ReefLink Database

CO2
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas used by primary producers, such as plants and algae, to produce sugars.
CMap
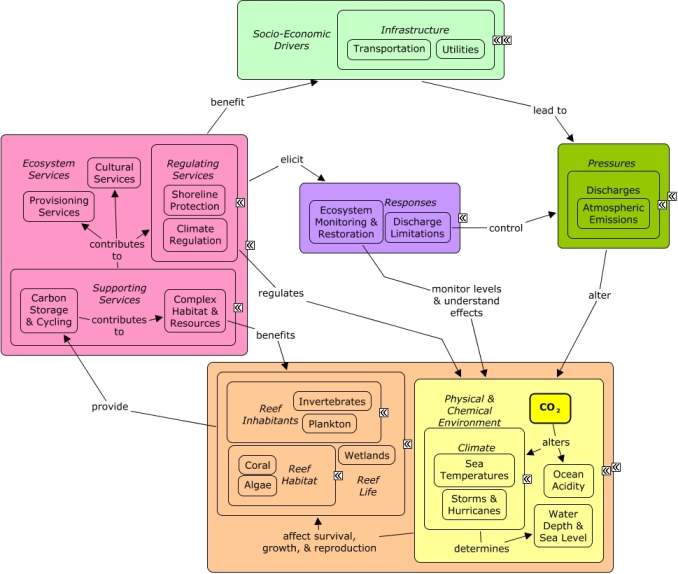
CMap Description
Atmospheric emissions of CO2 contribute to changing climate, rising sea temperatures, and ocean acidification. Sea temperatures can affect the growth, reproduction, and survival of reef species. Pathogen growth and disease outbreaks may be accelerated in warm waters, and extended periods of elevated temperatures are known to cause coral bleaching. Ocean acidity can affect the growth, reproduction, and survival of reef species, particularly stony coral, calcareous macroalgae, crustose coralline algae, crustaceans, mollusks, and bivalves which deposit calcium carbonate during growth to form hard skeletons or shells. Changes in reef condition will impact the availability of ecosystem goods and services, including climate regulation through carbon storage and cycling, and shoreline protection which can ameliorate the damaging effects of storms. Many of the same socio-economic sectors which cause pollution benefit indirectly from goods and services provided by the reef, such as recreational opportunities or essential habitat for fish and other invertebrates. Monitoring and scientific research can be used to track CO2 levels and better understand the consequences for reef life. Discharge limitations, such as point-source controls, can be used to control atmospheric pollution.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corporate Response: Standardized Environmental Certifications and Labels | Product labeling initiatives are based on the premise that product information represented by or contained on the label is otherwise not readily available (or apparent) and is of value in consumer purchase decisions. For example, warning labels highlight product safety and toxic exposure hazards and advise consumers on ways to minimize risks. Likewise, a number of environmental certification programs (ECPs) identify products' environmental burdens and/or set standards for products' environmental attributes. Properly designed environmental labeling efforts can change consumer and manufacturer attitudes and behaviors, thus reducing environmental burdens. The specific metrics used to measure environmental label effectiveness include: 1) consumer awareness of labels, 2) consumer acceptance of labels (credibility and understanding), 3) changes in consumer behavior, 4) changes in manufacturer behavior, and 5) improvement of end goals, such as environmental quality. | Malcohn, E., Bentham Paulos, Andrew Stoeckle, Herbert Han-Pu Wang, and Julie Lynch. Determinants of Effectiveness for Environmental Certification and Labeling Programs. EPA-742-R-94-001, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; CO2; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Forestry; Health; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Birds; Medical Care; Medical Centers; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Resource Use Management; Toxics; Transportation; Utilities; Whales & Dolphins; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Discharge Controls: Carbon Sequestration | Carbon sequestration is the process through which practices remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. The term "sink" is also used to describe agricultural and forestry lands that absorb CO2, the major global warming gas emitted by human activities. Agricultural and forestry practices can also release CO2 and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. In the ocean, phytoplankton are another major carbon sink. | Houghton, R.A. 2002. Magnitude, distribution and causes of terrestrial carbon sinks and some implications for policy. Climate Policy 2:71-88. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Algae; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Forestry; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Plankton; Political Pressure; Solid Waste Disposal |
| Discharge Controls: Air Filtration & Scrubbing | The management option reduces emissions of air contaminants from structures through interception and/or collection. These filters and scrubbers can be implemented on ventilation emitting particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, ammonia, odorous sulfur compounds, methane or other greenhouse gasses. There are many alternative filters and scrubbers depending on the ventilation system and the characteristics of the emissions. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; CO2; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Manufacturing & Trade; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ocean Acidity; Regulating Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Energy Efficiency Initiatives | Energy efficiency is one of the lowest cost strategies for reducing greenhouse gases. Energy efficiency is also one of the few options that actually reduce user costs as well, since using less energy should reduce energy bills. Energy efficiency can be promoted across the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. In the US, the ENERGY STAR program has served as a trusted source of information to help consumers and organizations throughout the nation adopt energy-efficient products and practices. Other ways to incentivize energy improvements include subsidizing (e.g. tax exemption) or issuing lower interest loans for investments in energy use reduction technologies and infrastructure (e.g. more efficient heating/cooling systems). | Environmental Protection Agency. ENERGY STAR and Other Climate Protection Partnerships. 2009 Annual Report. US EPA. |
