|
|
Methodology and Interpretation
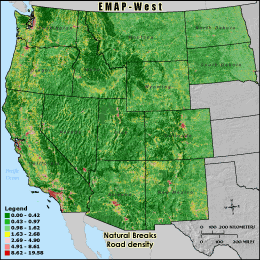
RDDENS - Road density
Road density is calculated by summing the length of roads by class and
dividing by the area of the 3 km grid cell reporting unit. Values are reported
as km of road class per km2. The three road classes included were
interstates, highways, and surface streets. High road densities are generally
well correlated with high human population and urban development. Roads increase
imperviousness, potentially decreasing water quality. Roads also fragment habitat
and may act as barriers, especially to large mammals. Wider roads and higher traffic
volumes will generally have more adverse affects, and impact a larger surrounding area
then smaller, less traveled roads.
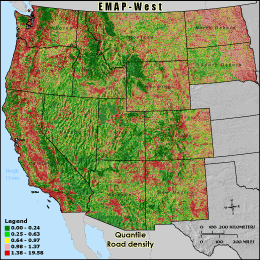
Quantile: Each class contains an approximately equal number (count) of features. A quantile
classification is well-suited to linearly distributed data. Because features are grouped by the number
within each class, the resulting map can be misleading, in that similar features can be separated into
adjacent classes, or features with widely different values can be lumped into the same class. This
distortion can be minimized by increasing the number of classes.
Natural Breaks: Classes are based on natural groupings of data values. Natural break points
are identified by looking for groupings and patterns inherent in the data. The features are divided
into classes whose boundaries are set where there are relatively large jumps in the distribution of
data values.
* EMAP-West Landscape Metrics Metadata (FGDC)
|
|

