ReefLink Database

Tourism & Recreation Policies
Tourism and recreation policies can be use to control the distribution and intensity of recreational activities such as through advertising, incentives, or visitors centers.
CMap
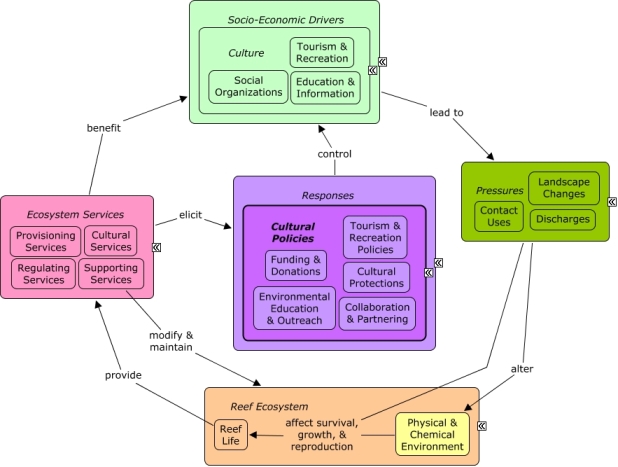
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to manage the distribution and functioning of cultural sectors. Cultural sectors, particularly tourism and recreation, create pressures on the reef ecosystem through primarily through contact uses, but also drive coastal development that can lead to landscape changes and increasing pollution. Cultural sectors benefit from reef ecosystem services, including recreational and educational opportunities. Government policies can have a dramatic effect on the tourism sector. The great destination success stories invariably include a government committed to policies that foster tourism development.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corporate Response: Invest & Co-finance Projects | Investing and co-financing projects that aim to conserve or restore habitats can be an effective means to preserving reef habitats as well as establishing positive working relationships between organizations. Investing in private sector projects will promote desired businesses and business practices, reducing barriers to entry and competitiveness as compared to traditional businesses and business practices to counterbalance advantages from undesired externalities. | World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. |
Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Increase Public Grounding Notification | Public notification of groundings can be increased through more centralized, accessible notification methods, and public education and outreach. Notification methods could include creating a �grounding hotline� with a central government agency as the enforcement dispatch center. By centralizing notification methods, public confusion over what agency to contact can be reduced. Education and outreach efforts should focus on the importance of grounding notification and awareness of notification methods (i.e. the hotline). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Wayside Exhibits/Signs | Creating wayside exhibits is an easy way to inform the public about sanctuary resources, policies, and boundaries. Wayside exhibits can be signs displayed at popular fishing and recreation areas. Coordination and collaboration among local, state, and federal agencies is essential to ensure there is not duplication in efforts, over-signage, and that consistent information is provided. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Docks & Marinas; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Distribute Educational Materials at Visitor Booths/Displays | Visitor booths at visitor centers, rental car agencies, airports, and chambers of commerce could hold an array of educational materials and brochures (#111) for walk-in visitors. Locations frequented by tourists are excellent targets for these booths and displays, as visitors are often less knowledgeable of the local ecosystems and the policies governing them. Materials should also be multilingual to enhance their effectiveness. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Outreach with the Tourism Development Council | Collaborating with the Tourism Development Council allows for more specific targeting of tourists and visitors for resource management outreach. Tourists and visitors are less familiar with local ecosystems and are therefore more prone to unintentionally damaging the environment or defying policies and regulations. The Tourism Development Council is also an important stakeholder to consider, in coastal zone management. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Multilingual Education and Outreach Materials | All forms of information regarding local sanctuary activities should be provided in multiple languages to better inform and educate patrons about environmental issues, stewardship skills, and other information. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Interactive Interpretive Exhibits | Interpretive exhibits combine an array of information types (pictures, sounds, interactive activities etc.) in an easy to understand, relevant way to visitors. On-water and on-land interpretive exhibits for maritime heritage resources and sanctuaries are helpful at increasing public knowledge/awareness of reefs. Interpretive exhibits can be established near the site of the resource (#126), in permanent (#131) or used as a traveling tool for (#127), and (#130). Such exhibits are beneficial as they allow for schools, the community, and tourists see resources first-hand and learn why they are important, at their leisure and without requiring a staff member to present the information. Expanding already-created exhibits is important to continue to draw in crowds and to continue to add/increase public knowledge and stewardship. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Washburne, R. and Wagar, J. 2010. Evaluating Visitor Response to Exhibit Content. Curator: The Museum Journal 15:248-256. Veverka, J. The Key to Successful Heritage Tourism Marketing Planning and Program Design. Interpretive Communication Accessed 7/7/2011. |
Decision Support; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Tourism & Recreation |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Provide Interpretive Information | Targeted information should be provided and interpreted for media, interest groups, periodicals, publications, and environmental organizations. This information may be about available programs/resources, research findings, policy changes, statistics, avoidance techniques, legal/financial consequences etc. This information should be provided specifically for these groups in such a way to best enhance public understanding regarding reef resources. It is important to interpret this information for these user groups, as this will help them convey the often technical information to the public. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Broadcasting, Publishing, & Libraries; Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Print Marine Etiquette on Marine-Related Products Packaging | Printing information on marine-related products regarding proper marine etiquette could be a possibility for raising awareness and improving public stewardship. Partnerships will be explored to help print etiquette information on materials such as bait boxes, ice bags, water buckets, etc. that are commonly used by stakeholders. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Information Booths for Trade Shows and Festivals | This option encourages local reef sanctuary staff to attend trade shows and local festivals and set up a booth with brochures, information, and photos regarding sanctuary resources. Such participation will enhance public education regarding local reef resources and education staff will evaluate which festivities would be the most optimum to attend and participate in (in order to be efficient with sanctuary funds). Specific trade shows, such as dive shows, should allow for a more targeted audience. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Eco-Discovery Centers in Reef Sanctuary Areas | Establishing low-cost, Eco-discovery centers would help educate visitors and residents about marine protected and managed areas. The Eco-discovery center will act as an initial orientation, informing visitors of education programs offered locally (#107), and acting as a source of information and resources (volunteer opportunities (#98), newsletter (#112) sign-up, brochure distribution (#111), etc.). Interactive exhibits (#123) and events at these locations will help to increase awareness and involvement of both visitors and residents. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Cultural Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Roadside Signs | Roadside signs and billboards in local reef watershed areas should be created to inform travelers that they are entering/exiting the reef watershed. Partnerships should be explored to create multi-logo signs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Permitting & Zoning; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Enforcement: Interpretive Enforcement | Interpretive enforcement, sometimes called �soft� or positive enforcement, refers to approaches geared towards encouraging widespread voluntary compliance with laws, rules and regulations. Interpretive enforcement is based on the premise that most people, once informed about MPA regulations, want to do the right thing. This is the greatest level of compliance because it advocates understanding and public support of goals for reef management. The main objective of this management action is to increase public understanding of the importance to comply with regulations, achieve voluntary compliance, and promote public stewardship of historical and cultural marine resources through interpretive enforcement. Strategies that can help achieve these goals include developing special training programs, organizing events, implementing social marketing, targeting indigenous learning systems and changing cultural value systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Bureau of Fisheries and Aquatic Resources of the Department of Agriculture, and Department of the Interior and Local Government. 2001. Philippine Coastal Management Guidebook No. 8 Coastal Law Enforcement. No.8 Coastal Law Enforcement, Coastal Resource Management Project of the Department of Environment and Natural Resources, Cebu City, Philippines. National Marine Sanctuaries. 2005. MPAs and Enforcement. Module 7, NOAA. |
Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Incentives; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Environmental Education: Experiential Reef Learning | This recommended option encourages taking youth and parents to experience the reefs and learn about them firsthand. Through this interactive experience, residents and visitors can learn about the benefits of corals and their importance to fisheries, ecological health, and the economy. Oftentimes, locals never experience the reefs firsthand and never learned about their importance. This educational experience would be very beneficial because locals will become more aware of the value of coral reefs, increasing their vested interest when making decisions in everyday life that impact reef health. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation |
| Environmental Education: Create a Public Awareness Program | This involves developing a spread of education tools like brochures (#111), newsletters (#118), displays (#127), web sites (#133) and a database (#98) to inform the public about different volunteer, education and training opportunities in regards to preserving the marine environment and maritime heritage resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Environmental Education: Develop Standardized Voluntary Certification Programs | This management option involves coordinating with leaders of various target businesses related to diving and snorkeling, marine mammal viewing, kayaking, eco-tours, and fishing. Through collaborations with these businesses, management areas can create a voluntary certification program for employees of these businesses to learn and receive accurate information about nearby corals, the ecosystem, and how they can better protect reefs in their everyday actions. These voluntary certifications can be used to educate employees and/or to develop self-regulating standards for these businesses. Depending on the standards and curriculum, voluntary certification programs can then be used by these businesses to convey knowledge or environmentally safe practices to customers through marketing. Educating employees of these businesses helps to assure that they are disseminating accurate information to visitors. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Sanctuary Use Patterns and Resource Value | This management option seeks to provide data and analysis of consumptive and non-consumptive use of all natural resources within sanctuary borders. Special emphasis is to be placed on artificial and natural reef resources used by residents and visitors. Wherever possible, market and non-market values of these resources should be elicited as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Services; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Use Patterns on Artificial and Natural Reefs | This management option seeks to provide data for decisions concerning creating new artificial reefs. Use data is important because justification for artificial reefs extends from their ability to shift use pressures (diving, fishing, etc.) from natural reefs. Once an artificial reef is decided on there is much more data to collect and factors to consider when deciding where the artificial reef (#189). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Defense; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Military; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Integrate Volunteer Monitoring Program | Monitoring by trained volunteers yields useful, cost-effective data that provides positive engagement for a variety of stakeholders. Such existing programs include The Ocean Conservancy, Atlantic Gulf Rapid Reef Assessment, and the Dolphin Ecology Project. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Fish Feeding Regulations | Divers in FL are already prohibited from fish feeding. Further review may show a need to prohibited anyone in state water from feeding fish. There will need to be investigations on the biological and behavioral impacts of fish feeding. This investigation can be used to keep the status quo, or may encourage further regulations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Supplemental Feeding; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Consider Regulations for Catch & Release Trolling | This plan seeks to reduce or eliminate catch-and-release fishing in many fragile areas. First an assessment must be conducted to measure the effects of catch-and -release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Change Personal Watercraft & Other Small Vessels Practices | This activity would aim to reduce noise and pollution, and conflicts among PWC users, the resources, and Sanctuary users. Practices could be changed through requiring certain training to drive such vessels, or restricting which types can be used in designated coastal areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Designated Uses; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Artificial Reef Regulations | Discharge/depositing of materials and constructions on the seabed are both prohibited without permits, regulating the construction of new artificial reefs. Likewise, existing artificial reefs are protected through permit requirements for any alternation of the seabed. There are still further considerations for protecting artificial reefs. Artificial reef materials and construction choices are very important and may change based on the specific location and desired impacts. An artificial reef to attract recreational fishing differs from one for recreational divers or shoreline storm protection. Many artificial reefs were formally large ships, oil rigs or other types of waste that have been decommissioned and would be too large and expensive to dismantle on land. In these cases it is important to put restrictions on the sinking process to ensure there won�t be any type of chemical leakage and that the structure is stable on the seabed. (#189) (#190) | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Solid Waste Disposal; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management; Waterborne Discharges |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Coral Touching Regulations | Currently touching, removing, damaging, distributing, and injuring any living or dead coral or coral formation is prohibited in Sanctuary Preservation Areas and Ecological Reserves. An investigation will be conducted to consider extending this prohibition to high-use, sensitive and vulnerable areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Contact Uses; Coral; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Spearfishing Regulations | Spearfishing is already prohibited in ecological reserves, sanctuary preservation areas, management areas, and special-use areas. There are additional considerations to be made to see if restrictions need to be extended in high priority areas. There may also be need to be further scientific study on the impacts of spearfishing. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Bait Fishing and/or Catch & Release Trolling Regulations | This option seeks to reduce or eliminate bait fishing, and catch & release trolling in fragile areas. First assessments must be conducted to measure the effects of bait fishing and catch & release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Regulations for Sponge Fisheries | Sponges play a vital role on reefs, providing structure, food and filtration. Depending on the method of removal, this process can be very destructive to other reef fauna and habitat. Research is needed to compare impacts of different sponge fishing methods in different areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boring Sponges; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Educational & Research Opportunities; Encrusting Sponges; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Live Collection Regulations | Live collection is often more destructive than capture of food fishes because of the destructive methods used to remove live fish and invertebrates from the reef habitat. These methods include use of cyanide and explosives. Current methods should be assessed and alternatives should be developed or collection prohibited. | World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Resource Use Management: Designated Uses | The water quality standards regulation requires that States and Tribes specify appropriate water uses to be achieved and protected. Appropriate uses are identified by taking into consideration the use and value of the water body for public water supply, for protection of fish, shellfish, and wildlife, and for recreational, agricultural, industrial, and navigational purposes. In designating uses for a water body, States and Tribes examine the suitability of a water body for the uses based on the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the water body, its geographical setting and scenic qualities, and economic considerations. Each water body does not necessarily require a unique set of uses. Instead, the characteristics necessary to support a use can be identified so that water bodies having those characteristics can be grouped together as supporting particular uses. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. Environmental Protection Agency. What are Water Quality Standards? Designated Uses. Water: Water Quality Standards Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Marine Products; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Marine Heritage Resource Protections | This management option involves protecting underwater items/sites that have historical, cultural, archaeological, or paleontological significance. This response advocates permits for action that may degrade the resource. This can be accomplished through creating an MHR field unit, monitoring MHR site degradation, and evaluating excavation and mitigation techniques. Field units can help conduct field research and coordinated, permitted research activities. Experts relating to archaeological research underwater can also be hired with additional funding. Through evaluation of excavation techniques, new technologies can be suggested such as: turbidity screens, sediment removal equipment, and seagrass restoration/relocation protocols to lead to less disturbance. Inventory and decision tools can also be used in the aid of Maritime Heritage Resource protection. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Mitigation; Physical Damage; Pipelines; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Valuation; Wetlands |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Water Quality Management: Reduce Pollution & Discharges from Marinas & Live-Aboards | This management option strives to reduce and eliminate the discharge of wastewater and pollution within zones near corals. In many instances, "no-discharge" zones already exist and are simply poorly enforced. In other instances the discharge limits are not stringent enough. Successful regulation requires marinas to be equipped with the proper infrastructure to support transfer of wastewater from vessels to shore-side for treatment. This infrastructure includes: pump-out facilities and mobile pump-out services. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Health; Health Policies; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Mooring Buoy Management | Installing mooring buoys is encouraged in order to prevent damage to corals from anchors. Areas that experience a lot of traffic from recreation and fishing will experience damage from vessel groundings and boat gear. Mooring buoys help to minimize damage to corals and at the same time provide access to water resources. Mooring buoys protect as well as lower resource-use conflicts. Mooring buoy management is achieved through maintaining existing mooring buoys; assessing current buoy technology; reviewing visitor-use and boating data; developing sitting criteria; recommending new sites; conducting site assessments; installing additional buoys; and implementing vessel size limits in high-use and sensitive areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Altmeier, Bernie. FKNMS Mooring Buoy Mainenance. NOAA: FKNMS Mooring Buoy Manual Accessed 3/23/2011. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 Virgin Islands Code. | Under Title 25, in addition to requirements for boat registration and administration of harbors, among other things, sections pertaining to the mooring and anchoring of vessels and houseboats provide for the protection of important marine resources in USVI waters. The Law requires mandatory boating education and safety courses for all boat operators. Application to Coral Reefs:Mooring and anchoring are restricted and not allowed near fragile systems. Not anchoring on coral reefs is abig plus of this legislation. Legislative Actions:Penalties for violation of the Chapter include fines not to exceed $1,000, a lien on the vessel and potential libel suit Comments:A houseboat or vessel is allowed to moor or anchor only in those areas designated by the Department. Section 404(g) of the legislation lists areas designated as areas of special concern. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Boating Regulations; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Environmental Education & Outreach; Large Ships; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Transportation Policies |
| Abandoned Shipwreck Act of 1987, 43 United States Code §§ 2101-2106. | To establish title to certain abandoned shipwrecks. U. S. Government asserted three categories of abandoned shipwrecks; embedded in a State's submerged lands, embedded in corralline formations protected by a State on its submerged lands, located on a State's submerged lands and included or determined eligible for inclusion in the National Register of historic Places. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act requires, but is not limited to, development by NPS of guidelines for States and Federal agencies to develop appropriate and consistant policies to protect national resources and habitat areas, and to provide for public and private sector recovery consistant with historical values and environmental integrety. Corralline structures are specifically protected by the Act. Legislative Actions:Specific response will vary from Federal agency to Federal agency and State to State. Comments:The NPS published non-binding, advisory guidelines for States and Federal agencies to establish, review, revise, and implement programs to manage shipwrecks under their ownership or control. The guidance is entitled "Abondoned Shipwreck Act Guidelines." |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States; US State Waters |
Artificial Habitat; Coral; Designated Uses; Marine Protected Areas; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Archaeological Resources Protection Act of 1979 as amended, 16 United States Code § 470. | To protect historic ruins, monuments, and objects of antiquity. Strenghtens and expands the protective provisions of the Antiquities Act of 1906 regarding archeological resources. It also revised the permitting process for conducting archeological research. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Chapter 1: Wildlife including protected areas, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates hunting, including for migratory birds, wildlife restoration, establishes and regulates wildlife and marine sactuaries and game preserves. Application to Coral Reefs:The coral reefs of the US Virgin Islands are within the boundaries off the marine sanctuaries and therefore have the same protection that marine sanctuaries have. Special licenses are required for scientific investigation and for collectors. In wildlife and marine sanctuaries, except under proper permit, taking or posessing any bird, fish, or other wildlife is illegal. Discharge of a firearm or release of arrows (spearfishing) in wildlife or marine sanctuaries is illegal. No form of waste can be thrown, placed or deposited in a wildlife or marine sanctuary. Legislative Actions:The Commissioner or any USVI resident can commence a civil action. Civil penalties for violators are not to exceed $50,000 per day. Any knowingly or negligently discharging polluants can be crimimnally punished with a fine of not less than $5,000 nor more Comments:Commissioner of Planning and Natural Resources can designate and establish wildlife and marine sanctuaries, and accept monitary and animal donations from the United States. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Arthropods; Bivalves; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Chapter 2: Protection of indigenous, endangered and threatened fish, wildlife and plants, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates activities, including scientific research, that could affect indigenous species and species considered at risk (threatened) or endangered, establishes species of special concern and habitats that should be protected, requires permits for trimming mangroves Application to Coral Reefs:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Legislative Actions:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Emergency Wetlands Resources Act of 1986, 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote the conservations of wetlands for public benefit and to assist in the compliance with international obligations under various treaties and conventions for migratory birds. Application to Coral Reefs:Indirect application to protection of coral reefs through wetland functions of nutrient (particularly nitrogen) and sediment removal from land-based discharges prior to their entrance into open coastal waters. Legislative Actions:Authorizied the purchase of wetlands from the land and Water Conservation Fund monies. Required States to include wetlands in their Comprehensive Outdoor Recreation Plans. Comments:Secretary of Interior was required to establish a National Wetland Priority Conservation Plan to identify the locations and types of wetlands that should be priorities for state and federal acquisition. The Act established various fee schedules for entering national wildlife refuges. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals, 73 Federal Register § 6895 (2008). | To make it unlawful, to import or export the species into or from the US, to take the species within the US or territorial seas of the US, to take the species upon the high seas, to possess, sell, deliver, carry, transport, or ship by any means whatsoever the species taken in violation, to deliver, receive, carry, transport, or ship in interstate or foreign commerce, by any means whatsoever and in the course of a commercial activity the species, to sell or offer for sale in interstate or foreign commerce the species, to violate any regulation pertaining to the species. Application to Coral Reefs:The deignation of Acropa palmeta and Acropa cervicornis as threathened species will allow the species advantages in recovery. The designation protects the reef habitat because the species must have the reef to reproduce and grow. Legislative Actions:Section 11 of the ESA provides civil and criminal penalties for a violation of the ESA. Comments: |
NOAA Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Recreational Opportunities; Skeletal Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals; Final Rule, 73 Federal Register § 72210. | We, the National Marine
Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final
rule designating critical habitat for
elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and
staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which
we listed as threatened under the
Endangered Species Act of 1973, as
amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four
specific areas are designated: the Florida
area, which comprises approximately
1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of
marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area,
which comprises approximately 1,383
square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine
habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area,
which comprises approximately 121
square miles (313 sq km) of marine
habitat; and the St. Croix area, which
comprises approximately 126 square
miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We
are excluding one military site,
comprising approximately 5.5 square
miles (14.3 sq km), because of national
security impacts. Application to Coral Reefs:The law protects coral habitat for elkhorn and staghorn coral which strenghtens their protection in the FKNMS, Puerto Rico, and US Virgin Islands. Legislative Actions: Comments:the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final rule designating critical habitat for elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which we listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act of 1973, as amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four specific areas are designated: the Florida area, which comprises approximately 1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area, which comprises approximately 1,383 square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area, which comprises approximately 121 square miles (313 sq km) of marine habitat; and the St. Croix area, which comprises approximately 126 square miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We are excluding one military site, comprising approximately 5.5 square miles (14.3 sq km), because of national security impacts. |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Exec. Order No. 12962, Recreational Fisheries, 60 Federal Register (1995). | Federal agencies are directed to improve the quantity, function, sustainable productivity, and distribution of U.S. aquatic resources for increased recreational fishing opportunities in cooperation with states and tribes. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Exec. Order No. 13089, Coral Reef Protection, 63 Federal Register 32701 (1998). | Protect coral reefs. Established the US Coral Reef Task Force Application to Coral Reefs:The Task Force was assigned duties including developing and implementing research, in conjunction with the scientific community, to identify the major causes of coral reef degradation. Legislative Actions:No penalties for noncompliance. Comments: |
12 federal agencies, 7 states and territories, 3 freely associated states Jurisdiction: United States; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Boating Regulations; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Hydrologic Management; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Exec. Order No. 13158, Marine Protected Areas, 65 Federal Register 34909 (2000). | This Executive Order is meant to help protect the significant natural and cultural resources within the marine environment for the benefit of present and future generations by strengthening and expanding the Nation�s system of marine protected areas. Application to Coral Reefs:Benefits to coral reefs within MPA's. Legislative Actions:One of the provisions of the Act requires that the Secretary develop a scientifically based, comprehensive system of MPA's representing diverse US marine ecosystems, and the Nation's natural and cultural resources. Comments: |
Department of Interior, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Service Act of 1956, 16 United States Code § 742. | Establishes a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on the commercial fishing industry but also includes the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment, and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife resources. Among other things, it authorizes the Secretary of the Interior to take such steps as may be required for the development, advancement, management, conservation, and protection of fish and wildlife resources, including, but not limited to, research, development of existing facilities, and acquisition by purchase or exchange of land and water or interests therein. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act is written for the support of commercial and recreational fisherpersons so that they enjoy the benefits of the Nation's fishery resources. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: |
Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Florida Aquatic Preserves, 18-20 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-20.001 Intent.
(1) All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency.
(2) Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(3) The preserves shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals: (a) To preserve, protect, and enhance these exceptional areas of sovereignty submerged lands by reasonable regulation of
human activity within the preserves through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program; (b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserves so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating, and fishing; (c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the Legislature in creating the preserves; (d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the act and these rules, and to assist in managing the preserves; (e) To encourage the protection, enhancement or restoration of the biological, aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions toward their natural condition, and discourage
activities which would degrade the aesthetic, biological, or scientific values, or the quality, or utility of a preserve, when reviewing applications, or when developing and implementing management plans for the preserves; (f) To preserve, promote, and utilize indigenous life forms and habitats, including but not limited to: sponges, soft coral, hard corals, submerged grasses, mangroves, salt water marshes, fresh water marshes, mud flats, estuarine, aquatic, and marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, estuarine, aquatic and marine invertebrates, estuarine, aquatic and marine mammals, birds, shellfish and mollusks; (g) To acquire additional title interests in lands wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological,
aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves; (h) To maintain those beneficial hydrologic and biologic functions, the benefits of which accrue to the public at large. (4) Nothing in these rules shall serve to eliminate or alter the requirements or authority of other governmental agencies, including counties and municipalities, to protect or enhance the preserves provided that such requirements or authority are not inconsistent with the act and this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:By maintaining coastal aquatic preserves in their natural condition, mangrove forests, wetlands and submerged aquatic vegetation will perform the functions of being sediment traps and removing some contaminants such as nutrients. Therefore, they will not reach marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Waste Management Policies |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Anchoring on Tortugas Bank, Federal Register § Volume 63, Number 158 (1998). | The regulation reinstates and makes permanent the temporary prohibition on anchoring by vessels 50 meters or greater in registered length on the Tortugas Bank west of the Dry Tortugas National Park within the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition on anchoring protects coral reefs and benthic habitats from physical damage. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| General Authorities Act of 1970, 16 United States Code §§ 1 et seq. | Reinforces the National Park Services Act by uniting all areas administered by the NPS into one National Park System. The Act assures a common preservation purpose for all units, regardless of title or designation. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Public Administration; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service General Partnership Authorities of 1970, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act supplemented and clarified the National Park Service's mandate with respect to the management of the National Park System. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Designated Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| National Park Service Organic Act of 1916, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act was created to start the National Park Service within the Department of Interior for the purpose of promoting and regulating the use of federal areas such as national parks and monuments. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Created the National Park Service to be supervised by a Director. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invasive Species; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act of 1966, 16 United States Code § 66. | The Act defines the National Wildlife Refuge System and authorizes the Secretary of Interior to permit any use of a refuge provided such use is compatible with the major purpose for which the refuge was established. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Serice Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Landuse Management; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Refuge Recreation Act of 1963, as amended, 16 United States Code § 1962. | Authorized the Secretary of the Interior to administer refuges, hatcheries, and other conservation areas for recreational use, when such uses do not interfere with the area's primary purpose. It authorizes construction and maintenance of recreational facilities and the acquisition of land for incidental fish and wildlife-oriented recreational development or protection of natural resources. It also authorizes the charging of fees for public uses. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act established public use fees and permits, and established penalties for violations of regulations. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary and Protection Act, Public Law 101-605 (H.R. 5909 United States Code (1990). | To protect the resources of the area delineated in section 5(b) of the Act, to educate and interpret for the public regarding the Florida Keys marine environment, and to manage such human uses of the Sanctuary consistent with the Act. Nothing in the Act is intended to restrict activities that do not cause adverse effects to the resources or property of the Sanctuary or that do not pose harm to the users of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the thrid largest coral reef barrier in the world. Included in the FKNMS are Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 squared nautical miles of coral reefs.The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive in the Sanctuary. From Miami to the Marquesas Keys there are over 6000 patch reefs. The Act also protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, futher protecting mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act required the preparation of a comprehensive mangement plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:Large vessel groundings on coral reefs in the Florida Keys was a major driver for the designation of the Sanctuary. In 1989, there were three groundings of large commercial vessels on the coral reef tract within an eighteen day period. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as lead agency and Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Florida Fish and Wildlife Commission, and Monroe County as Co-Trustees Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Wetland applications, 62-611 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To provide qualitative and quantitative design criteria discharge limits, permitting requirements, and monitoring requirements for wetlands, man-made and natural, receiving domestic wastewater. Application to Coral Reefs:Because wetlands act as buffers and remove nutrients from contaminated water, in many case the nutrients will not reach the estuarine and marine environments and potentially have an adverse effect on coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative in nature and specific pollutant limits and monitoring requirements are specified in individual permits Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Education & Outreach; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
