ReefLink Database

Littering
Littering is a type of pollution that occurs when garbage, including plastics, paper, and metal, are not disposed of properly and can enter coastal waters.
CMap
CMap Description
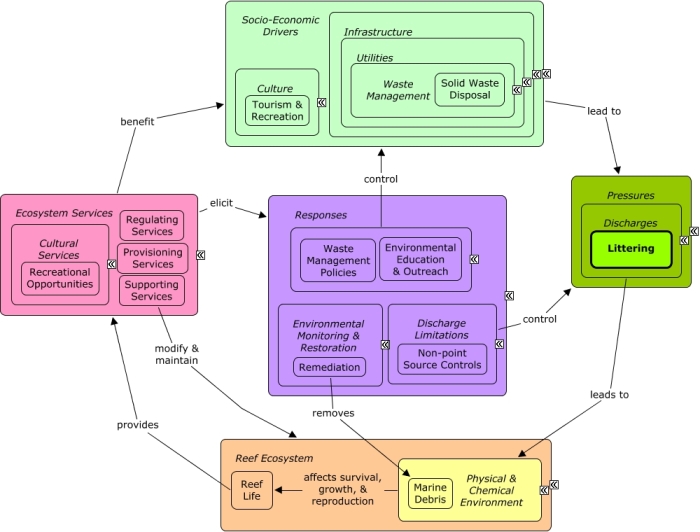
Littering can result from insufficient solid waste disposal and may be particularly high along roads and bridges, or in areas frequented by tourists. Littering introduces debris into the marine environment, including glass, plastics, and metal which can damage reef species and reduce the aesthetic and recreational value of reefs. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that create pollution benefit indirectly from goods and services provided by the reef which provides recreational opportunities and contributes to the cultural identity of the local community and drives coastal development. Waste management policies to improve solid waste disposal, non-point source controls such as littering fines, increased law enforcement, and environmental education can all be enacted to reduce littering. Remediation, such as coastal clean-up programs, can be enacted to remove trash and debris.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Munoz, PD; Murillo, FJ; Sayago-Gil, M; Serrano, A; Laporta, M; Otero, I; Gomez, C. 2011. Effects of deep-sea bottom longlining on the Hatton Bank fish communities and benthic ecosystem, north-east Atlantic. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 91:939-952. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Littering; Marine Birds; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bartley, R., J. P. Corfield, B. N. Abbott, A. A. Hawdon, S. N. Wilkinson, and B. Nelson. 2010. Impacts of improved grazing land management on sediment yields, Part 1: Hills lope processes. Journal of Hydrology 389:237-248. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Littering; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Shank, G. C., R. G. Zepp, A. Vahatalo, R. Lee, and E. Bartels. 2010. Photobleaching kinetics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter derived from mangrove leaf litter and floating Sargassum colonies. Marine Chemistry 119:162-171. | 2010 | Florida | CO2; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Littering; Mangroves; Seagrasses | |
| Shank, G. C., R. Lee, A. Vahatalo, R. G. Zepp, and E. Bartels. 2010. Production of chromophoric dissolved organic matter from mangrove leaf litter and floating Sargassum colonies. Marine Chemistry 119:172-181. | 2010 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Cuba; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Remote Sensing | Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Littering; Mangroves; Seagrasses |
| Abu-Hilal, A. and T. Al-Najjar. 2009. Marine litter in coral reef areas along the Jordan Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Journal of Environmental Management 90:1043-1049. | 2009 | Finfish Harvest; Littering; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Water Environment Servicves. 2008. Three Creeks Restoration. | 2008 | Invasive Species; Littering; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands | ||
| Talbot, L. M., S. M. Turton, and A. W. Graham. 2003. Trampling resistance of tropical rainforest soils and vegetation in the wet tropics of north east Australia. Journal of Environmental Management 69:63-69. | 2003 | Australia | Littering; Seagrasses; Trampling | |
| Zepp, R. G. 2003. UV exposure of coral assemblages in the Florida Keys. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC. | 2003 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Light; Littering; Mangroves; Plankton; Seagrasses; Zooxanthellae |
| Baker, J. 2000. The Eastern Bristlebird: Cover-dependent and fire-sensitive. Emu 100:286-298. | 2000 | Littering | ||
| Debrot, A. O. and J. Sybesma. 2000. The Dutch Antilles. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 595-614. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Health Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| [No author name available]. 1999. Valdez sentence begins. Marine Pollution Bulletin 38:627. | 1999 | Littering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Al-Awadhi, F. M. A. 1999. The Year of the Ocean and its crucial importance to the Gulf. Desalination 123:127-133. | 1999 | Global | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Littering; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waste Management Policies | |
| Ochieng, C. A. and P. L. A. Erftemeijer. 1999. Accumulation of seagrass beach cast along the Kenyan coast: A quantitative assessment. Aquatic Botany 65:221-238. | 1999 | Kenya | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Fleshy Macroalgae; Littering; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses |
| Zann, L. P. 1996. The state of the Marine Environment Report for Australia (SOMER): Process, findings and perspectives. Ocean and Coastal Management 33:63-86. | 1996 | Global; Australia | Invasive Species; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Evans, S. M., M. Dawson, J. Day, C. L. J. Frid, M. E. Gill, L. A. Pattisina, and J. Porter. 1995. Domestic waste and TBT pollution in coastal areas of Ambon Island (Eastern Indonesia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 30:109-115. | 1995 | Indonesia | Fish; Littering; Snails & Conch | |
| Laur, D. R., A. W. Ebeling, and D. A. Coon. 1988. Effects of sea otter foraging on subtidal reef communities off central California. Pages 151-168 The community ecology of sea otters. | 1988 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Coralline Algae; Littering; Sea Urchins | |
| Goforth, GF; Diniz, EV; Rauhut, JB. 1983. Stormwater hydrological characteristics of porous and conventional paving systems., NTIS, SPRINGFIELD, VA (USA), 1983., 302 pp. | 1983 | Review | Impervious Surfaces; Littering; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Stone, R. B. 1972. Artificial reefs of waste material for habitat improvement. Marine Pollution Bulletin 3:27-28. | 1972 | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Littering |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Composting | Composting involves the controlled aerobic decomposition of manure or other organic material by micro-organisms into a biologically stable organic material that is suitable for use as a soil supplement. Composting should be part of nutrient management plans because it reduces the pollution potential of organic wastes. Smaller scale household composting may reduce the amount of material that enters the waste stream, where again it may have greater pollution potential. Larger volumes of material may require construction of containment facilities to ensure pollutants aren't able to enter runoff water in high concentrations. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Landscaping & Household Services; Littering; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Print Marine Etiquette on Marine-Related Products Packaging | Printing information on marine-related products regarding proper marine etiquette could be a possibility for raising awareness and improving public stewardship. Partnerships will be explored to help print etiquette information on materials such as bait boxes, ice bags, water buckets, etc. that are commonly used by stakeholders. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Develop Mobile Source Discharge Controls | Pollution discharge controls regulate where different types of discharges are allowed and what acceptable quantities released are. Typically discharge controls target point sources in the form of effluent pipes (#280), but discharges also occur from mobile sources such as boats and ships. There may need to be revisions on where depositing fish, fish parts, bait, cooling water, engine exhaust, deck wash, and effluent can be released. In many areas, these items are often excluded as prohibited, and they should possibly be included. Pollution discharge controls are different from Water Quality Standards (#22) which set acceptable environmental limits and leave it up to the manager to meet those criteria. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Chemical Variables; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Large Ships; Littering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Restoration: Environmental Remediation | Environmental Remediation is a type of restoration that's focus ranges from Brownfields to Oil Spills to Hazardous Waste Sites. These restoration activities aim to restore the site to a previous condition, or to a condition that is not a threat to human health or other forms of life. Several standards can be used to determine when remediation is necessary and to what extent the environment should be restores. Biocriteria can be used to determine the degree of degradation to biological components of the site. Often it is the presence of a particular pollutant in the soil, water or air, which is above acceptable limits and will not degrade fast enough over a short period of time and therefore must be removed. Physical and chemical water quality criteria can be used to set maximum acceptable limits of water quality parameters. Air quality criteria can be used to set acceptable maximum and minimum air standards for remediation. | Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 2005. Contaminated Sediment Remediation Guidance for Hazardous Waste Sites. EPA-540-R-05-012, US Environmental Protection Agency. Environment Protection Authority. EPA Guidelines for Environmental management of on-site remediation. Environment Protection Authority, Adelaide, Australia. |
Applied Chemicals; Biocriteria; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Health; Health Policies; Landuse Management; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Military; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Solid Waste Disposal; Supporting Services; Toxics; Valuation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water Quality Management: Landfill & Solid Waste Disposal Site Assessment Strategy | This option seeks to reduce/eliminate pollution from leaching at landfill sites. High risk, old landfill sites that may have hazardous waste must be identified. Once identified, monitoring at these landfills should be intensified to insure leaching does not occur into marine systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health; Health Policies; Littering; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |