ReefLink Database

Non-point Source Controls
Non-point source controls are designed to monitor, regulate, and limit pollution from non-point sources, such as urban runoff, agricultural runoff, domestic animals, road construction, timber harvests, boats, and septic systems. Examples include setting and monitoring total maximum daily loads (TMDLs) from non-point source discharges.
CMap
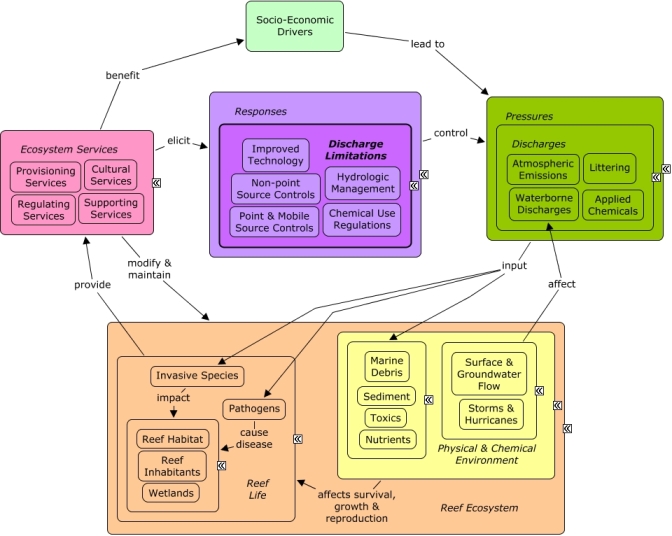
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to reduce or manage discharges of pollutants into coastal waters. Atmospheric pollution can be controlled with point-source regulations and updating technology to reduce emissions. Non-point source controls can set limitations on the quantity and frequency of discharges. Implementing new or upgraded technology in factories or waste treatment facilities can also reduce emissions or discharges. Regulation of chemical use, including registration, labeling, and evaluation of risk, can be used to identify potentially toxic chemicals. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that create pollution benefit indirectly from goods and services provided by the reef which provides recreational opportunities and contributes to the cultural identity of the local community and drives coastal development.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cannon, J. 2008. A bargain for clean water. | 2008 | Review | Agriculture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. | 2008 | Puerto Rico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Improved Technology; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Greiner, R., A. Herr, J. Brodie, and D. Haynes. 2005. A multi-criteria approach to Great Barrier Reef catchment (Queensland, Australia) diffuse-source pollution problem. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:128-137. | 2005 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wright, J. and D. Morton. 1999. Promoting erosion control in the Virgin Islands. Pages 8-May in Investing in the protection of our environment. Proceedings of conference 30, Nashville, 1999. (International Erosion Control Association). | 1999 | US Virgin Islands | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Grigg, R. W. 1995. Coral reefs in an urban embayment in Hawaii: a complex case history controlled by natural and anthropogenic stress. Coral Reefs 14:253-266. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Discharges; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. | 1993 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Docks & Marinas; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Robert Pitt and K. Dunkers. 1993. Lake Water Quality Improvements from Treatment of Stormwater Using the Flow Balancing Method, 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. Anaheim, CA. October 1993.; Detecting Water Quality Trends from Stormwater Discharge Reductions, Engineerin. in 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. | 1993 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Algae; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Bannerman, R.; Baun, K.; Bohn, M.; Hughes, P.; Graczyk, D. 1983. Nationwide Urban Runoff Program, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Evaluation of Urban Nonpoint Source Pollution Management in Milwaukee County, Wisconsin. Volume 2. Feasibility and Application of Urban Nonpoint Source Pollution. | 1983 | Field Study & Monitoring | Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| North Carolina Dept. of Natural Resources and Community Development, Div. of Environmental Management. 1983. Nationwide Urban Runoff Program, Winston-Salem, North Carolina: An Evaluation of Street Sweeping as a Runoff Pollution Control. Final rept. Sep 79-Oct 83. | 1983 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Livestock Waste Storage and Utilization | Confined animal facilities often produce large amounts of animal waste. This waste can be stored and disposed of in a variety of ways, and it is important to consider how rainwater may carry these wastes in groundwater. Wastes can be kept in temporary storage ponds, storage structures, or treatment lagoons. Once composted, these wastes may be applied to agricultural land in an environmentally acceptable manner in place of other fertilizers. Site selection, timing of application and rate of application must be properly managed to reduce the potential for degradation of ground water. Additionally, this practice may increase microbial action in the soil surface, which helps keep pesticides and other pollutants in place. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Food & Raw Materials; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Bivalve Aquaculture Biofouling Control | These management options reduce, clean or remove biofouling organisms and other waste from bivalve production areas while minimizing environmental risk. Aquaculture shellfish production requires adequate food availability and water of dependable quantity and quality. Aquaculture operations and gear must have a minimal adverse impact on the surrounding water, plant, animal and human resources. Biofouling is detrimental to shellfish production, increasing exposure to pathogens, reducing the available food stuffs, and increasing organic loading. Only environmentally appropriate biofoul control methods should be used, and fouling organisms and algae should be disposed of appropriately to avoid local degradation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. |
Algae; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Improved Technology; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Octopus & Squid; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Snails & Conch; Supplemental Feeding |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Change Agricultural Cover Crop Practices | Cover crop outreach entails changing agricultural practices in an area to leave vegetation and cover on the soil while growing other crops (e.g. Coffee). Agricultural practices that encourage leaving soil bare are extremely susceptible to erosion (e.g. sun grown Coffee). Cover crop methods and shade-grown crops (e.g. shade-grown Coffee) would reduce the large amount of sediment that is eroding, particularly from high elevations, and ultimately will reduce the amount of sediment that reaches the coral reefs. Options to encourage transition to cover crop practices include outreach to raise awareness of benefits and cost share programs to help farmers with the burden of the extra expense. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Conservation Cover. CODE 327. US Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Responses; Sediment |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Contour Farming | Contour Farming involves sloping land in such a way that field preparation, planting and cultivating are done on the contour. This includes following established grades of terraces or diversions. During heavy rains the crop rows formed slow water runoff reducing erosion and water runoff of non-point source pollutants such as agricultural herbicides and fertilizers. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Fertilizer Application Management | This agricultural best management practice involves the development, implementation and periodic update of nutrient management plans. Nutrient management plans are used to efficiently apply nutrients at appropriate rates so as to still achieve desired crop yields. There are several important measures and considerations that must be taken before developing the nutrient plan. Farm and field maps, yield expectations, nutrient resources, and geologic field limitations are all important. Some crops fix nitrogen, such as legumes, and have a nitrogen credit that must be factored. Field limitations include shallow aquifers, nearby surface water, sinkholes, and highly erodible soils. If the nutrients to be applied aren�t commercial they must be assessed to determine the nutrient value and the rate of availability of the nutrients. The nutrient plan�s timing and application methods should use the limiting nutrient concept and avoid applications to frozen soil and during periods of leaching or runoff. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Jokela, Bill, Peter Kleinman, John Peters, and Ann Wolf,. 2011. Manure Spreader Calibration & Manure Testing. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Grazing Land Management | This management option protects range, pasture and other types of grazing lands for agricultural animals. Special actions should be taken to protect sensitive areas such as streams, wetlands and estuaries if livestock is to have access to these areas. Grazing management practices can be categorized into four types, vegetative stabilization, grazing management systems, access limitations and alternative water supplies. Vegetative stabilization involves reestablishing the vegetative cover on ranges after it has been removed by grazing to reduce erosion rates. Grazing management systems typically reduce the time livestock spend in each pasture to increase the quantity and quality of vegetation in those pastures. Grazing frequency, timing, duration, area allocation, and livestock distribution kind, class, distribution and stocking rates should all be considered in the management system to ensure adequate pasture rehabilitation. Access limitations, such as fencing and stream crossings are used to herd and control livestock movement. Physical disturbance from livestock can increase erosion, so crossings and watering access points should be hardened. Alternative water supplies are an alternative to more sensitive water sources that may be vulnerable to erosion and discharges from grazing areas. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges |
| Chemical Discharge Controls: Integrated pest Management Modify mosquito control programs/regulations | The results of pesticide research program can be used to modify the existing mosquito control program as necessary. (312) | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructure; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Pressures; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Water |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Research and Model Causal Linkage Between Pollutants and Ecological Impact | This involves conducting research to identify and document causal linkages between discharge water pollutants and specific, quantifiable ecological problems. The natural environment naturally assimilates some pollutants, but has thresholds for this type of contaminant processing. Different hydrology, biology and spatial/temporal factors are all going to play a roll in the linkage between pollutants and ecological problems, meaning modeling and risk assessment can be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Sewage Treatment; Stormwater Management; Sunscreen Use; Supporting Services; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Discharge Controls: Survey and Manage Household Chemical Use | This management option targets household indoor and outdoor chemical use (pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, cleaners, detergents, solvents, etc). Though these chemicals are typically used in small amounts, many make their way into the watershed because of improper use. Before designing a plan to manage these chemicals, data must be gathered from the local community through surveys. An ideal survey would gather information on what chemicals are being used, how they are used, and how they are disposed of. Enforcing proper use and disposal is very difficult, making a strong education program in response to findings from the study essential. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Culture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Housing; Improved Technology; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Shelter; Textiles & Apparel; Toxics |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Management Planning | There are many aspects to properly managing forestry sites to reduce point source and non-point source pollutants. Forestry activities can degrade water quality with several types of pollutants and impacts, including: sediment, nutrients, forest chemicals like pesticides, organic debris from tree litter, increased water temperature and increased streamflow. The Forestry management plan and practices include, but are not limited to: pre-harvest planning, road construction and use, prescribed burning and fire management, brush management, timber harvest, regeneration, and application of forest chemicals. Wetlands Forest Management has additional best practices. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Biological Harvest; Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Forestry Policy: Forest Chemical Management | Pesticides and fertilizers are commonly used in forestry to reduce mortality of desired trees, improve forest production, and ease harvest/extraction. The rate of application is typically very low, but given the overall area covered, pesticides can still accumulate within watersheds. Some forest management chemical use considerations to reduce nonpoint source pollution impacts include: Develop an effective spill contingency plan to contain spills, and immediately report accidental spills into surface waters to the appropriate State agency. Prior to application, inspect the mixing and loading process and the calibration of equipment, and identify the appropriate weather conditions, the spray area, and buffer areas for surface waters. Buffer areas for surface waters are especially important for aerial applications. Carefully prescribe the type and amount of pesticides appropriate for the insect, fungus, or herbaceous species. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Provisioning Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Water Resources; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Landuse Management: Mine Reclamation | Lands disturbed by mining must be reclaimed to their Approximate Original Contour (AOC). Mine operators must backfill, compact, and grade in order to restore the AOC of the land with all highwalls, spoil piles, and depressions eliminated. Spoil material is prone to erosion, and may carry various disturbed toxics into groundwater if not properly managed. Temporary roads and impervious surfaces may have also been constructed for mining purposes. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement. POSTMINING LAND USE: Exceptions to Approximate Original Contour Requirements for Mountaintop Removal Operations and steep Slope Mining Operations. Washington, DC. |
Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Valuation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Landuse Management: Household Landscaping Best Management Practices | Homeowners manipulate the visible features of the land surrounding their home through landscaping. This includes flora, fauna, and terrain. Best Management Practices (BMPs) for landscaping include selection of indigenous flora and fauna, landscape irrigation (sprinkler systems etc), stormwater runoff BMPs, reducing water use, integrated pest management, composting, and incorporation of permeable surfaces. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Addition; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shelter; Supplemental Feeding; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Researching Other Pollutants and Water Quality Issues: Estimate other pollutant loadings | This activity involves documenting the locations and magnitude of pollution impact other than wastewater. Sources can be from inside and outside of the Sanctuary. Pollutants can include hydrocarbons, heavy metals, and pesticides. Water Quality standards (#22) Waste water (#21) | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pressures; Responses; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Restoration: Land Reclamation Integrating Toxic Discharge Controls | This option aims to eliminate unsightly residues, reduce erosion and control acid or otherwise toxic aqueous discharges from abandoned coal mines, coalmine waste or other types of land change. For toxic mine drainage, preventative actions include mine sealing, infiltration control, day lighting, and neutralization with alkaline material such as hydrated lime. Which action to take relies heavily on groundwater and runoff in the region of the mine. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Aquaculture; Coal Mining; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Rainwater Collection Systems | Creating a rainwater collection system (either through policy change or the initiative of homeowners) would help in many ways. These systems would utilize water in an efficient manner. It would reduce the pressure of water as a finite resource. Water would be collected and utilized before it reaches the ground. Once rain falls to the ground, it picks up nutrients, chemicals, and pathogens on the ground and transports them in the form of runoff. Eventually this contaminated stormwater runoff enters water resources through the drainage basin. Collecting a considerable amount of water would prevent contamination of that water, and allow for it to be usable. Also, it would reduce the amount of water that is lost when it is contaminated as runoff. An overall reduced amount of stormwater runoff would reduce the amount of contaminants that would harm corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Cisterns used for water harvesting. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shelter; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. Water collection can be selective, targeting the first flush of water, which is typically the most polluted. Water retention has the additional benefit of later release at a place and time when the water is needed (e.g. for irrigation). Rainwater Collection Systems (#11) can be an important water resource in areas where freshwater is limited. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Detention Devices for Dry/Wet Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Water and Sediment Control Basin. CODE 638. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Volume Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of natural structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. These structures are typically characterized as retention ponds and incorporate natural vegetation such as grass. These ponds may be dry, or may drain into nearby wetlands. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Infiltration | This management option attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that control the volume of surface water, facilitating faster absorption of the stormwater into the ground. Often these structures are able to infiltrate larger amounts of water faster while reducing exposure to surface sediments and pollutants. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. US EPA. EPA Infiltration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Transportation Policy: Dust Control Application | This action is taken to control dust from unpaved roads and other surfaces, which is generated by traffic and/or wind. Some dust control products (palliatives) for application include: water, hydroscopic palliatives, adhesive, petroleum emulsion, polymer emulsion, clay additive, and bituminous. There are specific considerations for application of each, including seasons and when to use which. For example, hygroscopic palliatives (control dust by absorbing water from the air) shall not be used in arid and semi-arid environments. Calcium chloride and magnesium chloride shall not be used in locations where the daily summertime relative humidity averages below 30%. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land & Air Transportation; Mining; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Wastewater Pollutants Impacts: Wastewater Pollutant Monitoring and Impact Studies | Potential approaches to this management option include experimental studies, eutrophication gradient studies, comparative studies of impacted and non-impacted sites, historical studies, geography comparison, use of biochemical and ecological indicators, use of sewage tracers, and high-frequency and spatially intensive water quality sampling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Infrastructure; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Public Administration; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Refine Pest Spraying Program | This strategy aims to reduce the amount of pesticides that could potentially enter the water from spraying for pests such as mosquitoes. A site-specific combination of pest prevention, pest avoidance, pest monitoring, and pest suppression strategies (PAMs) should be used. Aerial spraying is often used only when the mosquito concentration reaches a specific threshold. The mosquito spraying strategy would review the aerial spraying threshold to see if it could be raised, to reduce frequency of use. Refining spraying technologies would be advocated to see if newer techniques/technologies would possibly reduce the amount of pesticides released over water. For identified water quality concerns related to pesticide leaching, solution runoff and adsorbed runoff, the current version of the USDA-NRCS WIN-PST program should be used to evaluate potential risks to humans and/or fish, as appropriate, for each pesticide to be used. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Integrated Pest Management (IPM). CODE 595. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Toxics |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, "Superfund", 42 United States Code §§ 9601-9675. | Provides Liability, compensation, cleanup, and emergency response for hazardous substances released into the environment. Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Remediation; Waste Management Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Emergency Wetlands Resources Act of 1986, 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote the conservations of wetlands for public benefit and to assist in the compliance with international obligations under various treaties and conventions for migratory birds. Application to Coral Reefs:Indirect application to protection of coral reefs through wetland functions of nutrient (particularly nitrogen) and sediment removal from land-based discharges prior to their entrance into open coastal waters. Legislative Actions:Authorizied the purchase of wetlands from the land and Water Conservation Fund monies. Required States to include wetlands in their Comprehensive Outdoor Recreation Plans. Comments:Secretary of Interior was required to establish a National Wetland Priority Conservation Plan to identify the locations and types of wetlands that should be priorities for state and federal acquisition. The Act established various fee schedules for entering national wildlife refuges. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969, 42 United States Code §§ 4321-4377. | Requires analysis, public comment, and reporting for environmental impacts of federal actions. It stipulates the factors to be considered in environmental impact statements, and requires that federal agencies employ an interdisciplinary approach in related decision-making and develop means to ensure unqualified environmental values are given appropriate consideration, along with economic and technical considerations. Application to Coral Reefs:Requires an Environmental Assessment(EA), and potentially an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) if the project review finds there will be a significant impact. The EIS must detail the environmental impacts of the proposed action, unavoidable adverse environmental impacts, and alternatives to the proposed action. The resulting studies could protect sensitive environmental ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The Act is completely procedural; it does not include specific regulations. The Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) was created by the Act. CEQ is part of the Executive Office of the President and one of the CEQ directives is to ensure that federal programs comply with NEPA. The puprose of the EIS is to disclose to the public and resource managers the probable long- and short-term impacts of the proposed project as well as consideration of less environmentally damaging alternatives to the recommended course of action. |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Permitting & Zoning; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Oil Pollution Act of 1990, 33 United States Code §§ 2701 et seq. | Established limitations on liability for damages resulting from oil pollution, established a fund for the payment of compensation for such damages, mandated the National Oil and Hazardous Substance Contingency Plan to provide organizational structure and procedures for responding to spills. Application to Coral Reefs:In the event of an oil spill that contaminates a coral reef, the Act could be used to determine liability and provide funds for rapid cleanup. Legislative Actions:Can provide fines for failing to notify the appropriate federal agency of a maximum of $250,000 per day for an individual and a maximum of $500,000 for an organization. Civil penalties are authorized at $25,000 per day of violation or $1,000 per barrel of oil discharged. Prison sentences up to a maximum of fifteen years can be imposed on violators. Comments:The Act was signed in 1990, largely in response to rising public concern following the Exxon Valdex incident. The Act improved the nation's ability to prevent and respond to oil spills by establishing provisions that expand the federal government's ability, and and provided the money and resources necessary, to respond to oil spills. The Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund was established and provided up to one billion dollars per spill incident. |
US Coast Guard/US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters |
Chemical Variables; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Non-point Source Controls; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Environment; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Toxics; Wetlands |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986, 42 United States Code §§ 9601 et seq. | Reautorized CERCLA Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA/SARA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions:The amended Act stressed the importance of permanent and innovative treatment technologies, required Superfund actions to consider the standards and requirements found in other State and Federal environmental laws, provided new enforcement authorities and settlement tools. Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Water Resource Implementation Rule, 62-40 Florida Administrative Code (2006). | The Chapter is intended to provide water resouirce implementation goals, objectives and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources. A goal of the Chapter is to coordinate the management of water and land resources. It is the objective of the State to protect the functions of the entire ecological systems, as developed and defined in the programs, rules, and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is a goal of the Chapter that sufficient water be available for all existing and future reasonable-beneficial uses and the natural systems and that adverse effects of competition for water supplies be avoided. Application to Coral Reefs:By protecting the functions of entire aquatic ecological systems, those waters will contain less contaminants when they are discharged and meet other natural water bodies including marine ecosystems. Cleaner water will result in less ecological strees to marine ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This Chapter is intended to provide water resource implementation goals, objectives, and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources, based on statutory policies and directives in Chapters 187, 373, and 403, Florida Statutes. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Waste Management Policies |
