ReefLink Database

Funding & Donations
Funding is to provide resources, usually in form of money or other values such as effort or time, for a project or to private or public institutions. A donation is a gift given, typically for charitable purposes and/or to benefit a cause. Funding and donations can provide monetary support to educational institutions or non-profit organizations for scientific research and monitoring, education, or outreach..
CMap
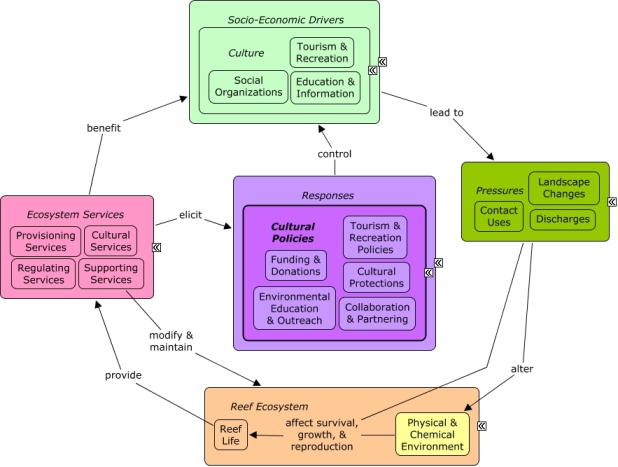
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to manage the distribution and functioning of cultural sectors. Cultural sectors, particularly tourism and recreation, create pressures on the reef ecosystem through primarily through contact uses, but also drive coastal development, which can lead to landscape changes and increasing pollution. Cultural sectors benefit from reef ecosystem services, including recreational and educational opportunities.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brodie, JE; Devlin, M; Haynes, D; Waterhouse, J. 2011. Assessment of the eutrophication status of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon (Australia). Biogeochemistry 106:281-302. | 2011 | Australia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Burke, L., K. Reytar, M. Spalding, and A. Perry. 2011. Reefs at Risk Revisited. World Research Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Panama; Tanzania; Indonesia | Biomedical Research Policies; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Cruz-Trinidad, A; Geronimo, RC; Cabral, RB; Alino, PM. 2011. How much are the Bolinao-Anda coral reefs worth? Ocean and Coastal Management 54:696-705. | 2011 | Philippines | Model; Index or Indicator | Aquaculture; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Anton, C., J. Young, P. A. Harrison, M. Musche, G. Bela, C. K. Feld, R. Harrington, J. R. Haslett, G. Pataki, M. D. A. Rounsevell, M. Skourtos, J. P. Sousa, M. T. Sykes, R. Tinch, M. Vandewalle, A. Watt, and J. Settele. 2010. Research needs for incorporating the ecosystem service approach into EU biodiversity conservation policy. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2979-2994. | 2010 | Review; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation | |
| Brandt, F., D. Bank, S. L. Cross, and R. Weiss. 2010. A Lidocaine-Containing Formulation of Large-Gel Particle Hyaluronic Acid Alleviates Pain. Dermatologic Surgery 36:1876-1885. | 2010 | |||
| Gleason, M., S. McCreary, M. Miller-Henson, J. Ugoretz, E. Fox, M. Merrifield, W. McClintock, P. Serpa, and K. Hoffman. 2010. Science-based and stakeholder-driven marine protected area network planning: A successful case study from north central California. Ocean and Coastal Management 53:52-68. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Klein, C. J., N. C. Ban, B. S. Halpern, M. Beger, E. T. Game, H. S. Grantham, A. Green, T. J. Klein, S. Kininmonth, E. Treml, K. Wilson, and H. P. Possingham. 2010. Prioritizing Land and Sea Conservation Investments to Protect Coral Reefs. PLoS One 5:e12431. | 2010 | Global | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Ocean Acidity | |
| Weiss, R., D. Bank, and F. Brandt. 2010. Randomized, Double-Blind, Split-Face Study of Small-Gel-Particle Hyaluronic Acid with and without Lidocaine During Correction of Nasolabial Folds. Dermatologic Surgery 36:750-759. | 2010 | |||
| Wielgus, J., A. Balmford, T. B. Lewis, C. Mora, and L. R. Gerber. 2010. Coral reef quality and recreation fees in marine protected areas. Conservation Letters 3:38-44. | 2010 | Global; Cuba | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| 2009. Federal Expenditures for U.S. Coral Reef Task Force Conservation Activities (2002-2004). Appendix A, NOAA. | 2009 | Global | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Butardo-Toribio, M. Z., P. M. Alino, and E. S. Guiang. 2009. Cost-Benefit Study of Marine Protected Areas: Implications on Financing and Institutional Needs. Philippine Agricultural Scientist 92:153-169. | 2009 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Social Organizations |
| Clifton, J. 2009. Science, funding and participation: key issues for marine protected area networks and the Coral Triangle Initiative. Environmental Conservation 36:91-96. | 2009 | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas | ||
| Edwards, P. E. T. 2009. Sustainable financing for ocean and coastal management in Jamaica: The potential for revenues from tourist user fees. Marine Policy 33:376-385. | 2009 | Jamaica | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Nunn, P. D. 2009. Responding to the challenges of climate change in the Pacific Islands: management and technological imperatives. Climate Research 40:211-231. | 2009 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Cultural Policies; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Parks, N. 2009. Is regulation on ocean acidification on the horizon? Environmental Science and Technology 6118-6119. | 2009 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; CO2; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Ocean Acidity; Special Use Permitting |
| Peters, H. and J. P. Hawkins. 2009. Access to marine parks: A comparative study in willingness to pay. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:219-228. | 2009 | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Reid-Grant, K. and M. G. Bhat. 2009. Financing marine protected areas in Jamaica: An exploratory study. Marine Policy 33:128-136. | 2009 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Shulzitski, K., M. A. McCartney, and M. L. Burton. 2009. Population connectivity among Dry Tortugas, Florida, and Caribbean populations of mutton snapper (Lutjanus analis), inferred from multiple microsatellite loci. Fishery Bulletin 107:501-509. | 2009 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Piscivorous Fish | |
