ReefLink Database

Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism
The Dive, Snorkeling, and Swimming Tourism sector includes businesses that provide equipment, instruction, and location to allow tourists to swim, snorkel, and SCUBA dive.
CMap
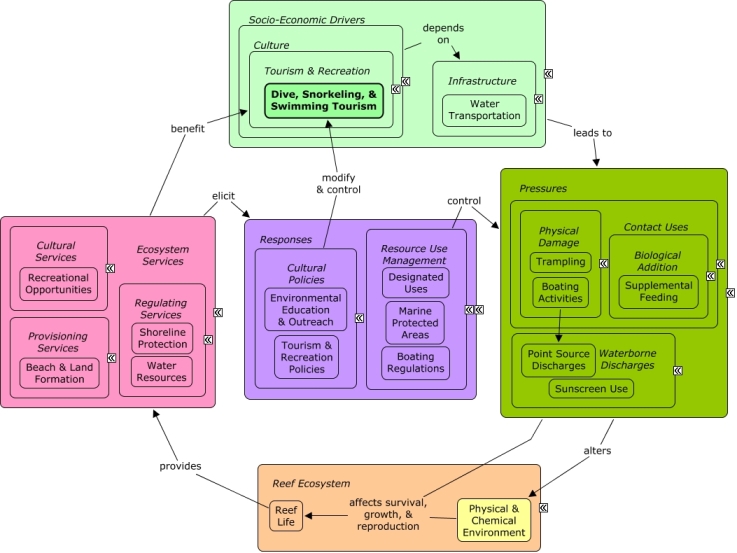
CMap Description
Dive, snorkeling, & swimming tourism and recreational activities may create pressures on the reef ecosystem through activities that cause physical damage to reef species, including walking on reef habitat or improper use of small boats that can lead to groundings, anchor damage, or resuspension of sediment. People may alter the behavior of fish through supplemental feeding, or release chemicals into the water, such as through wash off of suntan oil, although effects on reef species are likely minimal. Dive, snorkeling, & swimming tourism sectors directly benefit from many ecosystem services, including the aesthetic & recreational value provided by a diverse and healthy coral reef, clean and calm water for swimming, and formation of beaches and land from the calcium carbonate skeletons of coral and other species. Decision-makers can enact policies to increase tourism, alter the location or intensity of recreational activities, or educate the public to modify their behavior.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Education: Develop Standardized Voluntary Certification Programs | This management option involves coordinating with leaders of various target businesses related to diving and snorkeling, marine mammal viewing, kayaking, eco-tours, and fishing. Through collaborations with these businesses, management areas can create a voluntary certification program for employees of these businesses to learn and receive accurate information about nearby corals, the ecosystem, and how they can better protect reefs in their everyday actions. These voluntary certifications can be used to educate employees and/or to develop self-regulating standards for these businesses. Depending on the standards and curriculum, voluntary certification programs can then be used by these businesses to convey knowledge or environmentally safe practices to customers through marketing. Educating employees of these businesses helps to assure that they are disseminating accurate information to visitors. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Use Patterns on Artificial and Natural Reefs | This management option seeks to provide data for decisions concerning creating new artificial reefs. Use data is important because justification for artificial reefs extends from their ability to shift use pressures (diving, fishing, etc.) from natural reefs. Once an artificial reef is decided on there is much more data to collect and factors to consider when deciding where the artificial reef (#189). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Defense; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Military; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Integrate Volunteer Monitoring Program | Monitoring by trained volunteers yields useful, cost-effective data that provides positive engagement for a variety of stakeholders. Such existing programs include The Ocean Conservancy, Atlantic Gulf Rapid Reef Assessment, and the Dolphin Ecology Project. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Environmental Education Foundation REEF | This program uses recreation divers who conduct fish biodiversity and abundance survey in the Keys and the Caribbean. This surveys work towards contributing to The Great Annual Fish Count. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fish; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Ecosystem Condition RECON | RECON trains volunteer divers to collect information about the reef environment, health of stony corals, presence of key reef organism, and human-induced impacts. The goal of RECON is to broaden knowledge of bottom-dwelling organisms on reefs. They also act as an alert system when there are abnormal and possibly harmful conditions present on the reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Stony Coral |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Channel & Reef Navigation Markers | This option would evaluate the need for proper marking to ensure better navigation. There are many types of markers, including buoys, charts, beacons, and GPS mapping. Such markers can also be used to advocate prohibition on vessel speeds greater than idle speed in areas designated as idle-speed only/no-wake and around shallow reef locations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beach & Land Formation; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Artificial Reef Regulations | Discharge/depositing of materials and constructions on the seabed are both prohibited without permits, regulating the construction of new artificial reefs. Likewise, existing artificial reefs are protected through permit requirements for any alternation of the seabed. There are still further considerations for protecting artificial reefs. Artificial reef materials and construction choices are very important and may change based on the specific location and desired impacts. An artificial reef to attract recreational fishing differs from one for recreational divers or shoreline storm protection. Many artificial reefs were formally large ships, oil rigs or other types of waste that have been decommissioned and would be too large and expensive to dismantle on land. In these cases it is important to put restrictions on the sinking process to ensure there won�t be any type of chemical leakage and that the structure is stable on the seabed. (#189) (#190) | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Solid Waste Disposal; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Mooring Buoy Management | Installing mooring buoys is encouraged in order to prevent damage to corals from anchors. Areas that experience a lot of traffic from recreation and fishing will experience damage from vessel groundings and boat gear. Mooring buoys help to minimize damage to corals and at the same time provide access to water resources. Mooring buoys protect as well as lower resource-use conflicts. Mooring buoy management is achieved through maintaining existing mooring buoys; assessing current buoy technology; reviewing visitor-use and boating data; developing sitting criteria; recommending new sites; conducting site assessments; installing additional buoys; and implementing vessel size limits in high-use and sensitive areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Altmeier, Bernie. FKNMS Mooring Buoy Mainenance. NOAA: FKNMS Mooring Buoy Manual Accessed 3/23/2011. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chapter 2: Protection of indigenous, endangered and threatened fish, wildlife and plants, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates activities, including scientific research, that could affect indigenous species and species considered at risk (threatened) or endangered, establishes species of special concern and habitats that should be protected, requires permits for trimming mangroves Application to Coral Reefs:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Legislative Actions:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals; Final Rule, 73 Federal Register § 72210. | We, the National Marine
Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final
rule designating critical habitat for
elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and
staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which
we listed as threatened under the
Endangered Species Act of 1973, as
amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four
specific areas are designated: the Florida
area, which comprises approximately
1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of
marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area,
which comprises approximately 1,383
square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine
habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area,
which comprises approximately 121
square miles (313 sq km) of marine
habitat; and the St. Croix area, which
comprises approximately 126 square
miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We
are excluding one military site,
comprising approximately 5.5 square
miles (14.3 sq km), because of national
security impacts. Application to Coral Reefs:The law protects coral habitat for elkhorn and staghorn coral which strenghtens their protection in the FKNMS, Puerto Rico, and US Virgin Islands. Legislative Actions: Comments:the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final rule designating critical habitat for elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which we listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act of 1973, as amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four specific areas are designated: the Florida area, which comprises approximately 1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area, which comprises approximately 1,383 square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area, which comprises approximately 121 square miles (313 sq km) of marine habitat; and the St. Croix area, which comprises approximately 126 square miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We are excluding one military site, comprising approximately 5.5 square miles (14.3 sq km), because of national security impacts. |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations, Federal Register § Volume 66, Number 11 (2001). | NOAA established the Tortugas Ecological Reserve (a no-take zone) in the Tortugas region (Tortugas or region) of the Florida Keys to protect significant coral resources and to protect an area that serves as a source of biodiversity for the Sanctuary as well as for the southwest shelf of Florida. Establishment of the Reserve included expansion of the Sanctuary boundary to ensure that the Reserve protects sensitive coral habitats lying outside the existing boundary of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Regulation protects significant coral resources and many marine species by providing a no-take zone. Legislative Actions:The regulation increased the no-take zones to 24 areas. Fishing is prohibited in Tortugas north for areas that are within State waters. Diving is prohibited in Tortugas south. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Anchoring on Tortugas Bank, Federal Register § Volume 63, Number 158 (1998). | The regulation reinstates and makes permanent the temporary prohibition on anchoring by vessels 50 meters or greater in registered length on the Tortugas Bank west of the Dry Tortugas National Park within the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition on anchoring protects coral reefs and benthic habitats from physical damage. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proposed Coral Reef Conservation Act Amendments of 2005, 2007 and 2009,. | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:When passed, the Amendments, among other issues, would reauthorize the Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000 and authorize appropriations through fiscal 2012 for the coral reef conservation program and community- based planning grants. Will authorize activities designed to minimize the likelihood of vessel impacts or other physical dammage to coral reefs, including activities to identify certain at-risk coral reefs. Promote international cooperation, codify the US Coral Reef Task Force. Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The amendments would not add regulations to the Act. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; CO2; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
