|
|
Methodology and Interpretation
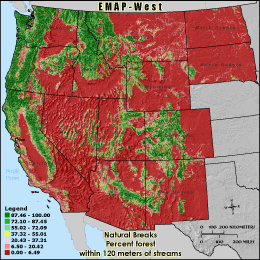
RFOR120 - Percent forest within 120 meters of streams
The percentage of forest land cover within 120 meters of a stream is
calculated by summing the total number of forest land cover cells underneath
stream segments in the 3 km grid cell reporting unit and within a three cell buffer
(120 meters) and dividing by the stream corridor's total land area (all cells 120 meters
adjacent to streams minus those classified as water). Cells inside the buffer
zone but outside of the grid cell boundary are ignored. Forests and wetlands act
as filters, removing pollutants from runoff before it enters streams. Forests
and wetlands also provide habitat for a wide variety of valuable plant and
wildlife species.
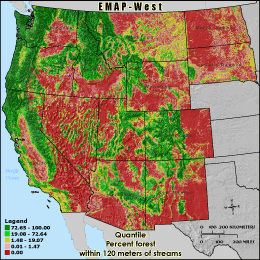
Quantile: Each class contains an approximately equal number (count) of features. A quantile
classification is well-suited to linearly distributed data. Because features are grouped by the number
within each class, the resulting map can be misleading, in that similar features can be separated into
adjacent classes, or features with widely different values can be lumped into the same class. This
distortion can be minimized by increasing the number of classes.
Natural Breaks: Classes are based on natural groupings of data values. Natural break points
are identified by looking for groupings and patterns inherent in the data. The features are divided
into classes whose boundaries are set where there are relatively large jumps in the distribution of
data values.
* EMAP-West Landscape Metrics Metadata (FGDC)
|
|

