ReefLink Database

Road Construction & Maintenance
Road Construction includes constructions of roads, highways, interstates, airport runways, and other physical infrastructure to aid transportation.
CMap
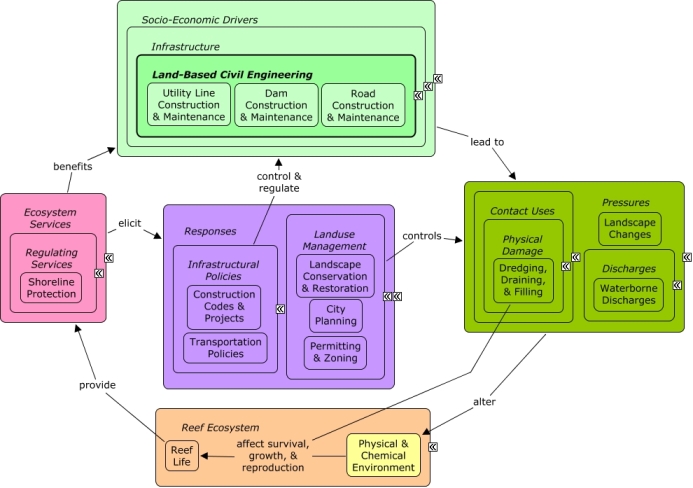
CMap Description
Land-based civil engineering creates pressures primarily through activities related to the construction and maintenance of physical infrastructure, leading to landscape changes, including devegetation, impervious surfaces, and soil disturbance, which can effect rates of pollutant runoff. In coastal areas, development may require shoreline armoring or dredging activities, which can directly impact coastal vegetation and alter patterns of waterflow. Civil engineering & construction projects and the physical infrastructure they create benefit from shoreline protection, as well as indirectly from other ecosystem services which improve the well-being of sectors, such as tourism & recreation, which drive coastal development. City planning can reduce impacts of development through use of construction codes, permitting, zoning, and transportation policies can influence location and intensity of road development. Landscape restoration, such as hydroseeding, may be used to reduce runoff along roads or other disturbed areas.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scholte, P; Al-Okaishi, A; Suleyman, AS. 2011. When conservation precedes development: a case study of the opening up of the Socotra archipelago, Yemen. ORYX 45:401-410. | 2011 | Indian Ocean; India | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Permitting & Zoning; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Special Use Permitting |
| Wilson, A. 2007. Nonwoven support - From Boscombe Pier to Palm Jumeirah. Technical Textiles International 16:25-28. | 2007 | Global; United Arab Emirates; Europe | Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Road Construction & Maintenance; Shoreline Protection | |
| Reid, J. M. and M. G. Winter. 2004. The use of post-consumer tyres in civil engineering. Pages 195-202 in Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Waste Management and Recycling: Used/Post-Consumer Tyres. | 2004 | Artificial Habitat; Civil Engineering & Construction; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Road Construction & Maintenance; Shoreline Protection; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies | ||
| Bullen, F. 2003. Use of Coral-Derived Aggregates for Construction of Low-Volume Roads. Transportation Research Record 1819:134-142. | 2003 | Road Construction & Maintenance; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Jimenez, C. and J. Cortes. 2003. Growth of seven species of scleractinian corals in an upwelling environment of the eastern Pacific (Golfo de Papagayo, Costa Rica). Bulletin of Marine Science 72:187-198. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica | Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Rollings, R. S., M. P. Rollings, and K. G. Sharp. 2003. Tropical pavement materials. Pages 1105-1120 in Proceedings - Conference of the Australian Road Research Board. | 2003 | Australia | Lab Study | Road Construction & Maintenance |
| Jackson, C. Rhett; Kolka, Randy. 2002. Forestry Best Management Practices And Their Effectiveness. in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | Chemical Use Regulations; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Botero, L. and R. Alvarez-Leon. 2000. The Caribbean coast of Colombia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 663-675. | 2000 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cultural Policies; Road Construction & Maintenance; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies | |
| Xue, C. 1999. Coastal sedimentation, erosion and management on the north coast of Kosrae, Federated States of Micronesia. Journal of Coastal Research 15:927-935. | 1999 | Micronesia | Land & Air Transportation; Mangroves; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment | |
| Rappa Peter, J. and J. Miller Bruce. 1989. Coastal resource management planning in the U.S.-affiliated Pacific Islands. Pages 2147-2160 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Micronesia | Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Mitigation; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance | |
| Vines, F. R. and D. Falconer Graeme. 1980. Experience With Coral And Volcanic Road Construction Materials In Western Samoa. Australian road research 10:32-38. | 1980 | Australia; Samoa | Lab Study | Road Construction & Maintenance |
| Hofmann, W. 1977. Waste Disposal In The Rubber Industry [Abfallbeseitigung In Der Gummiindustrie]. VERFAHRENSTECHNIK 11:28-34. | 1977 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Road Construction & Maintenance | ||
| Hofmann, W. 1975. Some problems relating to the removal of rubber wastes [EINIGE PROBLEME BEI DER BESEITIGUNG VON GUMMIABFALLEN]. GUMMI ASBEST KUNSTSTOFFE 28:38-39. | 1975 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Road Construction & Maintenance |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delegation of the Environmental Resource Program to Local Governments, 62-344 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) This chapter guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient,
streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental
resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments in accordance with the
provisions of Sections 373.103(8) and 373.441, F.S. This chapter also constitutes the Department�s authorization, in accordance with
Section 373.103(8), F.S., for delegations of the environmental resource permit program from the water management districts to local
governments provided that the procedures for delegation contained in this chapter are followed by the Districts. Delegations from
the Department and Districts shall be for the respective environmental resource permit program responsibilities of the Department
and the Suwannee River, St. Johns River, Southwest Florida and South Florida Water Management Districts, as set forth in
operating agreements listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C. Delegation agreements between the Department and local governments shall
be listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C., and delegation agreements between the Districts and local governments shall be listed in
Chapters 40B-1, 40C-1, 40D-1, and 40E-1, F.A.C.
(2) Nothing in this chapter shall preclude the Department, Districts, and local governments from entering into contracts or
interagency agreements as provided by law.
(3) Except as specifically provided in this chapter, nothing herein shall prevent a local government from adopting and
implementing an environmental regulatory program pursuant to its own authority.
(4) It is an objective of the Department and Districts to protect the functions of entire ecological systems, as defined and
developed in the programs, rules and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is the intent of the Department and
Districts that any local government receiving delegation of all or a portion of the environmental resource program carry out that
program in a manner consistent with this objective. This paragraph shall not be construed or applied as additional permitting criteria
beyond those adopted by the reviewing agency or the local government. Application to Coral Reefs:In theory, delegating stormwater pond construction and wetland functional determinations, as well as most otrher issues related to stormwater and wetlands, to local government will produce more efficient permitting and oversight. Therefore, treated water that is discharged and reaches any ecosystem should contain less contamination than the same water if it had not treated. Legislative Actions: Comments:Guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient, streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Delineation of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters, 62-340 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2000). | The Rule's intent is to provide a unified statewide methodology for the delineation of the extent of wetlands to satisfy the mandate of Section 373.421, F. S. Application to Coral Reefs:Preservation of wetlands will allow them to continue to function as buffers for sediment and contaminant control keeping them from reaching estuarine and marine waters and eventually habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative and methodological for delineation purposes. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Energy Policy & Development; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Environmental resource permitting procedures, 62-343 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2003). | The rule provides the procedural requirements for processing environmental resource permits and obtaining formal determinations of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring permits for projects related to environmental resources will indirectly protect environmental habitats. The permits are related to stormwater managemnt systems including discharges to wetlands. The permit conditions can limit toxics, nutrients and sediment that would be discharged to the environment if the rule were not in place. Legislative Actions:The rule is procedural and does not have fines or penalties. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Permitting & Zoning; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| Environmental Resource Permitting, 62-330 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2005). | Under the Chapter, DEP exercises its independent authority under Part IV, Chapter 373, F.S., to regulate surface water management systems, including activities in, on or over wetlands or other surface waters. The term "surface water management system" or "system" include stormwater mangement systems, dams, impoundments, reservoirs, appurtenant works, or works, or any combination thereof, and includes dredging and filling. "Dredging" means excavation, by any means, in surface waters or wetlands Application to Coral Reefs:Regulating stormwater management systems, dams, reservoirs and dredging will contribute to controlling contaminates from entering estuarine and marine environments and protect ecosystems including coral reefs., Legislative Actions:Individual permits will contain the conditions for environmental protection. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Surface water quality standards in table format, 62.302.500 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | This section of Chapter 62-302 presents the water quality standards in a tabular format for each class of waters of the State. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Uniform Mitigation Assessment Method, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-345 (2005). | Establishes a methodology that provides a standard procedure for assessing the functions provided by wetlands and other surface waters, the amount that those functions are reduced by a proposed impact, and the amount of mitigation necessary to offset that loss. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting wetlands provides wetland areas that can act as buffers against nutrients, pollutants and contaminants from reaching habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is administrative and provides methods to assess wetland value and appropriate mitigation to offset impact. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Water quality based effluent limitations, 62-650 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To implement the provisions of Section 403.051, 403.085 through 403.088 concerning the development of effluent limitations for wastewater facilities. Application to Coral Reefs:The Florida Air and Water Pollution Act establishes that no wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessay to protect the beneficial uses of such water. Requiring treatment of industrial and domestic waste water indirectly protects adjoining ecosystem, such as reefs, by limiting the pollutant that reach these other systems. Legislative Actions:The Department shall not issue a permit for a discharge to waters of the state, unless the Department has established an efflent limit for those pollutants in the discharge that are present in quantities or concentrations which can be reasonably expected to cause or contribute, directly or indirectly, to a violation of any water quality standard established in rule 62-302. The effluent limit may be a technology based effluent limit (TBEL), a water quality based effluent limit (WQBEL) determined by a Level 1 process, or where applicable, a WQBEL determined by a Level 2 process. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Domestic Animal Waste; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
