ReefLink Database

Social Organizations
Social Organizations are devoted to improving social well-being, and include churches, grant making organizations, and charities.
CMap
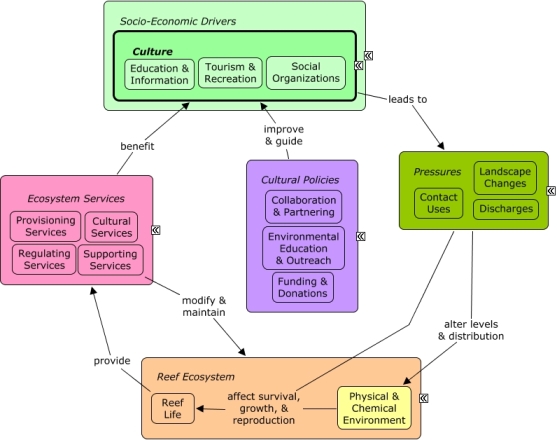
CMap Description
Growing coastal development contributes to the cultural identity of a community, reflected through the need for social organizations that depend on infrastructure to operate, including buildings and roads, and contribute to landscape changes in coastal areas. Social organizations may benefit from shoreline protection, as well as indirectly from other ecosystem services that improve the well-being of sectors, such as tourism & recreation, which drive coastal development. Decision-makers may depend on social organizations to improve environmental education and outreach, or to guide funding of research, monitoring, or restoration activities.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative & Interagency Policy: Participate in Science Community Networking | It can be advantageous to actively participating in science-related committees, review panels, and other groups that collaborate on science issues relating to coral reefs, resource management, and other topics. This management option ensures that the local sanctuary is considered in regional planning, that there is broad-based recognition of scientific findings concerning the sanctuary, and that sanctuary expertise is shared with partners. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Public Administration; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Implementing Notification and Response Protocols: Implement �Eyes on the Water� | This plan would entail teaming with volunteers and education staff to develop a volunteer training program to help report groundings. Training would include: incident recognition, documentation, and notification. Possible volunteers could be pulled from Team OCEAN, Reef Medics, Mote Marine Laboratory, professional fishing guides, etc. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Socio-Economic Drivers |
| Marine Zoning: Special Use Areas | Special use areas are set aside for specific scientific or educational purposes. This is in order to encourage the recovery or restoration of injured or degraded resources. Also, the areas may be designated to facilitate access to, or use of, resources, and prevent other user conflicts. Special-use areas are achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts; and determining/establishing appropriate zones for high-impact or user-conflict activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Biomedical Research Policies; Complex Habitat & Resources; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Integrate Volunteer Monitoring Program | Monitoring by trained volunteers yields useful, cost-effective data that provides positive engagement for a variety of stakeholders. Such existing programs include The Ocean Conservancy, Atlantic Gulf Rapid Reef Assessment, and the Dolphin Ecology Project. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Reef Life; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Manage Public Participation Projects | Public participation projects have significant potential; they not only address the project goals but also encourage public stewardship for important marine resources. Long term public projects require continued involvement, guidance and encouragement to reach project completion. Developing an inventory/database (#98) can be important for successful management of multiple projects. The public cannot participate in such projects if they are not aware of them, so effective marketing (#86) is an essential component of public participation management. Many of these tasks can be performed by volunteers. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Environmental Education Foundation REEF | This program uses recreation divers who conduct fish biodiversity and abundance survey in the Keys and the Caribbean. This surveys work towards contributing to The Great Annual Fish Count. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fish; Scientific Research; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef Ecosystem Condition RECON | RECON trains volunteer divers to collect information about the reef environment, health of stony corals, presence of key reef organism, and human-induced impacts. The goal of RECON is to broaden knowledge of bottom-dwelling organisms on reefs. They also act as an alert system when there are abnormal and possibly harmful conditions present on the reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical & Chemical Environment; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Social Organizations; Stony Coral |
| Public Participation: Assist Queen Conch Restoration Activities | Volunteers assist with raising juvenile queen conchs at a hatchery located at Keys Marine Lab through this volunteer program. They also locate and tag wild, adult conchs for population and reproduction studies. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Molluscs; Snails & Conch; Social Organizations |
| Public Participation: Assist Local Volunteer Organizations | This management approach encourages collaboration with local volunteer organizations that have missions similar to the coral management area. This way, the sanctuary is working efficiently with other groups to help accomplish the same goals instead of wasting resources trying to accomplish the same ends. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Social Organizations |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|
