ReefLink Database

Water
Water Sectors include those that pertain to provisioning of water for public use, including the drinking water supply, irrigation systems for agriculture, and water for critical services (such as firefighting and hospitals).
CMap
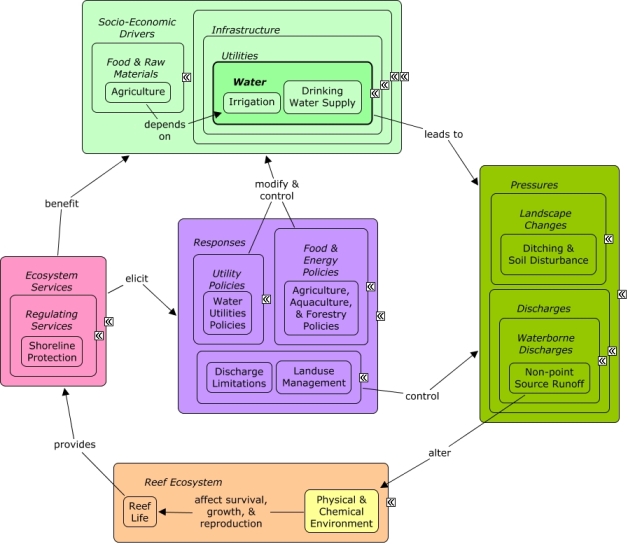
CMap Description
Development of systems for irrigation can lead to ditching & soil disturbance that modify the landscape and can modify rates of non-point source runoff. Runoff can alter the levels of sediment, toxics, and nutrients within the physical & chemical environment, affecting the survival & growth of reef life and the provision of ecosystem services. Water sectors may benefit from shoreline protection, as well as indirectly from other ecosystem services that improve the well-being of sectors that depend on water. Agricultural policies can be enacted to modify irrigation practices, or landscape changes, such as ditches and canals, can be modified or restored to reduce runoff.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D'Arrigo, R; Abram, N; Ummenhofer, C; Palmer, J; Mudelsee, M. 2011. Reconstructed streamflow for Citarum River, Java, Indonesia: linkages to tropical climate dynamics. Climate Dynamics 36:451-462. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India; Java; Indonesia | Climate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Bivalves; Discharges; Fish; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pipelines; Salinity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation Policies; Waste Management; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands | |
| Navalgund, RR; Singh, RP. 2011. Climate Change Studies Using Space Based Observation. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing 39:281-295. | 2011 | Global; India | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Forestry; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Irrigation; Light; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Uddin, S; Al Ghadban, AN; Khabbaz, A. 2011. Localized hyper saline waters in Arabian Gulf from desalination activity-an example from South Kuwait. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 181:587-594. | 2011 | Saudi Arabia; Kuwait; Bahrain; Qatar; United Arab Emirates | Salinity; Water | |
| Iacona, G. D., L. K. Kirkman, and E. M. Bruna. 2010. Effects of resource availability on seedling recruitment in a fire-maintained savanna. Oecologia 163:171-180. | 2010 | Index or Indicator | Water | |
| Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Irrigation | |
| Lenahan, M. J. and K. L. Bristow. 2010. Understanding sub-surface solute distributions and salinization mechanisms in a tropical coastal floodplain groundwater system. Journal of Hydrology 390:131-142. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Discharges; Irrigation; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Mondal, N. C., V. S. Singh, S. C. Puranik, and V. P. Singh. 2010. Trace element concentration in groundwater of Pesarlanka Island, Krishna Delta, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 163:215-227. | 2010 | India | Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Richlen, M. L., S. L. Morton, E. A. Jamali, A. Rajan, and D. M. Anderson. 2010. The catastrophic 2008-2009 red tide in the Arabian gulf region, with observations on the identification and phylogeny of the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 9:163-172. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Malaysia; United Arab Emirates; Oman; Mexico | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Veal, C. J., M. Carmi, G. Dishon, Y. Sharon, K. Michael, D. Tchernov, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, and M. Fine. 2010. Shallow-water wave lensing in coral reefs: a physical and biological case study. Journal of Experimental Biology 213:4304-4312. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Irrigation; Light; Stony Coral | |
| Dodds, W. K., W. A. Bouska, J. L. Eitzmann, T. J. Pilger, K. L. Pitts, A. J. Riley, J. T. Schloesser, and D. J. Thornbrugh. 2009. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environmental Science and Technology 43:13-19. | 2009 | Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Kundzewicz, Z. W. and P. Doll. 2009. Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrological Sciences Journal-journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques 54:665-675. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Drinking Water Supply; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Muniz, M. A., J. G. Barbosa, J. A. S. Grossi, M. Y. Orbes, and P. G. Sa. 2009. Production And Quality Of Pot Chrysanthemum Fertirrigated With Different Nitrate/Ammonium Relations. Bioscience Journal 25:75-82. | 2009 | India | Domestic Animal Waste; Irrigation | |
| Mutschler, T. and T. Triantafyllidis. 2009. Geotechnical Aspects of the Construction of an Underground Dam in Karstic Reef Limestones. Wasserwirtschaft 99:53-56. | 2009 | Java; Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Drinking Water Supply; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Nelson, M., W. F. Dempster, and J. P. Allen. 2009. The water cycle in closed ecological systems: Perspectives from the Biosphere 2 and Laboratory Biosphere systems. Advances in Space Research 44:1404-1412. | 2009 | Global | Lab Study | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Irrigation; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| UNCWI. 2009. Healthy Watersheds through Healthy Forests. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Drinking Water Supply; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| 2008. DRAFT PROPOSED REVISIONS TO: U.S. VIRGIN ISLANDS WATER QUALITY STANDARDS. Chapter 7. Water Pollution Control, Subchapter 186. Water Quality Standards for Waters of the Virgin Islands, US Virgin Islands. | 2008 | US Virgin Islands | Index or Indicator | Biocriteria; Designated Uses; Discharges; Irrigation; Mangroves; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Banerjee, P., D. Sarwade, and V. S. Singh. 2008. Characterization of an island aquifer from tidal response. Environmental Geology 55:901-906. | 2008 | Drinking Water Supply; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Guzman, H. M., R. Cipriani, and J. B. C. Jackson. 2008. Historical decline in coral reef growth after the Panama Canal. Ambio 37:342-346. | 2008 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Stony Coral; Water | |
| Ogston, A. S., R. W. Sternberg, C. A. Nittrouer, D. P. Martin, M. A. Goni, and J. S. Crockett. 2008. Sediment delivery from the Fly River tidally dominated delta to the nearshore marine environment and the impact of El Nino. Journal of Geophysical Research F: Earth Surface 113. | 2008 | Papua New Guinea | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| White, I., T. Falkland, T. Metutera, M. Katatia, T. Abete-Reema, M. Overmars, P. Perez, and A. Dray. 2008. Safe water for people in low, small Island Pacific Nations: The rural-urban dilemma. Development 51:282-287. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Water |
| World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Iran; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. | 2007 | Aquaculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | ||
| Hao, A., A. Marui, T. Haraguchi, and Y. Nakano. 2007. Estimation of wet bulb formation in various soil during drip irrigation. Journal of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University 52:187-193. | 2007 | Model | Irrigation | |
| Hwang, S. 2007. Page 111 in SEVENTH CARIBBEAN ISLANDS WATER RESOURCES CONGRESS. St. Croix, USVI. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Drinking Water Supply; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Schools & Colleges; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Narayan, K. A., C. Schleeberger, and K. L. Bristow. 2007. Modelling seawater intrusion in the Burdekin Delta Irrigation Area, North Queensland, Australia. Agricultural Water Management 89:217-228. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Irrigation; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water |
| White, I., T. Falkland, P. Perez, A. Dray, T. Metutera, E. Metai, and M. Overmars. 2007. Challenges in freshwater management in low coral atolls. Journal of Cleaner Production 15:1522-1528. | 2007 | Agriculture; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Waterborne Discharges | ||
| White, I., T. Falkland, T. Metutera, E. Metai, M. Overmars, P. Perez, A. Dray, and A. C. Falkland. 2007. Climatic and human influences on groundwater in low atolls. Vadose Zone Journal 6:581-590. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Wilson, A. 2007. Nonwoven support - From Boscombe Pier to Palm Jumeirah. Technical Textiles International 16:25-28. | 2007 | Global; United Arab Emirates; Europe | Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Road Construction & Maintenance; Shoreline Protection | |
| Dykes, A. P. and J. Gunn. 2006. Hoga island, Sulawesi, Indonesia: Geomorphology and groundwater resources of a small tropical carbonate island. Cave and Karst Science 33:21-28. | 2006 | Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring | Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water |
| Jensen, L. T., E. Rosenqvist, and J. M. Aaslyng. 2006. A daylight climate chamber for testing greenhouse climate control strategies and calculating canopy carbon dioxide exchange. HortTechnology 16:191-198. | 2006 | CO2; Irrigation; Light; Primary Production | ||
| Kelley Hart. 2006. The upper Neuse Clean Water Iniative Conservation Plan. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Improved Technology; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Utilities Policies |
| Madhusoodanan, G., P. P. Ouseph, and S. Kumar. 2006. Bacterial contamination of drinking water and its impact on primary health at Kavaratti Island, Lakshadweep, Union Territory of India. Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Environmental Sciences 8:839-843. | 2006 | Global; India | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Water Utilities Policies | |
| Stewart, L. K., P. B. Charlesworth, K. L. Bristow, and P. J. Thorburn. 2006. Estimating deep drainage and nitrate leaching from the root zone under sugarcane using APSIM-SWIM. Agricultural Water Management 81:315-334. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Turton, A., C. Schultz, H. Buckle, M. Kgomongoe, T. Malungani, and M. Drackner. 2006. Gold, scorched earth and water: The hydropolitics of Johannesburg. International Journal of Water Resources Development 22:313-335. | 2006 | South Africa | Housing; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Ahmadipour, M. 2005. The effect of sinkholes on leakage of water from the Sarabchenar dam, southwest Iiran. Journal of Environmental Hydrology 13. | 2005 | Iran | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Irrigation; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Brown, T. P. 2005. Diagnosis and management of injuries from dangerous marine life. MedGenMed [electronic resource] : Medscape general medicine7:5. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Irrigation; Sea Urchins | |
| Mitchell, C., J. Brodie, and I. White. 2005. Sediments, nutrients and pesticide residues in event flow conditions in streams of the Mackay Whitsunday Region, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:23-36. | 2005 | Australia | Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Noonburg, G. E. 2005. Management of extremity trauma and related infections occurring in the aquatic environment. The Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 13:243-253. | 2005 | Irrigation; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Perna, C. and D. Burrows. 2005. Improved dissolved oxygen status following removal of exotic weed mats in important fish habitat lagoons of the tropical Burdekin River floodplain, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:138-148. | 2005 | Australia | Agriculture; Fish; Irrigation; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bath, A., B. Shackleton, and C. Botica. 2004. Development of temperature criteria for marine discharge from a large industrial seawater supplies project in Western Australia. Water SA 30:648-654. | 2004 | Australia | Discharges; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pipelines; Water | |
| Tutken, T., H.-U. Pfretzschner, T. W. Vennemann, G. Sun, and Y. D. Wang. 2004. Paleobiology and skeletochronology of Jurassic dinosaurs: Implications from the histology and oxygen isotope compositions of bones. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 206:217-238. | 2004 | China | Climate; Water | |
| Walter, A. and S. C. Lambrecht. 2004. Biosphere 2 Center as a unique tool for environmental studies. Journal of Environmental Monitoring 6:267-277. | 2004 | Global; Columbia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; CO2; Forestry; Irrigation |
| Bandara, N. J. G. J. 2003. Water and wastewater related issues in Sri Lanka. Water Science and Technology 47:305-312. | 2003 | Sri Lanka | Agriculture; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Finkl, C. W. and R. H. Charlier. 2003. Sustainability of Subtropical Coastal Zones in Southeastern Florida: Challenges for Urbanized Coastal Environments Threatened by Development, Pollution, Water Supply, and Storm Hazards. Journal of Coastal Research 19:934-943. | 2003 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Cuba | Model | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Remediation; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water; Wetlands |
| Rayment, G. E. 2003. Water quality in sugar catchments of Queensland. Water Science and Technology 48:35-47. | 2003 | Australia | Review; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Thorburn, P. J., J. S. Biggs, K. L. Weier, and B. A. Keating. 2003. Nitrate in groundwaters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal Northeastern Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 94:49-58. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Buckley, R. 2002. Surf tourism and sustainable development in Indo-Pacific Islands. I. The industry and the islands. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 10:405-424. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Cultural Policies; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Textiles & Apparel; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ono, Y. 2002. Landform conservation and flood control: The issue of the Chitose Diversion Channel project in Hokkaido, Japan. Australian Geographical Studies 40:143-154. | 2002 | Japan | Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Reckhow, Kenneth H.; Stow, Craig A.; Borsuk, Mark E. 2002. Uncertainty Between The Criterion And The Designated Use: Implications For Standards And Tmdl Margin Of Safety. Pages 1223-1228 in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | Model; Index or Indicator | Designated Uses; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Water | |
| Reise, K. 2002. Sediment mediated species interactions in coastal waters. Journal of Sea Research 48:127-141. | 2002 | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Irrigation; Microorganisms; Sediment | ||
| Renken, R. A., W. C. Ward, I. P. Gill, F. Gomez-Gomez, and J. Rodriguez-Martinez. 2002. Geology and hydrogeology of the Caribbean Islands aquifer system of the commonwealth of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands. US Geological Survey Professional Paper 1-139. | 2002 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Climate; Discharges; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Bingham, B. L. 2001. Biology of mangroves and mangrove ecosystems. Advances in Marine Biology 40:81-251. | 2001 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Algae; Aquaculture; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Plankton; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation |
| Ghassemi, F., K. Alam, and K. W. F. Howard. 2000. Fresh-water lenses and practical limitations of their three-dimensional simulation. Hydrogeology Journal 8:521-537. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India | Model | Water |
| Hajkowicz, S., M. Young, S. Wheeler, D. MacDonald, and D. Young. 2000. Supporting Decisions: Understanding Natural Resource Management Assessment Techniques - A report to the Land and Water Resources Research and Development Corporation. Primary Industries and Resources SA, Adelaide (South Australia). | 2000 | Australia | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Resource Use Management; Salinity | |
| Ramachandran, S. 2000. Southeast India. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 161-173. | 2000 | India | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Fishing Sector; Irrigation; Mangroves; Seawater Flow; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sabti, H., M. M. Hossain, R. R. Brooks, and R. B. Stewart. 2000. The current environmental impact of base-metal mining at the Tui Mine, Te Aroha, New Zealand. Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand 30:197-207. | 2000 | Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Al-Awadhi, F. M. A. 1999. The Year of the Ocean and its crucial importance to the Gulf. Desalination 123:127-133. | 1999 | Global | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Littering; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waste Management Policies | |
| Chandrasena, N. and R. Sim. 1999. Managing entrenched weed problems in botany wetlands - An urban stormwater basin in Sydney. Pages 313-319 in Water Supply. | 1999 | Chemical Use Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation; Water; Wetlands | ||
| Ghassemi, F., J. W. Molson, A. Falkland, and K. Alam. 1999. Three-dimensional simulation of the home island freshwater lens: Preliminary results. Environmental Modelling & Software 14:181-190. | 1999 | Model | Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Newnham, R. E. 1999. ECerS Plenary Address: Ceramics into next millennium. British Ceramic Transactions 98:251-255. | 1999 | Global | Aquaculture; Irrigation | |
| Testezlaf, R., C. A. Larsen, T. H. Yeager, and F. S. Zazueta. 1999. Tensiometric monitoring of container substrate moisture status. HortTechnology 9:105-109. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Irrigation; Substrate | |
| Duwig, C., T. Becquer, B. E. Clothier, and M. Vauclin. 1998. Nitrate leaching through oxisols of the Loyalty Islands (New Caledonia) under intensified agricultural practices. Geoderma 84:29-43. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Fuchs, A. and U. Radtke. 1998. Ecological problems on the carribean island of Barbados [Okologische probleme auf der karibischen insel Barbados]. Geographische Rundschau 50:706-713. | 1998 | Cuba | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water | |
| Gauthier, F., S. Gagnon, and B. Dansereau. 1998. Incorporation Of Organic Residues To Peat-Lite Substrates For Production Of Impatiens And Geraniums [Incorporation De Residus Organiques Dans Un Substrat Tourbeux Pour La Production D'Impatiens Et De Geraniums]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 78:131-138. | 1998 | Index or Indicator | Forestry; Irrigation; Substrate | |
| Hower Amy, E. 1998. Combining wave energy and artificial reef technology for sustainable coastal resource development. Pages 1691-1695 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1998 | Review | Artificial Habitat; Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Morris, G.L., Fan, J. 1998. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. Ver. 1.04 edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY. | 1998 | Puerto Rico; Costa Rica; Venezuela; India | Model | Agriculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Forestry; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water |
| Dvorak, J. 1997. Geology of palaeozoic sediments in the surroundings of Ostrov u Macochy (Moravian Karst, Moravia) [Geologie paleozoika v okoli Ostrova u Macochy (Moravský kras, Morava)]. Journal of the Czech Geological Society 42:105-110. | 1997 | Drinking Water Supply; Sediment | ||
| Tole, M. P. 1997. Pollution of groundwater in the coastal Kwale District, Kenya. IAHS-AISH Publication 240:287-297. | 1997 | Kenya | Hotel & Food Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Anisko, T. and O. M. Lindstrom. 1996. Cold hardiness of evergreen azaleas is increased by water stress imposed at three dates. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science 121:296-300. | 1996 | Lab Study | Water | |
| Hicklenton, P. R. and K. G. Cairns. 1996. Plant water relations and mineral nutrition of containerized nursery plants in relation to irrigation method. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 76:155-160. | 1996 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients | ||
| Richards, R. P., D. B. Baker, N. L. Creamer, J. W. Kramer, D. E. Ewing, B. J. Merryfield, and L. K. Wallrabenstein. 1996. Well water quality, well vulnerability, and agricultural contamination in the midwestern United States. Journal of Environmental Quality 25:389-402. | 1996 | India | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Cultural Protections; Drinking Water Supply; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Brits, P. C., A. L. R. Carvalho, and J. T. Pressly. 1995. Evaluation of the effectiveness of bromochlorodimethylhydantoin as a disinfectant for mine underground service water. Pages 25-34 in Water Supply. | 1995 | South Africa | Drinking Water Supply; Microorganisms; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Pathogens; Water | |
| Chen, K. M. 1995. Disappearance of ALS from Guam: Implications for exogenous causes. Pages 1549-1553 in Clinical Neurology. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Guam | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Housing; Military; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Kopko, S., M. Seamans, J. E. Nemeth, and I. C. Watson. 1995. Desalting in Cape Coral, FL - An operating update. Desalination 102:245-253. | 1995 | Drinking Water Supply | ||
| Pisano William, C., ST EV E Kiss, DA VI D Connelly, and TO M Giles. 1995. Holistic stormwater master planning for Cape Coral, Fl. Pages 137-140 in [No source information available]. | 1995 | Florida | Finfish Harvest; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Falkland, A. C. 1994. Management of freshwater lenses on small coral islands. Pages 417-422 in National Conference Publication - Institution of Engineers, Australia. | 1994 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water |
| Wright Robert, R. 1994. Best of both worlds. Water Environment and Technology 6:40-44. | 1994 | Discharges; Irrigation; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Haider, T., R. Sommer, and G. Stanek. 1993. Microflora in external auditory canals of recreational scuba-divers and swimmers related to the tropical waterflora of a coral island. Water Science and Technology 27:187-193. | 1993 | Cuba | Climate; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Medeiros, C. and B. Kjerfve. 1993. Hydrology of a Tropical Estuarine System: Itamaraca, Brazil. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 36:495-515. | 1993 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Discharges; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Wetlands | |
| El-Sadek, S. and B. Mabrouk. 1992. Tourism development and desalination systems: Comparative analysis of systems' suitability for coastal areas of the Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Desalination 88:161-177. | 1992 | Egypt | Beaches & Nature Parks; Drinking Water Supply; Infrastructure; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Navarra, L. 1992. The island of San Pietro [L'isola di S. Pietro]. Universo 72:64-75. | 1992 | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Tourism & Recreation; Water | ||
| Oteri, A. U. 1991. Geophysical investigations of sea water intrusion into the Cainozoic aquifers of South Coast Kenya - a review. Journal of African Earth Sciences 13:221-227. | 1991 | Kenya | Review | Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water |
| Rathnau Mary, M. 1991. Restoration for Arizona aquifers. Water Engineering and Management 138:20-22. | 1991 | Model | Agriculture; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Stroud, H. B. 1991. Water resources at Cape Coral, Florida. Problems created by poor planning and development. Land Use Policy 8:143-157. | 1991 | Florida | Drinking Water Supply; Water | |
| Wells, S. and A. Edwards. 1989. Gone with the waves. New Scientist 124:1989. | 1989 | Global; Maldives | Shoreline Protection; Water | |
| Russell Gary, M., MA RK Stewart, and L. Higer Aaron. 1987. Examples Of Landfill-Generated Plumes In Low-Relief Areas, Southeast Florida. Water Resources Bulletin 23:863-866. | 1987 | Florida | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Solid Waste Disposal | |
| Hwang, Jing-San. 1986. Water Problems On The Penghu Islands In Taiwan. Pages 1622-1629 in [No source information available]. | 1986 | Taiwan | Water | |
| Slocum, DE AN, RI CH AR D Berlandy, and RO BE RT Wardwell. 1986. Facilities Planning In The Caribbean A Case Study. Pages 1351-1357 in [No source information available]. | 1986 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Improved Technology; Sea Turtles; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Aldridge, B. N. and J. H. Eychaner. 1984. Floods Of October 1977 In Southern Arizona And March 1978 In Central Arizona. US Geological Survey Water Supply Paper. | 1984 | South & Central America; Mexico | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Castaing, P., O. Weber, and R. Assor. 1984. (Study of current systems in the Grand Cul-de-Sac Marin (Guadeloupe) at the beginning of the dry season). [Etude courantologique de grand cul-de-sac marin ( Guadeloupe) en debut de saison seche.]. Bulletin - Institut de Geologie du Bassin d'Aquitaine 35:123-134. | 1984 | Water | ||
| Hatch Randolph, T., KE NN ET H Workman, and R. Comeau Peter. 1984. Operating Results After Replacement Of Acid And Shmp With The Af 100 Antiscalant At The Cape Coral Municipal Ro Facility. in Technical Proceedings - Annual Conference and Trade Fair of the Water Supply Improvement Associati. | 1984 | Index or Indicator | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Water | |
| Aiba, MI ZU O. 1983. Irrigation Water Resources Development Project By Groundwater Storage Dam. Civil engineering in Japan 22:152-163. | 1983 | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Irrigation; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Falkland, A. C. 1983. Groundwater resource study of Christmas Island, Republic of Kiribati. in [No source information available]. | 1983 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Kiribati | Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water | |
| Kuberski, T., T. Flood, and T. Tera. 1979. Cholera in the Gilbert Islands. I. Epidemiological features. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 28:677-684. | 1979 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Water | |
| Rahaman, M. M., M. M. Khan, and K. M. S. Aziz. 1975. An outbreak of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on a coral island in the Bay of Bengal. Journal of Infectious Diseases 132:15-19. | 1975 | Drinking Water Supply; Pathogens; Water Utilities Policies | ||
| CROSBY, L. G. 1974. Design Of An Inter Island Barge Harbor For The Island Tau, American Samoa; Hydraulic Model Investigation. in [No source information available]. | 1974 | Samoa; American Samoa | Model | Irrigation; Ports & Harbors; Shoreline Protection; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Jalal, K. F. Regional water resources situation: quantitative and qualitative aspects. in [No source information available]. | Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Waterspreading | This management option uses a system of dams, dikes, ditches, or other means of diverting or collecting runoff from natural channels, gullies, or streams and spreading it over relatively flat areas. Waterspreading differs from irrigation in that applications are timed by the availability of natural runoff flow rather than scheduled to meet plant needs. Waterspreading is most beneficial in areas with an average annual precipitation of 8 to 25 inches. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Resources |
| Chemical Discharge Controls: Integrated pest Management Modify mosquito control programs/regulations | The results of pesticide research program can be used to modify the existing mosquito control program as necessary. (312) | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructure; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Pressures; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Water |
| Chemical Discharge Controls: Research impacts and alternatives | This plan involves researching the impacts of current spraying practices on sanctuary resources and indentifying alternative means of mosquito control. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructure; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Pressures; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Water |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Research and Model Causal Linkage Between Pollutants and Ecological Impact | This involves conducting research to identify and document causal linkages between discharge water pollutants and specific, quantifiable ecological problems. The natural environment naturally assimilates some pollutants, but has thresholds for this type of contaminant processing. Different hydrology, biology and spatial/temporal factors are all going to play a roll in the linkage between pollutants and ecological problems, meaning modeling and risk assessment can be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Sewage Treatment; Stormwater Management; Sunscreen Use; Supporting Services; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Research Historical Hydrology | This activity involves a historical assessment of the hydrology of the surrounding water area around the sanctuary as it has affected water quality and biological communities within the sanctuary. It will clarify the role of freshwater inflows and water quality from local freshwater bodies. Also, this activity will examine the effects of structural modification and changes in quality, quantity, timing and distribution of freshwater releases from existing structures and will examine land-based practices affecting the water quality of runoff. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Physical Variables; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Water Efficiency Initiatives | Reducing water use through cost effective water efficiency improvements can be beneficial as it reduces pressure on water as a finite resource and saves money. There are several ways water efficiency can be promoted. Some Water Efficiency BMPs recommended by the EPA include: Water Management Planning; Information and Education Programs; Distribution System Audits, Leak Detection and Repair; Water-Efficient Landscaping, Water-Efficient Irrigation; Toilets and Urinals; Faucets and Showerheads; Boiler/Steam Systems; Single-Pass Cooling Equipment; Cooling Tower Management; Commercial Kitchen Equipment; Laboratory/ Medical Equipment; Other Water Intensive Processes; Alternative Water Sources. One of the ways the US government has promoted Water Efficiency Initiatives is through Executive order 13123 which places certain water use reduction requirements on Federal Agencies. There are also existing funding and incentives for non-government sectors. Project funding comes in many forms, such as appropriations, energy savings performance contract (ESPC) and Utility Energy Service Contract (UESCs) programs; ratepayer incentive programs such as rebates from public benefit funds or utilities; and the retention of energy and water cost savings. | US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Water Efficiency Best Management Practices. Federal Energy Management Program Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Textiles & Apparel; Utilities; Utility Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Rainwater Collection Systems | Creating a rainwater collection system (either through policy change or the initiative of homeowners) would help in many ways. These systems would utilize water in an efficient manner. It would reduce the pressure of water as a finite resource. Water would be collected and utilized before it reaches the ground. Once rain falls to the ground, it picks up nutrients, chemicals, and pathogens on the ground and transports them in the form of runoff. Eventually this contaminated stormwater runoff enters water resources through the drainage basin. Collecting a considerable amount of water would prevent contamination of that water, and allow for it to be usable. Also, it would reduce the amount of water that is lost when it is contaminated as runoff. An overall reduced amount of stormwater runoff would reduce the amount of contaminants that would harm corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Cisterns used for water harvesting. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shelter; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of natural structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. These structures are typically characterized as retention ponds and incorporate natural vegetation such as grass. These ponds may be dry, or may drain into nearby wetlands. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. Water collection can be selective, targeting the first flush of water, which is typically the most polluted. Water retention has the additional benefit of later release at a place and time when the water is needed (e.g. for irrigation). Rainwater Collection Systems (#11) can be an important water resource in areas where freshwater is limited. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Detention Devices for Dry/Wet Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Water and Sediment Control Basin. CODE 638. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Volume Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Sustained Reservoir Minimum Release of Minimum Baseflow to Sustain Aquatic Habitat | In some regions, even high intensity rivers (e.g. Rio Loco, Puerto Rico) are seasonal, drying for long enough to kill aquatic vegetation. Creating a constant baseflow would help sustain aquatic life and ultimately help to process nutrients. High intensity rivers are already prone to extreme channel erosion from the high flow rates, this erosion is even greater without any benthic biota to hold sediment on the river bottom. Restricting the release of reservoir water to that required to maintain aquatic biota would reduce the intensity of flow, stabilize the river bottom, create habitat and naturally process nutrients that could potentially contribute to eutrophication out on the coral reef. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Algae; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Infiltration | This management option attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that control the volume of surface water, facilitating faster absorption of the stormwater into the ground. Often these structures are able to infiltrate larger amounts of water faster while reducing exposure to surface sediments and pollutants. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. US EPA. EPA Infiltration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Wastewater Pollutants Impacts: Wastewater Pollutant Monitoring and Impact Studies | Potential approaches to this management option include experimental studies, eutrophication gradient studies, comparative studies of impacted and non-impacted sites, historical studies, geography comparison, use of biochemical and ecological indicators, use of sewage tracers, and high-frequency and spatially intensive water quality sampling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Infrastructure; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Public Administration; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Pet Waste Cleanup Ordinance & Education | In residential areas, pet waste can contributes to the large amount of nutrients and pathogens that enter the water through stormwater runoff. This is especially useful in regions such as Gu�nica, Puerto Rico where there are a lot of stray dogs. Education for pet-owners and possible ordinance would help decrease harmful pathogens reaching corals through stormwater runoff and reduce eutrophication. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Animal Waste Collection. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Clary, J., Leisenring, M., and Jeray, J. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Pollutant Category Summary: Fecal Indicator Bacteria. Wright Water Engineers. |
Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Domestic Animal Waste; Environmental Education & Outreach; Health; Health Policies; Invasive Species; Landscaping & Household Services; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Stormwater Management; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Starting slower releases for longer durations from high-intensity rivers in coastal watershed and other methods of reducing sediment transport | Slower releases with longer durations would be an advantage to short, intense releases. This is because current short, high intensity releases from rivers that are in the coastal watershed (like Rio Loco into Lagos Loco and Lucchetti) contributes to additional channel erosion and increase of suspending sediments in the water. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Light; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Control River Volume Using Dams and Resevoirs | Constructing dams and creating reservoirs can have many affects, both positive and negative. Like smaller scale structural stormwater retention (#263), this management option retains groundwater for later controlled release. On this scale, the creation of a reservoir may require flooding of an area behind the dam that had other uses (e.g. agriculture). Proper vegetation can be used in and around the reservoir to incorporate biological filtration (#261). Slowing the release of water into rivers reduces the intensity of flow, reducing channel erosion. However, water should still be released consistently to allow for aquatic habitat to be maintained on the river bottom (#8). Lastly, with the correct infrastructure, a dam can be used as a sustainable hydroelectric energy source. | Morris, G.L., Fan, J. 1998. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. Ver. 1.04 edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY. Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Delineation of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters, 62-340 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2000). | The Rule's intent is to provide a unified statewide methodology for the delineation of the extent of wetlands to satisfy the mandate of Section 373.421, F. S. Application to Coral Reefs:Preservation of wetlands will allow them to continue to function as buffers for sediment and contaminant control keeping them from reaching estuarine and marine waters and eventually habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative and methodological for delineation purposes. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Energy Policy & Development; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Identification of impaired surface waters, 62-303 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2002). | The Chapter established a methodology to identify surface waters of the state that will be included on the state's planning list of waters that will be assessed pursuant to subsections 403.067(2) and (3), Florida Statutes. It also establishes a methodology to identify impaired waters based on representative data that will be included on the state's verified list of impaired waters, for which the Department will calculate Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDLs), pursuant to subsection 403.067(4), F.S., and which will be submitted to the United States Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to paragraph 303(d)(1) of the Clean Water Act (CWA). Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Microorganisms; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Total maximum daily loads, 62-304 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | The Chapter establishes Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), and their allocations, for waters that have been verified to be impaired by a pollutant pursuant to Chapter 62-303. F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Envitonmental Protection Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Biomedical Research Policies; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Impervious Surfaces; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water quality based effluent limitations, 62-650 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To implement the provisions of Section 403.051, 403.085 through 403.088 concerning the development of effluent limitations for wastewater facilities. Application to Coral Reefs:The Florida Air and Water Pollution Act establishes that no wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessay to protect the beneficial uses of such water. Requiring treatment of industrial and domestic waste water indirectly protects adjoining ecosystem, such as reefs, by limiting the pollutant that reach these other systems. Legislative Actions:The Department shall not issue a permit for a discharge to waters of the state, unless the Department has established an efflent limit for those pollutants in the discharge that are present in quantities or concentrations which can be reasonably expected to cause or contribute, directly or indirectly, to a violation of any water quality standard established in rule 62-302. The effluent limit may be a technology based effluent limit (TBEL), a water quality based effluent limit (WQBEL) determined by a Level 1 process, or where applicable, a WQBEL determined by a Level 2 process. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Domestic Animal Waste; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water Resource Implementation Rule, 62-40 Florida Administrative Code (2006). | The Chapter is intended to provide water resouirce implementation goals, objectives and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources. A goal of the Chapter is to coordinate the management of water and land resources. It is the objective of the State to protect the functions of the entire ecological systems, as developed and defined in the programs, rules, and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is a goal of the Chapter that sufficient water be available for all existing and future reasonable-beneficial uses and the natural systems and that adverse effects of competition for water supplies be avoided. Application to Coral Reefs:By protecting the functions of entire aquatic ecological systems, those waters will contain less contaminants when they are discharged and meet other natural water bodies including marine ecosystems. Cleaner water will result in less ecological strees to marine ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This Chapter is intended to provide water resource implementation goals, objectives, and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources, based on statutory policies and directives in Chapters 187, 373, and 403, Florida Statutes. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Waste Management Policies |
