Glossary
SiteID: 35078E62169502
35078E62169502: "35078E6" (QuadID)
35078E62169502: "21" (QuarterQuad)
35078E62169502: "6" (Indicator number):
0 = normal
1 = SRS (Stratified random sample) row crop (1998 only)
2 = split plot
3 = special indicator (nad83 to nad27)
4 = SRS non row crop
5 = riparian (stream order 1)
6 = riparian (stream order 2)
35078E62169502: "9502" (unique point number)
Quad ID: Ohio Index, nomenclature
used by the USGS to identify DRG (digital raster graphic) topographic quadrangles.
For more detailed information, please refer to http://www.umesc.usgs.gov/data_library/maps_quads_figs/quad_indexes.html.![]()
UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator projection) Zone: Zone 17 = WEST of 78 degrees longitude and Zone 18 = EAST of 78 degrees longitude.
Quarter Quad: 7.5x7.5 minute USGS quadrangle.
Original Coordinates: Original coordinates for randomly generated plot locations.
Measured Coordinates: GPS plot location.
Actual Coordinates: Final plot location.
Plot: 0.41 hectare circular plot (36.5m radius) where field observations were recorded. Figure 1 shows a non-split plot that meets the 80/20 rule.

Figure 1
Split Plot: Initial plot location fell where it didn't meet the 80/20 rule - thus 2 plots measured to capture both landcover types.
Non-Split 80/20: 80 percent or greater of plot falls within one landcover type.
Moved Plot: Inaccessible - access problems.
Pull Azimuth and Distance: Distance and direction from measured coordinates to actual plot location.
Differential Correction Method: Satellite beacon - OMNISTAR, Ground beacon - Coast Guard, none.
SITE DESCRIPTION: Description of the plot from a ground perspective.
General Site Description: Generalized description of the 0.41 hectare plot (circle with a radius of 36.5 meters).
Subplot: An internal 15 meter radius circle located within the center of the plot (Figure 2).

Figure 2
LAND COVER: Description of the plot from a satellite perspective.
Impervious Cover: Land cover that resists the penetration of water into the soil or plant roots, non-porous; for example, blacktop/concrete roads, parking lots, and buildings.
Bare Surface: Porous land surface that lacks vegetation; for example, dirt roads.
Agriculture: Land in farms regularly used for agricultural production; all land devoted to crop or livestock enterprises, for example, farmstead lands, cropland, and grazing land.
Forest: Land which is at least 20 percent occupied
by forest trees of any size or formerly having had such tree cover and not
currently developed for non-forest use.
Non-Forest: Lands developed for non-forest use include areas for crops,
improved pasture, residential, or administrative areas, improved roads of
any width, and adjoining road clearing and power line clearing of any width.
Shrub: A woody plant which at maturity is usually less than 2 m tall
and generally exhibits several erect, spreading, or prostrate stems and has
a bushy appearance.
Ground Cover: Herbaceous non-wood.
Other: Any other type of land cover not described above (Impervious Cover, Bare Surface, Agriculture, or Vegetation).
Dominant: Trees with
crowns extending above the general level of the crown cover and receiving
full light from above and partly from the side; larger than the average trees
in the stands, and with crowns well developed but possibly
somewhat crowded on the sides.
Codominant: Trees with crowns forming
the general level of the crown cover and receiving full light from above but
comparatively little from the sides; usually with medium-sized crowns more
or less crowded on the sides.
Intermediate: Trees shorter than those
in the two preceding classes but with crowns extending into the crown cover
formed by codominant and dominant trees; receiving a little direct light from
above but none from the sides; usually with small crowns considerably crowded
on the sides.
Understory: Trees with crowns entirely
below the general level of the crown cover, receiving no direct light either
from above or from the sides.
Ground Cover: Herbaceous, non-woody.
Average Height (m): Average height (meters) of the particular species measured with Sunto hypsometer.
Average DBH (in): Diameter at breast height (dbh) - Measurement of tree diameter taken at 4 ½ feet above the ground (Figure 3).
