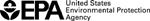Clear Skies
Clear Skies in Iowa
Highlights of Clear Skies in Iowa

- Iowa sources would reduce emissions of SO2 by 7%, NOx by 67%,
and mercury by 25% by 2020 due to Clear Skies.
- The health benefits in Iowa would total $1.2 billion annually
($240 million under the alternative estimate) and include 200
fewer premature deaths (100 under the alternative estimate) and
400 fewer hospitalizations/emergency room visits for asthma.
- In addition, Iowa would receive environmental benefits including
improved visibility and reduced nitrogen deposition.
- Clear Skies does not significantly impact electricity prices. With or without Clear Skies, electricity prices in the electricity supply region that includes Iowa are expected to remain below 2000 prices.
Clear Skies: An Innovative Approach to Improving Human Health and the Environment
Why Clear Skies?
- Air quality has improved, but serious concerns persist
- Iowa's citizens suffer ill effects from air pollution, including asthma attacks and premature death.
- Electricity generation sector remains a major emissions source
- Very cost-effective to control the power sector, relative to other sources
- Sources are concerned about upcoming complex and burdensome regulations.
Advantages of the Clear Skies Approach
- Guarantees significant nationwide emissions reductions - beginning years before full implementation
- Iowa sources would reduce emissions of SO2, NOx, and mercury
- Delivers dramatic progress towards achievement of critical health and environmental goals.
- Uses proven, market-based flexible approach with incentives
for innovation
- Recognizes environmental needs as well as industry constraints,
allowing industry to better manage
its operations and finances while lowering risks to the public
- Sources are projected to install pollution controls to enable continued reliance on coal.
- Recognizes environmental needs as well as industry constraints,
allowing industry to better manage
- Increases certainty across the board for industry, regulators, and consumers.
Under Current Clean Air Act Power Plants Would Face a Complex Set of Requirements
For a larger image, click here.Clear Skies Sets a Firm Timeline for Emission Reductions
| The existing Title IV SO2 cap-and-trade program provides an incentive and a mechanism to begin reductions upon enactment of Clear Skies years before regulatory action under the current Act. |
2004: The NOx SIP call (summertime NOx cap in 19 Eastern States + D.C.)
2008: Clear Skies NOx Phase I (2.1 million ton annual cap assigned to two Zones with trading programs)
2010:
- Clear Skies Hg Phase I (26 ton annual cap with a national trading program)
- SO2 Phase I (4.5 million ton annual cap with a national trading program)
2018:
- Clear Skies NOx Phase II (1.7 million ton annual cap assigned to two Zones with trading programs)
- Clear Skies Hg Phase II (15 ton annual cap with a national trading program)
- Clear Skies SO2 Phase II (3.0 million ton annual cap with a national trading program)
Emissions in Iowa under Clear Skies
|
Emissions in Iowa (2020) would be reduced from 2000 levels:
|
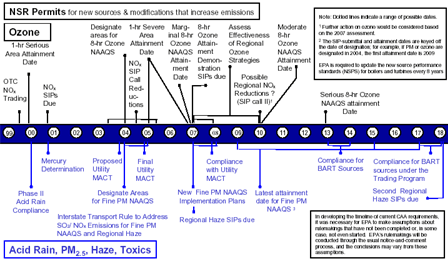
Emissions: Current (2000) and Existing Clean Air Act Regulations (base case*) vs. Clear Skies in Iowa in 2010 and 2020
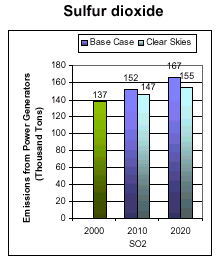
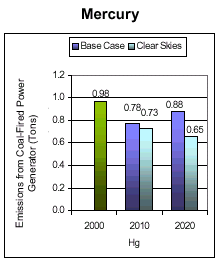
Note: The base case using IPM includes Title IV, the NOx SIP Call, NSR settlements, and state-specific caps in CT, MA, MO, NC, NH, TX, and WI. It does not include mercury MACT in 2007 or any other potential future regulations to implement the current air quality standards or other parts of the Clean Air Act. Base case emissions in 2020 will likely be lower due to state and federal regulatory actions that have not yet been promulgated.
SO2 and NOx Emissions Reductions under Clear Skies
| Emissions in Iowa and surrounding states would decrease considerably. These emission reductions would help Iowa maintain compliance with national air quality standards. |
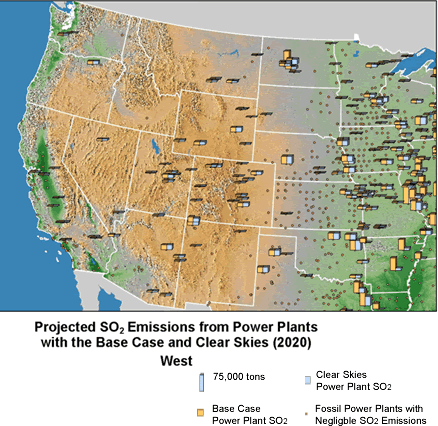
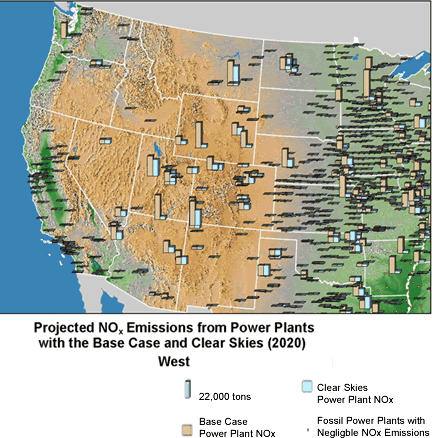
Note: The base case using IPM includes Title IV, the NOx SIP Call, NSR settlements, and state-specific caps in CT, MA, MO, NC, NH, TX, and WI. It does not include mercury MACT in 2007 or any other potential future regulations to implement the current ambient air quality standards or other parts of the Clean Air Act. Base case emissions in 2020 will likely be lower due to state and federal regulatory actions that have not yet been promulgated.
Clear Skies Health and Air Quality Benefits in Iowa
| By 2020, Iowa would receive approximately $1.2 billion in annual health benefits from reductions in fine particle and ozone concentrations alone due to Clear Skies. (see note 1) |
Improve Public Health
- Reduced ozone and fine particle exposure by 2020 would result
in public health benefits of:
- approximately 200 fewer premature deaths each year (see note 1)
- approximately 100 fewer cases of chronic bronchitis each year
- approximately 300 fewer nonfatal heart attacks each year
- approximately 400 fewer hospital and emergency room visits each year
- approximately 18,000 fewer days workers are out sick due to respiratory symptoms each year
- approximately 3,800 fewer school absences each year
- Reduced mercury emissions would reduce exposure to mercury through consumption of contaminated fish, resulting in additional, unquantified benefits for those who eat fish from Iowa's mercury-contaminated lakes and streams.
Help Maintain Health-Based Air Quality Standards (see note 2)
- Currently, all counties in Iowa meet the 8-hour ozone and fine particle standards.
- Clear Skies would further reduce concentrations of ozone and fine particles throughout Iowa.
Clear Skies Environmental Benefits in Iowa
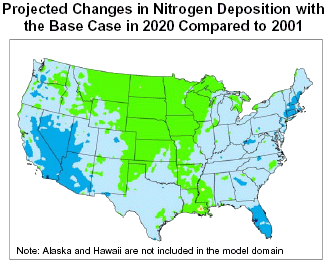
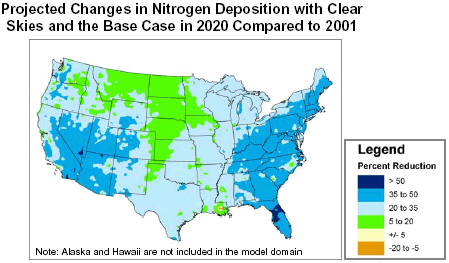
In comparison to existing programs,
- Visibility would improve perceptibly.
- The value of this benefit for Iowans who visit National
Parks
and Wilderness Areas nationwide is $21 million.
- The value of this benefit for Iowans who visit National
Parks
- Sulfur deposition would decrease by 15-30% in most central and eastern portions of the state and up to 15% in the rest of the state.
- Nitrogen deposition would decrease 5-20% in Iowa.
- Mercury deposition would decrease up to 15% in isolated parts of the state.*
* These results are based on modeling the Clear Skies mercury cap without triggering the safety valve.
Electricity Generation in Iowa under Clear Skies
|
Current and Projected Generation by Fuel Type in Iowa under Clear Skies (GWh) 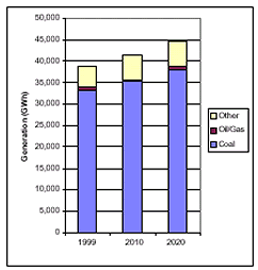 |
|
|
Emission Controls in Iowa under Clear Skies
|
|
Units in Iowa Projected to Be Retrofitted Due to Clear Skies by 2020
| Plant Name | Unit ID | Technology |
| COUNCIL BLUFFS | 3 | SCR/ACI |
| GEORGE NEAL NORTH | 1 | SCR |
| GEORGE NEAL NORTH | 2 | SCR |
| GEORGE NEAL SOUTH | 4 | SCR |
| LOUISA | 101 | SCR |
| MILTON L KAPP | 2 | SCR |
| OTTUMWA | 1 | SCR* |
* Retrofit was installed under Clear Skies by 2010
Note: 1. Retrofits and total coal-fired capacity apply to coal units greater than 25 MW.
2. Dubuque unit 1 and Prairie Creek unit 3 are projected to be removed from operation by 2005 with Clear Skies due to excess gas-fired capacity in the marketplace, unless otherwise needed for voltage purposes. The recent overbuild of gas-fired generation reduces the need for less efficient units operating at lower capacity factors. These units are inefficient compared to other coal- fired plants and newer gas-fired generation. Less conservative assumptions regarding natural gas prices or electricity demand would create a greater incentive to keep these units operational.
Electricity Prices in Iowa under Clear Skies
|
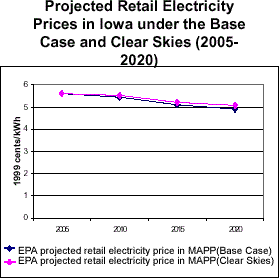
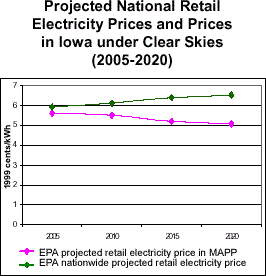
| In 2000, the average retail electricity price in Iowa was approximately 5.9 cents/kWh, which was above the average national retail price of approximately 6.7 cents/kWh. |
Note: The base case using IPM includes Title IV, the NOx SIP Call, NSR settlements, and state-specific caps in CT, MA, MO, NC, NH, TX, and WI. It does not include mercury MACT in 2007 or any other potential future regulations to implement the current ambient air quality standards or other parts of the Clean Air Act. Base case emissions in 2020 will likely be lower due to state and federal regulatory actions that have not yet been promulgated.
Costs and Benefits in Iowa under Clear Skies
Benefits Outweigh the Costs
Clear Skies....
|
- In Iowa, economic modeling projects that the cost of generating electricity, of which a component is the cost of installing and operating pollution controls, is less under Clear Skies than under the base case. This is because power production shifts within the region enable the power sector to comply in the most cost-effective manner. Total annual health benefits in 2020 for Iowa are projected to be $1.2 billion.
- Nationwide, the projected annual costs of Clear Skies (in $1999)
are $4.3 billion in 2010 and $6.3 billion in 2020; the nationwide
benefits of Clear Skies are expected to be over $113 billion annually
by 2020.
- An alternative estimate projects annual health benefits totaling $23 billion.
Note: Costs include capital costs, fuel, and other operation and maintenance costs (both fixed and variable) associated with the achievement of the emissions caps in the legislation (for example, the installation and operation of pollution controls). These state-level production costs are estimates; they do not account for the costs associated with the transfer of electricity across regions, nor the costs or savings that could be associated with allowance movement between sources.
Notes on EPA's Analysis
- The information presented in this analysis reflects EPA's modeling
of the Clear Skies Act of 2003.
- EPA has updated this information to reflect modifications:
- Changes included in the Clear Skies Act of 2003.
- Revisions to the Base Case to reflect newly promulgated rules at the state and federal level since the initial analysis was undertaken.
- The Clear Skies modeling results presented include the safety valve feature
- EPA has updated this information to reflect modifications:
- This analysis compares new programs to a Base Case (Existing Control Programs), which is typical when calculating costs and benefits of Agency rulemakings.
- The Base Case reflects implementation of current control programs
only:
- Does not include yet-to-be developed regulations such as those to implement the National Ambient Air Quality Standards.
- The EPA Base Case for power sector modeling includes:
- Title IV, the NOx SIP Call, NSR settlements, and state-specific caps in Connecticut, Massachusetts, Missouri, New Hampshire, North Carolina, Texas, and Wisconsin finalized before March 2003.
- For air quality modeling, the Base Case also includes federal and state control programs, as well as the Tier II, Heavy Duty Diesel, and Nonroad Diesel rules.
-
Clear Skies in Iowa 2002 (PDF 339KB)

1. An alternative methodology for calculating health-related benefits projects approximately 100 premature deaths prevented and $240 million in health benefits each year in Iowa by 2020.
2. Based on 1999-2001 data for counties with monitors that have three years of complete data.
|
State information based on EPA's modeling of the Clear Skies Act of 2002 is presented here for archival reasons. |