
The Greenhouse Effect
If it were not for greenhouse gases trapping heat in the atmosphere, the Earth would be a very cold place. Greenhouse gases keep the Earth warm through a process called the greenhouse effect. Play the video to learn more »
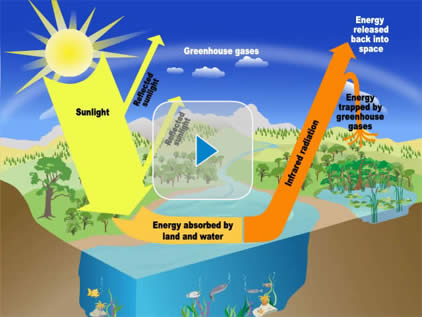
The Earth gets energy from the sun in the form of sunlight. The Earth's surface absorbs some of this energy and heats up. That's why the surface of a road can feel hot even after the sun has gone down—because it has absorbed a lot of energy from the sun. The Earth cools down by giving off a different form of energy, called infrared radiation. But before all this radiation can escape to outer space, greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb some of it, which makes the atmosphere warmer. As the atmosphere gets warmer, it makes the Earth's surface warmer, too.
Learn where the term “greenhouse effect” comes from.
Greenhouse gases keep the Earth warm through a process called the greenhouse effect.
What Is Radiation?
You might hear the word radiation and think that it's a bad thing. It's true that there are certain types of radiation that are bad for you, but other types of radiation are important parts of your life. When you feel heat from the sun, see all the colors around you, or listen to the radio, you are actually experiencing different types of radiation.
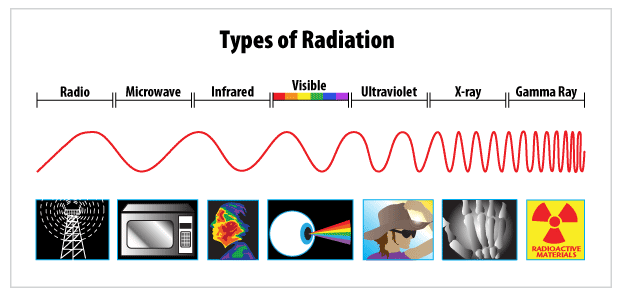
These types of radiation are all part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which means they involve energy traveling in the form of a wave. Different types of radiation have different wavelengths.
What's in a Name? The “Greenhouse Effect”

A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside. Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the “greenhouse effect.” The greenhouse effect works somewhat differently from an actual greenhouse, but the name stuck, so that's how we still refer to it today.