ReefLink Database

Petroleum Spills
Petroleum Spills are releases of oil or natural gas into the environment related to the development, transportation, and application of petroleum products.
CMap
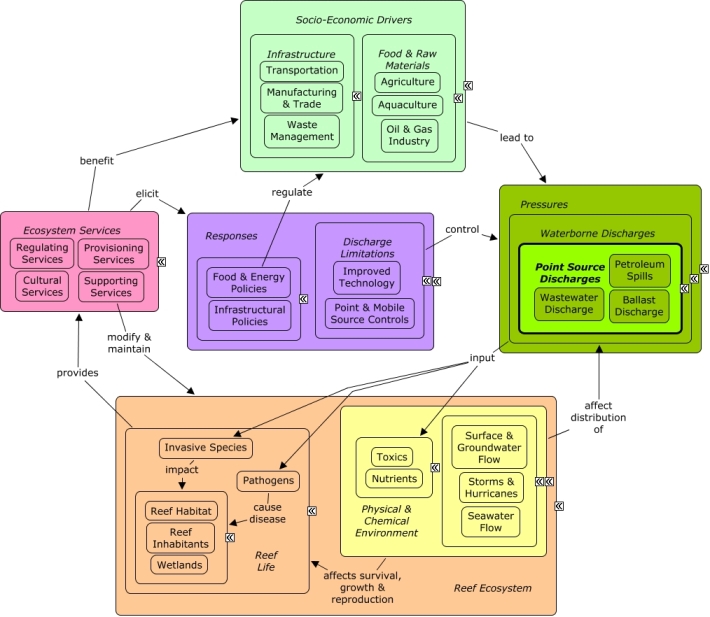
CMap Description
Petroleum spills can originate from a number of sources, including pipelines, oil and gas rigs, oil and gas tankers, and operation of vehicles and ships. Inputs of toxic chemicals into the reef environment can affect the survival and growth of reef species, including fish, coral, and other invertebrates. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that create pollution benefit indirectly from goods and services provided by the reef which provides recreational opportunities and contributes to the cultural identity of the local community and drives coastal development. Coastal zoning, boating regulations, and implementing new technology can limit risk of petroleum spills.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Coordinated Oil & Hazardous Spill Response | This management option calls for developing unified response protocols to deal with containment and clean-up of oil spills. This is important to protect corals, mangroves, and seagrasses from adverse impacts of hazardous materials. Given the limited number of spills and the importance of responding quickly, interagency coordination of reporting and response is essential for success. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Puerto Rico and USVI Area Planning Committees. 2008. Hazardous Substances Pollution Area Contingency Plan. Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin islands. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Toxics; Transportation; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Research and Model Causal Linkage Between Pollutants and Ecological Impact | This involves conducting research to identify and document causal linkages between discharge water pollutants and specific, quantifiable ecological problems. The natural environment naturally assimilates some pollutants, but has thresholds for this type of contaminant processing. Different hydrology, biology and spatial/temporal factors are all going to play a roll in the linkage between pollutants and ecological problems, meaning modeling and risk assessment can be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Sewage Treatment; Stormwater Management; Sunscreen Use; Supporting Services; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Energy Policy & Development: Pipeline Maintenance Requirements | The best way to ensure a high level of safety and reliability in operation of pipelines is to have a maintenance and inspection plan in place that targets damage, degradation or defects before they lead to failures. Economically, expenditures for maintenance and inspection are significantly less than those for emergency service in reaction to unforeseen situations. However, legislative requirements for plans, procedures and documentation ensures compliance with these best management practices. | Environmental Protection Agency. 2008. Pipeline Maintenance Best Practices: Lessons Learned from the Natural Gas STAR Program. Charlotte (North Carolina). United Kingdom Onshore Pipeline Operators� Association. 2006. UKOPA Recommendations for Pipeline Maintenance and Inspection. UKOPA/06/0032, |
Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig Maintenance and Use Regulations | There are regulated procedures and documentation required during production operations to prevent major incidents that may harm workers or the environment. A major part of incident prevention is inspection and maintenance. | Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies | |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig Construction Regulations | The Minerals Management Service (MMS) has several requirements for leasing and permits for construction of new drilling rigs and platforms. Placement is very important so as to not interfere with other uses or the environment. These permits also cover exploratory structures for research and test sites. | Minerals Management Service. 2006. Leasing Oil and Natural Gas Resources. U.S. Department of the Interior. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Offshore Wind and Hydrokinetic Alternative Energies | Policies encouraging or authorizing construction of offshore facilities are evolving, and there are many sides to the issue of how to best manage them. Alternative energies are desirable and would reduce the dependence on fossil fuel resources. However, hydrokinetic technologies are just becoming viable, meaning long term impacts are still unknown. Facilitative policies reduce barriers for alternative energy development or increase barriers or costs for incumbent technologies. These include research and innovation policies, technology improvement subsidies, market based policies that internalize externalities, and regulatory changes that simplify the permitting process. | Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. Portman, M.E. 2010. Marine Renewable Energy Policy: Some US and International Perspectices Compared. Oceanography 23:98-105. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Seawater Flow; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Cable and Pipeline Construction Assessments | Pre-assessments must be conducted to ensure pipelines and cables buried on the ocean floor will not disrupt or destroy natural or cultural resources. | Reach Networks Hong Kong Ltd. 2007. Project Profile: Asia-America Gateway (AAG) Cable Network, South Lantau. Wanchai, Hong Kong SAR. |
Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Restoration: Environmental Remediation | Environmental Remediation is a type of restoration that's focus ranges from Brownfields to Oil Spills to Hazardous Waste Sites. These restoration activities aim to restore the site to a previous condition, or to a condition that is not a threat to human health or other forms of life. Several standards can be used to determine when remediation is necessary and to what extent the environment should be restores. Biocriteria can be used to determine the degree of degradation to biological components of the site. Often it is the presence of a particular pollutant in the soil, water or air, which is above acceptable limits and will not degrade fast enough over a short period of time and therefore must be removed. Physical and chemical water quality criteria can be used to set maximum acceptable limits of water quality parameters. Air quality criteria can be used to set acceptable maximum and minimum air standards for remediation. | Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response. 2005. Contaminated Sediment Remediation Guidance for Hazardous Waste Sites. EPA-540-R-05-012, US Environmental Protection Agency. Environment Protection Authority. EPA Guidelines for Environmental management of on-site remediation. Environment Protection Authority, Adelaide, Australia. |
Applied Chemicals; Biocriteria; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Health; Health Policies; Landuse Management; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Military; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Solid Waste Disposal; Supporting Services; Toxics; Valuation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water Quality Management: Protection of Resources from Hazardous Materials & Spills | Wherever possible, take actions to decrease the likelihood of hazardous materials spills near corals. Even when risks are reduced significantly, spills may still occur, necessitating contingency plans (#56). In order for reef managers to stay informed of the latest spills/updates, a spill-reporting system should be established along with a geo-referenced database that keeps track of all spills within a certain distance of reefs. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Puerto Rico and USVI Area Planning Committees. 2008. Hazardous Substances Pollution Area Contingency Plan. Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin islands. USCG. 2007. Hazardous Substances Pollution Area Contingency Plan. Florida Keys. |
Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Small Boats; Toxics; Transportation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administrative fines for damaging State Lands of products thereof, 18-14 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-14.003 Violations.
It shall be a violation of this rule for any person or the agent of any person to knowingly refuse to comply with any provision of
Chapter 253, F.S., willfully violate any provision of Chapter 253, F.S., or to willfully damage state land (the ownership or
boundaries of which have been established by the state) or products thereof, by doing any of the following:
(1) Fill, excavate, or dredge, including prop dredging in a manner which produces a defined channel, on state land without the
lease, license, easement or other form of consent required by the Board.
(2) Remove, in violation of state or federal law, any product from state land without written approval or specific exemption
from the Board or Department.
(3) Discharge contaminants, wastes, effluents, sewage or any other pollutant as defined in Chapter 376 or Chapter 403, F.S.,
on, under or over state land; when such discharge is in violation of Chapter 403 or conditions of a permit issued pursuant to that
chapter, or conditions of a lease or easement issued pursuant to Chapter 253, F.S.
- 37
(4) Maintain, place or build permanent or temporary structures, including, but not limited to, additions to existing structures;
all structures whose use is not water-dependent; sanitary septic systems; fences, docks and pilings; houses; oil rigs; and utility
installations on or over state land without consent or authority from the Board or Department.
(5) Place garbage, refuse, or debris on or over state land without approval by the Board or Department.
(6) Any other willful act that causes damage to state land, or products thereof, when such activity occurs without the required
approval by the Board or Department. Application to Coral Reefs:Controlling and limiting excavation and dredging, as well as discharge of contaminants, wastes, sewage, and other pollutants will assist in keeping sediment and pollutants from reaching the coral reefs and causing degradation of reef organisms.. Legislative Actions: Comments:Administrative Fines for Damaging State Lands or Products Thereof |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Petroleum Spills; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Substrate; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 17: Oil soil prevention and pollution control, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Prohibits the discharge of oil, petroleum products or their by-products, and other pollutants into or upon any coastal waters, estuaries, tidal flats, beaches, and land adjoining the seacoast of the Territory. Requires prompt containment and removal of petroleum. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects ecosystems, including coral reefs, from petroleum spills and provides for cleanup. Legislative Actions:Established the Virgin Island Coastal Protection Fund of $1,000,000 for cleanup response. Prohibits derilict vessels upon any public waters or ports. Provides for civil penaltiesup to $50,000per day. Requires a National Contingency Plan. Comments:Because it is the intent of this chapter to provide the means for rapid and effective cleanup and to minimize damages, any licensee and its agents or servants, including vessels destined for or leaving a licensee's terminal facility, who permits or suffers a prohibited discharge or other polluting condition to take place within territorial boundaries shall be liable to the territory for all costs of cleanup or other damage incurred by the territory and for damages resulting from injury to others. The territory shall have an absolute maritime lien which shall attach to any vessel and its freight on behalf of the territory or any person injured, for all costs of cleanup and other damages incurred as a result of a prohibited discharge. In any suit to enforce claims of the territory under this chapter, it shall not be necessary for the territory to plead or prove negligence in any form or manner on the part of the licensee or any vessel. If the territory is damaged by a discharge prohibited by this chapter it need only plead and prove the fact of the prohibited discharge or other polluting condition and that it occurred. In addition to the civil penalty, the pilot and the master of any vessel or person in charge of any licensee's terminal facility who fails to give immediate notification of a discharge to the harbor master and nearest U.S. Coast Guard station shall be guilty of a misdemeanor and fined not less than $5,000 nor more than $10,000. The Department shall, by rules and regulations, require that the licensee designate a person at the terminal facility who shall be the person in charge of that facility for the purposes specified by this section. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Water Resources |
| Marine Sanitation Devices (MSDs); Regulations to establish a No Discharge Zone (NDZ) for State waters within the boundary of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary,Code of Federal Regulations § 40 CFR Part 140, 67 FR 35735. | US EPA established a no discharge zone within the boundaies of the FKNMS pursuant to section 312 (f) (4) (a) of the Clean Water Act. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition of waste discharges protects reefs system from eutrophication by the nutrients in waste (particularly nitrogen and phosphorus) as well as the debris and sediment in the waste. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Algae; Ballast Discharge; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Oil Pollution Act of 1990, 33 United States Code §§ 2701 et seq. | Established limitations on liability for damages resulting from oil pollution, established a fund for the payment of compensation for such damages, mandated the National Oil and Hazardous Substance Contingency Plan to provide organizational structure and procedures for responding to spills. Application to Coral Reefs:In the event of an oil spill that contaminates a coral reef, the Act could be used to determine liability and provide funds for rapid cleanup. Legislative Actions:Can provide fines for failing to notify the appropriate federal agency of a maximum of $250,000 per day for an individual and a maximum of $500,000 for an organization. Civil penalties are authorized at $25,000 per day of violation or $1,000 per barrel of oil discharged. Prison sentences up to a maximum of fifteen years can be imposed on violators. Comments:The Act was signed in 1990, largely in response to rising public concern following the Exxon Valdex incident. The Act improved the nation's ability to prevent and respond to oil spills by establishing provisions that expand the federal government's ability, and and provided the money and resources necessary, to respond to oil spills. The Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund was established and provided up to one billion dollars per spill incident. |
US Coast Guard/US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters |
Chemical Variables; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Non-point Source Controls; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Environment; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Toxics; Wetlands |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
