Worker Protection Measures Fact Sheet
Soil Fumigant Mitigation Measures
Current as of May 27, 2009
EPA is requiring important new safety measures for soil fumigant pesticides. This fact sheet summarizes new requirements to protect fumigant handlers and workers from fumigant exposures. When new fumigant labels appear in the market place in 2010, fumigant users will need to comply with these new requirements to protect fumigant handlers and other workers.
Due to their volatile nature, soil fumigants have the potential to pose risk concerns to people involved in the application (handlers), workers who re-enter fumigated fields (workers), and people who may be near the treated area (bystanders). EPA’s Amended Reregistration Eligibility Decisions (REDs) for the fumigants chloropicrin, dazomet, metam sodium/potassium, and methyl bromide include a suite of measures designed to work together to reduce exposures, enhance safety, and facilitate compliance and enforcement. These mitigation measures include:
- worker protections
- fumigant management plans
- stewardship and training programs
- good agricultural practices
- buffer zones
- posting requirements
- emergency preparedness and response measures
The Amended REDs are based on public comments and new scientific data and information submitted in response to EPA’s July 2008 Soil Fumigant REDs. For additional information, please see the Agency’s Web page on risk mitigation measures for the soil fumigants.
New Requirements to Protect Handlers and Workers
To address risks to fumigant handlers, the Agency is requiring:
- A clear description of handler activities on labels. All persons performing fumigant-handler activities must be trained and equipped as handlers in accordance with the requirements in the WPS (40 CFR Part 170). Handler activities include:
- Participating in the application as supervisors, loaders, drivers, tractor co-pilots, shovelers, cross ditchers, or as other direct application participants (note: the application starts when the fumigant is first introduced into the soil and ends after the fumigant has stopped being delivered/dispensed to the soil);
- Monitoring fumigant air concentrations;
- Cleaning up fumigant spills (this does not include emergency personnel not associated with the fumigation application);
- Handling or disposing of fumigant containers;
- Cleaning, handling, adjusting, or repairing the parts of fumigation equipment that may contain fumigant residues;
- Installing, repairing, or operating irrigation equipment in the fumigant application block or surrounding buffer zone during the buffer zone period;
- Entering the application site or surrounding buffer zone during the buffer zone period to perform scouting or crop advising tasks;
- Installing, perforating (cutting, punching, slicing, poking), removing, repairing, or monitoring tarps:
- until 14 days after application is complete if tarps are not perforated and removed during those 14 days, or
- until tarp removal is complete if tarps are both perforated and removed less than 14 days after application; or
- until 48 hours after tarp perforation is complete if they will not be removed within 14 days after application.
On-site supervision and training
- Direct, on-site supervision by certified applicators during most fumigant applications
- New training provided by registrants for certified applicators who supervise fumigant applications
- New training information for other handlers.
Respiratory protection requirements
- Handlers must either stop work and leave the area or use air-purifying respirators if they experience sensory irritation (this does not apply to formulations with greater than 80% methyl bromide)
- For formulations with greater than 80% methyl bromide handlers must wear air-purifying respirators during handling activities
- Air monitoring while handlers use respirators to ensure concentrations do not exceed the upper working limit of respirators
- All handlers who will wear a respirator must be fit-tested, trained, and medically examined to ensure they do not have health problems such as a heart condition that could make use of a respirator dangerous
- Respirator and cartridges must be available for each handler who will wear a respirator.
Tarp perforation and removal requirements
- If tarps are used, they may not be perforated until at least 5 days (120 hours) have elapsed after the fumigation is complete unless a weather condition exists that necessitates early removal
- Tarp removal may not begin until at least 2 hours after tarp perforation is complete and tarp removers must follow respiratory protection requirements
- For formulations with greater than 80% methyl bromide, air monitoring with direct-read instruments is required before tarp removal can begin
- If tarps are not removed, planting may not begin until at least 48 hours after tarp perforation is complete
- If tarps are left on the soil for at least 14 days after the fumigation is complete, planting may begin when the tarps are being perforated
- Tarps must be perforated using mechanical methods (e.g., all-terrain vehicles with cutting implements) except for small areas (less than 1 acre), at the start of a row, and during flood prevention activities.
Entry-restricted period requirements
- Entry into treated fields (including early entry that would otherwise be permitted under the WPS) by any person other than a trained and equipped handler is prohibited from the start of the application until
- 5 days (120 hours) after application has ended for untarped applications, or
- After tarps are perforated and removed if tarp removal is completed less than 14 days after application, or
- 48 hours after tarps are perforated if they will not be removed prior to planting, or
- 5 days (120 hours) after application is complete if tarps are not perforated and removed 14 days after the application is complete.
Figures 1, 2, 3, and 4 provide illustrations of tarp perforation/removal and entry prohibition mitigation for different application scenarios. The intervals depicted are the minimum that must be followed.
Figure 1. Untarped Bed or Broadcast Applications (no tarp is used)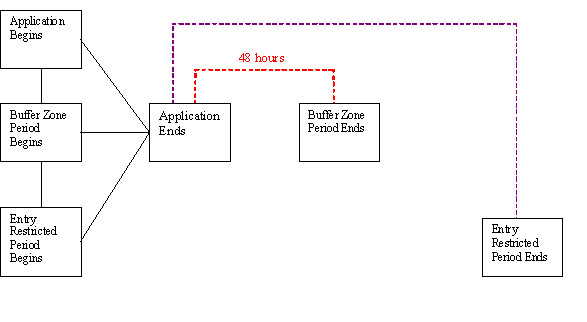 |
Figure 2. Tarp Broadcast Applications (tarps removed before planting)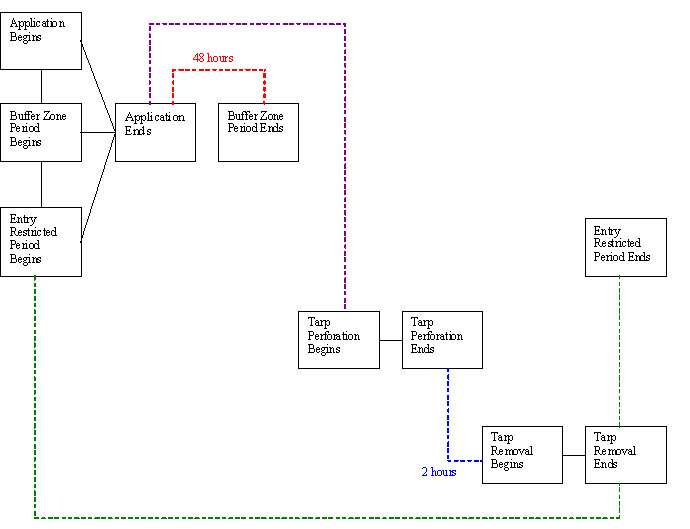 |
Figure 3. Bed Tarp Applications (tarps not removed before planting)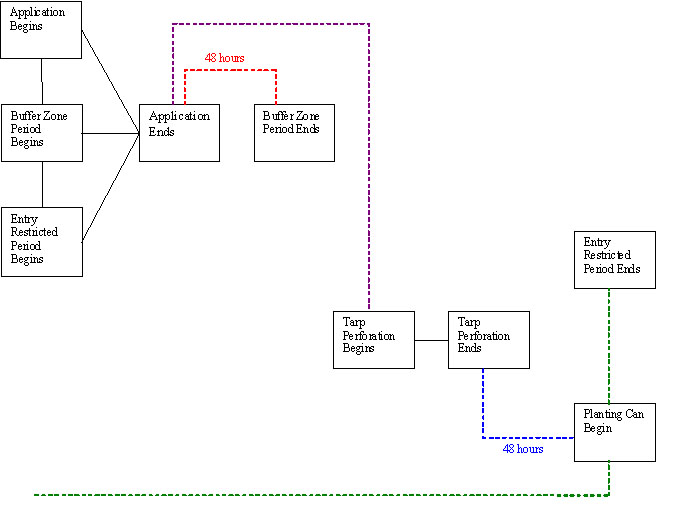 |
Figure 4. Bed or Broadcast Tarp Applications (when tarps are not perforated until 14 days after application)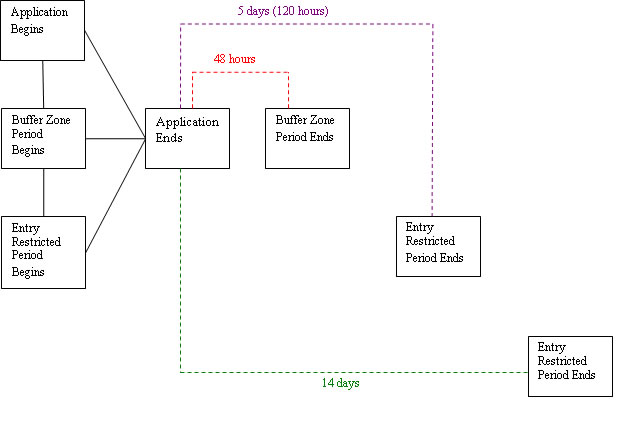 |
![[logo] US EPA](../gif/logo_epaseal.gif)