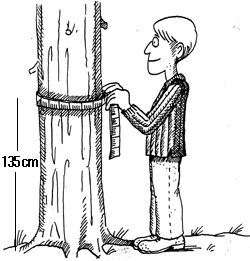
Figure 3
Relative abundance: The percentage of that particular species found within that particular height class.
Leaf Form: Percentage of
Deciduous vs. Evergreen in
that particular crown class.
Deciduous: Trees that lose leaves annually at end of growing period.
Evergreen: Remaining verdant, as coniferous trees and many tropical plants. Contrasted deciduous whose leaves, fruit, or petals fall at the end of the growing period.
Layer Density: 1= sparse/none, 2 = medium density, 3 = dense/thick.
Layer Distribution: 1 = homogeneous, 2 = clumped.
Land Form: A discernible natural landscape that exists as a result of wind, water or geological activity. Possible landforms are the following:
Ridge Top/Upper Slope:
The higher ground of a region, in contrast with a valley, plain, or other
low lying, adjacent land.
Midslope: A point of which its location is
approximately midway between the highest and lowest elevations of a slope.
Midslope Bench: A small level or nearly
level area in a midslope.
Lower Slope: A point whose location is near
the bottom of a slope.
Flatland: Having, or marked by a continuous
surface or stretch of land that is smooth, even, or horizontal, or nearly
so, and that lacks any significant curvature, slope, elevations, or depressions.
Bottomland/Wet Bottomland: The nearly level
plain that borders a and is subject to inundation under flood stage conditions
unless protected artificially. It is usually a constructional landform built
of sediment deposited during overflow and lateral migration of streams.
Aspect: Aspect in azimuth
degrees (0-360). Aspect is documented for slopes >3%.
Slope: Ratio of elevation
over distance. Plot measurement of dominant slope in sample area (in percent).
Computed by averaging upslope and downslope clinometer readings from site center.
Ecological System:
Estuarine:
Consists of deep water, tidal habitats and adjacent tidal wetlands that are
usually semi-enclosed by land but have open, partly obstructed, or sporadic
access to the open ocean, and in which the ocean water is, at least occasionally,
diluted by fresh water runoff from the land (brackish).
Lacustrine: Includes wetlands and deep water
habitats with all of the following characteristics: 1) situated in a topographic
depression or a dammed river channel; 2) Lacking trees, shrubs, persistent
emergents, emergent mosses or lichens with greater than 30% areal coverage;
3) Total area is greater than 8 acres.
Riverine: Includes all wetlands and deep
water habitats contained within a channel, except 1) Wetlands dominated by
trees, shrubs, persistent emergents, emergent mosses, or lichens; 2) Habitats
with water containing ocean-derived salts greater than 0.5%. A channel is
AAn open
conduit either naturally or artificially created which periodically or continuously
contains moving water, or which forms a connecting link between two bodies
of standing water."
Palustrine: Includes all non-tidal wetlands
dominated by trees, shrubs, persistent emergents, emergent mosses or lichens,
and all such wetlands that occur in tidal areas where salinity due to ocean-derived
salts is below 0.5%. Also includes wetlands lacking such vegetation, but with
all of the following characteristics: 1) The area is less than 20 acres; 2)
Active wave-formed or bedrock shoreline features are lacking; 3) Water depth
in the deepest part of the basin is less than two meters at low water; 4)
Salinity due to ocean derived salts is less than 0.5%. (Also called marsh,
swamp, bog).
Terrestrial: Includes habitats with no significant
water content.
Marine: Includes ocean or sea habitats with ocean-derived
salts greater than 0.5%.
Successional State:
Primary: Establishment of plants on land not
previously vegetated.
Secondary: Invasion of land that has been previously vegetated, the
pre-existing vegetation having been destroyed by natural or human disturbance,
such as windthrow, fire, logging, or cultivation.
Early: Cropland, grasses, weed species, pine seedlings.
Mid-1: Pine (shortleaf, loblolly, etc.).
Mid-2: Pine with hardwood understory (poplar, sweetgum, oak, etc.).
Late: Oak-Hickory (white oak, post oak, hickory, dogwood, loblolly
pine etc.).
Vegetated wetland: Vegetated palustrine, riverine,
or lacustrine area.
Stream: A narrow (10 ft. or less) body of running water.
