ReefLink Database

Marine Debris
Marine debris includes garbage, plastics, glass, and metal, which are not disposed of properly and can enter coastal waters.
CMap
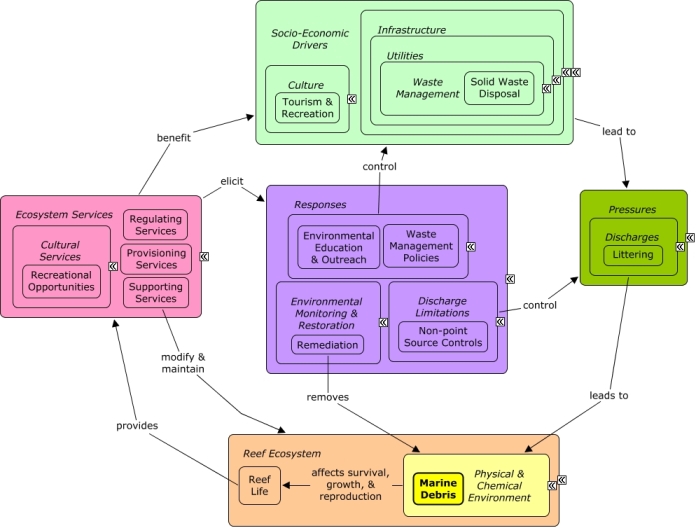
CMap Description
Littering can result from insufficient solid waste disposal and may be particularly high along roads and bridges, or in areas frequented by tourists. Littering introduces debris into the marine environment, including glass, plastics, and metal which can damage reef species and reduce the aesthetic and recreational value of reefs. Many of the same socio-economic sectors which create pollution benefit indirectly from reef goods and services including fishing and recreational opportunities which contribute to the cultural identity of the local community and drive coastal development. Waste management policies to improve solid waste disposal, non-point source controls such as littering fines, increased law enforcement, and environmental education can all be enacted to reduce littering. Remediation, such as coastal clean-up programs, can be enacted to remove trash and debris.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Richards, ZT; Beger, M. 2011. A quantification of the standing stock of macro-debris in Majuro lagoon and its effect on hard coral communities. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:1693-1701. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Marshall Islands | Finfish Harvest; Housing; Marine Debris; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Whitall, D. R., B. M. Costa, L. J. Bauer, A. Dieppa, and S. D. Hile, editors. 2011. A Baseline Assessment of the Ecological Resources of Jobos Bay, Puerto Rico. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 133, NOAA, Silver Spring, (MD, USA). | 2011 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics |
| Love, M. S., B. Lenarz, and L. Snook. 2010. A Survey Of The Reef Fishes, Purple Hydrocoral (Stylaster Californicus), And Marine Debris Of Farnsworth Bank, Santa Catalina Island. Bulletin of Marine Science 86:35-52. | 2010 | Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Hydrocoral; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Pittman, S. J., C. F. G. Jeffrey, R. Clark, K. Woody, B. D. Herlach, C. Caldow, M. E. Monaco, and R. Appledoorn. 2010. Coral reef ecosystems of Reserva Natural de La Parguera (Puerto Rico): spatial and temporal patterns in fish and benthic communities (2001-2007). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Silver Spring, MD. | 2010 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Tourism & Recreation |
| Abu-Hilal, A. and T. Al-Najjar. 2009. Marine litter in coral reef areas along the Jordan Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Journal of Environmental Management 90:1043-1049. | 2009 | Finfish Harvest; Littering; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Selkoe, K. A., B. S. Halpern, C. M. Ebert, E. C. Franklin, E. R. Selig, K. S. Casey, J. Bruno, and R. J. Toonen. 2009. A map of human impacts to a "pristine" coral reef ecosystem, the Papahanaumokuakea Marine National Monument. Coral Reefs 16-Jan. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | GIS & Maps | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Light; Marine Debris; Pathogens; Sea Temperatures; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Bauer, L. J., M. S. Kendall, and C. F. G. Jeffrey. 2008. Incidence of marine debris and its relationships with benthic features in Gray's Reef National Marine Sanctuary, Southeast USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:402-413. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Boating Activities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Kim, C. G. and H. S. Kim. 2008. Post-placement management of artificial reefs in Korea. Fisheries 33:61-68. | 2008 | Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Scaps, P. and F. Runtukahu. 2008. Assessment of the coral reefs of the luwuk peninsula, central sulawesi, indonesia [evaluation des recifs coralliens de la peninsule de Luwuk, Sulawesi central, Indonesie]. Bulletin de la Societe Zoologique de France 133:341-355. | 2008 | Cuba; Indonesia | Corallivorous Fish; Echinoderms; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Octocoral; Pathogens; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Seastars; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral | |
| Smith, S. D. A., M. J. Rule, M. Harrison, and S. J. Dalton. 2008. Monitoring the sea change: Preliminary assessment of the conservation value of nearshore reefs, and existing impacts, in a high-growth, coastal region of subtropical eastern Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:525-534. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Marine Debris; Molluscs |
| Dameron, O. J., M. Parke, M. A. Albins, and R. Brainard. 2007. Marine debris accumulation in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands: An examination of rates and processes. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:423-433. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Pichel, W. G., J. H. Churnside, T. S. Veenstra, D. G. Foley, K. S. Friedman, R. E. Brainard, J. B. Nicoll, Q. Zheng, and P. Clemente-Colon. 2007. Marine debris collects within the North Pacific Subtropical Convergence Zone. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:1207-1211. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Whales & Dolphins |
| Boland, R., B. Zgliczynski, J. Asher, A. Hall, K. Hogrefe, and M. Timmers. 2006. Dynamics of debris densities removal at the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands coral reefs. Atoll Research Bulletin 461-470. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| SeafoodWatch. 2005. Sustainable Seafood Business Practices. Monteray Bay. | 2005 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Sea Turtles; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Chiappone, M., D. W. Swanson, S. L. Miller, and H. Dienes. 2004. Spatial distribution of lost fishing gear on fished and protected offshore reefs in the Florida Keys national marine sanctuary. Caribbean Journal of Science 40:312-326. | 2004 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Boland, R. C. and M. J. Donohue. 2003. Marine debris accumulation in the nearshore marine habitat of the endangered Hawaiian monk seal, Monachus schauinslandi 1999-2001. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:1385-1394. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Debris; Mitigation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Coates, A. G., M.-P. Aubry, W. A. Berggren, L. S. Collins, and M. Kunk. 2003. Early neogene history of the central American arc from Bocas del Toro, western Panama. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 271-287. | 2003 | South & Central America; Costa Rica; Panama | Marine Debris; Sediment | |
| Donohue, M. J. 2003. How multiagency partnerships can successfully address large-scale pollution problems: A Hawaii case study. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:700-702. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Debris; Mitigation; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges |
| Kershaw, S. and L. Guo. 2003. Pleistocene cyanobacterial mounds in the Perachora Peninsula, Gulf of Corinth, Greece: Structure and applications to interpreting sea-level history and terrace sequences in an unstable tectonic setting. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 193:503-514. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring | Construction Codes & Projects; Cyanobacteria; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Plankton; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Chiappone, M., A. White, D. W. Swanson, and S. L. Miller. 2002. Occurrence and biological impacts of fishing gear and other marine debris in the Florida Keys. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:597-604. | 2002 | Florida | Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Turgeon, D. D., R. G. Asch, B. D. Causey, R. E. Dodge, W. Jaap, K. Banks, J. Delaney, B. D. Keller, R. Speiler, C. A. Matos, J. R. Garcia, E. Diaz, D. Catanzaro, C. S. Rogers, Z. Hillis-Starr, R. Nemeth, M. Taylor, G. P. Schmahl, M. W. Miller, D. A. Gulko, J. E. Maragos, A. M. Friedlander, C. L. Hunter, R. S. Brainard, P. Craig, R. H. Richond, G. Davis, J. Starmer, M. Trianni, P. Houk, C. E. Birkeland, A. Edward, Y. Golbuu, J. Gutierrez, N. Idechong, G. Paulay, A. Tafileichig, and N. V. Velde. 2002. The state of coral reef ecosystems of the United States and Pacific Freely Associated States: 2002. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Ocean Service/National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD. | 2002 | Global; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Samoa; Guam | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Donohue, M. J., R. C. Boland, C. M. Sramek, and G. A. Antonelis. 2001. Derelict fishing gear in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands: Diving surveys and debris removal in 1999 confirm threat to Coral Reef ecosystems. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1301-1312. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Marine Debris; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Maragos, J. E. 2000. Hawaiian Islands (U.S.A.). Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 791-812. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Military; Pathogens; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| UMIAMI-RSMAS,. 1998. Ocean Status Information Management System (OSIMS) oil spill data and information. Ocean Status Information Management System (OSIMS) oil spill data and information. | 1998 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; Mexico | Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Marine Debris; Non-point Source Runoff; Petroleum Spills; Plankton; Point Source Discharges |
| Haynes, D. 1997. Marine debris on continental islands and sand cays in the Far Northern Section of the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 34:276-279. | 1997 | Australia | Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Bohm, F., J.-L. Dommergues, and C. Meister. 1995. Breccias of the Adnet Formation: indicators of a Mid-Liassic tectonic event in the Northern Calcareous Alps (Salzburg/Austria). Geologische Rundschau 84:272-286. | 1995 | Model; Index or Indicator | Marine Debris; Sediment |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels | Semi- permanent/permanent vessels can have a negative impact on the surrounding local environment both due to the effects of shade and from the direct contact with the substrate. Sunken vessels that cannot be seen from the surface may present a danger to navigation. Derelict vessels that do not remain stationary may cause harm in multiple locations before becoming stationary. If fishing gear is still intact, it may cause further biological damage through "ghost fishing� (#283). Early response, creating mooring fields, pump-out stations, and providing support for removing derelict vessels, reduces the impact of these vessels. Also, the removal of intrusive vessels will help contribute to the restoration of reef areas to previous conditions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Military; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Stony Coral; Substrate; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Print Marine Etiquette on Marine-Related Products Packaging | Printing information on marine-related products regarding proper marine etiquette could be a possibility for raising awareness and improving public stewardship. Partnerships will be explored to help print etiquette information on materials such as bait boxes, ice bags, water buckets, etc. that are commonly used by stakeholders. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Public Participation: Assist Save the Manatee Club | Volunteers are active in helping to remove monofilament line. This is especially dangerous to manatees. Volunteers from Save the Manatees can help with education and monitoring in the local coral management area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Debris; Marine Vertebrates; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Public Participation: Assist Reef and Coastal Cleanups | Reef and coastal cleanups are organized by a network of environmental and civic organizations, government agencies, industries, and individuals. These efforts help to educate the public on marine debris issues and how to help reduce debris along beaches. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) and The Ocean Conservancy. 2005. Good Environmental Practices: Underwater Clearnup. CORAL RP-103:2002, |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Debris |
| Water Quality Management: Reduce Pollution & Discharges from Marinas & Live-Aboards | This management option strives to reduce and eliminate the discharge of wastewater and pollution within zones near corals. In many instances, "no-discharge" zones already exist and are simply poorly enforced. In other instances the discharge limits are not stringent enough. Successful regulation requires marinas to be equipped with the proper infrastructure to support transfer of wastewater from vessels to shore-side for treatment. This infrastructure includes: pump-out facilities and mobile pump-out services. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Health; Health Policies; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6401 (2000). | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:Allowed the development of programs and projects, and provided financing for developing sound scientific data to preserve and restore coral reefs. Continued the Coral Reef Task Force and Coral Reef Initiative started under Executive Order 13089 (1998). Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The Act is administrative, not regulatory. It established four major programs; (1) The National Coral Reef Action Strategy established goals for research, monitoring and conservation, (2, 3) The Coral Reef Conservation Program and Coral Reef Conservation Fund provided financial assistance for coral reef projects, (4) the National Program facilitated cooperative work between federal, state and regional efforts that work to improve coral reef ecosystems. The National Program also enhanced the public awareness of coral reefs through educational programs. The Act incorporated Executive Order 13,089 and provided coordinated funding activities through twelve federal agencies and seven states. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States; US Coral Reefs |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corporate Responses; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Public Administration; Remediation; Utilities |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Marine Sanitation Devices (MSDs); Regulations to establish a No Discharge Zone (NDZ) for State waters within the boundary of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary,Code of Federal Regulations § 40 CFR Part 140, 67 FR 35735. | US EPA established a no discharge zone within the boundaies of the FKNMS pursuant to section 312 (f) (4) (a) of the Clean Water Act. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition of waste discharges protects reefs system from eutrophication by the nutrients in waste (particularly nitrogen and phosphorus) as well as the debris and sediment in the waste. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Algae; Ballast Discharge; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969, 42 United States Code §§ 4321-4377. | Requires analysis, public comment, and reporting for environmental impacts of federal actions. It stipulates the factors to be considered in environmental impact statements, and requires that federal agencies employ an interdisciplinary approach in related decision-making and develop means to ensure unqualified environmental values are given appropriate consideration, along with economic and technical considerations. Application to Coral Reefs:Requires an Environmental Assessment(EA), and potentially an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) if the project review finds there will be a significant impact. The EIS must detail the environmental impacts of the proposed action, unavoidable adverse environmental impacts, and alternatives to the proposed action. The resulting studies could protect sensitive environmental ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The Act is completely procedural; it does not include specific regulations. The Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) was created by the Act. CEQ is part of the Executive Office of the President and one of the CEQ directives is to ensure that federal programs comply with NEPA. The puprose of the EIS is to disclose to the public and resource managers the probable long- and short-term impacts of the proposed project as well as consideration of less environmentally damaging alternatives to the recommended course of action. |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Permitting & Zoning; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899, 33 United States Code § 1252. | This law prohibits the discharge of any type of refuse matter in U.S. waters without permission (section 13). In addition, the excavation, fill, or alteration of the course, condition, or capacity of any port, channel, river, or other areas within the limits of this law is prohibited. This law prohibits the construction or alteration of a structure in wetlands of the U.S. (sections 9 and 10). Construction in wetlands and waters of the U.S. requires a permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Application to Coral Reefs:Under section 10, excavation or fill within navigable waters requires approval of the Chief of Engineers and concerns about contaminated sediments with dredge and fill projects in navigable waters is addressed within the permitting process. Indirect protection of coral reefs is offered by the Act and its prohibition of dumping refuse into navigable waters and the process of anaylzing sediment in proposed dredge and fill operations. Legislative Actions:Violations of the law are punished under section 309 of the Clean Water Act and section 205 of National Fishing Enhancement Act. Fines imposed for violation will not be less than $10,000 per violation or more than $25,000 per violation. Comments:Many states, including Florida, require additional permits for constuction of docks, piers, wharfs, jetties and other structures in navigable waters and wetlands in addition to the Corps of Engineers permit. Authority to issue permits for discharge of refuse matter under section 13 was modified by the amendments to Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972 and established the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Permit process. The Act was initially established to protect interstate commerce in navigable waters. The permit review process involves factors including economics, aethetics, general envitonmental concerns, historical values, water quality, and fish and wildlife impact before project approval is granted. |
US Army Corps of Engineers (COE), and US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: United States |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary and Protection Act, Public Law 101-605 (H.R. 5909 United States Code (1990). | To protect the resources of the area delineated in section 5(b) of the Act, to educate and interpret for the public regarding the Florida Keys marine environment, and to manage such human uses of the Sanctuary consistent with the Act. Nothing in the Act is intended to restrict activities that do not cause adverse effects to the resources or property of the Sanctuary or that do not pose harm to the users of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the thrid largest coral reef barrier in the world. Included in the FKNMS are Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 squared nautical miles of coral reefs.The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive in the Sanctuary. From Miami to the Marquesas Keys there are over 6000 patch reefs. The Act also protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, futher protecting mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act required the preparation of a comprehensive mangement plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:Large vessel groundings on coral reefs in the Florida Keys was a major driver for the designation of the Sanctuary. In 1989, there were three groundings of large commercial vessels on the coral reef tract within an eighteen day period. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as lead agency and Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Florida Fish and Wildlife Commission, and Monroe County as Co-Trustees Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Transportation |