Atmospheric Emissions; City Planning; Climate Regulation; CO2; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Oil & Gas Industry; Shelter; Utilities; Utility Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Monitor & Research: Water Quality Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term, comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of water quality parameters. Parameters that should be measured include temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, relative fluorescence, light attenuation, nutrients, chlorophyll, and alkaline phosphatase activity. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Regulating Services; Salinity; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Supporting Services; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Research Global Change | This management option involves research to examine the effects of stresses associated with global change on the ecosystem. Stresses can include changes in temperature, hydrology, salinity, frequency and intensity of storms, turbidity, sea level change, and ultra violet and visible radiation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Regulating Services; Salinity; Sea Temperatures; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Transportation Policy: Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards | The purpose of Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAF�) standards is to reduce fuel consumption by increasing the fuel economy of cars and light trucks. NHTSA sets fuel economy standards for cars and light trucks sold in the US while EPA calculates the average fuel economy for each manufacturer. Since the standard only dictates the average fuel economy, manufacturers can sell vehicles with higher or lower fuel economy than the standard. | National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE). Accessed 8/11/2011. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Food & Energy Policies; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Industry; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Supporting Services; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Transportation Policy: Airline Carbon Policy | Civil aviation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, and this contribution has grown as the industry has grown. Some regions are implementing policies such as cap and trade that apply to the airline industry. | Bruce Duguid. 2009. Fasten Your Seat Belt: Airlines and cap-and-trade. CTC764, Carbon Trust, United Kingdom. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Supporting Services; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air Pollution Control, 62-204 Florida Administrative Code (1996). | 62-204.100 Purpose and Scope.
(1) This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods.
(2) In addition, this chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassifiable with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have been adopted; further designates certain attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as air quality maintenance areas for particular pollutants; classifies all areas of the state as Class I, Class II, or Class III for determining which set of prevention of significant deterioration (PSD) increments apply; and designates all attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as one or more PSD areas for determining which pollutant-specific PSD baseline dates apply. This chapter also sets forth procedures for redesignating and reclassifying areas as above.
(3) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to identify the Florida State Implementation Plan (SIP) required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51; to set forth the public notice and hearing requirements that the Department will adhere to for making SIP revisions; and to set forth the definitions, criteria, and procedures that the Department will use to review a federal agency�s general conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart W; and to adopt by reference an interagency memorandum of agreement that the Department will comply with to review any transportation conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart T. The provisions to 40 C.F.R. 51.853 require that a federal agency make a general conformity determination for any federal agency action in a nonattainment or maintenance area, to ensure that such action is consistent with the SIP and that such federal conformity determination be reviewed by the affected state. The provisions of 40 C.F.R. 51.394 require that a transportation conformity determination be made for the adoption, acceptance, approval, or support of certain transportation plans, transportation improvement programs, and transportation projects in nonattainment and maintenance areas for transportation-related criteria pollutants to ensure that such actions are consistent with the SIP.
