|
|
Methodology and Interpretation
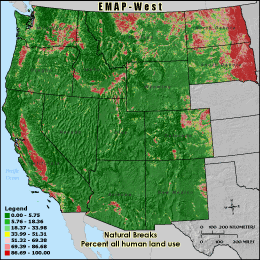
U_INDEX - Percent all human land use
The U-Index (human use index) metric is the percentage of land cover
cells located within the 3 km grid cell reporting unit that are classified as either
agriculture, urban, or non-natural barren (transitional and mines/quarries) to
the total number of cells inside the grid cell boundary minus those cells classified as
water (total land area). This gives the proportion of land area in the grid cell
that is influenced by human activity. High U-Index values depict areas in which
land use practices could have profound effects on wildlife habitat, soil erosion and
water quality. The values seen here are generally lower than in the central
United States and areas along the eastern seaboard of the United States.
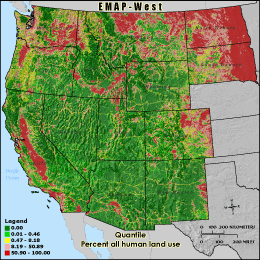
Quantile: Each class contains an approximately equal number (count) of features. A quantile
classification is well-suited to linearly distributed data. Because features are grouped by the number
within each class, the resulting map can be misleading, in that similar features can be separated into
adjacent classes, or features with widely different values can be lumped into the same class. This
distortion can be minimized by increasing the number of classes.
Natural Breaks: Classes are based on natural groupings of data values. Natural break points
are identified by looking for groupings and patterns inherent in the data. The features are divided
into classes whose boundaries are set where there are relatively large jumps in the distribution of
data values.
* EMAP-West Landscape Metrics Metadata (FGDC)
|
|

