Tutorials on Systems Thinking
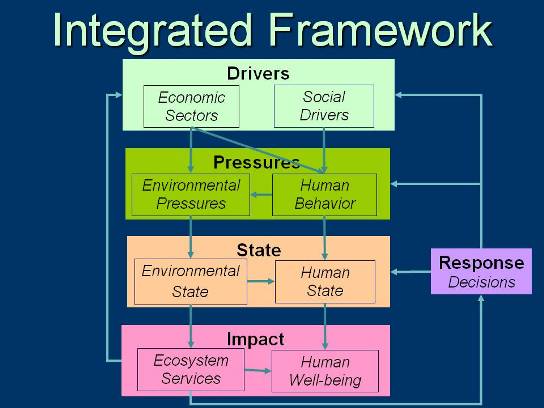
Integrated Framework: Impact
8 / 26
Changes in the quality and functioning of the ecosystem or human condition have an Impact on the welfare (well-being) of humans. Ecosystem services, in particular, are the benefits that ecosystems can provide. Other factors, such as human health, habitat, & behavior also contribute to human well-being.
Ecosystem Services - Functions and products of the ecosystem that benefit humans in the short term or long term. Services depend on the attributes of the ecosystem. The Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (Hassan et al. 2005) defined four categories of ecosystem services:
- Supporting services - biophysical processes that maintain the functioning of the ecosystem, and are necessary for the production of other ecosystem services, but may not have direct impacts to humans, including soil stabilization, wave energy attenuation, nutrient & contaminant processing, water cycling, carbon storage & cycling, and provision of resources and habitat to critical species.
- Regulating services - biophysical processes that regulate the ecosystem, including air quality regulation, climate regulation, water regulation, erosion regulation, water purification, waste treatment, disease & pest regulation, pollination, or natural hazard regulation.
- Provisioning services - the biological, chemical, or products obtained or harvested from ecosystems for human use including water resources, food resources, biochemical or genetic resources, fuel, fiber, or ornamental resources.
- Cultural services - include the nonmaterial benefits people obtain from the ecological integrity of ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences, including recreational value & ecotourism, aesthetic value, cultural value, spiritual or religious value, sense of place, educational or knowledge value, research potential, or untapped future potential.
Human Well-Being - a quantification of the degree of fulfillment of basic human needs for food, water, health, security, culture, and shelter. The State of Human condition (e.g. physical and psycho-social growth and development, presence of diseases) and the provisioning of ecosystem services are major contributors to human well-being. Socio-economic drivers depend upon the availability of natural capital (ecosystem services) and function to maintain or improve human well-being.
- Health & safety - life span, medical or insurance costs, sick days, pain & suffering
- Economic prosperity - productivity, ability to work, ability to afford needed things (income)
- Cultural and Social Well-Being - �happiness�, love, sense of belonging