ReefLink Database

Invertivorous Fish
Invertivorous fish are fish that primarily feed on invertebrates.
CMap
CMap Description
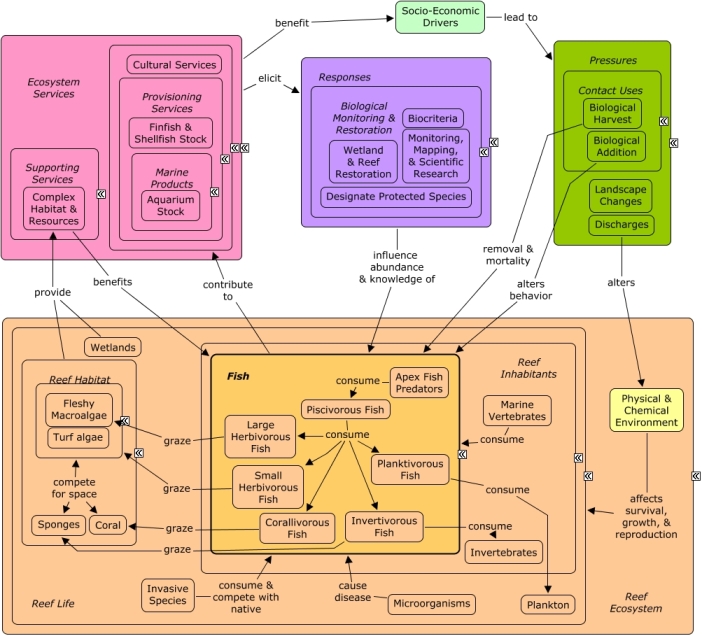
The fish found on coral reefs are essential for coastal communities and extremely important in the wider world. Invertivorous fish, such as goatfish, filefish, squirrelfish and rays, consume benthic invertebrates. A few invertivorous fish species are important as aquarium stock and all species are important to cultural services of coral reefs. Invertivorous fish are supported by the complex habitat & resources provided by the reef ecosystem. Wetlands provide nursery habitat that supports the fish. Invertivorous fish provide a valuable link in the trophic food web as they are consumed by piscivorous fish, apex fish predators, and marine vertebrates. Like all fish species, invertivorous fish are stressed and killed by competing invasive species, disease-causing microorganisms, and disturbances of the physical & chemical environment. Socio-economic drivers lead to the removal & mortality of invertivorous fish through harvesting pressures. Biological monitoring, mapping, research, and restoration is paramount to ensure the flow of services from reef fish.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ang, TZ; Manica, A. 2011. Effect of the Presence of Subordinates on Dominant Female Behaviour and Fitness in Hierarchies of the Dwarf Angelfish Centropyge bicolor. Ethology 117:1111-1119. | 2011 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Funding & Incentives; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Hedouin, L; Metian, M; Gates, RD. 2011. Ecotoxicological approach for assessing the contamination of a Hawaiian coral reef ecosystem (Honolua Bay, Maui) by metals and a metalloid. Marine Environmental Research 71:149-161. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Ilves, KL; Kellogg, LL; Quattrini, AM; Chaplin, GW; Hertler, H; Lundberg, JG. 2011. Assessing 50-Year Change In Bahamian Reef Fish Assemblages: Evidence For Community Response To Recent Disturbance? Bulletin of Marine Science 87:567-588. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Bahamas; India; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral | |
| Konow, N; Bellwood, DR. 2011. Evolution of High Trophic Diversity Based on Limited Functional Disparity in the Feeding Apparatus of Marine Angelfishes (f. Pomacanthidae). PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Corallivorous Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Kuwamura, T; Suzuki, S; Kadota, T. 2011. Reversed sex change by widowed males in polygynous and protogynous fishes: female removal experiments in the field. Naturwissenschaften 98:1041-1048. | 2011 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish |
| McClanahan, TR. 2011. Coral reef fish communities in management systems with unregulated fishing and small fisheries closures compared with lightly fished reefs - Maldives vs. Kenya. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 21:186-198. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; Kenya; Maldives; India | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Strubin, C; Steinegger, M; Bshary, R. 2011. On Group Living and Collaborative Hunting in the Yellow Saddle Goatfish (Parupeneus cyclostomus). Ethology 117:961-969. | 2011 | Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Alva-Campbell, Y., S. R. Floeter, D. R. Robertson, D. R. Bellwood, and G. Bernardi. 2010. Molecular phylogenetics and evolution of Holacanthus angelfishes (Pomacanthidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 56:456-461. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Panama | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Cleveland, D. W. and K. L. Lavalli. 2010. Factors influencing the establishment of dominance hierarchies of the grey triggerfish Balistes capriscus. Current Zoology 56:18-35. | 2010 | Index or Indicator | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Garcia-Sais, J. R. 2010. Reef habitats and associated sessile-benthic and fish assemblages across a euphotic-mesophotic depth gradient in Isla Desecheo, Puerto Rico. Coral Reefs 29:277-288. | 2010 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Sponges; Stony Coral |
| Meyer, C. G., Y. P. Papastamatiou, and T. B. Clark. 2010. Differential movement patterns and site fidelity among trophic groups of reef fishes in a Hawaiian marine protected area. Marine Biology 157:1499-1511. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Munoz, R. C., M. L. Burton, K. J. Brennan, and R. O. Parker. 2010. Reproduction, Habitat Utilization, And Movements Of Hogfish (Lachnolaimus Maximus) In The Florida Keys, Usa: Comparisons From Fished Versus Unfished Habitats. Bulletin of Marine Science 86:93-116. | 2010 | Florida; Cuba | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Stephen, J. A. and P. J. Harris. 2010. Commercial catch composition with discard and immediate release mortality proportions off the southeastern coast of the United States. Fisheries Research 103:18-24. | 2010 | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Bray, R. A., T. H. Cribb, and J. L. Justine. 2009. New observations on the genus Hypocreadium Ozaki, 1936 (Digenea: Lepocreadiidae) in the Indo-West Pacific region, including the description of one new species. Zootaxa 22-40. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Palau; New Caledonia | Invertivorous Fish | |
| Feeley, M. W., O. J. Luiz, and N. Zurcher. 2009. Colour morph of a probable queen angelfish Holacanthus ciliaris from Dry Tortugas, Florida. Journal of Fish Biology 74:2415-2421. | 2009 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Gallo, V., M. S. S. D. Carvalho, and A. A. Souto. 2009. A possible occurrence of Diodontidae (Teleostei, Tetraodontiformes) in the Upper Cretaceous of the Paraiba Basin, northeastern Brazil. Cretaceous Research 30:599-604. | 2009 | Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Headley, M., H. A. Oxenford, M. S. Peterson, and P. Fanning. 2009. Size related variability in the summer diet of the blackfin tuna (Thunnus atlanticus Lesson, 1831) from Tobago, the Lesser Antilles. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 25:669-675. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Tobago | Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Octopus & Squid; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Jayewardene, D., M. J. Donahue, and C. Birkeland. 2009. Effects of frequent fish predation on corals in Hawaii. Coral Reefs 8-Jan. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral |
| Kolasinski, J., P. Frouin, A. Sallon, K. Rogers, H. J. Bruggemann, and M. Potier. 2009. Feeding ecology and ontogenetic dietary shift of yellowstripe goatfish Mulloidichthys flavolineatus (Mullidae) at Reunion Island, SW Indian Ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series 386:181-195. | 2009 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Worms |
| Krajewski, J. P. 2009. How do follower reef fishes find nuclear fishes? Environmental Biology of Fishes 86:379-387. | 2009 | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Moreno, X. G., L. A. Abitia, A. Favila, F. J. Gutierrez, and D. S. Palacios. 2009. Trophic ecology of the fish Arothron meleagris (Tetraodontiformes: Tetraodontidae) from Los Frailes reef, Southern Baja California, Mexico. Revista de Biologia Tropical 57:113-123. | 2009 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral |
| Redman, R. A. and S. T. Szedlmayer. 2009. The effects of epibenthic communities on reef fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Fisheries Management and Ecology 16:360-367. | 2009 | South & Central America; Cuba; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Seki, S., M. Kohda, G. Takamoto, K. Karino, Y. Nakashima, and T. Kuwamura. 2009. Female defense polygyny in the territorial triggerfish Sufflamen chrysopterum. Journal of Ethology 27:215-220. | 2009 | Japan | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Sonnenholzner, J. I., L. B. Ladah, and K. D. Lafferty. 2009. Cascading effects of fishing on Galapagos rocky reef communities: Reanalysis using corrected data. Marine Ecology Progress Series 375:209-218. | 2009 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Urchins | ||
| Bartholomew, A., J. A. Bohnsack, S. G. Smith, J. S. Ault, D. E. Harper, and D. B. McClellan. 2008. Influence of marine reserve size and boundary length on the initial response of exploited reef fishes in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary, USA. Landscape Ecology 23:55-65. | 2008 | Florida | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Courtney, A. J., M. J. Campbell, D. P. Roy, M. L. Tonks, K. E. Chilcott, and P. M. Kyne. 2008. Round scallops and square meshes: A comparison of four codend types on the catch rates of target species and by-catch in the Queensland (Australia) saucer scallop (Amusium balloti) trawl fishery. Marine and Freshwater Research 59:849-864. | 2008 | Australia | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Bivalves; Echinoderms; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Sponges | |
| Dornburg, A., F. Santini, and M. E. Alfaro. 2008. The influence of model averaging on clade posteriors: An example using the triggerfishes (Family Balistidae). Systematic Biology 57:905-919. | 2008 | Model | Invertivorous Fish | |
| Feitosa, C. V., B. P. Ferreira, and M. Elisabeth De Araujo. 2008. A rapid new method for assessing sustainability of ornamental fish by-catch from coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 59:1092-1100. | 2008 | Index or Indicator | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Huebert, K. B. 2008. Barokinesis and depth regulation by pelagic coral reef fish larvae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 367:261-269. | 2008 | Florida | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Konow, N., D. R. Bellwood, P. C. Wainwright, and A. M. Kerr. 2008. Evolution of novel jaw joints promote trophic diversity in coral reef fishes. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 93:545-555. | 2008 | GIS & Maps | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Menard, A., K. Turgeon, and D. L. Kramer. 2008. Selection of diurnal refuges by the nocturnal squirrelfish, Holocentrus rufus. Environmental Biology of Fishes 82:59-70. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish |
| Rudershausen, P. J., E. H. Williams, J. A. Buckel, J. C. Potts, and C. S. Manooch III. 2008. Comparison of reef fish catch per unit effort and total mortality between the 1970s and 2005-2006 in Onslow Bay, North Carolina. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 137:1389-1405. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Slattery, M. and V. J. Paul. 2008. Indirect effects of bleaching on predator deterrence in the tropical Pacific soft coral Sinularia maxima. Marine Ecology Progress Series 354:169-179. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octocoral; Sunscreen Use; Zooxanthellae |
| Van Nguyen, L. and H. Kim Phan. 2008. Distribution and factors influencing on structure of reef fish communities in Nha Trang Bay Marine Protected Area, South-Central Vietnam. Environmental Biology of Fishes 82:309-324. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; China; Vietnam | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Fish; Hydrocoral; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Physical Variables; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Venmathi Maran, B. A., S. Ohtsuka, and G. A. Boxshall. 2008. A new species of Anuretes Heller, 1865 (Copepoda: Caligidae) from the yellowbanded sweetlips Plectorhinchus lineatus (Haemulidae) off New Caledonia. Systematic Parasitology 70:35-40. | 2008 | New Caledonia | Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Weiss, H. M., E. Lozano-Alvarez, and P. Briones-Fourzan. 2008. Circadian shelter occupancy patterns and predator-prey interactions of juvenile Caribbean spiny lobsters in a reef lagoon. Marine Biology 153:953-963. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Octopus & Squid | |
| Affonso, P. R. A. M. and P. M. Galetti Jr. 2007. Genetic diversity of three ornamental reef fishes (Families Pomacanthidae and Chaetodontidae) from the Brazilian coast. Brazilian Journal of Biology 67:925-933. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Alfaro, M. E., F. Santini, and C. D. Brock. 2007. Do reefs drive diversification in marine teleosts? Evidence from the pufferfish and their allies (order tetraodontiformes). Evolution 61:2104-2126. | 2007 | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Brown-Saracino, J., P. Peckol, H. Allen Curran, and M. L. Robbart. 2007. Spatial variation in sea urchins, fish predators, and bioerosion rates on coral reefs of Belize. Coral Reefs 26:71-78. | 2007 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins | |
| Burgess, S. C., M. J. Kingsford, and K. P Black. 2007. Influence of tidal eddies and wind on the distribution of presettlement fishes around One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 341:233-242. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invertivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Cardona, L., M. Sales, and D. Lopez. 2007. Changes in fish abundance do not cascade to sea urchins and erect algae in one of the most oligotrophic parts of the Mediterranean. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 72:273-282. | 2007 | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Colvocoresses, J. and A. Acosta. 2007. A large-scale field comparison of strip transect and stationary point count methods for conducting length-based underwater visual surveys of reef fish populations. Fisheries Research 85:130-141. | 2007 | Florida; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hawkins, J. P., C. M. Roberts, F. R. Gell, and C. Dytham. 2007. Effects of trap fishing on reef fish communities. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 17:111-132. | 2007 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Jamaica; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting |
| Hobbs, J.-P.A., A. J. Frisch, J. Hender, and J. J. Gilligan. 2007. New records of Angelfishes (Pomacanthidae) and butterflyfishes (Chaetodontidae) from Christmas and Cocos (Keeling) Islands, Indian Ocean. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia 90:107-109. | 2007 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Corallivorous Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Kulbicki, M. 2007. Biogeography of reef fishes of the French Territories in the South Pacific. Cybium 31:275-288. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Fiji; Tonga; Cook Islands | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Mantyka, C. S. and D. R. Bellwood. 2007. Macroalgal grazing selectivity among herbivorous coral reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 352:177-185. | 2007 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| McBride, R. S. and A. K. Richardson. 2007. Evidence of size-selective fishing mortality from an age and growth study of hogfish (Labridae: Lachnolaimus maximus), a hermaphroditic reef fish. Bulletin of Marine Science 80:401-417. | 2007 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| McBride, R. S. and M. R. Johnson. 2007. Sexual development and reproductive seasonality of hogfish (Labridae: Lachnolaimus maximus), an hermaphroditic reef fish. Journal of Fish Biology 71:1270-1292. | 2007 | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Meyer, C. G. 2007. The impacts of spear and other recreational fishers on a small permanent Marine Protected Area and adjacent pulse fished area. Fisheries Research 84:301-307. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ross, P. M., S. F. Thrush, J. C. Montgomery, J. W. Walker, and D. M. Parsons. 2007. Habitat complexity and predation risk determine juvenile snapper (Pagrus auratus) and goatfish (Upeneichthys lineatus) behaviour and distribution. Marine and Freshwater Research 58:1144-1151. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Sediment | |
| Sazima, C., J. P. Krajewski, R. M. Bonaldo, and I. Sazima. 2007. Nuclear-follower foraging associations of reef fishes and other animals at an oceanic archipelago. Environmental Biology of Fishes 80:351-361. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Sonnenholzner, J. I., L. B. Ladah, and K. D. Lafferty. 2007. Cascading effects of fishing on Galapagos rocky reef communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 343:77-85. | 2007 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Urchins | ||
| Taquet, M., G. Sancho, L. Dagorn, J.-C. Gaertner, D. Itano, R. Aumeeruddy, B. Wendling, and C. Peignon. 2007. Characterizing fish communities associated with drifting fish aggregating devices (FADs) in the Western Indian Ocean using underwater visual surveys. Aquatic Living Resource 20:331-341. | 2007 | Indian Ocean; Seychelles; Reunion; India | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Bowen, B. W., A. L. Bass, A. Muss, J. Carlin, and D. R. Robertson. 2006. Phylogeography of two Atlantic squirrelfishes (family Holocentridae): Exploring links between pelagic larval duration and population connectivity. Marine Biology 149:899-913. | 2006 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Briones-Fourzan, P., M. Perez-Ortiz, and E. Lozano-Alvarez. 2006. Defense mechanisms and antipredator behavior in two sympatric species of spiny lobsters, Panulirus argus and P. guttatus. Marine Biology 149:227-239. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Frisch, A. J. 2006. Are juvenile coral-trouts (Plectropomus) mimics of poisonous pufferfishes (Canthigaster) on coral reefs? Marine Ecology 27:247-252. | 2006 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Galetti Jr., P. M., W. F. Molina, P. R. A. M. Affonso, and C. T. Aguilar. 2006. Assessing genetic diversity of Brazilian reef fishes by chromosomal and DNA markers. Genetica 126:161-177. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Pacific Ocean | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Kavanagh, K. D. and J. E. Olney. 2006. Ecological correlates of population density and behavior in the circumtropical black triggerfish Melichthys niger (Balistidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 76:387-398. | 2006 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Belize; Johnston Atoll | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Krajewski, J. P. and R. M. Bonaldo. 2006. Plankton-picking by the goatfish Pseudupeneus maculatus (Mullidae), a specialized bottom forager. Journal of Fish Biology 68:925-930. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Plankton | |
| Sazima, C., J. P. Krajewski, R. M. Bonaldo, and P. R. Guimaraes Jr. 2006. The goatfish Pseudupeneus maculatus and its follower fishes at an oceanic island in the tropical west Atlantic. Journal of Fish Biology 69:883-891. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Ben-David, J. and J. P. Kritzer. 2005. Early life history and settlement of the slender filefish, Monacanthus tuckeri (Monacanthidae), at Calabash Caye, Turneffe Atoll, Belize. Environmental Biology of Fishes 73:275-282. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2005. The importance of the marine ornamental reef fish trade in the wider Caribbean. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:127-137. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Maldives; Sri Lanka; India; Japan; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Caribbean; Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| De Mello Affonso, P. R. A. and P. M. Galetti Jr. 2005. Chromosomal diversification of reef fishes from genus Centropyge(Perciformes, Pomacanthidae). Genetica 123:227-233. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Pacific Ocean; Philippines | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Dominici-Arosemena, A. and M. Wolff. 2005. Reef fish community structure in Bocas del Toro (Caribbean, Panama): Gradients in habitat complexity and exposure. Caribbean Journal of Science 41:613-637. | 2005 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Plankton; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Fisher, R. 2005. Swimming speeds of larval coral reef fishes: Impacts on self-recruitment and dispersal. Marine Ecology Progress Series 285:223-232. | 2005 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Konow, N. and D. R. Bellwood. 2005. Prey-capture in Pomacanthus semicirculatus (Teleostei, Pomacanthidae): Functional implications of intramandibular joints in marine angelfishes. Journal of Experimental Biology 208:1421-1433. | 2005 | Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Schumacher, B. D. and J. D. Parrish. 2005. Spatial relationships between an introduced snapper and native goatfishes on Hawaiian reefs. Biological Invasions 7:925-933. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Stimson, J. 2005. Archipelago-wide episodic recruitment of the file fish Pervagor spilosoma in the Hawaiian Islands as revealed in long-term records. Environmental Biology of Fishes 72:19-31. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Watters, M. R. 2005. Tropical marine neurotoxins: Venoms to drugs. Seminars in Neurology 25:278-289. | 2005 | Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Invertivorous Fish; Microorganisms; Octopus & Squid; Snails & Conch | |
| Westneat, M. W. and M. E. Alfaro. 2005. Phylogenetic relationships and evolutionary history of the reef fish family Labridae. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 36:370-390. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Model | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Arias-Gonzalez, J. E., R. Galzin, and M. Harmelin-Vivien. 2004. Spatial, ontogenetic, and temporal variation in the feeding habits of the squirrelfish Sargocentron microstoma on reefs in Moorea, French Polynesia. Bulletin of Marine Science 75:473-480. | 2004 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish | ||
| Heemstra, E., P. Heemstra, M. Smale, T. Hooper, and D. Pelicier. 2004. Preliminary checklist of coastal fishes from the Mauritian island of Rodrigues. Journal of Natural History 38:3315-3344. | 2004 | Indian Ocean; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius; India | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Mateo, I. and W. J. Tobias. 2004. Survey of nearshore fish communities on tropical backreef lagoons on the southeastern coast of St. Croix. Caribbean Journal of Science 40:327-342. | 2004 | US Virgin Islands | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Seagrasses; Skeletal Coral | |
| Rezai, H. and A. Savari. 2004. Observation on reef fishes in the coastal waters off some Iranian Islands in the Persian Gulf. Zoology in the Middle East 31:67-75. | 2004 | Middle East; Iran | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Caley, M. J. and D. Schluter. 2003. Predators favour mimicry in a tropical reef fish. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 270:667-672. | 2003 | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Chiappone, M., H. Dienes, D. W. Swanson, and S. L. Miller. 2003. Density and Gorgonian host-occupation patterns by Flamingo Tongue snails (Cyphoma gibbosum) in the Florida keys. Caribbean Journal of Science 39:116-127. | 2003 | Florida | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octocoral; Snails & Conch | |
| Garpe, K. C. and M. C. Ohman. 2003. Coral and fish distribution patterns in Mafia Island Marine Park, Tanzania: Fish-habitat interactions. Hydrobiologia 498:191-211. | 2003 | Indian Ocean; Tanzania; India | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Stanley, D. R. and C. A. Wilson. 2003. Seasonal and spatial variation in the biomass and size frequency distribution of fish associated with oil and gas platforms in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Pages 123-153 in American Fisheries Society Symposium. | 2003 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda; Mexico | Apex Fish Predators; Artificial Habitat; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Rigs; Piscivorous Fish; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Surman, C. A. and R. D. Wooller. 2003. Comparative foraging ecology of five sympatric terns at a sub-tropical island in the eastern Indian Ocean. Journal of Zoology 259:219-230. | 2003 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Birds; Octopus & Squid | |
| Takamoto, G., S. Seki, Y. Nakashima, K. Karino, and T. Kuwamura. 2003. Protogynous sex change in the haremic triggerfish Sufflamen chrysopterus (Tetraodontiformes). Ichthyological Research 50:281-283. | 2003 | Japan | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Vargas-Angel, B. 2003. Coral community structure off the Pacific coast of Colombia: Onshore vs offshore coral reefs. Atoll Research Bulletin 21-Jan. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Complex Habitat & Resources; Discharges; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Turf Algae | |
| Bean, K., G. P. Jones, and M. J. Caley. 2002. Relationships among distribution, abundance and microhabitat specialisation in a guild of coral reef triggerfish (family Balistidae). Marine Ecology Progress Series 233:263-272. | 2002 | Papua New Guinea | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| De M Affonso, P. R. A., W. Guedes, E. Pauls, and P. M. Galetti Jr. 2002. Close karyotypical relationship between two species of marine angelfishes from South Atlantic: Pomacanthus arcuatus and P. paru (Perciformes, Pomacanthidae). Caryologia 55:323-329. | 2002 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Holbrook, S. J. and R. J. Schmitt. 2002. Competition for shelter space causes density-dependent predation mortality in damselfishes. Ecology 83:2855-2868. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Plankton; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Jiddawi, N. S. and M. C. Ohman. 2002. Marine fisheries in Tanzania. Ambio 31:518-527. | 2002 | Tanzania | Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Small Boats; Small Herbivorous Fish; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Kokita, T. 2002. The role of female behavior in maintaining monogamy of a coral-reef filefish. Ethology 108:157-168. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| McClanahan, T. R., J. N. Uku, and H. Machano. 2002. Effect of macroalgal reduction on coral-reef fish in the Watamu Marine National Park, Kenya. Marine and Freshwater Research 53:223-231. | 2002 | Kenya | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Moura, R. L. and R. M. C. Castro. 2002. Revision of Atlantic sharpnose pufferfishes (Tetraodontiformes: Tetraodontidae: Canthigaster), with description of three new species. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 115:32-50. | 2002 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Mexico | Invertivorous Fish | |