| Tallis, H., R. Goldman, M. Uhl, and B. Brosi. 2009. Integrating conservation and development in the field: implementing ecosystem service projects. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:12�20. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| UNCWI. 2009. Healthy Watersheds through Healthy Forests. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Drinking Water Supply; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Andrefouet, S. 2008. Coral reef habitat mapping using remote sensing: A user vs producer perspective. Implications for research, management and capacity building. Journal of Spatial Science 53:113-129. | 2008 | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Complex Habitat & Resources; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Pittman, S. J., S. D. Hile, C. F. G. Jeffrey, C. Caldow, M. S. Kendall, M. E. Monaco, and Z. Hillis-Starr. 2008. Fish assemblages and benthic habitats of Buck Island Reef National Monument (St. Croix, U.S. Virgin Islands) and the surrounding seascape: a characterization of spatial and temporal patterns. NOAA, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Seagrasses |
| Sammarco, P. W. 2008. Crises on coral reefs and in coral reef science in the 21st century: The need for a new peer-review system. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8:109-119. | 2008 | Global | Review; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Pathogens |
| Shivlani, M., V. R. Leeworthy, T. J. Murray, D. O. Suman, and F. Tonioli. 2008. Knowledge, attitudes and perceptions of management strategies and regulations of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuaries by commercial fishers, dive operators, and environmental group members: a baseline characterization and 10-year comparison. U.S. Department of Commerce, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Office of National Marine Sanctuaries, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | Florida | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Commercial Fisheries; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Waddell, J. E. and A. M. Clarke, editors. 2008. The state of coral reef ecosystems of the United States and Pacific Freely Associated States: 2008. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 73. NOS NCCOS 73, NOAA/NCCOS Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment�s Biogeography Team, Silver Spring, MD. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Internet & Telecommunications |
| Wantiez, L. 2008. Coral reefs of New Caledonia in 2006: Status report and monitoring network [Les recifs coralliens de nouvelle-caledonie en 2006: etat des lieux et reseau de suivi]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:117-132. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Cruise Ships; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Mining; Mining Policies; Seastars; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Iran; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Fisher, W.S. 2007. Stony soral rapid bioassessment protocol. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Biocriteria; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Stony Coral; Valuation | |
| Halpern, B. S., K. A. Selkoe, F. Micheli, and C. V. Kappel. 2007. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conservation Biology 21:1301-1315. | 2007 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Point Source Discharges; Sea Temperatures | |
| Heck Jr., K. L. and J. F. Valentine. 2007. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 30:371-381. | 2007 | Review | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Mohamed, M. 2007. ECONOMIC VALUATION OF CORAL REEFS: A CASE STUDY OF THE COSTS AND BENEFITS OF IMPROVED MANAGEMENT OF DHIGALI HAA, A MARINE PROTECTED AREA IN BAA ATOLL, MALDIVES. Masters Thesis. University of Canterbury, (Christchurch, New Zealand). | 2007 | Maldives | Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation | |
| Relini, G., M. Relini, G. Palandri, S. Merello, and E. Beccornia. 2007. History, ecology and trends for artificial reefs of the Ligurian sea, Italy. Hydrobiologia 580:193-217. | 2007 | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Sammarco, P. W., P. Hallock, J. C. Lang, and R. S. Legore. 2007. Roundtable discussion groups summary papers: Environmental bio-indicators in coral reef ecosystems: The need to align research, monitoring, and environmental regulation. Environmental Bioindicators 2:35-46. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Toxics | |
| 2006. NOAA Essential Fish Habitat Research Implementation Plan for Alaska for FY 2007 - 2011. NOAA. | 2006 | GIS & Maps | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sponges; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Bortone, S. A. 2006. A perspective of artificial reef research: The past, present, and future. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:8-Jan. | 2006 | Artificial Habitat; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Kaiser, M. J. 2006. The Louisiana artificial reef program. Marine Policy 30:605-623. | 2006 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Construction Codes & Projects; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Kaiser, M. J. 2006. The texas artificial reef program. Marine Technology Society Journal 40:62-72. | 2006 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Kirkman, H. 2006. The east Asian seas UNEP regional seas programme. International Environmental Agreements: Politics, Law and Economics 6:305-316. | 2006 | Global; China | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Minerals Management Service. 2006. Leasing Oil and Natural Gas Resources. U.S. Department of the Interior. | 2006 | South & Central America; India; Mexico | Monetary Valuation; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Special Use Permitting; Utility Policies | |
