 Northern
California Metric Maps Northern
California Metric Maps
 3
Kilometer Grid 3
Kilometer Grid
 U_INDEX
Human Land Use U_INDEX
Human Land Use
 RHUM0
Stream Corridor RHUM0
Stream Corridor
 RHUM30
30 Meter RHUM30
30 Meter
 RHUM90
90 Meter RHUM90
90 Meter
 N_INDEX
Natural Land Use N_INDEX
Natural Land Use
 RNAT0
Stream Corridor RNAT0
Stream Corridor
 RNAT30
30 Meter RNAT30
30 Meter
 RNAT90
90 Meter RNAT90
90 Meter
 PBAR
Barren PBAR
Barren
 RBAR0
Stream Corridor RBAR0
Stream Corridor
 RBAR30
30 Meter RBAR30
30 Meter
 RBAR90
90 Meter RBAR90
90 Meter
 PAGT
Agriculture PAGT
Agriculture
 RAGT0
Stream Corridor RAGT0
Stream Corridor
 RAGT30
30 Meter RAGT30
30 Meter
 RAGT90
90 Meter RAGT90
90 Meter
 PAGC
Cropland PAGC
Cropland
 RAGC0
Stream Corridor RAGC0
Stream Corridor
 RAGC30
30 Meter RAGC30
30 Meter
 RAGC90
90 Meter RAGC90
90 Meter
 PAGP
Pasture PAGP
Pasture
 RAGP0
Stream Corridor RAGP0
Stream Corridor
 RAGP30
30 Meter RAGP30
30 Meter
 RAGP90
90 Meter RAGP90
90 Meter
 PURB
Urban PURB
Urban
 RURB0
Stream Corridor RURB0
Stream Corridor
 RURB30
30 Meter RURB30
30 Meter
 RURB90
90 Meter RURB90
90 Meter
 PWETL
Wetland PWETL
Wetland
 RWETL0
Stream Corridor RWETL0
Stream Corridor
 RWETL30
30 Meter RWETL30
30 Meter
 RWETL90
90 Meter RWETL90
90 Meter
 PFOR
Forest PFOR
Forest
 RFOR0
Stream Corridor RFOR0
Stream Corridor
 RFOR30
30 Meter RFOR30
30 Meter
 RFOR90
90 Meter RFOR90
90 Meter
 PNG
Natural Grassland PNG
Natural Grassland
 RNG0
Stream Corridor RNG0
Stream Corridor
 RNG30
30 Meter RNG30
30 Meter
 RNG90
90 Meter RNG90
90 Meter
 PSHRB
Shrubland PSHRB
Shrubland
 RSHRB0
Stream Corridor RSHRB0
Stream Corridor
 RSHRB30
30 Meter RSHRB30
30 Meter
 RSHRB90
90 Meter RSHRB90
90 Meter
 AGCSL3
Ag Steep Slopes AGCSL3
Ag Steep Slopes
 AGPSL3
Pasture Steep Slopes AGPSL3
Pasture Steep Slopes
 AGTSL3
Total Steep Slopes AGTSL3
Total Steep Slopes
 C
Diversity C
Diversity
 H
Diversity, Shannon Weiner Index H
Diversity, Shannon Weiner Index
 H
- prime Diversity, Shannon Weiner Index H
- prime Diversity, Shannon Weiner Index
 S
Diversity S
Diversity
 N_Load
Nitrogen Load N_Load
Nitrogen Load
 P_Load
Phosphorus Load P_Load
Phosphorus Load
 Impervious/Land
Class Impervious/Land
Class
 Impervious/Road
Density Impervious/Road
Density
 STRMLEN
Stream Length STRMLEN
Stream Length
 STRMDENS
Stream Density STRMDENS
Stream Density
 RDLEN
Road Length RDLEN
Road Length
 RDLENCINTE
Interstates RDLENCINTE
Interstates
 RDLENCHIGH
Highways RDLENCHIGH
Highways
 RDLENCROAD
Surface Road RDLENCROAD
Surface Road
 RDDENS
Road Density RDDENS
Road Density
  RDDENSCINT
Interstates RDDENSCINT
Interstates  
 RDDENSCHIG
Highways RDDENSCHIG
Highways
 RDDENSCROA
Surface Road RDDENSCROA
Surface Road
 FNUMBER
Forest Patches FNUMBER
Forest Patches
 FPATDENS
Forest Density FPATDENS
Forest Density
 FLARGEST
Largest Forest FLARGEST
Largest Forest
 FAVGSIZE
Average Forest FAVGSIZE
Average Forest
 PLGP
Proportion of Forest PLGP
Proportion of Forest
 FEDGE210
Forest Edge FEDGE210
Forest Edge
 FCORE210
Forest Interior FCORE210
Forest Interior
 FEA210
Forest Edge/Total FEA210
Forest Edge/Total
 PFF9
Forest Cell PFF9
Forest Cell
 PFPTCH9
Grid/Patch Forest PFPTCH9
Grid/Patch Forest
 PFTRAN9
Grid/Transitional PFTRAN9
Grid/Transitional
 PFEDGE9
Watershed/Edge Forest PFEDGE9
Watershed/Edge Forest
 PFPERF9
Grid/Perforated PFPERF9
Grid/Perforated
 PFINTR9
Grid/Interior PFINTR9
Grid/Interior
 REGFAC_COUNT
Regulated Facilities REGFAC_COUNT
Regulated Facilities
 MINES_COUNT
Mines MINES_COUNT
Mines
 POPDENS
Population Density POPDENS
Population Density
|
 Larger
Image Larger
Image
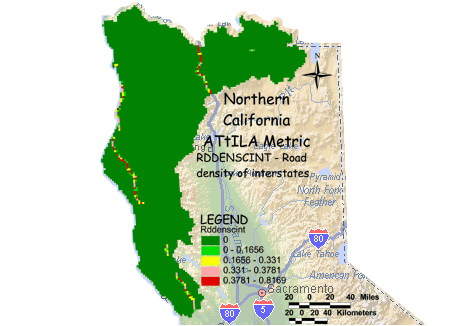
RDDENSCINT - Road density of interstates
Interstate density is calculated by summing the length of interstates and dividing by the area of the 3 km grid cell reporting unit. Values are reported as km of road
class per km2. High road densities are generally well correlated with high human population and urban development. Roads increase imperviousness, potentially
decreasing water quality. Roads also fragment habitat and may act as barriers, especially to large mammals. Wider roads and higher traffic volumes will generally
have more adverse affects, and impact a larger surrounding area then smaller, less traveled roads.
|
![[logo] US EPA](../gif/logo_epaseal.gif)