| Tupper, M. and M. A. Rudd. 2002. Species-specific impacts of a small marine reserve on reef fish production and fishing productivity in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Environmental Conservation 29:484-492. | 2002 | Turks and Caicos | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Funding & Incentives; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting |
| Turpin, R. K. and S. A. Bortone. 2002. Pre- and post-hurricane assessment of artificial reefs: Evidence for potential use as refugia in a fishery management strategy. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Chen, T.-C., R. F. G. Ormond, and H.-K. Mok. 2001. Feeding and territorial behaviour in juveniles of three co-existing triggerfishes. Journal of Fish Biology 59:524-532. | 2001 | Taiwan | Algae; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Eagle, J. V., G. P. Jones, and M. I. McCormick. 2001. A multi-scale study of the relationships between habitat use and the distribution and abundance patterns of three coral reef angelfishes (Pomacanthidae). Marine Ecology Progress Series 214:253-265. | 2001 | Australia | Algae; Invertivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Gilbert, C. R. 2001. Holacanthus dilaris bermudensis Goode, 1876 (currently Holacanthus bermudensis; Osteichthyes, Perciformes): Proposed conservation of usage of the subspecific name by the designation of a neotype. Bulletin of Marine Science 68:242. | 2001 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Kokita, T. and A. Nakazono. 2001. Rapid response of an obligately corallivorous filefish Oxymonacanthus longirostris (Monacanthidae) to a mass coral bleaching event. Coral Reefs 20:155-158. | 2001 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral | ||
| McClanahan, T. R. and R. Arthur. 2001. The effect of marine reserves and habitat on populations of East African coral reef fishes. Ecological Applications 11:559-569. | 2001 | Indian Ocean; India | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Chan, T.T.C. and Y. Sadovy. 2000. Profile of the marine aquarium fish trade in Hong Kong. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 2:197-213. | 2000 | Global | Review | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Designate Protected Species; Invertivorous Fish; Live Collection; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Chapman, M. R. and D. L. Kramer. 2000. Movements of fishes within and among fringing coral reefs in Barbados. Environmental Biology of Fishes 57:24-Nov. | 2000 | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Plankton; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Kokita, T. and A. Nakazono. 2000. Seasonal variation in the diel spawning time of the coral reef fish Oxymonacanthus longirostris (Monacanthidae): Parental control of progeny development. Marine Ecology Progress Series 199:263-270. | 2000 | Cuba; Japan | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| McClanahan, T. R. 2000. Recovery of a coral reef keystone predator, Balistapus undulatus, in East African marine parks. Biological Conservation 94:191-198. | 2000 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins | ||
| Meyer, C. G., K. N. Holland, B. M. Wetherbee, and C. G. Lowe. 2000. Movement patterns, habitat utilization, home range size and site fidelity of whitesaddle goatfish, Parupeneus porphyreus, in a marine reserve. Environmental Biology of Fishes 59:235-242. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral |
| Sancho, G., C. W. Petersen, and P. S. Lobel. 2000. Predator-prey relations at a spawning aggregation site of coral reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 203:275-288. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Johnston Atoll | Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Spanier, E. 2000. Changes in the ichthyofauna of an artificial reef in the southeastern Mediterranean in one decade. Scientia Marina 64:279-284. | 2000 | Cuba | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Kokita, T. and A. Nakazono. 1999. Spawning substrate selection by female longnose filefish, Oxymonacanthus longirostris. Ichthyological Research 46:429-432. | 1999 | Invertivorous Fish; Substrate | ||
| Kulbicki, M. and S. Sarramegna. 1999. Comparison of density estimates derived from strip transect and distance sampling for underwater visual censuses: A case study of Chaetodontidae and Pomacanthidae. Aquatic Living Resource 12:315-325. | 1999 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| McClanahan, T. R. 1999. Predation and the control of the sea urchin Echinometra viridis and fleshy algae in the patch reefs of Glovers Reef, Belize. Ecosystems 2:511-523. | 1999 | South & Central America; Belize; Madagascar; Caribbean | Algae; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| McClanahan, T. R., N. A. Muthiga, A. T. Kamukuru, H. Machano, and R. W. Kiambo. 1999. The effects of marine parks and fishing on coral reefs of northern Tanzania. Biological Conservation 89:161-182. | 1999 | Kenya; Tanzania | Model | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| McClanahan, T. R., V. Hendrick, M. J. Rodrigues, and N. V. C. Polunin. 1999. Varying responses of herbivorous and invertebrate-feeding fishes to macroalgal reduction on a coral reef. Coral Reefs 18:195-203. | 1999 | Kenya | Index or Indicator | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Parker, P. G. 1999. Fish assemblages at Julian Rocks and the adjacent waters of northern New South Wales, Australia. Australian Zoologist 31:134-144. | 1999 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Sazima, I., R. L. Moura, and C. Sazima. 1999. Cleaning activity of juvenile angelfish, Pomacanthus paru, on the reefs of the Abrolhos Archipelago, western South Atlantic. Environmental Biology of Fishes 56:399-407. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Takama, K., T. Suzuki, K. Yoshida, H. Arai, and T. Mitsui. 1999. Phosphatidylcholine levels and their fatty acid compositions in teleost tissues and squid muscle. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 124:109-116. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octopus & Squid | |
