ReefLink Database

Bivalves
Bivalves are a class of molluscs known for their hinged shells, including clams, oysters, and scallops.
CMap
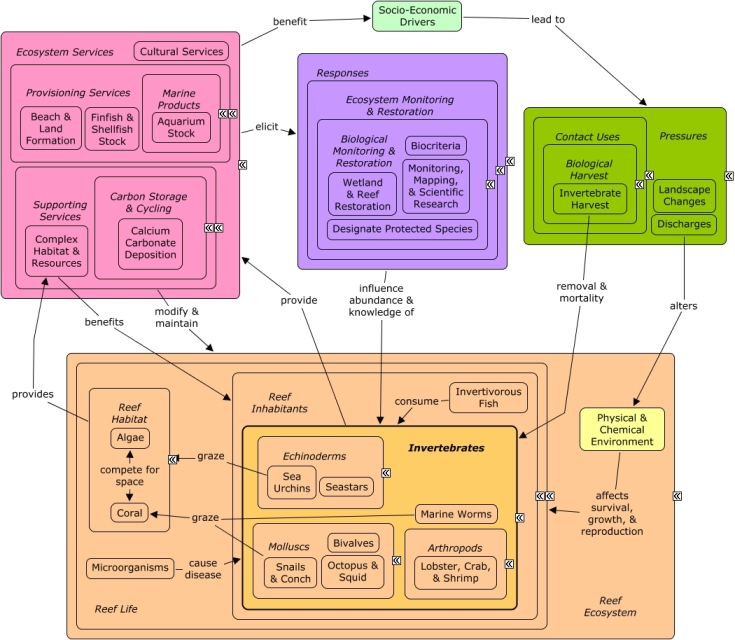
CMap Description
Molluscs, such as snails & conch, octopus & squid, and bivalves, fulfill several functions on a coral reef; the most significant being the contribution to the finfish & shellfish stock as a critical provisioning service. Bivalves provide a link in the trophic food web as they are consumed by humans. The calcium carbonate deposition by bivalves ultimately contributes to sand & land production through the processing of other marine organisms. Also, a few bivalve species are important as aquarium stock, and all species are important to cultural services of coral reefs. Socio-economic drivers lead to bivalve removal & mortality through harvesting pressures; also, the survival, growth, and reproduction of bivalves are reduced by disease-causing microorganisms and a disturbed physical & chemical environment. Biological monitoring, mapping, and restoration is needed to identify changes in the abundance and condition of molluscs; and ultimately, determine the appropriate responses to maintain the supply of ecosystem services and ensure the benefits to human health and well-being.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Bivalve Aquaculture Biofouling Control | These management options reduce, clean or remove biofouling organisms and other waste from bivalve production areas while minimizing environmental risk. Aquaculture shellfish production requires adequate food availability and water of dependable quantity and quality. Aquaculture operations and gear must have a minimal adverse impact on the surrounding water, plant, animal and human resources. Biofouling is detrimental to shellfish production, increasing exposure to pathogens, reducing the available food stuffs, and increasing organic loading. Only environmentally appropriate biofoul control methods should be used, and fouling organisms and algae should be disposed of appropriately to avoid local degradation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. |
Algae; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Improved Technology; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Octopus & Squid; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Snails & Conch; Supplemental Feeding |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chapter 1: Wildlife including protected areas, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates hunting, including for migratory birds, wildlife restoration, establishes and regulates wildlife and marine sactuaries and game preserves. Application to Coral Reefs:The coral reefs of the US Virgin Islands are within the boundaries off the marine sanctuaries and therefore have the same protection that marine sanctuaries have. Special licenses are required for scientific investigation and for collectors. In wildlife and marine sanctuaries, except under proper permit, taking or posessing any bird, fish, or other wildlife is illegal. Discharge of a firearm or release of arrows (spearfishing) in wildlife or marine sanctuaries is illegal. No form of waste can be thrown, placed or deposited in a wildlife or marine sanctuary. Legislative Actions:The Commissioner or any USVI resident can commence a civil action. Civil penalties for violators are not to exceed $50,000 per day. Any knowingly or negligently discharging polluants can be crimimnally punished with a fine of not less than $5,000 nor more Comments:Commissioner of Planning and Natural Resources can designate and establish wildlife and marine sanctuaries, and accept monitary and animal donations from the United States. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Arthropods; Bivalves; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations, Federal Register § Volume 66, Number 11 (2001). | NOAA established the Tortugas Ecological Reserve (a no-take zone) in the Tortugas region (Tortugas or region) of the Florida Keys to protect significant coral resources and to protect an area that serves as a source of biodiversity for the Sanctuary as well as for the southwest shelf of Florida. Establishment of the Reserve included expansion of the Sanctuary boundary to ensure that the Reserve protects sensitive coral habitats lying outside the existing boundary of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Regulation protects significant coral resources and many marine species by providing a no-take zone. Legislative Actions:The regulation increased the no-take zones to 24 areas. Fishing is prohibited in Tortugas north for areas that are within State waters. Diving is prohibited in Tortugas south. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
