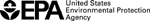Assessing Outdoor Air Near Schools
Follansbee Middle School and Jefferson Primary School - Follansbee, WV
- Understanding the Monitoring Data
- Initial Sample Results
- Initial Analysis
- Additional Sample Results
- Final Analysis
Results and Analysis of EPA’s monitoring
EPA selected this school for monitoring because it is located near a coke oven, steel mill, and tar plant which are sources of air toxics emissions. For the purposes of this study, results from the air monitoring at Follansbee Middle School are considered to be indicative of conditions at the nearby Jefferson Primary School. Computer models were used to determine which air toxics may be present at elevated levels in the outdoor air near the school. These models showed that manganese and pollutants associated with coke oven emissions, including benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene, could be present in the air around the school and prompted EPA to test to see if the levels present may be of concern.
| Primary Findings | Levels of manganese in the air at the school are below levels of concern for short-term and long-term exposure. Our analysis found that levels of pollutants associated with coke oven emissions, including benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene, indicate a potential for levels of concern for long-term, continuous exposure to the mixture of pollutants in the air, particularly in areas of the community closer to the source of emissions. Additionally, operating information for the coke oven facility indicates that it was operating at less than half of typical levels. |
| Key Pollutants Monitored | Manganese. Inhalation may affect the nervous system if people are exposed to high levels. Benzene. Inhalation of benzene at high levels can affect the bone marrow and can cause anemia and leukemia. Arsenic. Inhalation may affect the affect the developing nervous system if people are exposed to high levels. Benzo(a)pyrene. Inhalation of benzo(a) pyrene at high levels can cause cancer if people are exposed to high levels. |
| Next Steps | EPA plans to conduct additional air toxics monitoring at Follansbee Middle School in the near future to better characterize the potential for exposures of concern in the community, and to monitor any changes in airborne pollutant concentrations that may be associated with more typical, higher, operating conditions at the key emissions sources. EPA remains concerned about emissions from sources of air toxics and continues to work to reduce those emissions across the country, through national rules and by providing information and suggestions to assist with reductions in local areas. The West Virginia Department of Environmental Protection (WVDEP) will continue to oversee industrial facilities in the Follansbee area through air permits and other programs. Ohio EPA will continue to oversee industrial facilities to the west of Follansbee on the other side of the Ohio River. |
Summary of Study Approach and Findings
Approach:
- A monitor collected air samples from August 11, 2009 through December 15, 2009 at the Follansbee Middle School in Follansbee, WV. For the purposes of this study, results from the air monitoring at Follansbee Middle School are considered to be indicative of conditions at the nearby Jefferson Primary School.
- We posted individual air sample results on this website throughout the monitoring period to keep your community informed during the monitoring period.
- During the monitoring period, we evaluated the monitored concentrations to see if there was a concern from short-term exposures (e.g., several weeks).
- When the monitoring was complete, we analyzed the results to see if there was a concern from long-term exposures (over a lifetime).
- Also, when the monitoring was complete, we evaluated all the air samples from the on-site monitor. We also evaluated information on wind speed and wind direction from a weather monitor at the school, along with historical weather information and information about a nearby source of manganese and nickel emissions.
Findings:
- Our analysis found that levels of manganese in the air at the school are below levels of concern for long-term exposure. However, levels of pollutants associated with coke oven emissions, including benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene, indicate a potential for levels of concern based on the combined presence of these pollutants in the air, particularly in areas of the community closer to the source of emissions.
- The concentrations of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene measured at the school are lower than those suggested by the information that helped identify this school for monitoring.
- The process to identify schools for monitoring relied on emissions estimates and other information. Ambient air monitoring at the school allowed measurement of what was actually in the air.
- One key source, a coke oven, was operating at less than half of typical levels during monitoring, but is now operating at normal levels. Another key source, a steel manufacturing complex, was not operating during the monitoring period. That source is not expected to be operating in the foreseeable future.
- Based on these findings, EPA plans to conduct more air toxics monitoring at the Follansbee Middle School to better characterize the potential for exposures of concern in the community, particularly under more typical operating conditions now that at least one of the facilities is operating at a higher level.
- Click here for additional information
How We Analyzed the Information We Collected at this School
The analysis considered whether the information collected at the school might raise concerns for the health of children or adults at the school. We looked at the following types of information:
- Measured manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene concentrations and information on manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene
- Measured wind direction and wind speed at the school.
- Information about nearby sources of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene emissions.
Analysis of Measured Manganese Concentrations:
1. Calculate the average: We calculated the average of the manganese measurements (shown by the black diamond in the graph below). We compared this average to the long-term comparison level (thick line on the graph below). The long-term comparison level represents the level of manganese in the air that is below levels associated with health concerns, even if someone breathed air containing manganese at that level all day, every day over their lifetime.