| Becerro, M. A., V. J. Paul, and J. Starmer. 1998. Intracolonial variation in chemical defenses of the sponge Cacospongia sp. and its consequences on generalist fish predators and the specialist nudibranch predator Glossodoris pallida. Marine Ecology Progress Series 168:187-196. | 1998 | Guam | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octopus & Squid; Sponges |
| Bunkley-Williams, L. and E. H. Williams Jr. 1998. Ability of Pederson cleaner shrimp to remove juveniles of the parasitic cymothoid isopod, Anilocra haemuli, from the host. Crustaceana 71:862-869. | 1998 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Planktivorous Fish | ||
| Jennings, S. and M. J. Kaiser. 1998. The effects of fishing on marine ecosystems. Advances in Marine Biology 201-352. | 1998 | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Birds; Sea Urchins; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Kokita, T. and A. Nakazono. 1998. Plasticity in the mating system of the longnose filefish, Oxymonacanthus longirostris, in relation to mate availability. Journal of Ethology 16:81-89. | 1998 | Japan | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Kuwamura, T. and Y. Nakashima. 1998. New aspects of sex change among reef fishes: Recent studies in Japan. Environmental Biology of Fishes 52:125-135. | 1998 | Japan | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Slattery, M., C. Avila, J. Starmer, and V. J. Paul. 1998. A sequestered soft coral diterpene in the aeolid nudibranch Phyllodesrnium guamensis Avila, Ballesteros, Slattery, Starmer and Paul. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 226:33-49. | 1998 | Guam | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octocoral |
| Allen, G. R. and D. R. Robertson. 1997. An annotated checklist of the fishes of Clipperton Atoll, tropical eastern Pacific. Revista de Biologia Tropical 45:813-843. | 1997 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Beets, J. 1997. Effects of a predatory fish on the recruitment and abundance of Caribbean coral reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 148:21-Nov. | 1997 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Seagrasses |
| Bortone, S. A., R. K. Turpin, R. C. Cody, C. M. Bundrick, and R. L. Hill. 1997. Factors associated with artificial-reef fish assemblages. Gulf of Mexico Science 15:17-34. | 1997 | South & Central America; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Artificial Habitat; Coralline Algae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish |
| Friedlander, A. M. and J. D. Parrish. 1997. Fisheries harvest and standing stock in a Hawaiian Bay. Fisheries Research 32:33-50. | 1997 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Jennings, S. and N. V. C. Polunin. 1997. Impacts of predator depletion by fishing on the biomass and diversity of non-target reef fish communities. Coral Reefs 16:71-82. | 1997 | Fiji | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish |
| Kuwamura, T. 1997. Evolution of female egg care in haremic triggerfish, Rhinecanthus aculeatus. Ethology 103:1015-1023. | 1997 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| McCormick, M. I. and L. J. Makey. 1997. Post-settlement transition in coral reef fishes: Overlooked complexity in niche shifts. Marine Ecology Progress Series 153:247-257. | 1997 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Mines, D., S. Stahmer, and S. M. Shepherd. 1997. Poisonings: Food, fish, shellfish. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America 15:157-177. | 1997 | Invertivorous Fish; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Pennings, S. C., S. R. Pablo, and V. J. Paul. 1997. Chemical defenses of the tropical, benthic marine cyanobacterium Hormothamnion enteromorphoides: Diverse consumers and synergisms. Limnology and Oceanography 42:911-917. | 1997 | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Urchins | ||
| Sakai, Y. and M. Kohda. 1997. Harem structure of the protogynous angelfish, Centropyge ferrugatus (Pomacanthidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 49:333-339. | 1997 | Japan | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Stobutzki, I. C. 1997. Energetic cost of sustained swimming in the late pelagic stages of reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 152:249-259. | 1997 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Dunlap, M. and J. R. Pawlik. 1996. Video-monitored predation by Caribbean reef fishes on an array of mangrove and reef sponges. Marine Biology 126:117-123. | 1996 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Corallivorous Fish; Encrusting Sponges; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Sponges | |
| Glynn, P. W., J. E. N. Veron, and G. M. Wellington. 1996. Clipperton Atoll (eastern Pacific): Oceanography, geomorphology, reef-building coral ecology and biogeography. Coral Reefs 15:71-99. | 1996 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Mexico | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fish; Hydrocoral; Invertivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Hobson, E. S. and J. R. Chess. 1996. Examination of a great abundance of filefish, Pervagor spilosoma, in Hawaii. Environmental Biology of Fishes 47:269-278. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Plankton | |
| Jennings, S. and N. V. C. Polunin. 1996. Effects of fishing effort and catch rate upon the structure and biomass of Fijian reef fish communities. Journal of Applied Ecology 33:400-412. | 1996 | Fiji | Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| McCormick, M. I. and B. A. Kerrigan. 1996. Predation and its influence on the condition of a newly settled tropical demersal fish. Marine and Freshwater Research 47:557-562. | 1996 | Lab Study | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Perez-Espana, H. and L. A. Abitia-Cardenas. 1996. Description of the digestive tract and feeding habits of the king angelfish and the Cortes angelfish. Journal of Fish Biology 48:807-817. | 1996 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Carr, M. H. and M. A. Hixon. 1995. Predation effects on early post-settlement survivorship of coral- reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 124:31-42. | 1995 | Bahamas | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Plankton; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Barshaw, D. E. and E. Spanier. 1994. Anti-predator behaviors of the Mediterranean slipper lobster, Scyllarides latus. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:375-382. | 1994 | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Substrate | ||