(4) Finally, this chapter adopts and incorporates by reference federal air pollution control regulations which are referenced in whole or in part throughout the Department�s air pollution control rules. Application to Coral Reefs:By reducing emmissions to air, particularly carbon dioxide, the pH of ocean waters will not be reduced and that is a direct benefit to coral reefs, since a reduction in pH is believed to be detrimental to corals. Legislative Actions:The Chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassified with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have benn adopted. Comments:This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Use Regulations; CO2; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Clean Air Act, 42 United States Code §§ 7400 et seq. | To ensure Americans have clean air to breath, and to protect the environment from air pollution. Regulates air emmissions from area, stationary and mobile sources. Charges federal land managers with direct responsibility to protect the "air quality and related values" of land under their control. The "related values" include fish and widlife and their habitats. The Clean Air Act is the law that defines EPA's responsibility for protecting and improving the nation's air quality and the stratospheric ozone layer. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act would decrease carbon dioxide emissions from sources in the United States, thereby making a contribution toward reducing ocean acidification, which is one of the problems contributing to coral reef decline. Legislative Actions:Response will differ from State to State because many Sates have been delegated to administer the Clean Air Act. However, States cannot have air quality standards less stringent then the federal standards. State air pollution agencies hold permit hearings and fines industries that violate air quality limits. States must develop state implementation plans that require approval by EPA. Comments:The 1990 amendments authorized the Acid Deposition Control Program, a program to control 189 toxic pollutants, established permit program requirements, expanded and modified the attainment of National Ambient Air Quality Standards, and expanded and modified enforcement authority. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Transportation Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction, 62-285 Florida Administrative Code. | Florida LEV Program. The Department of Environmental Protection (Department) adopts this rule to establish a Florida low emission vehicle (LEV) program that implements California motor vehicle emission standards pursuant to s. 177 of the Clean Air Act. This rule refers to many sections of chapter 1, division 3, title 13 of the California Code of Regulations (CCR), adopted and incorporated by reference at subsection 62-285.400(9), F.A.C. This rule also includes provisions specific to implementation in Florida. Application to Coral Reefs:Reducing greenhouse gases will contibute to a decrease in ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:To protect air quality, this rule applies to any heavy-duty diesel engine powered motor vehicle. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Climate Regulation; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Transportation Policies |
| Motor Vehicle Emissions Standards and Test Procedures, 62-242 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter pursuant to the Florida Clean Outdoor Air Law, Section
325.201, F.S., and in order to provide the Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles with the necessary rules, standards,
and criteria to administer the Florida Motor Vehicle Inspection Program.
(2) The Legislature has directed that in order to implement the Motor Vehicle Inspection Program, the Department of
Environmental Protection will set the standards and criteria listed below.
(a) Designation of program area (Section 325.204, F.S.).
(b) Emissions testing and inspection procedures (Section 325.206, F.S.).
(c) Inspection pass/fail criteria (Section 325.206, F.S.).
(d) Test equipment performance specifications (Sections 325.206, .212, and .213, F.S.).
(e) Definition of low emission adjustment (Section 325.209, F.S.).
(f) Inspection personnel training criteria (Section 325.213(1)(d), F.S.).
(3) The Department has set the vehicle in-use emission standards at levels that are achievable with proper operation and
maintenance of the various model year vehicles, if they have not been tampered with, and which will result in a significant reduction
in ozone-causing air pollutant emissions from automobiles and light duty trucks. It is the Department�s intent that eligibility for
emission control system performance warranty repairs of these vehicles be protected by reference to 40 CFR 85.2201 (Subpart W) �
Emission Control System Performance Warranty Short Tests.
(4) This chapter, and the Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles rules it references, are intended as an integral part
of the Department�s program to achieve and maintain the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone, carbon monoxide, and
particulate matter; and to control nuisance exhaust. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation and stanards for air emissions will contribute to lower greenhouse gasses and assist in combating ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Climate Regulation; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Nutrients; Transportation Policies |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Proposed Coral Reef Conservation Act Amendments of 2005, 2007 and 2009,. | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:When passed, the Amendments, among other issues, would reauthorize the Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000 and authorize appropriations through fiscal 2012 for the coral reef conservation program and community- based planning grants. Will authorize activities designed to minimize the likelihood of vessel impacts or other physical dammage to coral reefs, including activities to identify certain at-risk coral reefs. Promote international cooperation, codify the US Coral Reef Task Force. Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The amendments would not add regulations to the Act. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; CO2; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency, 62-016 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter implements the Florida Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency Act, providing for grants for renewable energy technologies and rebates for solar energy systems. This chapter also implements applications for corporate tax credits for renewable energy technologies provided for in Section 220.192, F.S.
Specific Authority 377.804(3), 377.806(7), 220.192(3) FS. Law Implemented 377.801, 377.802, 377.803, 377.804, 377.806, 220.192 FS. History � New 10-22-07. Application to Coral Reefs:The regulation could reduce greenhouse gas emissions from coal fired electric generating plants and thus reduce ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter implements the Florida Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency Act, providing for grants for renewable energy technologies and rebates for solar energy systems. This chapter also implements applications for corporate tax credits for renewable energy technologies |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration |
| Requirements for Sources Subject to the Federal Acid Rain Program, 62-214 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter outlines the additional permitting requirements for Title V sources that are subject to the Federal Acid Rain Program. The rules under this chapter set forth requirements for the Acid Rain Part of an operation permit for a Title V source which is subject to the Federal Acid Rain Program. The Department intends that this chapter shall implement and be consistent with the federal requirements of 40 C.F.R. Part 72. Words and phrases used in this chapter, unless clearly indicated otherwise, are defined at either 40 CFR 72.2 or 76.2 or Rule 62-210.200, F.A.C. The provisions of 40 CFR Parts 72, 73, 74, 75, and 76 referenced in this rule are adopted and incorporated by reference at Rule 62-204.800, F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:Controlling toxic air emissions will contribute to a decrease in greenhouse gasses and assist in reducing ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter outlines the additional permitting requirements for Title V sources that are subject to the Federal Acid Rain Program. The rules under this chapter set forth requirements for the Acid Rain Part of an operation permit for a Title V source which is subject to the Federal Acid Rain Program. The Department intends that this chapter shall implement and be consistent with the federal requirements of 40 CFR. Part 72. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Ocean Acidity |
| Stationary Sources - Emission Standards, 62-296 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to establish emission limiting standards and compliance requirements for stationary sources of air pollutant emissions.
(2) The chapter includes emission limitations for specific categories of facilities and emissions units, and it establishes reasonably available control technology requirements. Where work practice standards, including requirements for specific types of pollution control equipment, are provided for in this chapter, such standards shall be of the same force and effect as emission limiting standards. The emission limiting and work practice standards of Rule 62-296.320, F.A.C., and Rules 62-296.401 through 62-296.480, F.A.C., are applicable statewide. The reasonably available control technology requirements are established for specific areas of the state as set forth in Rules 62-296.500, 62-296.600, and 62-296.700, F.A.C.
(3) A facility or emissions unit subject to any standard or requirement of 40 CFR. Part 60, 61, 63 or 65, adopted and incorporated by reference at Rule 62-204.800, F.A.C., shall comply with such standard or requirement. Nothing in this chapter shall relieve a facility or emissions unit from complying with such standard or requirement, provided, however, that where a facility or emissions unit is subject to a standard established in this chapter, such standard shall also apply.
(4) Words and phrases used in this chapter, unless clearly indicated otherwise, are defined at Rule 62-210.200, F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:Controlling air emission pollutants can assist in controlling ocean acid acidification and the damaging effect of ocean water acidification on coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:To protect air quality, the chapter includes emission limitations for specific categories of facilities and emissions units, and it establishes reasonably available control technology requirements. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate Regulation; CO2; Corporate Responses; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients |
| Tampering with Motor Vehicle Air Pollution Control Equipment, 62-243 Florida Administrative Code. | The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to establish
procedures to determine compliance with those parts of Section 316.2935, F.S., which
provide that no person shall operate on the public roads or streets of this state any
motor vehicle that has been tampered with and that no person or motor vehicle dealer
as defined in Section 320.27, F.S., shall offer or display for retail sale or lease, sell,
lease or transfer title to a motor vehicle in Florida that has been tampered with.
Specific Authority: 316.2935, F.S.
Law Implemented: 316.2935, 316.6105, 318.18, 325.209, F.S.
History.: New 2-21-90, Amended 5-29-90, Formerly 17-243.100. Application to Coral Reefs:Vehicles with properly operating air pollution control equipment will dischage less air polllutants and will contribute to a decrease in ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:To achieve and maintain the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter; and to control nuisance exhaust by ensuring that that the air pollution control equipment of the motor vehicle has not been tampered with. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Transportation Policies |