| Teeter, A. M. and B. H. Johnson. 2006. Sediment and fluid mud modeling of atchafalaya pro-delta channel. Pages 714-733 in Proceedings of the International Conference on Estuarine and Coastal Modeling. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| The Coastal Theme Team, editor. 2006. IGOS Coastal Theme Report: For the monitoring of our environment from space and from earth. Integrated Global Observing Strategy. | 2006 | Global; Florida; China; France | Field Study & Monitoring | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives |
| Granek, E. E. and M. A. Brown. 2005. Co-management approach to marine conservation in Moheli, Comoros Islands. Conservation Biology 19:1724-1732. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; Comoros; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation |
| Kaiser, M. J. 2005. Models predict cost savings of Louisiana program. Oil and Gas Journal 103:38-41. | 2005 | Model | Funding & Donations | |
| Kaiser, M. J. and A. G. Pulsipher. 2005. Rigs-to-reef programs in the Gulf of Mexico. Ocean Development and International Law 36:119-134. | 2005 | South & Central America; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Oil & Gas Rigs | |
| Kim, J.-K. and J.-H. Kim. 2005. Optimal mapping for artificial reef facility using remote sensing and GIS. Pages 314-319 in Proceedings of the International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. | 2005 | Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Merrick, J. R. W., G. S. Parnell, J. Barnett, M. Garcia. 2005. A Multiple-objective decision analysis of stakeholder values to identify watershed improvement needs. Decision Analysis 2:44-57. | 2005 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Roberts, M. and S. Gass. 2005. Looking for Lophelia. Planet Earth 26-27. | 2005 | Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Internet & Telecommunications; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | |
| Rohmann, S. and M. Monaco, editors. 2005. Mapping Southern Florida�s Shallow-water Coral Ecosystems: An Implementation Plan. NOAA Coral Reef Conservation Program, Silver Spring, (Maryland, USA). | 2005 | Florida | GIS & Maps | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Schools & Colleges |
| Sadovy, Y. 2005. Trouble on the reef: The imperative for managing vulnerable and valuable fisheries. Fish and Fisheries 6:167-185. | 2005 | Global | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Live Collection | |
| Sifling, J., R. A. Nall, J. Stettler, T. Busch, F. Igaz, J. G. Hoff, and S. Wiegman. 2005. American Samoa longliner response, wreck removal, and restoration project. Pages 259-264 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Samoa; American Samoa | Coastal Defense; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Petroleum Spills; Ports & Harbors; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Cooney, C. M. 2004. EPA's First Science Advisor Focuses on the Basics. Environmental Science and Technology 38:181A-184A. | 2004 | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Kelty, R., K. Andrews, J. Wheaton, L. Nall, C. Beaver, W. Japp, B. Keller, V. R. Leeworthy, J. A. Bohnsack, T. Matthews, J. Ault, F. Ferro, G. Delgado, D. Harper, J. Hunt, B. Sharp, C. Pattengil-Semmens, S. Smith, R. Spieler, R.E. Dodge, D. Gilliam, B. Goodwin, G. Schmahl, E. Hickerson, J. R. Garcia, C. Lilyestrom, R. Appeldoorn, A. Bruckner, E. Williams, C. .F.G. Jeffrey, U. Alauf, A. Riedlander, C. Rogers, J. Miller, J. Beets, R. Nemeth, S. Herzlieb, V. Mayor, W. Toller, Z. Hillis-Starr, S. Caseau, and M. Miller. 2004. Status of coral reefs in the U.S. Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico: Florida, Flower Garden Banks, Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands, Navassa. Pages 431-450 Status of coral reefs of the world: 2004. Volume 2. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, Queensland, Australia. | 2004 | South & Central America; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Climate; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| Pomeroy, R. S., J. E. Parks, and L. M. Watson. 2004. How is your MPA doing? a guidebook of natural and social indicators for evaluating marine protected area management effectiveness. he World Conservation Union, Gland, Switzerland. | 2004 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies | |
| Bhat, M. G. 2003. Application of non-market valuation to the Florida Keys marine reserve management. Journal of Environmental Management 67:315-325. | 2003 | Florida | Model | Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Firn, R. D. 2003. Bioprospecting - why is it so unrewarding? Biodiversity and Conservation 12:207-216. | 2003 | Columbia | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Haley, M. and A. Clayton. 2003. The role of NGOs in environmental policy failures in a developing country: The mismanagement of Jamaica's coral reefs. Environmental Values 12:29-54. | 2003 | Jamaica | Corporate Responses; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Stachowitsch, M. 2003. Research on intact marine ecosystems: A lost era. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:801-805. | 2003 | Global | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Bohnsack, J. A., A. Y. Cantillo, and M. J. Bello (eds.). 2002. Resource Survey of Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary 1983. NOAA/NOS National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD. | 2002 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Fish; Scientific Research; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2002. NOAA Technical Memorandum NMFS-OPR-22. | 2002 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Sayer, M. D. J. and T. A. Wilding. 2002. Planning, licensing, and stakeholder consultation in an artificial reef development: The Loch Linnhe reef, a case study. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | Europe | Artificial Habitat | |
| Harborne, A. R., D. C. Afzal, and M. J. Andrews. 2001. Honduras: Caribbean Coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1221-1235. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Schuttenberg, editor. 2001. Coral Bleaching: Causes, Consequences and Response - Selected Papers Presented at the 9th International Coral Reef Symposium October 2000. Coastal Management Report #2230, Coastal Resources Center, Narragansett, (Rhode Island, USA). | 2001 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia; Philippines | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Harborne, A. R., M. D. McField, and E. K. Delaney. 2000. Belize. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 501-516. | 2000 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| White, A. T., H. P. Vogt, and T. Arin. 2000. Philippine coral reefs under threat: The economic losses caused by reef destruction. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:598-605. | 2000 | Philippines | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Monetary Valuation; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Wilson, S. C. and R. Klaus. 2000. The Gulf of Aden. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 47-61. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; India; Djibouti | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Beaches & Nature Parks; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| [No author name available]. 1999. Proceedings of the Sand Rights'99. Bringing back the beaches. in Sand Rights 1999 Bringing Back the Beaches. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Security Policies; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Wright, J. and D. Morton. 1999. Promoting erosion control in the Virgin Islands. Pages 8-May in Investing in the protection of our environment. Proceedings of conference 30, Nashville, 1999. (International Erosion Control Association). | 1999 | US Virgin Islands | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Whittington, I. D. 1998. Diversity 'down under': monogeneans in the Antipodes (Australia) with a prediction of monogenean biodiversity worldwide. International Journal for Parasitology 28:1481-1493. | 1998 | Global; Australia | Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Culbertson Jan, C. 1997. Alternative donation options with the Texas Artificial Reef Program. Pages 421-431 in Proceedings of the Annual Offshore Technology Conference. | 1997 | South & Central America; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Sando, W. J. 1997. Late Paleozoic coral genera and subgenera. State of the art, 1814-1994. Boletin - Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural: Seccion Geologica 91:61-71. | 1997 | China; Europe | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | |
| Suman, D. O. 1997. The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary: A case study of an innovative federal-state partnership in marine resource management. Coastal Management 25:293-324. | 1997 | Florida | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Resource Use Management | |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 1996. Linking the Economy and Environment of Florida Keys/Florida Bay. | 1996 | Florida | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Pilcher, J. R. 1996. The past global changes (PAGES) project. Geological Society Special Publication 251-256. | 1996 | Global; Australia; China; Europe | Climate; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kangas, P., M. Shave, and P. Shave. 1995. Economics of an ecotouriasm in Belize. Environmental Management 19:669-673. | 1995 | South & Central America; Belize | Funding & Donations; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Wells, S. M. 1995. Science and management of coral reefs: problems and prospects. Coral Reefs 14:177-181. | 1995 | Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| NOAA. 1992. Oil spill case histories 1967-1991: summaries of significant U.S. and international spills. Hazardous Materials Response and Assessment Division, Seattle, Washington. | 1992 | Coastal Defense; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Side, J. 1985. Alternative uses of offshore installations. in [No source information available]. | 1985 | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives | ||
| Karr, J. R. and D. R. Dudley. 1981. Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environmental Management 5:55-68. | 1981 | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Change Agricultural Cover Crop Practices | Cover crop outreach entails changing agricultural practices in an area to leave vegetation and cover on the soil while growing other crops (e.g. Coffee). Agricultural practices that encourage leaving soil bare are extremely susceptible to erosion (e.g. sun grown Coffee). Cover crop methods and shade-grown crops (e.g. shade-grown Coffee) would reduce the large amount of sediment that is eroding, particularly from high elevations, and ultimately will reduce the amount of sediment that reaches the coral reefs. Options to encourage transition to cover crop practices include outreach to raise awareness of benefits and cost share programs to help farmers with the burden of the extra expense. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Conservation Cover. CODE 327. US Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Responses; Sediment |