River: A wide (greater than 10 ft.) body of running water.
Lake: A body of water larger than eight acres.
Pond: A body of water smaller than eight acres.
Ditch: A maintained waterway for irrigation.
Estuary: Consists of deep water, tidal habitats and adjacent tidal
wetlands that are usually semi-enclosed by land but have open, party obstructed,
or sporadic access to the open ocean, and in which the ocean water is, at
least occasionally, diluted by fresh water runoff from the land.
Ocean: Deep water, tidal habitats that have unobstructed access to
the open ocean.
None: No significant water at the site.
Figure 4
HUC (Hydrologic Unit): The 6-digit number represents the last six digits in the 11-digit HUC.
The United States is divided and sub-divided into successively
smaller hydrologic units which are classified into four hierarchal levels
by the USGS: regions (Atlantic-Gulf), sub-regions (Neuse-Pamilico), accounting
units (Neuse), and cataloging units which account for the first 8 digits of
the 11 digit HUC. The four cataloging units found in the Neuse Basin (Upper
Neuse, Middle Neuse, Lower Neuse, Contentnea) are classified further into
subcataloging units to produce the full 11-digit HUC. As an example, point
number 34076H52150612 has HUC = 204070. This comes from the full 11-digit
HUC 03020204070. For more information, visit http://water.usgs.gov/GIS/huc.html.
![]()
LU/LC (Land Use/Land Cover) code: Land use codes for original plot location generated from 1992, 1993 Multi-Resolution Land Characteristics (MRLC).
1- Urban
2- Agriculture
3- Forest
4- Herbaceous
5- Water
Crown Density Data:
Crown closure was measured over 0.07 hectares of the 0.42 hectare plot using two measurement techniques, the Vertical Tube (VT) and the Spherical Densiometer (SD). At plot center, two 30-meter transects were established and VT measurements were taken every 2 meters for a total of 29 readings (Figure 5 - notated as red dots). For each VT reading the researcher would hold the tube directly above his/her head and record whether sun (light) was visible or not. If sun was visible then the researcher would record whether ground vegetation < 3 meters was present or not. If the crosshair sighting in the VT was blocked the researcher would record the tree type (deciduous or evergreen) and crown class (substory, intermediate, or dominate) of the blocking vegetation. If the crown class of the blocking vegetation was not dominant then the researcher would sight beyond the blocking understory vegetation to sight the dominant canopy and thus record whether or not light was visible. If the VT sighting was blocked by the dominant canopy the researcher would record the tree type (deciduous or evergreen).
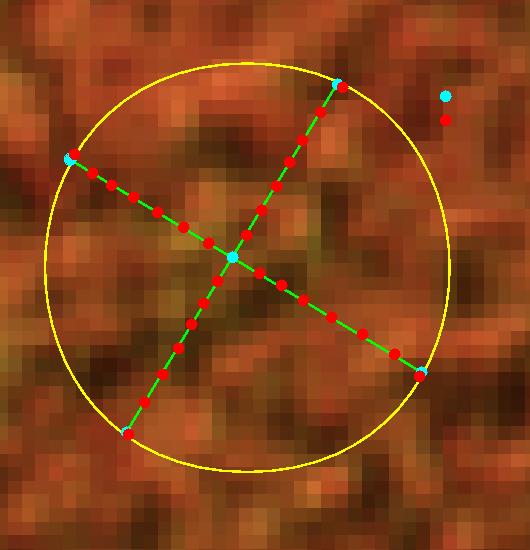
Figure 5
The Spherical Densiometer measurements were taken at five locations, one at plot center and the other four at the ends of the two transects (Figure 5 - notated as light blue dots). At each of the five locations, four readings at 90-degree intervals were taken by recording the number of dots out of 96 that showed no vegetative obstruction.
Vertical Tube (VT): The Vertical Tube is constructed of a 7.6 cm long, 6.4 cm diameter PVC tube with sighting crosshairs secured at one end of the tube and a sighting weight deployed on a 20.3 cm string hanging approximately 10.2 cm below base of Vertical Tube (Figure 6). The observer notes either closed or open crown by sighting directly overhead and aligning the hanging weight and the crosshairs to insure a perpendicular crown closure reading (Figure 7).
