ReefLink Database

Sea Turtles
Sea turtles are any of various large turtles with limbs modified into flippers.
CMap
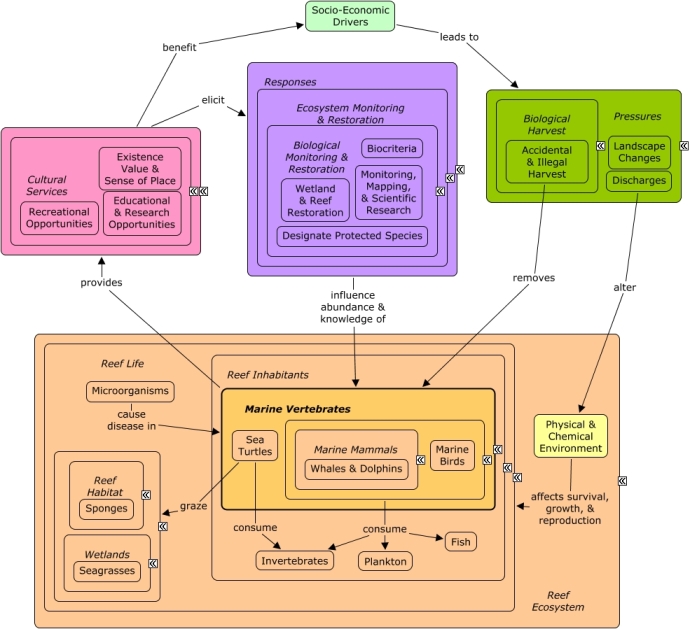
CMap Description
Sea turtles are most notable for their contribution to aesthetic & recreational value; but are also significant contributors to existence value, sense of place, and the educational & research value of coral reef ecosystems. Sea turtles consume invertebrates, especially jellyfish and sponges. They also render a critical service of maintaining wetland environments; sea turtle grazing encourages seagrass beds to grow laterally, ultimately creating more habitat & resources for themselves and other species. Disease-causing microorganisms, and a disturbed physical & chemical environment will stress or kill sea turtles. Accidental & illegal harvest, caused by socio-economic drivers, also removes sea turtles and reduces the ecosystem services they provide. Biological monitoring & restoration is essential in identifying changes in the abundance and condition of sea turtles; as well as determining appropriate responses to maintain the supply of ecosystem services and ensure the benefits to human health and well-being.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agusa, T; Takagi, K; Miller, TW; Kubota, R; Anan, Y; Iwata, H; Tanabe, S. 2011. Intake and excretion of arsenicals in green (Chelonia mydas) and hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata). Environmental Chemistry 8:19-29. | 2011 | Sea Turtles | ||
| Booth, DT; Evans, A. 2011. Warm Water and Cool Nests Are Best. How Global Warming Might Influence Hatchling Green Turtle Swimming Performance. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Global; Cuba | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Fish; Sea Turtles | |
| Gonzalez, C; Jentoft, S. 2011. MPA in Labor: Securing the Pearl Cays of Nicaragua. Environmental Management 47:617-629. | 2011 | South & Central America; Nicaragua; Oman; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles | |
| Krueger, BH; Chaloupka, MY; Leighton, PA; Dunn, JA; Horrocks, JA. 2011. Somatic growth rates for a hawksbill turtle population in coral reef habitat around Barbados. Marine Ecology Progress Series 432:269-276. | 2011 | Bahamas | Model; Rate functions; Index or Indicator | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles |
| Rincon-Diaz, MP; Diez, CE; van Dam, RP; Sabat, AM. 2011. Effect of Food Availability on the Abundance of Juvenile Hawksbill Sea Turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) in Inshore Aggregation Areas of the Culebra Archipelago, Puerto Rico. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 10:213-221. | 2011 | Puerto Rico | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles | |
| Rincon-Diaz, MP; Diez, CE; Van Dam, RP; Sabat, AM. 2011. Foraging Selectivity of the Hawksbill Sea Turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) in the Culebra Archipelago, Puerto Rico. Journal of Herpetology 45:277-282. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fleshy Macroalgae; Sea Turtles; Sponges; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Scales, KL; Lewis, JA; Lewis, JP; Castellanos, D; Godley, BJ; Graham, RT. 2011. Insights into habitat utilisation of the hawksbill turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata (Linnaeus, 1766), using acoustic telemetry. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 407:122-129. | 2011 | South & Central America; Belize | Field Study & Monitoring | Sea Turtles |
| Bell, C. D., J. M. Blumenthal, A. C. Broderick, and B. J. Godley. 2010. Investigating Potential for Depensation in Marine Turtles: How Low Can You Go? Conservation Biology 24:226-235. | 2010 | Global | Sea Turtles | |
| Bjorndal, K. A. and A. B. Bolten. 2010. Hawksbill sea turtles in seagrass pastures: success in a peripheral habitat. Marine Biology 157:135-145. | 2010 | South & Central America; Bahamas; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Blumenthal, J. M., T. J. Austin, J. B. Bothwell, A. C. Broderick, G. Ebanks-Petrie, J. R. Olynik, M. F. Orr, J. L. Solomon, M. J. Witt, and B. J. Godley. 2010. Life in (and out of) the lagoon: fine-scale movements of green turtles tracked using time-depth recorders. Aquatic Biology 9:113-121. | 2010 | Cayman Islands | Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Eguchi, T., J. A. Seminoff, R. A. LeRoux, P. H. Dutton, and D. L. Dutton. 2010. Abundance and survival rates of green turtles in an urban environment: coexistence of humans and an endangered species. Marine Biology 157:1869-1877. | 2010 | Model | Sea Turtles | |
| Fuentes, M. M. P. B., C. J. Limpus, M. Hamann, and J. Dawson. 2010. Potential impacts of projected sea-level rise on sea turtle rookeries. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:132-139. | 2010 | Australia | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Sea Turtles; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Fuentes, M. M. P. B., J. L. Dawson, S. G. Smithers, M. Hamann, and C. J. Limpus. 2010. Sedimentological characteristics of key sea turtle rookeries: potential implications under projected climate change. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:464-473. | 2010 | Global; Australia; Cuba | Review | Climate; Molluscs; Ocean Acidity; Sea Turtles; Sediment |
| Fuentes, M. M. P. B., M. Hamann, and C. J. Limpus. 2010. Past, current and future thermal profiles of green turtle nesting grounds: Implications from climate change. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 383:56-64. | 2010 | Global; Australia; Cuba | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Sea Turtles |
| Fuentes, M. M. P. P. and J. E. Cinner. 2010. Using expert opinion to prioritize impacts of climate change on sea turtles' nesting grounds. Journal of Environmental Management 91:2511-2518. | 2010 | Australia | Climate; Sea Turtles; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Garcon, J. S., A. Grech, J. Moloney, and M. Hamann. 2010. Relative Exposure Index: an important factor in sea turtle nesting distribution. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:140-149. | 2010 | Australia | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Climate; Coastal Development; Sea Turtles |
| Gilman, E., J. Gearhart, B. Price, S. Eckert, H. Milliken, J. Wang, Y. Swimmer, D. Shiode, O. Abe, S. H. Peckham, M. Chaloupka, M. Hall, J. Mangel, J. Alfaro-Shigueto, P. Dalzell, and A. Ishizaki. 2010. Mitigating sea turtle by-catch in coastal passive net fisheries. Fish and Fisheries 11:57-88. | 2010 | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mitigation; Sea Turtles | |
| Hansen, L., J. Hoffman, C. Drews, and E. Mielbrecht. 2010. Designing Climate-Smart Conservation: Guidance and Case Studies. Conservation Biology 24:63-69. | 2010 | South & Central America; Florida; Tanzania; Madagascar; India; Fiji; Caribbean | Climate; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Sea Turtles | |
| Jean, C., S. Ciccione, K. Ballorain, J. Y. Georges, and J. Bourjea. 2010. Ultralight aircraft surveys reveal marine turtle population increases along the west coast of Reunion Island. ORYX 44:223-229. | 2010 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Substrate | |
| Landry, M. S. and C. T. Taggart. 2010. Turtle watching conservation guidelines: green turtle (Chelonia mydas) tourism in nearshore coastal environments. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:305-312. | 2010 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Sea Turtles; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Obura, D. O., A. Harvey, T. Young, M. M. Eltayeb, and R. von Brandis. 2010. Hawksbill turtles as significant predators on hard coral. Coral Reefs 29:759-759. | 2010 | Sea Turtles; Stony Coral | ||
| Perez, E., A. Ruiz, G. Espinosa, and I. Lee. 2010. Gonadic histology and phenotypical maturation criteria in the marine turtles Chelonia mydas and Eretmochelys imbricata (Testudines: Chelonidae) from Cuba. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:287-298. | 2010 | Cuba | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles | |
| Pilcher, N. 2010. Population Structure and Growth of Immature Green Turtles at Mantanani, Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Herpetology 44:168-171. | 2010 | Malaysia; Southeast Asia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Santos, A. J. B., E. M. X. Freire, C. Bellini, and G. Corso. 2010. Body Mass and the Energy Budget of Gravid Hawksbill Turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) during the Nesting Season. Journal of Herpetology 44:352-359. | 2010 | Sea Turtles | ||
| Sazima, C., A. Grossman, and I. Sazima. 2010. Turtle cleaners: reef fishes foraging on epibionts of sea turtles in the tropical Southwestern Atlantic, with a summary of this association type. Neotropical Ichthyology 8:187-192. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Sea Turtles | |
| Settar, C. and T. Turner. 2010. Coral reefs and residents of the U S Virgin Islands A relationship of knowledge, outdoor activities and stewardship. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:197-212. | 2010 | US Virgin Islands | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Sea Turtles; Stony Coral | |
| Sherwood, O. A., B. E. Lapointe, M. J. Risk, and R. E. Jamieson. 2010. Nitrogen Isotopic Records of Terrestrial Pollution Encoded in Floridian and Bahamian Gorgonian Corals. Environmental Science and Technology 44:874-880. | 2010 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sea Turtles; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Southwood, A. and L. Avens. 2010. Physiological, behavioral, and ecological aspects of migration in reptiles. Journal Of Comparative Physiology B-biochemical Systemic And Environmental Physiology 180:1-23. | 2010 | Sea Turtles | ||
| von Brandis, R. G., J. A. Mortimer, and B. K. Reilly. 2010. In-Water Observations of the Diving Behaviour of Immature Hawksbill Turtles, Eretmochelys imbricata, on a Coral Reef at D'Arros Island, Republic of Seychelles. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 9:26-32. | 2010 | Seychelles | Sea Turtles | |
| Wallace, B. P., R. L. Lewison, S. L. McDonald, R. K. McDonald, C. Y. Kot, S. Kelez, R. K. Bjorkland, E. M. Finkbeiner, S. Helmbrecht, and L. B. Crowder. 2010. Global patterns of marine turtle bycatch. Conservation Letters [inpress]. | 2010 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Birds; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Witt, M. J., A. McGowan, J. M. Blumenthal, A. C. Broderick, S. Gore, D. Wheatley, J. White, and B. J. Godley. 2010. Inferring vertical and horizontal movements of juvenile marine turtles from time-depth recorders. Aquatic Biology 8:169-177. | 2010 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; British Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles |
| [No author name available]. 2009. Green light for Gorgon gas project, but environmental conditions apply. Chemical Engineer 816:13. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pipelines; Sea Turtles; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Blumenthal, J. M., T. J. Austin, C. D. L. Bell, J. B. Bothwell, A. C. Broderick, G. Ebanks-Petrie, J. A. Gibb, K. E. Luke, J. R. Olynik, M. F. Orr, J. L. Solomon, and B. J. Godley. 2009. Ecology of Hawksbill Turtles, Eretmochelys imbricata, on a Western Caribbean Foraging Ground. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 8:1-10. | 2009 | South & Central America; Cayman Islands; Caribbean | Octocoral; Sea Turtles; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Blumenthal, J. M., T. J. Austin, J. B. Bothwell, A. C. Broderick, G. Ebanks-Petrie, J. R. Olynik, M. F. Orr, J. L. Solomon, M. J. Witt, and B. J. Godley. 2009. Diving behavior and movements of juvenile hawksbill turtles Eretmochelys imbricata on a Caribbean coral reef. Coral Reefs 28:55-65. | 2009 | Global; South & Central America; Cayman Islands; Caribbean | Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Sea Turtles | |
| Booth, D. T. 2009. Swimming for your life: Locomotor effort and oxygen consumption during the green turtle (Chelonia mydas) hatchling frenzy. Journal of Experimental Biology 212:50-55. | 2009 | Sea Turtles | ||
| Casale, P., A. D. Mazaris, D. Freggi, C. Vallini, and R. Argano. 2009. Growth rates and age at adult size of loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta) in the Mediterranean Sea, estimated through capture-mark-recapture records. Scientia Marina 73:589-595. | 2009 | Model | Sea Turtles | |
| Flint, M., J. C. Patterson-Kane, C. J. Limpus, T. M. Work, D. Blair, and P. C. Mills. 2009. Postmortem diagnostic investigation of disease in free-ranging marine turtle populations: a review of common pathologic findings and protocols. Journal Of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 21:733-759. | 2009 | Review | Pathogens; Sea Turtles | |
| Ischer, T., K. Ireland, and D. T. Booth. 2009. Locomotion performance of green turtle hatchlings from the Heron Island Rookery, Great Barrier Reef. Marine Biology 11-Jan. | 2009 | Australia; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Sea Turtles |
