ReefLink Database

Non-Monetary Valuation
Non-monetary valuation methods are used to quantify ecosystem goods and services in terms of units other than economic ones, such as stakeholder preferences or quality of life. Formal methods for decision analysis, such as multi-attribute utility theory, have been developed (Hajkowicz 2007).
CMap
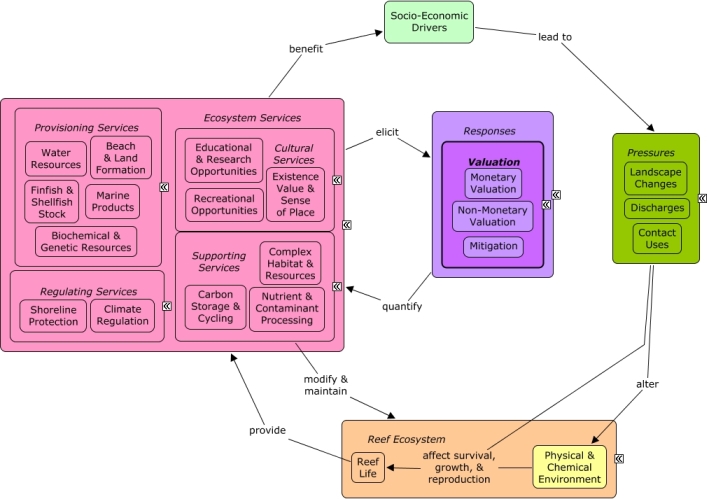
CMap Description
Valuation methods can be used to quantify the monetary or non-monetary value of coral reef ecosystem goods and services. Non-monetary methods, which quantify stakeholder preferences or quality of life, may also be used to evaluate decision options or quantify changes in the quality of ecosystem services. A change in the value of ecosystem services, or a desire to increase the total value of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to protect or restore the reef ecosystem by reducing pressures.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grafton, RQ; Akter, S; Kompas, T. 2011. A Policy-enabling framework for the ex-ante evaluation of marine protected areas. Ocean and Coastal Management 54:478-487. | 2011 | Review | Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation | |
| Kragt, M. E., L. T. H. Newham, J. Bennett, and A. J. Jakeman. 2011. An integrated approach to linking economic valuation and catchment modelling. Environmental Modelling & Software 26:92-102. | 2011 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation |
| Nava, H; Ramirez-Herrera, MT. 2011. Government conservation policies on Mexican coastal areas: is "top-down" management working? Revista de Biologia Tropical 59:1487-1501. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Sediment; Skeletal Coral |
| Harrison, P. A., M. Vandewalle, M. T. Sykes, P. M. Berry, R. Bugter, F. de Bello, C. K. Feld, U. Grandin, R. Harrington, J. R. Haslett, R. H. G. Jongman, G. W. Luck, P. M. da Silva, M. Moora, J. Settele, J. P. Sousa, and M. Zobel. 2010. Identifying and prioritising services in European terrestrial and freshwater ecosystems. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2791-2821. | 2010 | Europe | Review | Agriculture; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Climate; Climate Regulation; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Non-Monetary Valuation; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Provisioning Services; Recreational Opportunities; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Haslett, J. R., P. M. Berry, G. Bela, R. H. G. Jongman, G. Pataki, M. J. Samways, and M. Zobel. 2010. Changing conservation strategies in Europe: a framework integrating ecosystem services and dynamics. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2963-2977. | 2010 | Europe | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities |
| Launio, C. C., Y. Morooka, H. Aizaki, and Y. Iiguni. 2010. Perceptions of small-scale fishermen on the value of marine resources and protected areas: case of Claveria, Northern Philippines. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 17:401-409. | 2010 | Philippines | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Housing; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management |
| Skourtos, M., A. Kontogianni, and P. A. Harrison. 2010. Reviewing the dynamics of economic values and preferences for ecosystem goods and services. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2855-2872. | 2010 | Review; Model | Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Valuation | |
| Ghermandi, A., P. A. L. D. Nunes, R. Portela, N. Rao, and S. S. Teelucksingh. 2009. Recrational, cultural, aesthetic services from estuarine and coastal ecosystems. Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei. | 2009 | Europe | Review | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Social Organizations; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Morgan, O. A., D. M. Massey, and W. L. Huth. 2009. Diving demand for large ship artificial reefs. Marine Resource Economics 24:43-59. | 2009 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Large Ships; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Remoundou, K., P. Koundouri, A. Kontogianni, P. A. L. D. Nunes, and M. Skourtos. 2009. Valuation of natural marine ecosystems: an economic perspective. Environmental Resources and Economics 12:1040-1051. | 2009 | Climate; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation | ||
| Wolanski, E., J. A. Martinez, and R. H. Richmond. 2009. Quantifying the impact of watershed urbanization on a coral reef: Maunalua Bay, Hawaii. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84:259-268. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-Monetary Valuation; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Barton, D. N., T. Saloranta, S.J. Moe, H.O. Eggestad, and S. Kuikka. 2008. Bayesian belief networks as a meta-modelling tool in integrated river basin management Pros and cons in evaluating nutrient abatement decisions under uncertainty in a Norwegian river basin. Ecological Economics 66:91-104. | 2008 | Norway | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Recreational Opportunities; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation |
| Boyd, J. 2008. Counting nonmarket, ecological public goods. Resources for th Future, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Index or Indicator | Housing; Non-Monetary Valuation; Valuation | |
