ReefLink Database

Water Resources
Water resources reflect the quality and quantity of seawater available for human use, including swimming, navigation, and other uses.
CMap
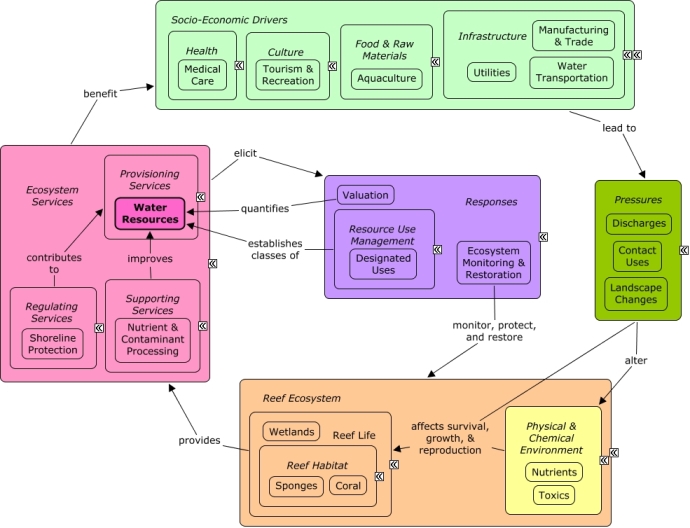
CMap Description
Reef organisms can alter the quality of water available for human use. Wave energy attenuation by wetlands and stony coral provide calm waters for swimming or navigation by small boats. Nutrient and contaminant processing by sponges and wetlands improves the quality of water for swimming, as well as its aesthetic value. Aquaculture facilities may also depend on seawater, and benefit from availability of calm, clean water. Waste management, such as sewage treatment facilities, can benefit from natural processing of waste by wetlands. Many of the same economic sectors that benefit from water resources also create pressures on the reef through coastal development, pollution, and contact uses. Decision-makers can better understand the value of water resources through valuation methods. Resource managers can designate uses for water resources (e.g., water contact recreation, protection of aquatic life, fishing, or navigation ), and require maintenance of a certain level of water quality in areas.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mondal, N. C., V. S. Singh, S. C. Puranik, and V. P. Singh. 2010. Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 163:215-227. | 2010 | India | Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Richlen, M. L., S. L. Morton, E. A. Jamali, A. Rajan, and D. M. Anderson. 2010. The catastrophic 2008-2009 red tide in the Arabian gulf region, with observations on the identification and phylogeny of the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 9:163-172. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Malaysia; United Arab Emirates; Oman; Mexico | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Dodds, W. K., W. A. Bouska, J. L. Eitzmann, T. J. Pilger, K. L. Pitts, A. J. Riley, J. T. Schloesser, and D. J. Thornbrugh. 2009. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environmental Science and Technology 43:13-19. | 2009 | Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Kundzewicz, Z. W. and P. Doll. 2009. Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrological Sciences Journal-journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques 54:665-675. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Drinking Water Supply; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| UNCWI. 2009. Healthy Watersheds through Healthy Forests. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Drinking Water Supply; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Cannon, J. 2008. A bargain for clean water. | 2008 | Review | Agriculture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Leibowitz, S. G., P. J. Wigington, and M. C. Rains. 2007. The effects of non-navigable streams and adjacent wetlands on navigable waters: an approach for addressing information needs following the US Supreme Court's Rapanos and Carabell decisions. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment [inpress]. | 2007 | Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | ||
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Military; Mitigation; Schools & Colleges | |
| Kelley Hart. 2006. The upper Neuse Clean Water Iniative Conservation Plan. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Improved Technology; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Utilities Policies |
| Madhusoodanan, G., P. P. Ouseph, and S. Kumar. 2006. Bacterial contamination of drinking water and its impact on primary health at Kavaratti Island, Lakshadweep, Union Territory of India. Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Environmental Sciences 8:839-843. | 2006 | Global; India | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Water Utilities Policies | |
| Mitchell, C., J. Brodie, and I. White. 2005. Sediments, nutrients and pesticide residues in event flow conditions in streams of the Mackay Whitsunday Region, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:23-36. | 2005 | Australia | Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Thorburn, P. J., J. S. Biggs, K. L. Weier, and B. A. Keating. 2003. Nitrate in groundwaters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal Northeastern Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 94:49-58. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Buckley, R. 2002. Surf tourism and sustainable development in Indo-Pacific Islands. I. The industry and the islands. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 10:405-424. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Cultural Policies; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Textiles & Apparel; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Hajkowicz, S., M. Young, S. Wheeler, D. MacDonald, and D. Young. 2000. Supporting Decisions: Understanding Natural Resource Management Assessment Techniques - A report to the Land and Water Resources Research and Development Corporation. Primary Industries and Resources SA, Adelaide (South Australia). | 2000 | Australia | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Resource Use Management; Salinity | |
| Al-Awadhi, F. M. A. 1999. The Year of the Ocean and its crucial importance to the Gulf. Desalination 123:127-133. | 1999 | Global | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Littering; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waste Management Policies | |
| Fuchs, A. and U. Radtke. 1998. Ecological problems on the carribean island of Barbados [Okologische probleme auf der karibischen insel Barbados]. Geographische Rundschau 50:706-713. | 1998 | Cuba | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water | |
| Dvorak, J. 1997. Geology of palaeozoic sediments in the surroundings of Ostrov u Macochy (Moravian Karst, Moravia) [Geologie paleozoika v okoli Ostrova u Macochy (Moravský kras, Morava)]. Journal of the Czech Geological Society 42:105-110. | 1997 | Drinking Water Supply; Sediment | ||
| Richards, R. P., D. B. Baker, N. L. Creamer, J. W. Kramer, D. E. Ewing, B. J. Merryfield, and L. K. Wallrabenstein. 1996. Well water quality, well vulnerability, and agricultural contamination in the midwestern United States. Journal of Environmental Quality 25:389-402. | 1996 | India | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Cultural Protections; Drinking Water Supply; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Brits, P. C., A. L. R. Carvalho, and J. T. Pressly. 1995. Evaluation of the effectiveness of bromochlorodimethylhydantoin as a disinfectant for mine underground service water. Pages 25-34 in Water Supply. | 1995 | South Africa | Drinking Water Supply; Microorganisms; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Pathogens; Water | |
| Chen, K. M. 1995. Disappearance of ALS from Guam: Implications for exogenous causes. Pages 1549-1553 in Clinical Neurology. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Guam | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Housing; Military; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. | 1993 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Docks & Marinas; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Karr, J. R. 1991. Biological integrity: a long-neglected aspect of water resource management. Ecological Applications 1:66-84. | 1991 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Resource Use Management; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Karr, J. R. and D. R. Dudley. 1981. Ecological perspective on water quality goals. Environmental Management 5:55-68. | 1981 | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges | ||
| Rahaman, M. M., M. M. Khan, and K. M. S. Aziz. 1975. An outbreak of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on a coral island in the Bay of Bengal. Journal of Infectious Diseases 132:15-19. | 1975 | Drinking Water Supply; Pathogens; Water Utilities Policies | ||
| Jalal, K. F. Regional water resources situation: quantitative and qualitative aspects. in [No source information available]. | Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Waterspreading | This management option uses a system of dams, dikes, ditches, or other means of diverting or collecting runoff from natural channels, gullies, or streams and spreading it over relatively flat areas. Waterspreading differs from irrigation in that applications are timed by the availability of natural runoff flow rather than scheduled to meet plant needs. Waterspreading is most beneficial in areas with an average annual precipitation of 8 to 25 inches. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Resources |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Shipping Businesses | This option requires the sanctuary to continue to alert shipping businesses about sanctuary regulations. Such regulations may include vessel waste discharge, ATBA, PSSA, etc. The targeted audiences will include importers, exporters, port authorities, commercial fishing companies, ship insurers. This information can be provided to the audience through NOAA nautical charts, trade publications, newsletters, trade shows, and direct mailings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finance & Insurance; Infrastructural Policies; Insurance; Manufacturing & Trade; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Increase Public Grounding Notification | Public notification of groundings can be increased through more centralized, accessible notification methods, and public education and outreach. Notification methods could include creating a �grounding hotline� with a central government agency as the enforcement dispatch center. By centralizing notification methods, public confusion over what agency to contact can be reduced. Education and outreach efforts should focus on the importance of grounding notification and awareness of notification methods (i.e. the hotline). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Large Vessel Achoring | Damage from freighter anchor is extreme due to the mere weight and size of the anchor and chain. The chain can even be more damaging as it drags along the benthic environment leaving behind catastrophic ruin. This management response would encourage the creation of restoration and monitoring methodologies in shallow reef areas as well as at greater depths. If unacceptable damages are occurring restrictions and regulations prohibiting the use of anchors in high risk areas should be instituted. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Cruise Ships; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Transportation; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels | Semi- permanent/permanent vessels can have a negative impact on the surrounding local environment both due to the effects of shade and from the direct contact with the substrate. Sunken vessels that cannot be seen from the surface may present a danger to navigation. Derelict vessels that do not remain stationary may cause harm in multiple locations before becoming stationary. If fishing gear is still intact, it may cause further biological damage through "ghost fishing� (#283). Early response, creating mooring fields, pump-out stations, and providing support for removing derelict vessels, reduces the impact of these vessels. Also, the removal of intrusive vessels will help contribute to the restoration of reef areas to previous conditions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Military; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Stony Coral; Substrate; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Develop Chain of Notification for Grounding Incidents | This option advocates coordinating with other agencies such as FWC, NOAA, and local coral managers to determine the standard protocol and responsibilities when there are groundings. Through coordination, these agencies can determine threshold levels of damage for different responses and for notifying other agencies higher up the chain. Enhancing inter-agency coordination will be beneficial in terms of dealing with groundings because it will allow the problem to be fixed in a more time-efficient manner. Having a centralized grounding notification system is the first step of this management option, as it ensures all incidents pass through a single agency to determine further actions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Operating Permits for Towing & Salvage Professionals | This management option evaluates the need for a permitting system for all towing and salvage operations. This type of permit would require salvage operators to notify injury response when there are groundings. The permit program would also reduce impacts by ensuring operators know the proper practices and use the proper equipment to most effectively minimize damage to the operating area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Water Transportation |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Database for Tracking Restoration, Repairs, and Monitoring Activities | This response involves adapting NOAA�s Damage Assessment Center�s seagrass injury assessment team component to local management areas. If previously established, the management option # 165, will allow this data to be compared to previously collected baseline data such as that collected with management option #164. This would also allow for comparisons across different types of data, such as use changes, that would be contained in a #166. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Vessel Grounding Database | This management approach would involve refining and maintaining a vessel grounding database and adequate staffing for on-going management, GIS processing of archived data, creating products for management case tracking, and developing a database that is user-friendly and useful. If previously established, the management option #165, will allow this data to be combined with similar data from other inventory management options such as #95, and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option #85. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Forestry Policy: Forest Chemical Management | Pesticides and fertilizers are commonly used in forestry to reduce mortality of desired trees, improve forest production, and ease harvest/extraction. The rate of application is typically very low, but given the overall area covered, pesticides can still accumulate within watersheds. Some forest management chemical use considerations to reduce nonpoint source pollution impacts include: Develop an effective spill contingency plan to contain spills, and immediately report accidental spills into surface waters to the appropriate State agency. Prior to application, inspect the mixing and loading process and the calibration of equipment, and identify the appropriate weather conditions, the spray area, and buffer areas for surface waters. Buffer areas for surface waters are especially important for aerial applications. Carefully prescribe the type and amount of pesticides appropriate for the insect, fungus, or herbaceous species. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Provisioning Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Water Resources; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Dredging Regulations | Dredging is oftentimes prohibited with certain exceptions. Dredging regulation often falls under other controls over the alteration of the seabed, discharging or depositing materials. At times dredging is necessary for navigation or other activities, necessitating .permitting mechanisms for allowing otherwise prohibited activities. Revising the regulations to help eliminate negative dredge-and-fill activities within a certain distance of corals would be beneficial because it would help promote the reestablishment of sensitive benthic communities. Reservoirs may require periodic dredging to remove sediment that may have collected. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sand & Rock Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Transportation; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Channel & Reef Navigation Markers | This option would evaluate the need for proper marking to ensure better navigation. There are many types of markers, including buoys, charts, beacons, and GPS mapping. Such markers can also be used to advocate prohibition on vessel speeds greater than idle speed in areas designated as idle-speed only/no-wake and around shallow reef locations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beach & Land Formation; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Water Efficiency Initiatives | Reducing water use through cost effective water efficiency improvements can be beneficial as it reduces pressure on water as a finite resource and saves money. There are several ways water efficiency can be promoted. Some Water Efficiency BMPs recommended by the EPA include: Water Management Planning; Information and Education Programs; Distribution System Audits, Leak Detection and Repair; Water-Efficient Landscaping, Water-Efficient Irrigation; Toilets and Urinals; Faucets and Showerheads; Boiler/Steam Systems; Single-Pass Cooling Equipment; Cooling Tower Management; Commercial Kitchen Equipment; Laboratory/ Medical Equipment; Other Water Intensive Processes; Alternative Water Sources. One of the ways the US government has promoted Water Efficiency Initiatives is through Executive order 13123 which places certain water use reduction requirements on Federal Agencies. There are also existing funding and incentives for non-government sectors. Project funding comes in many forms, such as appropriations, energy savings performance contract (ESPC) and Utility Energy Service Contract (UESCs) programs; ratepayer incentive programs such as rebates from public benefit funds or utilities; and the retention of energy and water cost savings. | US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Water Efficiency Best Management Practices. Federal Energy Management Program Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Textiles & Apparel; Utilities; Utility Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Resource Use Management: Designated Uses | The water quality standards regulation requires that States and Tribes specify appropriate water uses to be achieved and protected. Appropriate uses are identified by taking into consideration the use and value of the water body for public water supply, for protection of fish, shellfish, and wildlife, and for recreational, agricultural, industrial, and navigational purposes. In designating uses for a water body, States and Tribes examine the suitability of a water body for the uses based on the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the water body, its geographical setting and scenic qualities, and economic considerations. Each water body does not necessarily require a unique set of uses. Instead, the characteristics necessary to support a use can be identified so that water bodies having those characteristics can be grouped together as supporting particular uses. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. Environmental Protection Agency. What are Water Quality Standards? Designated Uses. Water: Water Quality Standards Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Marine Products; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Water Quality Management: Pet Waste Cleanup Ordinance & Education | In residential areas, pet waste can contributes to the large amount of nutrients and pathogens that enter the water through stormwater runoff. This is especially useful in regions such as Gu�nica, Puerto Rico where there are a lot of stray dogs. Education for pet-owners and possible ordinance would help decrease harmful pathogens reaching corals through stormwater runoff and reduce eutrophication. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Animal Waste Collection. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Clary, J., Leisenring, M., and Jeray, J. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Pollutant Category Summary: Fecal Indicator Bacteria. Wright Water Engineers. |
Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Domestic Animal Waste; Environmental Education & Outreach; Health; Health Policies; Invasive Species; Landscaping & Household Services; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Stormwater Management; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Mooring Buoy Management | Installing mooring buoys is encouraged in order to prevent damage to corals from anchors. Areas that experience a lot of traffic from recreation and fishing will experience damage from vessel groundings and boat gear. Mooring buoys help to minimize damage to corals and at the same time provide access to water resources. Mooring buoys protect as well as lower resource-use conflicts. Mooring buoy management is achieved through maintaining existing mooring buoys; assessing current buoy technology; reviewing visitor-use and boating data; developing sitting criteria; recommending new sites; conducting site assessments; installing additional buoys; and implementing vessel size limits in high-use and sensitive areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Altmeier, Bernie. FKNMS Mooring Buoy Mainenance. NOAA: FKNMS Mooring Buoy Manual Accessed 3/23/2011. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Aquatic Organism Passage | This management action allows for upstream and downstream passage for fish and other aquatic organisms. The passage of these organisms is often restricted by barriers which must be modified, removed, or worked around with fishways. Sites should be evaluated for variations in discharge, tidal influence, hydraulics, geomorphic impacts, sediment transport and continuity, and organic debris movement. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Water Resources |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 17: Oil soil prevention and pollution control, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Prohibits the discharge of oil, petroleum products or their by-products, and other pollutants into or upon any coastal waters, estuaries, tidal flats, beaches, and land adjoining the seacoast of the Territory. Requires prompt containment and removal of petroleum. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects ecosystems, including coral reefs, from petroleum spills and provides for cleanup. Legislative Actions:Established the Virgin Island Coastal Protection Fund of $1,000,000 for cleanup response. Prohibits derilict vessels upon any public waters or ports. Provides for civil penaltiesup to $50,000per day. Requires a National Contingency Plan. Comments:Because it is the intent of this chapter to provide the means for rapid and effective cleanup and to minimize damages, any licensee and its agents or servants, including vessels destined for or leaving a licensee's terminal facility, who permits or suffers a prohibited discharge or other polluting condition to take place within territorial boundaries shall be liable to the territory for all costs of cleanup or other damage incurred by the territory and for damages resulting from injury to others. The territory shall have an absolute maritime lien which shall attach to any vessel and its freight on behalf of the territory or any person injured, for all costs of cleanup and other damages incurred as a result of a prohibited discharge. In any suit to enforce claims of the territory under this chapter, it shall not be necessary for the territory to plead or prove negligence in any form or manner on the part of the licensee or any vessel. If the territory is damaged by a discharge prohibited by this chapter it need only plead and prove the fact of the prohibited discharge or other polluting condition and that it occurred. In addition to the civil penalty, the pilot and the master of any vessel or person in charge of any licensee's terminal facility who fails to give immediate notification of a discharge to the harbor master and nearest U.S. Coast Guard station shall be guilty of a misdemeanor and fined not less than $5,000 nor more than $10,000. The Department shall, by rules and regulations, require that the licensee designate a person at the terminal facility who shall be the person in charge of that facility for the purposes specified by this section. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Water Resources |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Water Resource Implementation Rule, 62-40 Florida Administrative Code (2006). | The Chapter is intended to provide water resouirce implementation goals, objectives and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources. A goal of the Chapter is to coordinate the management of water and land resources. It is the objective of the State to protect the functions of the entire ecological systems, as developed and defined in the programs, rules, and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is a goal of the Chapter that sufficient water be available for all existing and future reasonable-beneficial uses and the natural systems and that adverse effects of competition for water supplies be avoided. Application to Coral Reefs:By protecting the functions of entire aquatic ecological systems, those waters will contain less contaminants when they are discharged and meet other natural water bodies including marine ecosystems. Cleaner water will result in less ecological strees to marine ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This Chapter is intended to provide water resource implementation goals, objectives, and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources, based on statutory policies and directives in Chapters 187, 373, and 403, Florida Statutes. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Waste Management Policies |
| Wetland applications, 62-611 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To provide qualitative and quantitative design criteria discharge limits, permitting requirements, and monitoring requirements for wetlands, man-made and natural, receiving domestic wastewater. Application to Coral Reefs:Because wetlands act as buffers and remove nutrients from contaminated water, in many case the nutrients will not reach the estuarine and marine environments and potentially have an adverse effect on coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative in nature and specific pollutant limits and monitoring requirements are specified in individual permits Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Education & Outreach; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