| Kubis, S., M. Chaloupka, L. Ehrhart, and M. Bresette. 2009. Growth rates of juvenile green turtles Chelonia mydas from three ecologically distinct foraging habitats along the east central coast of Florida, USA. Marine Ecology Progress Series 389:257-269. | 2009 | South & Central America; Florida; Costa Rica; India; Mexico | Model; Rate functions | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Limpus, C. J., D. J. Limpus, M. A. Read, and N. N. Fitzsimmons. 2009. When Is a Male Turtle Not a Male?-Observations on Intersex Turtles. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 8:102-105. | 2009 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Purgley, H., J. Jewell, J. E. Deacon, R. M. Winokur, and V. M. Tripoli. 2009. Vitamin D-3 in Captive Green Sea Turtles (Chelonia mydas). Chelonian Conservation and Biology 8:161-167. | 2009 | Review | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Hotel & Food Services; Light; Sea Turtles | |
| Roark, A. M., K. A. Bjorndal, and A. B. Bolten. 2009. Compensatory responses to food restriction in juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas). Ecology 90:2524-2534. | 2009 | Nutrients; Sea Turtles | ||
| Uyarra, M. C., A. R. Watkinson, and I. M. Cote. 2009. Managing dive tourism for the sustainable use of coral reefs: Validating diver perceptions of attractive site features. Environmental Management 43:16-Jan. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Sea Turtles; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Wallace, B. P., L. Avens, J. Braun-McNeill, and C. M. McClellan. 2009. The diet composition of immature loggerheads: Insights on trophic niche, growth rates, and fisheries interactions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373:50-57. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short, and S. L. Williams. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:12377-12381. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Coastal Development; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Amorocho, D. F. and R. D. Reina. 2008. Intake passage time, digesta composition and digestibility in East Pacific green turtles (Chelonia mydas agassizii) at Gorgona National Park, Colombian Pacific. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 360:117-124. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Cleaner & Solvent Use; Mangroves; Sea Turtles | |
| Blanvillain, G., L. D. Wood, A. B. Meylan, and P. A. Meylan. 2008. Sex ratio prediction of juvenile Hawksbill sea turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) from South Florida, USA. Herpetological Conservation and Biology 3:21-27. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Cuba; Panama; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Sea Turtles |
| Bologna, P. A. X., R. Papagian, S. Regetz, and C. Dale. 2008. Assessment of turtle grass (Thalassia testudinum ex Banks Konig) community structure in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 365:148-155. | 2008 | US Virgin Islands | Marine Worms; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Chaloupka, M., K. A. Bjorndal, G. H. Balazs, A. B. Bolten, L. M. Ehrhart, C. J. Limpus, H. Suganuma, S. Troeng, and M. Yamaguchi. 2008. Encouraging outlook for recovery of a once severely exploited marine megaherbivore. Global Ecology and Biogeography 17:297-304. | 2008 | Global; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Costa Rica; Japan | Review | Sea Turtles |
| Daley, B., P. Griggs, and H. Marsh. 2008. Exploiting marine wildlife in Queensland: The commercial dugong and marine turtle fisheries, 1847-1969. Australian Economic History Review 48:227-265. | 2008 | Australia; Europe | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles | |
| Dryden, J., A. Grech, J. Moloney, and M. Hamann. 2008. Rezoning of the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area: Does it afford greater protection for marine turtles? Wildlife Research 35:477-485. | 2008 | Australia | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Siddiqui, P. J. A., S. Farooq, S. Shafique, Z.-u.-N. Burhan, and Z. Farooqi. 2008. Conservation and management of biodiversity in Pakistan through the establishment of marine protected areas. Ocean and Coastal Management 51:377-382. | 2008 | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Plankton; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Wabnitz, C. C., S. Andrefouet, D. Torres-Pulliza, F. E. Muller-Karger, and P. A. Kramer. 2008. Regional-scale seagrass habitat mapping in the Wider Caribbean region using Landsat sensors: Applications to conservation and ecology. Remote Sensing of Environment 112:3455-3467. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Allen, M. S. 2007. Three millennia of human and sea turtle interactions in Remote Oceania. Coral Reefs 26:959-970. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Sea Turtles | |
| Bowen, B. W., W. S. Grant, Z. Hillis-Starr, D. J. Shaver, K. A. Bjorndal, A. B. Bolten, and A. L. Bass. 2007. Mixed-stock analysis reveals the migrations of juvenile hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) in the Caribbean Sea. Molecular Ecology 16:49-60. | 2007 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Dobbs, K. A., J. D. Miller, and A. M. Landry Jr. 2007. Laparoscopy of nesting hawksbill turtles, Eretmochelys imbricata, at Milman Island, Northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 6:270-274. | 2007 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Dobbs, K. A., J. D. Miller, D. W. Owens, and A. M. Landry. 2007. Serum testosterone and estradiol-17β levels during the peak period in a year-round Hawksbill Turtle Eretmochelys imbricata L. nesting population. Pacific Conservation Biology 13:151-157. | 2007 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Dobbs, K., L. Fernandes, S. Slegers, B. Jago, L. Thompson, J. Hall, J. Day, D. Cameron, J. Tanzer, F. MacDonald, and C. Lumpus. 2007. Incorporating marine turtle habitats into the marine protected area design for the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, Queensland, Australia. Pacific Conservation Biology 13:293-302. | 2007 | Australia | Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles | |
| Jokiel, P. L. and K. S. Rodgers. 2007. Ranking coral ecosystem "health and value" for the islands of the Hawaiian Archipelago. Pacific Conservation Biology 13:60-68. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Index or Indicator | Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles |
| Murdoch, T. J. T., A. F. Glasspool, M. Outerbridge, J. Ward, S. Manuel, J. Gray, A. Nash, K. A. Coates, J. Pitt, J. W. Fourqurean, P. A. Barnes, M. Vierros, K. Holzer, and S. R. Smith. 2007. Large-scale decline in offshore seagrass meadows in Bermuda. Marine Ecology Progress Series 339:123-130. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Short, F., T. Carruthers, W. Dennison, and M. Waycott. 2007. Global seagrass distribution and diversity: A bioregional model. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350:3-20. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Whiting, S. D., M. L. Guinea, C. J. Limpus, and K. Fomiatti. 2007. Blood chemistry reference values for two ecologically distinct populations of foraging green turtles, eastern Indian Ocean. Comparative Clinical Pathology 16:109-118. | 2007 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Witmer, G. W., F. Boyd, and Z. Hillis-Starr. 2007. The successful eradication of introduced roof rats (Rattus rattus) from Buck Island using diphacinone, followed by an irruption of house mice (Mus musculus). Wildlife Research 34:108-115. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Housing; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Turtles |
| Booth, D. T. and C. Freeman. 2006. Sand and nest temperatures and an estimate of hatchling sex ratio from the Heron Island green turtle (Chelonia mydas) rookery, Southern Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 25:629-633. | 2006 | Australia; Cuba | Beaches & Nature Parks; Sea Turtles | |
| Bujang, J. S., M. H. Zakaria, and A. Arshad. 2006. Distribution and significance of seagrass ecosystems in Malaysia. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 9:203-214. | 2006 | Malaysia | Review | Bivalves; Echinoderms; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Substrate |
| Burgess, E. A., D. T. Booth, and J. M. Lanyon. 2006. Swimming performance of hatchling green turtles is affected by incubation temperature. Coral Reefs 25:341-349. | 2006 | Cuba | Lab Study | Sea Turtles |
| Fuentes, M. M. P. B., I. R. Lawler, and E. Gyuris. 2006. Dietary preferences of juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas) on a tropical reef flat. Wildlife Research 33:671-678. | 2006 | Australia | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Grossman, A., C. Sazima, C. Bellini, and I. Sazima. 2006. Cleaning symbiosis between Hawksbill turtles and reef fishes at Fernando de Noronha Archipelago, off Northeast Brazil. Chelonian Conservation and Biology 5:284-288. | 2006 | Planktivorous Fish; Sea Turtles; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Kolinski, S. P., R. K. Hoeke, S. R. Holzwarth, L. I. Ilo, E. F. Cox, R. C. O'Conner, and P. S. Vroom. 2006. Nearshore distribution and an abundance estimate for green sea turtles, Chelonia mydas, at Rota Island, Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. Pacific Science 60:509-522. | 2006 | Northern Mariana Islands | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Sea Turtles |
| Makowski, C., J. A. Seminoff, and M. Salmon. 2006. Home range and habitat use of juvenile Atlantic green turtles (Chelonia mydas L.) on shallow reef habitats in Palm Beach, Florida, USA. Marine Biology 148:1167-1179. | 2006 | Global; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles; Sponges | |
| Pocock, C. 2006. Turtle riding on the great barrier reef. Society and Animals 14:129-146. | 2006 | Australia | Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Sazima, I. and A. Grossman. 2006. Turtle riders: Remoras on marine turtles in Southwest Atlantic. Neotropical Ichthyology 4:123-126. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Sea Turtles | |
| Schroeder, R. E. and J. D. Parrish. 2006. Ecological characteristics of coral patch reefs at Midway Atoll, Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. Atoll Research Bulletin 439-460. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Substrate; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Southwood, A. L., R. D. Reina, V. S. Jones, J. R. Speakman, and D. R. Jones. 2006. Seasonal metabolism of juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas) at Heron Island, Australia. Canadian Journal of Zoology 84:125-135. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Sea Turtles |
| Steadman, D. W. and S. Jones. 2006. Long-term trends in prehistoric fishing and hunting on Tobago, West Indies. Latin American Antiquity 17:316-334. | 2006 | Tobago; India | Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Sea Turtles | |
| Taquet, C., M. Taquet, T. Dempster, M. Soria, S. Ciccione, D. Roos, and L. Dagorn. 2006. Foraging of the green sea turtle Chelonia mydas on seagrass beds at Mayotte Island (Indian Ocean), determined by acoustic transmitters. Marine Ecology Progress Series 306:295-302. | 2006 | Indian Ocean; Comoros; Mayotte; India | Index or Indicator | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Andre, J., E. Gyuris, and I. R. Lawler. 2005. Comparison of the diets of sympatric dugongs and green turtles on the Orman Reefs, Torres Strait, Australia. Wildlife Research 32:53-62. | 2005 | Australia; Papua New Guinea | Algae; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Barile, P. J. and B. E. Lapointe. 2005. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition from a remote source enriches macroalgae in coral reef ecosystems near Green Turtle Cay, Abacos, Bahamas. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:1262-1272. | 2005 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Nutrients; Sea Turtles | |
| Chaloupka, M. and C. Limpus. 2005. Estimates of sex- and age-class-specific survival probabilities for a southern Great Barrier Reef green sea turtle population. Marine Biology 146:1251-1261. | 2005 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Copley, J. 2005. From shore to shining shore. New Scientist 186:51. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Sea Turtles | |
| Granek, E. E. and M. A. Brown. 2005. Co-management approach to marine conservation in Moheli, Comoros Islands. Conservation Biology 19:1724-1732. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; Comoros; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hamann, M., T. S. Jessop, C. J. Limpus, and J. M. Whittier. 2005. Regional and annual variation in plasma steroids and metabolic indicators in female green turtles, Chelonia mydas. Marine Biology 148:427-433. | 2005 | Index or Indicator | Sea Turtles; Substrate | |
| Makowski, C., R. Slattery, and M. Salmon. 2005. \Shark fishing\": A method for determining the abundance and distribution of sea turtles at shallow reef habitats". Herpetological Review 36:36-38. | 2005 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Sea Turtles | ||