Result: The average manganese level for the samples collected was well below the long-term comparison level. The health concern is low.
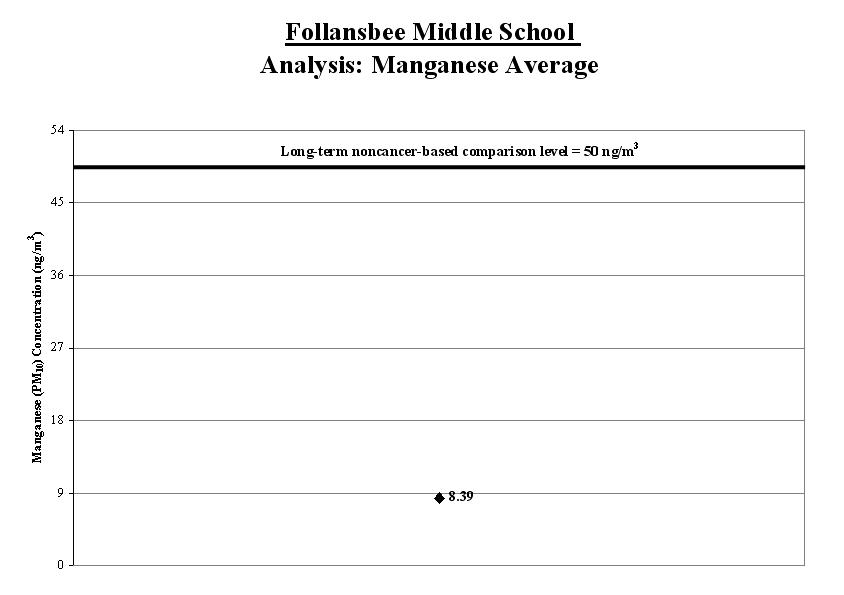
2. Calculate a range: To account for varying air concentrations of manganese, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the “upper bound”) to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The high end of the range is lower than the comparison level. The health concern is low.
Measured Concentrations for Other Pollutants:
Although the concentrations of benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene, are individually below long-term comparison levels (as shown below), the benzene concentrations and concentrations of some other source-related pollutants are near their long-term comparison levels. These analyses and additional information about these pollutants indicate the potential for levels of concern for long-term, continuous exposure to the mixture of pollutants, particularly in areas of the community closer to the source of emissions.
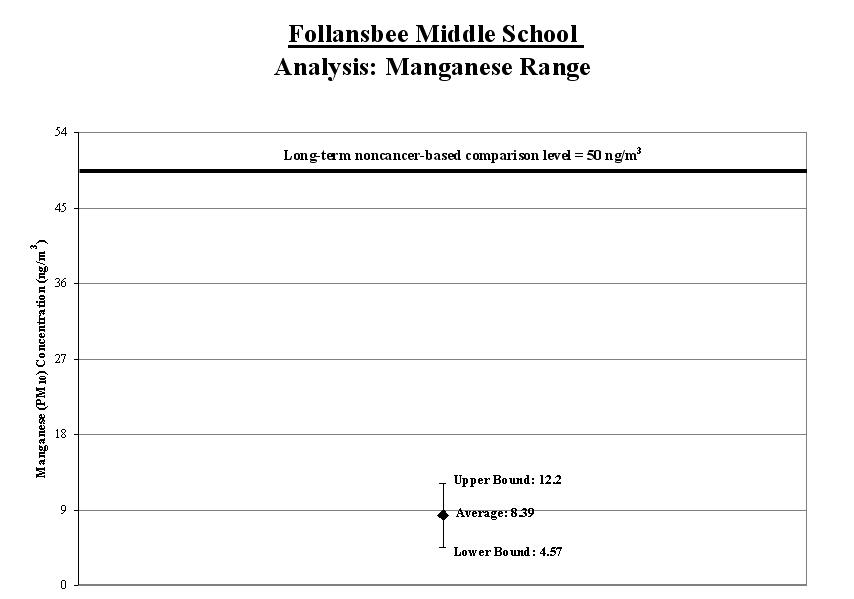
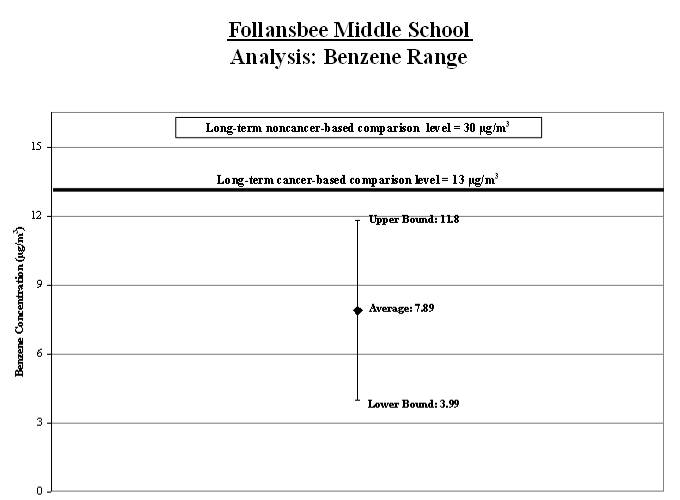
1a. Calculate the benzene average: To account for varying air concentrations of benzene, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the "upper bound") to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The average benzene level for the samples collected was below the long-term comparison level.
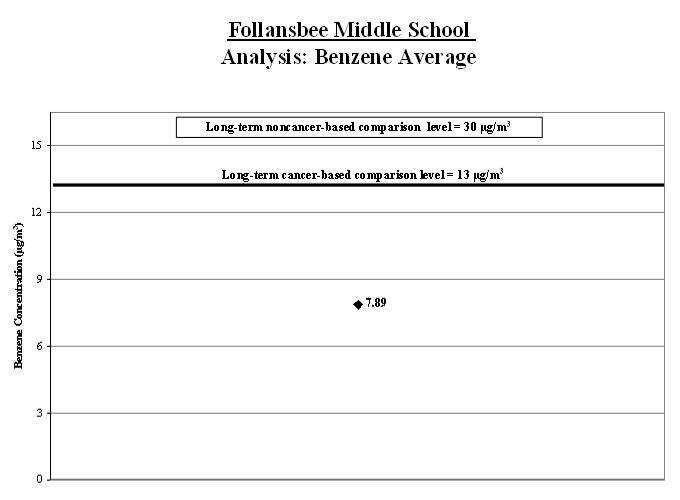
1b. Calculate a range for the benzene average: To account for varying air concentrations of benzene, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the "upper bound") to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The high end of the range is near the comparison level.
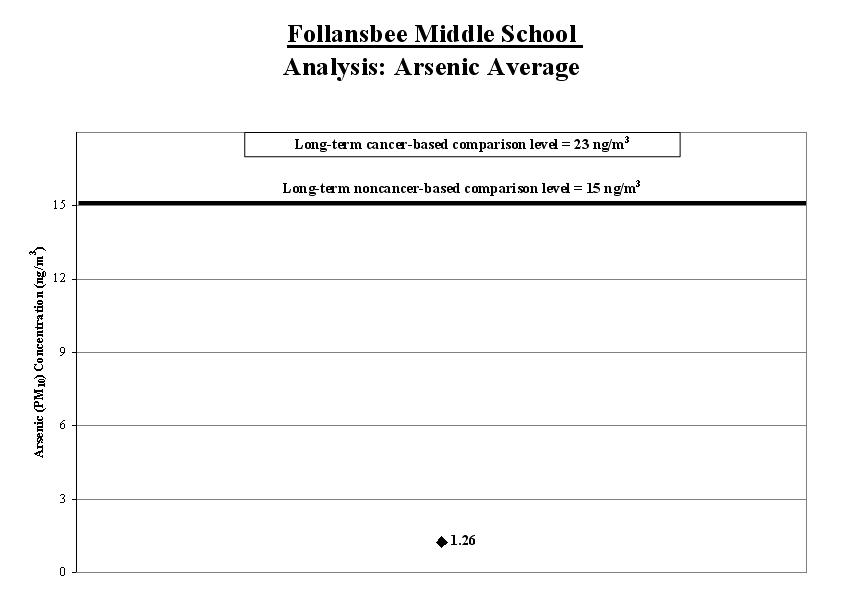
2a. Calculate the arsenic average: To account for varying air concentrations of arsenic, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the “upper boundâ€) to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The average arsenic level for the samples collected was well below the long-term comparison level.
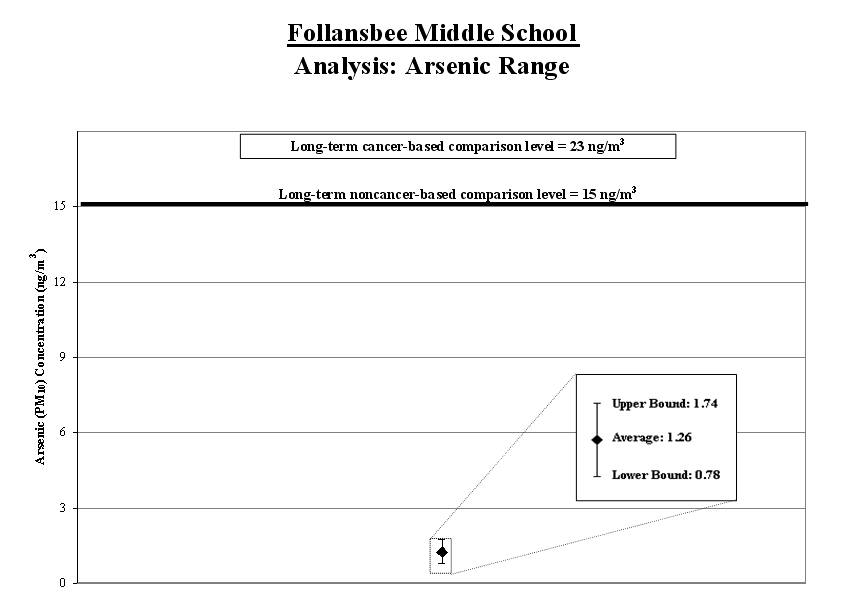
2b. Calculate a range for the arsenic average: To account for varying air concentrations of arsenic, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the "upper bound") to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The high end of the range is lower than the comparison level.
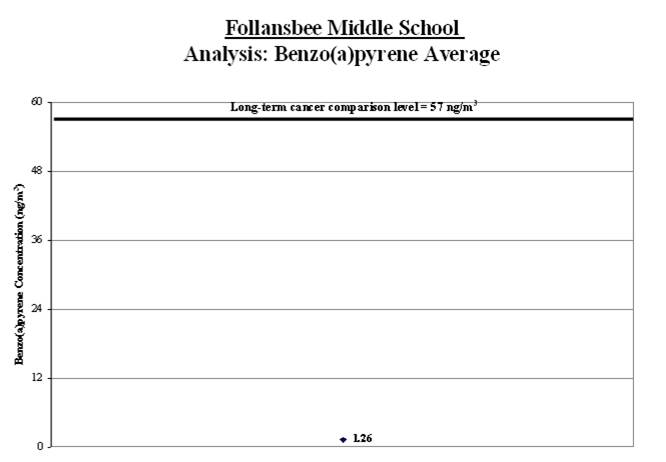
3a. Calculate the benzo(a)pyrene average: We calculated the average of the benzo(a)pyrene measurements (shown by the black diamond in the graph below). We compared this average to the long-term comparison level (thick line on the graph below).
Result: The average benzo(a)pyrene level for the samples collected was well below the long-term comparison level.
3b. Calculate a range for the benzo(a)pyrene average: Calculate a range for the benzo(a)pyrene average: To account for varying air concentrations of benzo(a)pyrene, we calculated a range around the average. We did this by estimating high and low values that the longer-term concentrations might reach using common statistical tools. We compared the highest point in the range (called the "upper bound") to the long-term comparison level.
Result: The high end of the range is lower than the comparison level.

Analysis of Measured Wind Direction and Wind Speed at the School
We took measurements of wind direction and speed every day during the sample period. We took special note of the wind speed and direction on the days we took measurements of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene.
| What we looked at | What we found |
| We looked at whether the wind data taken on the days we took measurements of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene are similar or different from the wind patterns during the entire sampling period. | We found the wind patterns taken on the days we took measurements of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene to be similar to those observed during the entire sampling period. |
| We looked at whether the wind pattern during the sampling period is reflective of regional wind patterns over the long term. | Although we lack long-term wind data at the monitoring site, the wind pattern at the NWS station during the sampling period is similar to the historical long-term wind flow pattern at that same NWS station. Therefore, the 4-month sampling period may be representative of year-round wind patterns. |
Analysis of Information on Nearby Sources of Manganese, Benzene, Arsenic, and Benzo(a)pyrene Emissions
| What we looked at | What we found |
| Whether we could determine if the sources were operating as usual during the sampling period. | One of the key sources, the coke oven, was operating at less than half of typical level during sampling , but is now operating at normal levels. Another key source, the steel manufacturing complex, was not operating during the sampling period. That source is not expected to be operating in the foreseeable future. |
| The concentrations of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene measured at the school are lower than those suggested by the information that helped identify this school for monitoring. | |
| The nearby sources of manganese, benzene, arsenic, and benzo(a)pyrene have Title V operating air permits issued by the WVDEP and Ohio EPA that includes operating requirements. |
Additional Information
Technical Report for School: Assessing Outdoor Air Near Schools: Follansbee Middle School and Jefferson Primary School, Follansbee, WV (PDF) (40pp, 599k). The technical report is geared toward risk assessors, risk managers, and other regulatory agencies.
Background on School Monitoring Effort