ReefLink Database

Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage
Activities of fishing boats can cause damage to reefs. Trawling is one type of fishing that usually occurs in deeper waters in which a large net is dragged behind a boat. Other fishing gear includes hooks, lines, spear guns, and seining nets.
CMap
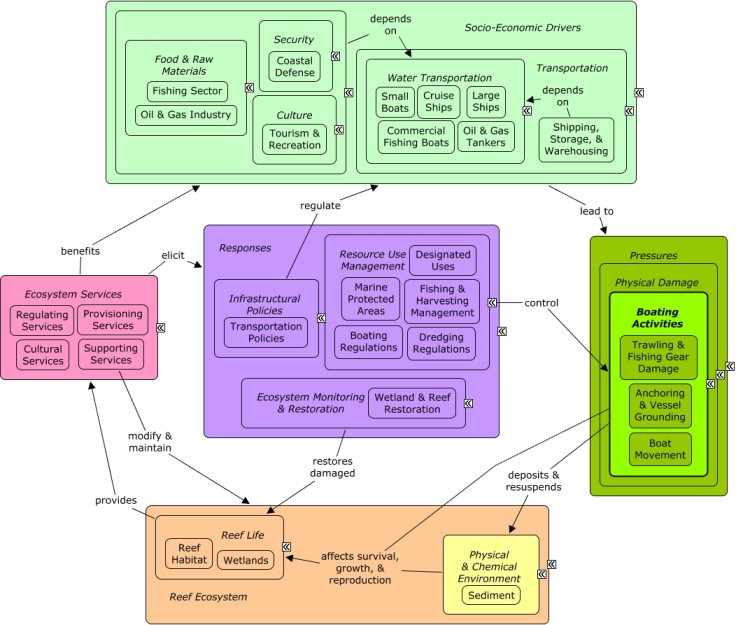
CMap Description
Fishing, tourism, recreation, shipping, and coastal defense rely on water transportation. Boat and ship activities can lead to groundings, anchor drops, or use of fishing gear that can damage reef habitat, and movement can cause deposition and resuspension of sediment in the reef environment. Fishing gear, such as trawling nets, can damage deepwater reefs, or cause injury to reef inhabitants, including fish and larger vertebrates. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that cause physical damage through boating activities also benefit from reef ecosystem services, including recreational value, shoreline protection, and provision of seafood and other marine products. Resource use management can be used to minimize physical damage by establishing protected areas and boating regulations, such as mooring buoys, fines, and low-wake zones to minimize sediment resuspension or groundings. Fishing regulations can influence activities and locations of fishing boats and types of fishing gear used.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Monitor & Respond to Damages From Fishing Gear | When a habitat is damaged or an injury occurs to natural resources as a result of fishing gear, it is beneficial to respond and assess. Responding appropriately is likely to involve other management options such as #91 if the injury was due to a violation. It is important to assess the damage and gather information as to why the injury occurred, so as to be able to find alternative fishing gear or practices that are less likely to cause such damages, for research such as #42. There should be protocols and methodologies for collecting damage assessment data to ensure it can be added to information systems such as #76 to track recovery, especially if repairing or restorative actions are taken. Standardized methods are also important when sharing this information with state and federal fisheries management (#64). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Dredging Regulations; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Establish VHF Radio Stations | The local sanctuary staff should work to secure a VHF radio station dedicated to provide information about local boating and water activities in multiple languages. Broadcast messages can include, but are not limited to information about regulations, navigation, resources, weather, and reef conditions. This will help prevent boaters, divers, and fishermen from negatively affecting the ecosystem. Assessments regarding cost and target audience areas must be conducted and external funding pursued to supplement the expense. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Evaluating Fishing Gear/Method Impacts: Evaluate impacts of existing fishing gear and methods on habitats | Research is needed to investigate impact on habitat of commercial and recreation fishing gear and methods. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Coral; Culture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Pressures; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Evaluating Fishing Gear/Method Impacts: Conduct research on the ecological impacts on sanctuary preservation areas of baiting fishing and catch-and-release fishing by trolling | It is necessary to asses the ecological effects of catch�and-release fishing by trolling and bait-fishing in order to make informed decisions regarding their provisions in protected areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Coral; Culture; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Pressures; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Fishing Gear/Fishing Methods Regulations | In most regions there are already regulations that prohibit fishing methods that incorporate explosives, poisons, oil, and bleach. Further investigation may reveal additional methods, materials, or gear that should be prohibited as well. Regulations should aim to increase the use of low-impact gear (#194) in place of more destructive gear and methods. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Management Enforcement | Marine protected areas and other types of coastal zone management areas have fisheries management policies that must be enforced in addition to the broader Statues, Regulation and Permit Requirements (#91). Illegal, unregulated and unreported (IUU) fishing is a major problem worldwide. Management area policies must be enforced to have an impact on the fisheries stock. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Regulations for Sponge Fisheries | Sponges play a vital role on reefs, providing structure, food and filtration. Depending on the method of removal, this process can be very destructive to other reef fauna and habitat. Research is needed to compare impacts of different sponge fishing methods in different areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boring Sponges; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Educational & Research Opportunities; Encrusting Sponges; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Live Collection Regulations | Live collection is often more destructive than capture of food fishes because of the destructive methods used to remove live fish and invertebrates from the reef habitat. These methods include use of cyanide and explosives. Current methods should be assessed and alternatives should be developed or collection prohibited. | World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Restoration: Restore Reef Habitat and Salvage Benthic Inhabitants Injured by Physical Damage | This management approach involves salvaging, maintenance, and re-stabilization or injured resources by management staff and private contractors in order to rescue and provide first aid following physical damage such as vessel groundings. This can be achieved using Reef Medics and other volunteer programs because these groups have experience with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, and SCUBA diving. Also, it allows for researchers to collect living coral material when relocation of such organisms is not possible. Salvage and re-stabilization is not limited to the living coral; octocorals, seagrasses, and the non-living framework may all be damaged of destabilized from groundings or other physical impacts. In addition to the habitat's structural integrity, it is important to re-establish aesthetics and ecological functionality. Funds from mitigation and case settlements should be used for this work, as long term costs of restoration and monitoring can be extensive. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Octocoral; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations, Federal Register § Volume 66, Number 11 (2001). | NOAA established the Tortugas Ecological Reserve (a no-take zone) in the Tortugas region (Tortugas or region) of the Florida Keys to protect significant coral resources and to protect an area that serves as a source of biodiversity for the Sanctuary as well as for the southwest shelf of Florida. Establishment of the Reserve included expansion of the Sanctuary boundary to ensure that the Reserve protects sensitive coral habitats lying outside the existing boundary of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Regulation protects significant coral resources and many marine species by providing a no-take zone. Legislative Actions:The regulation increased the no-take zones to 24 areas. Fishing is prohibited in Tortugas north for areas that are within State waters. Diving is prohibited in Tortugas south. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Sovereign submerged lands management, 18-21 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | To manage, protect, and enhance sovereignty lands so that the public may continue to enjoy traditional uses, including, but not limited to, navigation, fishing and swimming, public drinking water supply, shellfish harvesting, public recreation, and fish and wildlife propagation and management. Application to Coral Reefs:Permitting activities on submerged lands owned by Florida will improve water quality which will indirectly protect reef systems. Legislative Actions:These rules are to implement the administration and management responsibilities of the board and department regarding sovereign submerged lands. Responsibility for environmental permitting of activities and water quality protection on sovereign lands is vested with the Department of Environmental Protection. These rules are considered cumulative. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Energy Policy & Development; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
