ReefLink Database

Stony Coral
Scleractinian, or stony corals, are marine animals with hard skeletons composed of calcium carbonate.
CMap
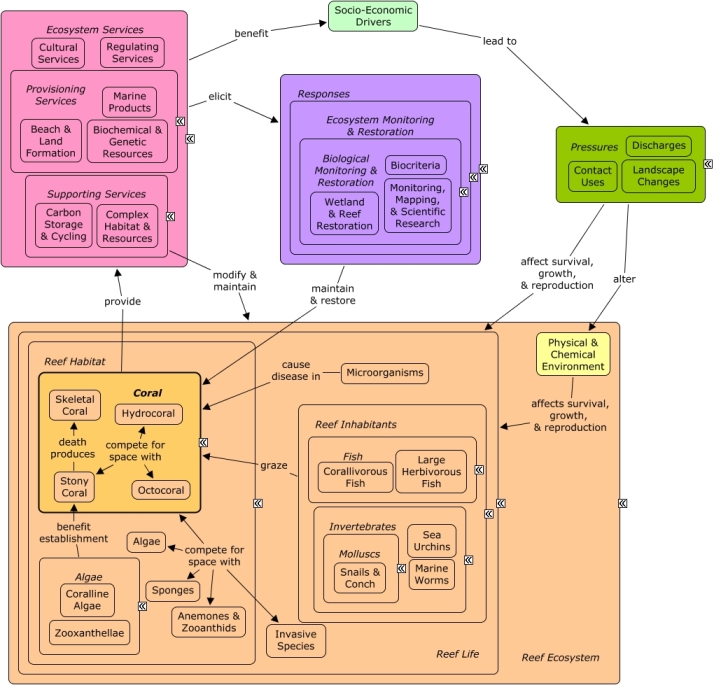
CMap Description
Corals provide the basis for all reef ecosystem services and thus the well-being and welfare supplied by the coral reef ecosystem. The most prominent, and also most significant, are the stony corals; directly contributing to biochemical & genetic resources, marine products, regulating services and cultural services. Stony coral produces large quantities of calcium carbonate skeleton. The resulting carbon storage & cycling builds the physical structure of the reef and creates complex habitat & resources, ultimately this process results in sand & land production. Coral species compete for space and resources with algae, sponges, and anemones & zooanthids. Reef inhabitants maintain the balance between the reef habitat species by selectively under grazing stony coral relative to the competing species. Pressures from socio-economic drivers can stress or kill coral by introducing competing invasive species, disease causing microorganisms, and disturbing the physical & chemical environment. To ensure the flow of services from coral and coral reef ecosystems, monitoring, mapping, research and restoration is paramount.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Vessel Groundings | This option involves assessing conditions and responding, as well as developing methodologies and protocols for coral dominated substrate, seagrass substrate, and mixed substrate. These protocols will help to determine how much damage has been done to the non-living coral framework. Ultimately, fine-tuning these protocols will allow for the most effective assessments. Evaluate these in light of current grounding regulations (#34). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Dredging Regulations; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Stony Coral; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels | Semi- permanent/permanent vessels can have a negative impact on the surrounding local environment both due to the effects of shade and from the direct contact with the substrate. Sunken vessels that cannot be seen from the surface may present a danger to navigation. Derelict vessels that do not remain stationary may cause harm in multiple locations before becoming stationary. If fishing gear is still intact, it may cause further biological damage through "ghost fishing� (#283). Early response, creating mooring fields, pump-out stations, and providing support for removing derelict vessels, reduces the impact of these vessels. Also, the removal of intrusive vessels will help contribute to the restoration of reef areas to previous conditions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Military; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Stony Coral; Substrate; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Regulate International Trade of Reef Species | Many coral reef species are harvested internationally for a variety of markets including the aquarium trade, food, curios, jewelry and pharmaceuticals. The US is the largest importer for many of these markets. The US strictly limits extraction of stony coral and many reef species in its waters; but as a major importer and consumer of coral reef species, more actions can be taken to decrease the demand on international imports. Setting and enforcing regulations on what can be imported (such as Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species CITES) is one approach that has been taken. More information is needed, leaving room to collect trade data and assess the impacts of extraction techniques to find sustainable methods. Demand for species collected this way will be increased with greater transparency to consumers, which can be accomplished through certifications for environmentally cognoscente collectors and those using alternatives like aquaculture and coral farming. Continued participation in Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) is also beneficial. | U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Live Collection; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Political Pressure; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Sponges; Stony Coral; Toxics; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Ecosystem Condition RECON | RECON trains volunteer divers to collect information about the reef environment, health of stony corals, presence of key reef organism, and human-induced impacts. The goal of RECON is to broaden knowledge of bottom-dwelling organisms on reefs. They also act as an alert system when there are abnormal and possibly harmful conditions present on the reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Stony Coral |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Coral Touching Regulations | Currently touching, removing, damaging, distributing, and injuring any living or dead coral or coral formation is prohibited in Sanctuary Preservation Areas and Ecological Reserves. An investigation will be conducted to consider extending this prohibition to high-use, sensitive and vulnerable areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Contact Uses; Coral; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Restoration: Restore Reef Habitat and Salvage Benthic Inhabitants Injured by Physical Damage | This management approach involves salvaging, maintenance, and re-stabilization or injured resources by management staff and private contractors in order to rescue and provide first aid following physical damage such as vessel groundings. This can be achieved using Reef Medics and other volunteer programs because these groups have experience with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, and SCUBA diving. Also, it allows for researchers to collect living coral material when relocation of such organisms is not possible. Salvage and re-stabilization is not limited to the living coral; octocorals, seagrasses, and the non-living framework may all be damaged of destabilized from groundings or other physical impacts. In addition to the habitat's structural integrity, it is important to re-establish aesthetics and ecological functionality. Funds from mitigation and case settlements should be used for this work, as long term costs of restoration and monitoring can be extensive. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Octocoral; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Restoration: Removal of Invasive Algae | Benthic organisms on reefs maintain a delicate balance competing for space. In many areas, the competition between coral and algae has fallen out of balance due to confounding factors. Factors such as decreased herbivorous fish and invertebrates, and invasive algae species have allowed faster growing algae to take over many reefs, often growing into smothering mats that cover and kill coral. In Hawaii, there has been some success physically removing invasive algae such as Kappaphycus using underwater vacuums extended down from barges or volunteer events in shallower areas. | The Nature Conservancy. 2010.Two Million Pounds of Invasive Algae Removed From Maunalua Bay. (not cited) |
Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcareous Macroalgae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Coralline Algae; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Reef Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Zooxanthellae |
| Restoration: Reintroduce Indigenous Living Corals | The approach reviews the policies and regulation regarding the re-introduction of living corals indigenous to a specific geographic location that were propagated in the lab. The concern about reintroduction of organisms from the lab and aquaria revolves around the possibility of introducing exotic or foreign strains of diseases to natural coral. Also, there is concern about introducing defective genetic material as well. One viable solution may be to reintroduce corals reared in in-situ coral nurseries. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coral; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Microorganisms; Reef Habitat; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations, Federal Register § Volume 66, Number 11 (2001). | NOAA established the Tortugas Ecological Reserve (a no-take zone) in the Tortugas region (Tortugas or region) of the Florida Keys to protect significant coral resources and to protect an area that serves as a source of biodiversity for the Sanctuary as well as for the southwest shelf of Florida. Establishment of the Reserve included expansion of the Sanctuary boundary to ensure that the Reserve protects sensitive coral habitats lying outside the existing boundary of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Regulation protects significant coral resources and many marine species by providing a no-take zone. Legislative Actions:The regulation increased the no-take zones to 24 areas. Fishing is prohibited in Tortugas north for areas that are within State waters. Diving is prohibited in Tortugas south. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