| Corporate Response: Invest & Co-finance Projects | Investing and co-financing projects that aim to conserve or restore habitats can be an effective means to preserving reef habitats as well as establishing positive working relationships between organizations. Investing in private sector projects will promote desired businesses and business practices, reducing barriers to entry and competitiveness as compared to traditional businesses and business practices to counterbalance advantages from undesired externalities. | World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. |
Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Dissemination of Findings: Support Journal Publication | This management option involves sponsoring the publication of journals that contain peer-reviewed scientific research. For sanctuaries this can be an excellent place to publish reports and research that used sanctuary areas or resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biotechnology Research & Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Scientific Research |
| Dissemination of Findings: Participate in Conferences | Conferences are beneficial as a means to garner and disseminate new information, technology, and methods. Conferences also serve as a networking opportunity to communicate with potential collaborators. Participation in local, state, and federal conferences by sanctuary staff is very important to reach out to the broader coral reef community. Sponsoring conferences would allow scientists and researchers to keep abreast of findings and ongoing research within the local sanctuary. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Scientific Research |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Offshore Wind and Hydrokinetic Alternative Energies | Policies encouraging or authorizing construction of offshore facilities are evolving, and there are many sides to the issue of how to best manage them. Alternative energies are desirable and would reduce the dependence on fossil fuel resources. However, hydrokinetic technologies are just becoming viable, meaning long term impacts are still unknown. Facilitative policies reduce barriers for alternative energy development or increase barriers or costs for incumbent technologies. These include research and innovation policies, technology improvement subsidies, market based policies that internalize externalities, and regulatory changes that simplify the permitting process. | Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. Portman, M.E. 2010. Marine Renewable Energy Policy: Some US and International Perspectices Compared. Oceanography 23:98-105. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Seawater Flow; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies |
| Marine Zoning: Utilize Marine Protected Areas for Research and Monitoring | Research and monitoring of marine protected areas determine the degree to which the zones meet goals and objectives for protecting natural resources, as well as human-use patterns, attitudes and compliance. Once data is gathered from within the protected zone it can than be compared to comprable data from outside the protected zone, as a control. It is necessary to compile and review data on use patterns to determine where additional Special-Use Areas would be appropriate. Research in the protected area should be non-invasive. It is important to make the protected area available for external research as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Develop Baseline Data | Baseline surveys of existing resources need to be conducted before monitoring can begin. The surveys must be conducted in Ecological Reserves, Sanctuary Preservation Areas, and Special-Use Areas to characterize the status of important marine species and their habitats. Establishing baseline data allows for later comparisons to monitoring data to gauge changes over time and revaluate current management actions being taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Wetlands |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Water Efficiency Initiatives | Reducing water use through cost effective water efficiency improvements can be beneficial as it reduces pressure on water as a finite resource and saves money. There are several ways water efficiency can be promoted. Some Water Efficiency BMPs recommended by the EPA include: Water Management Planning; Information and Education Programs; Distribution System Audits, Leak Detection and Repair; Water-Efficient Landscaping, Water-Efficient Irrigation; Toilets and Urinals; Faucets and Showerheads; Boiler/Steam Systems; Single-Pass Cooling Equipment; Cooling Tower Management; Commercial Kitchen Equipment; Laboratory/ Medical Equipment; Other Water Intensive Processes; Alternative Water Sources. One of the ways the US government has promoted Water Efficiency Initiatives is through Executive order 13123 which places certain water use reduction requirements on Federal Agencies. There are also existing funding and incentives for non-government sectors. Project funding comes in many forms, such as appropriations, energy savings performance contract (ESPC) and Utility Energy Service Contract (UESCs) programs; ratepayer incentive programs such as rebates from public benefit funds or utilities; and the retention of energy and water cost savings. | US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Water Efficiency Best Management Practices. Federal Energy Management Program Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Textiles & Apparel; Utilities; Utility Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, "Superfund", 42 United States Code §§ 9601-9675. | Provides Liability, compensation, cleanup, and emergency response for hazardous substances released into the environment. Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Remediation; Waste Management Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6401 (2000). | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:Allowed the development of programs and projects, and provided financing for developing sound scientific data to preserve and restore coral reefs. Continued the Coral Reef Task Force and Coral Reef Initiative started under Executive Order 13089 (1998). Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The Act is administrative, not regulatory. It established four major programs; (1) The National Coral Reef Action Strategy established goals for research, monitoring and conservation, (2, 3) The Coral Reef Conservation Program and Coral Reef Conservation Fund provided financial assistance for coral reef projects, (4) the National Program facilitated cooperative work between federal, state and regional efforts that work to improve coral reef ecosystems. The National Program also enhanced the public awareness of coral reefs through educational programs. The Act incorporated Executive Order 13,089 and provided coordinated funding activities through twelve federal agencies and seven states. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States; US Coral Reefs |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corporate Responses; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Public Administration; Remediation; Utilities |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Exec. Order No. 12962, Recreational Fisheries, 60 Federal Register (1995). | Federal agencies are directed to improve the quantity, function, sustainable productivity, and distribution of U.S. aquatic resources for increased recreational fishing opportunities in cooperation with states and tribes. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Improvement Act of 1978, 16 United States Code § 7421. | Passed to improve the administration of fish and wildlife programs and amends several earlier laws, including the Refuge Recreation Act, the National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act, and the Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956. It authorizes the Secretary to accept gifts and bequests of real and personal property on behalf of the United States. It also authorizes the use of volunteers on Service projects and appropriations to carry out volunteer programs. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Secretaries were authorized to establish, conduct and assist with national training programs for State fish and wildlife enforcement personnel. Comments:The law provided authority to the Secretaries to enter into law enforcement cooperatives with State and other federal agencies.It expanded the use of fines, penalties and forfeiture funds received under the Endangered Species Act and Lacey Act to include the cost of shipping, storing and disposing of items. |
Secretary of Interior and Secretary of Commerce, administration primarily through US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Land and Water Conservation Fund Act of 1965, 16 United States Code § 4601. | Provides funding through receipts from the sale of surplus federal land, appropriations from oil and gas receipts from the outer continental shelf, and other sources of land acquisition. Appropriations from the fund may be used for matching grants to states for outdoor recreation projects and for land acquisition by various federal agencies, including the Fish and Wildlife Service. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of wetlands benefits coral reefs through nutrient removal and the control of sedimentation so that they do not enter near shore waters. Legislative Actions:The legislation was amended in 1986 by the Emergency Wetlands Resources Act and required the States to identify the agencies and organizations involved in wetland management, evaluate existing and proposed wetlands protection mechanisms, assess wetlands resources, identify wetlands loss and degradation factors, and establish priorities for protection. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Funding & Donations; Landuse Management; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service General Partnership Authorities of 1970, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act supplemented and clarified the National Park Service's mandate with respect to the management of the National Park System. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Designated Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| National Park Service Organic Act of 1916, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act was created to start the National Park Service within the Department of Interior for the purpose of promoting and regulating the use of federal areas such as national parks and monuments. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Created the National Park Service to be supervised by a Director. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invasive Species; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act of 1966, 16 United States Code § 66. | The Act defines the National Wildlife Refuge System and authorizes the Secretary of Interior to permit any use of a refuge provided such use is compatible with the major purpose for which the refuge was established. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Serice Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Landuse Management; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Neotropical Migratory Bird Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6101. | Established a matching grant program to fund projects that promote the conservation of neotropical migratory birds in the United States, Latin America, and the Caribbean. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act provided competitive grants in Latin America, the Carribean, and the United States for neotropical migratory birds that winter south of the border and summer in North America. The law encourages habitat protection, education, research, monitoring, and capacity building to provide for long-term protection of neotropical migratory birds. Comments:Over 800 species of birds are found in the United States and 500 migrate South of the border for the winter. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; Latin America; Caribbean |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| North American Wetlands Conservation Act of 1989, 16 United States Code § 4411. | Provides funding and administrative direction for the implementation of the North American Waterfowl Management Plan and the Tripartite Agreement between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:A North American Wetlands Conservation Council was created to recommend projects to be funded under the Act to the Migratory Bird Conservation Commission. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Canada; Mexico |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| Partnerships for Wildlife Act of 1992, 16 United States Code §§ 3741-3744. | Established a Wildlife Conservation and Appreciation Fund to receive appropriated funds and donations from the National Fish and Wildlife Foundation and other private sources to assist the state fish and game agencies in carrying out their responsibilities for conservation of non-game species. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act authorized grants to match contributions from the Wildlife Conservation and Appreciarion Fund, and authorized grants to states for conservation programs and projects to conserve nongame wildlife species. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Reef Life |
| Refuge Revenue Sharing Act of 1935, as amended, 16 United States Code § 715. | Provided for payment to counties in lieu of taxes from areas administered by the Fish and Wildlife Service. Counties are required to pass payments along to other units of local government within the county, which suffer losses in tax revenues due to the establishment of Service areas. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Congress can appropriate funds to make up any shortfall of payments to local governments, all lands administered by the USFWS qualify for revenue sharing payments, and payments to units of local governments can be used for any governmental purpose. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Servicw Jurisdiction: United States |
Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Public Administration |
| Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986, 42 United States Code §§ 9601 et seq. | Reautorized CERCLA Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA/SARA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions:The amended Act stressed the importance of permanent and innovative treatment technologies, required Superfund actions to consider the standards and requirements found in other State and Federal environmental laws, provided new enforcement authorities and settlement tools. Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, 62-043 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-43.010 Intent.
(1) In Section 373.451, F.S., the Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, the Legislature finds and declares that the water quality of many of the surface waters of the state has been degraded or is in danger of being degraded, and that it is the duty of the state through the state�s agencies and subdivisions to enhance the environmental and scenic value of surface waters.
(2) Pursuant to Section 373.026(7), F.S., the Department is responsible for the exercise of general supervisory authority over all water management districts. The Department also has the responsibility, under the Surface Water Improvement and Management Act, to establish the criteria for the water management districts� development of their priority surface water lists; to approve the priority lists and management plan schedules; to review and recommend modifications or additions to the plans as needed to ensure consistency with the state water policy and the State Comprehensive Plan; to establish the uniform format for management plans; and to administer the Surface Water Improvement and Management Trust Funds. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Te SWIM Trust Fund is no langer available. Comments:The Legislature finds and declares that the water quality of many of the surface waters of the state has been degraded or is in danger of being degraded, and that it is the duty of the state through the state�s agencies and subdivisions to enhance the environmental and scenic value of surface waters. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |