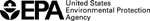Contact EPA Pacific Southwest Water Division
Pacific Southwest, Region 9
Serving: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Pacific Islands, Tribal Nations
Calleguas Creek Watershed
Partners & Contact Info
Los Angeles Regional Water Quality Control Board ![]() is the State of California regional water quality agency responsible for implementing the federal Clean Water Act as well as state water quality laws and regulations in the coastal watersheds of Los Angeles and Ventura Counties.
is the State of California regional water quality agency responsible for implementing the federal Clean Water Act as well as state water quality laws and regulations in the coastal watersheds of Los Angeles and Ventura Counties.
Contacts
Jenny Newman(jnewman@waterboards.ca.gov),
Senior Environmental Scientist,
Los Angeles Water Board
(213) 576-6691
Sam Ziegler (ziegler.sam@epa.gov)
Phone: 415-972-3399
US EPA Region 9
You will need Adobe Reader to view some of the files on this page. See EPA's PDF page to learn more about PDF, and for a link to the free Adobe Reader.
On this page:
The Watershed
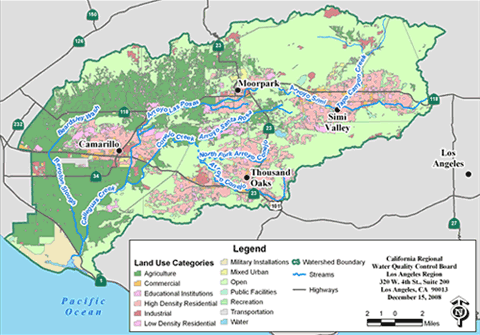
The Calleguas Creek watershed consists of 343 square miles in Southern California. This greater watershed is made of up 7 sub-watersheds at the 12 digit HUC (hydrologic unit code) scale. Undeveloped areas account for 50% of the land in the greater watershed while 25% is urban, and 25% is agricultural. Most of the urban areas, including the communities of Moorpark, Simi Valley and Thousand Oaks are located in the upper sub-watershed and most of the agriculture is located in the middle and lower sub-watersheds.
Land Use in the Calleguas Creek Watershed
Water quality in the Calleguas Creek watersheds is currently listed by the State of California as impaired by many different pollutants including legacy pesticides, OP pesticides, DDT, PCBs, metals (copper, mercury, nickel, zinc, and lead), Trash, bacteria and fecal coliform, Nutrients (nitrate, nitrite, nitrogen), Ammonia, Sulfates, Selenium, TDS, Sediment/Siltation, Toxicity, Sediment Toxicity, and Boron (California 2006 303(d) List of Impaired Waters (PDF) (299 pp, 1.1M) ![]() ).
).
Watershed stakeholders at all levels are working to restore these impaired watersheds, while some progress has been achieved, much work remains to be done. EPA recognizes success will involve a watershed approach relying on both regulatory and non-regulatory mechanisms.
Full Report Documenting Watershed Wide Improvement (EPA Strategic Measure SP12)
Reducing Ammonia loads in Reach 7 of Calleguas Creek (PDF) (8 pp, 626K)
Progress and Environmental Results
EPA is tracking progress to restore watersheds and water quality throughout the nation (see EPA National Water Program Strategic Plan and Guidance). One measure of progress is where improved water quality conditions in impaired watersheds have been achieved by implementing a watershed approach (see: SP-12).
Under this measure (SP12), in 2010, EPA and the Los Angeles Water Board produced a report to document the successful efforts to achieve statistically significant reductions in ammonia levels in one sub-watershed of Calleguas Creek.
Reducing Ammonia
The Calleguas Creek Reach 7 watershed, a subunit of the Calleguas Creek watershed also known as Arroyo Simi, runs through two sub-watersheds: the Upper Simi Arroyo and Lower Simi Arroyo. The largest sources of ammonia in the Calleguas Creek watershed are six wastewater treatment plants or publicly owned treatment works (POTW). In the Arroyo Simi watershed, the Simi Valley Water Quality Control Plant (WQCP) contributes 78% of the flow and 98% of the dry-weather ammonia load.
The Simi Valley WQCP is the major source of ammonia in the Arroyo Simi watershed; thus, restoration work consisted of installing advanced treatment (N/DN) at the Simi Valley WQCP to remove ammonia. Monitoring results demonstrate that focusing on the largest source of ammonia loading in the watershed resulted in statistically significant reductions in ammonia concentrations in Calleguas Creek Reach 7 (Arroyo Simi) watershed. The N/DN was installed in September 2004. Ammonia levels immediately decreased, improving water quality in the Arroyo Simi watershed