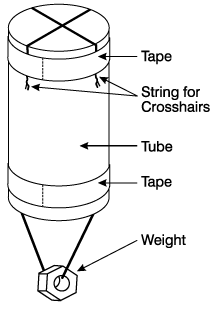
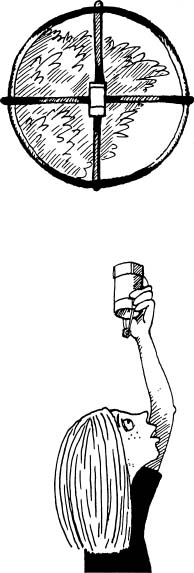
Figure 6 Figure
7
Pictures courtesy of NASA GLOBE PROJECT
Vertical tube % gap: Percent of forest canopy where sun penetration occurs using a vertical tube.
Densiometer: The convex Spherical Densiometer is a circular mirror that projects a 60° angle from the point of origin . The mirror is etched with a grid containing 24, 1.3 cm x 1.3 cm squares. Each square has four points centered in each .3 cm x 1.3 cm square for a total of 96 dots. At a height of one meter above the ground the Densiometer is leveled at arms distance away from the observer. The Densiometer is read by counting dots unobstructed by the crown. Percent crown closure is determined for that one reading by computing (1-(No Crown dots/96))*100.
Densiometer % gap: Percent of forest canopy where sun penetration occurs using a densiometer.
Basal Area Measurements
Basal area (BA) is the combined cross-sectional area (m*m) of all trees on a
hectare at 1.35 m above the ground. At each plot a point sample was taken using
a 2.296 Basal Area Factor (BAF) prism to determine BA per hectare, a useful
measurement in the determination of forest carbon stock and stand density. This
point sampling method also allows the extraction of forest stand information
such as trees per hectare and cubic foot volume. The following table illustrates
the relationship between the number of trees counted by diameter class and the
corresponding calculation of BA. Thus one 14" dbh tree counted at a plot
accounts for 23.11 trees of that size in one hectare and 2.296 m*m basal area/hectare.
|
Tree |
Trees |
Trees |
Basal area |
Basal area |
Basal area |
Basal area |
Basal area |
|
dbh (in) |
per acre |
per hectare |
per tree (sq ft) |
per tree (m*m) |
per hectare (m*m) |
per acre (sq ft) |
per acre (m*m) |
|
4 |
114.59 |
283.15 |
0.087 |
0.008 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
6 |
50.93 |
125.85 |
0.196 |
0.018 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
8 |
28.65 |
70.79 |
0.349 |
0.032 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
10 |
18.33 |
45.30 |
0.545 |
0.051 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
12 |
12.73 |
31.46 |
0.785 |
0.073 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
14 |
9.35 |
23.11 |
1.069 |
0.099 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
16 |
7.16 |
17.70 |
1.396 |
0.130 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
18 |
5.66 |
13.98 |
1.767 |
0.164 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
20 |
4.58 |
11.33 |
2.182 |
0.203 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
22 |
3.79 |
9.36 |
2.640 |
0.245 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
24 |
3.18 |
7.87 |
3.142 |
0.292 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
26 |
2.71 |
6.70 |
3.687 |
0.343 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
28 |
2.34 |
5.78 |
4.276 |
0.397 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
30 |
2.04 |
5.03 |
4.909 |
0.456 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
32 |
1.79 |
4.42 |
5.585 |
0.519 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
34 |
1.59 |
3.92 |
6.305 |
0.586 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
|
36 |
1.41 |
3.50 |
7.068 |
0.657 |
2.296 |
10 |
0.929 |
Riparian: Pertaining to the banks of a river, stream, waterway, or other, typically, flowing body of water as well as to plant and animal communities along such bodies of water.
Stand: A group of forest trees of sufficiently uniform species, composition, age, and condition to be considered a homogeneous unit for management purposes.
Nad83 (North American Datum of 1983) and Nad27 (North American Datum of 1927): For more information, please refer to the .pdf document, http://geology.er.usgs.gov/eespteam/GISLab/Cyprus/datums.htm.
![[logo] US EPA](../gif/logo_epaseal.gif)