| Peterson, C. H. and M. J. Bishop. 2005. Assessing the environmental impacts of beach nourishment. Bioscience 55:887-896. | 2005 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Mitigation; Sea Turtles; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Roos, D., D. Pelletier, S. Ciccione, M. Taquet, and G. Hughes. 2005. Aerial and snorkelling census techniques for estimating green turtle abundance on foraging areas: A pilot study in Mayotte Island (Indian Ocean). Aquatic Living Resource 18:193-198. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; Mayotte; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| SeafoodWatch. 2005. Sustainable Seafood Business Practices. Monteray Bay. | 2005 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Sea Turtles; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Troeng, S., P. H. Dutton, and D. Evans. 2005. Migration of hawksbill turtles Eretmochelys imbricata from Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Ecography 28:394-402. | 2005 | South & Central America; Cuba; Honduras; Nicaragua; Costa Rica; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Sea Turtles; Sponges | |
| Waycott, M., B. J. Longstaff, and J. Mellors. 2005. Seagrass population dynamics and water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: A review and future research directions. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:343-350. | 2005 | Australia | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Toxics |
| Balazs, G. H. and M. Chaloupka. 2004. Spatial and temporal variability in somatic growth of green sea turtles (Chelonia mydas) resident in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Marine Biology 145:1043-1059. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Caribbean | Model; Rate functions | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles |
| Chaloupka, M., C. Limpus, and J. Miller. 2004. Green turtle somatic growth dynamics in a spatially disjunct Great Barrier Reef metapopulation. Coral Reefs 23:325-335. | 2004 | Australia | Model; Rate functions | Algae; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Enge, K. M., K. L. Krysko, K. R. Hankins, T. S. Campbell, and F. W. King. 2004. Status of the nile monitor (Varanus niloticus) in southwestern Florida. Southeastern Naturalist 3:571-582. | 2004 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Marine Birds; Sea Turtles |
| Jessop, T. S., M. Hamann, and C. J. Limpus. 2004. Body condition and physiological changes in male green turtles during breeding. Marine Ecology Progress Series 276:281-288. | 2004 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Sea Turtles |
| Gribble, N.A. 2003. GBR-prawn: modelling ecosystem impacts of changes in fisheries management of the commercial prawn (shrimp) trawl fishery in the far northern Great Barrier Reef. Fisheries Research 65:493-506. | 2003 | Australia | Model | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Piscivorous Fish; Sea Turtles; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Houghton, J. D. R., M. J. Callow, and G. C. Hays. 2003. Habitat utilization by juvenile hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata, Linnaeus, 1766) around a shallow water coral reef. Journal of Natural History 37:1269-1280. | 2003 | Indian Ocean; Seychelles; India | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles | |
| Limpus, C. J., J. D. Miller, C. J. Parmenter, and D. J. Limpus. 2003. The Green turtle, Chelonia mydas, population of Raine Island and the northern Great Barrier Reef: 1843-2001. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 49:349-440. | 2003 | Australia; Europe | Review | Sea Turtles |
| Miller, M. W., D. B. McClellan, and C. Begin. 2003. Observations on fisheries activities at Navassa Island. Marine Fisheries Review 65:43-49. | 2003 | South & Central America; Haiti; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch | |
| Russell, D. J., G. H. Balazs, R. C. Phillips, and A. K. H. Kam. 2003. Discovery of the sea grass Halophila decipiens (Hydrocharitaceae) in the diet of the Hawaiian green turtle, Chelonia mydas. Pacific Science 57:393-397. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Sea Turtles | |
| Southwood, A. L., R. D. Reina, V. S. Jones, and D. R. Jones. 2003. Seasonal diving patterns and body temperatures of juvenile green turtles at Heron Island, Australia. Canadian Journal of Zoology 81:1014-1024. | 2003 | Australia | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles | |
| Stachowitsch, M. 2003. Research on intact marine ecosystems: A lost era. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:801-805. | 2003 | Global | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Worm, B., H. K. Lotze, and R. A. Myers. 2003. Predator diversity hotspots in the blue ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100:9884-9888. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Pacific Ocean | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Plankton; Sea Turtles |
| Abuodha, J. O. Z. 2002. Environmental impact assessment of the proposed titanium mining project in Kwale District, Kenya. Marine Georesources and Geotechnology 20:199-207. | 2002 | Kenya | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mining Policies; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Whales & Dolphins |
| Carruthers, T. J. B., W. C. Dennison, B. J. Longstaff, M. Waycott, E. G. Abal, L. J. McKenzie, and W. J. Lee Long. 2002. Seagrass habitats of northeast Australia: Models of key processes and controls. Bulletin of Marine Science 71:1153-1169. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Chaloupka, M. 2002. Stochastic simulation modelling of southern Great Barrier Reef green turtle population dynamics. Ecological Modelling 148:79-109. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Chaloupka, M. Y. and C. J. Limpus. 2002. Survival probability estimates for the endangered loggerhead sea turtle resident in southern Great Barrier Reef waters. Marine Biology 140:267-277. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Diez, C. E. and R. P. Van Dam. 2002. Habitat effect on hawksbill turtle growth rates on feeding grounds at Mona and Monito Islands, Puerto Rico. Marine Ecology Progress Series 234:301-309. | 2002 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Australia; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Sea Turtles |
| Leon, Y. M. and K. A. Bjorndal. 2002. Selective feeding in the hawksbill turtle, an important predator in coral reef ecosystems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 245:249-258. | 2002 | South & Central America; Florida; Dominican Republic; Columbia; Caribbean | Sea Turtles; Sponges; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Salazar-Vallejo, S. I. 2002. Huracanes y biodiversidad costera tropical. Revista de Biologia Tropical 50:415-428. | 2002 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| [No author name available]. 2001. News: Protection for sponge gardens. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:4. | 2001 | Australia | Marine Birds; Sea Turtles; Sponges | |
