|
|
Methodology and Interpretation
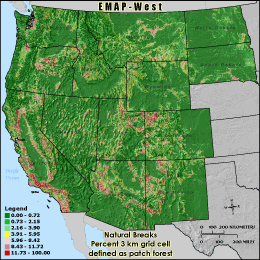
PFPTCH9 - Percent 3 km grid cell defined as patch forest
Percent patch forest is calculated using a moving 270 meter square
window (9 pixels x 9 pixels) across the land cover. When the percent forest in
the window is less than 40%, the forest cell in the center of the window is
classified as patch. The number of patch forest cells in the 3 km grid cell
reporting unit is then divided by the grid cell's total land area (the total
number cells in the grid cell boundary minus those cells classified as water)
to derive PFPTCH9. Patch forest is unlikely to be connected across an area or
provide any interior habitat.
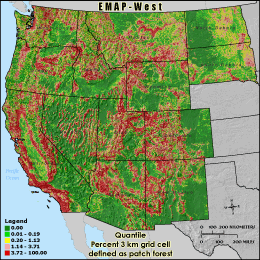
Quantile: Each class contains an approximately equal number (count) of features. A quantile
classification is well-suited to linearly distributed data. Because features are grouped by the number
within each class, the resulting map can be misleading, in that similar features can be separated into
adjacent classes, or features with widely different values can be lumped into the same class. This
distortion can be minimized by increasing the number of classes.
Natural Breaks: Classes are based on natural groupings of data values. Natural break points
are identified by looking for groupings and patterns inherent in the data. The features are divided
into classes whose boundaries are set where there are relatively large jumps in the distribution of
data values.
* EMAP-West Landscape Metrics Metadata (FGDC)
|
|