| Frazer, T. K. and W. J. Lindberg. 1994. Refuge spacing similarly affects reef-associated species from three phyla. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:388-400. | 1994 | South & Central America; Mexico | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Octopus & Squid | |
| McCormick, M. I. 1994. Variability in age and size at settlement of the tropical goatfish Upeneus tragula (Mullidae) in the northern Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 103:16-Jan. | 1994 | Australia | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Vose, F. E. and W. G. Nelson. 1994. Gray triggerfish (Balistes capriscus Gmelin) feeding from artificial and natural substrate in shallow Atlantic waters of Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:1316-1323. | 1994 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Artificial Habitat; Bivalves; Fish; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Holland, K. N., J. D. Peterson, C. G. Lowe, and B. M. Wetherbee. 1993. Movements, distribution and growth rates of the white goatfish Mulloides flavolineatus in a fisheries conservation zone. Bulletin of Marine Science 52:982-992. | 1993 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| McCormick, M. I. 1993. Development and changes at settlement in the barbel structure of the reef fish, Upeneus tragula (Mullidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 37:269-282. | 1993 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Plankton | ||
| McCormick, M. I. and B. W. Molony. 1993. Quality of the reef fish Upeneus tragula (Mullidae) at settlement: is size a good indicator of condition? Marine Ecology Progress Series 98:45-54. | 1993 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Shand, J. 1993. Changes in the spectral absorption of cone visual pigments during the settlement of the goatfish Upeneus tragula: the loss of red sensitivity as a benthic existence begins. Journal of Comparative Physiology A: Neuroethology, Sensory, Neural, and Behavioral Physiology 173:115-121. | 1993 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Acero P., A. and M. Rivera. 1992. Chaetodontidae and Pomacanthidae fish in the Santa Marta region (Colombia): density and relation with reef quality [Peces de las familias Chaetodontidae y Pomacanthidae en la region de Santa Marta (Colombia): densidad y relacion con la calidad del arrecif. Caribbean Journal of Science 28:184-190. | 1992 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| McCormick, M. I. and B. W. Molony. 1992. Effects of feeding history on the growth characteristics of a reef fish at settlement. Marine Biology 114:165-173. | 1992 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Roberts, C. M., A. R. D. Shepherd, and R. F. G. Ormond. 1992. Large-scale variation in assemblage structure of Red Sea butterflyfishes and angelfishes. Journal of Biogeography 19:239-250. | 1992 | Corallivorous Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral | ||
| Colin, P. L. and L. J. Bell. 1991. Aspects of the spawning of labrid and scarid fishes (Pisces: Labroidei) at Enewetak Atoll, Marshall Islands with notes on other families. Environmental Biology of Fishes 31:229-260. | 1991 | Marshall Islands | Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Uiblein, F. 1991. Ontogenetic shifts in resource use and shoaling tendency related to body size in Red Sea goatfish (Parupeneus forsskali, Mullidae). Marine Ecology 12:153-161. | 1991 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Sediment | ||
| Matsuura, K. and T. Sunobe. 1990. First record of the filefish, Pervagor nigrolineatus, from Japan. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology 37:198-199. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Philippines | Invertivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral | |
| McClanahan, T. R. 1990. Kenyan coral reef-associated gastropod assemblages: distribution and diversity patterns. Coral Reefs 9:63-74. | 1990 | Indian Ocean; Kenya; Tanzania; India | Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| McClanahan, T. R. and S. H. Shafir. 1990. Causes and consequences of sea urchin abundance and diversity in Kenyan coral reef lagoons. Oecologia 83:362-370. | 1990 | Kenya | Algae; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Sponges; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Moyer, J. T. 1990. Social and reproductive behavior of Chaetodontoplus mesoleucus (Pomacanthidae) at Bantayan island, Philippines, with notes on pomacanthid relationships. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology 36:459-467. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Japan; Philippines | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Bauchot, R., J.-M. Ridet, and M.-L. Bauchot. 1989. The brain organization of butterflyfishes. Environmental Biology of Fishes 25:205-219. | 1989 | Index or Indicator | Corallivorous Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Sponges | |
| Guzman, H. M. and J. Cortes. 1989. Coral reef community structure at Cano Island, Pacific Costa Rica. Marine Ecology 10:23-41. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Seastars; Stony Coral | |
| Guzman, Hector M., and D. Ross Robertson. 1989. Population and feeding responses of the corallivorous pufferfish Arothron meleagris to coral mortality in the eastern Pacif. Marine Ecology Progress Series 55:121-31. | 1989 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Heck Jr, K. L. and M. P. Weinstein. 1989. Feeding habits of juvenile reef fishes associated with Panamanian seagrass meadows. Bulletin of Marine Science 45:629-636. | 1989 | Panama | Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Hixon, M. A. and J. P. Beets. 1989. Shelter characteristics and Caribbean fish assemblages: experiments with artificial reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 44:666-680. | 1989 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Artificial Habitat; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Hourigan, T. F., F. G. Stanton, P. J. Motta, C. D. Kelley, and B. Carlson. 1989. The feeding ecology of three species of Caribbean angelfishes (family Pomacanthidae). Environmental Biology of Fishes 24:105-116. | 1989 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Algae; Invertivorous Fish; Octocoral; Sponges | |
| Lobel, P. S. 1989. Ocean current variability and the spawning season of Hawaiian reef fishes. Environmental Biology of Fishes 24:161-171. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Seaman Jr, W., W. J. Lindberg, C. R. Gilbert, and T. K. Frazer. 1989. Fish habitat provided by obsolete petroleum platforms off Southern Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 44:1014-1022. | 1989 | Florida | Apex Fish Predators; Artificial Habitat; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Stroud, G. J., B. Goldman, and W. Gladstone. 1989. Larval development, growth and age determination in the sharpnose pufferfish Canthigaster valentini (Teleostei: Tetraodontidae). Japanese Journal of Ichthyology 36:327-337. | 1989 | Australia; Cuba; Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Dominguez, J. H. and M. L. Reaka. 1988. Temporal activity patterns in reef-dwelling stomatopods: a test of alternative hypotheses. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 117:47-69. | 1988 | US Virgin Islands | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms | |
| Johnson, W. S. and P. Ruben. 1988. Cleaning behavior of Bodianus rufus, Thalassoma bifasciatum, Gobiosoma evelynae, and Periclimenes pedersoni along a depth gradient at Salt River Submarine Canyon, St. Croix. Environmental Biology of Fishes 23:225-232. | 1988 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Planktivorous Fish; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Barlow, G. W. 1987. Spawning, eggs and larvae of the longnose filefish Oxymonacanthus longirostris, a monogamous coralivore. Environmental Biology of Fishes 20:183-194. | 1987 | Algae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Plankton | ||
| Eales, J. G. and S. Shostak. 1987. Total and free thyroid hormones in plasma of tropical marine teleost fish. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 3:127-131. | 1987 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | ||
| Aldenhoven, J. M. 1986. Different reproductive strategies in a sex-changing coral reef fish Centropyge bicolor ( Pomacanthidae). Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 37:353-360. | 1986 | Model | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Grizzle, J. M. 1986. Lesions in fishes captured near drilling platforms in the Gulf of Mexico. Marine Environmental Research 18:267-276. | 1986 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Pathogens; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Hoffman, S. G. 1985. Effects of size and sex on the social organization of reef-associated hogfishes, Bodianus spp. Environmental Biology of Fishes 14:185-197. | 1985 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish |
| Shulman, M. J. 1985. Coral reef fish assemblages: intra- and interspecific competition for shelter sites. Environmental Biology of Fishes 13:81-92. | 1985 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Chester, A. J., G. R. Huntsman, P. A. Tester, and C. S. Manooch III. 1984. South Atlantic Bight reef fish communities are represented in hook-and-line catches. Bulletin of Marine Science 34:267-279. | 1984 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Reinthal, P. N., B. Kensley, and S. M. Lewis. 1984. Dietary shifts in the queen triggerfish, Balistes vetula, in the absence of its primary food item, Diadema antillarum. Marine Ecology 5:191-195. | 1984 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Urchins | |
| Robblee, M. B. and J. C. Zieman. 1984. Diel variation in the fish fauna of a tropical seagrass feeding ground. Bulletin of Marine Science 34:335-345. | 1984 | US Virgin Islands | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Gladfelter, W. B. and W. S. Johnson. 1983. Feeding niche separation in a guild of tropical reef fishes ( Holocentridae). Ecology 64:552-563. | 1983 | US Virgin Islands; India | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Hoffman, S. G. 1983. Sex-related foraging behavior in sequentially hermaphroditic hogfishes ( Bodianus spp.). Ecology 64:798-808. | 1983 | South & Central America; Panama; Mexico | Invertivorous Fish | |
| Walsh, W. J. 1983. Stability of a coral reef fish community following a catastrophic storm. Coral Reefs 2:49-63. | 1983 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Reynolds, W. W. and M. E. Casterlin. 1981. Thermoregulatory behavior of the triggerfish Balistes fuscus in an electronic shuttlebox. Hydrobiologia 83:255-256. | 1981 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Itzkowitz, M. 1977. Social dynamics of mixed-species groups of Jamaican reef fishes. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 2:361-384. | 1977 | Jamaica | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral; Substrate | |
| Eisler, R. 1975. Acute toxicities of crude oils and oil dispersant mixtures to Red Sea fishes and invertebrates. Israel Journal of Zoology 24:16-27. | 1975 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Octocoral; Sea Urchins |
| Phleger, C. F. 1975. Bone lipids of Kona Coast reef fish: skull buoyancy in the hawkfish, Cirrhites pinnulatus. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 52:101-104. | 1975 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish | ||
| Banner, A. H. 1973. Hallucinatory mullet poisoning: A case from Oahu. Hawaii Medical Journal 32:330-331. | 1973 | South Africa | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Pathogens; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Randall, J. E. and W. D. Hartman. 1968. Sponge-feeding fishes of the West Indies. Marine Biology 1:216-225. | 1968 | India | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Sponges |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Monitor & Research: Fisheries Sampling | Improved fisheries sampling programs require improving the spatial resolution of commercial and recreation fisheries-dependent and fisheries-independent sampling programs to provide statistics on catch and effort. Improved sampling can be achieved through evaluating and enhancing census programs by using smaller sampling areas. Also, fishery pre-recruitment monitoring efforts should be continued for long-term prediction of fishery stocks. Last, investigating life histories of fishery species needs to be conducted because it is currently a gap. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|