken, and A. M. Smith. 2005. The bathymetry of the Aliwal Shoal, Scottburgh, South Africa. South African Journal of Science 101:255-257. | 2005 | South Africa | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2005. The importance of the marine ornamental reef fish trade in the wider Caribbean. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:127-137. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Maldives; Sri Lanka; India; Japan; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Caribbean; Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Campos-Davila, L., V. H. Cruz-Escalona, F. Galvan-Magana, A. Abitia-Cardenas, F. J. Gutierrez-Sanchez, and E. F. Balart. 2005. Fish assemblages in a Gulf of California Marine Reserve. Bulletin of Marine Science 77:347-362. | 2005 | Fish | ||
| Capili, E. B., A. C. S. Ibay, and J. R. T. Villarin. 2005. Climate change impacts and adaptation on Philippine coasts. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Pathogens; Plankton; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting | |
| Chapman, D. D., E. K. Pikitch, E. Babcock, and M. S. Shiyji. 2005. Marine reserve design and evaluation using automated acoustic telemetry: A case-study involving coral reef-associated sharks in the mesoamerican Caribbean. Marine Technology Society Journal 39:42-55. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest | |
| Chateau-Degat, M.-L., M. Chinain, N. Cerf, S. Gingras, B. Hubert, and E. Dewailly. 2005. Seawater temperature, Gambierdiscus spp. variability and incidence of ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia. Harmful Algae 4:1053-1062. | 2005 | Global | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Climate; Pathogens |
| Cinner, J. E., M. J. Marnane, T. R. McClanahan, T. H. Clark, and J. Ben. 2005. Trade, tenure, and tradition: Influence of sociocultural factors on resource use in melanesia. Conservation Biology 19:1469-1477. | 2005 | Papua New Guinea | Cultural Policies; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Stony Coral | |
| Clua, E., B. Beliaeff, C. Chauvet, G. David, J. Ferraris, M. Kronen, M. Kulbicki, P. Labrosse, Y. Letourneur, D. Pelletier, O. Thebaud, and M. Leopold. 2005. Towards multidisciplinary indicator dashboards for coral reef fisheries management. Aquatic Living Resource 18:199-213. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Crosse, W. 2005. The opportunities and constraints in using cost-effective satellite remote sensing for biodiversity monitoring. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves |
| Elliott, J. E. 2005. Responding to vessel groundings and oil spills in national parks and marine sanctuaries. Pages 10012-10017 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Florida | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Petroleum Spills; Seagrasses | |
| Fernandes, L., J. Day, A. Lewis, S. Slegers, B. Kerrigan, D. Breen, D. Cameron, B. Jago, J. Hall, D. Lowe, J. Innes, J. Tanzer, V. Chadwick, L. Thompson, K. Gorman, M. Simmons, B. Barnett, K. Sampson, G. De�Ath, B. Mapstone, H. Marsh, H. Possingham, I. Ball, T. Ward, K. Dobbs, J. Aumend, D. Slater, and K. Stapleton. 2005. Establishing representative no-take areas in the great barrier reef: Large-scale implementation of theory on marine protected areas. Conservation Biology 19:1733-1744. | 2005 | Global; Australia; Japan | Cultural Protections; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Finkl, C. W., L. Benedet, and J. L. Andrews. 2005. Interpretation of seabed geomorphology based on spatial analysis of high-density airborne laser bathymetry. Journal of Coastal Research 21:501-514. | 2005 | Florida | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Gasparini, J. L., S. R. Floeter, C. E. L. Ferreira, and I. Sazima. 2005. Marine ornamental trade in Brazil. Biodiversity and Conservation 14:2883-2899. | 2005 | Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Molluscs; Stony Coral | |
| Goulet, T. L., C. B. Cook, and D. Goulet. 2005. Effect of short-term exposure to elevated temperatures and light levels on photosynthesis of different host-symbiont combinations in the Aiptasia pallidal Symbiodinium symbiosis. Limnology and Oceanography 50:1490-1498. | 2005 | Florida; Bermuda | Lab Study | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Govender, Y., M. R. Jury, A. Mthembu, S. Hatesse, and E. Bulfoni. 2005. Socio-economic status and development potential for a rural community on the Maputaland coast of South Africa. South African Geographical Journal 87:37-42. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India; South Africa | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Housing; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Granek, E. E. and M. A. Brown. 2005. Co-management approach to marine conservation in Moheli, Comoros Islands. Conservation Biology 19:1724-1732. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; Comoros; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation |
| Gribble, N. A. 2005. MODSIM 2005 International Congress on Modelling and Simulation. Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand. | 2005 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation |
| Heal, G. M., E. B. Barbier, K. J. Boyle, A. P. Covich, S. P. Gloss, C. H. Hershner, J. P. Hoehn, C. M. Pringle, S. Polasky, K. Segerson, and K. Shrader-Frechette. 2005. Valuing ecosystem services: toward better environmental decision making. The National Academies Press, Washington DC. | 2005 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Military; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation; Wetlands |
| Hewitt, J. E., M. J. Anderson, and S. F. Thrush. 2005. Assessing and monitoring ecological community health in marine systems. Ecological Applications 15:942-953. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Jimenez-Rodriguez, L. O., A. Umana-Diaz, J. Diaz-Santos, G. Neira-Carolina, J. Morales-Morales, and E. Rodriguez. 2005. Subsurface object recognition by means of regularization techniques for mappimg coastal waters floor. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 5977. | 2005 | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kim, J.-K. and J.-H. Kim. 2005. Optimal mapping for artificial reef facility using remote sensing and GIS. Pages 314-319 in Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. | 2005 | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Lang, M. A. 2005. Smithsonian institution coral reef research. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Belize; Panama; Caribbean | Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Pathogens; Sea Urchins | |
| Lang, M. A. and A. H. Hines. 2005. Smithsonian institution marine science network. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Panama; India | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| LeDrew, E. and A. Lim. 2005. The application of the getis statistic to high resolution imagery to detect change in the spatial structure of submerged tropical corals between image dates. Pages 217-219 in Proceedings of the Third International Workshop on the Analysis of Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Images 2005. | 2005 | Remote Sensing | Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses | |
| Madden, C. J., D. H. Grossman, and K. L. Goodin. 2005. Coastal and marine systems of North America: framework for an ecological classification standard: version II. Coastal and marine systems of North America: framework for an ecological classification standard: version II, Arlington, Virginia. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Salinity; Substrate | |
| Matsuda, F., M. Saito, R. Iwahashi, H. Oda, and Y. Tsuji. 2005. Computer simulation of carbonate sedimentary and shallow diagenetic processes. AAPG Memoir 365-382. | 2005 | Japan; Indonesia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Mel'nikov, N. V., V. S. Sitnikov, V. I. Vasil'ev, S. I. Doronina, and L. V. Kolotova. 2005. Bioherms of the Lower Cambrian Osa Horizon in the Talakan-Upper Chona zone of petroleum accumulation. Geologiya i Geofizika 46:856-864. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Merrick, J. R. W., G. S. Parnell, J. Barnett, M. Garcia. 2005. A Multiple-objective decision analysis of stakeholder values to identify watershed improvement needs. Decision Analysis 2:44-57. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Mills, D. J., C. Gardner, and M. Oliver. 2005. Survival and movement of naïve juvenile spiny lobsters returned to the wild. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 324:20-30. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Nash, S. M. B., K. McMahon, G. Eaglesham, and J. F. Muller. 2005. Application of a novel phytotoxicity assay for the detection of herbicides in Hervey Bay and the Great Sandy Straits. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:351-360. | 2005 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| National Marine Sanctuaries. 2005. MPAs and Enforcement. Module 7, NOAA. | 2005 | Special Use Permitting | ||
| Neitsch, S. L., J. G. Arnold, J. R. Kiniry, and J. R. Williams. 2005. Soli and water assessment tool theoretical documentation. Agricultural Research Service, Temple, Texas. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 2005. Contaminated Sediment Remediation Guidance for Hazardous Waste Sites. EPA-540-R-05-012, US Environmental Protection Agency. | 2005 | India | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Health Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Remediation; Security Policies; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Overfield, M. L. 2005. Corrosion on Deep Gulf Shipwrecks of World War II. Pages 11242-11248 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Petroleum Spills |
| Pelletier, D. and S. Mahevas. 2005. Spatially explicit fisheries simulation models for policy evaluation. Fish and Fisheries 6:307-349. | 2005 | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Pelletier, D., J. A. Garcia-Charton, J. Ferraris, G. David, O. Thebaud, Y. Letourneur, J. Claudet, M. Amand, M. Kulbicki, and R. Galzin. 2005. Designing indicators for assessing the effects of marine protected areas on coral reef ecosystems: A multidisciplinary standpoint. Aquatic Living Resource 18:15-33. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Petit, C. C. and J. J. Vandenabeele. 2005. Supporting coastal and lake applications with the help of remote sensing. Pages 2771-2774 in International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). | 2005 | Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Coastal Development; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Plankton; Sediment |
| Pons-Branchu, E., C. Hillaire-Marcel, P. Deschamps, B. Ghaleb, and D. J. Sinclair. 2005. Early diagenesis impact on precise U-series dating of deep-sea corals: Example of a 100-200-year old Lophelia pertusa sample from the northeast Atlantic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69:4865-4879. | 2005 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Ralph, P. J. and R. Gademann. 2005. Rapid light curves: A powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquatic Botany 82:222-237. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Rohmann, S. and M. Monaco, editors. 2005. Mapping Southern Florida�s Shallow-water Coral Ecosystems: An Implementation Plan. NOAA Coral Reef Conservation Program, Silver Spring, (Maryland, USA). | 2005 | Florida | GIS & Maps | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Schools & Colleges |
| Rosenberg, A. A., W. J. Bolster, K. E. Alexander, W. B. Leavenworth, A. B. Cooper, and M. G. McKenzie. 2005. The history of ocean resources: Modeling cod biomass using historical records. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 3:84-90. | 2005 | Global; England | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives |
| Sadovy, Y. 2005. Trouble on the reef: The imperative for managing vulnerable and valuable fisheries. Fish and Fisheries 6:167-185. | 2005 | Global | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Live Collection | |
| Salcido, R. E. 2005. Enduring optimism: Examining the rig-to-reef bargain. Ecology Law Quarterly 32:863-937. | 2005 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Oil & Gas Rigs | |
| Saunders, S. M., B. Radford, S. A. Bourke, Z. Thiele, T. Bech, and J. Mardon. 2005. A rapid method for determining lipid fraction ratios of hard corals under varying sediment and light regimes. Environmental Chemistry 2:331-336. | 2005 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Sayer, M. D. J., S. H. Magill, T. J. Pitcher, L. Morissette, and C. Ainsworth. 2005. Simulation-based investigations of fishery changes as affected by the scale and design of artificial habitats. Journal of Fish Biology 67:218-243. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Artificial Habitat; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Schleyer, M. H. and L. Celliers. 2005. Modelling reef zonation in the Greater St Lucia Wetland Park, South Africa. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 63:373-384. | 2005 | Global; South Africa | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Decision Support; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands |
| Schroeder, C. A., D. E. Breen, C. D. Cera, and W. C. Regli. 2005. Stochastic microgeometry for displacement mapping. Pages 166-175 in Proceedings - International Conference on Shape Modeling and Applications, SMI'05. | 2005 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Shapiro, A. C. and S. O. Rohmann. 2005. Summit-to-Sea mapping and change detection using satellite imagery: Tools for conservation and management of coral reefs. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:185-193. | 2005 | US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research |
| Sharp, W. C., R. D. Bertelsen, and V. R. Leeworthy. 2005. Long-term trends in the recreational lobster fishery of Florida, United States: Landings, effort, and implications for management. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 39:733-747. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Sifling, J., R. A. Nall, J. Stettler, T. Busch, F. Igaz, J. G. Hoff, and S. Wiegman. 2005. American Samoa longliner response, wreck removal, and restoration project. Pages 259-264 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Samoa; American Samoa | Coastal Defense; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Petroleum Spills; Ports & Harbors; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Sinclair, D. J. 2005. Correlated trace element \vital effects\" in tropical corals: A new geochemical tool for probing biomineralization". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69:3265-3284. | 2005 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral |
| Smith, A., D. Helton, and I. Zelo. 2005. Developing a database to support and prioritize the removal of abandoned vessels impacting coral resources. Pages 9582-9585 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Petroleum Spills | |
| Sordelli, C. and N. Garcia. 2005. Venezuelan national oil spill training program. Page 8972 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Venezuela | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Mangroves; Military; Oil & Gas Industry; Petroleum Spills |
| Steel, G. and A. Bundy. 2005. Attacking group multicast key management protocols using coral. Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science 125:125-144. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Swann, P. 2005. Commissions. Crafts 192:26-29. | 2005 | Model | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Symons, L. C. and J. Morris. 2005. Development of multi-hazard contingency plans and tools for the National Marine Sanctuary System. Pages 9628-9631 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Samoa; American Samoa | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Cultural Protections; Marine Protected Areas; Petroleum Spills; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Whales & Dolphins |
| Symons, L. C., M. Hodges, and M. S. Devany. 2005. Flexibility for NOAA in development and application of multi-hazard contingency plans and response tools: The Sanctuaries Hazardous Incident Logistics Database System (SHIELDS). Pages 11158-11160 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Regulations; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Petroleum Spills; Small Boats; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Symons, L. C., R. Pavia, and M. Hodges. 2005. Emergency response in National Marine Sanctuaries. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Coastal Defense; Security Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Taban, F., E. Acar, I. Fidan, and A. Zora. 2005. Teaching basic engineering concepts in a K-12 environment using LEGO bricks and robotics. Pages 13727-13736 in ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Conference Proceedings. | 2005 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Pipelines; Schools & Colleges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Trudel, B. K., R. C. Belore, B. J. Jessiman, and S. L. Ross. 2005. A microcomputer-based spill impact assessment system for untreated and chemically dispersed oil spills in the U.S. Gulf of Mexico. Page 4770 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Model | Coastal Defense; Petroleum Spills; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting |
| U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2005. Reviewing environmental impact statements for fishery management plans. Office of Federal Activities, Washington DC. | 2005 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Fishing Sector; Internet & Telecommunications; Special Use Permitting | |
| U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). 2005. Reviewing environmental impact statements for fishery management plans. Washington DC. | 2005 | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting | |
| Vidal, L. and D. Pauly. 2005. Integration of subsystems models as a tool toward describing feeding interactions and fisheries impacts in a large marine ecosystem, the Gulf of Mexico. Ocean and Coastal Management 47:709-725. | 2005 | South & Central America; Mexico | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| White, A. T., R.-L. Eisma-Osorio, and S. J. Green. 2005. Integrated coastal management and marine protected areas: Complementarity in the Philippines. Ocean and Coastal Management 48:948-971. | 2005 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Wooldridge, S., T. Done, R. Berkelmans, R. Jones, and P. Marshall. 2005. Precursors for resilience in coral communities in a warming climate: A belief network approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 295:157-169. | 2005 | Global; Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Stony Coral |
| WRI and NOAA. 2005. Land-based Sources of Threat to Coral Reefs in the U.S. Virgin Islands. Washington, DC. | 2005 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment |
| 2004. Collaborative Network of Facilities for Science. US Environmental Protection Agency. | 2004 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Amand, M., D. Pelletier, J. Ferraris, and M. Kulbicki. 2004. A step toward the definition of ecological indicators of the impact of fishing on the fish assemblage of the Abore reef reserve (New Caledonia). Aquatic Living Resource 17:139-149. | 2004 | New Caledonia | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Arias-Gonzalez, J.E., E. Nunez-Lara, C. Gonzalez-Salas, and R. Galzin. 2004. Trophic models for investigation of fishing effect on coral reef ecosystems. Ecological Modelling 172:197-212. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Primary Production |
| Beger, M., A. R. Harborne, T. P. Dacles, J.-L. Solandt, and G. L. Ledesma. 2004. A framework of lessons learned from community-based marine reserves and its effectiveness in guiding a new coastal management initiative in the Philippines. Environmental Management 34:786-801. | 2004 | Philippines | Review | Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management |
| Berlinck, R. G. S., E. Hajdu, R. M. Da Rocha, J. H. H. L. De Oliveira, I. L. C. Hernandez, M. H. R. Seleghim, A. C. Granato, E. V. R. De Almeida, C. V. Nunez, G. Muricy, S. Peixinho, C. Pessoa, M. O. Moraes, B. C. Cavalcanti, G. G. F. Nascimento, O. Thiemann, M. Silva, A. O. Souza, C. L. Silva, and P. R. Minarini. 2004. Challenges and Rewards of Research in Marine Natural Products Chemistry in Brazil. Journal of Natural Products 67:510-522. | 2004 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Brock, R. J. and B. F. Culhane. 2004. The no-take research natural area of Dry Tortugas National Park (Florida): Wishful thinking or responsible planning? Pages 67-74 in American Fisheries Society Symposium. | 2004 | Florida | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Regulations; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Seagrasses | |
| Bruggemann, J. H., R. T. Buffler, M. M. M. Guillaume, R. C. Walter, R. Von Cosel, B. N. Ghebretensae, and S. M. Berhe. 2004. Stratigraphy, palaeoenvironments and model for the deposition of the Abdur Reef Limestone: Context for an important archaeological site from the last interglacial on the Red Sea coast of Eritrea. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 203:179-206. | 2004 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Burke, L. and J. Maidens. 2004. Reefs at Risk in the Caribbean. World Resources Institute, Washington, D.C. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Pathogens; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Chapman, B. and J. R. Turner. 2004. Development of a geographical information system for the marine resources of Rodrigues. Journal of Natural History 38:2937-2957. | 2004 | Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Octopus & Squid; Skeletal Coral |
| Claudet, J. and D. Pelletier. 2004. Marine protected areas and artificial reefs: A review of the interactions between management and scientific studies. Aquatic Living Resource 17:129-138. | 2004 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Scientific Research | |
| Cooney, C. M. 2004. EPA's First Science Advisor Focuses on the Basics. Environmental Science and Technology 38:181A-184A. | 2004 | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Corson, M. R., J. H. Bowles, W. Chen, C. O. Davis, K. H. Gallelli, D. R. Konvan, P. G. Lucey, T. J. Mosher, and R. Holasek. 2004. The HICO Program - Hyperspectral Imaging of the Coastal Ocean from the international space station. Pages 4184-4186 in International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). | 2004 | Lab Study; Remote Sensing | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Elvidge, C. D., J. B. Dietz, R. Berkelmans, S. Andrefouet, W. Skirving, A. E. Strong, and B. T. Tuttle. 2004. Satellite observation of Keppel Islands (Great Barrier Reef) 2002 coral bleaching using IKONOS data. Coral Reefs 23:123-132. | 2004 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Fabricius, K. E. and G. De'ath. 2004. Identifying ecological change and its causes: A case study on coral reefs. Ecological Applications 14:1448-1465. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Goodrich, M. S., J. Garrison, P. Tong, and A. Lunsford. 2004. Risk assessment model for evaluating ex-navy vessels as reef material. Pages 537-550 in Remediation of Contaminated Sediments - 2003: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Remediation of Contaminated Sediments. | 2004 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Coastal Defense; Military; Remediation; Sediment | |
| Gribble, N. A. 2004. A spatially explicit multi-competitor coexistence model of penaeid (shrimp) distribution on the Australian Great Barrier Reef. Ecological Modelling 177:61-74. | 2004 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Storms & Hurricanes; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Gutierrez-Rodriguez, C. and H. R. Lasker. 2004. Microsatellite variation reveals high levels of genetic variability and population structure in the gorgonian coral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae across the Bahamas. Molecular Ecology 13:2211-2221. | 2004 | South & Central America; Bahamas; Caribbean | Octocoral | |
| Irisson, J.-O., A. LeVan, M. De Lara, and S. Planes. 2004. Strategies and trajectories of coral reef fish larvae optimizing self-recruitment. Journal of Theoretical Biology 227:205-218. | 2004 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish | |
| Karr, J. R. and C. O. Yoder. 2004. Biological assessment and criteria improve TMDL decision making. Journal of Environmental Engineering [inpress]. | 2004 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Designated Uses; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kelty, R., K. Andrews, J. Wheaton, L. Nall, C. Beaver, W. Japp, B. Keller, V. R. Leeworthy, J. A. Bohnsack, T. Matthews, J. Ault, F. Ferro, G. Delgado, D. Harper, J. Hunt, B. Sharp, C. Pattengil-Semmens, S. Smith, R. Spieler, R.E. Dodge, D. Gilliam, B. Goodwin, G. Schmahl, E. Hickerson, J. R. Garcia, C. Lilyestrom, R. Appeldoorn, A. Bruckner, E. Williams, C. .F.G. Jeffrey, U. Alauf, A. Riedlander, C. Rogers, J. Miller, J. Beets, R. Nemeth, S. Herzlieb, V. Mayor, W. Toller, Z. Hillis-Starr, S. Caseau, and M. Miller. 2004. Status of coral reefs in the U.S. Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico: Florida, Flower Garden Banks, Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, Navassa. Pages 431-450 Status of coral reefs of the world: 2004. Volume 2. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, Queensland, Australia. | 2004 | South & Central America; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Climate; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| Kritzer, J. P. 2004. Effects of noncompliance on the success of alternative designs of marine protected-area networks for conservation and fisheries management. Conservation Biology 18:1021-1031. | 2004 | Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Lan, C.-H., C.-C. Chen, and C.-Y. Hsui. 2004. An approach to design spatial configuration of artificial reef ecosystem. Ecological Engineering 22:217-226. | 2004 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat | |
| Little, L. R., S. Kuikka, A. E. Punt, F. Pantus, C. R. Davies, and B. D. Mapstone. 2004. Information flow among fishing vessels modelled using a Bayesian network. Environmental Modelling & Software 19:27-34. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector |
| Lord-Boring, C., I. J. Zelo, and Z. J. Nixon. 2004. Abandoned vessels: Impacts to coral reefs, seagrass and mangroves in the US Caribbean and pacific territories with implications for removal. Marine Technology Society Journal 38:26-28. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Security Policies; Storms & Hurricanes |
| McConochie, J. D., T. A. Hardy, and L. B. Mason. 2004. Modelling tropical cyclone over-water wind and pressure fields. Ocean Engineering 31:1757-1782. | 2004 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Storms & Hurricanes |
| McManus, J. W. and J. F. Polsenberg. 2004. Coral-algal phase shifts on coral reefs: Ecological and environmental aspects. Progress in Oceanography 60:263-279. | 2004 | Review; Model | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Musick, J. A. and J. K. Ellis. 2004. Constraints on sustainable marine fisheries in the United States: A look at the record. Pages 44-66 in American Fisheries Society Symposium. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); England | Review; Model | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Fishing Sector |
| Pomeroy, R. S., J. E. Parks, and L. M. Watson. 2004. How is your MPA doing? a guidebook of natural and social indicators for evaluating marine protected area management effectiveness. he World Conservation Union, Gland, Switzerland. | 2004 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies | |
| Schroeder, D. M. and M. S. Love. 2004. Ecological and political issues surrounding decommissioning of offshore oil facilities in the Southern California Bight. Ocean and Coastal Management 47:21-48. | 2004 | South & Central America; Mexico | Climate; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Rigs | |
| Shuman, C. S., G. Hodgson, and R. F. Ambrose. 2004. Managing the marine aquarium trade: Is eco-certification the answer? Environmental Conservation 31:339-348. | 2004 | Global; Indonesia; Philippines | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector |
| Steel, G., A. Bundy, and M. Maidl. 2004. Attacking a protocol for group key agreement by refuting incorrect inductive conjectures. Pages 137-151 in Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence (Subseries of Lecture Notes in Computer Science). | 2004 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Toscas, P. J., M. J. Faddy, and C. Y. Burridge. 2004. Analysis of the impact of prawn trawling on benthic species in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Environmetrics 15:279-289. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Uthicke, S., D. Welch, and J. A. H. Benzie. 2004. Slow growth and lack of recovery in overfished holothurians on the Great Barrier Reef: Evidence from DNA fingerprints and repeated large-scale surveys. Conservation Biology 18:1395-1404. | 2004 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Echinoderms; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Nutrients |
| Verheij, E., S. Makoloweka, and H. Kalombo. 2004. Collaborative coastal management improves coral reefs and fisheries in Tanga, Tanzania. Ocean and Coastal Management 47:309-320. | 2004 | Tanzania | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Mangroves |
| Wooldridge, S. and T. Done. 2004. Learning to predict large-scale coral bleaching from past events: A Bayesian approach using remotely sensed data, in-situ data, and environmental proxies. Coral Reefs 23:96-108. | 2004 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| [No author name available]. 2003. Projects: Broward-Bahamas pipeline gets preliminary FERC nod. Pipeline and Gas Journal 230. | 2003 | Florida; Bahamas | Fish; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pipelines | |
| Aubanel, A., C. Monier, A. Benet, J.-A. Di Jorio, and B. Salvat. 2003. Management plan for marine environment in French Polynesia [Les plans de gestion de l'espace maritime en Polynesie Francaise]. Oceanis 29:375-395. | 2003 | Special Use Permitting | ||
| Baine, M. and J. Side. 2003. The role of fishermen and other stakeholders in the North Sea rigs-to-reefs debate. Pages 14-Jan in American Fisheries Society Symposium. | 2003 | Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Oil & Gas Rigs | ||
| Bhat, M. G. 2003. Application of non-market valuation to the Florida Keys marine reserve management. Journal of Environmental Management 67:315-325. | 2003 | Florida | Model | Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Bouvet, G., J. Ferraris, and S. Andrefouet. 2003. Evaluation of large-scale unsupervised classification of New Caledonia reef ecosystems using Landsat 7 ETM+ imagery. Oceanologica Acta 26:281-290. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Algae; Seagrasses |
| Cerepi, A., J.-P. Barde, and N. Labat. 2003. High-resolution characterization and integrated study of a reservoir formation: The danian carbonate platform in the Aquitaine Basin (France). Marine and Petroleum Geology 20:1161-1183. | 2003 | France | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment |
| Conruyt, N. and D. Grosser. 2003. Knowledge engineering in environmental sciences with IKBS. Pages 267-278 in AI Communications. | 2003 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Internet & Telecommunications | |
| Donohue, M. J. 2003. How multiagency partnerships can successfully address large-scale pollution problems: A Hawaii case study. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:700-702. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Debris; Mitigation; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges |
| Evans, B. K., D. Hill, J. E. Miller, J. R. Smith, and J. B. Weirich. 2003. Collaborative nautical charting and scientific seabed mapping missions: A case study in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Page 986 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering |
| Ferguson, N. M., M. J. Keeling, W. J. Edmunds, R. Gani, B. T. Grenfell, R. M. Anderson, and S. Leach. 2003. Planning for smallpox outbreaks. Nature 425:681-685. | 2003 | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pathogens | |
| Firn, R. D. 2003. Bioprospecting - why is it so unrewarding? Biodiversity and Conservation 12:207-216. | 2003 | Columbia | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Gabrie, C., M. Oberlinkens, M. Porcher, and J.-P. Quod. 2003. A management plan for the lagoon of Mayotte [Plan de gestion du lagon de Mayotte]. Oceanis 29:355-373. | 2003 | Mayotte | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Guimera, R., B. Uzzi, J. Spiro, L. A. Nunes Amaral. 2003. Team Assembly Mechanisms Determine Collaboration Network Structure and Team Performance. Science 308:697-702. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Haley, M. and A. Clayton. 2003. The role of NGOs in environmental policy failures in a developing country: The mismanagement of Jamaica's coral reefs. Environmental Values 12:29-54. | 2003 | Jamaica | Corporate Responses; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Jimenez-Rodriguez, L. O., E. Rodriguez-Diaz, M. Velez-Reyes, and C. A. DiMarzio. 2003. Image reconstruction and subsurface detection by the application of Tikhonov regularization to inverse problems in hyperspectral images. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 4892:398-407. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jull, A. J. T., G. S. Burr, J. W. Beck, D. J. Donahue, D. Biddulph, A. L. Hatheway, T. E. Lange, and L. R. McHargue. 2003. Accelerator mass spectrometry at Arizona: Geochronology of the climate record and connections with the ocean. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 69:19-Mar. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment | |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 2003. Profiles and economic contribution: general visitors to Monroe County, Florida 2000-2001. | 2003 | Florida | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Lemmens, S. 2003. Periphyton collectors as a tool to measure environmental performance of ocean outlets. Water Science and Technology 47:125-131. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Wastewater Discharge |
| Lindsey, G., J. A. Todd, and S. J. Hayter. 2003. A Handbook for Planning and Conducting Charrettes for High-Performance Projects. NREL/BK-710-33425, National Renewable Energy Lab, Golden, (Colorado, USA). | 2003 | Collaboration & Partnering; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Lirman, D. and M. W. Miller. 2003. Modeling and monitoring tools to assess recovery status and convergence rates between restored and undisturbed coral reef habitats. Restoration Ecology 11:448-456. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Complex Habitat & Resources; Physical Damage; Stony Coral; Substrate |
| Louchard, E. M., R. P. Reid, F. C. Stephens, C. O. Davis, R. A. Leathers, and T. V. Downes. 2003. Optical remote sensing of benthic habitats and bathymetry in coastal environments at Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas: A comparative spectral classification approach. Limnology and Oceanography 48:511-521. | 2003 | Bahamas | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Light; Seagrasses; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Merks, R., A. Hoekstra, J. Kaandorp, and P. Sloot. 2003. A problem solving environment for modelling stony coral morphogenesis. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 2657:639-648. | 2003 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Monaco, M. E., M. S. Kendall, J. L. Higgins, C. E. Alexander, and M. S. Tartt. 2003. Biogeographic assessments of NOAA National Marine Sanctuaries: The integration of ecology and GIS technology. Pages 1489-1498 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2003 | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Monroy, J. and M. Sato. 2003. A VOF Numerical Model of Storm Waves on Coral Reefs. Pages 2066-2073 in Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. | 2003 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Pattengill-Semmens C.V., Semmens B.X. 2003. Conservation and management applications of the reef volunteer fish monitoring program. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 81:43-50. | 2003 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Social Organizations |
| Rodriguez-Diaz, E., L. O. Jimenez-Rodriguez, M. Velez-Reyes, F. Gilbes, and C. A. DiMarzio. 2003. Subsurface Detection of Coral Reefs in Shallow Waters using Hyperspectral Data. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 5093:538-546. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Sale, P. F. and J. P. Kritzer. 2003. Determining the extent and spatial scale of population connectivity: Decapods and coral reef fishes compared. Fisheries Research 65:153-172. | 2003 | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Scheffers, S. R., J. De Goeij, F. C. Van Duyl, and R. P. M. Bak. 2003. The cave-profiler: a simple tool to describe the 3-D structure of inaccessible coral reef cavities. Coral Reefs 22:49-53. | 2003 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Schroter, U. 2003. Modelling of magnetic effects in near-field optics. European Physical Journal B 33:297-310. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Stachowitsch, M. 2003. Research on intact marine ecosystems: A lost era. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:801-805. | 2003 | Global | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Thompson, A. 2003. Victorian collaboration: Anglo-Indian embroidery. Embroidery 54:28-29. | 2003 | India | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Tian, W.-M. 2003. Positioning of Artificial Benthic Habitats off Mito, Southwestern Coast of Taiwan. Pages 794-801 in Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. | 2003 | Taiwan | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Sediment |
| Van Buskirk, P., C. Ryffel, and D. Clare. 2003. Smart tool. Planning 69:32-36. | 2003 | Florida | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Willis, T. J., R. B. Millar, and R. C. Babcock. 2003. Protection of exploited fish in temperate regions: High density and biomass of snapper Pagrus auratus (Sparidae) in northern New Zealand marine reserves. Journal of Applied Ecology 40:214-227. | 2003 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Beattie, A., U.R. Sumaila, V. Christensen, D. Pauly. 2002. A Model for the Bioeconomic Evaluation of Marine Protected Area Size and Placement in the North Sea. Natural Resource Modeling 15:413-437. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Bernabeu-Tello, A. M., J. J. Munoz-Perez, and R. Medina-Santamaria. 2002. Influence of a rocky platform in the profile morphology: Victoria Beach, Cadiz (Spain) [Influencia de un sustrato rocoso en la morfologia del perfil de playa: Playa Victoria, Cadiz]. Ciencias Marinas 28:181-192. | 2002 | Spain | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2002. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-OPR-22. | 2002 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Burris, M. W., C. R. Swenson, and G. L. Crawford. 2002. Lee County's variable pricing project. ITE Journal (Institute of Transportation Engineers) 72:36-41. | 2002 | Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. | 2002 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Day, J. C. 2002. Zoning - Lessons from the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Ocean and Coastal Management 45:139-156. | 2002 | Australia; United Kingdom | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas |
| Don, C. 2002. Could the San Juan Islands National Wildlife Refuge serve to protect marine areas? Building on existing institutions and legal authorities to create marine protected areas. Coastal Management 30:421-426. | 2002 | Collaboration & Partnering; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Galal, N., R. F. G. Ormond, and O. Hassan. 2002. Effect of a network of no-take reserves in increasing catch per unit effort and stocks of exploited reef fish at Nabq, South Sinai, Egypt. Marine and Freshwater Research 53:199-205. | 2002 | Egypt | Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Fishing Sector; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Green, D. R. and S. T. Ray. 2002. Using GIS for siting artificial reefs - Data issues, problems and solutions: 'Real World' to 'Real World'. Journal of Coastal Conservation 8:16-Jul. | 2002 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Hedley, J. D. and P. J. Mumby. 2002. Biological and remote sensing perspectives of pigmentation in coral reef organisms. Advances in Marine Biology 43:279-317. | 2002 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Algae; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Skeletal Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Helvey, M. 2002. Are southern California oil and gas platforms essential fish habitat? ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Fishing Sector; Oil & Gas Rigs |
| Herbert, N. A., R. M. G. Wells, and J. Baldwin. 2002. Correlates of choroid rete development with the metabolic potential of various tropical reef fish and the effect of strenuous exercise on visual performance. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 275:31-46. | 2002 | Fish | ||
| Hickey, T. E., M. M. J. Seymour, and S. D. Sayle. 2002. A management plan for the offshore disposal of drilling muds & cuttings in Brunei - A receiving environment based approach. Pages 459-466 in American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Petroleum Division (Publication) PD. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Hooper, J. N. A., J. A. Kennedy, and R. J. Quinn. 2002. Biodiversity 'hotspots', patterns of richness and endemism, and taxonomic affinities of tropical Australian sponges (Porifera). Biodiversity and Conservation 11:851-885. | 2002 | Australia; Thailand; Palau; Vanuatu | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Resource Use Management; Sponges |
| Jensen, A. 2002. Artificial reefs of Europe: Perspective and future. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Oman; Europe; Spain; Poland; France; Norway; United Kingdom | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Seagrasses | |
| Jull, A. J., G. S. Burr, J. W. Beck, D. J. Donahue, D. Biddulph, A. L. Hatheway, T. E. Lange, and L. R. McHargue. 2002. Accelerator mass spectrometry at Arizona: geochronology of the climatic record and connections with the ocean. TheScientificWorldJournal 2:1579-1593. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment | |
| Kvernevik, T.-I., M. Zambri Mohd Akhir, and J. Studholme. 2002. A low-cost procedure for automatic seafloor mapping, with particular reference to coral reef conservation in developing nations. Hydrobiologia 474:67-79. | 2002 | Malaysia | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Internet & Telecommunications |
| Monaco, M. E. 2002. NOAA National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science-Biogeography Program: Integration of ecology and GIS to assess impacts of climate change on living marine resources. Pages 456-466 in Solutions to Coastal Disasters 2002. | 2002 | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Pathogens | |
| NOAA Marine Sanctuaries Division. 2002. Environmental assessment: M/V Wellwood grounding site restoration. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Marine Sanctuaries Division, Silver Spring, Maryland. | 2002 | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Cultural Policies; Mitigation | ||
| Osenberg, C. W., C. M. St. Mary, J. A. Wilson, and W. J. Lindberg. 2002. A quantitative framework to evaluate the attraction-production controversy. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat | |
| Park T., J. M. Bowker, and V. R. Leeworthy. 2002. Valuing snorkeling visits to the Florida Keys with stated and revealed preference models. Journal of Environmental Management 64:301-312. | 2002 | Florida | Model | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Remediation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Pitcher, T. J., E. A. Buchary, and T. Hutton. 2002. Forecasting the benefits of no-take human-made reefs using spatial ecosystem simulation. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | China | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Sala, E., O. Aburto-Oropeza, G. Paredes, I. Parra, J. C. Barrera, and P. K. Dayton. 2002. A general model for designing networks of marine reserves. Science 298:1991-1993. | 2002 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources | |
| Salvat, B. and A. Aubanel. 2002. The management of coral reefs of French Polynesia [La gestion des recifs coralliens de Polynesie francaise]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 57:193-251. | 2002 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; France | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Aquaculture; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Echinoderms; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Molluscs; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation |
| Sayer, M. D. J. and M. S. P. Baine. 2002. Rigs to reefs: A critical evaluation of the potential for reef development using decommissioned rigs. Underwater Technology 25:93-97. | 2002 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Fish; Fishing Sector |
| Spash, C. L. 2002. Informing and forming preferences in environmental valuation: Coral reef biodiversity. Journal of Economic Psychology 23:665-687. | 2002 | Review; Model | Valuation | |
| Tupper, M. and M. A. Rudd. 2002. Species-specific impacts of a small marine reserve on reef fish production and fishing productivity in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Environmental Conservation 29:484-492. | 2002 | Turks and Caicos | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Funding & Incentives; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting |
| Turpin, R. K. and S. A. Bortone. 2002. Pre- and post-hurricane assessment of artificial reefs: Evidence for potential use as refugia in a fishery management strategy. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Voss, G. L. 2002. An environmental assessment of the John Pennekamp Coral Reef State Park and the Key Largo Coral Reef Marine Sanctuary (Unpublished 1983 Report). Page 445pp. | 2002 | |||
| White, A. T., C. A. Courtney, and A. Salamanca. 2002. Experience with marine protected area planning and management in the Philippines. Coastal Management 30:26-Jan. | 2002 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Yamano, H., M. Tamura, Y. Kunii, and M. Hidaka. 2002. Hyperspectral remote sensing and radiative transfer simulation as a tool for monitoring coral reef health. Marine Technology Society Journal 36:13-Apr. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Skeletal Coral | |
| [No author name available]. 2001. News: Protection for sponge gardens. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:4. | 2001 | Australia | Marine Birds; Sea Turtles; Sponges | |
| Alcolado, P. M., G. Alleng, K. Bonair, D. Bone, K. Buchan, P. G. Bush, K. De Meyer, J. R. Garcia, J. Garzon-Ferreira, P. M. H. Gayle, D. T. Gerace, F. X. Geraldes, E. Jordan-Dahlgren, B. Kjferve, E. Klein, K. Koltes, R. S. Laydoo, D. M. Linton, J. C. Ogden, H. A. ***Oxenford, C. Parker, P. Penchaszadeh, L. P. P. J Pors, J. Ramirez-Ramirez, F. Ruiz-Renteria, J. D. Ryan, S. R. Smith, J. Tshirky, R. Varela, S. Walker, E. Weil, W. J. Wiebe, J. D. Woodley, and J. C. Zieman. 2001. The Caribbean coastal marine productivity program (CARICOMP). Bulletin of Marine Science 69:819-829. | 2001 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Seagrasses | |
| Baine, M. 2001. Artificial reefs: A review of their design, application, management and performance. Ocean and Coastal Management 44:241-259. | 2001 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2001. Tracking the trade in ornamental coral reef organisms: The importance of CITES and its limitations. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:79-94. | 2001 | Fiji; Indonesia | Octocoral; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Budd, A. F., JR . Foster C.T., J. P. Dawson, and K. G. Johnson. 2001. The Neogene Marine Biota of Tropical America (\NMITA\") database: Accounting for biodiversity in paleontology". Journal of Paleontology 75:743-751. | 2001 | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Cain, J. 2001. Planning improvements in natural resources management: Guidelines for using Bayesian networks to support the planning and management of development programmes in the water sector and beyond. Center for Ecology and Hydrology, Wallingford (Oxon, UK). | 2001 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Resource Use Management | |
| Campbell, D. E. 2001. Proposal for including what is valuable to ecosystems in environmental assessments. Environmental Science and Technology 35:2867-2873. | 2001 | Model | Valuation | |
| CARICOMP. 2001. Caribbean Coastal Marine Productivity (CARICOMP); a cooperative research and monitoring network of marine laboratories, parks, and reserves. University of the West Indies, Kingston, Jamaica. | 2001 | Global; South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Jamaica; Panama; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses |
| Castro, C. B. and D. O. Pires. 2001. Brazilian coral reefs: What we already know and what is still missing. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:357-371. | 2001 | Review | Algae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coralline Algae; Stony Coral | |
| Daw, T. M., G. C. C. Rogers, P. Mapson, and J. E. Kynoch. 2001. Structure and management issues of the emerging ornamental fish trade in Eritrea. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:53-64. | 2001 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Collaboration & Partnering; Corallivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Demicco, R. V. and G. J. Klir. 2001. Stratigraphic simulations using fuzzy logic to model sediment dispersal. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 31:135-155. | 2001 | Model | Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture, and Department of the Interior and Local Government. 2001. Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook No. 8 Coastal Law Enforcement. No.8 Coastal Law Enforcement, Coastal Resource Management Project of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Cebu City, Philippines. | 2001 | Philippines | Military; Resource Use Management | |
| Done, T. J. 2001. Useful science for coral reef management: The cooperative research centre model. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:309-315. | 2001 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Ballast Discharge; Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Seastars; Special Use Permitting; Wastewater Discharge |
| Elliott, G., B. Mitchell, B. Wiltshire, I. A. Manan, and S. Wismer. 2001. Community participation in marine protected area management Wakatobi National Park, Sulawesi, Indonesia. Coastal Management 29:295-316. | 2001 | Indonesia | Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Gorfine, H. K. and C. D. Dixon. 2001. Diver behaviour and its influence on assessments of a quota-managed abalone fishery. Journal of Shellfish Research 20:787-794. | 2001 | Australia | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Special Use Permitting | |
| Gorfine, H. K., B. L. Taylor, and T. I. Walker. 2001. Triggers and targets: What are we aiming for with abalone fisheries models in Australia? Journal of Shellfish Research 20:803-811. | 2001 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector |
| Harborne, A. R., D. C. Afzal, and M. J. Andrews. 2001. Honduras: Caribbean Coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1221-1235. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Iakovou, E. T. and J. E. Pachon. 2001. Optimization of the transportation system at a university campus: A continuous improvement quality management methodology. Quality Engineering 13:427-435. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Monetary Valuation | |
| Losada-Tosteson, V., J. M. Posada, and F. Losada. 2001. Size and reproductive status of fished spotted spiny lobster, Panulirus guttatus, in Morrocoy National Park, Venezuela: A preliminary report. Marine and Freshwater Research 52:1599-1603. | 2001 | South & Central America; Venezuela; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Special Use Permitting |
| Mikkelsen, P. M. and J. Cracraft. 2001. Marine biodiversity and the need for systematic inventories. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:525-534. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Echinoderms; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges | |
| Mitchell, A. W., J. R. Reghenzani, and M. J. Furnas. 2001. Nitrogen levels in the Tully River - A long-term view. Water Science and Technology 43:99-105. | 2001 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Monaco, M. E., J. D. Christensen, and S. O. Rohmann. 2001. Mapping and monitoring of U.S. coral reef ecosystems. Earth System Monitor 12:16-Jan. | 2001 | US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Samoa; American Samoa; Guam | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Resource Use Management |
| Naughton, J. and P. L. Jokiel. 2001. Coral reef mitigation and restoration techniques employed in the Pacific Islands: I. Overview. Pages 306-312 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Mitigation |
| Parras, D. A. 2001. Coastal resource management in the Philippines: A case study in the Central Visayas region. Journal of Environment and Development 10:80-103. | 2001 | Oman; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Petersen, D. and R. Tollrian. 2001. Methods to enhance sexual recruitment for restoration of damaged reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:989-1000. | 2001 | Florida | Lab Study | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Phinn, S. R., P. Scarth, M. Stanford, C. Menges, and G. Hill. 2001. Quantitative monitoring of environmental health and dynamics from the ADAR-1000 low-cost airborne digital multi-spectral camera. Pages 378-380 in International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Riegl, B., J. L. Korrubel, and C. Martin. 2001. Mapping and monitoring of coral communities and their spatial patterns using a surface-based video method from a vessel. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:869-880. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Algae; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | |
| Ritchie, K. B., S. W. Polson, and G. W. Smith. 2001. Microbial disease causation in marine invertebrates: Problems, practices, and future prospects. Hydrobiologia 460:131-139. | 2001 | Lab Study | Collaboration & Partnering; Microorganisms; Pathogens | |
| Schuttenberg, editor. 2001. Coral Bleaching: Causes, Consequences and Response - Selected Papers Presented at the 9th International Coral Reef Symposium October 2000. Coastal Management Report #2230, Coastal Resources Center, Narragansett, (Rhode Island, USA). | 2001 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia; Philippines | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Stoll, H. M. and D. P. Schrag. 2001. Sr/Ca variations in Cretaceous carbonates: Relation to productivity and sea level changes. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 168:311-336. | 2001 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Plankton; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Talbot, F. and C. Wilkinson. 2001. Coral reefs, mangroves and seagrasses: a sourcebook for managers. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville (Australia). | 2001 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Forestry; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation |
| Thorburn, C. C. 2001. The house that poison built: Customary marine property rights and the live food fish trade in the Kei Islands, southeast Maluku. Development and Change 32:151-180. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Oman; Southeast Asia; Indonesia; Philippines | Fishing Sector; Housing; Military | |
| U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2001. Better Assessment Science Integrating Point & Nonpoint Sources. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Uthicke, S. and J. A. H. Benzie. 2001. Restricted gene flow between Holothuria scabra (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea) populations along the north-east coast of Australia and the Solomon Islands. Marine Ecology Progress Series 216:109-117. | 2001 | Australia; Solomon Islands | Echinoderms; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates | |
| Verkhusha, V. V., H. Otsuna, T. Awasaki, H. Oda, S. Tsukita, and K. Ito. 2001. An Enhanced Mutant of Red Fluorescent Protein DsRed for Double Labeling and Developmental Timer of Neural Fiber Bundle Formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276:29621-29624. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| West, K. and R. Van Woesik. 2001. Spatial and temporal variance of river discharge on Okinawa (Japan): Inferring the temporal impact on adjacent coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:864-872. | 2001 | Global; Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Westmacott, S. 2001. Developing decision support systems for integrated coastal management in the tropics: Is the ICM decision-making environment too complex for the development of a useable and useful DSS? Journal of Environmental Management 62:55-74. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Mangroves | |
| Wilson, J., C. W. Osenberg, C. M. St. Mary, C. A. Watson, and W. J. Lindberg. 2001. Artificial reefs, the attraction-production issue, and density dependence in marine ornamental fishes. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:95-105. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Fish | |
| Yang, W. A. N. 2001. Estimation of duration of subaerial exposure in shallow-marine limestones-an isotopic approach. Journal of Sedimentary Research 71:778-789. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment | |
| Alder, J., R. Hilliard, and G. Pobar. 2000. Integrated marine planning for Cocos (Keeling), an isolated Australian Atoll (Indian Ocean). Coastal Management 28:109-117. | 2000 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Cultural Policies | |
| Australian Institute of Marine, SC IE NC E. 2000. Reef monitoring: interactive data summaries for the Great Barrier Reef. Reef monitoring: interactive data summaries for the Great Barrier Reef. | 2000 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Seastars |
| Ball, I. and H. Possingham. 2000. Marxan (v1.8.2): Marine reserve design using spatially explicit annealing. University of Queensland, Queensland, Australia. | 2000 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management | |
| Boyer, J. N., P. Sterling, and R. D. Jones. 2000. Maximizing information from a water quality monitoring network through visualization techniques. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 50:39-48. | 2000 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Salinity |
| Cervi, G. A. 2000. War wrecks and the environment: Who's responsible for the legacy of war? A case study: Solomon Islands and the United States. Journal of Environmental Law and Litigation 14:351-399. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Japan; Solomon Islands | Finfish Harvest; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Christiansen, I. and R. Hunt. 2000. Research, extension and industry - Working together can achieve results. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41:310-318. | 2000 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Coleman, F. C., C. C. Koenig, G. R. Huntsman, J. A. Musick, A. M. Eklund, J. C. McGovern, R. W. Chapman, G. R. Sedberry, and C. B. Grimes. 2000. Long-lived reef fishes: The grouper-snapper complex. Fisheries 25:14-21. | 2000 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Courtney, C. A. and A. T. White. 2000. Integrated coastal management in the Philippines: Testing new paradigms. Coastal Management 28:39-53. | 2000 | Philippines | Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Resource Use Management | |
| Dahlgren, C. P. and D. B. Eggleston. 2000. Ecological processes underlying ontogenetic habitat shifts in a coral reef fish. Ecology 81:2227-2240. | 2000 | Bahamas | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Fish; Piscivorous Fish |
| Debrot, A. O. and J. Sybesma. 2000. The Dutch Antilles. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 595-614. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Health Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Estes, J. A. and C. H. Peterson. 2000. Marine ecological research in seashore and seafloor systems: Accomplishments and future directions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 195:281-289. | 2000 | Collaboration & Partnering; Substrate | ||
| Goddard Space Flight, CE NT ER. 2000. Remote sensing of coral reefs. Remote sensing of coral reefs. | 2000 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering |
| Gourbesville, PH . and B. A. Thomassin. 2000. Coastal environment assessment procedure for sustainable wastewater management in tropical islands: The Mayotte example. Ocean and Coastal Management 43:997-1014. | 2000 | Global; Indian Ocean; Comoros; Mayotte; India | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Wastewater Discharge |
| Harborne, A. R., M. D. McField, and E. K. Delaney. 2000. Belize. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 501-516. | 2000 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| Haskell, B. D., V. R. Leeworthy, P. C. Wiley, T. M. Beuttler, M. R. Haflich, J. Delaney, B. L. Richards, and E. Franklin. 2000. Final supplemental environmental impact statement and final supplemental management plan for the Tortugas Ecological Reserve. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. | 2000 | Florida | Algae; Fish; Marine Birds; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Huber Richard, M. and KE NT Gustavson. 2000. Economic decision support models for ICZM of coral reefs. Sea Technology 41. | 2000 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support | |
| Jayaraman, B. and K. Moon. 2000. Subset-logic programs and their implementation. Journal of Logic Programming 42:71-110. | 2000 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Kalakaua Marine Education, CE NT ER. 2000. Hawaii coral reef network. Hawaii coral reef network. | 2000 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 2000. Proposed Tortugas 2000 ecological reserve: socioeconomic impact analysis of alternatives. | 2000 | Florida | Review | |
| Maloney, K. A., L. A. Maguire, and E. A. Lind. 2000. NEUSE RIVER ESTUARY MODELING AND MONITORING PROJECT STAGE 1: ASSESSMENT OF STAKEHOLDER INTEREST AND CONCERNS TO INFORM LONG-TERM MODELING. 50237, Fuqua School of Business, Duke University, Durham, (NC, USA). | 2000 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Marshall, P. A. 2000. Skeletal damage in reef corals: Relating resistance to colony morphology. Marine Ecology Progress Series 200:177-189. | 2000 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Neil, M., N. Fenton, and L. Nielsen. 2000. Building large-scale Bayesian networks. The Knowledge Engineering Review 15:1-33. | 2000 | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support | |
| Pauly, D., V. Christensen, and C. Walters. 2000. Ecopath, Ecosim, and Ecospace as tools for evaluating ecosystem impact of fisheries. Journal of Marine Science 57:697-706. | 2000 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector | |
| Ramachandran, S. 2000. Southeast India. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 161-173. | 2000 | India | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Fishing Sector; Irrigation; Mangroves; Seawater Flow; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Rilov, G. and Y. Benayahu. 2000. Fish assemblage on natural versus vertical artificial reefs: The rehabilitation perspective. Marine Biology 136:931-942. | 2000 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish | |
| Shivlani, M. P. and D. O. Suman. 2000. Dive operator use patterns in the designated no-take zones of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). Environmental Management 25:647-659. | 2000 | Florida | GIS & Maps | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Landuse Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Stejskal, I. V. 2000. Obtaining Approvals for Oil and Gas Projects in Shallow Water Marine Areas in Western Australia using an Environmental Risk Assessment Framework. Spill Science and Technology Bulletin 6:69-76. | 2000 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Industry; Petroleum Spills |
| Stewart, L. K., A. D. Heap, and K. J. Woolfe. 2000. Evaluating the influence of tidal currents on the distribution of silt in Nara Inlet, central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Sedimentary Geology 136:59-69. | 2000 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sediment |
| Towler, P. H. and J. D. Smith. 2000. Studies of the influence of graded storm layers on 210Pb and heavy metals profiles in Great Barrier Reef sediments. Environmental Science and Technology 34:2947-2951. | 2000 | Australia | Lab Study; Model | Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Turner, J., C. Jago, D. Daby, and R. Klaus. 2000. The Mascarene Region. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 253-268. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Mauritius; Reunion; India | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands | |
| Turner, R.K., Brouwer R, Georgiou S and Bateman IJ. 2000. Ecosystem functions and services: an integrated framework and case study for environmental valuation. The Centre for Social and Economic Research on the Global Environment. | 2000 | England | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. | 2000 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Wall, M. A., M. Socolich, and R. Ranganathan. 2000. The structural basis for red fluorescence in the tetrameric GFP homolog DsRed. Nature Structural Biology 7:1133-1138. | 2000 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anemones & Zooanthids | |
| Werner, T. B., L. P. Pinto, G. F. Dutra, and P. G. Do Prado Pereira. 2000. Abrolhos 2000: Conserving the southern Atlantic's richest coastal biodiversity into the next century. Coastal Management 28:99-108. | 2000 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Wilson, S. C. and R. Klaus. 2000. The Gulf of Aden. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 47-61. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; India; Djibouti | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Beaches & Nature Parks; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| [No author name available]. 1999. Digging for oil: An economic petroleum source is being exploited on Queensland's coast. Chemical Engineer 686:22. | 1999 | Global; Australia | Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mining Policies; Sediment | |
| [No author name available]. 1999. Proceedings of the Sand Rights'99. Bringing back the beaches. in Sand Rights 1999 Bringing Back the Beaches. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Security Policies; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Al-Awadhi, F. M. A. 1999. The Year of the Ocean and its crucial importance to the Gulf. Desalination 123:127-133. | 1999 | Global | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Littering; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waste Management Policies | |
| Al-Jufaili, S., M. Al-Jabri, A. Al-Baluchi, R. M. Baldwin, S. G. Wilson, F. West, and A. D. Matthews. 1999. Human impacts on coral reefs in the Sultanate of Oman. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 49:65-74. | 1999 | Oman | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Pathogens; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Beecham, B. 1999. 'Reef jet' and 'Oceania' - debis finances two different designs to service dive cruise markets. Work Boat World 18:53-54. | 1999 | Australia | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products | |
| Boutaud, O. and A. R. Brash. 1999. Purification and catalytic activities of the two domains of the allene oxide synthase-lipoxygenase fusion protein of the coral Plexaura homomalla. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274:33764-33770. | 1999 | Collaboration & Partnering; Substrate | ||
| Caldwell, P. 1999. Coral reef mapping: Local partnerships in the Pacific support national effort. Geographic Information Systems help manage fragile coral reef ecosystem. Earth System Monitor 9:2-Jan. | 1999 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | GIS & Maps | Algae; Collaboration & Partnering |
| Cragg, G. M. and D. J. Newman. 1999. Discovery and development of antineoplastic agents from natural sources. Cancer Investigation 17:153-163. | 1999 | Collaboration & Partnering; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Cruickshank Michael, J. and JU N Dai. 1999. Progress in beach maintenance efforts for the State of Hawaii. Pages 277-283 in Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Beaches & Nature Parks; Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. | 1999 | South & Central America; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Corporate Responses; Funding & Incentives; Oil & Gas Rigs; Valuation | |
| Done T.J. 1999. Coral community adaptability to environmental change at the scales of regions, reefs and reef zones. American Zoologist 39:66-79. | 1999 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Coralline Algae; Fish; Octocoral; Pathogens; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Fenton, N. E. and M. Neil. 1999. Software metrics: successes, failures and new directions. Journal of Systems and Software 47:149-157. | 1999 | Europe | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support |
| Fernandes, L., M. A. Ridgley, and T. Van't Hof. 1999. Multiple criteria analysis integrates economic, ecological and social objectives for coral reef managers. Coral Reefs 18:393-402. | 1999 | Global | Model | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Gladstone, W., N. Tawfiq, D. Nasr, I. Andersen, C. Cheung, H. Drammeh, F. Krupp, and S. Lintner. 1999. Sustainable use of renewable resources and conservation in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden: Issues, needs and strategic actions. Ocean and Coastal Management 42:671-697. | 1999 | Global | Review | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses |
| Jesinghaus, J. and R. Montgomery. 1999. Towards environmental pressure indicators for the EU. | 1999 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Kershaw, S. and F. R. Brunton. 1999. Palaeozoic stromatoporoid taphonomy: Ecologic and environmental significance. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 149:313-328. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| MacDonald Craig, D., A. Mitsuyasu Carol, and EL IZ AB ET H Corbin. 1999. Planned underwater dive attractions program for Hawaii. Pages 180-188 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Artificial Habitat; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Infrastructure; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Martinez, F. A. and E. A. Marschall. 1999. A dynamic model of group-size choice in the coral reef fish Dascyllus albisella. Behavioral Ecology 10:572-577. | 1999 | Model | Fish | |
| Mearns Alan, J., BR AD Benggio, and D. Waite Thomas. 1999. Ballast water treatment during emergency response: the case of the M/T igloo moon. Pages 1463-1468 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1999 | Florida | Ballast Discharge; Oil & Gas Tankers; Security Policies | |
| Pet-Soede, L., H. S. J. Cesar, and J. S. Pet. 1999. An economic analysis of blast fishing on Indonesian coral reefs. Environmental Conservation 26:83-93. | 1999 | Indonesia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Risk, M. J. 1999. Paradise lost: How marine science failed the world's coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 50:831-837. | 1999 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mitigation; Nutrients |
| Russ, G. R. and A. C. Alcala. 1999. Management histories of Sumilon and Apo Marine Reserves, Philippines, and their influence on national marine resource policy. Coral Reefs 18:307-319. | 1999 | Philippines | Lab Study; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Smeets, E. and R. Weterings. 1999. Environmental indicators: typology and overview. Technical Report No 25, European Environment Agency, Copenhagen. | 1999 | Europe | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Tom, M., J. Douek, I. Yankelevich, T. C. G. Bosch, and B. Rinkevich. 1999. Molecular characterization of the first heat shock protein 70 from a reef coral. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 262:103-108. | 1999 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Stony Coral | |
| Walker, P. A., R. Greiner, D. McDonald, and V. Lyne. 1999. The Tourism Futures Simulator: A systems thinking approach. Environmental Modelling & Software 14:59-67. | 1999 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation |
| Walters, C., D. Pauly, and V. Christensen. 1999. Ecospace: prediction of mesoscale spatial patterns in trophic relationships of exploited ecosystems, with emphasis on the impacts of marine protected areas. Ecosystems 2:539-554. | 1999 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Wilson, M. E. J., J. L. C. Chambers, M. J. Evans, S. J. Moss, and D. S. Nas. 1999. Cenozoic carbonates in Borneo: Case studies from northeast Kalimantan. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 17:183-201. | 1999 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Sediment | |
| Wright, J. and D. Morton. 1999. Promoting erosion control in the Virgin Islands. Pages 8-May in Investing in the protection of our environment. Proceedings of conference 30, Nashville, 1999. (International Erosion Control Association). | 1999 | US Virgin Islands | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Bak, R.P.M. and E. H. Meesters. 1998. Coral population structure: the hidden information of colony size-frequency distributions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 162:301-306. | 1998 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Berg, H., M. C. Ohman, S. Troeng, and O. Linden. 1998. Environmental economics of coral reef destruction in Sri Lanka. Ambio 27:627-634. | 1998 | Sri Lanka; Southeast Asia | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Brown, K., W. N. Adger, E. Tompkins, P. Bacon, D. Shim, and K. Young. 1998. A framework for incorporating stakeholder participation in marine resource management: A case study in Tobago. Working Paper - Centre for Social and Economic Research on the Global Environment. | 1998 | Global; Trinidad; Tobago | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Cansfield-Smith, T. 1998. The 25 Year Strategic Plan for the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area: A model for strategic planning in the Wadden Sea Area? Senckenbergiana Maritima 29:165-171. | 1998 | Australia | Model | Marine Protected Areas |
| Chichilnisky, G. and G. Heal. 1998. Economic returns from the biosphere. Nature 391:629-630. | 1998 | China | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Special Use Permitting | |
| Cote, I. M., C. Arnal, and J. D. Reynolds. 1998. Variation in posing behaviour among fish species visiting cleaning stations. Journal of Fish Biology 53:256-266. | 1998 | Model | Fish | |
| Cuthill, M. 1998. Managing the Yongala Historic Shipwreck. Coastal Management 26:33-46. | 1998 | Australia; Cuba | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Protected Areas; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Tourism & Recreation | |
| DeVantier, L. M., G. De'ath, T. J. Done, and E. Turak. 1998. Ecological assessment of a complex natural system: A case study from the Great Barrier Reef. Ecological Applications 8:480-496. | 1998 | Australia | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Skeletal Coral |
| Done, T. 1998. Science for management of the Great Barrier Reef. Nature and Resources 34:16-29. | 1998 | Australia | Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Gibson, J., M. McField, and S. Wells. 1998. Coral reef management in Belize: An approach through integrated coastal zone management. Ocean and Coastal Management 39:229-244. | 1998 | South & Central America; Belize | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Permitting & Zoning; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Graham, T. and N. Idechong. 1998. Reconciling customary and constitutional law: Managing marine resources in Palau, Micronesia. Ocean and Coastal Management 40:143-164. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Palau; Micronesia; Europe | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hansen, M. C. and J. Jutting. 1998. Navigating the barrier reef: QEE to successful restructuring. Seminars for nurse managers 6:69-74. | 1998 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Kasprzak, R. A. 1998. Use of oil and gas platforms as habitat in Louisiana's artificial reef program. Gulf of Mexico Science 16:37-45. | 1998 | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Defense; Corporate Responses; Finfish Harvest; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting; Utility Policies | ||
| Lewis, AL AN. 1998. National Marine Aquarium, Plymouth. 32:22-23. | 1998 | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Docks & Marinas | ||
| McConney, P. and R. Mahon. 1998. Introducing fishery management planning to Barbados. Ocean and Coastal Management 39:189-195. | 1998 | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Urchins; Special Use Permitting | |
| NEPA. 1998. MARICULTURE DRAFT POLICY AND REGULATION NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION AUTHORITY COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT DIVISION. National Environment & Planning agency. | 1998 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands | |
| Oliveira, P., A. Pascoal, V. Silva, and C. Silvestre. 1998. Mission control of the MARIUS autonomous underwater vehicle: System design, implementation and sea trials. International Journal of Systems Science 29:1065-1080. | 1998 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Price, A. R. G., G. Jobbins, A. R. Dawson Shepherd, and R. F. G. Ormond. 1998. An integrated environmental assessment of the Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Environmental Conservation 25:65-76. | 1998 | Saudi Arabia | Mangroves; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Pugliese, R. 1998. Final habitat plan for the South Atlantic Region. South Atlantic Fishery Management Council, Charleston, SC. | 1998 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Agriculture; Aquaculture; Commercial Fisheries; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Piscivorous Fish; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Rilov, G. and Y. Benayahu. 1998. Vertical artificial structures as an alternative habitat for coral reef fishes in disturbed environments. Marine Environmental Research 45:431-451. | 1998 | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Taniguchi, H. 1998. Knowledge, expertise and enthusiasm. Governments need the collaboration of the private sector including NGOs in effectively and timely tackling the global issues. Integration (Tokyo, Japan) 56:3-Feb. | 1998 | Global; Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering |
| UMIAMI-RSMAS,. 1998. Ocean Status Information Management System (OSIMS) oil spill data and information. Ocean Status Information Management System (OSIMS) oil spill data and information. | 1998 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; Mexico | Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Marine Debris; Non-point Source Runoff; Petroleum Spills; Plankton; Point Source Discharges |
| Whittington, I. D. 1998. Diversity 'down under': monogeneans in the Antipodes (Australia) with a prediction of monogenean biodiversity worldwide. International Journal for Parasitology 28:1481-1493. | 1998 | Global; Australia | Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Attwood, C. G., J. M. Harris, and A. J. Williams. 1997. International experience of marine protected areas and their relevance to South Africa. South African Journal of Marine Science 311-332. | 1997 | South Africa | Field Study & Monitoring | Corporate Responses; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Dight, I. J. and L. M. Scherl. 1997. The International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI): Global priorities for the conservation and management of coral reefs and the need for partnerships. Coral Reefs 16. | 1997 | Global | Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Resource Use Management | |
| Gomez, E. D. 1997. Reef management in developing countries: A case study in the Philippines. Coral Reefs 16. | 1997 | Philippines | Infrastructure | |
| Hildebrand Lawrence, P. 1997. Introduction to the special issue on community-based coastal management. Ocean and Coastal Management 36:9-Jan. | 1997 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Makoloweka, S. and K. Shurcliff. 1997. Coastal management in Tanga, Tanzania: A decentralized community-based approach. Ocean and Coastal Management 37:349-357. | 1997 | Indian Ocean; Tanzania; India | Aquaculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Landuse Management; Mangroves | |
| Pandey, J. S. and P. Khanna. 1997. Sensitivity analysis of a mangrove ecosystem model. Journal of Environmental Systems 26:57-72. | 1997 | Model | Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Phillips, J. C., G. A. Kendrick, and P. S. Lavery. 1997. A test of a functional group approach to detecting shifts in macroalgal communities along a disturbance gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 153:125-138. | 1997 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae |
| Planes, S. and R. Galzin. 1997. New perspectives in biogeography of coral reef fish in the pacific using phylogeography and population genetics approaches. Vie et Milieu 47:375-380. | 1997 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia; Philippines | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish |
| Preen, A. R., H. Marsh, I. R. Lawler, R. I. T. Prince, and R. Shepherd. 1997. Distribution and abundance of Dugongs, Turtles, Dolphins and other Megafauna in Shark Bay, Ningaloo Reef and Exmouth Gulf, Western Australia. Wildlife Research 24:185-208. | 1997 | Australia; Middle East | Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Roberts, C. M. 1997. Connectivity and management of Carribean coral reefs. Science 278:1454-1457. | 1997 | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sando, W. J. 1997. Late Paleozoic coral genera and subgenera. State of the art, 1814-1994. Boletin - Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural: Seccion Geologica 91:61-71. | 1997 | China; Europe | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Suman, D. O. 1997. The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary: A case study of an innovative federal-state partnership in marine resource management. Coastal Management 25:293-324. | 1997 | Florida | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Resource Use Management | |
| Venier, J.M., D. Pauly. 1997. Trophic Dynamics of a Florida Keys Coral Reef Ecosystem. Pages 915-920 in Proceedings of the 8th International Coral Reef Symposium. | 1997 | Florida | Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish |
| Walters, C., V. Christensen, and D. Pauly. 1997. Structuring dynamic models of exploited ecosystems from trophic mass-balance assessments. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 7:139-172. | 1997 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector | |
| World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. | 1997 | Global; Tanzania; Maldives; Fiji; Papua New Guinea; Southeast Asia; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Germany | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Health Policies; Live Collection; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Zeller, D. C. 1997. Home range and activity patterns of the coral trout Plectropomus leopardus (Serranidae). Marine Ecology Progress Series 154:65-77. | 1997 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| [No author name available]. 1996. Guidelines for integrated coastal zone management. Guidelines for integrated coastal zone management. | 1996 | Beaches & Nature Parks; Fishing Sector; Wetlands | ||
| Burrage, D. M., C. R. Steinberg, W. J. Skirving, and J. A. Kleypas. 1996. Mesoscale circulation features of the great barrier reef region inferred from NOAA satellite imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment 56:21-41. | 1996 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Chou, C. and C.-T. Sun. 1996. A computer-network-supported cooperative distance learning system for technical communication education. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication 39:205-214. | 1996 | Taiwan | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Drake, S. F. 1996. The International Coral Reef Initiative: A strategy for the sustainable management of coral reefs and related ecosystems. Coastal Management 24:279-299. | 1996 | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves | |
| Dumbleton, B. 1996. Shore thing. Surveyor 183:16-18. | 1996 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Hinrichsen, DO N. 1996. Coasts in Crisis: The earth's most biologically productive habitats are being smothered by development. Only coordinated international action can save them. Issues in Science and Technology 12:39-47. | 1996 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Pathogens; Resource Use Management; Wetlands | |
| Katz, M. 1996. The Florida Keys ecosystem monitoring integration project. Earth System Monitor 6:13-Dec. | 1996 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Internet & Telecommunications; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 1996. Linking the Economy and Environment of Florida Keys/Florida Bay. | 1996 | Florida | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Luckett, C., W.H. Adey, J. Morrissey and D.M. Spoon. 1996. Coral reef mesocosms and microcosms - successes, problems, and the future of laboratory models. Ecological Engineering 6:57-72. | 1996 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Bahamas; Caribbean | Lab Study; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Plankton |
| Markham, A. 1996. Potential impacts of climate change on ecosystems: A review of implications for policymakers and conservation biologists. Climate Research 6:179-191. | 1996 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Wetlands |
| Nayak, S., P. Chauhan, H. B. Chauhan, A. Bahuguna, and A. Narendra Nath. 1996. IRS-1C applications for coastal zone management. Current Science 70:614-618. | 1996 | Remote Sensing | Mangroves; Sediment | |
| Osborn, TI M, KE VI N Bodge, MI LE S Croom, MA RK Schroeder, and CH AR LI E Wahle. 1996. Structural restoration of two coral reefs in the Florida keys national marine sanctuary. Pages 14-17 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1996 | Florida | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Collaboration & Partnering; Military | |
| Pilcher, J. R. 1996. The past global changes (PAGES) project. Geological Society Special Publication 251-256. | 1996 | Global; Australia; China; Europe | Climate; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Boon John, D., JE FF RE Y Claassen, and F. Pieters Renaldo. 1995. Environmentally responsive artificial beach design, Curacao, Netherlands antilles. Pages 17-18 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Antilles | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Hotel & Food Services; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ewing, LE SL EY, RI CK Page, and DA N Burden. 1995. Surf restoration collaboration in California. Pages 537-538 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Mitigation | ||
| French Jonathan, A. 1995. Gulf of Aqaba: a common cause in the Middle East peace process. Pages 524-527 in [No source information available]. | 1995 | Middle East | Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Hale Lynne, Z. and YV ES Renard. 1995. Collaborative and community coral reef management. Pages 45-46 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Hooten, A. J. and M. E. Hatziolos. 1995. Sustainable financing mechanisms for coral reef conservation. Proceedings of a workshop, Washington, DC, June 1995. in Sustainable financing mechanisms for coral reef conservation. Proceedings of a workshop, Washington, DC, June 1995. | 1995 | Global | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Jordan-Dahlgren, ER IC. 1995. Caribbean coastal marine productivity project (CARICOMP). Pages 98-99 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Martin, WI LL and SU SA N Drake. 1995. U.S. contribution to the coral reef initiative. Pages 41-42 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Minneman, SC OT T, ST EV E Harrison, BI LL Janssen, GO RD ON Kurtenbach, TH OM AS Moran, IA N Smith, and BI LL van Melle. 1995. Confederation of tools for capturing and accessing collaborative activity. Pages 523-534 in Proceedings of the ACM International Multimedia Conference & Exhibition. | 1995 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Infrastructure | |
| Monty, C. L. V. 1995. The rise and nature of carbonate mud-mounds; an introductory actualistic approach. Pages Nov-48 Carbonate mud-mounds; their origin and evolution. | 1995 | Algae; Collaboration & Partnering; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms | ||
| Petrae, Lcdr. G. 1995. Barge Morris J. Berman Spill: NOAA�s Scientific Response. HAZMAT Report No. 95-10. Hazardous Materials Response and Assessment Division, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle. | 1995 | Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Strenge, U. 1995. The beginning of a beautiful friendship. Bekleidung/Wear 47:14-16. | 1995 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Wells, S. M. 1995. Science and management of coral reefs: problems and prospects. Coral Reefs 14:177-181. | 1995 | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Gabrie, C., S. Planes, J. Baldwin, J. Bonvallot, C. Chauvet, Y. Vernaudon, C. Payri, and R. Galzin. 1994. Study of the coral reefs of Bora-Bora (society archipelago, French Polynesia) for the development of a conservation and management plan. Ocean and Coastal Management 25:189-216. | 1994 | Field Study & Monitoring | Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Hinrichsen, D. 1994. Coasts under pressure. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 3:9-Jun. | 1994 | South & Central America; China; Caribbean; Spain | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Morton, B. 1994. Hong Kong's coral communities status, threats and management plans. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:74-83. | 1994 | Review | Climate; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral | |
| Murray, J. D. 1994. A policy and management assessment of US artificial reef programs. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:960-969. | 1994 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Artificial Habitat | |
| Salm, R. 1994. Coral's hidden riches. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 3:19-21. | 1994 | Indian Ocean; India | Model | Aquaculture; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Forestry; Hotel & Food Services; Housing; Mangroves; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Santavy, D. L. 1994. An Environmental Assessment of Microbial Community Responses to a Compromised Host. in Proceedings of the 5th Investigators' Meeting for EPA's Environmental Releases of Biotechnology Products Risk Assessment Program. Duluth, Minn. | 1994 | Biotechnology Research & Development | ||
| Tunstall, B. R. 1994. Technical Memorandum - CSIRO, Australia, Division of Water Resources. | 1994 | Australia | Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Military | |
| White, A. T., L. Z. Hale, Y. Renard, and L. Cortesi. 1994. Collaborative and community-based management of coral reefs: lessons from experience. Collaborative and community-based management of coral reefs: lessons from experience. | 1994 | South & Central America; Florida; Thailand; Indonesia; Philippines; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management |
| Alder, J. 1993. Permits, an evolving tool for the day-to-day management of the Cairns Section of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Coastal Management 21:25-36. | 1993 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management |
| Baker, D. J. 1993. Sustainable development and NOAA's special role in meeting national goals. Marine Technology Society Journal 27:49-54. | 1993 | Fishing Sector; Waterborne Discharges; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Fanning Lucia, M. and G. Miller Winston. 1993. Institutional considerations for the integrated coastal zone management of Belize. Pages 2683-2697 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | South & Central America; Belize | ||
| Gallagher Charmaine, MA RI E and J. Lee Donna. 1993. Economic contribution to marine park management for Hanauma Bay, Hawaii. Pages 142-155 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation |
| Muir, F. and G. Chester. 1993. Managing tourism to a seabird nesting island. Tourism Management 14:99-105. | 1993 | Australia | Review | Marine Birds; Tourism & Recreation |
| Nakayama, AK IY OS HI, NO BU YU KI Horikosi, and HI RO SH I Kobayashi. 1993. Planning and design of multipurpose artificial barrier reefs. Pages 183-197 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | Japan | Model | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fishing Sector; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Salm, R. V. 1993. Coral reefs of the Sultanate of Oman. Atoll Research Bulletin | 1993 | Oman | ||
| Walters, C. J. 1993. Dynamic models and large scale field experiments in environmental impact assessment and management. Australian Journal of Ecology 18:53-61. | 1993 | Florida; Australia; Columbia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector |
| Yoshioka, KA ZU NO RI, TA KA SH I Kawakami, TA NA KA Shigenobu, MA MO RU Koarai, and TA KA AK I Uda. 1993. Design manual for artificial reefs. Pages 93-107 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | Japan | Model | Artificial Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Fabbri, P. 1992. Ocean management in global change. Ocean management in global change. | 1992 | Global; Southeast Asia; China | Collaboration & Partnering | |
| Gravens, M. 1992. User's guide to the shoreline modeling system (SMS). CERC-92-1, Coastal Entineering Researcch Center, Department of the Army, Vicksburg,(Mississippi, USA). | 1992 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Engineering; Sediment | |
| Martindale, W. 1992. Calcified epibionts as palaeoecological tools: examples from the Recent and Pleistocene reefs of Barbados. Coral Reefs 11:167-177. | 1992 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Coralline Algae; Marine Worms; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| NOAA. 1992. Oil spill case histories 1967-1991: summaries of significant U.S. and international spills. Hazardous Materials Response and Assessment Division, Seattle, Washington. | 1992 | Coastal Defense; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Sathi, NE EN A, S. Fox Mark, RA JA Y Goyal, and S. Kott Alexander. 1992. Resource configuration and allocation--A case study of constrained heuristic search. IEEE Expert 7:26-35. | 1992 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support | |