| Oh, C.-O., R. Ditton, and J. Stoll. 2008. The economic value of scuba-diving use of natural and artificial reef habitats. Society and Natural Resources 21:455-468. | 2008 | Cuba | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Parsons, G. R. and S. M. Thur. 2008. Valuing changes in the quality of coral reef ecosystems: A stated preference study of SCUBA diving in the Bonaire National Marine Park. 40:593-608. | 2008 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Valuation | |
| Oles, B. 2007. Transformations in the sociocultural values and meanings of reefs and resources on Mwoakilloa. Coral Reefs 26:971-981. | 2007 | Global; Micronesia | Cultural Policies; Non-Monetary Valuation | |
| Samonte-Tan, G. P. B., A. T. White, M. A. Tercero, J. Diviva, E. Tabara, and C. Caballes. 2007. Economic valuation of coastal and marine resources: Bohol Marine Triangle, Philippines. Coastal Management 35:319-338. | 2007 | Philippines | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation | |
| Boyd, J. and S. Banzhaf. 2006. What are ecosystem services? Resources for the Future, Washington, DC. | 2006 | Index or Indicator | Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation | |
| Hajkowicz, S. 2006. Multi-attributed environmental index construction. Ecological Economics 57:122-139. | 2006 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Pendleton, L. H. 2005. Understanding the potential economic impacts of sinking ships for SCUBA recreation. Marine Technology Society Journal 39:47-52. | 2005 | Australia; Cuba; Columbia; Europe | Review | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Social Organizations; Tourism & Recreation |
| Bhat, M. G. 2003. Application of non-market valuation to the Florida Keys marine reserve management. Journal of Environmental Management 67:315-325. | 2003 | Florida | Model | Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Joannot, P. 2003. The role and importance of protected areas of coral reefs: The example of French overseas territories [Role et importance des aires protegees dans les recifs coralliens. L'exemple de l'outre-mer francais]. Oceanis 29:415-427. | 2003 | Australia; Indonesia; Philippines; France | Field Study & Monitoring | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Non-Monetary Valuation |
| Rees, W. E. 2003. Economic development and environmental protection: An ecological economics perspective. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 86:29-45. | 2003 | Global | Model | Cultural Protections; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mining Policies; Non-Monetary Valuation |
| Sadovy, Y., M. Kulbicki, P. Labrosse, Y. Letourneur, P. Lokani, and T. J. Donaldson. 2003. The humphead wrasse, Cheilinus undulatus: Synopsis of a threatened and poorly known giant coral reef fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 13:327-364. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Live Collection; Non-Monetary Valuation; Planktivorous Fish; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting |
| Park T., J. M. Bowker, and V. R. Leeworthy. 2002. Valuing snorkeling visits to the Florida Keys with stated and revealed preference models. Journal of Environmental Management 64:301-312. | 2002 | Florida | Model | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Remediation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Pocock, C. 2002. Sense matters: Aesthetic values of the Great Barrier Reef. International Journal of Heritage Studies 8:365-381. | 2002 | Australia | Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities | |
| Bunce, L., K. Gustavson, J. Williams, and M. Miller. 1999. The human side of reef management: A case study analysis of the socioeconomic framework of Montego Bay Marine Park. Coral Reefs 18:369-380. | 1999 | Jamaica | Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Non-Monetary Valuation | |
| Leeworthy, V. R. and P. C. Wiley. 1996. Linking the Economy and Environment of Florida Keys/Florida Bay. | 1996 | Florida | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Eid, E.-M., E., and M. A. Fawzi. 1991. Egyptian approach towards appropriate use of coastal zones on the Red Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 23:331-337. | 1991 | Egypt | Mangroves; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bockstael, N. E., K. E. McConnell, and I. E. Strand. 1989. A aandom utility model for sportfishing: some preliminary results for florida. Marine Resource Economics 6:245-260. | 1989 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Finfish Harvest; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Fishing |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monitor & Research: Utilize Managed Areas for Socioeconomic Research | Data are needed to test hypotheses about the socioeconomic impact of marine zoning and user-group perceptions about changes in natural resources within the sanctuary area. User-group perception of changes in natural resources can be compared with quantitative ecological data to identify misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Providing funding opportunities for external scientists to conduct research in the managed area is another option. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Permitting & Zoning; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Valuation |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Sanctuary Use Patterns and Resource Value | This management option seeks to provide data and analysis of consumptive and non-consumptive use of all natural resources within sanctuary borders. Special emphasis is to be placed on artificial and natural reef resources used by residents and visitors. Wherever possible, market and non-market values of these resources should be elicited as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Services; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
