ReefLink Database

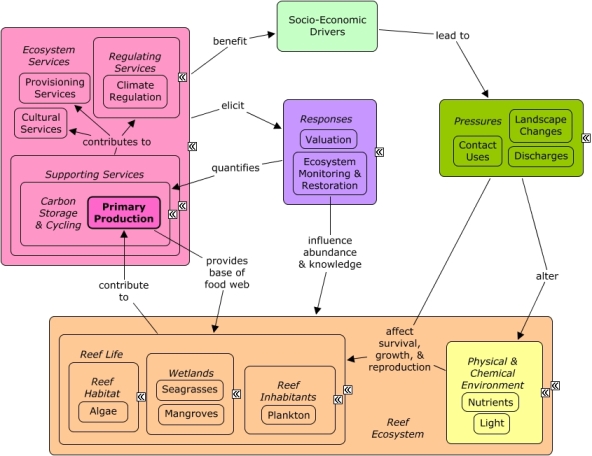
Primary Production
Primary Production is the production of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and sunlight, principally through the process of photosynthesis, forming the basis of the food web.
CMap
CMap Description
Algae and wetland plants, including seagrasses and mangroves, obtain nutrients through primary production. Stony coral also obtain nutrients through symbiotic algae called zooxanthellae. Primary production forms the foundation of the aquatic food web, providing complex habitat and resources for invertebrates and fish, which ultimately benefits humans through provision of goods, such as seafood, and recreational opportunities. Because photosynthesis converts atmospheric CO2 into biomass, primary production also contributes to climate regulation. Many of the same economic sectors that benefit from primary production also create pressures on the reef through harvesting, as well as contributing to coastal development and pollution. Decision-makers can better understand the value of reef primary productivity through valuation methods. Scientific monitoring and research can be used to better understand rates of primary production under various environmental conditions.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmad, SM; Padmakumari, VM; Raza, W; Venkatesham, K; Suseela, G; Sagar, N; Chamoli, A; Rajan, RS. 2011. High-resolution carbon and oxygen isotope records from a scleractinian (Porites) coral of Lakshadweep Archipelago. Quaternary International 238:107-114. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; India | Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Al Balushi, SAK; Macquaker, JHS. 2011. Sedimentological evidence for bottom-water oxygenation during deposition of the Natih-B Member intrashelf-basinal sediments: Upper Cretaceous carbonate source rock, Natih Formation, North Sultanate of Oman. GeoArabia 16:47-84. | 2011 | Global; Oman | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Echinoderms; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Allison, N; Cohen, I; Finch, AA; Erez, J. 2011. Controls on Sr/Ca and Mg/Ca in scleractinian corals: The effects of Ca-ATPase and transcellular Ca channels on skeletal chemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75:6350-6360. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Anthony, KRN; Kleypas, JA; Gattuso, JP. 2011. Coral reefs modify their seawater carbon chemistry - implications for impacts of ocean acidification. Global Change Biology 17:3655-3666. | 2011 | Australia | Review; Model | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Baker, DM; Kim, K; Andras, JP; Sparks, JP. 2011. Light-mediated (15)N fractionation in Caribbean gorgonian octocorals: implications for pollution monitoring. Coral Reefs 30:709-717. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Bannister, RJ; Hoogenboom, MO; Anthony, KRN; Battershill, CN; Whalan, S; Webster, NS; de Nys, R. 2011. Incongruence between the distribution of a common coral reef sponge and photosynthesis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 423:95-100. | 2011 | Australia | Complex Habitat & Resources; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Beaufort, L; Probert, I; de Garidel-Thoron, T; Bendif, EM; Ruiz-Pino, D; Metzl, N; Goyet, C; Buchet, N; Coupel, P; Grelaud, M; Rost, B; Rickaby, REM; de Vargas, C. 2011. Sensitivity of coccolithophores to carbonate chemistry and ocean acidification. Nature 476:80-83. | 2011 | CO2; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Behrendt, L; Larkum, AWD; Norman, A; Qvortrup, K; Chen, M; Ralph, P; Sorensen, SJ; Trampe, E; Kuhl, M. 2011. Endolithic chlorophyll d-containing phototrophs. ISME Journal 5:1072-1076. | 2011 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Docks & Marinas; Microorganisms; Primary Production | ||
| Bertucci, A; Innocenti, A; Scozzafava, A; Tambutte, S; Zoccola, D; Supuran, CT. 2011. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies with anions and sulfonamides of a new cytosolic enzyme from the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21:710-714. | 2011 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Bertucci, A; Tambutte, S; Supuran, CT; Allemand, D; Zoccola, D. 2011. A New Coral Carbonic Anhydrase in Stylophora pistillata. Marine Biotechnology 13:992-1002. | 2011 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | ||
| Brading, P; Warner, ME; Davey, P; Smith, DJ; Achterberg, EP; Suggett, DJ. 2011. Differential effects of ocean acidification on growth and photosynthesis among phylotypes of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae). Limnology and Oceanography 56:927-938. | 2011 | Model | CO2; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Chauvin, A; Denis, V; Cuet, P. 2011. Is the response of coral calcification to seawater acidification related to nutrient loading? Coral Reefs 30:911-923. | 2011 | Indian Ocean; Cuba; India | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Discharges; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae | |
| Coma, R; Serrano, E; Linares, C; Ribes, M; Diaz, D; Ballesteros, E. 2011. Sea Urchins Predation Facilitates Coral Invasion in a Marine Reserve. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Algae; Invasive Species; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Cooper, TF; Ulstrup, KE; Dandan, SS; Heyward, AJ; Kuhl, M; Muirhead, A; O'Leary, RA; Ziersen, BEF; Van Oppen, MJH. 2011. Niche specialization of reef-building corals in the mesophotic zone: metabolic trade-offs between divergent Symbiodinium types. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 278:1840-1850. | 2011 | Australia | Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cuet, P; Atkinson, MJ; Blanchot, J; Casareto, BE; Cordier, E; Falter, J; Frouin, P; Fujimura, H; Pierret, C; Susuki, Y; Tourrand, C. 2011. CNP budgets of a coral-dominated fringing reef at La Reunion, France: coupling of oceanic phosphate and groundwater nitrate. Coral Reefs 30:45-55. | 2011 | Australia; Reunion; France | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| de Putron, SJ; McCorkle, DC; Cohen, AL; Dillon, AB. 2011. The impact of seawater saturation state and bicarbonate ion concentration on calcification by new recruits of two Atlantic corals. Coral Reefs 30:321-328. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| del Hoyo, A; Alvarez, R; del Campo, EM; Gasulla, F; Barreno, E; Casano, LM. 2011. Oxidative stress induces distinct physiological responses in the two Trebouxia phycobionts of the lichen Ramalina farinacea. Annals of Botany 107:109-118. | 2011 | Algae; Primary Production | ||
| Eynaud, Y; Nisbet, RM; Muller, EB. 2011. Impact of excess and harmful radiation on energy budgets in scleractinian corals. Ecological Modelling 222:1315-1322. | 2011 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Falter, JL; Atkinson, MJ; Schar, DW; Lowe, RJ; Monismith, SG. 2011. Short-term coherency between gross primary production and community respiration in an algal-dominated reef flat. Coral Reefs 30:53-58. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Faxneld, S., T. Lund J�rgensen, N. D. Nguyen, M. Nystr�m, and M. Tedengren. 2011. Differences in physiological response to increased seawater temperature in nearshore and offshore corals in northern Vietnam. Marine Environmental Research 71:225-233. | 2011 | Vietnam | Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Faxneld, S; Jorgensen, TL; Nguyen, ND; Nystrom, M; Tedengren, M. 2011. Differences in physiological response to increased seawater temperature in nearshore and offshore corals in northern Vietnam. Marine Environmental Research 71:225-233. | 2011 | Vietnam | Climate; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Fukuda, S; Suzuki, I; Hama, T; Shiraiwa, Y. 2011. Compensatory response of the unicellular-calcifying alga Emiliania huxleyi (Coccolithophoridales, Haptophyta) to ocean acidification. Journal of Oceanography 67:17-25. | 2011 | Cuba | Algae; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Godinot, C; Houlbreque, F; Grover, R; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. Coral Uptake of Inorganic Phosphorus and Nitrogen Negatively Affected by Simultaneous Changes in Temperature and pH. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Cuba | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gopinath, A; Muraleedharan, NS; Chandramohanakumar, N; Jayalakshmi, KV. 2011. Statistical Significance of BioMonitoring of Marine Algae for Trace Metal Levels in a Coral Environment. Environmental Forensics 12:98-105. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Primary Production | |
| Haas, AF; Nelson, CE; Kelly, LW; Carlson, CA; Rohwer, F; Leichter, JJ; Wyatt, A; Smith, JE. 2011. Effects of Coral Reef Benthic Primary Producers on Dissolved Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Australia; Cuba | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coralline Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | |
| Hurd, CL; Cornwall, CE; Currie, K; Hepburn, CD; McGraw, CM; Hunter, KA; Boyd, PW. 2011. Metabolically induced pH fluctuations by some coastal calcifiers exceed projected 22nd century ocean acidification: a mechanism for differential susceptibility? Global Change Biology 17:3254-3262. | 2011 | Global | Algae; CO2; Coralline Algae; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Inoue, M; Suwa, R; Suzuki, A; Sakai, K; Kawahata, H. 2011. Effects of seawater pH on growth and skeletal U/Ca ratios of Acropora digitifera coral polyps. Geophysical Research Letters 38. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Jiang, ZP; Huang, JC; Dai, MH; Kao, SJ; Hydes, DJ; Chou, WC; Jan, S. 2011. Short-term dynamics of oxygen and carbon in productive nearshore shallow seawater systems off Taiwan: Observations and modeling. Limnology and Oceanography 56:1832-1849. | 2011 | Taiwan | Model | CO2; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Jokiel, PL. 2011. Ocean Acidification And Control Of Reef Coral Calcification By Boundary Layer Limitation Of Proton Flux. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:639-657. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | ||
| Jokiel, PL. 2011. The reef coral two compartment proton flux model: A new approach relating tissue-level physiological processes to gross corallum morphology. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 409:1-12. | 2011 | Model | Light; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kemp, DW; Oakley, CA; Thornhill, DJ; Newcomb, LA; Schmidt, GW; Fitt, AK. 2011. Catastrophic mortality on inshore coral reefs of the Florida Keys due to severe low-temperature stress. Global Change Biology 17:3468-3477. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Climate; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Kjaer, KH; Ottosen, CO. 2011. Growth of Chrysanthemum in Response to Supplemental Light Provided by Irregular Light Breaks during the Night. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 136:3-9. | 2011 | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Utility Policies | ||
| Kleypas, JA; Anthony, KRN; Gattuso, JP. 2011. Coral reefs modify their seawater carbon chemistry - case study from a barrier reef (Moorea, French Polynesia). Global Change Biology 17:3667-3678. | 2011 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Kolasinski, J; Rogers, K; Cuet, P; Barry, B; Frouin, P. 2011. Sources of particulate organic matter at the ecosystem scale: a stable isotope and trace element study in a tropical coral reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 443:77-93. | 2011 | Reunion; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Koreny, L; Sobotka, R; Janouskovec, J; Keeling, PJ; Obornik, M. 2011. Tetrapyrrole Synthesis of Photosynthetic Chromerids Is Likely Homologous to the Unusual Pathway of Apicomplexan Parasites. Plant Cell 23:3454-3462. | 2011 | GIS & Maps | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Larkum, AWD; Salih, A; Kuhl, M. 2011. Rapid Mass Movement of Chloroplasts during Segment Formation of the Calcifying Siphonalean Green Alga, Halimeda macroloba. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Negri, AP; Flores, F; Rothig, T; Uthicke, S. 2011. Herbicides increase the vulnerability of corals to rising sea surface temperature. Limnology and Oceanography 56:471-485. | 2011 | Global | Model | Agriculture; Algae; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Coralline Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| O'Gorman, EJ; Yearsley, JM; Crowe, TP; Emmerson, MC; Jacob, U; Petchey, OL. 2011. Loss of functionally unique species may gradually undermine ecosystems. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 278:1886-1893. | 2011 | Primary Production | ||
| Perry, RI. 2011. Potential impacts of climate change on marine wild capture fisheries: an update. Journal of Agricultural Science 149:63-75. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting |
| Price, NN; Hamilton, SL; Tootell, JS; Smith, JE. 2011. Species-specific consequences of ocean acidification for the calcareous tropical green algae Halimeda. Marine Ecology Progress Series 440:67-78. | 2011 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Palmyra Atoll | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Rasher, DB; Stout, EP; Engel, S; Kubanek, J; Hay, ME. 2011. Macroalgal terpenes function as allelopathic agents against reef corals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108:17726-17731. | 2011 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Climate; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral |
| Reymond, CE; Uthicke, S; Pandolfi, JM. 2011. Inhibited growth in the photosymbiont-bearing foraminifer Marginopora vertebralis from the nearshore Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 435:97-U117. | 2011 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Climate; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ries, JB. 2011. A physicochemical framework for interpreting the biological calcification response to CO(2)-induced ocean acidification. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75:4053-4064. | 2011 | Model | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Rodolfo-Metalpa, R; Houlbreque, F; Tambutte, E; Boisson, F; Baggini, C; Patti, FP; Jeffree, R; Fine, M; Foggo, A; Gattuso, JP; Hall-Spencer, JM. 2011. Coral and mollusc resistance to ocean acidification adversely affected by warming. Nature Climate Change 1:308-312. | 2011 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | CO2; Molluscs; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Rollion-Bard, C; Blamart, D; Trebosc, J; Tricot, G; Mussi, A; Cuif, JP. 2011. Boron isotopes as pH proxy: A new look at boron speciation in deep-sea corals using (11)B MAS NMR and EELS. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75:1003-1012. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Primary Production | |
| Sawall, Y; Teichberg, MC; Seemann, J; Litaay, M; Jompa, J; Richter, C. 2011. Nutritional status and metabolism of the coral Stylophora subseriata along a eutrophication gradient in Spermonde Archipelago (Indonesia). Coral Reefs 30:841-853. | 2011 | Cuba; Indonesia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Schottner, S; Pfitzner, B; Grunke, S; Rasheed, M; Wild, C; Ramette, A. 2011. Drivers of bacterial diversity dynamics in permeable carbonate and silicate coral reef sands from the Red Sea. Environmental Microbiology 13:1815-1826. | 2011 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Schutter, M; Kranenbarg, S; Wijffels, RH; Verreth, J; Osinga, R. 2011. Modification of light utilization for skeletal growth by water flow in the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Marine Biology 158:769-777. | 2011 | Cuba | Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | |
| Shamberger, KEF; Feely, RA; Sabine, CL; Atkinson, MJ; DeCarlo, EH; Mackenzie, FT; Drupp, PS; Butterfield, DA. 2011. Calcification and organic production on a Hawaiian coral reef. Marine Chemistry 127:64-75. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Shefferson, RP; McCormick, MK; Whigham, DF; O'Neill, JP. 2011. Life history strategy in herbaceous perennials: inferring demographic patterns from the aboveground dynamics of a primarily subterranean, myco-heterotrophic orchid. Oikos 120:1291-1300. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Primary Production | |
| Sinutok, S; Hill, R; Doblin, MA; Wuhrer, R; Ralph, PJ. 2011. Warmer more acidic conditions cause decreased productivity and calcification in subtropical coral reef sediment-dwelling calcifiers. Limnology and Oceanography 56:1200-1212. | 2011 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Sjoo, GL; Mork, E; Andersson, S; Melander, I. 2011. Differences in top-down and bottom-up regulation of macroalgal communities between a reef crest and back reef habitat in Zanzibar. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 91:511-518. | 2011 | South & Central America; Tanzania; Caribbean | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Storlazzi, CD; Elias, E; Field, ME; Presto, MK. 2011. Numerical modeling of the impact of sea-level rise on fringing coral reef hydrodynamics and sediment transport. Coral Reefs 30:83-96. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Tanaka, Y; Miyajima, T; Watanabe, A; Nadaoka, K; Yamamoto, T; Ogawa, H. 2011. Distribution of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a coral reef. Coral Reefs 30:533-541. | 2011 | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | ||
| Tolosa, I; Treignier, C; Grover, R; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. Impact of feeding and short-term temperature stress on the content and isotopic signature of fatty acids, sterols, and alcohols in the scleractinian coral Turbinaria reniformis. Coral Reefs 30:763-774. | 2011 | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Tremblay, P; Peirano, A; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. Heterotrophy in the Mediterranean symbiotic coral Cladocora caespitosa: comparison with two other scleractinian species. Marine Ecology Progress Series 422:165-177. | 2011 | Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Tseng, LC; Dahms, HU; Hsu, NJ; Hwang, JS. 2011. Effects of sedimentation on the gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa (Pallas, 1766). Marine Biology 158:1301-1310. | 2011 | Australia | Lab Study; Model; Index or Indicator | Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Ulstrup, KE; Kuhl, M; van Oppen, MJH; Cooper, TF; Ralph, PJ. 2011. Variation in photosynthesis and respiration in geographically distinct populations of two reef-building coral species. Aquatic Biology 12:241-248. | 2011 | Australia | Algae; Climate; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Venn, A; Tambutte, E; Holcomb, M; Allemand, D; Tambutte, S. 2011. Live Tissue Imaging Shows Reef Corals Elevate pH under Their Calcifying Tissue Relative to Seawater. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Wagner, D; Pochon, X; Irwin, L; Toonen, RJ; Gates, RD. 2011. Azooxanthellate? Most Hawaiian black corals contain Symbiodinium. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 278:1323-1328. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Johnston Atoll | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Walker, RA; Hallock, P; Torres, JJ; Vargo, GA. 2011. Photosynthesis And Respiration In Five Species Of Benthic Foraminifera That Host Algal Endosymbionts. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 41:314-325. | 2011 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Light; Primary Production | |
| Yamazaki, A; Watanabe, T; Ogawa, NO; Ohkouchi, N; Shirai, K; Toratani, M; Uematsu, M. 2011. Seasonal variations in the nitrogen isotope composition of Okinotori coral in the tropical western Pacific: A new proxy for marine nitrate dynamics. Journal Of Geophysical Research-biogeosciences 116. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Zooxanthellae |
| Yang, WF; Huang, YP; Chen, M; Qiu, YS; Li, HB; Zhang, L. 2011. Unusually high (210)Po activities in the surface water of the Zhubi Coral Reef Lagoon in the South China Sea. Science of the Total Environment 409:4612-4617. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Zhu, BH; Pan, KH; Wang, GC. 2011. Effects of host starvation on the symbiotic dinoflagellates from the sea anemone Stichodactyla mertensii. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 32:15-23. | 2011 | Index or Indicator | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| A. V. Borges and N. Gypens. 2010. Carbonate chemistry in the coastal zone responds more strongly to eutrophication than to ocean acidification. Limnology and Oceanography 55:346-353. | 2010 | Model | Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Allison, N. and A. A. Finch. 2010. delta B-11, Sr, Mg and B in a modern Porites coral: the relationship between calcification site pH and skeletal chemistry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 74:1790-1800. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model; Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Bertucci, A., E. Tambutte, S. Tambutte, D. Allemand, and D. Zoccola. 2010. Symbiosis-dependent gene expression in coral-dinoflagellate association: cloning and characterization of a P-type H+-ATPase gene. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 277:87-95. | 2010 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bielmyera, G. K., M. Grosell, R. Bhagooli, A. C. Baker, C. Langdon, P. Gillette, and T.R. Capo. 2010. Differential effects of copper on three species of scleractinian corals and their algal symbionts (Symbiodinium spp.). Aquatic Toxicology 97:125-133. | 2010 | Lab Study | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bourgeois, S., S. Hochard, and O. Pringault. 2010. Subtidal microphytobenthos: effects of inorganic and organic compound supplies on migration, production, and respiration in a tropical coastal environment. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 61:13-29. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Cebrian, E. 2010. Grazing on coral reefs facilitates growth of the excavating sponge Cliona orientalis (Clionaidae, Hadromerida). Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 31:533-538. | 2010 | Australia | Algae; Boring Sponges; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Primary Production; Sponges; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Charpy, L., K. A. Palinska, B. Casareto, M. J. Langlade, Y. Suzuki, R. M. M. Abed, and S. Golubic. 2010. Dinitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria in Microbial Mats of Two Shallow Coral Reef Ecosystems. Microbial Ecology 59:174-186. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; Reunion; India; Pacific Ocean | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Cheng, Y. R. and C. F. Dai. 2010. Endosymbiotic copepods may feed on zooxanthellae from their coral host, Pocillopora damicornis. Coral Reefs 29:13-18. | 2010 | Taiwan | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Colombo-Pallotta, M. F., A. Rodriguez-Roman, and R. Iglesias-Prieto. 2010. Calcification in bleached and unbleached Montastraea faveolata: evaluating the role of oxygen and glycerol. Coral Reefs 29:899-907. | 2010 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Crabbe, M. J. C. 2010. Computational Biology Approaches to Plant Metabolism and Photosynthesis: Applications for Corals in Times of Climate Change and Environmental Stress. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 52:698-703. | 2010 | Review | Climate; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Crawley, A., D. I. Kline, S. Dunn, K. Anthony, and S. Dove. 2010. The effect of ocean acidification on symbiont photorespiration and productivity in Acropora formosa. Global Change Biology 16:851-863. | 2010 | CO2; Light; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Csaszar, N. B. M., P. J. Ralph, R. Frankham, R. Berkelmans, and M. J. H. van Oppen. 2010. Estimating the Potential for Adaptation of Corals to Climate Warming. PLoS One 5:e9751. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Edmunds, P. J. and H. S. Lenihan. 2010. Effect of sub-lethal damage to juvenile colonies of massive Porites spp. under contrasting regimes of temperature and water flow. Marine Biology 157:887-897. | 2010 | Cuba | Corallivorous Fish; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | |
| Faxneld, S., T. L. Jorgensen, and M. Tedengren. 2010. Effects of elevated water temperature, reduced salinity and nutrient enrichment on the metabolism of the coral Turbinaria mesenterina. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 88:482-487. | 2010 | Vietnam | Climate; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., C. Rottier, E. Beraud, and O. Levy. 2010. Experimental assessment of the feeding effort of three scleractinian coral species during a thermal stress: Effect on the rates of photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 390:118-124. | 2010 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Gaither, M. R. and R. Rowan. 2010. Zooxanthellar symbiosis in planula larvae of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 386:45-53. | 2010 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Garland, K. F., S. E. Burnett, L. B. Stack, and D. L. Zhang. 2010. Minimum Daily Light Integral for Growing High-quality Coleus. HortTechnology 20:929-933. | 2010 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Green, D. H., P. J. Edmunds, X. Pochon, and R. D. Gates. 2010. The effects of substratum type on the growth, mortality, and photophysiology of juvenile corals in St. John, US Virgin Islands. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 384:18-29. | 2010 | US Virgin Islands | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Grenz, C., L. Denis, O. Pringault, and R. Fichez. 2010. Spatial and seasonal variability of sediment oxygen consumption and nutrient fluxes at the sediment water interface in a sub-tropical lagoon (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:399-412. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Hallegraeff, G. M. 2010. Ocean Climate Change, Phytoplankton Community Responses, And Harmful Algal Blooms: A Formidable Predictive Challenge. Journal of Phycology 46:220-235. | 2010 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Climate; CO2; Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Harii, S., M. Yamamoto, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2010. The relative contribution of dinoflagellate photosynthesis and stored lipids to the survivorship of symbiotic larvae of the reef-building corals. Marine Biology 157:1215-1224. | 2010 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Hartmann, A. C., J. E. Carilli, R. D. Norris, C. D. Charles, and D. D. Deheyn. 2010. Stable isotopic records of bleaching and endolithic algae blooms in the skeleton of the boulder forming coral Montastraea faveolata. Coral Reefs 29:1079-1089. | 2010 | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Heindel, K., D. Birgel, J. Peckmann, H. Kuhnert, and H. Westphal. 2010. Formation Of Deglacial Microbialites In Coral Reefs Off Tahiti (Iodp 310) Involving Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Palaios 25:618-635. | 2010 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Hennige, S. J., D. J. Smith, S. J. Walsh, M. P. McGinley, M. E. Warner, and D. J. Suggett. 2010. Acclimation and adaptation of scleractinian coral communities along environmental gradients within an Indonesian reef system. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 391:143-152. | 2010 | Indonesia | Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hill, R. W., C. Li, A. D. Jones, J. P. Gunn, and P. R. Frade. 2010. Abundant betaines in reef-building corals and ecological indicators of a photoprotective role. Coral Reefs 29:869-880. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hoogenboom, M., E. Beraud, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2010. Relationship between symbiont density and photosynthetic carbon acquisition in the temperate coral Cladocora caespitosa. Coral Reefs 29:21-29. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hoogenboom, M., R. Rodolfo-Metalpa, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2010. Co-variation between autotrophy and heterotrophy in the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa. Journal of Experimental Biology 213:2399-2409. | 2010 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Jantzen, C., C. Wild, M. Rasheed, M. El-Zibdah, and C. Richter. 2010. Enhanced pore-water nutrient fluxes by the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp in a Red Sea coral reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 411:117-U162. | 2010 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Juranek, L. W. and P. D. Quay. 2010. Basin-wide photosynthetic production rates in the subtropical and tropical Pacific Ocean determined from dissolved oxygen isotope ratio measurements. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 24:GB2006. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Primary Production |
| Kim, S., K. K. Hammerstom, K. E. Conlan, and A. R. Thurber. 2010. Polar Ecosystem Dynamics: Recovery of Communities from Organic Enrichment in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Integrative And Comparative Biology 50:1031-1040. | 2010 | Primary Production; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Kroeker, K. J., R. L. Kordas, R. N. Crim, and G. G. Singh. 2010. Meta-analysis reveals negative yet variable effects of ocean acidification on marine organisms. Ecology Letters 13:1419-1434. | 2010 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | ||
| Kuguru, B., Y. Achituv, D. F. Gruber, and D. Tchernov. 2010. Photoacclimation mechanisms of corallimorpharians on coral reefs: Photosynthetic parameters of zooxanthellae and host cellular responses to variation in irradiance. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 394:53-62. | 2010 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| LaVigne, M., K. A. Matthews, A. G. Grottoli, K. M. Cobb, E. Anagnostou, G. Cabioch, and R. M. Sherrell. 2010. Coral skeleton P/Ca proxy for seawater phosphate: Multi-colony calibration with a contemporaneous seawater phosphate record. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 74:1282-1293. | 2010 | Panama | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lilley, R. M., P. J. Ralph, and A. W. D. Larkum. 2010. The determination of activity of the enzyme Rubisco in cell extracts of the dinoflagellate alga Symbiodinium sp by manganese chemiluminescence and its response to short-term thermal stress of the alga. Plant Cell And Environment 33:995-1004. | 2010 | Invertebrates; Microorganisms; Primary Production | ||
| MacNeil, M. A., N. A. J. Graham, J. E. Cinner, N. K. Dulvy, P. A. Loring, S. Jennings, N. V. C. Polunin, A. T. Fisk, and T. R. McClanahan. 2010. Transitional states in marine fisheries: adapting to predicted global change. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 365:3753-3763. | 2010 | Global; Indian Ocean; India | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Primary Production | |
| Magnusson, M., K. Heimann, P. Quayle, and A. P. Negri. 2010. Additive toxicity of herbicide mixtures and comparative sensitivity of tropical benthic microalgae. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1978-1987. | 2010 | Australia | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production | |
| Maier, C., M. G. Weinbauer, and J. Patzold. 2010. Stable isotopes reveal limitations in C and N assimilation in the Caribbean reef corals Madracis auretenra, M. carmabi and M. formosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 412:103-112. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae | |
| Mass, T., A. Genin, U. Shavit, M. Grinstein, and D. Tchernov. 2010. Flow enhances photosynthesis in marine benthic autotrophs by increasing the efflux of oxygen from the organism to the water. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107:2527-2531. | 2010 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | ||
| Mass, T., D. I. Kline, M. Roopin, C. J. Veal, S. Cohen, D. Iluz, and O. Levy. 2010. The spectral quality of light is a key driver of photosynthesis and photoadaptation in Stylophora pistillata colonies from different depths in the Red Sea. Journal of Experimental Biology 213:4084-4091. | 2010 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Murali, M. R., S. B. Raja, and S. N. Devaraj. 2010. Neutralization of radical toxicity by temperature-dependent modulation of extracellular SOD activity in coral bleaching pathogen Vibrio shiloi and its role as a virulence factor. Archives of Microbiology 192:619-623. | 2010 | Algae; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Ogston, A. S. and M. E. Field. 2010. Predictions of Turbidity Due to Enhanced Sediment Resuspension Resulting from Sea-Level Rise on a Fringing Coral Reef: Evidence from Molokai, Hawaii. Journal of Coastal Research 26:1027-1037. | 2010 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Ogston, A. S. and M. E. Field. 2010. Predictions of turbidity due to enhanced sediment resuspension resulting from sea-level rise on f Fringing coral reef: evidence from Molokai, Hawaii. Journal of Coastal Research 26:1027-1037. | 2010 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Ramirez-Llodra, E., A. Brandt, R. Danovaro, B. De Mol, E. Escobar, C. R. German, L. A. Levin, P. M. Arbizu, L. Menot, P. Buhl-Mortensen, B. E. Narayanaswamy, C. R. Smith, D. P. Tittensor, P. A. Tyler, A. Vanreusel, and M. Vecchione. 2010. Deep, diverse and definitely different: unique attributes of the world's largest ecosystem. Biogeosciences 7:2851-2899. | 2010 | Global | Review | Finfish Harvest; Microorganisms; Primary Production |
| Ries, J. B. 2010. Review: geological and experimental evidence for secular variation in seawater Mg/Ca (calcite-aragonite seas) and its effects on marine biological calcification. Biogeosciences 7:2795-2849. | 2010 | Global | Review; Lab Study | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Echinoderms; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Roder, C., L. Fillinger, C. Jantzen, G. M. Schmidt, S. Khokiattiwong, and C. Richter. 2010. Trophic response of corals to large amplitude internal waves. Marine Ecology Progress Series 412:113-128. | 2010 | Thailand | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Rodolfo-Metalpa, R., S. Martin, C. Ferrier-Pages, and J. P. Gattuso. 2010. Response of the temperate coral Cladocora caespitosa to mid- and long-term exposure to pCO(2) and temperature levels projected for the year 2100 AD. Biogeosciences 7:289-300. | 2010 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | ||
| Schoon, R., A. Bissett, and D. de Beer. 2010. Resilience of pore-water chemistry and calcification in photosynthetic zones of calcifying sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 55:377-385. | 2010 | Australia | Lab Study | Primary Production; Sediment |
| Schutter, M., J. Crocker, A. Paijmans, M. Janse, R. Osinga, A. J. Verreth, and R. H. Wijffels. 2010. The effect of different flow regimes on the growth and metabolic rates of the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Coral Reefs DOI10.1007/s00338-010-0617-2. | 2010 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | ||
| Sorokin, Y. I. and P. Y. Sorokin. 2010. Plankton of the central Great Barrier Reef: abundance, production and trophodynamic roles. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 90:1173-1187. | 2010 | Australia | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| Springer, Y. P., C. G. Hays, M. H. Carr, and M. R. Mackey. 2010. Toward Ecosystem-Based Management Of Marine Macroalgae-The Bull Kelp, Nereocystis Luetkeana. Pages 1-41 Oceanography And Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol 48. | 2010 | Review | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Stanley, S. M., J. B. Ries, and L. A. Hardie. 2010. Increased Production Of Calcite And Slower Growth For The Major Sediment-Producing Alga Halimeda As The Mg/Ca Ratio Of Seawater Is Lowered To A "Calcite Sea" Level. Journal of Sedimentary Research 80:6-16. | 2010 | Lab Study | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Tait, L. W. and D. R. Schiel. 2010. Primary productivity of intertidal macroalgal assemblages: comparison of laboratory and in situ photorespirometry. Marine Ecology Progress Series 416:115-125. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Titlyanov, E. A., S. I. Kiyashko, T. V. Titlyanova, and J. A. Raven. 2010. delta C-13 and delta N-15 in tissue of coral polyps and epilithic algae inhabiting damaged coral colonies under the influence of different light intensities. Aquatic Ecology 44:13-21. | 2010 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Torreton, J. P., E. Rochelle-Newall, O. Pringault, S. Jacquet, V. Faure, and E. Briand. 2010. Variability of primary and bacterial production in a coral reef lagoon (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:335-348. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Unsworth, R. K. F., S. De Grave, and L. Y. D. Goulding. 2010. Influence Of Environmental Cycles Upon A Seagrass Caridean Shrimp Assemblage. Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 58:349-355. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| van Doorn, W. G. and K. Yoshimoto. 2010. Role of chloroplasts and other plastids in ageing and death of plants and animals: A tale of Vishnu and Shiva. Ageing Research Reviews 9:117-130. | 2010 | Algae; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Primary Production; Sponges; Stony Coral | ||
| Yost, D. M., R. J. Jones, and C. L. Mitchelmore. 2010. Alterations in dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) levels in the coral Montastraea franksi in response to copper exposure. Aquatic Toxicology 98:367-373. | 2010 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Becker, E. L., E. E. Cordes, S. A. Macko, and C. R. Fisher. 2009. Importance of seep primary production to Lophelia pertusa and associated fauna in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 56:786-800. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Snails & Conch | |
| Brandano, M., V. Frezza, L. Tomassetti, and M. Cuffaro. 2009. Heterozoan carbonates in oligotrophic tropical waters: The Attard member of the lower coralline limestone formation (Upper Oligocene, Malta). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 274:54-63. | 2009 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Buxton, L., M. Badger, and P. Ralph. 2009. Effects Of Moderate Heat Stress And Dissolved Inorganic Carbon Concentration On Photosynthesis And Respiration Of Symbiodinium Sp (Dinophyceae) In Culture And In Symbiosis. Journal of Phycology 45:357-365. | 2009 | Model | CO2; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Buxton, L., M. Badger, and P. Ralph. 2009. Effects of moderate heat stress and dissolved inorganic carbon concentration on photosynthesis and respiration of symbiodinium sp. (dinophyceae) in culture and in symbiosis. Journal of Phycology 45:357-365. | 2009 | Model | CO2; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Copertino, M. S., A. Cheshire, and T. Kildea. 2009. Photophysiology of a turf algal community: Integrated responses to ambient light and standing biomass. Journal of Phycology 45:324-336. | 2009 | Australia | Primary Production; Substrate; Turf Algae | |
| Einbinder, S., T. Mass, E. Brokovich, Z. Dubinsky, J. Erez, and D. Tchernov. 2009. Changes in morphology and diet of the coral Stylophora pistillata along a depth gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 381:167-174. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., E. Tambutte, T. Zamoum, N. Segonds, P. L. Merle, N. Bensoussan, D. Allemand, J. Garrabou, and S. Tambutte. 2009. Physiological response of the symbiotic gorgonian Eunicella singularis to a long-term temperature increase. Journal of Experimental Biology 212:3007-3015. | 2009 | Global | Lab Study | Climate; Octocoral; Primary Production |
| Figueroa, F. L., B. Martinez, A. Israel, A. Neori, E. J. Malta, P. Ang, S. Inken, R. Marquardt, T. Rachamim, U. Arazi, S. Frenk, and N. Korbee. 2009. Acclimation of Red Sea macroalgae to solar radiation: photosynthesis and thallus absorptance. Aquatic Biology 7:159-172. | 2009 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Goffredo, S., E. Caroselli, G. Mattioli, E. Pignotti, Z. Dubinsky, and F. Zaccanti. 2009. Inferred level of calcification decreases along an increasing temperature gradient in a Mediterranean endemic coral. Limnology and Oceanography 54:930-937. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Light; Primary Production | |
| Granek, E. F., J. E. Compton, and D. L. Phillips. 2009. Mangrove-exported nutrient incorporation by sessile coral reef invertebrates. Ecosystems 12:462-472. | 2009 | Panama | Model | Algae; Bivalves; Mangroves; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates |
| Guenette, S. and R. L. Hill. 2009. A trophic model of the coral reef ecosystem of La Parguera, Puerto Rico: synthesizing fisheries and ecological data. Caribbean Journal of Science 45:317-337. | 2009 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Model | Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Primary Production |
| Hanelt, D. and M. Y. Roleda. 2009. UVB radiation may ameliorate photoinhibition in specific shallow-water tropical marine macrophytes. Aquatic Botany 91:12-Jun. | 2009 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Higuchi, T., H. Fujimura, H. Ikota, T. Arakaki, and T. Oomori. 2009. The effects of hydrogen peroxide on metabolism in the coral Goniastrea aspera. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 370:48-55. | 2009 | Cuba | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Higuchi, T., H. Fujimura, T. Arakaki, and T. Oomori. 2009. The synergistic effects of hydrogen peroxide and elevated seawater temperature on the metabolic activity of the coral Galaxea fascicularis. Marine Biology 156:589-596. | 2009 | Cuba | Primary Production | |
| Hoogenboom, M. O. and S. R. Connolly. 2009. Defining fundamental niche dimensions of corals: Synergistic effects of colony size, light, and flow. Ecology 90:767-780. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | |
| Hoogenboom, M. O., S. R. Connolly, and K. R. N. Anthony. 2009. Effects of photoacclimation on the light niche of corals: a process-based approach. Marine Biology 156:2493-2503. | 2009 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Houlbreque, F. and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Heterotrophy in tropical scleractinian corals. Biological Review 84:17-Jan. | 2009 | Review | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Houlbreque, F. and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Heterotrophy in Tropical Scleractinian Corals. Biological Reviews 84:1-17. | 2009 | Review | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Khalesi, M. K., H. H. Beeftink, and R. H. Wijffels. 2009. Light-dependency of growth and secondary metabolite production in the captive zooxanthellate soft coral sinularia flexibilis. Marine Biotechnology 11:488-494. | 2009 | Algae; Light; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Kramarsky-Winter, E., C. A. Downs, A. Downs, and Y. Loya. 2009. Cellular responses in the coral Stylophora pistillata exposed to eutrophication from fish mariculture. Evolutionary Ecology Research 11:381-401. | 2009 | Egypt | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Fish; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Lasram, F. B., F. Guilhaumon, and D. Mouillot. 2009. Fish diversity patterns in the Mediterranean Sea: deviations from a mid-domain model. Marine Ecology Progress Series 376:253-267. | 2009 | Model; GIS & Maps | Climate; Fish; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lee, T.-C. and B.-D. Hsu. 2009. Disintegration of the cells of siphonous green alga codium edule (bryopsidales, chlorophyta) under mild heat stress. Journal of Phycology 45:348-356. | 2009 | Cuba; Taiwan | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production |
| Levin, L. A., G. F. Mendoza, T. Konotchick, and R. Lee. 2009. Macrobenthos community structure and trophic relationships within active and inactive Pacific hydrothermal sediments. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 56:1632-1648. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Papua New Guinea | Field Study & Monitoring | Bivalves; Invertebrates; Marine Worms; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Lirman, D. and D. Manzello. 2009. Patterns of resistance and resilience of the stress-tolerant coral Siderastrea radians (Pallas) to sub-optimal salinity and sediment burial. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 369:72-77. | 2009 | Florida | Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Luz, B. and E. Barkan. 2009. Net and gross oxygen production from O-2/Ar, O-17/O-16 and O-18/O-16 ratios. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 56:133-145. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Cuba; Bermuda | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Primary Production |
| Miller, R. J., D. C. Reed, and M. A. Brzezinski. 2009. Community structure and productivity of subtidal turf and foliose algal assemblages. Marine Ecology Progress Series 388:1-11. | 2009 | Algae; Invertebrates; Primary Production; Turf Algae | ||
| Millero, F. J., R. Woosley, B. Ditrolio, and J. Waters. 2009. Effect of ocean acidification on the speciation of metals in seawater. Oceanography 22:72-85. | 2009 | Review | CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | |
| Mortillaro, J. M., K. A. Pitt, S. Y. Lee, and T. Meziane. 2009. Light intensity influences the production and translocation of fatty acids by zooxanthellae in the jellyfish Cassiopea sp. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 378:22-30. | 2009 | Australia | Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Myers, J. L. and L. L. Richardson. 2009. Adaptation of cyanobacteria to the sulfide-rich microenvironment of black band disease of coral. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 67:242-251. | 2009 | Global; Europe | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production | |
| Nakamura, T. and T. Nakamori. 2009. Estimation of photosynthesis and calcification rates at a fringing reef by accounting for diurnal variations and the zonation of coral reef communities on reef flat and slope: A case study for the Shiraho reef, Ishigaki Island, southwest Japan. Coral Reefs 28:229-250. | 2009 | Cuba; Japan | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Olbers, J. M., L. Celliers, and M. H. Schleyer. 2009. Zonation of benthic communities on the subtropical Aliwal Shoal, Durban, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. African Zoology 44:8-23. | 2009 | Cuba; South Africa | Algae; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Worms; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Omann, I., A. Stocker, and J. Jager. 2009. Climate change as a threat to biodiversity: an application of the DPSIR approach. Ecological Economics 69:24-31. | 2009 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mitigation; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Oxford Economics. 2009. Valuing the effects of Great Barrier Reef bleaching. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Review | Climate; CO2; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Richardson, L. L., A. W. Miller, E. Broderick, L. Kaczmarsky, M. Gantar, D. Stanic, and R. Sekar. 2009. Sulfide, microcystin, and the etiology of black band disease. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 87:79-90. | 2009 | Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production | |
| Ries, J. B. 2009. Effects of secular variation in seawater Mg/Ca ratio (calcite-aragonite seas) on CaCO3 sediment production by the calcareous algae Halimeda, Penicillus and Udotea- evidence from recent experiments and the geological record. Terra Nova 21:323-339. | 2009 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Ries, J. B., A. L. Cohn, and D. C. McCorkle. 2009. Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO2-induced ocean acidification. Geology 37:1131-1134. | 2009 | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | |
| Sauchyn, L. K. and R. E. Scheibling. 2009. Degradation of sea urchin feces in a rocky subtidal ecosystem: implications for nutrient cycling and energy flow. Aquatic Biology 6:99-108. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sea Urchins | |
| Schneider, K., O. Levy, Z. Dubinsky, and J. Erez. 2009. In situ diel cycles of photosynthesis and calcification in hermatypic corals. Limnology and Oceanography 54:1995-2002. | 2009 | Cuba | Algae; Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Semesi, I. S., J. Kangwe, and M. Bjork. 2009. Alterations in seawater pH and CO2 affect calcification and photosynthesis in the tropical coralline alga, Hydrolithon sp (Rhodophyta). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84:337-341. | 2009 | Indian Ocean; India | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Coralline Algae; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Shaw, M., A. Negri, K. Fabricius, and J. F. Mueller. 2009. Predicting water toxicity: Pairing passive sampling with bioassays on the Great Barrier Reef. Aquatic Toxicology 95:108-116. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Stony Coral |
| Sheikh, M. A., T. Higuchi, H. Fujimura, T. S. Imo, T. Miyagi, and T. Oomori. 2009. Contamination and impacts of new antifouling biocide Irgarol-1051 on subtropical coral reef waters. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 6:353-358. | 2009 | Japan | Fishing Sector; Primary Production | |
| Sisma-Ventura, G., B. Guzner, R. Yam, M. Fine, and A. Shemesh. 2009. The reef builder gastropod Dendropoma petreaum - A proxy of short and long term climatic events in the Eastern Mediterranean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73:4376-4383. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Tice, M. M. 2009. Environmental Controls on Photosynthetic Microbial Mat Distribution and Morphogenesis on a 3.42 Ga Clastic-Starved Platform. Astrobiology 9:989-1000. | 2009 | Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Utility Policies | ||
| Titlyanov, E. A., S. I. Kiyashko, T. V. Titlyanova, and J. A. Raven. 2009. δ13C and δ15N in tissue of coral polyps and epilithic algae inhabiting damaged coral colonies under the influence of different light intensities. Aquatic Ecology 9-Jan. | 2009 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Todd, P. A., J. H. Lee, and L. M. Chou. 2009. Polymorphism and crypsis in the boring giant clam (Tridacna crocea): potential strategies against visual predators. Hydrobiologia 635:37-43. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Malaysia; Oman | Bivalves; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Treignier, C., I. Tolosa, R. Grover, S. Reynaud, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Carbon isotope composition of fatty acids and sterols in the scleractinian coral Turbinaria reniformis: Effect of light and feeding. Limnology and Oceanography 54:1933-1940. | 2009 | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Venn, A. A., E. Tambutte, S. Lotto, D. Zoccola, D. Allemand, and S. Tambutte. 2009. Imaging intracellular pH in a reef coral and symbiotic anemone. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:16574-16579. | 2009 | Global; Cuba | Model; GIS & Maps | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Climate; Primary Production |
| Voolstra, C. R., S. Sunagawa, J. A. Schwarz, M. A. Coffroth, D. Yellowlees, W. Leggat, and M. Medina. 2009. Evolutionary analysis of orthologous cDNA sequences from cultured and symbiotic dinoflagellate symbionts of reef-building corals (Dinophyceae: Symbiodinium). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology - Part D: Genomics and Proteomics 4:67-74. | 2009 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bell, J. J. 2008. The functional roles of marine sponges. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 79:341-353. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Borell, E. M., A. R. Yuliantri, K. Bischof, and C. Richter. 2008. The effect of heterotrophy on photosynthesis and tissue composition of two scleractinian corals under elevated temperature. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 364:116-123. | 2008 | Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bruschetti, M., T. Luppi, E. Fanjul, A. Rosenthal, and O. Iribarne. 2008. Grazing effect of the invasive reef-forming polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus (Fauvel) on phytoplankton biomass in a SW Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 354:212-219. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seawater Flow | |
| Burns, K. A., G. Brunskill, D. Brinkman, and I. Zagorskis. 2008. Organic carbon and nutrient fluxes to the coastal zone from the Sepik River outflow. Continental Shelf Research 28:283-301. | 2008 | Papua New Guinea | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Caras, T., A. Bachar, and Z. Pasternak. 2008. Morphological variation in the oral disc of the scleractinian coral Favia speciosa (Dana) at Indonesia. Computational Biology and Chemistry 32:345-348. | 2008 | Indonesia | Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Cherbadgy, I. I. and L. N. Propp. 2008. Photosynthesis and respiration of a deep-water periphyton community (Macclesfield Bank, South China Sea). Russian Journal of Marine Biology 34:301-308. | 2008 | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Light; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Substrate |
| Clavier, J., L. Chauvaud, P. Cuet, C. Esbelin, P. Frouin, D. Taddei, and G. Thouzeau. 2008. Diel variation of benthic respiration in a coral reef sediment (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 76:369-377. | 2008 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | CO2; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| De Paiva, A. C. G., P. D. T. D. C. Chaves, and M. E. De Araujo. 2008. Trophic organization and structure of shallow water ichthyofauna in a tropical estuary [Estrutura e organizacão trofica da ictiofauna de aguas rasas em um estuario tropical]. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 25:647-661. | 2008 | Fish; Mangroves; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Dimond, J. and E. Carrington. 2008. Symbiosis regulation in a facultatively symbiotic temperate coral: Zooxanthellae division and expulsion. Coral Reefs 27:601-604. | 2008 | England | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Dong, J., Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Zhang, and H. Wang. 2008. Spatial and seasonal variations of cyanobacteria and their nitrogen fixation rates in Sanya Bay, South China Sea. Scientia Marina 72:239-251. | 2008 | China | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Dove, S. G., C. Lovell, M. Fine, J. Deckenback, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, R. Iglesias-Prieto, and K. R. N. Anthony. 2008. Host pigments: Potential facilitators of photosynthesis in coral symbioses. Plant, Cell and Environment 31:1523-1533. | 2008 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Dupouy, C., A. Minghelli-Roman, M. Despinoy, R. Rottgers, J. Neveux, C. Pinazo, and M. Petit. 2008. MODIS/Aqua chlorophyll monitoring of the New Caledonia lagoon during the 2008 La Nina event. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 7150:715014. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Climate; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Erwin, P. M. and R. W. Thacker. 2008. Phototrophic nutrition and symbiont diversity of two Caribbean sponge-cyanobacteria symbioses. Marine Ecology Progress Series 362:139-147. | 2008 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sponges |
| Foubert, A., D. Depreiter, T. Beck, L. Maignien, B. Pannemans, N. Frank, D. Blamart, and J.-P. Henriet. 2008. Carbonate mounds in a mud volcano province off north-west Morocco: Key to processes and controls. Marine Geology 248:74-96. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Freire, K. M. F., V. Christensen, and D. Pauly. 2008. Description of the East Brazil Large Marine Ecosystem using a trophic model. Scientia Marina 72:477-491. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins |
| Fujimura, H., T. Higuchi, K. Shiroma, T. Arakaki, A. M. Hamdun, Y. Nakano, and T. Oomori. 2008. Continuous-flow complete-mixing system for assessing the effects of environmental factors on colony-level coral metabolism. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods 70:865-872. | 2008 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Fujita, K. and H. Fujimura. 2008. Organic and inorganic carbon production by algal symbiont-bearing foraminifera on northwest Pacific coral-reef flats. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 38:117-126. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Pacific Ocean | Ports & Harbors; Primary Production | |
| Gibson. T., H. Wanless, J. Klaus, P. Foster-Turley, K. Florini, T. Olson. 2008. Corals and Climate Change: Florida�s Natural Treasures at Risk. Environmental Defense Fund. | 2008 | Global; Florida | Climate; CO2; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Recreational Fishing; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Gruner, D. S., J. E. Smith, E. W. Seabloom, S. A. Sandin, J. T. Ngai, H. Hillebrand, W. S. Harpole, J. J. Elser, E. E. Cleland, M. E. S. Bracken, E. T. Borer, and B. M. Bolker. 2008. A cross-system synthesis of consumer and nutrient resource control on producer biomass. Ecology Letters 11:740-755. | 2008 | Review; Model | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Hajkowicz, S. A. 2008. Supporting multi-stakeholder environmental decisions. Journal of Environmental Management 88:607-614. | 2008 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Primary Production |
| Herfort, L., B. Thake, and I. Taubner. 2008. Bicarbonate stimulation of calcification and photosynthesis in two hermatypic corals. Journal of Phycology 44:91-98. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hoch, MA TT HE W. P., K. S. Dillon, R. B. Coffin, and L. A. Cifuentes. 2008. Sensitivity of bacterioplankton nitrogen metabolism to eutrophication in sub-tropical coastal waters of Key West, Florida. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:913-926. | 2008 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Hochberg, E. J. and M. J. Atkinson. 2008. Coral reef benthic productivity based on optical absorptance and light-use efficiency. Coral Reefs 27:49-59. | 2008 | Model; Remote Sensing | Light; Primary Production | |
| Hoogenboom, M. O., S. R. Connolly, and K. R. N. Anthony. 2008. Interactions between morphological and physiological plasticity optimize energy acquisition in corals. Ecology 89:1144-1154. | 2008 | Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Iglesias-Rodriguez, M. D., P. R. Halloran, R. E. M. Rickaby, I. R. Hall, E. Colmenero-Hidalgo, J. R. Gittins, D. R. H. Green, T. Tyrrell, S. J. Gibbs, P. Von Dassow, E. Rehm, E. V. Armbrust, and K. P. Boessenkool. 2008. Phytoplankton calcification in a high-CO2 world. Science 320:336-340. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Jantzen, C., C. Wild, M. El-Zibdah, H. A. Roa-Quiaoit, C. Haacke, and C. Richter. 2008. Photosynthetic performance of giant clams, Tridacna maxima and T. squamosa, Red Sea. Marine Biology 155:211-221. | 2008 | Cuba; Egypt | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kaniewska, P., K. R. N. Anthony, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2008. Variation in colony geometry modulates internal light levels in branching corals, Acropora humilis and Stylophora pistillata. Marine Biology 155:649-660. | 2008 | Australia | Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Kuhl, M. and L. Polerecky. 2008. Functional and structural imaging of phototrophic microbial communities and symbioses. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 53:99-118. | 2008 | GIS & Maps | CO2; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Leichter, J. J., M. D. Stokes, and S. J. Genovese. 2008. Deep water macroalgal communities adjacent to the Florida Keys reef tract. Marine Ecology Progress Series 356:123-138. | 2008 | Florida; Cuba | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Magnusson, M., K. Heimann, and A. P. Negri. 2008. Comparative effects of herbicides on photosynthesis and growth of tropical estuarine microalgae. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:1545-1552. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production | |
| Margolin, C. L. 2008. Use of the coral-sel technique in the study of small scale water flow environments on coral growth. Pages 479-483 in Proceedings of the 11th International Coral Reef Symposium. | 2008 | Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Marubini, F., C. Ferrier-Pages, P. Furla, and D. Allemand. 2008. Coral calcification responds to seawater acidification: A working hypothesis towards a physiological mechanism. Coral Reefs 27:491-499. | 2008 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Marynowski, L., P. Filipiak, and A. Pisarzowska. 2008. Organic geochemistry and palynofacies of the Early-Middle Frasnian transition (Late Devonian) of the Holy Cross Mountains, Southern Poland. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 269:152-165. | 2008 | Poland | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Mass, T. and A. Genin. 2008. Environmental versus intrinsic determination of colony symmetry in the coral Pocillopora verrucosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 369:131-137. | 2008 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Moya, A., S. Tambutte, A. Bertucci, E. Tambutte, S. Lotto, D. Vullo, C. T. Supuran, D. Allemand, and D. Zoccola. 2008. Carbonic anhydrase in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: Characterization, localization, and role in biomineralization. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283:25475-25484. | 2008 | Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | ||
| Nakamura, T. and H. Yamasaki. 2008. Flicker light effects on photosynthesis of symbiotic algae in the reef-building coral Acropora digitifera (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Pacific Science 62:341-350. | 2008 | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Omata, T., A. Suzuki, T. Sato, K. Minoshima, E. Nomaru, A. Murakami, S. Murayama, H. Kawahata, and T. Maruyama. 2008. Effect of photosynthetic light dosage on carbon isotope composition in the coral skeleton: Long-term culture of Porites spp. Journal of Geophysical Research G: Biogeosciences 113. | 2008 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Piniak, G. A. and C. D. Storlazzi. 2008. Diurnal variability in turbidity and coral fluorescence on a fringing reef flat: Southern Molokai, Hawaii. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 77:56-64. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Light; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Pinkerton, M. H., C. J. Lundquist, C. A. J. Duffy, and D. J. Freeman. 2008. Trophic modelling of a New Zealand rocky reef ecosystem using simultaneous adjustment of diet, biomass and energetic parameters. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 367:189-203. | 2008 | Model | Algae; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Polerecky, L., C. Lott, and M. Weber. 2008. In situ measurement of gross photosynthesis using a microsensor-based light-shade shift method. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 6:373-383. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Primary Production | |
| Pomar, L. and P. Hallock. 2008. Carbonate factories: A conundrum in sedimentary geology. Earth-Science Reviews 87:134-169. | 2008 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Riegel, W. 2008. The Late Palaeozoic phytoplankton blackout - Artefact or evidence of global change? Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 148:73-90. | 2008 | Global | Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Riul, P., C. H. Targino, J. D. N. Farias, P. T. Visscher, and P. A. Horta. 2008. Decrease in Lithothamnion sp. (Rhodophyta) primary production due to the deposition of a thin sediment layer. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 88:17-19. | 2008 | Oman; United Kingdom | Agriculture; Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Coralline Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Light; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Rochelle-Newall, E. J., J.-P. Torreton, X. Mari, and O. Pringault. 2008. Phytoplankton-bacterioplankton coupling in a subtropical South Pacific coral reef lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 50:221-229. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Cuba; New Caledonia | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Rodolfo-Metalpa, R., Y. Huot, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2008. Photosynthetic response of the Mediterranean zooxanthellate coral Cladocora caespitosa to the natural range of light and temperature. Journal of Experimental Biology 211:1579-1586. | 2008 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Roopin, M., R. P. Henry, and N. E. Chadwick. 2008. Nutrient transfer in a marine mutualism: Patterns of ammonia excretion by anemonefish and uptake by giant sea anemones. Marine Biology 154:547-556. | 2008 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Rosa, R., H. M. Dierssen, L. Gonzalez, and B. A. Seibel. 2008. Ecological biogeography of cephalopod molluscs in the Atlantic Ocean: Historical and contemporary causes of coastal diversity patterns. Global Ecology and Biogeography 17:600-610. | 2008 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model | Climate; Complex Habitat & Resources; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Primary Production |
| Schonberg, C. H. L., R. Suwa, M. Hidaka, and W. K. W. Loh. 2008. Sponge and coral zooxanthellae in heat and light: Preliminary results of photochemical efficiency monitored with pulse amplitude modulated fluorometry. Marine Ecology 29:247-258. | 2008 | Boring Sponges; Climate; Primary Production; Sponges; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Schutter, M., B. van Velthoven, M. Janse, R. Osinga, M. Janssen, R. Wijffels, and J. Verreth. 2008. The effect of irradiance on long-term skeletal growth and net photosynthesis in Galaxea fascicularis under four light conditions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 367:75-80. | 2008 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Shaw, C. M., P. K. S. Lam, and J. F. Mueller. 2008. Photosystem II herbicide pollution in Hong Kong and its potential photosynthetic effects on corals. Marine Pollution Bulletin 57:473-478. | 2008 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Shaw, E. C., A. J. Gabric, and G. H. McTainsh. 2008. Impacts of aeolian dust deposition on phytoplankton dynamics in Queensland coastal waters. Marine and Freshwater Research 59:951-962. | 2008 | Australia | Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Stambler, N., O. Levy, and L. Vaki. 2008. Photosynthesis and respiration of hermatypic zooxanthellate Red Sea corals from 5-75-m depth. Israel Journal of Plant Sciences 56:45-53. | 2008 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Suggett, D. J., M. E. Warner, D. J. Smith, P. Davey, S. Hennige, and N. R. Baker. 2008. Photosynthesis and production of hydrogen peroxide by Symbiodinium (Pyrrhophyta) phylotypes with different thermal tolerances. Journal of Phycology 44:948-956. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Sun, D., R. Su, T. A. McConnaughey, and J. Bloemendal. 2008. Variability of skeletal growth and δ13C in massive corals from the South China Sea: Effects of photosynthesis, respiration and human activities. Chemical Geology 255:414-425. | 2008 | China | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, I. Koike, T. Hayashibara, and H. Ogawa. 2008. Production of dissolved and particulate organic matter by the reef-building corals Porites cylindrica and Acropora pulchra. Bulletin of Marine Science 82:237-245. | 2008 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Treignier, C., R. Grover, C. Ferrier-Pages, and I. Tolosa. 2008. Effect of light and feeding on the fatty acid and sterol composition of zooxanthellae and host tissue isolated from the scleractinian coral Turbinaria reniformis. Limnology and Oceanography 53:2702-2710. | 2008 | Algae; Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Venn, A. A., J. E. Loram, and A. E. Douglas. 2008. Photosynthetic symbioses in animals. Pages 1069-1080 in Journal of Experimental Botany. | 2008 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Wang, L.-H., Y.-H. Liu, Y.-M. Ju, Y.-Y. Hsiao, L.-S. Fang, and C.-S. Chen. 2008. Cell cycle propagation is driven by light-dark stimulation in a cultured symbiotic dinoflagellate isolated from corals. Coral Reefs 27:823-835. | 2008 | Primary Production | ||
| Werner, U., A. Blazejak, P. Bird, G. Eickert, R. Schoon, R. M. M. Abed, A. Bissett, and D. de Beer. 2008. Microbial photosynthesis in coral reef sediments (Heron Reef, Australia). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 76:876-888. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Wilmsen, M. and F. Neuweiler. 2008. Biosedimentology of the Early Jurassic post-extinction carbonate depositional system, central High Atlas rift basin, Morocco. Sedimentology 55:773-807. | 2008 | Climate; Echinoderms; Marine Worms; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Wolanski, E., K. E. Fabricius, T. F. Cooper, and C. Humphrey. 2008. Wet season fine sediment dynamics on the inner shelf of the Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 77:755-762. | 2008 | Australia | Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Zepp, R. G., G. C. Shank, E. Stabenau, K. W. Patterson, M. Cyterski, W. Fisher, E. Bartels, and S. L. Anderson. 2008. Spatial and temporal variability of solar ultraviolet exposure of coral assemblages in the Florida Keys: Importance of colored dissolved organic matter. Limnology and Oceanography 53:1909-1922. | 2008 | Florida | Model | Light; Primary Production |
| Alongi, D. M., L. A. Trott, and J. Pfitzner. 2007. Deposition, mineralization, and storage of carbon and nitrogen in sediments of the far northern and northern Great Barrier Reef shelf. Continental Shelf Research 27:2595-2622. | 2007 | Australia; Cuba; Europe | CO2; Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Biel, K. Y., R. D. Gates, and L. Muscatine. 2007. Effects of free amino acids on the photosynthetic carbon metabolism of symbiotic dinoflagellates. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 54:171-183. | 2007 | Cuba | Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Brando, V. E., B. J. Robson, N. R. C. Cherukuru, A. G. Dekker, and I. T. Webster. 2007. Towards assimilation of ocean colour satellite observation into coastal ocean biogeochemical models: The tropical Fitzroy River Estuary case study. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 6685. | 2007 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Camilli, R., O. Pizarro, and L. Camilli. 2007. Rapid swath mapping of reef ecology and associated water column chemistry in the Gulf of Chiriqui, Panama. in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Panama; Pacific Ocean | GIS & Maps | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Complex Habitat & Resources; Primary Production |
| Campbell, S. J., L. J. McKenzie, S. P. Kerville, and J. S. Bite. 2007. Patterns in tropical seagrass photosynthesis in relation to light, depth and habitat. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 73:551-562. | 2007 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Seagrasses |
| Cantin, N. E., A. P. Negri, and B. L. Willis. 2007. Photoinhibition from chronic herbicide exposure reduces reproductive output of reef-building corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 344:81-93. | 2007 | Australia | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Carleton, J. H. and A. D. McKinnon. 2007. Resident mysids: Secondary production, consumption, and trophic role in a coral reef lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 336:89-98. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Carpenter, L. W. and M. R. Patterson. 2007. Water flow influences the distribution of photosynthetic efficiency within colonies of the scleractinian coral Montastrea annularis (Ellis and Solander, 1786); implications for coral bleaching. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 351:26-Oct. | 2007 | Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Carpenter, R. C. and S. L. Williams. 2007. Mass transfer limitation of photosynthesis of coral reef algal turfs. Marine Biology 151:435-450. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Primary Production | |
| Charpy, L., R. Alliod, M. Rodier, and S. Golubic. 2007. Benthic nitrogen fixation in the SW New Caledonia lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 47:73-81. | 2007 | New Caledonia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Dawson, T. L. 2007. Light-harvesting and light-protecting pigments in simple life forms. Coloration Technology 123:129-142. | 2007 | Review | Algae; Light; Primary Production | |
| De Goeij, J. M. and F. C. Van Duyl. 2007. Coral cavities are sinks of dissolved organic carbon (DOC). Limnology and Oceanography 52:2608-2617. | 2007 | Antilles; Indonesia | Primary Production | |
| Debrenne, F. 2007. Lower Cambrian archaeocyathan bioconstructions. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 6:19-May. | 2007 | Primary Production | ||
| Downs, C. and A. Downs. 2007. Preliminary examination of short-term cellular toxicological responses of the coral Madracis mirabilis to acute Irgarol 1051 exposure. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 52:47-57. | 2007 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Elahi, R. and P. J. Edmunds. 2007. Determinate growth and the scaling of photosynthetic energy intake in the solitary coral Fungia concinna (Verrill). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 349:183-193. | 2007 | Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Fagan, K. E. and F. T. Mackenzie. 2007. Air-sea CO2 exchange in a subtropical estuarine-coral reef system, Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. Marine Chemistry 106:174-191. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Finelli, C. M., B. S. Helmuth, N. D. Pentcheff, and D. S. Wethey. 2007. Intracolony variability in photosynthesis by corals is affected by water flow: Role of oxygen flux. Marine Ecology Progress Series 349:103-110. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fishe, W. S., W. P. Davis, R. L. Quarles, J. Patrick, J. G. Campbell, P. S. Harris, B. L. Hemmer, and M. Parsons. 2007. Characterizing coral condition using estimates of three-dimensional colony surface area. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 125:347-360. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Primary Production; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Furnas, M. 2007. Intra-seasonal and inter-annual variations in phytoplankton biomass, primary production and bacterial production at North West Cape, Western Australia: Links to the 1997-1998 El Nino event. Continental Shelf Research 27:958-980. | 2007 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Indonesia | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Goffredo, S., E. Caroselli, E. Pignotti, G. Mattioli, and F. Zaccanti. 2007. Variation in biometry and population density of solitary corals with solar radiation and sea surface temperature in the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Biology 152:351-361. | 2007 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Hirayama, H., M. Sunamura, K. Takai, T. Nunoura, T. Noguchi, H. Oida, Y. Furushima, H. Yamamoto, T. Oomori, and K. Horikoshi. 2007. Culture-dependent and -independent characterization of microbial communities associated with a shallow submarine hydrothermal system occurring within a coral reef off Taketomi Island, Japan. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73:7642-7656. | 2007 | Japan | Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Janssen, J., J. E. Marsden, C. R. Bronte, D. J. Jude, S. P. Sitar, and F. W. Goetz. 2007. Challenges to deep-water reproduction by lake trout: Pertinence to restoration in Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 33:59-74. | 2007 | Cuba | Invasive Species; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Khalesi, M. K., H. H. Beeftink, and R. H. Wijffels. 2007. Flow-dependent growth in the zooxanthellate soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 351:106-113. | 2007 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Lau, R. K. L., A. C. M. Kwok, W. K. Chan, T. Y. Zhang, and J. T. Y. Wong. 2007. Mechanical characterization of cellulosic thecal plates in dinoflagellates by nanoindentation. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 7:452-457. | 2007 | Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Lesser, M. P., L. I. Falcon, A. Rodriguez-Roman, S. Enriquez, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, and R. Iglesias-Prieto. 2007. Nitrogen fixation by symbiotic cyanobacteria provides a source of nitrogen for the scleractinian coral Montastraea cavernosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 346:143-152. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Masotti, I., D. Ruiz-Pino, and A. Le Bouteiller. 2007. Photosynthetic characteristics of Trichodesmium in the southwest Pacific Ocean: Importance and significance. Marine Ecology Progress Series 338:47-59. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Mass, T., S. Einbinder, E. Brokovich, N. Shashar, R. Vago, J. Erez, and Z. Dubinsky. 2007. Photoacclimation of Stylophora pistillata to light extremes: Metabolism and calcification. Marine Ecology Progress Series 334:93-102. | 2007 | Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| McKinnon, A. D., J. H. Carleton, and S. Duggan. 2007. Pelagic production and respiration in the Gulf of Papua during May 2004. Continental Shelf Research 27:1643-1655. | 2007 | Cuba | Discharges; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Miyajima, T., H. Hata, Y. Umezawa, H. Kayanne, and I. Koike. 2007. Distribution and partitioning of nitrogen and phosphorus in a fringing reef lagoon of Ishigaki Island, northwestern Pacific. Marine Ecology Progress Series 341:45-57. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Myers, J. L., R. Sekar, and L. L. Richardson. 2007. Molecular detection and ecological significance of the cyanobacterial genera Geitlerinema and Leptolyngbya in black band disease of corals. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73:5173-5182. | 2007 | Florida; US Virgin Islands; Bahamas; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Nakamura, T. and T. Nakamori. 2007. A geochemical model for coral reef formation. Coral Reefs 26:741-755. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Primary Production | |
| Nisbet, E. G., N. V. Grassineau, C. J. Howe, P. I. Abell, M. Regelous, and R. E. R. Nisbet. 2007. The age of Rubisco: The evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis. Geobiology 5:311-335. | 2007 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Oren, A. and N. Gunde-Cimerman. 2007. Mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids: UV protectants or multipurpose secondary metabolites? FEMS Microbiology Letters 269:10-Jan. | 2007 | Europe | Review | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sunscreen Use |
| Pawlik, J. R., L. Steindler, T. P. Henkel, S. Beer, and M. Ilan. 2007. Chemical warfare on coral reefs: Sponge metabolites differentially affect coral symbiosis in situ. Limnology and Oceanography 52:907-911. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Primary Production; Sponges; Zooxanthellae | |
| Peirano, A. 2007. In vivo measurements of the seasonal photosynthetic fluorescence of the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa (L.). Scientia Marina 71:629-635. | 2007 | Cuba | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ralph, P. J., A. W. D. Larkum, and M. Kuhl. 2007. Photobiology of endolithic microorganisms in living coral skeletons: 1. Pigmentation, spectral reflectance and variable chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of endoliths in the massive corals Cyphastrea serailia, Porites lutea and Goniastrea australensis. Marine Biology 152:395-404. | 2007 | Light; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Rodrigues, L. J. and A. G. Grottoli. 2007. Energy reserves and metabolism as indicators of coral recovery from bleaching. Limnology and Oceanography 52:1874-1882. | 2007 | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rosenberg, E., O. Koren, L. Reshef, R. Efrony, and I. Zilber-Rosenberg. 2007. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nature Reviews Microbiology 5:355-362. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production | |
| Silverman, J., B. Lazar, and J. Erez. 2007. Community metabolism of a coral reef exposed to naturally varying dissolved inorganic nutrient loads. Biogeochemistry 84:67-82. | 2007 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, I. Koike, T. Hayashibara, and H. Ogawa. 2007. Imbalanced coral growth between organic tissue and carbonate skeleton caused by nutrient enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 52:1139-1146. | 2007 | Cuba | Lab Study | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Thiel, M., E. C. Macaya, E. Acuna, W. E. Arntz, H. Bastias, K. Brokordt, P. A. Camus, J. C. Castilla, L. R. Castro, M. Cortes, C. P. Dumont, R. Escribano, M. Fernandez, J. A. Gajardo, C. F. Gaymer, I. Gomez, A. E. Gonzalez, H. E. Gonzalez, P. A. Haye, and J.-E. Illanes. 2007. The Humboldt Current System of northern and central Chile - Oceanographic processes, ecological interactions and socioeconomic feedback. Oceanography and Marine Biology 45:195-344. | 2007 | South & Central America | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| Titlyanov, E. A., I. M. Yakovleva, and T. V. Titlyanova. 2007. Interaction between benthic algae (Lyngbya bouillonii, Dictyota dichotoma) and scleractinian coral Porites lutea in direct contact. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 342:282-291. | 2007 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Ulstrup, K. E., M. J. H. Van Oppen, M. Kuhl, and P. J. Ralph. 2007. Inter-polyp genetic and physiological characterisation of Symbiodinium in an Acropora valida colony. Marine Biology 153:225-234. | 2007 | Algae; Climate; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Ulstrup, K. E., M. Kuhl, and D. G. Bourne. 2007. Zooxanthellae harvested by ciliates associated with brown band syndrome of corals remain photosynthetically competent. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73:1968-1975. | 2007 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| van der Velde, M., S. R. Green, M. Vanclooster, and B. E. Clothier. 2007. Sustainable development in small island developing states: Agricultural intensification, economic development, and freshwater resources management on the coral atoll of Tongatapu. Ecological Economics 61:456-468. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean; Japan; Tonga | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Primary Production; Tourism & Recreation |
| Zepp, R.G., G.C. Shank, E. Stabenau, K.W. Patterson, and M. Cyterski. 2007. Geographic and seasonal variations in UV exposure of coral assemblages in the Florida Keys. Limnology and Oceanography | 2007 | Florida | Model | Light; Primary Production |
| Zhukova, N. V. 2007. Changes in the fatty acid composition of symbiotic dinoflagellates from the hermatypic coral Echinopora lamellosa during adaptation to the irradiance level. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 54:763-769. | 2007 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Alongi, D. M., J. Pfitzner, and L. A. Trott. 2006. Deposition and cycling of carbon and nitrogen in carbonate mud of the lagoons of Arlington and Sudbury Reefs, Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 25:123-143. | 2006 | Australia; Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Beach, K. S., L. J. Walters, and H. B. Borgeas. 2006. Irradiance and nutrient limitation of Dicytota spp. populations on Conch Reef, Florida Keys, USA. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 329:101-112. | 2006 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Bjorn, L. O. and N. G. A. Ekelund. 2006. Corals and zooxanthellae - A marine partnership [Koraller och zooxantheller - Ett marint partnerskap]. Svensk Botanisk Tidskrift 100:263-270. | 2006 | Algae; Climate; CO2; Petroleum Spills; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Brock, J. C., K. K. Yates, R. B. Halley, I. B. Kuffner, C. W. Wright, and B. G. Hatcher. 2006. Northern Florida reef tract benthic metabolism scaled by remote sensing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 312:123-139. | 2006 | Florida; Cuba | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Bruno, J. F., S. C. Lee, J. S. Kertesz, R. C. Carpenter, Z. T. Long, and J. Emmett Duffy. 2006. Partitioning the effects of algal species identity and richness on benthic marine primary production. Oikos 115:170-178. | 2006 | Jamaica | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production |
| Carbery, K., R. Owen, T. Frickers, E. Otero, and J. Readman. 2006. Contamination of Caribbean coastal waters by the antifouling herbicide Irgarol 1051. Marine Pollution Bulletin 52:635-644. | 2006 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mangroves; Primary Production | |
| Copertino, M. S., A. Cheshire, and J. Watling. 2006. Photoinhibition and photoacclimation of turf algal communities on a temperate reef, after in situ transplantation experiments. Journal of Phycology 42:580-592. | 2006 | Australia | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Substrate; Turf Algae | |
| Crabbe, M. J. C. and D. J. Smith. 2006. Modelling variations in corallite morphology of Galaxea fascicularis coral colonies with depth and light on coastal fringing reefs in the Wakatobi Marine National Park (S.E. Sulawesi, Indonesia). Computational Biology and Chemistry 30:155-159. | 2006 | Indonesia | Model | Light; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Davy, S. K., K. J. T. Withers, and R. Hinde. 2006. Effects of host nutritional status and seasonality on the nitrogen status of zooxanthellae in the temperate coral Plesiastrea versipora (Lamarck). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 335:256-265. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| DeBoer, M. L., D. A. Krupp, and V. M. Weis. 2006. Two atypical carbonic anhydrase homologs from the planula larva of the scleractinian coral Fungia scutaria. Biological Bulletin 211:18-30. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Dominik, C. M. and R. C. Zimmerman. 2006. Dynamics of carbon allocation in a deep-water population of the deciduous kelp Pleurophycus gardneri (Laminariales). Marine Ecology Progress Series 309:143-157. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Light; Primary Production; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Downs, C. and A. Downs. 2006. Preliminary examination of short-term cellular toxicologic responsesof the coral Madracis mirabilis to acute irgarol 1051 exposure. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 20:1-10. | 2006 | Primary Production | ||
| Enriquez, S. and A. Rodriguez-Roman. 2006. Effect of water flow on the photosynthesis of three marine macrophytes from a fringing-reef lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 323:119-132. | 2006 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow | ||
| Field, S. F., M. Y. Bulina, I. V. Kelmanson, J. P. Bielawski, and M. V. Matz. 2006. Adaptive evolution of multicolored fluorescent proteins in reef-building corals. Journal of Molecular Evolution 62:332-339. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Finelli, C. M., B. S. T. Helmuth, N. D. Pentcheff, and D. S. Wethey. 2006. Water flow influences oxygen transport and photosynthetic efficiency in corals. Coral Reefs 25:47-57. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring | Mitigation; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gattuso, J.-P., B. Gentili, C. M. Duarte, J. A. Kleypas, J. J. Middelburg, and D. Antoine. 2006. Light availability in the coastal ocean: Impact on the distribution of benthic photosynthetic organisms and contribution to primary production. Biogeosciences Discussions 3:895-959. | 2006 | Global | Review | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Seagrasses |
| Gili, J.-M., S. Rossi, F. Pages, C. Orejas, N. Teixido, P. J. Lopez-Gonzalez, and W. E. Arntz. 2006. A new trophic link between the pelagic and benthic systems on the Antarctic shelf. Marine Ecology Progress Series 322:43-49. | 2006 | Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Gimenez Casalduero, F. and C. Muniain. 2006. Photosynthetic activity of the solar-powered lagoon mollusc Elysia timida (Risso, 1818) (Opisthobranchia: Sacoglossa). Symbiosis 41:151-158. | 2006 | Model | Calcareous Macroalgae; Light; Molluscs; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Grant, A. J., D. A. Trautman, I. Menz, and R. Hinde. 2006. Separation of two cell signalling molecules from a symbiotic sponge that modify algal carbon metabolism. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 348:92-98. | 2006 | Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Grant, A. J., M. Remond, T. Starke-Peterkovic, and R. Hinde. 2006. A cell signal from the coral Plesiastrea versipora reduces starch synthesis in its symbiotic alga, Symbiodinium sp. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 144:458-463. | 2006 | Cuba | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Halpern, B.S., K. Cottenie, B.R. Broitman. 2006. Strong Top-Down Control in Southern California Kelp Forest Ecosystems. Science 312:1230-1232. | 2006 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Hase, C., M. Al-Qutob, Z. Dubinsky, E. A. Ibrahim, B. Lazar, N. Stambler, and M. M. Tilzer. 2006. A system in balance? - Implications of deep vertical mixing for the nitrogen budget in the northern Red Sea, including the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat). Biogeosciences Discussions 3:383-408. | 2006 | Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Hirose, E., S. Hirabayashi, K. Hori, F. Kasai, and M. M. Watanabe. 2006. UV protection in the photosymbiotic ascidian Didemnum molle inhabiting different depths. Zoological Science 23:57-63. | 2006 | Japan | Light; Primary Production | |
| Hoogenboom, M. O., K. R. N. Anthony, and S. R. Connolly. 2006. Energetic cost of photoinhibition in corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 313:12-Jan. | 2006 | Lab Study | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Jensen, L. T., E. Rosenqvist, and J. M. Aaslyng. 2006. A daylight climate chamber for testing greenhouse climate control strategies and calculating canopy carbon dioxide exchange. HortTechnology 16:191-198. | 2006 | CO2; Irrigation; Light; Primary Production | ||
| Kahn, A. E. and M. J. Durako. 2006. Thalassia testudinum seedling responses to changes in salinity and nitrogen levels. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 335:12-Jan. | 2006 | Florida | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting | |
| Lee, J. J. 2006. Algal symbiosis in larger foraminifera. Symbiosis 42:63-75. | 2006 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Primary Production |
| Levy, O., Y. Achituv, Y. Z. Yacobi, N. Stambler, and Z. Dubinsky. 2006. The impact of spectral composition and light periodicity on the activity of two antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) in the coral Favia favus. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 328:35-46. | 2006 | Lab Study | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Levy, O., Y. Achituv, Y. Z. Yacobi, Z. Dubinsky, and N. Stambler. 2006. Diel 'tuning' of coral metabolism: Physiological responses to light cues. Journal of Experimental Biology 209:273-283. | 2006 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Levy, O., Z. Dubinsky, Y. Achituv, and J. Erez. 2006. Diurnal polyp expansion behavior in stony corals may enhance carbon availability for symbionts photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 333:11-Jan. | 2006 | Algae; Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Montagna, P., M. McCulloch, M. Taviani, C. Mazzoli, and B. Vendrell. 2006. Phosphorus in cold-water corals as a proxy for seawater nutrient chemistry. Science 312:1788-1791. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Moya, A., S. Tambutte, E. Tambutte, D. Zoccola, N. Caminiti, and D. Allemand. 2006. Study of calcification during a daily cycle of the coral Stylophora pistillata: Implications for 'light-enhanced calcification'. Journal of Experimental Biology 209:3413-3419. | 2006 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Olson, J. M. 2006. Photosynthesis in the Archean era. Photosynthesis Research 88:109-117. | 2006 | Australia; South Africa | Cyanobacteria; Primary Production | |
| Ramade, F. and H. Roche. 2006. Pollutant effects on coral reefs ecosystems [Effets des polluants sur les ecosystemes recifaux]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 61:Mar-33. | 2006 | Global | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ravindran, J. and C. Raghukumar. 2006. Pink-line syndrome, a physiological crisis in the scleractinian coral Porites lutea. Marine Biology 149:347-356. | 2006 | Index or Indicator | CO2; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rodolfo-Metalpa, R., C. Richard, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2006. Growth and photosynthesis of two Mediterranean corals, Cladocora caespitosa and Oculina patagonica, under normal and elevated temperatures. Journal of Experimental Biology 209:4546-4556. | 2006 | Cuba | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rodriguez-Roman, A., X. Hernandez-Pech, P. E. Thome, S. Enriquez, and R. Iglesias-Prieto. 2006. Photosynthesis and light utilization in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata recovering from a bleaching event. Limnology and Oceanography 51:2702-2710. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Saito, H. and K. Furuya. 2006. Endosymbiosis in microalgae with special attention to Noctiluca scintillans. Bulletin of the Plankton Society of Japan 53:14-21. | 2006 | Southeast Asia | Lab Study | Algae; Primary Production |
| Schneider, K. and J. Erez. 2006. The effect of carbonate chemistry on calcification and photosynthesis in the hermatypic coral Acropora eurystoma. Limnology and Oceanography 51:1284-1293. | 2006 | Lab Study | CO2; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Sinclair, D. J. and M. J. Risk. 2006. A numerical model of trace-element coprecipitation in a physicochemical calcification system: Application to coral biomineralization and trace-element 'vital effects'. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70:3855-3868. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | |
| Stanley, S. M. 2006. Influence of seawater chemistry on biomineralization throughout phanerozoic time: Paleontological and experimental evidence. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 232:214-236. | 2006 | Lab Study | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Tentori, E. and D. Allemand. 2006. Light-enhanced calcification and dark decalcification in isolates of the soft coral Cladiella sp. during tissue recovery. Biological Bulletin 211:193-202. | 2006 | Lab Study | Octocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Tice, M. M. and D. R. Lowe. 2006. The origin of carbonaceous matter in pre-3.0 Ga greenstone terrains: A review and new evidence from the 3.42 Ga Buck Reef Chert. Earth-Science Reviews 76:259-300. | 2006 | South Africa | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Titlyanov, E. A., T. V. Titlyanova, I. M. Yakovleva, and O. S. Sergeeva. 2006. Influence of winter and spring/summer algal communities on the growth and physiology of adjacent scleractinian corals. Botanica Marina 49:200-207. | 2006 | Japan | Algae; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Tribollet, A., C. Langdon, S. Golubic, and M. Atkinson. 2006. Endolithic microflora are major primary producers in dead carbonate substrates of Hawaiian coral reefs. Journal of Phycology 42:292-303. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Substrate; Turf Algae | |
| Tribollet, A., M. J. Atkinson, and C. Langdon. 2006. Effects of elevated pCO2 on epilithic and endolithic metabolism of reef carbonates. Global Change Biology 12:2200-2208. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Algae; CO2; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral |
| Ulstrup, K. E., P. J. Ralph, A. W. D. Larkum, and M. Kuhl. 2006. Intra-colonial variability in light acclimation of zooxanthellae in coral tissues of Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Biology 149:1325-1335. | 2006 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Uthicke, S. 2006. Photosynthetic efficiency and rapid light curves of sediment-biofilms along a water quality gradient in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 322:61-73. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Villanueva, R. D., H. T. Yap, and M. N. E. Montano. 2006. Intensive fish farming in the Philippines is detrimental to the reef-building coral Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 316:165-174. | 2006 | Philippines | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Watanabe, A., H. Kayanne, H. Hata, S. Kudo, K. Nozaki, K. Kato, A. Negishi, Y. Ikeda, and H. Yamano. 2006. Analysis of the seawater CO2 system in the barrier reef-lagoon system of Palau using total alkalinity-dissolved inorganic carbon diagrams. Limnology and Oceanography 51:1614-1628. | 2006 | Palau | CO2; Primary Production; Seawater Flow | |
| Werner, U., P. Bird, C. Wild, T. Ferdelman, L. Polerecky, G. Eickert, R. Jonstone, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, and D. De Beer. 2006. Spatial patterns of aerobic and anaerobic mineralization rates and oxygen penetration dynamics in coral reef sediments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 309:93-105. | 2006 | Australia | Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Zhukova, N. V. and E. A. Titlyanov. 2006. Effect of light intensity on the fatty acid composition of dinoflagellates symbiotic with hermatypic corals. Botanica Marina 49:339-346. | 2006 | Hydrocoral; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Al-Horani, F. A. 2005. Effects of changing seawater temperature on photosynthesis and calcification in the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis, measured with O2, Ca2+ and pH microsensors. Scientia Marina 69:347-354. | 2005 | Cuba | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Al-Horani, F. A., T. Ferdelman, S. M. Al-Moghrabi, and D. De Beer. 2005. Spatial distribution of calcification and photosynthesis in the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Coral Reefs 24:173-180. | 2005 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Al-Horani, F., S. Al-Rousan, R. Manasrah, and M. Rasheed. 2005. Coral calcification: Use of radioactive isotopes and metabolic inhibitors to study the interactions with photosynthesis and respiration. Chemistry and Ecology 21:325-335. | 2005 | Lab Study | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Anthony, K. R. N., M. O. Hoogenboom, and S. R. Connolly. 2005. Adaptive variation in coral geometry and the optimization of internal colony light climates. Functional Ecology 19:17-26. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Climate; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Badran, M. I., M. Rasheed, R. Manasrah, and T. Al-Najjar. 2005. Nutrient flux fuels the summer primary productivity in the oligotrophic waters of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Oceanologia 47:47-60. | 2005 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Burghardt, I., J. Evertsen, G. Johnsen, and H. Wagele. 2005. Solar powered seaslugs - Mutualistic symbiosis of aeolid nudibranchia (Mollusca, Gastropoda, Opisthobranchia) with Symbiodinium. Symbiosis 38:227-250. | 2005 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Housing; Light; Molluscs; Octocoral; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Castillo, K. D. and B. S. T. Helmuth. 2005. Influence of thermal history on the response of Montastraea annularis to short-term temperature exposure. Marine Biology 148:261-270. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Clavier, J., G. Boucher, L. Chauvaud, R. Fichez, and S. Chifflet. 2005. Benthic response to ammonium pulses in a tropical lagoon: Implications for coastal environmental processes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 316:231-241. | 2005 | New Caledonia | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Cox, G. and A. Salih. 2005. Fluorescence lifetime imaging of symbionts and fluorescent proteins in reef corals. Pages 162-170 in Progress in Biomedical Optics and Imaging - Proceedings of SPIE. | 2005 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., F. Houlbreque, E. Wyse, C. Richard, D. Allemand, and F. Boisson. 2005. Bioaccumulation of zinc in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Coral Reefs 24:636-645. | 2005 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Furnas, M., A. Mitchell, M. Skuza, and J. Brodie. 2005. In the other 90%: Phytoplankton responses to enhanced nutrient availability in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:253-265. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Gischler, E. and W. Oschmann. 2005. Historical climate variation in Belize (Central America) as recorded in scleractinian coral skeletons. Palaios 20:159-174. | 2005 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Belize | GIS & Maps | Climate; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Goulet, T. L., C. B. Cook, and D. Goulet. 2005. Effect of short-term exposure to elevated temperatures and light levels on photosynthesis of different host-symbiont combinations in the Aiptasia pallidal Symbiodinium symbiosis. Limnology and Oceanography 50:1490-1498. | 2005 | Florida; Bermuda | Lab Study | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Harrington, L., K. Fabricius, G. Eaglesham, and A. Negri. 2005. Synergistic effects of diuron and sedimentation on photosynthesis and survival of crustose coralline algae. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:415-427. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Hernando, M.P., G.A. Ferreyra. 2005. The effects of UV radiation on photosynthesis in an Antarctic diatom (Thalassiosira sp.): Does vertical mixing matter? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 325:35-45. | 2005 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Light; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Jones, R. 2005. The ecotoxicological effects of Photosystem II herbicides on corals. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:495-506. | 2005 | Review | Agriculture; Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production | |
| Kayanne, H., H. Hata, S. Kudo, H. Yamano, A. Watanabe, Y. Ikeda, K. Nozaki, K. Kato, A. Negishi, and H. Saito. 2005. Seasonal and bleaching-induced changes in coral reef metabolism and CO2 flux. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 19:11-Jan. | 2005 | Japan; Palau | Field Study & Monitoring | CO2; Primary Production |
| Knap, A. H., S. C. Wyers, R. E. Dodge, T. D. Sleeter, H. R. Frith, S. R. Smith, and C. B. Cook. 2005. The effects of chemically and physically dispersed oil on the brain coral diploria strigosa (dana)-a summary review. Page 2303 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Bermuda | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Petroleum Spills; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Langdon, C. and M. J. Atkinson. 2005. Effect of elevated pCO2 on photosynthesis and calcification of corals and interactions with seasonal change in temperature/ irradiance and nutrient enrichment. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 110:16-Jan. | 2005 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Leletkin, V. A. 2005. Nitrogen and photosynthetic function of hermatypic corals. Oxygen exchange of Stylophora pistillata coral under artificial feeding. Zhurnal Obshchei Biologii 66:164-169. | 2005 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Lin, Q. and I. A. Mendelssohn. 2005. Dispersants as countermeasures in nearshore oil spills for coastal habitat protection. Pages 10781-10785 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Petroleum Spills; Primary Production; Wetlands | ||
| Lugomela, C., E. Soderback, and M. Bjork. 2005. Photosynthesis rates in cyanobacteria-dominated sub-tidal biofilms near Zanzibar, Tanzania. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 63:439-446. | 2005 | Tanzania | Index or Indicator | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production |
| McClanahan, T. R. and N. A. J. Graham. 2005. Recovery trajectories of coral reef fish assemblages within Kenyan marine protected areas. Marine Ecology Progress Series 294:241-248. | 2005 | Kenya | Algae; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Primary Production | |
| McMahon, K., S. B. Nash, G. Eaglesham, J. F. Muller, N. C. Duke, and S. Winderlich. 2005. Herbicide contamination and the potential impact to seagrass meadows in Hervey Bay, Queensland, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:325-334. | 2005 | Australia | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Nakamura, T., R. Van Woesik, and H. Yamasaki. 2005. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis is reduced by water flow in the reef-building coral Acropora digitifera. Marine Ecology Progress Series 301:109-118. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | |
| Negri, A., C. Vollhardt, C. Humphrey, A. Heyward, R. Jones, G. Eaglesham, and K. Fabricius. 2005. Effects of the herbicide diuron on the early life history stages of coral. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:370-383. | 2005 | Lab Study | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Omata, T., A. Suzuki, H. Kawahat, and M. Okamoto. 2005. Annual fluctuation in the stable carbon isotope ratio of coral skeletons: The relative intensities of kinetic and metabolic isotope effects. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69:3007-3016. | 2005 | Model | Climate; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral | |
| Raja, R., P. K. Saraswati, K. Rogers, and K. Iwao. 2005. Magnesium and strontium compositions of recent symbiont-bearing benthic foraminifera. Marine Micropaleontology 58:31-44. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India; Japan | Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Ralph, P. J. and R. Gademann. 2005. Rapid light curves: A powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquatic Botany 82:222-237. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Ralph, P. J., U. Schreiber, R. Gademann, M. Kuhl, and A. W. D. Larkum. 2005. Coral photobiology studied with a new imaging pulse amplitude modulated fluorometer. Journal of Phycology 41:335-342. | 2005 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Shick, J. M., C. Ferrier-Pages, R. Grover, and D. Allemand. 2005. Effects of starvation, ammonium concentration, and photosynthesis on the UV-dependent accumulation of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in the coral Stylophora pistillata. Marine Ecology Progress Series 295:135-156. | 2005 | Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Sunscreen Use; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Smith, D. J., D. J. Suggett, and N. R. Baker. 2005. Is photoinhibition of zooxanthellae photosynthesis the primary cause of thermal bleaching in corals? Global Change Biology 11:11-Jan. | 2005 | Review | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Sunda, W. G., R. W. Litaker, D. R. Hardison, and P. A. Tester. 2005. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) and its relation to algal pigments in diverse waters of the Belize coastal lagoon and barrier reef system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 287:22-Nov. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Cyanobacteria; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Swart, P. K., A. Szmant, J. W. Porter, R. E. Dodge, J. I. Tougas, and J. R. Southam. 2005. The isotopic composition of respired carbon dioxide in scleractinian corals: Implications for cycling of organic carbon in corals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 69:1495-1509. | 2005 | Florida; Cuba | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ulstrup, K. E., R. Hill, and P. J. Ralph. 2005. Photosynthetic impact of hypoxia on in hospite zooxanthellae in the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 286:125-132. | 2005 | Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Wild, C., M. Rasheed, C. Jantzen, P. Cook, U. Struck, M. Huettel, and A. Boetius. 2005. Benthic metabolism and degradation of natural particulate organic matter in carbonate and silicate reef sands of the northern Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 298:69-78. | 2005 | Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Yanez-Arancibia, A. and J. W. Day. 2005. Environmental sub-regions in the Gulf of Mexico coastal zone: The ecosystem approach as an integrated management tool. Ocean and Coastal Management 47:727-757. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; Mexico | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Apex Fish Predators; Cultural Policies; Discharges; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| [No author name available]. 2004. Proceedings of SPIE - Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Sea Ice 2004. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 5569. | 2004 | Taiwan | Field Study & Monitoring; Remote Sensing | Petroleum Spills; Primary Production |
| Anthony, K. R. N. and S. R. Connolly. 2004. Environmental limits to growth: Physiological niche boundaries of corals along turbidity-light gradients. Oecologia 141:373-384. | 2004 | Light; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Arias-Gonzalez, J.E., E. Nunez-Lara, C. Gonzalez-Salas, and R. Galzin. 2004. Trophic models for investigation of fishing effect on coral reef ecosystems. Ecological Modelling 172:197-212. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Primary Production |
| Bhagooli, R. and M. Hidaka. 2004. Release of zooxanthellae with intact photosynthetic activity by the coral Galaxae fascicularis in response to high temperature stress. Marine Biology 145:329-337. | 2004 | Discharges; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bozec, Y-M., D. Gascuel, M. Kulbicki. 2004. Trophic model of lagoonal communities in a large open atoll (Uvea, Loyalty islands, New Caledonia). Aquatic Living Resource 17:151-162. | 2004 | New Caledonia | Model | Plankton; Primary Production |
| Chen, M.-C., Y.-M. Cheng, M.-C. Hong, and L.-S. Fang. 2004. Molecular cloning of Rab5 (ApRab5) in Aiptasia pulchella and its retention in phagosomes harboring live zooxanthellae. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 324:1024-1033. | 2004 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Cohen, A. L. and R. A. Sohn. 2004. Tidal modulation of Sr/Ca ratios in a Pacific reef coral. Geophysical Research Letters 31. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Light; Primary Production |
| Cosgrove, J., D. Walker, P. Morrison, and K. Hillman. 2004. Periphyton indicate effects of wastewater discharge in the near-coastal zone, Perth (Western Australia). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 61:331-338. | 2004 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Wastewater Discharge |
| Dove, S. 2004. Scleractinian corals with photoprotective host pigments are hypersensitive to thermal bleaching. Marine Ecology Progress Series 272:99-116. | 2004 | Australia | Light; Primary Production; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral | |
| Franklin, D. J., O. Hoegh-Guldberg, R. J. Jones, and J. A. Berges. 2004. Cell death and degeneration in the symbiotic dinoflagellates of the coral Stylophora pistillata during bleaching. Marine Ecology Progress Series 272:117-130. | 2004 | Global; Australia | Algae; Climate; Primary Production; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral | |
| Gardinali, P. R., M. D. Plasencia, and C. Maxey. 2004. Occurrence and transport of Irgarol 1051 and its major metabolite in coastal waters from South Florida. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49:1072-1083. | 2004 | Florida | Model | Algae; Docks & Marinas; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Goldshmid, R., R. Holzman, D. Weihs, and A. Genin. 2004. Aeration of corals by sleep-swimming fish. Limnology and Oceanography 49:1832-1839. | 2004 | Lab Study | Algae; Fish; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Goreau, T. J., J. M. Cervino, and R. Pollina. 2004. Increased zooxanthellae numbers and mitotic index in electrically stimulated corals. Symbiosis 37:107-120. | 2004 | Global; Indonesia | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Grant, A. J., T. Starke-Peterkovic, K. J. T. Withers, and R. Hinde. 2004. Aposymbiotic Plesiastrea versipora continues to produce cell-signalling molecules that regulate the carbon metabolism of symbiotic algae. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 138:253-259. | 2004 | Australia | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Grottoli, A. G., L. J. Rodrigues, and C. Juarez. 2004. Lipids and stable carbon isotopes in two species of Hawaiian corals, Porites compressa and Montipora verrucosa, following a bleaching event. Marine Biology 145:621-631. | 2004 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Grunwald, B. and M. Kuhl. 2004. A system for imaging variable chlorophyll fluorescence of aquatic phototrophs. Ophelia 58:79-89. | 2004 | GIS & Maps | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Guidetti, P., S. Fraschetti, A. Terlizzi, and F. Boero. 2004. Effects of desertification caused by Lithophaga lithophaga (Mollusca) fishery on littoral fish assemblages along rocky coasts of southeastern Italy. Conservation Biology 18:1417-1423. | 2004 | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing Sector; Molluscs; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Hill, R., U. Schreiber, R. Gademann, A. W. D. Larkum, M. Kuhl, and P. J. Ralph. 2004. Spatial heterogeneity of photosynthesis and the effect of temperature-induced bleaching conditions in three species of corals. Marine Biology 144:633-640. | 2004 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Hohenegger, J. 2004. Depth coenoclines and environmental considerations of Western Pacific larger foraminifera. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 34:Sep-33. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Honisch, B., N. G. Hemming, A. G. Grottoli, A. Amat, G. N. Hanson, and J. Bijma. 2004. Assessing scleractinian corals as recorders for paleo-pH: Empirical calibration and vital effects. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 68:3675-3685. | 2004 | Lab Study | Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Houlbreque, F., E. Tambutte, C. Richard, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2004. Importance of a micro-diet for scleractinian corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 282:151-160. | 2004 | Cuba | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Houlbreque, F., E. Tambutte, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2004. Interactions between zooplankton feeding, photosynthesis and skeletal growth in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Biology 207:1461-1469. | 2004 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Jones, R. J. 2004. Testing the 'photoinhibition' model of coral bleaching using chemical inhibitors. Marine Ecology Progress Series 284:133-145. | 2004 | Model | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Leggat, W., S. Whitney, and D. Yellowlees. 2004. Is coral bleaching due to the instability of the zooxanthellae dark reactions? Symbiosis 37:137-153. | 2004 | Global | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Sponges; Zooxanthellae | |
| Levy, O., Z. Dubinsky, K. Schneider, Y. Achituv, D. Zakai, and M. Y. Gorbunov. 2004. Diurnal hysteresis in coral photosynthesis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 268:105-117. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Caribbean | Algae; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Nakamura, E., Y. Yokohama, and J. Tanaka. 2004. Photosynthetic activity of a temperate coral Acropora pruinosa (Scleractinia, Anthozoa) with symbiotic algae in Japan. Phycological Research 52:38-44. | 2004 | Japan | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Nishihara, G. N., R. Terada, and T. Noro. 2004. Photosynthesis and growth rates of Laurencia brongniartii J. Agardh (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales) in preparation for cultivation. Journal of Applied Phycology 16:303-308. | 2004 | Japan | Light; Primary Production | |
| Okey, T.A., G.A. Vargo, S. Mackinson, M. Vasconcellos, B. Mahmoudie, and C.A. Meyer. 2004. Simulating community effects of sea floor shading by plankton blooms over the West Florida Shelf. Ecological Modelling 172:339-359. | 2004 | Florida | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invertebrates; Light; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Parrish, F. A. and R. C. Boland. 2004. Habitat and reef-fish assemblages of banks in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Marine Biology 144:1065-1073. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Primary Production |
| Piniak, G. A. and F. Lipschultz. 2004. Effects of nutritional history on nitrogen assimilation in congeneric temperate and tropical scleractinian corals. Marine Biology 145:1085-1096. | 2004 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Porat, D. and N. E. Chadwick-Furman. 2004. Effects of anemonefish on giant sea anemones: Expansion behavior, growth, and survival. Hydrobiologia 513-520. | 2004 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Primary Production | ||
| Rasheed, M., C. Wild, U. Franke, and M. Huettel. 2004. Benthic photosynthesis and oxygen consumption in permeable carbonate sediments at Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 59:139-150. | 2004 | Australia | Lab Study | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Rosenberg, E. and L. Falkovitz. 2004. The Vibrio shiloi/Oculina patagonica model system of coral bleaching. Annual Review of Microbiology 58:143-159. | 2004 | Model | Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Serisawa, Y., Y. Yokohama, Y. Aruga, and A. Bellgrove. 2004. Photosynthetic performance of transplanted ecotypes of Ecklonia cava (Laminariales, Phaeophyta). Journal of Applied Phycology 16:227-235. | 2004 | Japan | Index or Indicator | Artificial Habitat; Primary Production |
| Stambler, N. and Z. Dubinsky. 2004. Stress effects on metabolism and photosynthesis of hermatypic corals. Pages 195-215 in E. Rosenberg and Y. Loya, editors. Coral health and disease. Springer, Berlin, Germany. | 2004 | Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Takahashi, S., T. Nakamura, M. Sakamizu, R. Van Woesik, and H. Yamasaki. 2004. Repair Machinery of Symbiotic Photosynthesis as the Primary Target of Heat Stress for Reef-Building Corals. Plant and Cell Physiology 45:251-255. | 2004 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wild, C., M. Huettel, A. Klueter, S. G. Kremb, M. Y. M. Rasheed, and B. B. Jorgensen. 2004. Coral mucus functions as an energy carrier and particle trap in the reef ecosystem. Nature 428:66-70. | 2004 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Yakovleva, I. and M. Hidaka. 2004. Different effects of high temperature acclimation on bleaching-susceptible and tolerant corals. Symbiosis 37:87-105. | 2004 | Japan | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Yentsch, C. S., C. M. Yentsch, D. A. Phinney, B. E. Lapointe, and S. F. W. Yentsch. 2004. The odyssey of new production. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 300:15-30. | 2004 | Florida; Bahamas | Lab Study; Remote Sensing | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae |
| Adkins, J. F., E. A. Boyle, W. B. Curry, and A. Lutringer. 2003. Stable isotopes in deep-sea corals and a new mechanism for \vital effects\"". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 67:1129-1143. | 2003 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Primary Production | ||
| Al-Horani, F. A., S. M. Al-Moghrabi, and D. De Beer. 2003. Microsensor study of photosynthesis and calcification in the scleractinian coral, Galaxea fascicularis: Active internal carbon cycle. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 288:15-Jan. | 2003 | Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Al-Horani, F. A., S. M. Al-Moghrabi, and D. De Beer. 2003. The mechanism of calcification and its relation to photosynthesis and respiration in the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Marine Biology 142:419-426. | 2003 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Anthony, K. R. N. and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2003. Kinetics of photoacclimation in corals. Oecologia 134:23-31. | 2003 | Model | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Anthony, K. R. N. and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2003. Variation in coral photosynthesis, respiration and growth characteristics in contrasting light microhabitats: An analogue to plants in forest gaps and understoreys? Functional Ecology 17:246-259. | 2003 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Arp, G., A. Reimer, and J. Reitner. 2003. Microbialite formation in seawater of increased alkalinity, Satonda Crater Lake, Indonesia. Journal of Sedimentary Research 73:105-127. | 2003 | Indonesia | Model | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges |
| Banin, E., D. Vassilakos, E. Orr, R. J. Martinez, and E. Rosenberg. 2003. Superoxide dismutase is a virulence factor produced by the coral bleaching pathogen Vibrio shiloi. Current Microbiology 46:418-422. | 2003 | Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Beach, K., L. Walters, H. Borgeas, C. Smith, J. Coyer, and P. Vroom. 2003. The impact of Dictyota spp. on Halimeda populations of Conch Reef, Florida Keys. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 297:141-159. | 2003 | Florida | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Beach, K., L. Walters, P. Vroom, C. Smith, J. Coyer, and C. Hunter. 2003. Variability in the ecophysiology of Halimeda spp. (Chlorophyta, bryopsidales) on Conch Reef, Florida Keys, USA. Journal of Phycology 39:633-643. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Chen, M.-C., Y.-M. Cheng, P.-J. Sung, C.-E. Kuo, and L.-S. Fang. 2003. Molecular identification of Rab7 (ApRab7) in Aiptasia pulchella and its exclusion from phagosomes harboring zooxanthellae. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 308:586-595. | 2003 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Chisholm, J. R. M. 2003. Primary productivity of reef-building crustose coralline algae. Limnology and Oceanography 48:1376-1387. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Light; Primary Production |
| Depczynski, M. and D. R. Bellwood. 2003. The role of cryptobenthic reef fishes in coral reef trophodynamics. Marine Ecology Progress Series 256:183-191. | 2003 | Australia | Fish; Primary Production | |
| Dizon, R. M. and H. T. Yap. 2003. Metabolic changes and compositional shifts in nutrient-enriched tropical reef sediment communities [Cambios metabolicos y de composicion en comunidades de sedimentos de arrecife tropical enriquecidos con nutrientes]. Scientia Marina 67:117-127. | 2003 | Philippines | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Edmundson, J. A., T. M. Willette, J. M. Edmundson, D. C. Schmidt, S. R. Carlson, B. G. Bue, and K. E. Tarbox. 2003. Sockeye Salmon Overescapement (Kenai River Component). Exxon Valdez Oil Spill Restoration Project Final Report. | 2003 | Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Non-point Source Runoff; Petroleum Spills; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Fu, F.-X. and P. R. F. Bell. 2003. Growth, N2 fixation and photosynthesis in a cyanobacterium, Trichodesmium sp., under Fe stress. Biotechnology Letters 25:645-649. | 2003 | Australia | Primary Production | |
| Grant, A. J., D. A. Trautman, S. Frankland, and R. Hinde. 2003. A symbiosome membrane is not required for the actions of two host signalling compounds regulating photosynthesis in symbiotic algae isolated from cnidarians. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 135:337-345. | 2003 | Cuba | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Grant, A. J., K. Graham, S. Frankland, and R. Hinde. 2003. Effect of copper on algal-host interactions in the symbiotic coral Plesiastrea versipora. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 41:383-390. | 2003 | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Gross, E. M. 2003. Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 22:313-339. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| Houlbreque, F., E. Tambutte, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2003. Effect of zooplankton availability on the rates of photosynthesis, and tissue and skeletal growth in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 296:145-166. | 2003 | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Jones, R. J. and A. J. Heyward. 2003. The effects of Produced Formation Water (PFW) on coral and isolated symbiotic dinoflagellates of coral. Marine and Freshwater Research 54:153-162. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Primary Production; Toxics |
| Kerswell, A. P. and R. J. Jones. 2003. Effects of hypo-osmosis on the coral Stylophora pistillata: Nature and cause of 'low-salinity bleaching'. Marine Ecology Progress Series 253:145-154. | 2003 | Algae; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral | ||
| Langdon, C., W. S. Broecker, D. E. Hammond, E. Glenn, K. Fitzsimmons, S. G. Nelson, T.-H. Peng, I. Hajdas, and G. Bonani. 2003. Effect of elevated CO2 on the community metabolism of an experimental coral beef. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 17:1-Nov. | 2003 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | ||
| Larkum, A. W. D., E.-M.W. Koch, and M. Kuhl. 2003. Diffusive boundary layers and photosynthesis of the epilithic algal community of coral reefs. Marine Biology 142:1073-1082. | 2003 | Australia | CO2; Light; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral | |
| Lemmens, S. 2003. Periphyton collectors as a tool to measure environmental performance of ocean outlets. Water Science and Technology 47:125-131. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Wastewater Discharge |
| Magoshi, J., T. Tanaka, H. Sasaki, M. Kobayashi, Y. Magoshi, H. Tsuda, M. A. Becker, S.-I. Inoue, and K. Ishimaru. 2003. Uptake of atmospheric carbon dioxide into silk fiber by silkworms. Biomacromolecules 4:778-782. | 2003 | Model | CO2; Primary Production | |
| Maier, C., J. Patzold, and R. P. M. Bak. 2003. The skeletal isotopic composition as an indicator of ecological and physiological plasticity in the coral genus Madracis. Coral Reefs 22:370-380. | 2003 | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Marshall, A. T. and P. L. Clode. 2003. Light-regulated Ca2+ uptake and O2 secretion at the surface of a scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 136:417-426. | 2003 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Mazel, C. H., M. P. Lesser, M. Y. Gorbunov, T. M. Barry, J. H. Farrell, K. D. Wyman, and P. G. Falkowski. 2003. Green-fluorescent proteins in Caribbean corals. Limnology and Oceanography 48:402-411. | 2003 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Lab Study | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Nordemar, I., M. Nystrom, and R. Dizon. 2003. Effects of elevated seawater temperature and nitrate enrichment on the branching coral Porites cylindrica in the absence of particulate food. Marine Biology 142:669-677. | 2003 | Global | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Oku, H., H. Yamashiro, and K. Onaga. 2003. Lipid biosynthesis from [14C]-glucose in the coral Montipora digitata. Fisheries Science 69:625-631. | 2003 | Cuba | Primary Production; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Owen, R., A. Knap, N. Ostrander, and K. Carbery. 2003. Comparative acute toxicity of herbicides to photosynthesis of coral zooxanthellae. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 70:541-548. | 2003 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Raberg, S., M. Nystrom, M. Eros, P. Plantman. 2003. Impact of the Herbicides 2, 4-D and diuron on the metabolism of the coral Porites Cylindrica. Marine Environmental Research 56:503-514. | 2003 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Reynaud, S., N. Leclercq, S. Romaine-Lioud, C. Ferrier-Pages, J. Jaubert, and J.-P. Gattuso. 2003. Interacting effects of CO2 partial pressure and temperature on photosynthesis and calcification in a scleractinian coral. Global Change Biology 9:1660-1668. | 2003 | Global | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Richardson, L. L. and K. G. Kuta. 2003. Ecological physiology of the black band disease cyanobacterium Phormidium corallyticum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 43:287-298. | 2003 | Europe | Lab Study | Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production |
| Rollon, R. N., E. D. De Ruyter Van Steveninck, and W. Van Vierssen. 2003. Spatio-temporal variation in sexual reproduction of the tropical seagrass Enhalus acoroides (L.f.) Royle in Cape Bolinao, NW Philippines. Aquatic Botany 76:339-354. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Philippines | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Saxby, T., W. C. Dennison, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2003. Photosynthetic responses of the coral Montipora digitata to cold temperature stress. Marine Ecology Progress Series 248:85-97. | 2003 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Sebens, K. P., B. Helmuth, E. Carrington, and B. Agius. 2003. Effects of water flow on growth and energetics of the scleractinian coral Agaricia tenuifolia in Belize. Coral Reefs 22:35-47. | 2003 | South & Central America; Belize | Complex Habitat & Resources; Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | |
| Suzuki, A., M. K. Gagan, K. Fabricius, P. J. Isdale, I. Yukino, and H. Kawahata. 2003. Skeletal isotope microprofiles of growth perturbations in Porites corals during the 1997-1998 mass bleaching event. Coral Reefs 22:357-369. | 2003 | Australia; Japan | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Winters, G., Y. Loya, R. Rottgers, and S. Beer. 2003. Photoinhibition in shallow-water colonies of the coral Stylophora pistillata as measured in situ. Limnology and Oceanography 48:1388-1393. | 2003 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Yates, K. K. and R. B. Halley. 2003. Measuring coral reef community metabolism using new benthic chamber technology. Coral Reefs 22:247-255. | 2003 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Substrate |
| Cebrian, J. 2002. Variability and control of carbon consumption, export, and accumulation in marine communities. Limnology and Oceanography 47:22-Nov. | 2002 | Mangroves; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Davy, S. K., D. A. Trautman, M. A. Borowitzka, and R. Hinde. 2002. Ammonium excretion by a symbiotic sponge supplies the nitrogen requirements of its rhodophyte partner. Journal of Experimental Biology 205:3505-3511. | 2002 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Durako, M. J. and J. I. Kunzelman. 2002. Photosynthetic characteristics of Thalassia testudinum measured in situ by pulse-amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorometry: methodological and scale-based considerations. Aquatic Botany 73:173-185. | 2002 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Light; Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Elfwing, T. and M. Tedengren. 2002. Effects of copper and reduced salinity on grazing activity and macroalgae production: A short-term study on a mollusc grazer, Trochus maculatus, and two species of macroalgae in the inner Gulf of Thailand. Marine Biology 140:913-919. | 2002 | Thailand | Index or Indicator | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Molluscs; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral |
| Grottoli, A. G. 2002. Effect of light and brine shrimp on skeletal δ13C in the Hawaiian coral Porites compressa: A tank experiment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 66:1955-1967. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Gullstrom, M., M. De La Torre Castro, S. O. Bandeira, M. Bjork, M. Dahlberg, N. Kautsky, P. Ronnback, and M. C. Ohman. 2002. Seagrass ecosystems in the Western Indian Ocean. Ambio 31:588-596. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; Tanzania; Mozambique; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius; Reunion; India; South Africa; France | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Hata, H., S. Kudo, H. Yamano, N. Kurano, and H. Kayanne. 2002. Organic carbon flux in Shiraho coral reef (Ishigaki Island, Japan). Marine Ecology Progress Series 232:129-140. | 2002 | Japan | Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Kayanne, H., H. Hata, K. Nozaki, K. Kato, A. Negishi, H. Saito, H. Yamano, T. Isamu, H. Kimoto, M. Tsuda, F. Akimoto, K. Kawate, and I. Iwata. 2002. Submergible system to measure seawater pCO2 on a shallow sea floor. Marine Technology Society Journal 36:23-28. | 2002 | Palau | CO2; Primary Production; Salinity | |
| Leclercq, N., J.-P. Gattuso, and J. Jaubert. 2002. Primary production, respiration, and calcification of a coral reef mesocosm under increased CO2 partial pressure. Limnology and Oceanography 47:558-564. | 2002 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Marshall, A. T. and P. L. Clode. 2002. Effect of increased calcium concentration in sea water on calcification and photosynthesis in the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Journal of Experimental Biology 205:2107-2113. | 2002 | Cuba | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| McArthur, C., R. Ferry, and J. Proni. 2002. Development of guidelines for dredged material disposal based on abiotic determinants of coral reef community structure. Pages 1897-1911 in Dredging, Key Technologies for Global Prosperity. | 2002 | Global | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Owen, R., A. Knap, M. Toaspern, and K. Carbery. 2002. Inhibition of coral photosynthesis by the antifouling herbicide Irgarol 1051. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:623-632. | 2002 | Florida; US Virgin Islands; Cuba; Bermuda | Algae; Docks & Marinas; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Zooxanthellae | |
| Perkins, R. G., K. Oxborough, A. R. M. Hanlon, G. J. C. Underwood, and N. R. Baker. 2002. Can chlorophyll fluorescence be used to estimate the rate of photosynthetic electron transport within microphytobenthic biofilms? Marine Ecology Progress Series 228:47-56. | 2002 | Primary Production | ||
| Ralph, P. J., R. Gademann, A. W. D. Larkum, and M. Kuhl. 2002. Spatial heterogeneity in active chlorophyll fluorescence and PSII activity of coral tissues. Marine Biology 141:639-646. | 2002 | Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Reynaud, S., C. Ferrier-Pages, R. Sambrotto, A. Juillet-Leclerc, J. Jaubert, and J.-P. Gattuso. 2002. Effect of feeding on the carbon and oxygen isotopic composition in the tissues and skeleton of the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata. Marine Ecology Progress Series 238:81-89. | 2002 | Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rosenberg, E. and Y. Ben-Haim. 2002. Microbial diseases of corals and global warming. Environmental Microbiology 4:318-326. | 2002 | Global | Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Schreiber, U., R. Gademann, P. Bird, P. J. Ralph, A. W. D. Larkum, and M. Kuhl. 2002. Apparent light requirement for activation of photosynthesis upon rehydration of desiccated beachrock microbial mats. Journal of Phycology 38:125-134. | 2002 | Australia | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Soreghan, G. S. and M. J. Soreghan. 2002. Atmospheric dust and algal dominance in the late Paleozoic: A hypothesis. Journal of Sedimentary Research 72:457-461. | 2002 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Stanley, S. M., J. B. Ries, and L. A. Hardie. 2002. Low-magnesium calcite produced by coralline algae in seawater of late cretaceous composition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99:15323-15326. | 2002 | Algae; CO2; Coralline Algae; Primary Production | ||
| Suzumura, M., T. Miyajima, H. Hata, Y. Umezawa, H. Kayanne, and I. Koike. 2002. Cycling of phosphorus maintains the production of microphytobenthic communities in carbonate sediments of a coral reef. Limnology and Oceanography 47:771-781. | 2002 | Cuba; Japan | Lab Study | Primary Production; Sediment |
| Underwood, G. J. C. 2002. Adaptations of tropical marine microphytobenthic assemblages along a gradient of light and nutrient availability in Suva Lagoon, Fiji. European Journal of Phycology 37:449-462. | 2002 | Fiji | Climate; Light; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Vermeij, M. J. A., L. Delvoye, G. Nieuwland, and R. P. M. Bak. 2002. Patterns in fluorescence over a Caribbean reef slope: The coral genus Madracis. Photosynthetica 40:423-429. | 2002 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Yentsch, C.S., C.M. Yentsch, J.J. Cullen, B. Lapointe, D.A. Phinney, S.W. Yentsch. 2002. Sunlight and water transparency: cornerstones in coral research. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 268:171-183. | 2002 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Alutoin, S., J. Boberg, M. Nystrom, and M. Tedengren. 2001. Effects of the multiple stressors copper and reduced salinity on the metabolism of the hermatypic coral Porites lutea. Marine Environmental Research 52:289-299. | 2001 | Thailand | Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral | |
| Banin, E., S. K. Khare, F. Naider, and E. Rosenberg. 2001. Proline-Rich Peptide from the Coral Pathogen Vibrio shiloi That Inhibits Photosynthesis of Zooxanthellae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 67:1536-1541. | 2001 | Cuba | Algae; Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Banin, E., T. Israely, M. Fine, Y. Loya, and E. Rosenberg. 2001. Role of endosymbiotic zooxanthellae and coral mucus in the adhesion of the coral-bleaching pathogen Vibrio shiloi to its host. FEMS Microbiology Letters 199:33-37. | 2001 | Europe | Algae; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cohen, A. L., G. D. Layne, S. R. Hart, and P. S. Lobel. 2001. Kinetic control of skeletal Sr/Ca in a symbiotic coral: Implications for the paleotemperature proxy. Paleoceanography 16:20-26. | 2001 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cook, C. B. and S. K. Davy. 2001. Are free amino acids responsible for the 'host factor' effects on symbiotic zooxanthellae in extracts of host tissue? Hydrobiologia 461:71-78. | 2001 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Davy, S. K. and C. B. Cook. 2001. The influence of 'host release factor' on carbon release by zooxanthellae isolated from fed and starved Aiptasia pallida (Verrill). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 129:487-494. | 2001 | Cuba | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Diaz, M.C., K. Rutzler. 2001. Sponges: an essential component of caribbean coral reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:535-546. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges |
| Dubinsky, Z. and I. Berman-Frank. 2001. Uncoupling primary production from population growth in photosynthesizing organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic Science 63:17-Apr. | 2001 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Edmunds, P., R. Gates, and D. Gleason. 2001. The biology of larvae from the reef coral Porites astreoides, and their response to temperature disturbances. Marine Biology 139:981-989. | 2001 | Global; Florida; Cuba | Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Enriquez, S., N. Marba, C. M. Duarte, B. I. Van Tussenbroek, and G. Reyes-Zavala. 2001. Effects of seagrass Thalassia testudinum on sediment redox. Marine Ecology Progress Series 219:149-158. | 2001 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., V. Schoelzke, J. Jaubert, L. Muscatine, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2001. Response of a scleractinian coral, Stylophora pistillata, to iron and nitrate enrichment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 259:249-261. | 2001 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Fitt, W. K. and C. B. Cook. 2001. Photoacclimation and the effect of the symbiotic environment on the photosynthetic response of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the tropical marine hydroid Myrionema amboinense. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 256:15-31. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; CO2; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Floeter, S. R., R. Z. P. Guimaraes, L. A. Rocha, C. E. L. Ferreira, C. A. Rangel, and J. L. Gasparini. 2001. Geographic variation in reef-fish assemblages along the Brazilian coast. Global Ecology and Biogeography 10:423-431. | 2001 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Primary Production | |
| Fonseca, M. S. 2001. Comparative analysis of the functioning of disturbed and undisturbed coral reef and seagrass ecosystems in the Tortugas: phase I- establishing a baseline. Center for Coastal Fisheries and Habitat Research, Beaufort, North Carolina. | 2001 | Florida | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Complex Habitat & Resources; Plankton; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Gorbunov, M. Y., Z. S. Kolber, M. P. Lesser, and P. G. Falkowaski. 2001. Photosynthesis and photoprotection in symbiotic corals. Limnology and Oceanography 46:75-85. | 2001 | Cuba | Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Grant, A. J., M. Remond, K. J. T. Withers, and R. Hinde. 2001. Inhibition of algal photosynthesis by a symbiotic coral. Hydrobiologia 461:63-69. | 2001 | Cuba | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Howe, S. A. and A. T. Marshall. 2001. Thermal compensation of metabolism in the temperate coral, Plesiastrea versipora (Lamarck, 1816). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 259:231-248. | 2001 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Lesser, M. P. and M. Y. Gorbunov. 2001. Diurnal and bathymetric changes in chlorophyll fluorescence yields of reef corals measured in situ with a fast repetition rate fluorometer. Marine Ecology Progress Series 212:69-77. | 2001 | Bahamas | Field Study & Monitoring | Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Levy, O., L. Mizrahi, N. E. Chadwick-Furman, and Y. Achituv. 2001. Factors controlling the expansion behavior of Favia favus (Cnidaria: Scleractinia): Effects of light, flow, and planktonic prey. Biological Bulletin 200:118-126. | 2001 | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Lourey, M. J., D. M. Alongi, D. A. J. Ryan, and M. J. Devlin. 2001. Variability of nutrient regeneration rates and nutrient concentrations in surface sediments of the northern Great Barrier Reef shelf. Continental Shelf Research 21:145-155. | 2001 | Australia | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Marubini, F., H. Barnett, C. Langdon, and M. J. Atkinson. 2001. Dependence of calcification on light and carbonate ion concentration for the hermatypic coral Porites compressa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 220:153-162. | 2001 | Global | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Muller, P., X.-P. Li, and K. K. Niyogi. 2001. Non-photochemical quenching. A response to excess light energy. Plant Physiology 125:1558-1566. | 2001 | Primary Production | ||
| Nystrom, M., I. Nordemar, and M. Tedengren. 2001. Simultaneous and sequential stress from increased temperature and copper on the metabolism of the hermatypic coral Porites cylindrica. Marine Biology 138:1225-1231. | 2001 | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Perez, S. F., C. B. Cook, and W. R. Brooks. 2001. The role of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the temperature-induced bleaching response of the subtropical sea anemone Aiptasia pallida. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 256:14-Jan. | 2001 | Florida; Cuba; Bermuda | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Pomory, C. M. and J. M. Lawrence. 2001. Arm regeneration in the field in Ophiocoma echinata (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea): Effects on body composition and its potential role in a reef food web. Marine Biology 139:661-670. | 2001 | Florida; China | Field Study & Monitoring | Echinoderms; Primary Production |
| Ralph, P. J., R. Gademann, and A. W. D. Larkum. 2001. Zooxanthellae expelled from bleached corals at 33°C are photosynthetically competent. Marine Ecology Progress Series 220:163-168. | 2001 | Primary Production; Salinity; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Reynaud-Vaganay, S., A. Juillet-Leclerc, J. Jaubert, and J.-P. Gattuso. 2001. Effect of light on skeletal δ13C and δ18O, and interaction with photosynthesis, respiration and calcification in two zooxanthellate scleractinian corals. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 175:393-404. | 2001 | Lab Study; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rosenqvist, E. 2001. Light acclimation maintains the redox state of the PS II electron acceptor QA within a narrow range over a broad range of light intensities. Photosynthesis Research 70:299-310. | 2001 | Index or Indicator | Light; Primary Production | |
| Shigenaka, G. 2001. Toxicity of Oil to Reef-Building Corals: A spill response perspective, NOAA technical memorandum NOS OR&R 8. | 2001 | Petroleum Spills; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Small, A. M. and W. H. Adey. 2001. Reef corals, zooxanthellae and free-living algae: A microcosm study that demonstrates synergy between calcification and primary production. Ecological Engineering 16:443-457. | 2001 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Titlyanov, E. A., T. V. Titlyanova, and K. Yamazato. 2001. Formation, growth and photo-acclimation of colonies of the hermatypic coral Galaxea fascicularis under different light conditions. Symbiosis 30:257-274. | 2001 | Japan; China | Algae; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Titlyanov, E. A., T. V. Titlyanova, K. Yamazato, and R. Van Woesik. 2001. Photo-acclimation of the hermatypic coral stylophora pistillata while subjected to either starvation or food provisioning. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 257:163-181. | 2001 | Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Wulff, J. 2001. Assessing and monitoring coral reef sponges: Why and how? Bulletin of Marine Science 69:831-846. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | |
| Anthony, K. R. N. and K. E. Fabricius. 2000. Shifting roles of heterotrophy and autotrophy in coral energetics under varying turbidity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 252:221-253. | 2000 | Light; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Anthony, K. R.N. and P. Larcombe. 2000. Coral reefs in turbid waters: sediment-induced stresses in corals and likely mechanisms of adaptation. in Proceedings 9th International Coral Reef Symposium. Bali,(Indonesia). | 2000 | Light; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Banin, F., Y. Ben-Haim, T. Israely, Y. Loya, and E. Rosenberg. 2000. Effect of the environment on the bacterial bleaching of corals. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 123:337-352. | 2000 | Global | Algae; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bourge, I. and M. Frankignoulle. 2000. Calcification does not stimulate photosynthesis in the zooxanthellate scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnology and Oceanography 45:246-250. | 2000 | Cuba | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| de Beer, D., M. Kuhl, N. Stambler, and L. Vaki. 2000. A microsensor study of light enhanced ca2+ uptake and photosynthesis in the reef-building hermatypic coral Favia sp. Marine Ecology Progress Series 194:75-85. | 2000 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Ferrier-Pages, C., J.-P. Gattuso, S. Dallot, and J. Jaubert. 2000. Effect of nutrient enrichment on growth and photosynthesis of the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata. Coral Reefs 19:103-113. | 2000 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Furla, P., I. Galgani, I. Durand, and D. Allemand. 2000. Sources and mechanisms of inorganic carbon transport for coral calcification and photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Biology 203:3445-3457. | 2000 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Heikoop, J. M., J. J. Dunn, M. J. Risk, H. P. Schwarcz, T. A. McConnaughey, and I. M. Sandeman. 2000. Separation of kinetic and metabolic isotope effects in carbon-13 records preserved in reef coral skeletons. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 64:975-987. | 2000 | Jamaica | Model | Light; Primary Production |
| Huber, M. E. and G. B. K. Baines. 2000. The Coral, Solomon and Bismarck Seas Region. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 425-446. | 2000 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Solomon Islands; Vanuatu; New Caledonia; Papua New Guinea | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Discharges; Echinoderms; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Mangroves; Molluscs; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Wetlands |
| Jones, R. J., S. Ward, A. Y. Amri, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2000. Changes in quantum efficiency of Photosystem II of symbiotic dinoflagellates of corals after heat stress, and of bleached corals sampled after the 1998 Great Barrier Reef mass bleaching event. Marine and Freshwater Research 51:63-71. | 2000 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Primary Production |
| Kawahata, H., I. Yukino, and A. Suzuki. 2000. Terrestrial influences on the Shiraho fringing reef, Ishigaki Island, Japan: High carbon input relative to phosphate. Coral Reefs 19:172-178. | 2000 | Japan | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kuta, K. 2000. Black band disease of corals: Ecology and physiology of Phormidium corallyticum. Florida International University, Miami. | 2000 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Leggat, W., T. A. V. Rees, and D. Yellowlees. 2000. Meeting the photosynthetic demand for inorganic carbon in an alga-invertebrate association: Preferential use of CO2 by symbionts in the giant clam Tridacna gigas. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 267:523-529. | 2000 | CO2; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Leletkin, V. A. 2000. The Energy Budget of Coral Polyps. Russian Journal of Marine Biology 26:389-398. | 2000 | Model | Algae; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Lesser, M. P. 2000. Depth-dependent photoacclimatization to solar ultraviolet radiation in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata. Marine Ecology Progress Series 192:137-151. | 2000 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Lesser, M. P., C. Mazel, D. Phinney, and C. S. Yentsch. 2000. Light absorption and utilization by colonies of the congeneric hermatypic corals Montastraea faveolata and Montastraea cavernosa. Limnology and Oceanography 45:76-86. | 2000 | South & Central America; Florida; Bahamas; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| McConnaughey, T. A., W. H. Adey, and A. M. Small. 2000. Community and environmental influences on reef coral calcification. Limnology and Oceanography 45:1667-1671. | 2000 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Ottosen, C.-O. and J. Mentz. 2000. Biomass accumulation and photosynthesis of ornamentals in elevated CO2 conditions. Gartenbauwissenschaft 65:35-39. | 2000 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Payri, C. E. 2000. Primary production and calcification of coral reef benthic algae [Production primaire et calcification des algues benthiques en milieu corallien]. Oceanis 26:427-463. | 2000 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Penchaszadeh, P. E., C. A. Leon, H. Alvarez, D. Bone, P. Castellano, M. M. Castillo, Y. Diaz, M. P. Garcia, M. Lemus, F. Losada, A. Martin, P. Miloslavich, C. Paredes, D. Perez, M. Sebastiani, D. Stecconi, V. Roa, and A. Villamizar. 2000. Venezuela. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 643-661. | 2000 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Venezuela; Caribbean | Beaches & Nature Parks; Bivalves; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Molluscs; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sakami, T. 2000. Effects of temperature, irradiance, salinity and inorganic nitrogen concentration on coral zooxanthellae in culture. Fisheries Science 66:1006-1013. | 2000 | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Salih, A., A. Larkum, G. Cox, M. Kuhl, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2000. Fluorescent pigments in corals are photoprotective. Nature 408:850-853. | 2000 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Scott, L. C., J. W. Boland, K. S. Edyvane, and G. K. Jones. 2000. Development of a seagrass-fish habitat model - I: A seagrass residency index for economically important species. Environmetrics 11:541-552. | 2000 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Fish; Fishing Sector; Molluscs; Monetary Valuation; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Sheppard, C. R. C. 2000. The Red Sea. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 35-45. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waste Management Policies | |
| Titlyanov, E. A., J. Tsukahara, T. V. Titlyanova, V. A. Leletkin, R. Van Woesik, and K. Yamazato. 2000. Zooxanthellae population density and physiological state of the coral Stylophora pistillata during starvation and osmotic shock. Symbiosis 28:303-322. | 2000 | Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Titlyanov, E. A., V. A. Leletkin, and Z. Dubinsky. 2000. Autotrophy and predation in the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata in different light habitats. Symbiosis 29:263-281. | 2000 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Ambariyanto, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1999. Influence of field-based nutrient enrichment on the photobiology of the giant clam Tridacna maxima. Marine Biology 133:659-664. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Babcock, R. C., S. Kelly, N. T. Shears, J. W. Walker, and T. J. Willis. 1999. Changes in community structure in temperate marine reserves. Marine Ecology Progress Series 189:125-134. | 1999 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Primary Production; Sea Urchins | |
| Ben-Haim, Y., E. Banim, A. Kushmaro, Y. Loya, and E. Rosenberg. 1999. Inhibition of photosynthesis and bleaching of zooxanthellae by the coral pathogen Vibrio shiloi. Environmental Microbiology 1:223-229. | 1999 | Algae; Pathogens; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Clavier, J. and C. Garrigue. 1999. Annual sediment primary production and respiration in a large coral reef lagoon (SW New Caledonia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 191:79-89. | 1999 | New Caledonia | Light; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Dizon, R. M. and H. T. Yap. 1999. Short-term responses of coral reef microphytobenthic communities to inorganic nutrient loading. Limnology and Oceanography 44:1259-1267. | 1999 | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Downing, J. A., M. McClain, R. Twilley, J. M. Melack, J. Elser, N. N. Rabalais, W. M. Lewis Jr., R. E. Turner, J. Corredor, D. Soto, A. Yanez-Arancibia, J. A. Kopaska, and R. W. Howarth. 1999. The impact of accelerating land-use change on the N-cycle of tropical aquatic ecosystems: Current conditions and projected changes. Biogeochemistry 46:109-148. | 1999 | Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Erftemeijer, P. L. A. and J. Stapel. 1999. Primary production of deep-water Halophila ovalis meadows. Aquatic Botany 65:71-82. | 1999 | Cuba; Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., J.-P. Gattuso, and J. Jaubert. 1999. Effect of small variations in salinity on the rates of photosynthesis and respiration of the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata. Marine Ecology Progress Series 181:309-314. | 1999 | Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral | ||
| Ganzon-Fortes, E. T. 1999. Photosynthetic and respiratory responses of the agarophyte Gelidiella acerosa collected from tidepool, intertidal and subtidal habitats. Hydrobiologia 321-328. | 1999 | Philippines | Algae; Primary Production; Salinity | |
| Gardella, D. J. and P. J. Edmunds. 1999. The oxygen microenvironment adjacent to the tissue of the scleractinian Dichocoenia stokesii and its effects on symbiont metabolism. Marine Biology 135:289-295. | 1999 | Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Gattuso, J.-P., D. Allemand, and M. Frankignoulle. 1999. Photosynthesis and calcification at cellular, organismal and community levels in coral reefs: A review on interactions and control by carbonate chemistry. American Zoologist 39:160-183. | 1999 | Global | Review | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Frankignoulle, and S. V. Smith. 1999. Measurement of community metabolism and significance in the coral reef CO2 source-sink debate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96:13017-13022. | 1999 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Grottoli, A. G. and G. M. Wellington. 1999. Effect of light and zooplankton on skeletal δ13C values in the eastern Pacific corals Pavona clavus and Pavona gigantea. Coral Reefs 18:29-41. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hall, L. W., J. M. Giddings, K. R. Solomon, and R. Balcomb. 1999. An ecological risk assessment for the use of Irgarol 1051 as an algaecide for antifoulant paints. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 29:367-437. | 1999 | Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Boating Regulations; Chemical Use Regulations; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation |
| Jones, R. J. and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1999. Effects of cyanide on coral photosynthesis: Implications for identifying the cause of coral bleaching and for assessing the environmental effects of cyanide fishing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 177:83-91. | 1999 | Cuba | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Jones, R. J., T. Kildea, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1999. PAM chlorophyll fluorometry: A new in situ technique for stress assessment in scleractinian corals, used to examine the effects of cyanide from cyanide fishing. Marine Pollution Bulletin 38:864-874. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Hotel & Food Services; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Toxics; Zooxanthellae |
| Kaandorp, J. A. 1999. Morphological analysis of growth forms of branching marine sessile organisms along environmental gradients. Marine Biology 134:295-306. | 1999 | Model | Hydrocoral; Primary Production; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Kawahata, H., A. Suzuki, and K. Goto. 1999. Coral reefs as sources of atmospheric CO2 - Spatial distribution of PCO2 in Majuro Atoll. Geochemical Journal 33:295-303. | 1999 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Leclercq, N., J.-P. Gattuso, and J. Jaubert. 1999. Measurement of oxygen metabolism in open-top aquatic mesocosms: Application to a coral reef community. Marine Ecology Progress Series 177:299-304. | 1999 | Primary Production | ||
| McClanahan, T. R. 1999. Predation and the control of the sea urchin Echinometra viridis and fleshy algae in the patch reefs of Glovers Reef, Belize. Ecosystems 2:511-523. | 1999 | South & Central America; Belize; Madagascar; Caribbean | Algae; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Mioche, D. and P. Cuet. 1999. Carbon, carbonate and nutrient fluxes in summer on a fringing reef subject to anthropogenic pressure (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean) [Metabolisme du carbone, des carbonates et des sels nutritifs en saison chaude, sur un recif frangeant soumis a une pressio. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie de Sciences - Serie IIa: Sciences de la Terre et des Planetes 329:53-59. | 1999 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Ochieng, C. A. and P. L. A. Erftemeijer. 1999. Accumulation of seagrass beach cast along the Kenyan coast: A quantitative assessment. Aquatic Botany 65:221-238. | 1999 | Kenya | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Fleshy Macroalgae; Littering; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses |
| Ohde, S. and R. Van Woesik. 1999. Carbon dioxide flux and metabolic processes of a coral reef, Okinawa. Bulletin of Marine Science 65:559-576. | 1999 | Japan | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Porter, J. W., S. K. Lewis, and K. G. Porter. 1999. The effect of multiple stressors on the Florida Keys coral reef ecosystem: A landscape hypothesis and a physiological test. Limnology and Oceanography 44:941-949. | 1999 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seawater Flow |
| Ralph, P. J., R. Gademann, A. W. D. Larkum, and U. Schreiber. 1999. In situ underwater measurements of photosynthetic activity of coral zooxanthellae and other reef-dwelling dinoflagellate endosymbionts. Marine Ecology Progress Series 180:139-147. | 1999 | Germany | Anemones & Zooanthids; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Light; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Schaffelke, B. 1999. Short-term nutrient pulses as tools to assess responses of coral reef macroalgae to enhanced nutrient availability. Marine Ecology Progress Series 182:305-310. | 1999 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Strasser, R. J., M. Tsimilli-Michael, and M. Pecheux. 1999. Perpetual adaptation in a perpetually changing environment as a survival strategy of plants: A case study in foraminifers concerning coral reef bleaching. Photosynthetica 37:71-85. | 1999 | Global; Mauritius | CO2; Light; Primary Production | |
| Suzuki, A. and H. Kawahata. 1999. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in coral reef lagoon waters: Comparative study of atolls and barrier reefs in the Indo-Pacific oceans. Journal of Oceanography 55:731-745. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; Maldives; India; Pacific Ocean; Palau | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Swart, P. K., G. Healy, L. Greer, M. Lutz, A. Saied, D. Anderegg, R. E. Dodge, and D. Rudnick. 1999. The use of proxy chemical records in coral skeletons to ascertain past environmental conditions in Florida Bay. Estuaries 22:384-397. | 1999 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral |
| Tarasov, V. G., A. V. Gebruk, V. M. Shulkin, G. M. Kamenev, V. I. Fadeev, V. N. Kosmynin, V. V. Malakhov, D. A. Starynin, and A. I. Obzhirov. 1999. Effect of shallow-water hydrothermal venting on the biota of Matupi Harbour (Rabaul Caldera, New Britain Island, Papua New Guinea). Continental Shelf Research 19:79-116. | 1999 | Papua New Guinea; Britain | Model | Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges |
| Titlyanov, E. A., T. V. Titlyanova, J. Tsukahara, R. Van Woesik, and K. Yamazato. 1999. Experimental increases of zooxanthellae density in the coral Stylophora pistillata elucidate adaptive mechanisms for zooxanthellae regulation. Symbiosis 26:347-362. | 1999 | Plankton; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Adey, W. H. 1998. Coral reefs: algal structured and mediated ecosystems in shallow, turbulent, alkaline waters. Journal of Phycology 34:393-406. | 1998 | Algae; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Allemand, D., P. Furla, and S. Benazet-Tambutte. 1998. Mechanisms of carbon acquisition for endosymbiont photosynthesis in Anthozoa. Canadian Journal of Botany 76:925-941. | 1998 | Review; Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Beer, S., B. Vilenkin, A. Weil, M. Veste, L. Susel, and A. Eshel. 1998. Measuring photosynthetic rates in seagrasses by pulse amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorometry. Marine Ecology Progress Series 174:293-300. | 1998 | Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Beer, S., M. Ilan, A. Eshel, A. Weil, and I. Brickner. 1998. Use of pulse amplitude modulated (PAM) fluorometry for in situ measurements of photosynthesis in two Red Sea faviid corals. Marine Biology 131:607-612. | 1998 | Cuba; Germany | Field Study & Monitoring | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Behrenfeld, M. J., O. Prasil, Z. S. Kolber, M. Babin, and P. G. Falkoski. 1998. Compensatory changes in photosystem II electron turnover rates protect photosynthesis from photoinhibition. Photochemistry Research 58:259-268. | 1998 | Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Boucher, G., J. Clavier, C. Hily, and J.-P. Gattuso. 1998. Contribution of soft-bottoms to the community metabolism (primary production and calcification) of a barrier reef flat (Moorea, French Polynesia). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 225:269-283. | 1998 | Cuba | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Charpy, L., C. Charpy-Roubaud, and P. Buat. 1998. Excess primary production, calcification and nutrient fluxes of a patch reef (Tikehau atoll, French Polynesia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 173:139-147. | 1998 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Chisholm, J. R. M. and D. J. Barnes. 1998. Anomalies in coral reef community metabolism and their potential importance in the reef CO2 source-sink debate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 95:6566-6569. | 1998 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., D. Allemand, J.-P. Gattuso, J. Jaubert, and F. Rassoulzadegan. 1998. Microheterotrophy in the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata: Effects of light and ciliate density. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1639-1648. | 1998 | Cuba | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Furla, P., S. Benazet-Tambutte, J. Jaubert, and D. Allemand. 1998. Functional polarity of the tentacle of the sea anemone Anemonia viridis: Role in inorganic carbon acquisition. American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology 274. | 1998 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Frankignoulle, and R. Wollast. 1998. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 29:405-434. | 1998 | Global | Review | Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Hader, D.-P., H. D. Kumar, R. C. Smith, and R. C. Worrest. 1998. Effects on aquatic ecosystems. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 46:53-68. | 1998 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Climate; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Wetlands |
| Hansen, C. W., J. Lynch, and C.-O. Ottosen. 1998. Response to phosphorus availability during vegetative and reproductive growth of chrysanthemum: I. Whole-plant carbon dioxide exchange. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 123:215-222. | 1998 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Jaubert Jean, M., R. M. Chisholm John, MA NU EL Marchioretti, and FA BR IC E Priouzeau. 1998. Submersible respirometer designed to measure the metabolism of benthic marine plants and invertebrates. Pages 1754-1756 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1998 | Cuba | Fleshy Macroalgae; Housing; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | |
| Jones, R. J., O. Hoegh-Guldberg, A. W. D. Larkum, and U. Schreiber. 1998. Temperature-induced bleaching of corals begins with impairment of the CO2 fixation mechanism in zooxanthellae. Plant, Cell and Environment 21:1219-1230. | 1998 | Model | CO2; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Muscatine, L., C. Ferrier-Pages, A. Blackburn, R. D. Gates, G. Baghdasarian, and D. Allemand. 1998. Cell-specific density of symbiotic dinoflagellates in tropical anthozoans. Coral Reefs 17:329-337. | 1998 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Jamaica | Index or Indicator | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Substrate |
| Robertson, A. I., P. Dixon, and D. M. Alongi. 1998. The influence of fluvial discharge on pelagic production in the Gulf of Papua, Northern Coral Sea. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 46:319-331. | 1998 | Papua New Guinea | Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Schaffelke, B. and D. W. Klumpp. 1998. Short-term nutrient pulses enhance growth and photosynthesis of the coral reef macroalga Sargassum baccularia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 170:95-105. | 1998 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Small, Allegra, and Walter H. Adey. 1998. Reef corals, zooxanthellae & free- living algae: interactions that optimize calcification and primary production. Coral Reefs | 1998 | Algae; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Stambler, N. 1998. Effects of light intensity and ammonium enrichment on the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata and its zooxanthellae. Symbiosis 24:127-146. | 1998 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Teai, T., J. H. Drollet, J.-P. Bianchini, A. Cambon, and P. M. V. Martin. 1998. Occurrence of ultraviolet radiation-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids in coral mucus and whole corals of french polynesia. Marine and Freshwater Research 49:127-132. | 1998 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Van Rooij, J. M., J. J. Videler, and J. H. Bruggemann. 1998. High biomass and production but low energy transfer efficiency of Caribbean parrotfish: Implications for trophic models of coral reefs. Journal of Fish Biology 53:154-178. | 1998 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Model | Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Primary Production |
| Whitaker, F. F. and P. L. Smart. 1998. Hydrology, geochemistry and diagenesis of fracture blue holes, South Andros, Bahamas. Cave and Karst Science 25:75-82. | 1998 | Bahamas | Index or Indicator | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Discharges; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Williams, S. L. and R. C. Carpenter. 1998. Effects of unidirectional and oscillatory water flow on nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) in coral reef algal turfs, Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 226:293-316. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow |
| Withers, K. J. T., A. J. Grant, and R. Hinde. 1998. Effects of free amino acids on the isolated symbiotic algae of the coral Plesiastrea versipora (Lamarck): Absence of a host release factor response. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 120:599-607. | 1998 | Cuba | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Boglio, E. C. and J. S. Lucas. 1997. Impacts of ectoparasitic gastropods on growth, survival, and physiology of juvenile giant clams (Tridacna gigas), including a simulation model of mortality and reduced growth rate. Aquaculture 150:25-43. | 1997 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Bivalves; Primary Production |
| Chakraborty, S. and R. Ramesh. 1997. Environmental significance of carbon and oxygen isotope ratios of banded corals from Lakshadweep, India. Quaternary International 37:55-65. | 1997 | India | Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Cheshire, A. C., C. R. Wilkinson, S. Seddon, and G. Westphalen. 1997. Bathymetric and seasonal changes in photosynthesis and respiration of the phototrophic sponge Phyllospongia lamellosa in comparison with respiration by the heterotrophic sponge Ianthella basta on Davies reef, Great Barrier Reef. Marine and Freshwater Research 48:589-599. | 1997 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Falkowski, Paul G., and John A. Raven. 1997. Aquatic Photosynthesis Blackwell Science p257. | 1997 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Franklin, L. A. and A. W. D. Larkum. 1997. Multiple strategies for a high light existence in a tropical marine macroalga. Photosynthesis Research 53:149-159. | 1997 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Franklin, L. A. and R. M. Forster. 1997. The changing irradiance environment: consequences for marine macrophyte physiology, productivity and ecology. European Journal of Phycology 32:207-232. | 1997 | Algae; Light; Primary Production | ||
| Ganzon-Fortes, E. T. 1997. Influence of tidal location on morphology, photosynthesis and pigments of the agarophyte, Gelidiella acerosa, from Northern Philippines. Journal of Applied Phycology 9:525-532. | 1997 | Philippines | Aquaculture; Light; Primary Production | |
| Gattuso, J.-P., C. E. Payri, M. Pichon, B. Delesalle, and M. Frankignoulle. 1997. Primary production, calcification, and air-sea CO2 fluxes of a macroalgal-dominated coral reef community (Moorea, French Polynesia). Journal of Phycology 33:729-738. | 1997 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Coralline Algae; Primary Production | ||
| Helmuth, B. S. T., K. P. Sebens, and T. L. Daniel. 1997. Morphological variation in coral aggregations: Branch spacing and mass flux to coral tissues. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 209:233-259. | 1997 | South & Central America; Belize | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Light; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae |
| Juillet-Leclerc, A., J.-P. Gattuso, L. F. Montaggioni, and M. Pichon. 1997. Seasonal variation of primary productivity and skeletal δ13C and δ18O in the zooxanthellate scleractinian coral Acropora formosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 157:109-117. | 1997 | Australia | Model | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Lesser, M. P. 1997. Oxidative stress causes coral bleaching during exposure to elevated temperatures. Coral Reefs 16:187-192. | 1997 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Invertebrates; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Magnusson, G. 1997. Diurnal measurements of Fv/Fm used to improve productivity estimates in macroalgae. Marine Biology 130:203-208. | 1997 | Algae; Light; Primary Production | ||
| McConnaughey, T. A., J. Burdett, J. F. Whelan, and C. K. Paull. 1997. Carbon isotopes in biological carbonates: Respiration and photosynthesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 61:611-622. | 1997 | CO2; Fish; Primary Production; Snails & Conch | ||
| Moberg, F., M. Nystrom, N. Kautsky, M. Tedengren, and P. Jarayabhand. 1997. Effects of reduced salinity on the rates of photosynthesis and respiration in the hermatypic corals Porites lutea and Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 157:53-59. | 1997 | Thailand | Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral | |
| Nudds, J. and A. Day. 1997. The effects of clastic sedimentation on a fasciculate rugose coral from the Lower Carboniferous of northern England. Boletin - Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural: Seccion Geologica 91:93-97. | 1997 | England | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Ribera, G., M. Coloreu, C. Rodriguez-Prieto, and E. Ballesteros. 1997. Phytobenthic assemblages of Addaia Bay (Menorca, western Mediterranean): Composition and distribution. Botanica Marina 40:523-532. | 1997 | Algae; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fleshy Macroalgae; Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Ritchie, R. J., A. J. Grant, K. Eltringham, and R. Hinde. 1997. Clotrimazole, a model compound for the host release factor of the coral Plesiastrea versipora. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology 24:283-290. | 1997 | Cuba | Model | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Invertebrates; Primary Production |
| Romaine, S., E. Tambutte, D. Allemand, and J.-P. Gattuso. 1997. Photosynthesis, respiration and calcification of a zooxanthellate scleractinian coral under submerged and exposed conditions. Marine Biology 129:175-182. | 1997 | Index or Indicator | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Schlichter, D., H. Kampmann, and S. Conrady. 1997. Trophic potential and photoecology of endolithic algae living within coral skeletons. Marine Ecology 18:299-317. | 1997 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Schreiber, U., R. Gademann, P. J. Ralph, and A. W. D. Larkum. 1997. Assessment of photosynthetic performance of Prochloron in Lissoclinum patella in hospite by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Plant and Cell Physiology 38:945-951. | 1997 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Stapel, J., R. Manuntun, and M. A. Hemminga. 1997. Biomass loss and nutrient redistribution in an Indonesian Thalassia hemprichii seagrass bed following seasonal low tide exposure during daylight. Marine Ecology Progress Series 148:251-262. | 1997 | Indonesia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Surge, D. M., M. Savarese, J. R. Dodd, and K. C. Lohmann. 1997. Carbon isotopic evidence for photosynthesis in early Cambrian oceans. Geology 25:503-506. | 1997 | Australia | Primary Production | |
| Tun, K. P. P., A. C. Cheshire, and L. M. Chou. 1997. Twenty-four hour in situ monitoring of oxygen production and respiration of the colonial zoanthid Palythoa. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 44:33-43. | 1997 | Field Study & Monitoring | Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production | |
| Allison, N., A. W. Tudhope, and A. E. Fallick. 1996. Factors influencing the stable carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of Porites lutea coral skeletons from Phuket, South Thailand. Coral Reefs 15:43-57. | 1996 | Thailand | Model | Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Al-Moghrabi, S., C. Goiran, D. Allemand, N. Speziale, and J. Jaubert. 1996. Inorganic carbon uptake for photosynthesis by the symbiotic coral- dinoflagellate association: II. Mechanisms for bicarbonate uptake. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 199:227-248. | 1996 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Duarte, C. M. and J. Cebrian. 1996. The fate of marine autotrophic production. Limnology and Oceanography 41:1758-1766. | 1996 | Global | Algae; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Mangroves; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Ellison, A. M. and E. J. Farnsworth. 1996. Spatial and temporal variability in growth of Rhizophora mangle saplings on coral cays: Links with variation in insolation, herbivory, and local sedimentation rate. Journal of Ecology 84:717-731. | 1996 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mangroves; Primary Production; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Estes, J. A. 1996. The influence of large, mobile predators in aquatic food webs: examples from sea otters and kelp forests. Pages 65-72 Aquatic predators and their prey. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Columbia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invertebrates; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses | |
| Frankignoulle, M., J.-P. Gattuso, R. Biondo, I. Bourge, G. Copin-Montegut, and M. Pichon. 1996. Carbon fluxes in coral reefs. II. Eulerian study of inorganic carbon dynamics and measurement of air-sea CO2 exchanges. Marine Ecology Progress Series 145:123-132. | 1996 | Global; Australia | CO2; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Franklin, L. A., G. G. R. Seaton, C. E. Lovelock, and A. W. D. Larkum. 1996. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis on a coral reef. Plant, Cell and Environment 19:825-836. | 1996 | Australia | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Primary Production | |
| Furnas, M. J. and A. W. Mitchell. 1996. Pelagic primary production in the Coral and southern Solomon Seas. Marine and Freshwater Research 47:695-706. | 1996 | Australia | Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Pichon, B. Delesalle, C. Canon, and M. Frankignoulle. 1996. Carbon fluxes in coral reefs. I. Lagrangian measurement of community metabolism and resulting air-sea CO2 disequilibrium. Marine Ecology Progress Series 145:109-121. | 1996 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Primary Production |
| Goiran, C., S. Al-Moghrabi, D. Allemand, and J. Jaubert. 1996. Inorganic carbon uptake for photosynthesis by the symbiotic coral/dinoflagellate association: I. Photosynthetic performances of symbionts and dependence on sea water bicarbonate. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 199:207-225. | 1996 | CO2; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Harris, P. T., C. B. Pattiaratchi, J. B. Keene, R. W. Dalrymple, J. V. Gardner, E. K. Baker, A. R. Cole, D. Mitchell, P. Gibbs, and W. W. Schroeder. 1996. Late quaternary deltaic and carbonate sedimentation in the Gulf of Papua foreland basin: Response to sea-level change. Journal of Sedimentary Research 66:801-819. | 1996 | Australia | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Kitheka, J. U., B. O. Ohowa, B. M. Mwashote, W. S. Shimbira, J. M. Mwaluma, and J. M. Kazungu. 1996. Water circulation dynamics, water column nutrients and plankton productivity in a well-flushed tropical bay in Kenya. Journal of Sea Research 35:257-268. | 1996 | Kenya | Discharges; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Leletkin, V. A., E. A. Titlyanov, and Z. Dubinsky. 1996. Photosynthesis and respiration of the zooxanthellae in hermatypic corals habitated on different depths of the Gulf of Filat. Photosynthetica 32:481-490. | 1996 | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Lesser, M. P. 1996. Elevated temperatures and ultraviolet radiation cause oxidative stress and inhibit photosynthesis in symbiotic dinoflagellates. Limnology and Oceanography 41:271-283. | 1996 | Algae; Invertebrates; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Lesser, M. P. and S. Lewis. 1996. Action spectrum for the effects of UV radiation on photosynthesis in the hermatypic coral Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 134:171-177. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Marubini, F. and P. S. Davies. 1996. Nitrate increases zooxanthellae population density and reduces skeletogenesis in corals. Marine Biology 127:319-328. | 1996 | Cuba | Lab Study; Model | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Nacorda, H. M. E. and H. T. Yap. 1996. Macroinfaunal biomass and energy flow in a shallow reef flat of the northwestern Philippines. Hydrobiologia 341:37-49. | 1996 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment; Substrate |
| Opitz, S. 1996. Trophic Interactions in Caribbean Coral Reefs. International Center for Living Aquatic Resources Management, Manila, Philippines. | 1996 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Philippines; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Apex Fish Predators; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Piscivorous Fish; Primary Production; Sediment; Snails & Conch |
| Shashar, N., S. Kinane, P. L. Jokiel, and M. R. Patterson. 1996. Hydromechanical boundary layers over a coral reef. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 199:17-28. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Swart, P. K., J. J. Leder, A. M. Szmant, and R. E. Dodge. 1996. The origin of variations in the isotopic record of scleractinian corals: II. Carbon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 60:2871-2885. | 1996 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Warner, M. E., W. K. Fitt, and G. W. Schmidt. 1996. The effects of elevated temperature on the photosynthetic efficiency of zooxanthellae in hospite from four different species of reef coral: A novel approach. Plant, Cell and Environment 19:291-299. | 1996 | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Yamashiro, H. and M. Nishihira. 1996. Phototaxis in Fungiidae corals (scleractinia). Marine Biology 124:461-465. | 1996 | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Clavier, J., P. Chardy, and C. Chevillon. 1995. Sedimentation of particulate matter in the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia: Spatial and temporal patterns. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 40:281-294. | 1995 | New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Dullo, W.-C., M. Gektidis, S. Golubic, G. A. Heiss, H. Kampmann, W. Kiene, D. K. Kroll, M. L. Kuhrau, G. Radtke, J. G. Reijmer, G. B. Reinicke, D. Schlichter, H. Schuhmacher, and K. Vogel. 1995. Factors controlling holocene reef growth: An interdisciplinary approach. Facies 32:145-188. | 1995 | Global; Bahamas; Egypt; Sudan; Djibouti | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae |
| Fabricius, K. E. and D. W. Klumpp. 1995. Widespread mixotrophy in reef-inhabiting soft corals: the influence of depth, and colony expansion and contraction on photosynthesis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 125:195-204. | 1995 | Australia | Light; Octocoral; Primary Production | |
| Flajs, G., M. Vigener, H. Keupp, D. Meischner, F. Neuweiler, J. Paul, J. Reitner, K. Warnke, H. Weller, P. Dingle, C. Hensen, P. Schafer, P. Gautret, R. R. Leinfelder, H. Hussner, and B. Kaufmann. 1995. Mud mounds: A polygenetic spectrum of fine-grained carbonate buildups. Facies 32:Jan-69. | 1995 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Complex Habitat & Resources; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Gates, R. D., O. Hoegh-Guldberg, M. J. McFall-Ngai, K. Y. Bil, and L. Muscatine. 1995. Free amino acids exhibit anthozoan 'host factor' activity: They induce the release of photosynthate from symbiotic dinoflagellates in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92:7430-7434. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Pichon, and M. Frankignoulle. 1995. Biological control of air-sea CO2 fluxes: effect of photosynthetic and calcifying marine organisms and ecosystems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 129:307-312. | 1995 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | |
| Johnson, C., D. Klumpp, J. Field, R. Bradbury. 1995. Carbon flux on coral reefs: effects of large shifts in community structure. Marine Ecology Progress Series 126:123-143. | 1995 | Australia | Model | Algae; Primary Production; Seastars; Zooxanthellae |
| Kayanne, H., A. Suzuki, and H. Saito. 1995. Diurnal changes in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in coral reef water. Science 269:214-216. | 1995 | Japan | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production | |
| Kuhl, M., Y. Cohen, T. Dalsgaard, B. B. Jorgensen, and N. P. Revsbech. 1995. Microenvironment and photosynthesis of zooxanthellae in scleractinian corals studied with microsensors for O2, pH and light. Marine Ecology Progress Series 117:159-177. | 1995 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| McClanahan, T. R. 1995. A coral reef ecosystem-fisheries model: Impacts of fishing intensity and catch selection on reef structure and processes. Ecological Modelling 80:19-Jan. | 1995 | Model | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Shoreline Protection; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Shick, J. M., M. P. Lesser, W. C. Dunlap, W. R. Stochaj, B. E. Chalker, and J. W. Won. 1995. Depth-dependent responses to solar ultraviolet radiation and oxidative stress in the zooxanthellate coral Acropora microphthalma. Marine Biology 122:41-51. | 1995 | Australia | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Suzuki, A., T. Nakamori, and H. Kayanne. 1995. The mechanism of production enhancement in coral reef carbonate systems: model and empirical results. Sedimentary Geology 99:259-280. | 1995 | Model | CO2; Primary Production | |
| Telesnicki, G. j. and W. M. Goldberg. 1995. Effects of Turbidity on the Photosynthesis and Respiration of Two South Florida Reef Coral Species. Bulletin of Marine Science 57:527-539. | 1995 | Florida | Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Van Tussenbroek, B. I. 1995. Thalassia testudinum leaf dynamics in a Mexican caribbean coral reef lagoon. Marine Biology 122:33-40. | 1995 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Discharges; Mangroves; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Yamashiro, H. 1995. The effects of HEBP, an inhibitor of mineral deposition, upon photosynthesis and calcification in the scleractinian coral, Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 191:57-63. | 1995 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Arsalane, W., B. Rousseau, and J. Duval. 1994. Influence of the pool size of the xanthophyll cycle on the effects of light stress in a diatom: competition between photoprotection and photoinhibition. Photochemistry and Photobiology 60:237-243. | 1994 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Branden, K. L., D. A. Pollard, and H. A. Reimers. 1994. A review of recent artificial reef developments in Australia. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:982-994. | 1994 | Australia | Review | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Primary Production; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hansen, J. A. and G. A. Skilleter. 1994. Effects of the gastropod Rhinoclavis aspera (Linnaeus, 1758) on microbial biomass and productivity in coral-reef-flat sediments. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 45:569-584. | 1994 | Australia | Algae; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Lobban, C. S. and P. J. Harrison. 1994. Seaweed ecology and physiology. Seaweed ecology and physiology. | 1994 | Review | Algae; Aquaculture; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses | |
| Burns, K. A., M. G. Ehrhardt, B. L. Howes, and C. D. Taylor. 1993. Subtidal benthic community respiration and production near the heavily oiled Gulf coast of Saudi Arabia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 27:199-205. | 1993 | Saudi Arabia | Algae; Light; Petroleum Spills; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Delesalle, B., M. Pichon, M. Frankignoulle, and J. P. Gattuso. 1993. Effects of a cyclone on coral reef phytoplankton biomass, primary production and composition (Moorea Island, French Polynesia). Journal of Plankton Research 15:1413-1423. | 1993 | Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Erftemeijer, P. L. A., R. Osinga, and A. E. Mars. 1993. Primary production of seagrass beds in South Sulawesi (Indonesia): a comparison of habitats, methods and species. Aquatic Botany 46:67-90. | 1993 | Indonesia | Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Pichon, B. Delesalle, and M. Frankignoulle. 1993. Community metabolism and air-sea CO2 fluxes in a coral reef ecosystem (Moorea, French Polynesia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 96:259-267. | 1993 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Hanelt, D., K. Huppertz, and W. Nultsch. 1993. Daily course of photosynthesis and photoinhibition in marine macroalgae investigated in the laboratory and field. Marine Ecology Progress Series 97:31-37. | 1993 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Harland, A. D., J. C. Navarro, P. Spencer Davies, and L. M. Fixter. 1993. Lipids of some Caribbean and Red Sea corals: total lipid, wax esters, triglycerides and fatty acids. Marine Biology 117:113-117. | 1993 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Kaiser, P., D. Schlichter, and H. W. Fricke. 1993. Influence of light on algal symbionts of the deep water coral Leptoseris fragilis. Marine Biology 117:45-52. | 1993 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kinzie III, R. A. 1993. Effects of ambient levels of solar ultraviolet radiation on zooxanthellae and photosynthesis of the reef coral Montipora verrucosa. Marine Biology 116:319-327. | 1993 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Quinn, T. M., F. W. Taylor, and T. J. Crowley. 1993. A 173 year stable isotope record from a tropical south pacific coral 0. Quaternary Science Reviews 12:407-418. | 1993 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Vanuatu | Climate; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Rougerie, F. and B. Wauthy. 1993. The endo-upwelling concept: from geothermal convection to reef construction. Coral Reefs 12:19-30. | 1993 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity |
| Bell, P. R. F. 1992. Eutrophication and coral reefs - Some examples in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Water Research 26:553-568. | 1992 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Seastars; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bosscher, H. and W. Schlager. 1992. Computer simulation of reef growth. Sedimentology 39:503-512. | 1992 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Australia; Belize; Mexico | Model | Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Dykens, J. A., J. M. Shick, C. Benoit, G. R. Buettner, and G. W. Winston. 1992. Oxygen radical production in the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima and its endosymbiotic algae. Journal of Experimental Biology 168:219-241. | 1992 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Franklin, L. A., G. Levavasseur, C. B. Osmond, W. J. Henley, and J. Ramus. 1992. Two components of onset and recovery during photoinhibition of Ulva rotundata. Planta 186:399-408. | 1992 | Primary Production | ||
| Frederiksen, R., A. Jensen, and H. Westerberg. 1992. The distribution of the scleractinian coral Lophelia pertusa around the Faroe Islands and the relation to internal tidal mixing. Sarsia, Bergen 77:157-171. | 1992 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hansen, J. A., D. W. Klumpp, D. M. Alongi, P. K. Dayton, and M. J. Riddle. 1992. Detrital pathways in a coral reef lagoon - II. Detritus deposition, benthic microbial biomass and production. Marine Biology 113:363-372. | 1992 | Australia | Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Iglesias-Prieto, R., J. L. Matta, W. A. Robins, and R. K. Trench. 1992. Photosynthetic response to elevated temperature in the symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium microadriaticum in culture. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 89:10302-10305. | 1992 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler. 1992. Results of the USSR-USA expedition in marine biology to the Seychelles Islands. Atoll Research Bulletin | 1992 | Indian Ocean; Seychelles; India | Algae; Invertebrates; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Patterson, M. R. 1992. A chemical engineering view of cnidarian symbioses. American Zoologist 32:566-582. | 1992 | Model | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Shashar, N. 1992. Endolithic algae within corals - Life in an extreme environment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 163:277-286. | 1992 | Algae; Light; Primary Production | ||
| [No author name available]. 1991. The natural release of amino acids from the symbiotic coral Heteroxenia fuscescens (Ehrb.) as a function of photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 150:83-90. | 1991 | Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Cheshire, A. C. and C. R. Wilkinson. 1991. Modelling the photosynthetic production by sponges on Davies Reef, Great Barrier Reef. Marine Biology 109:13-18. | 1991 | Australia | Model | Light; Primary Production; Sponges |
| Chisholm, J. R. M. and J.-P. Gattuso. 1991. Validation of the alkalinity anomaly technique for investigating calcification and photosynthesis in coral reef communities. Limnology and Oceanography 36:1232-1239. | 1991 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Davies, P. S. 1991. Effect of daylight variations on the energy budgets of shallow-water corals. Marine Biology 108:137-144. | 1991 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae |
| Hopkinson Jr, C. S., R. D. Fallon, B.-O. Jansson, and J. P. Schubauer. 1991. Community metabolism and nutrient cycling at Gray's Reef, a hard bottom habitat in the Georgia Bight. Marine Ecology Progress Series 73:105-120. | 1991 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Lewis, J. B. and J. J. Boers. 1991. Patchiness and composition of coral reef demersal zooplankton. Journal of Plankton Research 13:1273-1289. | 1991 | Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Littler, M. M. 1991. Deep-water rhodolith distribution, productivity, and growth history at sites of formation and subsequent degradation. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 150:163-182. | 1991 | Bahamas; Cuba | Algae; Boring Sponges; Calcareous Macroalgae; Light; Marine Worms; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and E. A. Titlyanov. 1991. Comparisons of N- and P-limited productivity between high granitic islands versus low carbonate atolls in the Seychelles Archipelago: a test of the relative-dominance paradigm. Coral Reefs 10:199-209. | 1991 | Seychelles | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Patterson, M. R., K. P. Sebens, and R. R. Olson. 1991. In situ measurements of flow effects on primary production and dark respiration in reef corals. Limnology and Oceanography 36:936-948. | 1991 | Primary Production | ||
| Rinkevich, B., Z. Wolodarsky, and Y. Loya. 1991. Coral-crab association: a compact domain of a multilevel trophic system. Hydrobiologia 279-284. | 1991 | Cuba | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Schlichter, D. and H. W. Fricke. 1991. Mechanisms of amplification of photosynthetically active radiation in the symbiotic deep-water coral Leptoseris fragilis. Hydrobiologia 389-394. | 1991 | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Schlichter, D., and G. Liebzit. 1991. The natural release of amino acids from the symbiotic coral Heteroxenia fuscescens (Ehrb) as a function of photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 150:83-90. | 1991 | Primary Production | ||
| Sorokin, Y. I. 1991. Biomass, metabolic rates and feeding of some common reef zoantharians and octocorals. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 42:729-741. | 1991 | Octocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Sorokin, YU .I . 1991. Parameters of productivity and metabolism of coral reef ecosystems off central Vietnam. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 33:259-280. | 1991 | Vietnam | Algae; Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Titlyanov, E. A. 1991. The stable level of coral primary production in a wide light range. Hydrobiologia 383-387. | 1991 | Indian Ocean; India; China | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Alongi, D. M. 1990. Effect of mangrove detrital outwelling on nutrient regeneration and oxygen fluxes in coastal sediments of the central Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 31:581-598. | 1990 | Australia; Cuba | Lab Study | Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Carpenter, R. C. 1990. Mass mortality of Diadema antillarum. I. Long-term effects on sea urchin population-dynamics and coral reef algal communities. Marine Biology 104:67-77. | 1990 | US Virgin Islands | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Chisholm, J. R. M. 1990. A novel in situ respirometer for investigating photosynthesis and calcification in crustose coralline algae. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 141:15-29. | 1990 | Australia | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Coralline Algae; Housing; Primary Production | |
| Coffroth, M. A. 1990. Mucous sheet formation on poritid corals: An evaluation of coral mucus as a nutrient source on reefs. Marine Biology 105:39-49. | 1990 | Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Panama | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Davidson, R. J. 1990. Pre-burial adsorption model for the genesis of gold in the Witwatersrand. Journal of The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 90:53-57. | 1990 | Model | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| Dubinsky, Z., N. Stambler, M. Ben-Zion, L. R. McCloskey, L. Muscatine, and P. G. Falkowski. 1990. The effect of external nutrient resources on the optical properties and photosynthetic efficiency of Stylophora pistillata. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 239:231-246. | 1990 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Furnas, M. J., A. W. Mitchell, M. Gilmartin, and N. Revelante. 1990. Phytoplankton biomass and primary production in semi-enclosed reef lagoons of the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 9:10-Jan. | 1990 | Australia | Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Gerard, V. A. 1990. Ecotypic differentiation in the kelp Laminaria saccharina: Phase-specific adaptation in a complex life cycle. Marine Biology 107:519-528. | 1990 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Light; Primary Production | |
| Hatcher, B. G. 1990. Coral reef primary productivity: A hierarchy of pattern and process. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 5:149-155. | 1990 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Lesser, M. P. and W. R. Stochaj. 1990. Photoadaptation and protection against active forms of oxygen in the symbiotic procaryote Prochloron sp. and its ascidian host. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 56:1530-1535. | 1990 | Australia | Light; Primary Production | |
| Lesser, M. P., W. R. Stochaj, D. W. Tapley, and J. M. Shick. 1990. Bleaching in coral reef anthozoans: effects of irradiance, ultraviolet radiation, and temperature on the activities of protective enzymes against active oxygen. Coral Reefs 8:225-232. | 1990 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Panama; Caribbean | Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Salinity; Zooxanthellae | |
| Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler. 1990. Productivity and nutrient relationships in psammophytic versus epilithic forms of Bryopsidales (Chlorophyta): comparisons based on a short-term physiological assay. Hydrobiologia 49-55. | 1990 | Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Mazda, Y., Y. Sato, S. Sawamoto, H. Yokochi, and E. Wolanski. 1990. Links between physical, chemical and biological processes in Bashita-minato, a mangrove swamp in Japan. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 31:817-833. | 1990 | Japan | Algae; Light; Mangroves; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Roman, M. R., M. J. Furnas, and M. M. Mullin. 1990. Zooplankton abundance and grazing at Davies Reef, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Biology 105:73-82. | 1990 | Australia | Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Williams, S. L. and R. C. Carpenter. 1990. Photosynthesis/photon flux density relationships among components of coral reef algal turfs. Journal of Phycology 26:36-40. | 1990 | US Virgin Islands | Primary Production; Sea Urchins | |
| Beiersdorf, H. 1989. Provenance and accumulation rates of Pliocene and Quaternary sediments from the western Coral Sea. Geologische Rundschau 78:987-998. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Edmunds, P. J. and P. S. Davies. 1989. An energy budget for Porites porites (Scleractinia), growing in a stressed environment. Coral Reefs 8:37-43. | 1989 | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Fang, L.-s., Y.-w.J. Chen, and C.-s. Chen. 1989. Why does the white tip of stony coral grow so fast without zooxanthellae? Marine Biology 103:359-363. | 1989 | Taiwan | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gladfelter, E. H., G. Michel, and A. Sanfelici. 1989. Metabolic gradients along a branch of the reef coral Acropora palmata. Bulletin of Marine Science 44:1166-1173. | 1989 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Klumpp, D. W. and A. D. McKinnon. 1989. Temporal and spatial patterns in primary production of a coral-reef epilithic algal community. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 131:22-Jan. | 1989 | Australia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coralline Algae; Light; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish; Turf Algae | |
| Le Borgne, R., J. Blanchot, and L. Charpy. 1989. Zooplankton of tikehau atoll (Tuamotu archipelago) and its relationship to particulate matter. Marine Biology 102:341-353. | 1989 | Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Lesser, M. P. and J. M. Shick. 1989. Effects of irradiance and ultraviolet radiation on photoadaptation in the zooxanthellae of Aiptasia pallida: primary production, photoinhibition, and enzymic defenses against oxygen toxicity. Marine Biology 102:243-255. | 1989 | Bermuda | Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Lucas, J. S., W. J. Nash, C. M. Crawford, and R. D. Braley. 1989. Environmental influences on growth and survival during the ocean-nursery rearing of giant clams, Tridacna gigas (L.). Aquaculture 80:45-61. | 1989 | Australia | Light; Primary Production | |
| McConnaughey, T. 1989. 13C and 18O isotopic disequilibrium in biological carbonates: I. Patterns. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 53:151-162. | 1989 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Muscatine, L., J. W. Porter, and I. R. Kaplan. 1989. Resource partitioning by reef corals as determined from stable isotope composition - I. δ13C of zooxanthellae and animal tissue vs depth. Marine Biology 100:185-193. | 1989 | Jamaica | Algae; CO2; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Nguyen Tac, AN. 1989. Energy flow in the tropical marine shelf ecosystems of Vietnam. Biologiya Morya (Vladivostok) 2:15-Sep. | 1989 | China; Vietnam | Fish; Mangroves; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Polunin, N. V. C. and D. W. Klumpp. 1989. Ecological correlates of foraging periodicity in herbivorous reef fishes of the Coral Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 126:20-Jan. | 1989 | Algae; Fish; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish; Turf Algae | ||
| Porter, J. W., W. K. Fitt, H. J. Spero, C. S. Rogers, and M. W. White. 1989. Bleaching in reef corals: physiological and stable isotopic responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 86:9342-9346. | 1989 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rinkevich, B. 1989. The contribution of photosynthetic products to coral reproduction. Marine Biology 101:259-263. | 1989 | Field Study & Monitoring | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Weis, V. M., G. J. Smith, and L. Muscatine. 1989. A \CO2 supply\" mechanism in zooxanthellate cnidarians: role of carbonic anhydrase". Marine Biology 100:195-202. | 1989 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; CO2; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Abdel-Salam, H.A., J.W. Porter. 1988. Physiological effects of sediment rejection on photosynthesis and respiration in three Caribbean reef corals. Pages 285-9 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Bethoux, J. P. 1988. Red Sea geochemical budgets and exchanges with the Indian Ocean. Marine Chemistry 24:83-92. | 1988 | Global; Indian Ocean; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Dennison, W. C. and D. J. Barnes. 1988. Effect of water motion on coral photosynthesis and calcification. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 115:67-77. | 1988 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Gladfelter, W. B. 1988. Marine organisms and communities. | 1988 | Echinoderms; Fish; Molluscs; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Hackney, J. M. and P. Sze. 1988. Photorespiration and productivity rates of a coral reef algal turf assemblage. Marine Biology 98:483-492. | 1988 | Algae; CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Hatcher, B. G. 1988. Coral reef primary productivity: A beggar's banquet. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 3:106-111. | 1988 | Review | Agriculture; Primary Production | |
| Hay, M. E., V. J. Paul, S. M. Lewis, K. Gustafson, J. Tucker, and R. N. Trindell. 1988. Can tropical seaweeds reduce herbivory by growing at night? Diel patterns of growth, nitrogen content, herbivory, and chemical versus morphological defenses. Oecologia 75:233-245. | 1988 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Payri, C. E. 1988. Halimeda contribution to organic and inorganic production in a Tahitian reef system. Coral Reefs 6:251-262. | 1988 | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production | |
| Polunin, N. V. C. 1988. Efficient uptake of algal production by a single resident herbivorous fish on the reef. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 123:61-76. | 1988 | Papua New Guinea | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Fish; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Farrant, P. A., M. A. Borowitzka, R. Hinde, and R. J. King. 1987. Nutrition of the temperate Australian soft coral Capnella gaboensis - I. Photosynthesis and carbon fixation. Marine Biology 95:565-574. | 1987 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Octocoral; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Farrant, P. A., M. A. Borowitzka, R. Hinde, and R. J. King. 1987. Nutrition of the temperate Australian soft coral Capnella gaboensis - II. The role of zooxanthellae and feeding. Marine Biology 95:575-581. | 1987 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Fricke, H. W., E. Vareschi, and D. Schlichter. 1987. Photoecology of the coral Leptoseris fragilis in the Red Sea twilight zone (an experimental study by submersible). Oecologia 73:371-381. | 1987 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Furnas, M. J. and A. W. Mitchell. 1987. Photosynthetic characteristics of Coral Sea picoplankton (<2 μm size fraction). Biological Oceanography 5:163-182. | 1987 | Australia | Light; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Furnas, M. J. and A. W. Mitchell. 1987. Phytoplankton dynamics in the central Great Barrier Reef-II. Primary production. Continental Shelf Research 7:1049-1062. | 1987 | Australia | Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Kinzie III, R. A. and T. Hunter. 1987. Effect of light quality on photosynthesis of the reef coral Montipora verrucosa. Marine Biology 94:95-109. | 1987 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Light; Primary Production | |
| Koop, K. and A. W. D. Larkum. 1987. Deposition of organic material in a coral reef lagoon, One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 25:9-Jan. | 1987 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Turf Algae | |
| Kyle, D. 1987. The biochemical basis for photoinhibition fo photosystem II. Pages 197-226 Topics in photosynthesis, volume 9. Elsevier, Amsterdam. | 1987 | Primary Production | ||
| Muller-Parker, G. 1987. Seasonal variation in light-shade adaptation of natural populations of the symbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia pulchella (Carlgren, 1943) in Hawaii. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 112:165-183. | 1987 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Anemones & Zooanthids; Light; Mangroves; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Tomascik, T. and F. Sander. 1987. Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals - III. Reproduction of the reef-building coral Porites porites. Marine Biology 94:77-94. | 1987 | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wyman, K. D., Z. Dubinsky, J. W. Porter, and P. G. Falkowski. 1987. Light absorption and utilization among hermatypic corals: a study in Jamaica, West Indies. Marine Biology 96:283-292. | 1987 | Jamaica | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Fricke, H. W. and B. Knauer. 1986. Diversity and spatial pattern of coral communities in the Red Sea upper twilight zone. Oecologia 71:29-37. | 1986 | Java | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Herndl, G. J. and B. Velimirov. 1986. Microheterotrophic utilization of mucus released by the Mediterranean coral Cladocora cespitosa. Marine Biology 90:363-369. | 1986 | Cuba; Iran | Lab Study | Microorganisms; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Jokiel, P. L. and J. I. Morrissey. 1986. Influence of size on primary production in the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis and the macroalga Acanthophora spicifera. Marine Biology 91:15-26. | 1986 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Schlichter, D., H. W. Fricke, and W. Weber. 1986. Light harvesting by wavelength transformation in a symbiotic coral of the Red Sea twilight zone. Marine Biology 91:403-407. | 1986 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Vareschi, E. and H. Fricke. 1986. Light responses of a scleractinian coral (Plerogyra sinuosa). Marine Biology 90:395-402. | 1986 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Adey, W. H. and R. S. Steneck. 1985. Highly productive eastern caribbean reefs: synergistic effects of biological, chemical, physical, and geological factors. Pages 163-187 | 1985 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Turf Algae; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Carpenter, R. C. 1985. Relationships between primary production and irradiance in coral reef algal communities. Limnology and Oceanography 30:784-793. | 1985 | Algae; Light; Primary Production | ||
| Delesalle, B. 1985. Environmental survey of Mataiva Atoll, Tuamotu Archipelago, French Polynesia. Atoll Research Bulletin | 1985 | Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Knap Anthony, H., C. Wyers Sheila, E. Dodge Richard, D. Sleeter Thomas, R. Frith Harold, S. RO BE RT SO N Smith, and B. Cook Clayton. 1985. Effects Of Chemically And Physically Dispersed Oil On The Brain Coral Diploria Strigosa (Dana) - A Summary Review. Pages 547-551 in [No source information available]. | 1985 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, S. M. Blair, and J. N. Norris. 1985. Deepest known plant life discovered on an uncharted seamount. Science 227:57-59. | 1985 | Light; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Moriarty, D. J. W., P. C. Pollard, and W. G. Hunt. 1985. Temporal and spatial variation in bacterial production in the water column over a coral reef. Marine Biology 85:285-292. | 1985 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Moriarty, D. J. W., P. C. Pollard, W. G. Hunt, C. M. Moriarty, and T. J. Wassenberg. 1985. Productivity of bacteria and microalgae and the effect of grazing by holothurians in sediments on a coral reef flat. Marine Biology 85:293-300. | 1985 | Australia | Algae; Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Pastorok, R. A., G. R. Bilyard. 1985. Effects of sewage pollution on coral-reef communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 21:175-189. | 1985 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Walton, RA YM ON D, W. MA RT IN Williams, P. Wang Ming, and A. Roesner Larry. 1985. Coral Reef Modeling: Key Largo Case Study. Pages 2420-2438 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1985 | Florida | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Atkinson, M. J. and R. W. Grigg. 1984. Model of a coral reef ecosystem - II. Gross and net benthic primary production at French Frigate Shoals, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 3:13-22. | 1984 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Primary Production; Sediment |
| Barnes, D. J. and M. J. Devereux. 1984. Productivity and calcification on a coral reef: A survey using pH and oxygen electrode techniques. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 79:213-231. | 1984 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production | ||
| Chalker, B. E., T. Cox, and W. C. Dunlap. 1984. Seasonal changes in primary production and photoadaptation by the reef-building coral Acropora granulosa on the Great Barrier Reef. Pages 73-87 in Marine phytoplankton and productivity. Proc. symposium, Taormina, 1983. | 1984 | Australia | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Davies, P. S. 1984. The role of zooxanthellae in the nutritional energy requirements of Pocillopora eydouxi. Coral Reefs 2:181-186. | 1984 | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Dubinsky, Z., P. G. Falkowski, J. W. Porter, and L. Muscatine. 1984. Absorption and utilization of radiant energy by light-and shade- adapted colonies of the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata. Page 1227 in Proceedings of the Royal Society. | 1984 | CO2; Light; Primary Production | ||
| Grigg, R. W., J. J. Polovina, and M. J. Atkinson. 1984. Model of a coral reef ecosystem - III. Resource limitation, community regulation, fisheries yield and resource management. Coral Reefs 3:23-27. | 1984 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Porter, J. W., L. Muscatine, Z. Dubinsky, and P. G. Falkowski. 1984. Primary production and photoadaptation in light- and shade-adapted colonies of the symbiotic coral, Stylophora pistillata. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B 222:161-80. | 1984 | Primary Production | ||
| Rayner, R. F. and E. A. Drew. 1984. Nutrient concentrations and primary productivity at the Peros Banhos and Salomon atolls in the Chagos Archipelago. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 18:121-132. | 1984 | Chagos Archipelago | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Rinkevich, B. and Y. Loya. 1984. Coral illumination through an optic glass-fiber: incorporation of 14C photosynthates. Marine Biology 80:15-Jul. | 1984 | Cuba | CO2; Primary Production | |
| Szmant-Froelich, A. and M. E. Q. Pilson. 1984. Effects of feeding frequency and symbiosis with zooxanthellae on nitrogen metabolism and respiration of the coral Astrangia danae. Marine Biology 81:153-162. | 1984 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Theil, H. and H. Weikert. 1984. Biological oceanography of the red oceanic system. Deep Sea Research Part A, Oceanographic Research Papers 31:829-831. | 1984 | Indian Ocean; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; India; Sudan | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Vandermeulen John, H. and S. Gilfillan Edward. 1984. Petroleum Pollution, Corals And Mangroves. Marine Technology Society Journal 18:62-72. | 1984 | Global | Lab Study | Mangroves; Primary Production |
| Burris, J.E., J.W. Porter, and W.A. Laing. 1983. Effects of carbon dioxide concentration on coral photosynthesis. Marine Biology 75:113-16. | 1983 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Chalker, B. E., W. C. Dunlap, and J. K. Oliver. 1983. Bathymetric adaptations of reef-building corals at davies reef, great barrier reef, Australia. II. Light saturation curves for photosynthesis and respiration. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 73:37-56. | 1983 | Australia | Lab Study | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Cook, C. B. and A. H. Knap. 1983. Effects of crude oil and chemical dispersant on photosynthesis in the brain coral Diploria strigosa. Marine Biology 78:21-27. | 1983 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Entsch, B., R. G. Sim, and B. G. Hatcher. 1983. Indications from photosynthetic components that iron is a limiting nutrient in primary producers on coral reefs. Marine Biology 73:17-30. | 1983 | Australia | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae |
| Jacques, T. G., N. Marshall, and M. E. Q. Pilson. 1983. Experimental ecology of the temperate scleractinian coral Astrangia danae - II. Effect of temperature, light intensity and symbiosis with zooxanthellae on metabolic rate and calcification. Marine Biology 76:135-148. | 1983 | Cuba | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Light; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Murphy, R. C. and J. N. Kremer. 1983. Community metabolism of Clipperton Lagoon, a coral atoll in the eastern Pacific. Bulletin of Marine Science 33:152-164. | 1983 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Primary Production | |
| Sheppard, C. R. C., Z. D. Dinesen, and E. A. Drew. 1983. Taxonomy, ecology and physiology of the geographically restricted scleractinian species Ctenella chagius Matthai. Bulletin of Marine Science 33:905-918. | 1983 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; Chagos Archipelago; India | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Suchanek, T. H. 1983. Control of seagrass communities and sediment distribution by Callianassa ( Crustacea, Thalassinidea) bioturbation. Journal of Marine Research 41:281-298. | 1983 | US Virgin Islands | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Swart, P. K. 1983. Carbon and oxygen isotope fractionation in scleractinian corals: a review. Earth Science Reviews 19:51-80. | 1983 | Review; Model | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Tytler, E. M., and P. S. Davies. 1983. A method of isolating clean and viable zooxanthellae by density gradient centrifugation. Limnology and Oceanography 28:1266-1268. | 1983 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Webb, L. and J. C. Coll. 1983. Effects of alcyonarian coral terpenes on scleractinian coral photosynthesis and respiration. Toxicon 21:485-488. | 1983 | Octocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Wilkinson, C. R. 1983. Net primary productivity in coral reef sponges. Science 219:410-412. | 1983 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Barnes, D. J. 1982. Light response curve for calcification in the staghorn coral, Acropora acuminata. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 73:41-45. | 1982 | Cuba | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Bay, D. 1982. (In situ study of the metabolism of three infralittoral benthic communities of the Aqaba Gulf- Red Sea, Halophila stipulacea). [Etude in situ du metabolisme de trois communautes benthiques infralittorales du Golfe d'Aqaba-Mer Rouge.]. Comptes Rendus des Seances - Academie des Sciences, Serie III 294:463-466. | 1982 | Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Clayton Jr., W. S. and H. R. Lasker. 1982. Effects of light and dark treatments on feeding by the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 63:269-279. | 1982 | Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Cummings, C. E. and H. B. McCarty. 1982. Stable carbon isotope ratios in Astrangia danae: evidence for algal modification of carbon pools used in calcification. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 46:1125-1129. | 1982 | Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Epstein, S. A. and G. M. Friedman. 1982. Processes controlling precipitation of carbonate cement and dissolution of silica in reef and near-reef settings. Sedimentary Geology 33:157-171. | 1982 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Hawkins, C. M. and J. B. Lewis. 1982. Benthic primary production on a fringing coral reef in barbados, West Indies. Aquatic Botany 12:355-363. | 1982 | Algae; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Hawkins, C. M. and J. B. Lewis. 1982. Ecological energetics of the tropical sea urchin Diadema antillarum Philippi in Barbados, West Indies. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 15:645-669. | 1982 | Algae; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Sediment | ||
| Ikeda, T., J. H. Carleton, A. W. Mitchell, and P. Dixon. 1982. Ammonia and phosphate excretion by zooplankton from the inshore waters of the Great Barrier Reef. II. Their in situ contributions to nutrient regeneration. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33:683-698. | 1982 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Saks, N. M. 1982. Primary production and release of assimilated carbon by Chlamydomonas provasolii in culture. Marine Biology 70:205-208. | 1982 | Algae; Primary Production | ||
| Chalker, B. E. 1981. Simulating light-saturation curves for photosynthesis and calcification by reef-building corals. Marine Biology 63:135-141. | 1981 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Rate functions | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Cherbadzhi, I. I. and M. V. Propp. 1981. Comparative characteristics of production indices of corals and periphyton on artificial and natural substrates. Soviet Journal of Marine Biology 7:238-242. | 1981 | Index or Indicator | Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Substrate | |
| Fankboner, P. V. and R. G. B. Reid. 1981. Mass expulsion of zooxanthellae by heat-stressed reef corals: a source of food for giant clams? Experientia 37:251-252. | 1981 | Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Leletkin, V. A., and V. I. Zvalinsky. 1981. Photosynthesis of coral zooxanthellae from different depths. Pages 33-7 in Proceedings of the 4th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1981 | Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Osmond, C. B. 1981. Photorespiration and photoinhibition. Biochimica et. Biophysica Acta 639:77-98. | 1981 | Primary Production | ||
| Propp, M. V. 1981. Release and uptake of ammonium, nitrate, and orthophosphate by some corals. Soviet Journal of Marine Biology 7:198-204. | 1981 | Octocoral; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Rogers, C. S. and N. H. Salesky. 1981. Productivity of Acropora palmata (Lamarck), macroscopic algae, and algal turf from Tague Bay Reef, St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 49:179-187. | 1981 | US Virgin Islands | Algae; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Sander, F. 1981. A preliminary assessment of the main causative mechanisms of the \island mass\" effect of Barbados". Marine Biology 64:199-205. | 1981 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | ||
| Smith, S. V. and P. Kroopnick. 1981. Carbon-13 isotopic fractionation as a measure of aquatic metabolism. Nature 294:252-253. | 1981 | CO2; Primary Production | ||
| Vooren, C. M. 1981. Photosynthetic rates of benthic algae from the deep coral reef of Curacao. Aquatic Botany 10:143-159. | 1981 | Cuba | Lab Study | Algae; Primary Production; Substrate |
| Collins, N. 1980. Population ecology of Ephydra cinerea Jones (Diptera: Ephydridae), the only benthic metazoan of the Great Salt Lake, U.S.A. Hydrobiologia 68:99-112. | 1980 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Special Use Permitting; Substrate | ||
| Jacques, T. G. and M. E. Q. Pilson. 1980. Experimental ecology of the temperate scleractinian coral Astrangia danae I. Partition of respiration, photosynthesis and calcification between host and symbionts. Marine Biology 60:167-178. | 1980 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Titlyanov, E.A., Marina G. Shaposhnikova, and V.I. Zvalinskii. 1980. Photosynthesis and adaptation of corals to irradiance 1: Contents and native state of photosynthetic pigments in symbiotic. Photosynthetica 14:413-21. | 1980 | Light; Primary Production | ||
| Kevin, K. M. and R. C. L. Hudson. 1979. The role of zooxanthellae in the hermatypic coral Plesiastrea urvillei (Milne Edwards and Haime) From cold waters. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 36:157-170. | 1979 | Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Levanon-Spanier, I., E. Padan, and Z. Reiss. 1979. Primary production in a desert-enclosed sea- the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba), Red Sea. Deep Sea Research Part A, Oceanographic Research Papers 26:673-685. | 1979 | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Rogers, C. S. 1979. The effect of shading on coral reef structure and function. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 41:269-288. | 1979 | Puerto Rico | Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Primary Production; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Smith, D. F., N. C. Bulleid, R. Campbell, H. W. Higgins, F. Rowe, D. J. Tranter, and H. Tranter. 1979. Marine food-web analysis: An experimental study of demersal zooplankton using isotopically labelled prey species. Marine Biology 54:49-59. | 1979 | Cuba | GIS & Maps | Marine Worms; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Chalker, B. E. and D. L. Taylor. 1978. Rhythmic variations in calcification and photosynthesis associated with the coral Acropora cervicornis (Lamarck). Pages 179-189 in Proceedings of the Royal Society of London - Biological Sciences. | 1978 | Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Erez, J. 1978. Vital effect on stable-isotope composition seen in foraminifera and coral skeletons. Nature 273:199-202. | 1978 | Algae; CO2; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Coles, S. L. and P. L. Jokiel. 1977. Effects of temperature on photosynthesis and respiration in hermatypic corals. Marine Biology 43:209-216. | 1977 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Marshall Islands | Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Gladfelter, Elizabeth H., and Rosemary K. Monahan. 1977. Primary production and calcium carbonate deposition rates in Acropora palmata from different positions in the reef. Pages 389-94 in Proceedings of the 3rd Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1977 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Mergner, H. and A. Svoboda. 1977. Productivity and seasonal changes in selected reef areas in the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea). Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 30:383-399. | 1977 | Algae; Echinoderms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Owen, R. M. 1977. An assessment of the environmental impact of mining on the continental shelf. Marine Mining 1:-85. | 1977 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Mining; Mining Policies; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Por, F. D., I. Dor, and A. Amir. 1977. The mangal of Sinai: Limits of an ecosystem. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 30:295-314. | 1977 | Model | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Schmitz, K. and B. P. Kremer. 1977. Carbon fixation and analysis of assimilates in a coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Marine Biology 42:305-313. | 1977 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Scott, B. D. and H. R. Jitts. 1977. Photosynthesis of phytoplankton and zooxanthellae on a coral reef. Marine Biology 41:307-315. | 1977 | Australia | Light; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Sebens, K. P. and K. DeRiemer. 1977. Diel cycles of expansion and contraction in coral reef anthozoans. Marine Biology 43:247-256. | 1977 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Sournia, A. 1976. Oxygen metabolism of a fringing reef in French polynesia. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 28:401-410. | 1976 | Algae; Primary Production | ||
| Wethey, D. S. and J. W. Porter. 1976. Sun and shade differences in productivity of reef corals. Nature 262:281-282. | 1976 | Lab Study | Algae; Energy Policy & Development; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Barnes, D. J. and D. L. Taylor. 1973. In situ studies of calcification and photosynthetic carbon fixation in the coral Montastrea annularis. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 24:284-291. | 1973 | CO2; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Drew, E. A. 1973. The biology and physiology of alga-invertebrate symbioses. III. In situ measurements of photosynthesis and calcification in some hermatypic corals. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 13:165-179. | 1973 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Hydrocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Taylor, D. L. 1973. Symbiotic pathways of carbon in coral reef ecosystems - Present status and future prospects. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 24:276-283. | 1973 | Primary Production | ||
| Wells, J. M., A. H. Wells, and J. G. VanDerwalker. 1973. In situ studies of metabolism in benthic reef communities. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 24:78-81. | 1973 | Florida | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gundersen, K. and P. Bienfang. 1972. Thermal Pollution: Use Of Deep, Cold, Nutrient Rich Sea Water For Power Plant Cooling And Subsequent Aquaculture In Hawaii [Marine Pollution And Sea Life]. Pages 513-516 FISHING NEWS. | 1972 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Light; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Vandermeulen, J. H., N. D. Davis, and L. Muscatine. 1972. The effect of inhibitors of photosynthesis on zooxanthellae in corals and other marine invertebrates. Marine Biology 16:185-191. | 1972 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Qasim, S. Z. and P. M. A. Bhattathiri. 1971. Primary production of a seagrass bed on Kavaratti Atoll (Laccadives). Hydrobiologia 38:29-38. | 1971 | Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Thompson, G. and H. D. Livingston. 1970. Strontium and uranium concentrations in aragonite precipitated by some modern corals. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 8:439-442. | 1970 | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Peres, J. M. and J. Picard. 1969. Reflexions sur la structure trophique des edifices recifaux. Marine Biology 3:227-232. | 1969 | Madagascar | Algae; Fish; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Wainwright, S. A. 1967. Diurnal activity of hermatypic gorgonians. Nature 216:1041. | 1967 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Lab Study | Octocoral; Primary Production |
| Barnes, D.J., and B.E. Chalker. Calcification and photosynthesis in reef-building corals and algae. Pages 109-32 in Z, editor. Coral Reefs: Ecosystems of the World Vol 25. | Algae; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |||
| Becker, E. L., E. E. Cordes, S. A. Macko, and C. R. Fisher. Importance of seep primary production to Lophelia pertusa and associated fauna in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers | South & Central America; Mexico | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Snails & Conch | ||
| Erickson, K. L., S. A. Macko, and C. L. Van Dover. Evidence for a chemoautotrophically based food web at inactive hydrothermal vents (Manus Basin). Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography | US Pacific & Hawaii; Papua New Guinea | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Fujimura, H., T. Higuchi, K. Shiroma, T. Arakaki, A. M. Hamdun, Y. Nakano, and T. Oomori. Continuous-flow complete-mixing system for assessing the effects of environmental factors on colony-level coral metabolism. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods | Model | Primary Production; Stony Coral |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Streamside Management Areas | There are often surface waters, such as streams and lakes, within forestry areas that require special protection. This management option involves establishing and maintaining management areas (35 to 50 feet) around these surface waters to buffer against changes in temperature, increases in sediments and nutrients, and to provide bank stability. Canopy species in these areas also provide woody debris needed for instream channel structure and aquatic species habitat. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Monitor & Research: Research and Monitor Wetlands | This management option involves monitoring and research of mangroves, both for biotic and abiotic factors. Some biotic factors include disease, species, invasive species, abundance, age and leaf litter. Important abiotic factors include sedimentation rates, types and causes of turbidity, and soil chemistry. The activity would document changes to the extent of mangrove vegetation by using historical aerial photography and other records. Wetland nutrient and contaminant processing productivity depends on maintaining a balance and not exceeding thresholds. There remain many unknowns in wetland restoration as to optimal capacity and how to achieve this. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Primary Production; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Stormwater BMPs: Sustained Reservoir Minimum Release of Minimum Baseflow to Sustain Aquatic Habitat | In some regions, even high intensity rivers (e.g. Rio Loco, Puerto Rico) are seasonal, drying for long enough to kill aquatic vegetation. Creating a constant baseflow would help sustain aquatic life and ultimately help to process nutrients. High intensity rivers are already prone to extreme channel erosion from the high flow rates, this erosion is even greater without any benthic biota to hold sediment on the river bottom. Restricting the release of reservoir water to that required to maintain aquatic biota would reduce the intensity of flow, stabilize the river bottom, create habitat and naturally process nutrients that could potentially contribute to eutrophication out on the coral reef. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Algae; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of natural structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. These structures are typically characterized as retention ponds and incorporate natural vegetation such as grass. These ponds may be dry, or may drain into nearby wetlands. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Treating Effluent Water Through Wetlands | Additional treatment of sewage is often a necessary management option because secondary treatment alone leaves 20,000 times more nutrients in the water than the safe limit for corals. High concentrations of nutrients in the water leads to eutrophication, and coral reefs are more sensitive to nutrient enrichment than any other coastal system. Wetlands are extremely successful at reducing nitrogen levels in water. Using natural wetlands or "living machines" to perform this task can actually be more cost effective than further sewage treatment. Each successive wetland treatment cell of the series can provide incredible levels of denitrification, and thus protect corals from nutrient enrichment. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2003. Waste Treatment Lagoon. CODE 359. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Starting slower releases for longer durations from high-intensity rivers in coastal watershed and other methods of reducing sediment transport | Slower releases with longer durations would be an advantage to short, intense releases. This is because current short, high intensity releases from rivers that are in the coastal watershed (like Rio Loco into Lagos Loco and Lucchetti) contributes to additional channel erosion and increase of suspending sediments in the water. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Light; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Pollution Control, 62-204 Florida Administrative Code (1996). | 62-204.100 Purpose and Scope.
(1) This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods.
(2) In addition, this chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassifiable with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have been adopted; further designates certain attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as air quality maintenance areas for particular pollutants; classifies all areas of the state as Class I, Class II, or Class III for determining which set of prevention of significant deterioration (PSD) increments apply; and designates all attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as one or more PSD areas for determining which pollutant-specific PSD baseline dates apply. This chapter also sets forth procedures for redesignating and reclassifying areas as above.
(3) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to identify the Florida State Implementation Plan (SIP) required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51; to set forth the public notice and hearing requirements that the Department will adhere to for making SIP revisions; and to set forth the definitions, criteria, and procedures that the Department will use to review a federal agency�s general conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart W; and to adopt by reference an interagency memorandum of agreement that the Department will comply with to review any transportation conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart T. The provisions to 40 C.F.R. 51.853 require that a federal agency make a general conformity determination for any federal agency action in a nonattainment or maintenance area, to ensure that such action is consistent with the SIP and that such federal conformity determination be reviewed by the affected state. The provisions of 40 C.F.R. 51.394 require that a transportation conformity determination be made for the adoption, acceptance, approval, or support of certain transportation plans, transportation improvement programs, and transportation projects in nonattainment and maintenance areas for transportation-related criteria pollutants to ensure that such actions are consistent with the SIP.
(4) Finally, this chapter adopts and incorporates by reference federal air pollution control regulations which are referenced in whole or in part throughout the Department�s air pollution control rules. Application to Coral Reefs:By reducing emmissions to air, particularly carbon dioxide, the pH of ocean waters will not be reduced and that is a direct benefit to coral reefs, since a reduction in pH is believed to be detrimental to corals. Legislative Actions:The Chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassified with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have benn adopted. Comments:This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Use Regulations; CO2; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |