ReefLink Database

Octocoral
Octocorals are thick and fleshy, colonial marine animals resembling stony corals in polyp size, but lacking calcium carbonite skeletons. Octocorals include blue coral, soft corals, sea pens, and gorgonia.
CMap
CMap Description
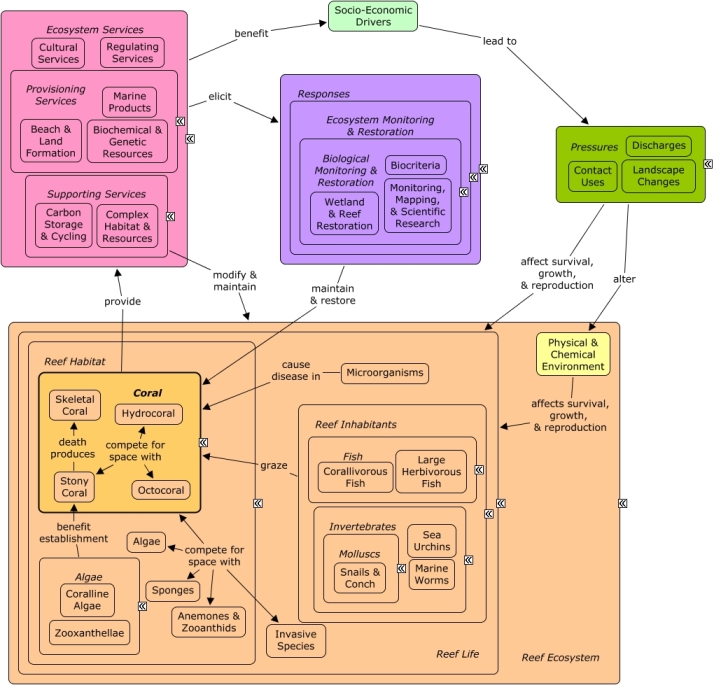
Octocoral, including gorgonians and soft corals, are important contributors of complex habitat & resources. They also provide biochemical & genetic resources, marine products, and regulating services in varying degrees; and are also important to the cultural services derived from the reef ecosystem. Octocoral species compete for space and resources with algae, sponges, anemones & zooanthids and other coral species. Reef inhabitants maintain the balance between reef habitat species by selectively under grazing coral relative species it competes with. Pressures from socio-economic drivers can stress or kill coral by introducing competing invasive species, disease causing microorganisms, and disturbing the physical & chemical environment. To ensure the flow of services from coral and coral reef ecosystems, monitoring, mapping, research and restoration is paramount.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Restoration: Restore Reef Habitat and Salvage Benthic Inhabitants Injured by Physical Damage | This management approach involves salvaging, maintenance, and re-stabilization or injured resources by management staff and private contractors in order to rescue and provide first aid following physical damage such as vessel groundings. This can be achieved using Reef Medics and other volunteer programs because these groups have experience with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, and SCUBA diving. Also, it allows for researchers to collect living coral material when relocation of such organisms is not possible. Salvage and re-stabilization is not limited to the living coral; octocorals, seagrasses, and the non-living framework may all be damaged of destabilized from groundings or other physical impacts. In addition to the habitat's structural integrity, it is important to re-establish aesthetics and ecological functionality. Funds from mitigation and case settlements should be used for this work, as long term costs of restoration and monitoring can be extensive. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Octocoral; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Restoration: Removal of Invasive Algae | Benthic organisms on reefs maintain a delicate balance competing for space. In many areas, the competition between coral and algae has fallen out of balance due to confounding factors. Factors such as decreased herbivorous fish and invertebrates, and invasive algae species have allowed faster growing algae to take over many reefs, often growing into smothering mats that cover and kill coral. In Hawaii, there has been some success physically removing invasive algae such as Kappaphycus using underwater vacuums extended down from barges or volunteer events in shallower areas. | The Nature Conservancy. 2010.Two Million Pounds of Invasive Algae Removed From Maunalua Bay. (not cited) |
Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcareous Macroalgae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Coralline Algae; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Reef Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Zooxanthellae |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|