| Booth, D. T. and K. Astill. 2001. Incubation temperature, energy expenditure and hatchling size in the green turtle (Chelonia mydas), a species with temperature-sensitive sex determination. Australian Journal of Zoology 49:389-396. | 2001 | Australia; Cuba | Sea Turtles | |
| Booth, D. T. and K. Astill. 2001. Temperature variation within and between nests of the green sea turtle, Chelonia mydas (Chelonia: Cheloniidae) on Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef. Australian Journal of Zoology 49:71-84. | 2001 | Australia; Cuba | Sea Turtles | |
| Chaloupka, M. and C. Limpus. 2001. Trends in the abundance of sea turtles resident in southern Great Barrier Reef waters. Biological Conservation 102:235-249. | 2001 | Australia | Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles | |
| Coberley, S. S., L. H. Herbst, L. M. Ehrhart, D. A. Bagley, S. Hirama, E. R. Jacobson, and P. A. Klein. 2001. Survey of Florida green turtles for exposure to a disease-associated herpesvirus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 47:159-167. | 2001 | Florida; India | Pathogens; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jackson, J. B. C. 2001. What was natural in the coastal oceans? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98:5411-5418. | 2001 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Jackson, J. B. C. and E. Sala. 2001. Unnatural Oceans. Scientia Marina 65:273-281. | 2001 | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Tucker, A. D. and M. A. Read. 2001. Frequency of foraging by gravid green turtles (Chelonia mydas) at Raine Island, Great Barrier Reef. Journal of Herpetology 35:500-503. | 2001 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Carbone, F. and G. Accordi. 2000. The Indian Ocean Coast of Somalia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41:141-159. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; Tanzania; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Substrate |
| Debrot, A. O. and I. Nagelkerken. 2000. User perceptions on coastal resource state and management options in Curacao. Revista de Biologia Tropical 48:95-106. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Review; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Huber, M. E. 2000. Torres Strait and the Gulf of Papua. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 593-610. | 2000 | Australia; Papua New Guinea | Agriculture; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jameson, S. C., L. B. Trott, M. J. Marshall, and M. J. Childress. 2000. Nicaragua: Caribbean coast. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 517-530. | 2000 | South & Central America; Nicaragua; Caribbean | Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Labrosse, P., R. Fichez, R. Farman, and T. Adams. 2000. New Caledonia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 723-736. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Europe; France | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Sea Turtles; Special Use Permitting; Valuation | |
| Lu, Y., Q. Yu, J. P. Zamzow, Y. Wang, G. S. Losey, G. H. Balazs, V. R. Nerurkar, and R. Yanagihara. 2000. Detection of green turtle herpesviral sequence in saddleback wrasse Thalassoma duperrey: A possible mode of transmission of green turtle fibropapilloma. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health 12:58-63. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Turtles | |
| Maragos, J. E. 2000. Hawaiian Islands (U.S.A.). Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 791-812. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Military; Pathogens; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Price, A. R. G. and J. E. Maragos. 2000. The Marshall Islands. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 773-789. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India; Micronesia; Marshall Islands | Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Military; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Seastars; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. | 2000 | Global | Agriculture; Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fishing Sector; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral | |
| Wilson, S. C. 2000. Northwest Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 17-33. | 2000 | India; United Arab Emirates; Iran; Oman | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Tankers; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Water Depth & Sea Level; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Wilson, S. C. and R. Klaus. 2000. The Gulf of Aden. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 47-61. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; India; Djibouti | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Beaches & Nature Parks; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Jessop, T. S., C. J. Limpus, and J. M. Whittier. 1999. Plasma steroid interactions during high-density green turtle nesting and associated disturbance. General and Comparative Endocrinology 115:90-100. | 1999 | Australia | Sea Turtles; Substrate | |
| Jessop, T. S., N. N. FitzSimmons, C. J. Limpus, and J. M. Whittier. 1999. Interactions between behavior and plasma steroids within the scramble mating system of the promiscuous green turtle, Chelonia mydas. Hormones and Behavior 36:86-97. | 1999 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Lee Long, W. J., R. G. Coles, and L. J. McKenzie. 1999. Issues for seagrass conservation management in Queensland. Pacific Conservation Biology 5:321-328. | 1999 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fitzsimmons, N. N. 1998. Single paternity of clutches and sperm storage in the promiscuous green turtle (Chelonia mydas). Molecular Ecology 7:575-584. | 1998 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Gribble, N. A., G. McPherson, and B. Lane. 1998. Effect of the Queensland Shark Control Program on non-target species: Whale, dugong, turtle and dolphin: A review. Marine and Freshwater Research 49:645-651. | 1998 | Australia | Review | Apex Fish Predators; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins |
| Herbst, L. H., E. C. Greiner, L. M. Ehrhart, D. A. Bagley, and P. A. Klein. 1998. Serological association between spirorchidiasis, herpesvirus infection, and fibropapillomatosis in green turtles from Florida. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 34:496-507. | 1998 | Florida | Pathogens; Sea Turtles | |
| Hill, M. S. 1998. Spongivory on Caribbean reefs releases corals from competition with sponges. Oecologia 117:143-150. | 1998 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Sea Turtles; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Menges, C. H., G. J. E. Hill, and W. Ahmad. 1998. Landsat TM data and potential feeding grounds for threatened marine turtle species in northern Australia. International Journal of Remote Sensing 19:1207-1221. | 1998 | Australia | Algae; Sea Turtles; Substrate | |
| Miller, J. D., K. A. Dobbs, C. J. Limpus, N. Mattocks, and A. M. Landry Jr. 1998. Long-distance migrations by the hawksbill turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata, from north-eastern Australia. Wildlife Research 25:89-95. | 1998 | Australia; Solomon Islands; Vanuatu; Papua New Guinea; Indonesia | Review | Sea Turtles |
| Van Dam, R. P. and C. E. Diez. 1998. Home range of immature hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata (Linnaeus)) at two Caribbean islands. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 220:15-24. | 1998 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles | |
| Chaloupka, M. Y. and C. J. Limpus. 1997. Robust statistical modelling of hawksbill sea turtle growth rates (southern Great Barrier Reef). Marine Ecology Progress Series 146:8-Jan. | 1997 | South & Central America; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Model; Rate functions | Sea Turtles |
| Fitzsimmons, N. N., C. J. Limpus, J. A. Norman, A. R. Goldizen, J. D. Miller, and C. Moritz. 1997. Philopatry of male marine turtles inferred from mitochondrial DNA markers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94:8912-8917. | 1997 | Australia | Beaches & Nature Parks; Sea Turtles | |
| Fitzsimmons, N. N., C. Moritz, C. J. Limpus, L. Pope, and R. Prince. 1997. Geographic structure of mitochondrial and nuclear gene polymorphisms in Australian green turtle populations and male-biased gene flow. Genetics 147:1843-1854. | 1997 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Jackson, J. B. C. 1997. Reefs since Columbus. Coral Reefs 16. | 1997 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Limpus, C. and M. Chaloupka. 1997. Nonparametric regression modelling of green sea turtle growth rates (southern Great Barrier Reef). Marine Ecology Progress Series 149:23-34. | 1997 | Australia | Model; Rate functions | Sea Turtles |
| Preen, A. R., H. Marsh, I. R. Lawler, R. I. T. Prince, and R. Shepherd. 1997. Distribution and abundance of Dugongs, Turtles, Dolphins and other Megafauna in Shark Bay, Ningaloo Reef and Exmouth Gulf, Western Australia. Wildlife Research 24:185-208. | 1997 | Australia; Middle East | Apex Fish Predators; Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Van Dam, R. P. and C. E. Diez. 1997. Diving behavior of immature hawksbill turtles (Eretmochelys imbricata) in a caribbean reef habitat. Coral Reefs 16:133-138. | 1997 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Sea Turtles | |
| Heppell, S. S., C. J. Limpus, D. T. Crouse, N. B. Frazer, and L. B. Crowder. 1996. Population model analysis for the loggerhead sea turtle, Caretta caretta, in Queensland. Wildlife Research 23:143-159. | 1996 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Brill, R. W., G. H. Balazs, K. N. Holland, R. K. Chang, S. Sullivan, and J. C. George. 1995. Daily movements, habitat use, and submergence intervals of normal and tumor-bearing juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas L.) within a foraging area in the Hawaiian Islands. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 185:203-218. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Sea Turtles | |
| Kare, B. D. 1995. A review of research on barramundi, reef fish, dugong, turtles and Spanish mackerel and their fisheries in the Torres Strait adjacent to Papua New Guinea. Science in New Guinea 21:43-55. | 1995 | Papua New Guinea | Review | Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles |
| Loop, K. A., J. D. Miller, and C. J. Limpus. 1995. Nesting by the hawksbill turtle (Eretmochelys imbricata) on Milman Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Wildlife Research 22:241-252. | 1995 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Maragos, J. E. and C. W. Cook Jr. 1995. The 1991-1992 rapid ecological assessment of Palau's coral reefs. Coral Reefs 14:237-252. | 1995 | Palau | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Mangroves; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| Limpus, C. J., P. J. Couper, and M. A. Read. 1994. The green turtle, Chelonia mydas in Queensland: population structure in a warm temperate feeding area. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 35:139-154. | 1994 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Chavez, ER NE ST O and JO HN Tunnell. 1993. Needs for management and conservation of the southern Gulf of Mexico. Pages 2040-2053 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Petroleum Spills; Piscivorous Fish; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Gyuris, E. 1993. Factors that control the emergence of green turtle hatchlings from the nest. Wildlife Research 20:345-353. | 1993 | Australia | Model | Sea Turtles |
| Limpus, C. J. 1993. The green turtle, Chelonia mydas, in Queensland: breeding males in the southern Great Barrier Reef. Wildlife Research 20:513-523. | 1993 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Limpus, C. J., P. J. Couper, and K. L. D. Couper. 1993. Crab Island revisited: reassessment of the world's largest flatback turtle rookery after twelve years. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 33:277-289. | 1993 | Australia | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Sea Turtles | |
| Price, A. R. G., C. R. C. Sheppard, and C. M. Roberts. 1993. The Gulf: Its biological setting. Marine Pollution Bulletin 27:15-Sep. | 1993 | Global; Iran | Review | Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Piscivorous Fish; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses |
| Hirth, H. F. and D. L. H. Rohovit. 1992. Marketing patterns of green and hawksbill turtles in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. ORYX 26:39-42. | 1992 | Papua New Guinea | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Sea Turtles |
| Limpus, C. J. 1992. The hawksbill turtle, Eretmochelys imbricata, in Queensland: population structure within a southern Great Barrier Reef feeding ground. Wildlife Research 19:489-506. | 1992 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Wibbels, T., D. W. Owens, P. Licht, C. Limpus, P. C. Reed, and M. S. Amoss Jr. 1992. Serum gonadotropins and gonadal steroids associated with ovulation and egg production in sea turtles. General and Comparative Endocrinology 87:71-78. | 1992 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| [No author name available]. 1991. Our living oceans. The first annual report on the status of US living marine resources. in [No source information available]. | 1991 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Mitchell, B. A. and J. R. Barborak. 1991. Developing coastal park systems in the tropics: planning in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Coastal Management 19:113-134. | 1991 | Global; Turks and Caicos | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Birds; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Walker, T. A. 1991. Tourism development and environmental limitations at Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef. Journal of Environmental Management 33:117-122. | 1991 | Australia | Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Craik, W., J. Glaister, and I. Poiner. 1990. The effects of fishing. The effects of fishing. | 1990 | Australia; New Caledonia | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Walker, T. A. and C. J. Parmenter. 1990. Absence of a pelagic phase in the life cycle of the flatback turtle, Natator depressa (Garman). Journal of Biogeography 17:275-278. | 1990 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Glazebrook, J. S., R. S. F. Campbell, and D. Blair. 1989. Studies on Cardiovascular fluke (Digenea: Spirorchiidae) infections in sea turtles from the Great Barrier Reef, Queensland, Australia. Journal of Comparative Pathology 101:231-250. | 1989 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Limpus, C. J., D. Zeller, D. Kwan, and W. Macfarlane. 1989. Sea-turtle rookeries in north-western Torres Strait. Australian Wildlife Research 16:517-525. | 1989 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Marsh, H. and W. K. Saalfeld. 1989. Aerial surveys of sea turtles in the northern Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Australian Wildlife Research 16:239-249. | 1989 | Australia | Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Gyuris, E. and C. J. Limpus. 1988. The loggerhead turtle, Caretta caretta, in Queensland: population breeding structure. Australian Wildlife Research 15:197-209. | 1988 | Australia | Beaches & Nature Parks; Marine Protected Areas; Sea Turtles | |
| Limpus, C. J. and N. Nicholls. 1988. The Southern Oscillation regulates the annual numbers of green turtles (Chelonia mydas) breeding around northern Australia. Australian Wildlife Research 15:157-161. | 1988 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Index or Indicator | Climate; Sea Turtles |
| Meylan, A. 1988. Spongivory in hawksbill turtles: A diet of glass. Science 239:393-395. | 1988 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Sea Turtles; Sponges | |
| Limpus, C. J. 1987. A turtle fossil on Raine Island, Great Barrier Reef. Search 18:254-256. | 1987 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Slocum, DE AN, RI CH AR D Berlandy, and RO BE RT Wardwell. 1986. Facilities Planning In The Caribbean A Case Study. Pages 1351-1357 in [No source information available]. | 1986 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Improved Technology; Sea Turtles; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Limpus, C. J. and P. C. Reed. 1985. The green turtle, Chelonia mydas, in Queensland: a preliminary description of the population structure in a coral reef feeding ground. Pages 47-52 The biology of Australasian frogs and reptiles. | 1985 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Limpus, C. J., C. J. Parmenter, V. Baker, and A. Fleay. 1983. The flatback turtle, Chelonia depressa, in Queensland: post- nesting migration and feeding ground distribution. Australian Wildlife Research 10:557-561. | 1983 | Australia | Sea Turtles | |
| Ogden, J. C., L. Robinson, K. Whitlock, H. Daganhardt, and R. Cebula. 1983. Diel foraging patterns in juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas L.) in St. Croix United States virgin islands. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 66:199-205. | 1983 | US Virgin Islands | Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Spring, S. C. 1982. Marine turtle conservation in Papua New Guinea. Pages 303-306 in Traditional conservation in Papua New Guinea: implications for today. Proc. conference 1980. | 1982 | Papua New Guinea | Sea Turtles | |
| Witzell, W. N. 1981. Predation on juvenile green sea turtles, Chelonia mydas, by a grouper, Promicrops lanceolatus (Pisces: Serranidae) in the Kingdom of Tonga, South Pacific. Bulletin of Marine Science 31:935-936. | 1981 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Tonga | Piscivorous Fish; Sea Turtles | |
| Balazs, G. H. 1976. Green turtle migrations in the Hawaiian archipelago. Biological Conservation 9:125-140. | 1976 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sea Turtles |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Zoning: Wildlife Management Areas (WMAs) | Wildlife Management Areas include bird nesting, resting, or feeding areas, turtle nesting beaches, and other sensitive habitats including shallow flats that are important feeding areas for fish. These areas seek to provide protection for endangered/threatened species or their habitats while at the same time providing opportunity for public use. Wildlife Management Areas are achieved through placing and maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; implementing management responsibilities; adjusting existing zone boundaries if needed; evaluating allowable activities within the boundaries and make changes if needed; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; monitoring the effectiveness of current zones; and revising GIS and NOAA charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Public Participation: Assist Sea Turtle Activities | Sea turtles are protected under the Endangered Species Act. Volunteers protect and preserve sea turtles and their habitats. Volunteers will do an array of tasks including monitoring known and potential nesting beaches, marking and recording the location of nests, and documenting nest success. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Marine Vertebrates; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Sea Turtles |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Turtle Conservation Act of 2004, 16 United States Code § 6601. | The law was created to aid in the conservation of sea turtles and their nesting habitats in foreign countries by providing funds for the conservation of nesting areas, sea turtles in in their nesting habitats, and dealing with threats to sea turtle survival. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Designate Protected Species; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