| Uthoff, D. 1992. Tourism and coastal change on Phuket, southern Thailand [Tourismus und Kustenveranderung auf Phuket/Sudthailand]. Erdkundliches Wissen 105:237-249. | 1992 | Thailand; Malaysia | Mangroves; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Eid, E.-M., E., and M. A. Fawzi. 1991. Egyptian approach towards appropriate use of coastal zones on the Red Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 23:331-337. | 1991 | Egypt | Mangroves; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Paw, J. N. and T.-E. Chua. 1991. Managing coastal resources in Cilacap, Indonesia, and Lingayen Gulf, Philippines - an ASEAN initiative. Marine Pollution Bulletin 23:779-783. | 1991 | Java; Indonesia; Philippines | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Pintukanok, AM PA N. 1991. Coastal zone management, national implementable plan and policy development. A case study of Phuket Island. Pages 1674-1684 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1991 | Thailand | Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| White Alan, T. and NE LS ON Lopez. 1991. Coastal resources management planning and implementation for the Fishery Sector Program of the Philippines. Pages 762-775 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1991 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Artificial Habitat; Cultural Policies; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management |
| Berwick, N. L. 1990. Guidelines for the analysis of biophysical impacts to tropical coastal marine resources. Pages Sep-62 in Conservation in developing countries. Proc. centenary seminar, Bombay Natural History Society. | 1990 | Mangroves; Seagrasses | ||
| Knowles, DI CK. 1990. Mapping a Mascot 3 design into Occam. Software engineering journal 5:207-213. | 1990 | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| McKenna, PE TE R. 1989. Application of estimation error studies for decision-making regarding sampling patterns on a South African gold mine. Pages 304-318 in Application of Computers and Operations Research in the Mineral Industry. | 1989 | South Africa | Model | Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining |
| McManus Liana, TA LA UE. 1989. Coralline resources of Lingayen Gulf, Philippines: a proposal for their management. Pages 3098-3107 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1989 | Philippines | Complex Habitat & Resources; Cultural Policies; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector | |
| Rappa Peter, J. and J. Miller Bruce. 1989. Coastal resource management planning in the U.S.-affiliated Pacific Islands. Pages 2147-2160 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Micronesia | Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Mitigation; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance | |
| Stadter, T. 1989. Microfacies, tectonics and diagenesis of the wulfrath limestone deposit (Devonian, Rheinisches Schiefergebirge) [Mikrofazies, Strukturverhaltnisse und Diagenese der Wulfrather Kalksteinlagerstatte (Devon, Rheinisches Schiefergebirge)]. Facies 21:57-97. | 1989 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sediment | |
| Gutherz, E. J. and G. J. Pellegrin. 1988. Estimate of the catch of red snapper, Lutjanus campechanus, by shrimp trawlers in the US Gulf of Mexico. Marine Fisheries Review 50:17-25. | 1988 | South & Central America; Mexico | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Rubec, P. J. 1988. The need for conservation and management of Philippine coral reefs. Environmental Biology of Fishes 23:141-154. | 1988 | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Anon,. 1987. New Way To Move Ai Into The Mainstream. Electronics 60:90-92. | 1987 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Done, T.J. 1987. Simulation of the effects of Acanthaster planci on the population structure of massive corals in the genus Porites:evidence of population resilience? Coral Reefs 6:75-90. | 1987 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Seastars; Stony Coral | |
| Bossad, P. and D. M. Karl. 1986. The direct measurement of ATP and adenine nucleotide pool turnover in microorganisms: a new method for environmental assessment of metabolism, energy flux, and phosphorus dynamics. Journal of Plankton Research 8:39826. | 1986 | Microorganisms | ||
| Dutton, I. M. 1986. Environmental Management Of The Proposed Floating Hotel At John Brewer Reef. Pages 263-269 in National Conference Publication - Institution of Engineers, Australia. | 1986 | Australia | Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Littleton, JE FF. 1986. Platform Abandonment Liabilities Uncertain. Petroleum Engineer International 58:35-36. | 1986 | Artificial Habitat | ||
| Savina, G. C. and A. T. White. 1986. A tale of two islands: Some lessons for marine resource management. Environmental Conservation 13:107-113. | 1986 | Philippines | Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Resource Use Management | |
| Slocum, DE AN, RI CH AR D Berlandy, and RO BE RT Wardwell. 1986. Facilities Planning In The Caribbean A Case Study. Pages 1351-1357 in [No source information available]. | 1986 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Improved Technology; Sea Turtles; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Madrid, A. P. 1985. Deep-water hydrocarbon exploration in the Philippines. Energy 10:493-504. | 1985 | Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Side, J. 1985. Alternative uses of offshore installations. in [No source information available]. | 1985 | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Walton, RA YM ON D, A. Roesner Larry, P. Wang Ming, and W. MA RT IN Williams. 1985. Water Quality Modeling Of Key Largo Coral Reef. Pages 1111-1120 in [No source information available]. | 1985 | Florida | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | |
| Walton, RA YM ON D, W. MA RT IN Williams, P. Wang Ming, and A. Roesner Larry. 1985. Coral Reef Modeling: Key Largo Case Study. Pages 2420-2438 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1985 | Florida | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Grigg, R. W., J. J. Polovina, and M. J. Atkinson. 1984. Model of a coral reef ecosystem - III. Resource limitation, community regulation, fisheries yield and resource management. Coral Reefs 3:23-27. | 1984 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Olsen, D. A., D. W. Nellis, and R. S. Wood. 1984. Ciguatera in the eastern Caribbean. Marine Fisheries Review 46:13-18. | 1984 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Martinique; Caribbean | Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Coppes, JA N, AD OL F Lubbers, SO EP AN GA T Soemarto, and SU GI YO Yuwono. 1983. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT FOR THE DREDGING AND RECLAMATION WORKS AT SOUTH BONTANG BAY, INDONESIA. Water Science and Technology 16:407-415. | 1983 | Indonesia | Lab Study | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Mitigation; Natural Gas & Electric Power |
| Madrid Apollo, P. 1983. Deep-Water Hydrocarbon Exploration In The Philippines. Energy 10:493-504. | 1983 | Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Parker, J. H., P. M. J. Woodhead, I. W. Duedall, and H. R. Carleton. 1983. Ocean disposal and construction with stabilized coal waste blocks. Water Science and Technology 15:83-95. | 1983 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Lab Study | Coal Mining; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| Karr, J. R. and D. R. Dudley. 1981. Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environmental Management 5:55-68. | 1981 | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges | ||
| Wells, S. M. 1981. International trade in corals. International trade in corals. | 1981 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Philippines; Taiwan; Caribbean; Europe | Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Wholesale & Retail Trade | |
| Davis, W. P., G. I. Scott, C. D. Getter, M. O. Hayes, and E. R. Gundlach. 1980. Methodology for environmental assessments oil and hazardous substance spills. Helgolander wiss Meeresuntersuchungen 33. | 1980 | Puerto Rico | Index or Indicator | Petroleum Spills |
| Meyers, P. A., J. W. Porter, and R. L. Chad. 1978. Depth Analysis of Fatty Acids in Two Caribbean Reef Corals. Marine Biology 49:197-202. | 1978 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Collaboration & Partnering; Stony Coral | |
| Baker, J. T. 1977. Management of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Pages 597-604 in Proc. 3rd international coral reef symposium, Miami, 1977, Volume 2, geology. | 1977 | Australia | Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Seymour John, L. 1975. Preliminary Legal Considerations In Developing Artificial Reefs. Coastal Zone Management Journal 2:149-169. | 1975 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Construction Codes & Projects; Fish; Fishing Sector; Permitting & Zoning | |
| Connell, D. W. 1971. The great barrier reef conservation issue-A case history. Biological Conservation 3:249-254. | 1971 | Australia | Oil & Gas Industry; Political Pressure; Seastars | |
| Peres, J. M. 1965. Reflexions sur les rapports entre l'ecologie et la paleoecologie marines. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 1:51-68. | 1965 | Collaboration & Partnering; Echinoderms; Salinity | ||
| Campo, P. C. and T. R. Villanueva. Improving the Triple Bottom line Returns from Small-scale Forestry. | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Forestry; Housing; Resource Use Management | ||
| Edson, G. M. The ancient Atlantic Reef trend. Pages 219-222 in IN: OCEANS '88. A PARTNERSHIP OF MARINE INTERESTS, PROC. CONF. & EXPO., (BALTIMORE, U.S.A.: OCT. 31-NOV. 2, 1988). | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Malcohn, E., Bentham Paulos, Andrew Stoeckle, Herbert Han-Pu Wang, and Julie Lynch. Determinants of Effectiveness for Environmental Certification and Labeling Programs. EPA-742-R-94-001, US EPA, Washington, DC. | Review | Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade | ||
| Santos, R. S., S. Christiansen, B. Christiansen, and S. Gubbay. Toward the conservation and management of Sedlo Seamount: A case study. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting | |
| Sibuet, M. and A. Vangriesheim. Deep-sea environment and biodiversity of the West African Equatorial margin. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Tissier, M. L., editor. The DPSIR Framework Technical assistance to SMAP III ICZM Projects: A tool for integrated modelling and analysis in coastal zones. | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Changes |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Develop a Collaborative Action Plan | To achieve the greatest efficiency and effectiveness from interagency collaborations it is important to first develop a project management plan and delegate tasks to agencies equipped with those competencies. Such a plan should designate each agencies roles, responsibilities and timelines. A flow chart is often useful for this task. Such a plan or chart can describe procedures for progress assessment, events of possible interest, and to notify permit holders of any changes in procedures. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) | Develop and maintain standard operating procedures based on federal, state and agency directives and regulation in order to provide staff and programs with consistent and clear direction. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Public Administration; Scientific Research; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Establish Partnerships | Local sanctuaries should explore and establish new partnerships with government and non-government agencies to meet goals of the sanctuary. Such partners should be pursued based on synergies between partner goals and competencies. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Develop a site database | Local managers could maintain a central database containing information about local shipwrecks. This data can be incorporated with geological, biological, and census data into GIS in order to interpret relationships. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Integrate Volunteer Assistance in Cultural Resources Inventory | Marine Heritage Resource managers should continue or begin to use volunteers to assist staff in collecting information, locating unrecorded sites, recording and documenting sites, assessing site significance, and developing sites for improved public access, interpretation, and protection. Often locals have interest and knowledge of unrecorded sites. If previously established, the management option (#165), will allow this data to be combined with data from other inventory management options such as (#81), and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option (#85). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Interagency Sharing of Information | This management option is designed to facilitate coordination among federal, state, and local agencies involved in management. Easier collaboration and sharing of information can often be facilitated by decision tools and information technology. There are several activities that can aid better interagency coordination of maritime heritage resources (MHR). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Internet & Telecommunications; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Promote Interagency Collaboration in Policy Making | The administrative office communicates with organizations and agencies involved in resource impacts or regulation to determine potential effects of Sanctuary management interest, to help develop policy statements, and to consult with affected agencies regarding sanctuary related policies. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. EPA Retention/Detention. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Education & Information; Public Administration; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Develop Cooperative Projects and Programs | This option involves NOAA seeking to develop cooperative projects, sharing information, and combining resources with other agencies involved in resource management, marine sanctuaries, monitoring and research. Enhanced interagency interaction will help to better manage the resources of the area at hand. Such projects and programs can be long term (e.g. monitoring) or short term (e.g. crisis management). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Create a Public Project Database & Website | An inventory and subsequent database of projects involving the public and non-governmental organizations is an important component of managing multiple public projects (#88). Having such an inventory can be important for identifying potential partners for collaboration, as well as for identifying sites (Marine Heritage or Natural Resource) of public interest. Such a database can easily be added to a sanctuary website (#133) in an effort to increase public awareness (#86). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Participate in Science Community Networking | It can be advantageous to actively participating in science-related committees, review panels, and other groups that collaborate on science issues relating to coral reefs, resource management, and other topics. This management option ensures that the local sanctuary is considered in regional planning, that there is broad-based recognition of scientific findings concerning the sanctuary, and that sanctuary expertise is shared with partners. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Public Administration; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Conduct Staff Meetings | Several types of staff meetings should be regularly scheduled to fulfill a variety of purposes. Management meetings are necessary to address administrative policy matters. Internal staff meetings should be conducted to ensure necessary information is communicated among staff as to any changes, concerns, or developments. Meetings are an opportunity to review the sanctuary management plan (#213) and standard operating procedures (#208). External collaborators should be involved in meetings when an issue is being discussed that the collaborator is involved in, such as when standard operating procedures are being developed across agencies. Meetings can also be used as important staff training sessions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Protected Areas; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Public Administration; Security & Public Administration Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Assess and Evaluate Sanctuary Management Plan Implementation | This assessment should be conducted internally by sanctuary staff on an annual basis. It is important to revisit the sanctuaries management plan every year, to consider the progress and effectiveness of activities implemented over the previous year. Monitoring and research can also provide information that was unavailable when the management plan was first written. Performance evaluations should be performed routinely and be based on consistent measures. These evaluations can also be used to populate NMSP Report Cards and other performance requirements. This new knowledge and experience can be integrated into the plan and its implementation, in a type of adaptive management (#275). Accomplishments, changes and targets should all be discerned for the year to come. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Public Administration; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Conduct Public Participation Projects Inventory | This plan calls for research and educational institutions (using students and volunteers) to conduct an inventory of projects involving the public and non-governmental organizations. In this way the public becomes involved with the inventory. Having such an inventory can be important for identifying potential partners for collaboration, as well as for identifying sites (Marine Heritage or Natural Resource) of public interest. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Participate in National Marine Sanctuary Program Activities | Local marine sanctuaries should actively participate in NMSP education and outreach and implement national education plans locally whenever possible. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Participate in Technical Advisory Committees | The technical advisory committee can meet once or twice a year with reef managers to help develop agendas on the design and prioritization of water quality and ecological research and monitoring. This provides managers the opportunity to list research/monitoring priorities to federal, state, and local government entities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Collaboratively Evaluate Management Plan Joint Actions | As the NMSP continues to increase the rigor of its self-evaluation, the program would like to increase the frequency with which partners formally join with the local sanctuary in assessing the effectiveness of the joint-management actions. Each quarter, sanctuary staff should facilitate collaborative evaluation of one action plan within the management plan. In result, systematic rotation through the actions plans will be completed every few years. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Education & Information; Public Administration; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Continued Staff Training | It is important that staff be properly educated and trained to perform their designated tasks, but it is equally important to keep staff familiar with applicable agency directive and regulation through training and communication. Some strategies for this include information technology-based reference and guidance, regularly scheduled meetings (#210), and through in-service trainings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Protected Areas; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Public Administration; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Phase Out Unwanted Subsidies | Subsidies are often offered to promote certain types of growth and development. At a later time, with changing priorities, it may be determined that these types of growth and development are no longer optimal. For example, sun grown coffee, was subsidized in Guancia Bay, PR, as it was expected to have higher future market demand. However, it requires clearing large tracts of land on steep, extremely erodible clay soils. This leads to high volumes of erosion because there is no vegetation to anchor the soil in place. Now these subsidies are promoting sun grown coffee even though shade grown is better for the land and reefs because it reduces erosion, extreme runoff, and adds vegetation to the land. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Banks, Credit, & Securities; City Planning; Corporate Responses; Decision Support; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Hydroseeding High Risk Soils | Hydroseeding is a process that creates a slurry of seeds, water, and mulch. This slurry can be applied with the use of trucks, trailers, and even aircrafts. This method is particularly useful because it promotes quick germination and reduces erosion. It is especially beneficial to use this method where there is a vastness of bare soil due to clearing vegetation for roads, homes, and farming. Higher elevations are typically steeper and often experience heavy rainfall, and ultimately an extreme amount of erosion occurs if soil is bare. Erosion from the highlands can fill the reservoirs in the drainage basin with sediment. Using hydroseeding would increase vegetation and ultimately the stabilization of the soil. Also, increased vegetation through hydroseeding would help with infiltration rates because the roots would aerate the soil. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 1999. Temporary Seeding. NRCS Planning and Design Manual. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Reef Life; Sediment |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Change Agricultural Cover Crop Practices | Cover crop outreach entails changing agricultural practices in an area to leave vegetation and cover on the soil while growing other crops (e.g. Coffee). Agricultural practices that encourage leaving soil bare are extremely susceptible to erosion (e.g. sun grown Coffee). Cover crop methods and shade-grown crops (e.g. shade-grown Coffee) would reduce the large amount of sediment that is eroding, particularly from high elevations, and ultimately will reduce the amount of sediment that reaches the coral reefs. Options to encourage transition to cover crop practices include outreach to raise awareness of benefits and cost share programs to help farmers with the burden of the extra expense. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Conservation Cover. CODE 327. US Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Responses; Sediment |
| Conducting Socioeconomic Research: Support science of socioeconomic analysis of marine protected areas | Little is known about applied socioeconomic analysis to marine protected areas. Funding support will be provided for scientists to meet and share information on this subject. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Contact Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Pressures; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Continued Development of Signs, Displays, Exhibits, and Visitor Centers: Develop interactive educational exhibits | Creating exhibits that are interactive can help to convey information regarding boundaries, regulations, resources, education programs, and research programs. Computers are a great way to create interactive exhibits. Funding can be provided from private and nonprofit organizations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Corporate Response: Invest & Co-finance Projects | Investing and co-financing projects that aim to conserve or restore habitats can be an effective means to preserving reef habitats as well as establishing positive working relationships between organizations. Investing in private sector projects will promote desired businesses and business practices, reducing barriers to entry and competitiveness as compared to traditional businesses and business practices to counterbalance advantages from undesired externalities. | World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. |
Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Shipping Businesses | This option requires the sanctuary to continue to alert shipping businesses about sanctuary regulations. Such regulations may include vessel waste discharge, ATBA, PSSA, etc. The targeted audiences will include importers, exporters, port authorities, commercial fishing companies, ship insurers. This information can be provided to the audience through NOAA nautical charts, trade publications, newsletters, trade shows, and direct mailings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finance & Insurance; Infrastructural Policies; Insurance; Manufacturing & Trade; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Local Businesses | Information should be provided to business along the water so that employees will be aware of environmentally sensitive business practices. This can be achieved through informative brochures, and distributing other educational materials. These interactions can also be used to inform businesses of opportunities for voluntary certifications (#104). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Infrastructural Policies; Manufacturing & Trade; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Corporate Response: Standardized Environmental Certifications and Labels | Product labeling initiatives are based on the premise that product information represented by or contained on the label is otherwise not readily available (or apparent) and is of value in consumer purchase decisions. For example, warning labels highlight product safety and toxic exposure hazards and advise consumers on ways to minimize risks. Likewise, a number of environmental certification programs (ECPs) identify products' environmental burdens and/or set standards for products' environmental attributes. Properly designed environmental labeling efforts can change consumer and manufacturer attitudes and behaviors, thus reducing environmental burdens. The specific metrics used to measure environmental label effectiveness include: 1) consumer awareness of labels, 2) consumer acceptance of labels (credibility and understanding), 3) changes in consumer behavior, 4) changes in manufacturer behavior, and 5) improvement of end goals, such as environmental quality. | Malcohn, E., Bentham Paulos, Andrew Stoeckle, Herbert Han-Pu Wang, and Julie Lynch. Determinants of Effectiveness for Environmental Certification and Labeling Programs. EPA-742-R-94-001, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; CO2; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Forestry; Health; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Birds; Medical Care; Medical Centers; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Resource Use Management; Toxics; Transportation; Utilities; Whales & Dolphins; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Increase Public Grounding Notification | Public notification of groundings can be increased through more centralized, accessible notification methods, and public education and outreach. Notification methods could include creating a �grounding hotline� with a central government agency as the enforcement dispatch center. By centralizing notification methods, public confusion over what agency to contact can be reduced. Education and outreach efforts should focus on the importance of grounding notification and awareness of notification methods (i.e. the hotline). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Natural Resource Injury Incident Litigation | This management option involves sharing information and documentation regarding an injury incident so that litigation teams can proceed with legal action against responsible parties. This is achieved through providing vessel grounding litigation management participation in order to process the information collected during assessment phase of injury to help build a case against the responsible party. Also, it involves providing vessel grounding litigation case management support through providing reports, site reconnaissance, deposition, and witness testimonies in support of litigation. Lastly it would involve documenting and tracking costs along the way from field assessment work, reporting, etc. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Contact Uses; Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Valuation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels | Semi- permanent/permanent vessels can have a negative impact on the surrounding local environment both due to the effects of shade and from the direct contact with the substrate. Sunken vessels that cannot be seen from the surface may present a danger to navigation. Derelict vessels that do not remain stationary may cause harm in multiple locations before becoming stationary. If fishing gear is still intact, it may cause further biological damage through "ghost fishing� (#283). Early response, creating mooring fields, pump-out stations, and providing support for removing derelict vessels, reduces the impact of these vessels. Also, the removal of intrusive vessels will help contribute to the restoration of reef areas to previous conditions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Military; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Stony Coral; Substrate; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Coastal Construction & Development | This involves assessing coral, seagrass, and hard bottom substrate that is impacted during coastal construction repair or alternation. If unacceptable damages are occurring this information will be useful in future permit decision making. If infringements have occurred, this information may be useful for compensatory mitigation and liability for restoration of those natural resources injured. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Ports & Harbors; Reef Habitat; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Special Use Permitting; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Vessel Groundings | This option involves assessing conditions and responding, as well as developing methodologies and protocols for coral dominated substrate, seagrass substrate, and mixed substrate. These protocols will help to determine how much damage has been done to the non-living coral framework. Ultimately, fine-tuning these protocols will allow for the most effective assessments. Evaluate these in light of current grounding regulations (#34). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Dredging Regulations; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Stony Coral; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Develop Chain of Notification for Grounding Incidents | This option advocates coordinating with other agencies such as FWC, NOAA, and local coral managers to determine the standard protocol and responsibilities when there are groundings. Through coordination, these agencies can determine threshold levels of damage for different responses and for notifying other agencies higher up the chain. Enhancing inter-agency coordination will be beneficial in terms of dealing with groundings because it will allow the problem to be fixed in a more time-efficient manner. Having a centralized grounding notification system is the first step of this management option, as it ensures all incidents pass through a single agency to determine further actions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Assist Direct Contact & Intervention Programs | Programs such as Team OCEAN and Professional Guides Association should be assisted by existing protected areas and sanctuaries. These already-existing programs can be assisted through providing technical support, data, advice, vessels, and/or equipment. Assisting pre-existing programs is useful because it helps to strengthen and expand their missions, and it also prevents unnecessary duplication of efforts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Collaborate with Towing & Salvage Operators in Grounding Notification | This option advocates the establishment of rapport between local operators and regulatory agencies. This is achieved through regular meetings and training sessions to emphasize the importance of operator cooperation in regards to vessel groundings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Large Ships; Military; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Mass Coral Bleaching Events | There are several actions managers can take to prepare for and respond to bleaching events. These strategies typically focus on developing and communicating reliable information about the bleaching event and its impacts, rather than providing a "cure." Developing a Bleaching response plan in advance allows managers to respond more effectively during these rapid onset events. Predicting the risk and severity of bleaching events can allow for more timely yet credible information for decision makers. After the bleaching event it is important to quickly access the ecological impacts for further management decisions. Bleached coral are in a vulnerable state, and are therefore less resilient to degraded water quality, physical damage from recreation, or pressure from fishing activities. This heightened sensitivity means that current protections may need to be increased temporarily following a bleaching event. | Marshall, P. and H. Schuttenberg. 2006. A reef manager's guide to coral bleaching. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Climate Regulation; Coral; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Sea Temperatures |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Coordinated Oil & Hazardous Spill Response | This management option calls for developing unified response protocols to deal with containment and clean-up of oil spills. This is important to protect corals, mangroves, and seagrasses from adverse impacts of hazardous materials. Given the limited number of spills and the importance of responding quickly, interagency coordination of reporting and response is essential for success. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Puerto Rico and USVI Area Planning Committees. 2008. Hazardous Substances Pollution Area Contingency Plan. Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin islands. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Toxics; Transportation; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop an Ecological Information System | Spatial and temporal information about ecological resources should be incorporated into an existing local GIS or database. Information should include benthic habitats, species distributions and life histories, water quality, etc. These will act as baseline data for ecological monitoring. If previously established, the management option #165, will allow this data to be combined with updated data from other inventory management options such as #76, and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option #85 or 165. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Climate; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Reef Habitat; Reef Life |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Conduct a Modeling Workshop | Conducting a workshop can be useful to discuss modeling approaches, develop preliminary conceptual models, and define specific information needs for models. There are decision tools to choose from other than traditional models, and many different modeling approached to choose from, making this type of workshop both an outreach effort, and an effort to collaborate. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Broadcasting, Publishing, & Libraries; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop a Geodatabase | A Geodatabase combines several GIS layers into one singular geospatial database. This allows for different resources and uses to be compared spatially and temporally. A standardized protocol, such as #165, is necessary when combined different types of data from different sources. Attention to and record keeping of meta-data if very important. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Reef Habitat; Reef Life |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Maintain the Maritime Heritage Resources inventory | Volunteers can help maintain the heritage resources inventory through collecting existing information, locating unrecorded sites, recording and documenting sites, assessing site significance, and developing sites for improved public access. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop a Geographic Information System Incorporating Satellite and Aerial Images | This option involves the acquisition of high-resolution, low altitude photos of management areas and grounding hotspots. These photos can then be used for baseline documentation for natural resource litigation, research, and management decisions. If these images are to be incorporated into larger geodatabase, such as that proposed in # 166, a standardized protocol should be developed in advance, as suggested in management option #166. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Ecosystem Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Vessel Grounding Database | This management approach would involve refining and maintaining a vessel grounding database and adequate staffing for on-going management, GIS processing of archived data, creating products for management case tracking, and developing a database that is user-friendly and useful. If previously established, the management option #165, will allow this data to be combined with similar data from other inventory management options such as #95, and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option #85. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop a Resource Site Database | Local managers could maintain a central database containing information about geological, biological and cultural marine resources. Standardized meta-data should be included for each entry site such as name, position, age, integrity, historical and cultural significance, sensitivity, and recreational value. This data can be incorporated with other data, such as census data or landuse data, into GIS in order to interpret relationships #166. This would combine efforts of multiple management options such as #164, and #81 into one consolidated place. Management options such as #76 & #75 could be incorporated to track changes to these sites over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Database for Tracking Restoration, Repairs, and Monitoring Activities | This response involves adapting NOAA�s Damage Assessment Center�s seagrass injury assessment team component to local management areas. If previously established, the management option # 165, will allow this data to be compared to previously collected baseline data such as that collected with management option #164. This would also allow for comparisons across different types of data, such as use changes, that would be contained in a #166. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Establish a Standardized Data Management Protocol | This management option involves creating a management protocol to standardize the way investigators manage data. This will be achieved by creating a single approach to maintaining, storing, and accessing digital data. With research shifting from single organisms to the entire ecosystem, integrating multiple databases is extremely beneficial. The database needs to be a dynamic, distributed system for annual data gathering and archiving. With different types of data often coming from different sources, it is very important to have standard processes for tracking meta-data as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Reef Life |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop Systems Framework | A systems framework can serve several research purposes. These can act as conceptual starting points for modeling. Frameworks can act as starting points for brainstorming and discussion of topics. Systems frameworks are particularly useful for identifying indirect relationships and overcoming boundaries between individual disciplines. | Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach | |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop a Modeling Plan | This would involve developing an overall plan for new predictive models focused on management needs. The plan will include discussion of preliminary conceptual models, data needs, data gathering, and model development and refinement. Models may incorporate both abiotic and biotic environmental factors. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Physical & Chemical Environment; Public Administration; Reef Life; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Research and Model Causal Linkage Between Pollutants and Ecological Impact | This involves conducting research to identify and document causal linkages between discharge water pollutants and specific, quantifiable ecological problems. The natural environment naturally assimilates some pollutants, but has thresholds for this type of contaminant processing. Different hydrology, biology and spatial/temporal factors are all going to play a roll in the linkage between pollutants and ecological problems, meaning modeling and risk assessment can be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Sewage Treatment; Stormwater Management; Sunscreen Use; Supporting Services; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Information Booths for Trade Shows and Festivals | This option encourages local reef sanctuary staff to attend trade shows and local festivals and set up a booth with brochures, information, and photos regarding sanctuary resources. Such participation will enhance public education regarding local reef resources and education staff will evaluate which festivities would be the most optimum to attend and participate in (in order to be efficient with sanctuary funds). Specific trade shows, such as dive shows, should allow for a more targeted audience. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop and Maintain Sanctuary Website | Marine sanctuary areas can create a website as an educational tool, providing information regarding new issues, educational resources, volunteer opportunities, and current initiatives such as research, restoration projects, or policy changes. If a website is already in use, it should be maintained and updated with new information, resources, and technologies to enhance effectiveness and visitation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Internet & Telecommunications |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Educational Materials | Producing educational materials such as CD-ROMS, posters, videos, and information sheets is beneficial for informing the public regarding reef health. Collaborations should be made to produce and disseminate such materials, and if the materials have been produced previously, evaluations should be made regarding the material�s effectiveness. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Establish VHF Radio Stations | The local sanctuary staff should work to secure a VHF radio station dedicated to provide information about local boating and water activities in multiple languages. Broadcast messages can include, but are not limited to information about regulations, navigation, resources, weather, and reef conditions. This will help prevent boaters, divers, and fishermen from negatively affecting the ecosystem. Assessments regarding cost and target audience areas must be conducted and external funding pursued to supplement the expense. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Environmental Atlas for the Sanctuary | This option involves collaboration with agencies such as NOAA, DEP, and other regional agencies to develop color atlases that reveal information regarding habitat types, populations, hurricane paths, and other environmental and social themes. Much of this information can be obtained from (#85) and (#166). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Interactive Interpretive Exhibits | Interpretive exhibits combine an array of information types (pictures, sounds, interactive activities etc.) in an easy to understand, relevant way to visitors. On-water and on-land interpretive exhibits for maritime heritage resources and sanctuaries are helpful at increasing public knowledge/awareness of reefs. Interpretive exhibits can be established near the site of the resource (#126), in permanent (#131) or used as a traveling tool for (#127), and (#130). Such exhibits are beneficial as they allow for schools, the community, and tourists see resources first-hand and learn why they are important, at their leisure and without requiring a staff member to present the information. Expanding already-created exhibits is important to continue to draw in crowds and to continue to add/increase public knowledge and stewardship. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Washburne, R. and Wagar, J. 2010. Evaluating Visitor Response to Exhibit Content. Curator: The Museum Journal 15:248-256. Veverka, J. The Key to Successful Heritage Tourism Marketing Planning and Program Design. Interpretive Communication Accessed 7/7/2011. |
Decision Support; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Tourism & Recreation |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Outreach with the Tourism Development Council | Collaborating with the Tourism Development Council allows for more specific targeting of tourists and visitors for resource management outreach. Tourists and visitors are less familiar with local ecosystems and are therefore more prone to unintentionally damaging the environment or defying policies and regulations. The Tourism Development Council is also an important stakeholder to consider, in coastal zone management. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Roadside Signs | Roadside signs and billboards in local reef watershed areas should be created to inform travelers that they are entering/exiting the reef watershed. Partnerships should be explored to create multi-logo signs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Permitting & Zoning; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop, and Implement New Technologies for Educational Resources | New technologies should be researched, developed, and adopted for sanctuary educational materials. They should be evaluated before they are adopted. Sanctuaries must make their educational materials available through technologies that the public is currently using. For example, mobile applications could allow visitors to access relevant information while recreating, where older technologies such as websites would be more difficult to access. Such technologies can also be used as decision tools for the public, tracking their use of reef resources to show the user what impact their total activities may have and opportunities to improve that. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Internet & Telecommunications; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Distribute Information in Utility Bills, and Vessel Registration | Distributing pertinant information through these pre-channels allows more efficient targeting of the public for relevant information. Information that is important for local residents, such as changes in policies or sanctuary activities in the area can be distributed with utility bills. This is also a great method for distributing best practices information, educating the public on how their activities in and around their residence can impact coral reef ecosystems. Vessel registration is an excellent method for distributing boating regulations and best practices to those that actually own boats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Provide Interpretive Information | Targeted information should be provided and interpreted for media, interest groups, periodicals, publications, and environmental organizations. This information may be about available programs/resources, research findings, policy changes, statistics, avoidance techniques, legal/financial consequences etc. This information should be provided specifically for these groups in such a way to best enhance public understanding regarding reef resources. It is important to interpret this information for these user groups, as this will help them convey the often technical information to the public. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Broadcasting, Publishing, & Libraries; Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Print Marine Etiquette on Marine-Related Products Packaging | Printing information on marine-related products regarding proper marine etiquette could be a possibility for raising awareness and improving public stewardship. Partnerships will be explored to help print etiquette information on materials such as bait boxes, ice bags, water buckets, etc. that are commonly used by stakeholders. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Discharge Controls: Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards | Effluent Toxicity is considered the aggregate toxic effect to aquatic organisms from all pollutants contained in a facility's wastewater (effluent). It is one part of the Water Quality Standards (#22) that prohibits the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts. Numerical criteria can be adopted from the Clean Water Act of based on scientifically-defensible methods. In addition to setting this numerical criteria, enforcement of the standards requires inspection programs and monitoring. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Improved Technology; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Discharge Controls: Carbon Sequestration | Carbon sequestration is the process through which practices remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. The term "sink" is also used to describe agricultural and forestry lands that absorb CO2, the major global warming gas emitted by human activities. Agricultural and forestry practices can also release CO2 and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. In the ocean, phytoplankton are another major carbon sink. | Houghton, R.A. 2002. Magnitude, distribution and causes of terrestrial carbon sinks and some implications for policy. Climate Policy 2:71-88. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Algae; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Forestry; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Plankton; Political Pressure; Solid Waste Disposal |
| Dissemination of Findings: Develop an Information Exchange Network | This management option involves developing a compendium of current and ongoing research that should be updated on a regular basis. This is important as it allows for collaborators to share information and resources. This type of exchange helps to maximize gains in economies of scale and reduce duplication of efforts. Decision tools such as inventories and databases can often be adapted for this use. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Internet & Telecommunications; Scientific Research |
| Dissemination of Findings: Distribute Periodic Sanctuary Health Reports | The management option involves creating monitoring/condition reports on the health of the sanctuary and reef that is released for the public. The findings can be released through newsletters, presentations, reports, publications, and other written and oral methods. Criteria reported on typically include water quality, critical habitats, and species of particular interest. These reports will ultimately help reveal the effectiveness of marine protections and policies based on the conditions researched. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Protections; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation |
| Dissemination of Findings: Participate in Conferences | Conferences are beneficial as a means to garner and disseminate new information, technology, and methods. Conferences also serve as a networking opportunity to communicate with potential collaborators. Participation in local, state, and federal conferences by sanctuary staff is very important to reach out to the broader coral reef community. Sponsoring conferences would allow scientists and researchers to keep abreast of findings and ongoing research within the local sanctuary. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Scientific Research |
| Dissemination of Findings: Support Journal Publication | This management option involves sponsoring the publication of journals that contain peer-reviewed scientific research. For sanctuaries this can be an excellent place to publish reports and research that used sanctuary areas or resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biotechnology Research & Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Scientific Research |
| Dissemination of Findings: Report Monitoring and Research Results | It is important to disseminate data and information gathered to collaborators and the wider scientific community. This can be accomplished through publication, such as journals (#161) or other networks (#159). It is important to share this data with other government agencies as well (#92). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Broadcasting, Publishing, & Libraries; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Create Alternative Livelihoods For Fishermen | Many fishermen rely on their catch as their family�s main source of income. When restrictions are placed on fishing it can be to the economic detriment of these fishermen. By creating alternative means of earning income for these fishermen, social and economic goals are accomplished while decreasing pressures on natural fish populations. These alternatives often come in the form of aquaculture, which helps to still meet the demand for fish. Another common alternative is tourism; fishermen can use their knowledge and equipment such as boats to accommodate tourism and recreational fishing. | All Islands Coral Reef Committee. Local Action Strategies. United States Coral Reef Task Force Accessed 6/13/2011. Sumaila, U.R., William W. L. Cheung and Louise The. 2007. Rebuilding Hong Kong's marine fisheries: an evaluation of management options. FCRR 2007, Vol. 15(3), Fisheries Centre, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Cultural Policies; Culture; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Health; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Social Assistance; Tourism & Recreation |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Regulate International Trade of Reef Species | Many coral reef species are harvested internationally for a variety of markets including the aquarium trade, food, curios, jewelry and pharmaceuticals. The US is the largest importer for many of these markets. The US strictly limits extraction of stony coral and many reef species in its waters; but as a major importer and consumer of coral reef species, more actions can be taken to decrease the demand on international imports. Setting and enforcing regulations on what can be imported (such as Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species CITES) is one approach that has been taken. More information is needed, leaving room to collect trade data and assess the impacts of extraction techniques to find sustainable methods. Demand for species collected this way will be increased with greater transparency to consumers, which can be accomplished through certifications for environmentally cognoscente collectors and those using alternatives like aquaculture and coral farming. Continued participation in Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) is also beneficial. | U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Live Collection; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Political Pressure; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Sponges; Stony Coral; Toxics; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Energy Efficiency Initiatives | Energy efficiency is one of the lowest cost strategies for reducing greenhouse gases. Energy efficiency is also one of the few options that actually reduce user costs as well, since using less energy should reduce energy bills. Energy efficiency can be promoted across the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. In the US, the ENERGY STAR program has served as a trusted source of information to help consumers and organizations throughout the nation adopt energy-efficient products and practices. Other ways to incentivize energy improvements include subsidizing (e.g. tax exemption) or issuing lower interest loans for investments in energy use reduction technologies and infrastructure (e.g. more efficient heating/cooling systems). | Environmental Protection Agency. ENERGY STAR and Other Climate Protection Partnerships. 2009 Annual Report. US EPA. |
Atmospheric Emissions; City Planning; Climate Regulation; CO2; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Oil & Gas Industry; Shelter; Utilities; Utility Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Energy Policy & Development: Cable and Pipeline Construction Assessments | Pre-assessments must be conducted to ensure pipelines and cables buried on the ocean floor will not disrupt or destroy natural or cultural resources. | Reach Networks Hong Kong Ltd. 2007. Project Profile: Asia-America Gateway (AAG) Cable Network, South Lantau. Wanchai, Hong Kong SAR. |
Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Offshore Wind and Hydrokinetic Alternative Energies | Policies encouraging or authorizing construction of offshore facilities are evolving, and there are many sides to the issue of how to best manage them. Alternative energies are desirable and would reduce the dependence on fossil fuel resources. However, hydrokinetic technologies are just becoming viable, meaning long term impacts are still unknown. Facilitative policies reduce barriers for alternative energy development or increase barriers or costs for incumbent technologies. These include research and innovation policies, technology improvement subsidies, market based policies that internalize externalities, and regulatory changes that simplify the permitting process. | Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. Portman, M.E. 2010. Marine Renewable Energy Policy: Some US and International Perspectices Compared. Oceanography 23:98-105. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Seawater Flow; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies |
| Enforcement: Interpretive Enforcement | Interpretive enforcement, sometimes called �soft� or positive enforcement, refers to approaches geared towards encouraging widespread voluntary compliance with laws, rules and regulations. Interpretive enforcement is based on the premise that most people, once informed about MPA regulations, want to do the right thing. This is the greatest level of compliance because it advocates understanding and public support of goals for reef management. The main objective of this management action is to increase public understanding of the importance to comply with regulations, achieve voluntary compliance, and promote public stewardship of historical and cultural marine resources through interpretive enforcement. Strategies that can help achieve these goals include developing special training programs, organizing events, implementing social marketing, targeting indigenous learning systems and changing cultural value systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture, and Department of the Interior and Local Government. 2001. Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook No. 8 Coastal Law Enforcement. No.8 Coastal Law Enforcement, Coastal Resource Management Project of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Cebu City, Philippines. National Marine Sanctuaries. 2005. MPAs and Enforcement. Module 7, NOAA. |
Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Enforcement: Enforce Statues, Regulation and Permit Requirements | This option ensures compliance with statues, regulations, and permit requirements. This is accomplished through intensive on-site patrols by authorized law enforcement officers. Agencies at the state level as well as NOAA can assist with enforcement. For success, it is important that law enforcement be trained in the compliance requirements of other agencies (e.g. Marine Heritage Resource (MHR) permitting compliance). A standardized training program to help better ensure cross- deputization of enforcement agencies would be necessary. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Protections; Dredging Regulations; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Permitting & Zoning; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Environmental Education: Promote Environmental Education in Local Schools | Volunteers can be used to assist education and outreach staff to bring environmental education to local schools. Volunteers can do things such as: chaperone during snorkel trips, and help students with water quality testing exercises. Volunteers should be trained to correctly use educational materials and equipment. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Schools & Colleges; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Develop Standardized Voluntary Certification Programs | This management option involves coordinating with leaders of various target businesses related to diving and snorkeling, marine mammal viewing, kayaking, eco-tours, and fishing. Through collaborations with these businesses, management areas can create a voluntary certification program for employees of these businesses to learn and receive accurate information about nearby corals, the ecosystem, and how they can better protect reefs in their everyday actions. These voluntary certifications can be used to educate employees and/or to develop self-regulating standards for these businesses. Depending on the standards and curriculum, voluntary certification programs can then be used by these businesses to convey knowledge or environmentally safe practices to customers through marketing. Educating employees of these businesses helps to assure that they are disseminating accurate information to visitors. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Environmental Education: Promote and Support Environmental Education | This management option requires developing education programs that increase students� understanding and knowledge of coral and other reef inhabitants. This can be facilitated through field trips, hands on experiences and by providing local schools with age-appropriate materials. Greatest success occurs with a wide reaching, well-developed network of educators, programs, and institutions. Examples of successful programs include: The Coral Reef Classroom- teaches basic reef biology and facilitates learning through water quality sampling, data collection, and analysis/evaluation. Build-An-Ocean- a program for elementary-age students that helps students learn how to identify mangroves, sea grasses, fish, and corals by "building-an-ocean" with color laminated pictures of the organisms that compose the ecosystem. Envirothons- inspire learning through competitive events and can be beneficial education tools. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Education Program. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Accessed 7/1/2011. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Life |
| Environmental Education: Support Adult Environmental Education Programs | This management option advocates the sponsoring and support of local reef management areas for adult, coral education programs. This education program would be used to inform community leaders, decision makers, and organized user groups through guest lectures, field trips, brochures, and support of local organizations offering adult education. This kind of education program would allow stakeholders to make more informed decisions regarding reef health and protection. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Create a Public Awareness Program | This involves developing a spread of education tools like brochures (#111), newsletters (#118), displays (#127), web sites (#133) and a database (#98) to inform the public about different volunteer, education and training opportunities in regards to preserving the marine environment and maritime heritage resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Provide mechanisms outside the law enforcement sector that can deliver resource education at the site of the resource | This plan involves acquiring other personnel such as volunteers to help with resource protection through education. Volunteers can hand out brochures, answer questions, and assist boaters on high-use days/areas. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Infrastructure; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Socio-Economic Drivers; Transportation; Water Transportation |
| Environmental Education: Competitive Educational Funding Opportunities | This response involves offering funding to teachers for field trips, scientific equipment, and reference material in support of curricula. Teachers may submit proposals for evaluation, and funding is administered on a competitive basis from a non-profit organization or a reef management area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Schools & Colleges; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Consult Partners to Increase Education and Outreach Participation and Effectiveness | This option is a strategy to continue collaboration with local learning institutions, local government agencies, and education advisory boards in order to develop new ideas for education and outreach measures to enhance reef health. The activities that will result from this collaboration can include: providing information on current activities in regards to education/outreach, encouraging cooperative efforts, providing direction for the local reef management area�s education plan, preventing the duplication of efforts, promoting stewardship, and guiding the development of natural and cultural resource education products. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Support Environmental Workshops for Educators | This management option involves using environmental education workshops in order to ameliorate educator�s knowledge of the importance of corals because of their cultural and natural resource value. Local management areas can co-sponsor these efforts, and up-to-date information will always be utilized. Involvement in such workshops not only promotes coral education, but can also show educators where resources and opportunities exist through institutional collaboration. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Schools & Colleges; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Environmental Education: Support Lecture Series | This option encourages coral management staff to speak at local forums to encourage greater public education regarding reef health. This involves collaborating with organizers of lecture series to take advantage of the opportunity to speak in front of an previously-organized audience. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Establishing an Maritime Heritage Resource Inventory: | This approach involves creating a bibliography and computerized database in a standard format and making it publicly accessible via internet. This inventory will contain basic information for each entry site such as name, age, integrity , historical and cultural significance, sensitivity, and recreational value. Many activities would be involved in creating this inventory. These include | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Establishing an Maritime Heritage Resource Inventory: Use volunteer assistance in cultural resources inventory | This plan advocates the use of volunteers to assist with collecting information, located unrecorded sites, documenting sites, etc. Volunteers can be greatly utilized for maritime heritage resources inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Streamside Management Areas | There are often surface waters, such as streams and lakes, within forestry areas that require special protection. This management option involves establishing and maintaining management areas (35 to 50 feet) around these surface waters to buffer against changes in temperature, increases in sediments and nutrients, and to provide bank stability. Canopy species in these areas also provide woody debris needed for instream channel structure and aquatic species habitat. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Implementing Notification and Response Protocols: Coordinate with Other Management and Enforcement Agencies to Develop Standardized Vessel Grounding and Spill-Response Protocols | This plan aims to coordinate with other management and enforcement agencies to create uniform spill response and vessel grounding protocols. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Dredging Regulations; Energy Policy & Development; Food & Energy Policies; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Implementing Notification and Response Protocols: Implement �Eyes on the Water� | This plan would entail teaming with volunteers and education staff to develop a volunteer training program to help report groundings. Training would include: incident recognition, documentation, and notification. Possible volunteers could be pulled from Team OCEAN, Reef Medics, Mote Marine Laboratory, professional fishing guides, etc. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Injury Prevention: Foster Reef Resilience | Resilience relates to how well the reef ecosystem is able to maintain key functions and processes while under abnormal pressure or stress. Two ways of supporting coral reef resilience are: incorporating known resilient areas into management design and by implementing strategies to either reinstate or protect factors that contribute to resilience, such as good environmental conditions, biological diversity, and connectivity. | Marshall, P. and H. Schuttenberg. 2006. A reef manager's guide to coral bleaching. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Contact Uses; Coral; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Pressures; Resource Use Management |
| Landuse Management: Mine Reclamation | Lands disturbed by mining must be reclaimed to their Approximate Original Contour (AOC). Mine operators must backfill, compact, and grade in order to restore the AOC of the land with all highwalls, spoil piles, and depressions eliminated. Spoil material is prone to erosion, and may carry various disturbed toxics into groundwater if not properly managed. Temporary roads and impervious surfaces may have also been constructed for mining purposes. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement. POSTMINING LAND USE: Exceptions to Approximate Original Contour Requirements for Mountaintop Removal Operations and steep Slope Mining Operations. Washington, DC. |
Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Valuation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Permitting Application & Award | This management approach is important because permits assure protection and conservation of coral resources from harmful activities and practices. Within sanctuary waters, special use permits (#157) can be used to allow scientists and others to conduct necessary work while following permitting regulations to reduce the impact of that work. General permits are often required for altering land-use, construction projects and certain discharges. To be eligible for a permit, the operator may be required to conduct impact assessments, institute best management practices and conduct monitoring of the project. Though permits are a necessary precaution, the process can be streamlined through ensuring clear submittal requirements, and reducing redundancy. Redundancy often occurs when multiple agencies must approve a permit, a single point of contact and standard, inter-agency protocols can reduce unnecessary redundancy. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Marine Zoning: Special Use Areas | Special use areas are set aside for specific scientific or educational purposes. This is in order to encourage the recovery or restoration of injured or degraded resources. Also, the areas may be designated to facilitate access to, or use of, resources, and prevent other user conflicts. Special-use areas are achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts; and determining/establishing appropriate zones for high-impact or user-conflict activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Biomedical Research Policies; Complex Habitat & Resources; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Marine Zoning: Develop Baseline Data | Baseline surveys of existing resources need to be conducted before monitoring can begin. The surveys must be conducted in Ecological Reserves, Sanctuary Preservation Areas, and Special-Use Areas to characterize the status of important marine species and their habitats. Establishing baseline data allows for later comparisons to monitoring data to gauge changes over time and revaluate current management actions being taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Utilize Marine Protected Areas for Research and Monitoring | Research and monitoring of marine protected areas determine the degree to which the zones meet goals and objectives for protecting natural resources, as well as human-use patterns, attitudes and compliance. Once data is gathered from within the protected zone it can than be compared to comprable data from outside the protected zone, as a control. It is necessary to compile and review data on use patterns to determine where additional Special-Use Areas would be appropriate. Research in the protected area should be non-invasive. It is important to make the protected area available for external research as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Wildlife Management Areas (WMAs) | Wildlife Management Areas include bird nesting, resting, or feeding areas, turtle nesting beaches, and other sensitive habitats including shallow flats that are important feeding areas for fish. These areas seek to provide protection for endangered/threatened species or their habitats while at the same time providing opportunity for public use. Wildlife Management Areas are achieved through placing and maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; implementing management responsibilities; adjusting existing zone boundaries if needed; evaluating allowable activities within the boundaries and make changes if needed; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; monitoring the effectiveness of current zones; and revising GIS and NOAA charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Ecological Reserves (ERs) | Ecological Reserves set aside areas with minimal human interference. These reserves aim to enhance and protect biodiversity through encompassing large, contiguous habitats. The goal of ecological reserves is to encourage spawning, nurseries, and residence areas that contribute to genetic protection of fish and marine life. Ecological Reserves can be achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Integrate Resource Information in Permits, Authorizations, or Certifications | Permitting usually includes assessing the natural and cultural resources of an area. Using this previosly gathered data would aid in creating an inventory for marine resources. If previosuly established, the management option (#165), will allow this data to be combined with data from other inventory management options such as (#95), and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option (#85). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Permitting & Zoning; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Marine Zoning: Existing Management Areas | The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS) uses this zoning category to identify areas that are managed by other agencies where restrictions already exist. These zones delineate the existing jurisdictional authority of other agencies (i.e., State parks, aquatic preserves, sanctuaries, and other restricted areas). Management of these areas within the Sanctuary may require additional regulations or restrictions to adequately protect resources. Any additional management measures will be developed and implemented in coordination with the agency having jurisdictional authority. Their function is not to establish another layer of bureaucracy, but to recognize established management areas and, at a minimum, to complement the existing management programs, ensuring cooperation and coordination with other agencies. Existing Management Areas will be maintained through revising GIS and NOAA charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Measuring Sanctuary Performance Over Time: Monitor existing performance measures consistently over time | The sanctuary staff should conduct routine performance evaluations to collect and record data on sanctuary performance over time. Using this data staff will determine effectiveness by evaluating progress towards achievement of each action plan�s desired outcomes, and assessing the role or added value of those outcomes in the overall accomplishment of site goals and objectives. Effectiveness will be evaluated for both the local sanctuary performance measures as well as NMSP national performance measure where applicable. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Public Administration; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Monitor & Research: Utilize Managed Areas for Socioeconomic Research | Data are needed to test hypotheses about the socioeconomic impact of marine zoning and user-group perceptions about changes in natural resources within the sanctuary area. User-group perception of changes in natural resources can be compared with quantitative ecological data to identify misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Providing funding opportunities for external scientists to conduct research in the managed area is another option. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Permitting & Zoning; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Valuation |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Create a Maritime Heritage Resource (MHR) Field Unit | A Maritime Heritage Resource (MHR) field unit would be developed to conduct field research and coordinate permitted research activities. Training is an important aspect of developing such a field unit, as improper field work can be very destructive to MHR sites. Additional funding may be needed to involve external underwater archaeological research experts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Funding & Incentives; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Monitor & Research: Integrate Volunteer Monitoring Program | Monitoring by trained volunteers yields useful, cost-effective data that provides positive engagement for a variety of stakeholders. Such existing programs include The Ocean Conservancy, Atlantic Gulf Rapid Reef Assessment, and the Dolphin Ecology Project. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Monitor & Research: Continue Stakeholder Research | It is beneficial to support monitoring and research projects that are developed by stakeholders because these present an opportunity to directly engage constituents in sanctuary resource issues and to increase understanding of the ecosystem. Sanctuaries can provide support in the form of helping to coordinate activities, assisting with field work, issuing research permits, assisting with identifying potential funding sources, and providing letters of support for grant proposals. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Monitor & Research: Develop Innovative Monitoring Tools | This management option calls for identifying and evaluating monitoring tools and methodologies used to detect pollutants and identify cause-and-effect relationships among water quality and biological resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Chemical Variables; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Scientific Research; Toxics |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Fisheries Sampling | Improved fisheries sampling programs require improving the spatial resolution of commercial and recreation fisheries-dependent and fisheries-independent sampling programs to provide statistics on catch and effort. Improved sampling can be achieved through evaluating and enhancing census programs by using smaller sampling areas. Also, fishery pre-recruitment monitoring efforts should be continued for long-term prediction of fishery stocks. Last, investigating life histories of fishery species needs to be conducted because it is currently a gap. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Use Patterns on Artificial and Natural Reefs | This management option seeks to provide data for decisions concerning creating new artificial reefs. Use data is important because justification for artificial reefs extends from their ability to shift use pressures (diving, fishing, etc.) from natural reefs. Once an artificial reef is decided on there is much more data to collect and factors to consider when deciding where the artificial reef (#189). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Defense; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Military; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Detect and Respond to Episodic Events | Sanctuaries should have centralized information about algal blooms, fish kills, large patches of discolored water, and other unusual episodes to determine whether a management action would be appropriate. For such decisions to be made in a timely fashion, monitoring data must be consistently collected and updated in the information system #203. This monitoring information can than be added to a #166, where models like those planned out in #207 can determine the degree of threat and where it may spread. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Physical Variables |
| Monitor & Research: Develop Scientific Research Study Program | Management areas can encourage scientific studies by coordinating efforts of research groups and institutions. Collaboration and integration of these scientific studies can be beneficial to both the research groups and the management area. For example, data from monitoring of restoration projects could be analyzed by an academic institution, helping to reduce the burden on funds and perhaps using data in ways outside the scope of management objectives. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Ecosystem Services; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Schools & Colleges; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Monitor & Research: Adaptive Management | By definition, adaptive management is a structured management approach that links science to decision-making, thereby improving the probability of restoration success. It provides an efficient process to address risk and uncertainty inherent within ecosystem restoration by encouraging flexible plans and designs. Monitoring (#) is an important component of adaptive management. The affect of different restoration alternatives can be seen using monitoring data, and compared against other environmental variables to determine what the best future actions are based on results of previous projects. | CERP Committee. 2006. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan Adaptive Management Strategy. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Physical Variables; Public Administration; Regulating Services; Remediation; Scientific Research; Supporting Services |
| Professional Development of Education and Outreach Staff: Attend conferences | Conferences are beneficial because they are a main way that new technologies, methodologies, and information are shared among educators. Participation in local, state, and federal conferences by sanctuary management staff is very important to reach out to education community. Local conferences should be participated in as much as possible. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Train Volunteers | Continuing volunteer training programs for general public involvement in research, documentation, and management is important to protect natural and maritime heritage resources. These same training programs also add value to the participants experience, as they are learning while volunteering. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Integrate Volunteer Support For GIS | Volunteers work with sanctuary management staff using GIS software to provide managers with information and photographs. Often such volunteers will come from educational institutions, as these projects require an existing knowledge and familiarity with GIS. Such projects are well suited for such volunteers or internships as they can often be seen to completion and provide the participant with real world application of their skills, often fulfilling requirements of their institution. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Conduct Public Forums | This option ensures public involvement in local reef management area decisions/events. Holding public forums on an as needed basis will encourage dialogue between management staff and stakeholders. During these forums reef staff can present information to help better educate the public through the forum as well as answering questions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Public Administration |
| Public Participation: Integrate Volunteer Assistance in Facilities Maintenance | Volunteers can assist management staff with routine marine and dock maintenance, mooring buoy installation, repair, and cleaning; vehicle and boat maintenance, ground maintenance, and storage and dock cleaning. This allows for management staff that would have been performing these tasks to perform other tasks. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Coordinate with Trained Volunteer Programs | Trained volunteer programs have volunteers that may be experienced with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, or SCUBA. An example of a trained volunteer program is Reef Medics. This program is hands-on and often assists with the Florida Keys Marine Sanctuary. These programs can be helpful in restabilization efforts and monitoring repaired sites. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Coordinate the Adopt-A-Reef Program | This program encourages local dive operators and volunteer divers to �adopt� a reef within the sanctuary and make species trips to the site to maintain the reef. Volunteers remove trash, fishing lines, and debris. Divers will be properly trained on how to clean the reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) and The Ocean Conservancy. 2005. Good Environmental Practices: Underwater Clearnup. CORAL RP-103:2002, |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Volunteer Recruitment | This option increases support for volunteers and their activities. Volunteers should be recruited based on their skills and placed according to their experiences, interests, and qualifications. Volunteers should be trained and oriented so they will be familiar with the management area and feel appreciated. To be successful, volunteer programs need to provide safety, and place volunteers in a worthwhile, meaningful job positions. Volunteer projects can then be evaluated based on effectiveness and communication should be kept with volunteers through phone calls, letters, and e-mail. Though volunteer positions are typically unpaid, funding would need to be provided from a variety of sources in order to support efforts. Potential programs and internships should be identified and created in order to enhance the program. Partnerships with local educational institutions can be very beneficial for recruiting volunteers. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Manage Public Participation Projects | Public participation projects have significant potential; they not only address the project goals but also encourage public stewardship for important marine resources. Long term public projects require continued involvement, guidance and encouragement to reach project completion. Developing an inventory/database (#98) can be important for successful management of multiple projects. The public cannot participate in such projects if they are not aware of them, so effective marketing (#86) is an essential component of public participation management. Many of these tasks can be performed by volunteers. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Seafood Watch | Assist Seafood Watch and other sustainable seafood consumption initiatives, in their efforts to educate the public and promote sustainable seafood. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. SeafoodWatch. 2005. Sustainable Seafood Business Practices. Monteray Bay. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Sectors Filling Human Needs |
| Public Participation: Assist Sea Turtle Activities | Sea turtles are protected under the Endangered Species Act. Volunteers protect and preserve sea turtles and their habitats. Volunteers will do an array of tasks including monitoring known and potential nesting beaches, marking and recording the location of nests, and documenting nest success. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Vertebrates; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Sea Turtles |
| Public Participation: Assist Save the Manatee Club | Volunteers are active in helping to remove monofilament line. This is especially dangerous to manatees. Volunteers from Save the Manatees can help with education and monitoring in the local coral management area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Debris; Marine Vertebrates; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Environmental Education Foundation REEF | This program uses recreation divers who conduct fish biodiversity and abundance survey in the Keys and the Caribbean. This surveys work towards contributing to The Great Annual Fish Count. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fish; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Ecosystem Condition RECON | RECON trains volunteer divers to collect information about the reef environment, health of stony corals, presence of key reef organism, and human-induced impacts. The goal of RECON is to broaden knowledge of bottom-dwelling organisms on reefs. They also act as an alert system when there are abnormal and possibly harmful conditions present on the reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Stony Coral |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef and Coastal Cleanups | Reef and coastal cleanups are organized by a network of environmental and civic organizations, government agencies, industries, and individuals. These efforts help to educate the public on marine debris issues and how to help reduce debris along beaches. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) and The Ocean Conservancy. 2005. Good Environmental Practices: Underwater Clearnup. CORAL RP-103:2002, |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Debris |
| Public Participation: Assist Queen Conch Restoration Activities | Volunteers assist with raising juvenile queen conchs at a hatchery located at Keys Marine Lab through this volunteer program. They also locate and tag wild, adult conchs for population and reproduction studies. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Molluscs; Snails & Conch; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Marine Ecosystem Event Response and Assessment MEERA | This volunteer program seeks to provide early detection and assessment of biological events occurring in sanctuaries and surrounding waters. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach |
| Public Participation: Assist Marine Animal Rescue Activities | There are many volunteers in marine areas that will help rescue distressed animals. Volunteers assist with reducing pain and suffering of marine animals, provide first aid, derive maximum scientific and education benefits from the live and dead marine mammals, and collect high-quality data. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Services; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Marine Vertebrates; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Assist Local Volunteer Organizations | This management approach encourages collaboration with local volunteer organizations that have missions similar to the coral management area. This way, the sanctuary is working efficiently with other groups to help accomplish the same goals instead of wasting resources trying to accomplish the same ends. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Florida Keys Watch | Volunteers participating in this program help collect seawater samples and environmental data. Florida Keys Watch help to assist scientific studies conducted by universities, agencies, and other institutions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Scientific Research |
| Public Participation: Assist Dolphin Ecology Project | This volunteer program photographs individual dolphins for identification, observes the activities of the dolphins, samples environmental parameters, and identifies and measures the abundance of important dolphin prey. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Marine Vertebrates; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Whales & Dolphins |
| Public Participation: Assist Wild Bird Rehabilitation | Many wildlife rescue organizations help and respond to injured birds including marine birds like sea gulls, pelicans, egrets, herons, osprey, and eagles. Collaborations with such organizations can be mutually beneficial as organization volunteers learn from training received from sanctuary staff. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Birds; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Implement and Assist "Eyes On the Water" Program | Programs such as Eyes On the Water allow dive-boat captains, crew, and other professionals to act as sanctuary eyes and ears; ensuring people are acting in accordance with reef restrictions and regulations. These programs are also useful for reporting groundings. Such programs require teaming with volunteers and education staff to develop volunteer training on incident recognition, documentation, and notification. Volunteers could be recruited from Team OCEAN, Reef Medics, Mote Marine Lab, professional fishing guides, etc. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Fishing Gear/Fishing Methods Regulations | In most regions there are already regulations that prohibit fishing methods that incorporate explosives, poisons, oil, and bleach. Further investigation may reveal additional methods, materials, or gear that should be prohibited as well. Regulations should aim to increase the use of low-impact gear (#194) in place of more destructive gear and methods. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Activities Allowed in Existing Regulatory Zones | There are five different types of regulatory zones within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary: Ecological Reserves, Sanctuary preservation Areas, Wildlife Management Areas, Existing Management Areas, and Special Use Areas. Each zone has a different set of prohibited or allowable activities. This type of diversity in zones allows for visitors to partake in the activity they desire, but in an area where the impact will be less severe. Allowable activities require periodic evaluation and may need to be changed or relocated to allow for recovery or to address other issues of concern. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Artificial Reef Regulations | Discharge/depositing of materials and constructions on the seabed are both prohibited without permits, regulating the construction of new artificial reefs. Likewise, existing artificial reefs are protected through permit requirements for any alternation of the seabed. There are still further considerations for protecting artificial reefs. Artificial reef materials and construction choices are very important and may change based on the specific location and desired impacts. An artificial reef to attract recreational fishing differs from one for recreational divers or shoreline storm protection. Many artificial reefs were formally large ships, oil rigs or other types of waste that have been decommissioned and would be too large and expensive to dismantle on land. In these cases it is important to put restrictions on the sinking process to ensure there won�t be any type of chemical leakage and that the structure is stable on the seabed. (#189) (#190) | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Solid Waste Disposal; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management; Waterborne Discharges |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Bait Fishing and/or Catch & Release Trolling Regulations | This option seeks to reduce or eliminate bait fishing, and catch & release trolling in fragile areas. First assessments must be conducted to measure the effects of bait fishing and catch & release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Channel & Reef Navigation Markers | This option would evaluate the need for proper marking to ensure better navigation. There are many types of markers, including buoys, charts, beacons, and GPS mapping. Such markers can also be used to advocate prohibition on vessel speeds greater than idle speed in areas designated as idle-speed only/no-wake and around shallow reef locations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beach & Land Formation; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Coral Touching Regulations | Currently touching, removing, damaging, distributing, and injuring any living or dead coral or coral formation is prohibited in Sanctuary Preservation Areas and Ecological Reserves. An investigation will be conducted to consider extending this prohibition to high-use, sensitive and vulnerable areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Contact Uses; Coral; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Ensure Consistency Among Fishing Regulations | Consistency will improve administrative and regulatory coordination between fisheries regulatory agencies. This involves using a protocol for drafting and revising fisheries regulations in order to implement a consistent set of regulations throughout the protected reef area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Dredging Regulations | Dredging is oftentimes prohibited with certain exceptions. Dredging regulation often falls under other controls over the alteration of the seabed, discharging or depositing materials. At times dredging is necessary for navigation or other activities, necessitating .permitting mechanisms for allowing otherwise prohibited activities. Revising the regulations to help eliminate negative dredge-and-fill activities within a certain distance of corals would be beneficial because it would help promote the reestablishment of sensitive benthic communities. Reservoirs may require periodic dredging to remove sediment that may have collected. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sand & Rock Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Transportation; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Change Salvaging & Towing Practices | This option seeks to protect natural resources and reduce damage resulting from improper vessel salvage methods. In the past, salvage techniques have caused collateral damage when removing vessels grounded on the reef. These injuries often occur in the immediate area surrounding the grounded vessel but can be avoided with the use of proper salvage techniques developed with reef resources in mind. The principal causes of collateral injuries are dragging a vessel off the reef instead of floating it off; the use of steel towing cables that can drop on or drag across the substrate, impacting and dislodging resources (reef structure, corals, and sponges); and propwash and surge, generated by tugboat propellers, that displace sediment and dislodge organisms. To avoid or minimize collateral injuries, a reconnaissance survey should be conducted while the vessel is grounded to evaluate reef resources in the immediate area surrounding the vessel and determine an appropriate extraction route. Bunker fuel and cargo may need to be offloaded. Floating or buoyed towlines should be used instead of steel cables, and towing activities should be conducted at or near high tide to facilitate floating the vessel. Before and during the extraction, global positioning system (GPS) coordinates at the bow and stern of the vessel should be recorded to assist with future injury assessment. GPS tracking should be operating on the grounded vessel during egress from the site and on all salvage vessels or tugboats involved with the salvage operation. The outbound path for vessel extraction may also need to be buoyed, to help avoid or identify injuries that may occur during the salvage operation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Spearfishing Regulations | Spearfishing is already prohibited in ecological reserves, sanctuary preservation areas, management areas, and special-use areas. There are additional considerations to be made to see if restrictions need to be extended in high priority areas. There may also be need to be further scientific study on the impacts of spearfishing. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Consider Regulations for Catch & Release Trolling | This plan seeks to reduce or eliminate catch-and-release fishing in many fragile areas. First an assessment must be conducted to measure the effects of catch-and -release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Water Efficiency Initiatives | Reducing water use through cost effective water efficiency improvements can be beneficial as it reduces pressure on water as a finite resource and saves money. There are several ways water efficiency can be promoted. Some Water Efficiency BMPs recommended by the EPA include: Water Management Planning; Information and Education Programs; Distribution System Audits, Leak Detection and Repair; Water-Efficient Landscaping, Water-Efficient Irrigation; Toilets and Urinals; Faucets and Showerheads; Boiler/Steam Systems; Single-Pass Cooling Equipment; Cooling Tower Management; Commercial Kitchen Equipment; Laboratory/ Medical Equipment; Other Water Intensive Processes; Alternative Water Sources. One of the ways the US government has promoted Water Efficiency Initiatives is through Executive order 13123 which places certain water use reduction requirements on Federal Agencies. There are also existing funding and incentives for non-government sectors. Project funding comes in many forms, such as appropriations, energy savings performance contract (ESPC) and Utility Energy Service Contract (UESCs) programs; ratepayer incentive programs such as rebates from public benefit funds or utilities; and the retention of energy and water cost savings. | US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Water Efficiency Best Management Practices. Federal Energy Management Program Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Textiles & Apparel; Utilities; Utility Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Live Collection Regulations | Live collection is often more destructive than capture of food fishes because of the destructive methods used to remove live fish and invertebrates from the reef habitat. These methods include use of cyanide and explosives. Current methods should be assessed and alternatives should be developed or collection prohibited. | World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Resource Use Management: Marine Heritage Resource Protections | This management option involves protecting underwater items/sites that have historical, cultural, archaeological, or paleontological significance. This response advocates permits for action that may degrade the resource. This can be accomplished through creating an MHR field unit, monitoring MHR site degradation, and evaluating excavation and mitigation techniques. Field units can help conduct field research and coordinated, permitted research activities. Experts relating to archaeological research underwater can also be hired with additional funding. Through evaluation of excavation techniques, new technologies can be suggested such as: turbidity screens, sediment removal equipment, and seagrass restoration/relocation protocols to lead to less disturbance. Inventory and decision tools can also be used in the aid of Maritime Heritage Resource protection. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Mitigation; Physical Damage; Pipelines; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Valuation; Wetlands |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Regulations for Sponge Fisheries | Sponges play a vital role on reefs, providing structure, food and filtration. Depending on the method of removal, this process can be very destructive to other reef fauna and habitat. Research is needed to compare impacts of different sponge fishing methods in different areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boring Sponges; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Educational & Research Opportunities; Encrusting Sponges; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Resource Use Management: Designated Uses | The water quality standards regulation requires that States and Tribes specify appropriate water uses to be achieved and protected. Appropriate uses are identified by taking into consideration the use and value of the water body for public water supply, for protection of fish, shellfish, and wildlife, and for recreational, agricultural, industrial, and navigational purposes. In designating uses for a water body, States and Tribes examine the suitability of a water body for the uses based on the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the water body, its geographical setting and scenic qualities, and economic considerations. Each water body does not necessarily require a unique set of uses. Instead, the characteristics necessary to support a use can be identified so that water bodies having those characteristics can be grouped together as supporting particular uses. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. Environmental Protection Agency. What are Water Quality Standards? Designated Uses. Water: Water Quality Standards Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Marine Products; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Management Enforcement | Marine protected areas and other types of coastal zone management areas have fisheries management policies that must be enforced in addition to the broader Statues, Regulation and Permit Requirements (#91). Illegal, unregulated and unreported (IUU) fishing is a major problem worldwide. Management area policies must be enforced to have an impact on the fisheries stock. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Resource Use Management: Prevent Introduction of Invasive Species | Preventing the introduction of invasive species involves public awareness of the invasive species, minimizing modes and prone areas for invasion, and detecting small populations for early eradication. Some common modes of terrestrial transportation include livestock and domestic animals, mowing equipment, and firewood. Clean equipment before transport to a new location. Remove soil from plants, and plant bare-root. Use high grade seed and weed free livestock feeds. Reduce opportunities for invasive plants by keeping native plant populations strong and healthy and seeding in cover crops to reduce barren soil. | Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Ballast Discharge; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Manufacturing & Trade; Transportation; Water Transportation | |
| Restoration: Restore Reef Habitat and Salvage Benthic Inhabitants Injured by Physical Damage | This management approach involves salvaging, maintenance, and re-stabilization or injured resources by management staff and private contractors in order to rescue and provide first aid following physical damage such as vessel groundings. This can be achieved using Reef Medics and other volunteer programs because these groups have experience with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, and SCUBA diving. Also, it allows for researchers to collect living coral material when relocation of such organisms is not possible. Salvage and re-stabilization is not limited to the living coral; octocorals, seagrasses, and the non-living framework may all be damaged of destabilized from groundings or other physical impacts. In addition to the habitat's structural integrity, it is important to re-establish aesthetics and ecological functionality. Funds from mitigation and case settlements should be used for this work, as long term costs of restoration and monitoring can be extensive. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Octocoral; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Restoration: Restore injured or destroyed coral reef framework | This approach would allow to use funds from case settlements to reconstruct/replace coral framework that has been compromised. This approach aids to restore the coral�s structural and ecological functionality, as well as reestablish aesthetic qualities associated with corals. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dredging Regulations; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Funding & Incentives; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Restoration: Acquire Blanket Permits for Restoration Programs | Restoration programs often span multiple areas and multiple agencies. With proper collaboration between resource managers, and restoration programs, multiple programs/initiatives can work together under blanket permits from regulating agencies. For example, NOAA�s Beaufort Lab/Seagrass Research team, NOAA�s Damage Assessment Center, and DEP all coordinate restoration projects together in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Permitting & Zoning; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Restoration: Environmental Remediation | Environmental Remediation is a type of restoration that's focus ranges from Brownfields to Oil Spills to Hazardous Waste Sites. These restoration activities aim to restore the site to a previous condition, or to a condition that is not a threat to human health or other forms of life. Several standards can be used to determine when remediation is necessary and to what extent the environment should be restores. Biocriteria can be used to determine the degree of degradation to biological components of the site. Often it is the presence of a particular pollutant in the soil, water or air, which is above acceptable limits and will not degrade fast enough over a short period of time and therefore must be removed. Physical and chemical water quality criteria can be used to set maximum acceptable limits of water quality parameters. Air quality criteria can be used to set acceptable maximum and minimum air standards for remediation. | Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 2005. Contaminated Sediment Remediation Guidance for Hazardous Waste Sites. EPA-540-R-05-012, US Environmental Protection Agency. Environment Protection Authority. EPA Guidelines for Environmental management of on-site remediation. Environment Protection Authority, Adelaide, Australia. |
Applied Chemicals; Biocriteria; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Health; Health Policies; Landuse Management; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Military; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Solid Waste Disposal; Supporting Services; Toxics; Valuation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Restoration: Removal of Invasive Algae | Benthic organisms on reefs maintain a delicate balance competing for space. In many areas, the competition between coral and algae has fallen out of balance due to confounding factors. Factors such as decreased herbivorous fish and invertebrates, and invasive algae species have allowed faster growing algae to take over many reefs, often growing into smothering mats that cover and kill coral. In Hawaii, there has been some success physically removing invasive algae such as Kappaphycus using underwater vacuums extended down from barges or volunteer events in shallower areas. | The Nature Conservancy. 2010.Two Million Pounds of Invasive Algae Removed From Maunalua Bay. (not cited) |
Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcareous Macroalgae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Coralline Algae; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Reef Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Zooxanthellae |
| Restoration: Reintroduce Indigenous Living Corals | The approach reviews the policies and regulation regarding the re-introduction of living corals indigenous to a specific geographic location that were propagated in the lab. The concern about reintroduction of organisms from the lab and aquaria revolves around the possibility of introducing exotic or foreign strains of diseases to natural coral. Also, there is concern about introducing defective genetic material as well. One viable solution may be to reintroduce corals reared in in-situ coral nurseries. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coral; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Microorganisms; Reef Habitat; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Restoration: Land Reclamation Integrating Toxic Discharge Controls | This option aims to eliminate unsightly residues, reduce erosion and control acid or otherwise toxic aqueous discharges from abandoned coal mines, coalmine waste or other types of land change. For toxic mine drainage, preventative actions include mine sealing, infiltration control, day lighting, and neutralization with alkaline material such as hydrated lime. Which action to take relies heavily on groundwater and runoff in the region of the mine. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Aquaculture; Coal Mining; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Rainwater Collection Systems | Creating a rainwater collection system (either through policy change or the initiative of homeowners) would help in many ways. These systems would utilize water in an efficient manner. It would reduce the pressure of water as a finite resource. Water would be collected and utilized before it reaches the ground. Once rain falls to the ground, it picks up nutrients, chemicals, and pathogens on the ground and transports them in the form of runoff. Eventually this contaminated stormwater runoff enters water resources through the drainage basin. Collecting a considerable amount of water would prevent contamination of that water, and allow for it to be usable. Also, it would reduce the amount of water that is lost when it is contaminated as runoff. An overall reduced amount of stormwater runoff would reduce the amount of contaminants that would harm corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Cisterns used for water harvesting. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shelter; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Transportation Policy: Airline Carbon Policy | Civil aviation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, and this contribution has grown as the industry has grown. Some regions are implementing policies such as cap and trade that apply to the airline industry. | Bruce Duguid. 2009. Fasten Your Seat Belt: Airlines and cap-and-trade. CTC764, Carbon Trust, United Kingdom. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Supporting Services; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Water Quality Management: Wastewater Management System Standards | This management option involves reducing the amount of pollutants entering groundwater by enforcing existing standards. Inspection and compliance programs for cesspits, Onsite Sewage Treatment and Disposal Systems (OSTDS) and septic tanks are necessary to do this. Municipal sewage treatment plants have a variety of means to meet these standards, including improving management of current treatment systems or upgrading treatment systems with newer technology. Some of these technologies include: Continuous-Flow, Suspended-Growth Aerobic Systems (CFSGAS), Fixed-film, Sequencing batch reactor systems, Stabilization ponds, FWS constructed wetlands, and other aquatic systems (#2), Enhanced nutrient removal: phosphorus & nitrogen, Recirculating sand/media filters and Land treatment systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Center for Watershed Protection. 2004. Illicit Discharge Detection and Elimination. US EPA. US Environmental Protection Agency. 2002. Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. EPA/625/R-00/008, US EPA. |
Chemical Variables; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Water Quality Standards | Water Quality Standards are the foundation of the water quality-based pollution control program mandated by the Clean Water Act. Water Quality Standards define the goals for a waterbody by establishing Designated Uses (#279), setting baseline waterbody minimum criteria to protect those uses, and establishing provisions that regulate Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards (#280). Since the baseline water quality standards are for the waterbody in its entirety, there is some flexibility on how that minimum criterion is accomplished. In some cases, Remediation (#281) may be preferable to more stringent effluent standards. The criteria include specific biochemical and ecological measures that would be good indicators of ecological health, including Biocriteria (#282). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biocriteria; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Toxics |
| Water Quality Management: Biocriteria | The President�s Ocean Action Plan directed the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to develop biological assessment methods and tools for evaluating the health of coral reefs so that States and Territories could more easily establish biological water quality standards, including descriptions for designated waterbody uses and biological criteria (biocriteria). Biocriteria are qualitative or quantitative thresholds of biological condition necessary to sustain the designated uses. Rigorous biological assessments are needed to identify metrics that reflect biological characteristics and are responsive to a gradient of human disturbance, and to generate defensible long-term monitoring programs. Implementation of biocriteria for freshwater ecosystems has forged a process that can be adopted for coral reefs. | Bradley, P., L. Fore, W. Fisher, and W. Davis. 2010. Coral reef biological criteria: using the clean water act to protect a national treasure. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, Narragansett, RI. |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Resource Use Management |
| Water Quality Management: Reduce Pollution & Discharges from Marinas & Live-Aboards | This management option strives to reduce and eliminate the discharge of wastewater and pollution within zones near corals. In many instances, "no-discharge" zones already exist and are simply poorly enforced. In other instances the discharge limits are not stringent enough. Successful regulation requires marinas to be equipped with the proper infrastructure to support transfer of wastewater from vessels to shore-side for treatment. This infrastructure includes: pump-out facilities and mobile pump-out services. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Health; Health Policies; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Landfill & Solid Waste Disposal Site Assessment Strategy | This option seeks to reduce/eliminate pollution from leaching at landfill sites. High risk, old landfill sites that may have hazardous waste must be identified. Once identified, monitoring at these landfills should be intensified to insure leaching does not occur into marine systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health; Health Policies; Littering; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Water Quality Management: Treating Effluent Water Through Wetlands | Additional treatment of sewage is often a necessary management option because secondary treatment alone leaves 20,000 times more nutrients in the water than the safe limit for corals. High concentrations of nutrients in the water leads to eutrophication, and coral reefs are more sensitive to nutrient enrichment than any other coastal system. Wetlands are extremely successful at reducing nitrogen levels in water. Using natural wetlands or "living machines" to perform this task can actually be more cost effective than further sewage treatment. Each successive wetland treatment cell of the series can provide incredible levels of denitrification, and thus protect corals from nutrient enrichment. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2003. Waste Treatment Lagoon. CODE 359. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Water Quality Management: Refine Pest Spraying Program | This strategy aims to reduce the amount of pesticides that could potentially enter the water from spraying for pests such as mosquitoes. A site-specific combination of pest prevention, pest avoidance, pest monitoring, and pest suppression strategies (PAMs) should be used. Aerial spraying is often used only when the mosquito concentration reaches a specific threshold. The mosquito spraying strategy would review the aerial spraying threshold to see if it could be raised, to reduce frequency of use. Refining spraying technologies would be advocated to see if newer techniques/technologies would possibly reduce the amount of pesticides released over water. For identified water quality concerns related to pesticide leaching, solution runoff and adsorbed runoff, the current version of the USDA-NRCS WIN-PST program should be used to evaluate potential risks to humans and/or fish, as appropriate, for each pesticide to be used. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Integrated Pest Management (IPM). CODE 595. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Toxics |
| Water Quality Plans: Resource Monitoring of Surface Discharges | This strategy will identify the impacts of point-source discharges by requiring all National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System dischargers to develop monitoring programs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health; Health Policies; Infrastructure; Physical & Chemical Environment; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Public Administration; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Collaborate with Projects Changing Water-Flow | Other organizations may be performing restorative freshwater projects (Everglades Restoration) or other flow altering projects (e.g. canals for small boats, agricultural irrigation etc) that affect the downstream marine management area (Florida Bay). Projects on the coast that involve hydrologic modifications (such as changing salinity) must be closely monitored in order to protect reef quality. Reefs are very sensitive systems and can only survive in a narrow salinity range. By taking an active role and monitoring freshwater flow projects, management staff can better ensure proper consideration of the impact on coastal marine environments. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan. 2010. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan: 2009 System Status Report. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Salinity; Security & Public Administration Policies; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 Virgin Islands Code. | Under Title 25, in addition to requirements for boat registration and administration of harbors, among other things, sections pertaining to the mooring and anchoring of vessels and houseboats provide for the protection of important marine resources in USVI waters. The Law requires mandatory boating education and safety courses for all boat operators. Application to Coral Reefs:Mooring and anchoring are restricted and not allowed near fragile systems. Not anchoring on coral reefs is abig plus of this legislation. Legislative Actions:Penalties for violation of the Chapter include fines not to exceed $1,000, a lien on the vessel and potential libel suit Comments:A houseboat or vessel is allowed to moor or anchor only in those areas designated by the Department. Section 404(g) of the legislation lists areas designated as areas of special concern. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Boating Regulations; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Environmental Education & Outreach; Large Ships; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Transportation Policies |
| 25-Year Permits for Maintenance Dredging in Deepwater Ports; Deepwater Ports Maintenance Dredging and Disposal Manual, 62-045 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-45.001 Authority, Intent and Policy.
(1) This chapter is promulgated under the authority of Sections 403.061(26) and 403.816(1), F.S.
(2) It is the intent of this chapter to establish a permitting system for maintenance dredging in deep water commercial navigation
areas of the ports listed in Rule 62-45.020, F.A.C. This chapter incorporates standards and criteria which recognize the present most
beneficial use of these waters for deep water commercial navigation. Since the implementation of a comprehensive maintenance
dredging management plan is a major factor in determining the adequacy of a long-term maintenance dredging program, it is the
further intent of this chapter to give a position of prominence to such a plan within this permit system.
(3) It is the policy of the Department to provide a regulatory process which will enable the ports to conduct maintenance
dredging in an environmentally sound, expeditious and efficient manner.62-45.020 Scope.
(1) The permit system established by this chapter applies only to the ports of Ft. Pierce, Jacksonville, Miami, Palm Beach,
Panama City, Pensacola, Port Canaveral, Port Everglades, Port Manatee, Port St. Joe, St. Petersburg, and Tampa.
(2) The activities which may be included within a permit issued under this chapter are limited to maintenance dredging and
disposal of the maintenance dredged material.
(3) Applicants for permits under this chapter are limited to the port authorities or private interests using the port for deep water
commercial shipping and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The Department shall not issue separate permits to the port authority or
private interests and the U. S. Army Corps of Engineers when the responsibility of maintenance dredging or the disposal of the
maintenance dredged material from the port is shared by any of the parties. The permit, if issued, shall clearly specify the duties and
responsibilities of each party.
(4) A permit may be issued for any length of time up to 25 years. There shall be no more than one such permit for each of the
ports listed in subsection (1).
(5) The area within which work under this permit system may take place is limited to the federally maintained, port authority
maintained, or private interest maintained navigation channels, turning basins, or harbor berths associated with deep water
commercial navigation and associated dredged material disposal sites. Eligible port maintenance dredging areas are depicted on
NOS Charts Nos. 11491 (Port of Jacksonville), 11478 (Port Canaveral), 11475 (Fort Pierce Harbor), 11466 (Port of Palm Beach),
11468 (Port of Miami), 11470 (Port Everglades), 11413 (Tampa Bay, Northern Part), 11414 (Tampa Bay, Southern Part), 11393
(Port St. Joe), 11391 (Panama City), and 11383 (Port of Pensacola) on file with the Department and adopted here by reference.
Copies are available at cost upon request from the Office of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, MS
300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000. Application to Coral Reefs:Proper, environmentally sound, dredging and disposal of dredged material, as reviewed by permit processers, will limit the amount of sediment and nutrients released to open water. The process will be particularly applicable to coral reefs for the dredging and disposal of Miiami harbor. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| American Indian Religious Freedom Act of 1978, 42 United States Code § 1996. | The Act protects the rights of Native Americans to believe, express and exercise their traditional religions, including access to important sites, use and possession of sacred objects, and the freedom to workshop through ceremonial and traditional rights. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
|
| Anadromous Fish Conservation Act of 1965, as amended, 16 United States Code § 757. | The Act is intended to conserve anadromous fish. It authorizes the Secretatries of Interior and Commerce to enter into cooperatve agreements with states and other non-federal interests for conservation, development and enhancement of anadromous fish and contribute up to fifty percent as the federal share of the cost of carrying out such agreements. Reclamation construction projects for water resource projects needed solely for such fish are also authorized. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Projects are for conservation, development, and enhancement on fisheries. Comments: |
Department of Interior/Department of Commerce Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act of 1940, as amended, 16 United States Code § 668. | Protects Bald and Golden Eagles by prohibiting possession, sale or transport, alive or dead, or part, nest or egg, except as permitted by the Secretary of the Interior for scientific and exhibition purposes, or for religious purposes of Indians Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Fines of $100,000 per incividual, or $200,000 for organizations, or one year in prison, or both, can be utilized. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Chapter 17: Oil soil prevention and pollution control, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Prohibits the discharge of oil, petroleum products or their by-products, and other pollutants into or upon any coastal waters, estuaries, tidal flats, beaches, and land adjoining the seacoast of the Territory. Requires prompt containment and removal of petroleum. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects ecosystems, including coral reefs, from petroleum spills and provides for cleanup. Legislative Actions:Established the Virgin Island Coastal Protection Fund of $1,000,000 for cleanup response. Prohibits derilict vessels upon any public waters or ports. Provides for civil penaltiesup to $50,000per day. Requires a National Contingency Plan. Comments:Because it is the intent of this chapter to provide the means for rapid and effective cleanup and to minimize damages, any licensee and its agents or servants, including vessels destined for or leaving a licensee's terminal facility, who permits or suffers a prohibited discharge or other polluting condition to take place within territorial boundaries shall be liable to the territory for all costs of cleanup or other damage incurred by the territory and for damages resulting from injury to others. The territory shall have an absolute maritime lien which shall attach to any vessel and its freight on behalf of the territory or any person injured, for all costs of cleanup and other damages incurred as a result of a prohibited discharge. In any suit to enforce claims of the territory under this chapter, it shall not be necessary for the territory to plead or prove negligence in any form or manner on the part of the licensee or any vessel. If the territory is damaged by a discharge prohibited by this chapter it need only plead and prove the fact of the prohibited discharge or other polluting condition and that it occurred. In addition to the civil penalty, the pilot and the master of any vessel or person in charge of any licensee's terminal facility who fails to give immediate notification of a discharge to the harbor master and nearest U.S. Coast Guard station shall be guilty of a misdemeanor and fined not less than $5,000 nor more than $10,000. The Department shall, by rules and regulations, require that the licensee designate a person at the terminal facility who shall be the person in charge of that facility for the purposes specified by this section. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Water Resources |
| Clean Air Act, 42 United States Code §§ 7400 et seq. | To ensure Americans have clean air to breath, and to protect the environment from air pollution. Regulates air emmissions from area, stationary and mobile sources. Charges federal land managers with direct responsibility to protect the "air quality and related values" of land under their control. The "related values" include fish and widlife and their habitats. The Clean Air Act is the law that defines EPA's responsibility for protecting and improving the nation's air quality and the stratospheric ozone layer. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act would decrease carbon dioxide emissions from sources in the United States, thereby making a contribution toward reducing ocean acidification, which is one of the problems contributing to coral reef decline. Legislative Actions:Response will differ from State to State because many Sates have been delegated to administer the Clean Air Act. However, States cannot have air quality standards less stringent then the federal standards. State air pollution agencies hold permit hearings and fines industries that violate air quality limits. States must develop state implementation plans that require approval by EPA. Comments:The 1990 amendments authorized the Acid Deposition Control Program, a program to control 189 toxic pollutants, established permit program requirements, expanded and modified the attainment of National Ambient Air Quality Standards, and expanded and modified enforcement authority. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Transportation Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 (CBRA), 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote more appropriate use and conservation of coastal barriers along the Atlantic, Gulf and Great Lakes coastlines. Minimize the loss of human life; reduce wasteful expenditures on shoreline development; minimize damage to wildlife, marine life, and other natural services, and establish a coastal barrier resources system. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restrict most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coral; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Wetlands |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, "Superfund", 42 United States Code §§ 9601-9675. | Provides Liability, compensation, cleanup, and emergency response for hazardous substances released into the environment. Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Remediation; Waste Management Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6401 (2000). | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:Allowed the development of programs and projects, and provided financing for developing sound scientific data to preserve and restore coral reefs. Continued the Coral Reef Task Force and Coral Reef Initiative started under Executive Order 13089 (1998). Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The Act is administrative, not regulatory. It established four major programs; (1) The National Coral Reef Action Strategy established goals for research, monitoring and conservation, (2, 3) The Coral Reef Conservation Program and Coral Reef Conservation Fund provided financial assistance for coral reef projects, (4) the National Program facilitated cooperative work between federal, state and regional efforts that work to improve coral reef ecosystems. The National Program also enhanced the public awareness of coral reefs through educational programs. The Act incorporated Executive Order 13,089 and provided coordinated funding activities through twelve federal agencies and seven states. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States; US Coral Reefs |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corporate Responses; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Public Administration; Remediation; Utilities |
| Emergency Wetlands Resources Act of 1986, 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote the conservations of wetlands for public benefit and to assist in the compliance with international obligations under various treaties and conventions for migratory birds. Application to Coral Reefs:Indirect application to protection of coral reefs through wetland functions of nutrient (particularly nitrogen) and sediment removal from land-based discharges prior to their entrance into open coastal waters. Legislative Actions:Authorizied the purchase of wetlands from the land and Water Conservation Fund monies. Required States to include wetlands in their Comprehensive Outdoor Recreation Plans. Comments:Secretary of Interior was required to establish a National Wetland Priority Conservation Plan to identify the locations and types of wetlands that should be priorities for state and federal acquisition. The Act established various fee schedules for entering national wildlife refuges. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals, 73 Federal Register § 6895 (2008). | To make it unlawful, to import or export the species into or from the US, to take the species within the US or territorial seas of the US, to take the species upon the high seas, to possess, sell, deliver, carry, transport, or ship by any means whatsoever the species taken in violation, to deliver, receive, carry, transport, or ship in interstate or foreign commerce, by any means whatsoever and in the course of a commercial activity the species, to sell or offer for sale in interstate or foreign commerce the species, to violate any regulation pertaining to the species. Application to Coral Reefs:The deignation of Acropa palmeta and Acropa cervicornis as threathened species will allow the species advantages in recovery. The designation protects the reef habitat because the species must have the reef to reproduce and grow. Legislative Actions:Section 11 of the ESA provides civil and criminal penalties for a violation of the ESA. Comments: |
NOAA Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Recreational Opportunities; Skeletal Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals; Final Rule, 73 Federal Register § 72210. | We, the National Marine
Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final
rule designating critical habitat for
elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and
staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which
we listed as threatened under the
Endangered Species Act of 1973, as
amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four
specific areas are designated: the Florida
area, which comprises approximately
1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of
marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area,
which comprises approximately 1,383
square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine
habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area,
which comprises approximately 121
square miles (313 sq km) of marine
habitat; and the St. Croix area, which
comprises approximately 126 square
miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We
are excluding one military site,
comprising approximately 5.5 square
miles (14.3 sq km), because of national
security impacts. Application to Coral Reefs:The law protects coral habitat for elkhorn and staghorn coral which strenghtens their protection in the FKNMS, Puerto Rico, and US Virgin Islands. Legislative Actions: Comments:the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final rule designating critical habitat for elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which we listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act of 1973, as amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four specific areas are designated: the Florida area, which comprises approximately 1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area, which comprises approximately 1,383 square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area, which comprises approximately 121 square miles (313 sq km) of marine habitat; and the St. Croix area, which comprises approximately 126 square miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We are excluding one military site, comprising approximately 5.5 square miles (14.3 sq km), because of national security impacts. |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered Species Act of 1973, 16 United States Code §§ 1531-1544, 1361-1407. | To protect animal and plant species currently in danger of extinction (endangered) and those that may become endangered in the foreseeable future (threatened). Authorized the determination and listing of species as endangered and threatened; Prohibited unauthorized taking, possession, sale, and transport of endangered species; Provided authority to acquire land for the conservation of listed species, using land and water conservation funds; Authorized establishment of cooperative agreements and grants-in-aid to states that establish and maintain active and adequate programs for endangered and threatened wildlife and plants; Authorized the assessment of civil and criminal penalties for violating the act or regulations; and Authorized the payment of rewards to anyone furnishing information leading to arrest and conviction for any violation of the act. Application to Coral Reefs:Two species of coral are listed as threatened; elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) and staghorn coral (Acropora cervicornis). They were placed on the list in 2006.Their habitat was listed as "critical habitat" in 2008. Legislative Actions:The Act provided for criminal and civil penalties dependent on the sections of the Act under which violations occured. Criminal penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $50,000 and not more than one year in prison. Civil penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $25,000. The Act provided for rewards to citizens that report violations leading to sucessful prosecution. The rewards are paid from the fine received. Comments:Listed species and critical habitats can be found in the Federal Register. The habitats for staghohn (73FR72210) and elkhorn (73FR72210) corals were declared critical in 2008. Since the entire coral reef is habitat for the species, critical designation could offer a method of protecting and conserving the reef. In this instance, by protecting individual species and their habitat, the entire reef is protected. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration /National Marine Fisheries Service/USFish and Wildlife Service (consultations with all federal agncies responsible for section 7(a)(1) compliance Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coral; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Environmental resource permitting procedures, 62-343 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2003). | The rule provides the procedural requirements for processing environmental resource permits and obtaining formal determinations of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring permits for projects related to environmental resources will indirectly protect environmental habitats. The permits are related to stormwater managemnt systems including discharges to wetlands. The permit conditions can limit toxics, nutrients and sediment that would be discharged to the environment if the rule were not in place. Legislative Actions:The rule is procedural and does not have fines or penalties. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Permitting & Zoning; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Estuaries Protection Act of 1968, 16 United States Code §§ 1221-1226. | Authorizes the Secretary of Interior in cooperation with other federal agencies and the states, to study and inventory estuaries of the united states, including land and water of the Great Lakes, and to determine whether such areas should be acquired for protection. The Secretary is also requied to encourage state and local governments to consider the importance of estuaries in their planning activities relative to federal natural resources grants. Application to Coral Reefs:Established the congressional policy on the values of wetlands and the need to conserve their natural resources. Protection of wetlands provide coral reefs with an indirect benefit as the wetland serves the functions of nutrient removal and sediment containment Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Secretary of Interior in conjunction with other federal agencies and States Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Seagrasses; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Exec. Order No. 11990, Protection of Wetlands, 42 Federal Register 26961 (1977). | Federal agencies are directed to provide leadership and take action to minimize the destruction, loss, or degradation of wetland and to preserve and enhance the natural and beneficial uses of wetlands. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and restoration of wetlands benefits coral reefs because wetlands stop nutrients and sediments from entering waterbodies and eventually reaching coral reefs and producing adverse effects. Legislative Actions:The Order protects wetlands on projects on Federal lands. The agencies are to provide leadership to minimize the destruction, loss or degradation of wetlands, to preserve and enhance natural and beneficial values when carrying our their responsibilities. Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Hydrologic Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Public Administration; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Wetlands |
| Exec. Order No. 12372, Intergovernmental Review of Federal Programs, 47 Federal Register 30953 (1982). | Seeks to foster intergovernmental partnerships by requiring federal agencies to use the state process to determine and address concerns of state and local elected officials with proposed federal assistance and development programs. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Public Administration |
| Exec. Order No. 12996, Management and General Public Use of the National Wildlife Refuge System, 61 Federal Register 13647 (1994). | Recommended that the Executive Branch develop, in cooperation with state, local, and tribal governments, and the private sector, a coordinated Spatial Data Infrastructure to support public and develop sector applications of geospatial data. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:EO 13286 defines the role of Homeland Security Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research |
| Exec. Order No. 13089, Coral Reef Protection, 63 Federal Register 32701 (1998). | Protect coral reefs. Established the US Coral Reef Task Force Application to Coral Reefs:The Task Force was assigned duties including developing and implementing research, in conjunction with the scientific community, to identify the major causes of coral reef degradation. Legislative Actions:No penalties for noncompliance. Comments: |
12 federal agencies, 7 states and territories, 3 freely associated states Jurisdiction: United States; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Boating Regulations; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Hydrologic Management; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Exec. Order No. 13112, Invasive Species, 68 Federal Register 6183 (1990). | Federal agencies are directed to prevent the introduction of invasive species, detect and rapidly respond to control populations of such species in a cost effective and environmentalyy sound manner, accurately monitor invasive species, provide for restoration of native species and habitat conditions, conduct research to prevent introduction and to control invasive species, and promote public education on invasive species and the means to address them. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:No enforcement provisions. Federal agencies are encouraged to prevent the introduction, detect and respond to control, monitor, and conduct research of invasives. Secretary of Interior established an "Invasive Species Council" to address invasive species issues. Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Invasive Species; Political Pressure; Remediation |
| Exec. Order No. 13158, Marine Protected Areas, 65 Federal Register 34909 (2000). | This Executive Order is meant to help protect the significant natural and cultural resources within the marine environment for the benefit of present and future generations by strengthening and expanding the Nation�s system of marine protected areas. Application to Coral Reefs:Benefits to coral reefs within MPA's. Legislative Actions:One of the provisions of the Act requires that the Secretary develop a scientifically based, comprehensive system of MPA's representing diverse US marine ecosystems, and the Nation's natural and cultural resources. Comments: |
Department of Interior, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Federal Advisory Committee Act of 1972, 5 United States Code § app. | Created a formal process for federal agencies to seek advice and assistance from citizens. Any council, panel, conference, task force, or similar group used by federal officials to obtain consensus advice or recommendations on issues and policies that fall under the purview of the Act. Application to Coral Reefs:The public sector had, and continues to participate, in many areas of the FKNMS. Legislative Actions:The Act is the legal foundation defining how federal advisory committees operate. The law has special emphasis on open meetings, chartering, public involvement, and reporting. Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act of 1980, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | Required the Service to monitor non-game bird and fish species, identify species of management concerns, and implement conservation measures to preclude the need for listing under the Endangered Species Act. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Designate Protected Species; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | To provide financial and technical assistance to the states for development, revision and implementation of conservation plans and programs for nongame fish and wildlife, and to encourage federal agencies to utilize their statutory and administrative authority to conserve and to promote the conservation of nongame fish and wildlife and their habitats. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Incentives; Microorganisms; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration |
| Fish and Wildlife Improvement Act of 1978, 16 United States Code § 7421. | Passed to improve the administration of fish and wildlife programs and amends several earlier laws, including the Refuge Recreation Act, the National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act, and the Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956. It authorizes the Secretary to accept gifts and bequests of real and personal property on behalf of the United States. It also authorizes the use of volunteers on Service projects and appropriations to carry out volunteer programs. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Secretaries were authorized to establish, conduct and assist with national training programs for State fish and wildlife enforcement personnel. Comments:The law provided authority to the Secretaries to enter into law enforcement cooperatives with State and other federal agencies.It expanded the use of fines, penalties and forfeiture funds received under the Endangered Species Act and Lacey Act to include the cost of shipping, storing and disposing of items. |
Secretary of Interior and Secretary of Commerce, administration primarily through US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| General Authorities Act of 1970, 16 United States Code §§ 1 et seq. | Reinforces the National Park Services Act by uniting all areas administered by the NPS into one National Park System. The Act assures a common preservation purpose for all units, regardless of title or designation. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Public Administration; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| General permit for activities seaward of the coastal construction control line, 62B-34 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2010). | To implement the provisions of Section 161.053(19) F. S. providing General Permits for activities performed seaward of the Coastal Construction Control line. Persons wishing to use one or more of the General Permits as set forth in Part II of this rule chapter shall be subject to the notice provisions of subsection 62B-34.030(4) F. A. C. before any activity is conducted as authorized herein.The general conditions provided pursuant to Section 62-B34-0.50, F. A. C. , shall apply to all of the General Permits issued under this rule chapter. Strict compliance with all of the terms, conditions, requirements, limitations, and restrictions applicable to a desired General Permit under this rule chapter is required to qualify for such a permit. Application to Coral Reefs:The rule requires erosion control BMP. Therefore, sediment from construction will not enter the marine environment and damage coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Civil fines are applicable for work done that was not authorized in the permit. Comments: |
Florida Departrment of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring |
| Lacey Act, 16 United States Code §§ 3372 et seq. | The Act provides that it is unlawful for any person to import, export, transport, sell, receive, acquire, or purchase any fish or wildlifeor plant taken, possessed, transported, or sold in violation of any law, treaty, or regulation of the United States or in violation of any Indian tribal law whether in interstate or foreign commerce. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act makes possession, selling, transporting, importing, exporting, receiving, acquiring, and purchasing illegal under specific cases. Corals would be included. Legislative Actions:Civil Penalties up to $10,000 per each violation or maximum criminal sanctions of $20,000 in fines and/or up to five years imprisonment. All plants and animals taken in violation of the Act are subject to forfeiture as well as all vessels, vehicles, aircraft, and other equipment used to aid in the importing, exporting, transporting, selling, receiving, acquiring, or purchasing of fish and wildlife or plants in a criminal violation for which a felony conviction is obtained where the owner should have known of the illegal transgression. Comments: |
US Department of Agriculture/Us Border Patrol Jurisdiction: United States |
Aquarium Stock; Coral; Improved Technology; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Act of 1976, as amended through 1996,. | Provided for conservation and management of commercial and recreational fisheries in the US Exclusive Economic Zone (3-200 nautical miles offshore). Application to Coral Reefs:The Act recognized, and stated, that one of the greatest long-term threats to viable commercial and recreational fisheries is the continued loss of marine, esturaine, and other aquatic habitats, and that habitat considerations should receive increased attention for the conservation and management of fishery resources. Legislative Actions:The amended Act through 1996 created eight regional Fishery Management Councils and reguired foreign vessels to apply for permits to fish in US waters. The Councils develop Management plans for every fishery within their geographic region regarding guidelines for quota, bycatch caps and gear restrictions.. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: |
Biocriteria; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Responses |
| Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, 16 United States Code § 1361. | With certain exceptions, the Act establishes a mortiorium on the taking and importation of marine mammals, as well as products that are made from them. DOI is responsible for sea otter, walrus, polar bear, diugong and manatee. The DOC is responsible for Cretaceans and piniped other than the walrus. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The legislation mandated the use of an ecosystem-based management approach to marine resource management. The Marine Mammal Commission was established and has specific advisory and research duties. Required that government observers aboard some fishing vessels. Comments:The Act covers all species of marine mammals and plants, including anadromous fish, except for marine ammmals, birds, and highly migratory species, all of which are covered under other laws or treaties. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Designate Protected Species; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins |
| Marine Mammals, 50 Code of Federal Regulations. | The regulations prohibit the capture of marine mammals on land or sea in US waters and prohibits the improtation of any marine mammal product to the US (CFR 216.11-216.12) unless the person has a permit for scientific purposes (CFR 216.33-216.37). Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Marine Turtle Conservation Act of 2004, 16 United States Code § 6601. | The law was created to aid in the conservation of sea turtles and their nesting habitats in foreign countries by providing funds for the conservation of nesting areas, sea turtles in in their nesting habitats, and dealing with threats to sea turtle survival. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Designate Protected Species; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles |
| Migratory Bird Treaty Act, 16 United States Code § 715. | The Act established a Federal prohibition, unless permitted by regulations, to pursue, hunt, take, capture, kill, attempt to take, capture or kill, possess, offer for sale, sell, offer to purchase, purchase, deliver for shipment, ship, caused to be shipped, deliver for transport, carry, or cause to be carried by any means whatever, receive for shipment, transport or carriage, or export, at any time,or in any manner, any migratory bird, included in the terms of this Convention�for the protection of migratory birds�or any part, nest, or egg of such a bird. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Recent amendments to the Act increased the fine for misdemeanor convictions from $5000 to $15,000. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Designate Protected Species; Marine Birds; Resource Use Management |
| National Environmental Education Act of 1990, 20 United States Code § 5501. | Established the Office of Environmental Education within USEPA to develop and administer a federal environmental education program in consultation with other federal natural reource management agencies. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act could be used as a tool to educate the public about the values of coral reefs Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 as amended through 1982,. | Declared a national policy that will encourage productive and enjoyable harmony between man and his environment : promote efforts that will prevent or eliminate damage to the environment and biosphere: stimulate the health and welfare of resources important to the Nation and establish a Council on Environmental Quality. Application to Coral Reefs:Re-athorizes NEPA of 1969. Provides additional funding. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The amendments did not add regulations to the Act |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Atmospheric Emissions; Chemical Variables; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Educational & Research Opportunities; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Mining; Oil & Gas Industry; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Toxics; Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969, 42 United States Code §§ 4321-4377. | Requires analysis, public comment, and reporting for environmental impacts of federal actions. It stipulates the factors to be considered in environmental impact statements, and requires that federal agencies employ an interdisciplinary approach in related decision-making and develop means to ensure unqualified environmental values are given appropriate consideration, along with economic and technical considerations. Application to Coral Reefs:Requires an Environmental Assessment(EA), and potentially an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) if the project review finds there will be a significant impact. The EIS must detail the environmental impacts of the proposed action, unavoidable adverse environmental impacts, and alternatives to the proposed action. The resulting studies could protect sensitive environmental ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The Act is completely procedural; it does not include specific regulations. The Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) was created by the Act. CEQ is part of the Executive Office of the President and one of the CEQ directives is to ensure that federal programs comply with NEPA. The puprose of the EIS is to disclose to the public and resource managers the probable long- and short-term impacts of the proposed project as well as consideration of less environmentally damaging alternatives to the recommended course of action. |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Permitting & Zoning; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service General Partnership Authorities of 1970, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act supplemented and clarified the National Park Service's mandate with respect to the management of the National Park System. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Designated Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| National Park Service Organic Act of 1916, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act was created to start the National Park Service within the Department of Interior for the purpose of promoting and regulating the use of federal areas such as national parks and monuments. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Created the National Park Service to be supervised by a Director. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invasive Species; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act of 1966, 16 United States Code § 66. | The Act defines the National Wildlife Refuge System and authorizes the Secretary of Interior to permit any use of a refuge provided such use is compatible with the major purpose for which the refuge was established. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Serice Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Landuse Management; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Wildlife Refuge System Improvement Act of 1997, 16 United States Code § 668. | Amends the National Wildlife Refuge System Act of 1966. This Act defines the mission of the National Wildlife Refuge System, establishes the legitimacy and appropriateness of six priority wildlife-dependent public uses, establishes a formal process for determining compatible uses of Refuge System lands, identifies the Secretary of the Interior as responsible for managing and protecting the Refuge System, and requires the development of comprehensive conservation plan for all refuges outside of Alaska. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Serice Jurisdiction: United States |
Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Neotropical Migratory Bird Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6101. | Established a matching grant program to fund projects that promote the conservation of neotropical migratory birds in the United States, Latin America, and the Caribbean. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act provided competitive grants in Latin America, the Carribean, and the United States for neotropical migratory birds that winter south of the border and summer in North America. The law encourages habitat protection, education, research, monitoring, and capacity building to provide for long-term protection of neotropical migratory birds. Comments:Over 800 species of birds are found in the United States and 500 migrate South of the border for the winter. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; Latin America; Caribbean |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| North American Wetlands Conservation Act of 1989, 16 United States Code § 4411. | Provides funding and administrative direction for the implementation of the North American Waterfowl Management Plan and the Tripartite Agreement between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:A North American Wetlands Conservation Council was created to recommend projects to be funded under the Act to the Migratory Bird Conservation Commission. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Canada; Mexico |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| Ocean Acidification and Marine pH Water Quality Criteria, 74 Federal Register § 17484 (2009). | The publication is a Notice of Data Availability. EPA was making data submitted from various sources available to the public. They also were requesting additon data from the public on ocean acidification and marine pH. The data was to be reviewed to determine if a revision of the Clean Water Act (Section 304) (a) (1) was warranted. Application to Coral Reefs:Coral reefs would be protected if ocean acidification could be controlled because it is a major detrimental parameter of living cora, contributing to their dying. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
EPA Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs |
Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Environmental Education & Outreach; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Ocean Acidity; Point Source Discharges |
| Oil Pollution Act of 1990, 33 United States Code §§ 2701 et seq. | Established limitations on liability for damages resulting from oil pollution, established a fund for the payment of compensation for such damages, mandated the National Oil and Hazardous Substance Contingency Plan to provide organizational structure and procedures for responding to spills. Application to Coral Reefs:In the event of an oil spill that contaminates a coral reef, the Act could be used to determine liability and provide funds for rapid cleanup. Legislative Actions:Can provide fines for failing to notify the appropriate federal agency of a maximum of $250,000 per day for an individual and a maximum of $500,000 for an organization. Civil penalties are authorized at $25,000 per day of violation or $1,000 per barrel of oil discharged. Prison sentences up to a maximum of fifteen years can be imposed on violators. Comments:The Act was signed in 1990, largely in response to rising public concern following the Exxon Valdex incident. The Act improved the nation's ability to prevent and respond to oil spills by establishing provisions that expand the federal government's ability, and and provided the money and resources necessary, to respond to oil spills. The Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund was established and provided up to one billion dollars per spill incident. |
US Coast Guard/US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters |
Chemical Variables; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Non-point Source Controls; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Environment; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Toxics; Wetlands |
| Partnerships for Wildlife Act of 1992, 16 United States Code §§ 3741-3744. | Established a Wildlife Conservation and Appreciation Fund to receive appropriated funds and donations from the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and other private sources to assist the state fish and game agencies in carrying out their responsibilities for conservation of non-game species. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act authorized grants to match contributions from the Wildlife Conservation and Appreciarion Fund, and authorized grants to states for conservation programs and projects to conserve nongame wildlife species. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Reef Life |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proposed Coral Reef Conservation Act Amendments of 2005, 2007 and 2009,. | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:When passed, the Amendments, among other issues, would reauthorize the Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000 and authorize appropriations through fiscal 2012 for the coral reef conservation program and community- based planning grants. Will authorize activities designed to minimize the likelihood of vessel impacts or other physical dammage to coral reefs, including activities to identify certain at-risk coral reefs. Promote international cooperation, codify the US Coral Reef Task Force. Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The amendments would not add regulations to the Act. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; CO2; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Refuge Recreation Act of 1963, as amended, 16 United States Code § 1962. | Authorized the Secretary of the Interior to administer refuges, hatcheries, and other conservation areas for recreational use, when such uses do not interfere with the area's primary purpose. It authorizes construction and maintenance of recreational facilities and the acquisition of land for incidental fish and wildlife-oriented recreational development or protection of natural resources. It also authorizes the charging of fees for public uses. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act established public use fees and permits, and established penalties for violations of regulations. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Refuge Revenue Sharing Act of 1935, as amended, 16 United States Code § 715. | Provided for payment to counties in lieu of taxes from areas administered by the Fish and Wildlife Service. Counties are required to pass payments along to other units of local government within the county, which suffer losses in tax revenues due to the establishment of Service areas. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Congress can appropriate funds to make up any shortfall of payments to local governments, all lands administered by the USFWS qualify for revenue sharing payments, and payments to units of local governments can be used for any governmental purpose. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Servicw Jurisdiction: United States |
Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Public Administration |
| Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899, 33 United States Code § 1252. | This law prohibits the discharge of any type of refuse matter in U.S. waters without permission (section 13). In addition, the excavation, fill, or alteration of the course, condition, or capacity of any port, channel, river, or other areas within the limits of this law is prohibited. This law prohibits the construction or alteration of a structure in wetlands of the U.S. (sections 9 and 10). Construction in wetlands and waters of the U.S. requires a permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Application to Coral Reefs:Under section 10, excavation or fill within navigable waters requires approval of the Chief of Engineers and concerns about contaminated sediments with dredge and fill projects in navigable waters is addressed within the permitting process. Indirect protection of coral reefs is offered by the Act and its prohibition of dumping refuse into navigable waters and the process of anaylzing sediment in proposed dredge and fill operations. Legislative Actions:Violations of the law are punished under section 309 of the Clean Water Act and section 205 of National Fishing Enhancement Act. Fines imposed for violation will not be less than $10,000 per violation or more than $25,000 per violation. Comments:Many states, including Florida, require additional permits for constuction of docks, piers, wharfs, jetties and other structures in navigable waters and wetlands in addition to the Corps of Engineers permit. Authority to issue permits for discharge of refuse matter under section 13 was modified by the amendments to Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972 and established the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Permit process. The Act was initially established to protect interstate commerce in navigable waters. The permit review process involves factors including economics, aethetics, general envitonmental concerns, historical values, water quality, and fish and wildlife impact before project approval is granted. |
US Army Corps of Engineers (COE), and US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: United States |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Significant amendments to the Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 include (1) Coastal Barrier Improvement Act of 1990, (2) Coastal Barrier Resources Reauthorization Act of 2000, (3) Coastal Barriers Resources Reauthorization Act of 2005,. | (1) Added additional areas along the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, the Florida Keys and the Virgin Islands and established "Otherwise Protected Areas OPAs); (2) amended the guidelines for making recommendations regarding additions to the CBRS and reqired a pilot digital mapping project; (3) reauthorized CBRA and required the submission of the final digital mapping pilot project. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restricted most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Forestry; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986, 42 United States Code §§ 9601 et seq. | Reautorized CERCLA Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA/SARA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions:The amended Act stressed the importance of permanent and innovative treatment technologies, required Superfund actions to consider the standards and requirements found in other State and Federal environmental laws, provided new enforcement authorities and settlement tools. Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, 62-043 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-43.010 Intent.
(1) In Section 373.451, F.S., the Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, the Legislature finds and declares that the water quality of many of the surface waters of the state has been degraded or is in danger of being degraded, and that it is the duty of the state through the state�s agencies and subdivisions to enhance the environmental and scenic value of surface waters.
(2) Pursuant to Section 373.026(7), F.S., the Department is responsible for the exercise of general supervisory authority over all water management districts. The Department also has the responsibility, under the Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, to establish the criteria for the water management districts� development of their priority surface water lists; to approve the priority lists and management plan schedules; to review and recommend modifications or additions to the plans as needed to ensure consistency with the state water policy and the State Comprehensive Plan; to establish the uniform format for management plans; and to administer the Surface Water Improvement and Management Trust Funds. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Te SWIM Trust Fund is no langer available. Comments:The Legislature finds and declares that the water quality of many of the surface waters of the state has been degraded or is in danger of being degraded, and that it is the duty of the state through the state�s agencies and subdivisions to enhance the environmental and scenic value of surface waters. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |