ReefLink Database

Cruise Ships
The Cruise Ship industry utilizes large ships to transport tourists between coastal locations, providing food, entertainment, and accommodation.
CMap
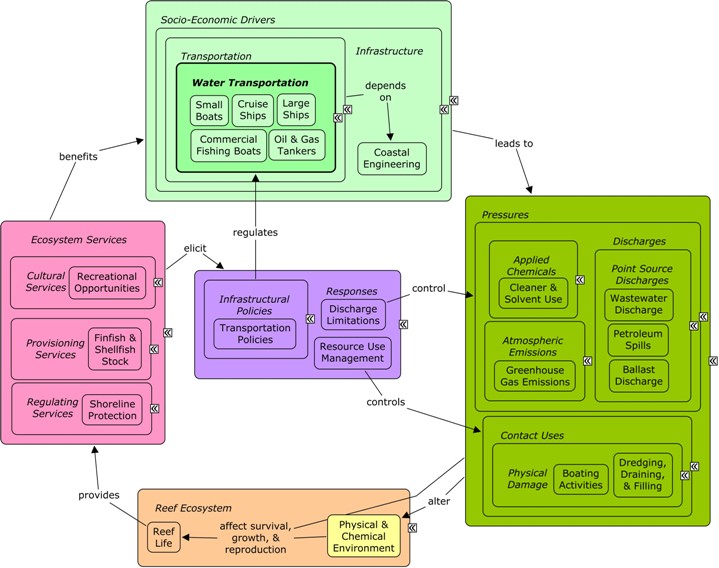
CMap Description
Operation of boats, ships and the ports, harbors, and docks they depend on, can create numerous pressures on the reef ecosystem. Boat and ship activities can lead to groundings, anchor drops, or use of fishing gear that can damage reef habitat, and movement can cause resuspension of sediment in the reef environment. Boats and ships may discharge wastewater into open water, and operators may use cleaners & solvents in harbor to maintain boats. Operation of ships and boats often leads to emissions of greenhouse gasses into the environment, and runs the risk, particularly for oil & gas tankers, of petroleum spills. Ballast discharge from large ships increases the risk of an invasive species entering the reef ecosystem, and competing with native species. Dredging of coastal vegetation or reef habitat may be needed for construction of ports, harbors, marinas, and docks, or to create channels for ship traffic. Maritime transportation sectors benefit from shoreline protection provided by the reef, including calm waters for boat activity and reducing the likelihood of damage to coastal engineering structures during storm events. Commercial fishing boat operators benefit from availability of finfish & shellfish stock. The aesthetic value of the reef provides recreational opportunities and contributes to the cultural identity of the local community, which can improve business for small boat and cruise ship operators. Decision-makers can influence numbers, distribution, technology, and discharges from boats and ships through policies and regulations. Resource use management can be used to control boating activities through mooring buoys or protected areas.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avellaneda, PM; Englehardt, JD; Olascoaga, J; Babcock, EA; Brand, L; Lirman, D; Rogge, WF; Solo-Gabriele, H; Tchobanoglous, G. 2011. Relative risk assessment of cruise ships biosolids disposal alternatives. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:2157-2169. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Cruise Ships; Discharges |
| Jones, RJ. 2011. Environmental Effects Of The Cruise Tourism Boom: Sediment Resuspension From Cruise Ships And The Possible Effects Of Increased Turbidity And Sediment Deposition On Corals (Bermuda). Bulletin of Marine Science 87:659-679. | 2011 | South & Central America; Australia; Bermuda; Panama; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Cruise Ships; Hotel & Food Services; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation |
| World Resources Institute. 2009. Value of coral reefs & mangroves in the caribbean: economic valuation methodology v3.0. | 2009 | South & Central America; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Belize; Caribbean | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Cruise Ships; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Wantiez, L. 2008. Coral reefs of New Caledonia in 2006: Status report and monitoring network [Les recifs coralliens de nouvelle-caledonie en 2006: etat des lieux et reseau de suivi]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:117-132. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Cruise Ships; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Mining; Mining Policies; Seastars; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| [No author name available]. 2007. Alien invaders - Nowhere to hide. Pages 31-33 MER - Marine Engineers Review. | 2007 | Review | Ballast Discharge; Collaboration & Partnering; Cruise Ships | |
| [No author name available]. 2007. 'Fantasea Ammari' - A \boutique\" cruise vessel for Barrier Reef luxury market". Work Boat World 25:23. | 2007 | Australia | Cruise Ships; Small Boats | |
| Jones, R. J. 2007. Chemical contamination of a coral reef by the grounding of a cruise ship in Bermuda. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:905-911. | 2007 | Bermuda | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Cruise Ships; Remediation; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Toxics | |
| Wright, D. A., R. Dawson, C. E. Orano-Dawson, and S. M. Moesel. 2007. A test of the efficacy of a ballast water treatment system aboard the vessel Coral Princess. Marine Technology 44:57-67. | 2007 | Florida; Panama; Columbia | Ballast Discharge; Cruise Ships; Light | |
| Davenport, J. and J. L. Davenport. 2006. The impact of tourism and personal leisure transport on coastal environments: A review. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 67:280-292. | 2006 | Cuba | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Regulations; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Hotel & Food Services; Infrastructure; Invasive Species; Land & Air Transportation; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling |
| World Resource Institute. 2006. Value of coral reefs in Caribbean islands: draft economic valuation methodology. | 2006 | South & Central America; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Caribbean | Review; GIS & Maps | Cruise Ships; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| [No author name available]. 2005. 'Oceanic Princess'-A very impressive \boutique\" cruise from Australia's NQEA". Work Boat World 24:42-43. | 2005 | Australia | Model | Cruise Ships; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products |
| Stedman, L. 2004. A Unanimous Vote of confidence? Pages 31-32 Water 21. | 2004 | Global | Ballast Discharge; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Invasive Species; Light; Wastewater Discharge | |
| [No author name available]. 2003. Aeroderivative gas turbines offer alternative power. Pages 31-32 Ship and Boat International. | 2003 | Coastal Defense; Cruise Ships; Military | ||
| [No author name available]. 2003. Coral princess debuts unique propulsion system. Diesel and Gas Turbine Worldwide 35:32-34. | 2003 | Cruise Ships | ||
| [No author name available]. 2003. Coral Princess: First of the new Princess pair from Atlantique. Pages 13-15 Naval Architect. | 2003 | Cruise Ships; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies | ||
| Rogers, C. S. and V. H. Garrison. 2001. Ten years after the crime: Lasting effects of damage from a cruise ship anchor on a coral reef in St. John, U.S. Virgin Islands. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:793-803. | 2001 | US Virgin Islands | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Cruise Ships; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 1996. Linking the Economy and Environment of Florida Keys/Florida Bay. | 1996 | Florida | Cruise Ships; Housing | |
| Smith, S. H. 1988. Cruise ships: A serious threat to coral reefs and associated organisms. Ocean and Shoreline Management 11:231-248. | 1988 | Cruise Ships; Fishing Sector; Tourism & Recreation |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Large Vessel Achoring | Damage from freighter anchor is extreme due to the mere weight and size of the anchor and chain. The chain can even be more damaging as it drags along the benthic environment leaving behind catastrophic ruin. This management response would encourage the creation of restoration and monitoring methodologies in shallow reef areas as well as at greater depths. If unacceptable damages are occurring restrictions and regulations prohibiting the use of anchors in high risk areas should be instituted. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Cruise Ships; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Transportation; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Collaborate with Towing & Salvage Operators in Grounding Notification | This option advocates the establishment of rapport between local operators and regulatory agencies. This is achieved through regular meetings and training sessions to emphasize the importance of operator cooperation in regards to vessel groundings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Large Ships; Military; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Ecological Reserves (ERs) | Ecological Reserves set aside areas with minimal human interference. These reserves aim to enhance and protect biodiversity through encompassing large, contiguous habitats. The goal of ecological reserves is to encourage spawning, nurseries, and residence areas that contribute to genetic protection of fish and marine life. Ecological Reserves can be achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Develop Mobile Source Discharge Controls | Pollution discharge controls regulate where different types of discharges are allowed and what acceptable quantities released are. Typically discharge controls target point sources in the form of effluent pipes (#280), but discharges also occur from mobile sources such as boats and ships. There may need to be revisions on where depositing fish, fish parts, bait, cooling water, engine exhaust, deck wash, and effluent can be released. In many areas, these items are often excluded as prohibited, and they should possibly be included. Pollution discharge controls are different from Water Quality Standards (#22) which set acceptable environmental limits and leave it up to the manager to meet those criteria. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Chemical Variables; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Large Ships; Littering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 Virgin Islands Code. | Under Title 25, in addition to requirements for boat registration and administration of harbors, among other things, sections pertaining to the mooring and anchoring of vessels and houseboats provide for the protection of important marine resources in USVI waters. The Law requires mandatory boating education and safety courses for all boat operators. Application to Coral Reefs:Mooring and anchoring are restricted and not allowed near fragile systems. Not anchoring on coral reefs is abig plus of this legislation. Legislative Actions:Penalties for violation of the Chapter include fines not to exceed $1,000, a lien on the vessel and potential libel suit Comments:A houseboat or vessel is allowed to moor or anchor only in those areas designated by the Department. Section 404(g) of the legislation lists areas designated as areas of special concern. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Boating Regulations; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Environmental Education & Outreach; Large Ships; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Transportation Policies |
| Air Pollution Control, 62-204 Florida Administrative Code (1996). | 62-204.100 Purpose and Scope.
(1) This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods.
(2) In addition, this chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassifiable with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have been adopted; further designates certain attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as air quality maintenance areas for particular pollutants; classifies all areas of the state as Class I, Class II, or Class III for determining which set of prevention of significant deterioration (PSD) increments apply; and designates all attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as one or more PSD areas for determining which pollutant-specific PSD baseline dates apply. This chapter also sets forth procedures for redesignating and reclassifying areas as above.
(3) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to identify the Florida State Implementation Plan (SIP) required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51; to set forth the public notice and hearing requirements that the Department will adhere to for making SIP revisions; and to set forth the definitions, criteria, and procedures that the Department will use to review a federal agency�s general conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart W; and to adopt by reference an interagency memorandum of agreement that the Department will comply with to review any transportation conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart T. The provisions to 40 C.F.R. 51.853 require that a federal agency make a general conformity determination for any federal agency action in a nonattainment or maintenance area, to ensure that such action is consistent with the SIP and that such federal conformity determination be reviewed by the affected state. The provisions of 40 C.F.R. 51.394 require that a transportation conformity determination be made for the adoption, acceptance, approval, or support of certain transportation plans, transportation improvement programs, and transportation projects in nonattainment and maintenance areas for transportation-related criteria pollutants to ensure that such actions are consistent with the SIP.
(4) Finally, this chapter adopts and incorporates by reference federal air pollution control regulations which are referenced in whole or in part throughout the Department�s air pollution control rules. Application to Coral Reefs:By reducing emmissions to air, particularly carbon dioxide, the pH of ocean waters will not be reduced and that is a direct benefit to coral reefs, since a reduction in pH is believed to be detrimental to corals. Legislative Actions:The Chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassified with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have benn adopted. Comments:This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Use Regulations; CO2; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Amendment to the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations revising the boundary of the northernmost area to be avoided off the coast of Florida, Federal Register § Volume 65, Number226 (2000). | NOAA, in conjunction with the US Coast Guard, proposed to revise the northernmost area to be avoided (ATBA) off the coast of the Florida Keys. The change was expected to increaase maritime safety and to avoid harm to the marine environment and its resources. Application to Coral Reefs:The amendments directly protect coral reefs because the change of the nothernmost area presented in the regulation as Area To Be Avoided resulted in large vessels not entering the area that had been the site of large vessel groundings. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in conjunction with the US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Civil Engineering & Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Cruise Ships; Fish; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Reef Inhabitants; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Dredge and Fill Activities, 62-312 Florida Administrative Code. | This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department pursuant to Sections 403.91 through 403.929, F.S. Dredging or filling which is grandfathered by subsections 403.913(6), (8) and (9), F.S., is governed by Rules 62-312.150 and 62-312.160, F.A.C. The requirements of this part are in addition to and not in lieu of the water quality standards which are required by other portions of these sections. Except for the definitions contained in Rule 62-312.020, F.A.C., which shall also apply to activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., the provisions of this Part shall only apply to activities in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District and to activities grandfathered under Sections 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15) and (16), F.S.
Specific Authority 373.414(11)-(16), 373.4145, 403.805(1) FS. Law Implemented 373.409, 373.413, 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15), (16), 373.4145, 373.416, 373.418, 403.061, 403.813, 403.814 FS. History�New 12-10-84, Amended 8-7-85, Formerly 17-12.010, 17-312.010, Amended 10-3-95. Application to Coral Reefs:The permit reviewers will require BMP for dredge and fill activities. This will include siltation reduction methods that will keep sediment, nutrient and other contaminants from leaving the work site and getting into the water column and potentially reaching sensitive ecosysten, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department for dredge and fill activities. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Toxics |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Marine Sanitation Devices (MSDs); Regulations to establish a No Discharge Zone (NDZ) for State waters within the boundary of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary,Code of Federal Regulations § 40 CFR Part 140, 67 FR 35735. | US EPA established a no discharge zone within the boundaies of the FKNMS pursuant to section 312 (f) (4) (a) of the Clean Water Act. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition of waste discharges protects reefs system from eutrophication by the nutrients in waste (particularly nitrogen and phosphorus) as well as the debris and sediment in the waste. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Algae; Ballast Discharge; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |