ReefLink Database

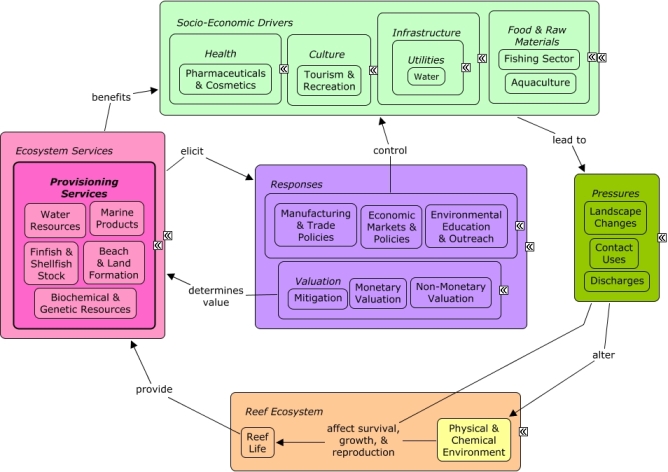
Provisioning Services
Provisioning services are the products or ecosystem goods obtained from ecosystems, including seafood, genetic and biochemical resources, pharmaceuticals, ornamental resources, and water resources.
CMap
CMap Description
Reefs provide goods and products which benefit a number of socio-economic sectors. Coral reefs play a role in replenishing sandy beaches, as coral and other calcified organisms break down, and reefs form the foundation for many islands. Beaches and swimmable water provide recreational opportunities which drive tourism and recreation. Availability of finfish and shellfish stock benefits the fishing sector, and providing seafood for local restaurants as well as wider markets. Non-food marine products such as aquarium fish or ornamental resources derived from fish, coral, or sponges, are often sold within the aquarium trade or decorative and souvenir trade. Biochemical & genetic resources provide unique research and product opportunities for the pharmaceuticals and cosmetics industry, and may provide wild genetic populations to interbreed with aquaculture stock. Many of the same economic sectors which benefit from reefs also create pressures on them through harvesting, as well as contributing to coastal development and pollution. Decision-makers can better understand the value of reef goods through valuation methods. Economic markets, including supply and demand, will influence the value of reef products. Resource use management through designated uses, species protections, and fishing regulations can establish water quality standards, control the amount of potential stock which is actually harvested, or limit harvest of vulnerable taxa.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Principe, P., P. Bradley, S. Yee, W. Fisher, E. Johnson, P. Allen, and D. Campbell. 2012. Quantifying Coral Reef Ecosystem Services. EPA/600/R-11/206, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Research Triangle Park, NC. | 2012 | Global | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beach & Land Formation; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Complex Habitat & Resources; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seagrasses; Shoreline Protection; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Zhang, S; Mao, T; Chen, F. 2011. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on ectopic bone formation of bone marrow stromal cells in porous coral. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 40:961-965. | 2011 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Guinchard, X; Roulland, E. 2011. Various Entries to Vinyl Chloride Derivatives and their Applications in Total Synthesis of Natural Products. Synlett 2779-2788. | 2011 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petchey, F; Clark, G. 2011. Tongatapu hardwater: Investigation into the (14)C marine reservoir offset in lagoon, reef and open ocean environments of a limestone island. Quaternary Geochronology 6:539-549. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Tonga | Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Matsuda, Y; Endo, Y; Satkawa, Y; Nakata, M. 2011. Synthetic Studies on Polymaxenolides: Synthesis and Structure Elucidation of Nominal Epoxyafricanane and Other Africane-Type Sesquiterpenoids. Journal of Organic Chemistry 76:6258-6263. | 2011 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Faria, AM; Muha, T; Morote, E; Chicharo, MA. 2011. Influence of starvation on the critical swimming behaviour of the Senegalese sole (Solea senegalensis) and its relationship with RNA/DNA ratios during ontogeny. Scientia Marina 75:87-94. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish | |
| Reimer, JD; Obuchi, M; Irei, Y; Fujii, T; Nozawa, Y. 2011. Shallow-Water Brachycnemic Zoanthids (Cnidaria: Hexacorallia) from Taiwan: A Preliminary Survey. Zoological Studies 50:363-371. | 2011 | Australia; Japan; Vietnam; Taiwan | Anemones & Zooanthids; Marine Products | |
| Betancur-R, R; Hines, A; Acero, A; Orti, G; Wilbur, AE; Freshwater, DW. 2011. Reconstructing the lionfish invasion: insights into Greater Caribbean biogeography. Journal of Biogeography 38:1281-1293. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Bermuda; Caribbean | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Torres-Pratts, H; Lado-Insua, T; Rhyne, AL; Rodriguez-Matos, L; Schizas, NV. 2011. Two distinct, geographically overlapping lineages of the corallimorpharian Ricordea florida (Cnidaria: Hexacorallia: Ricordeidae). Coral Reefs 30:391-396. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting | |
| Anthony, KRN; Maynard, JA; Diaz-Pulido, G; Mumby, PJ; Marshall, PA; Cao, L; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 2011. Ocean acidification and warming will lower coral reef resilience. Global Change Biology 17:1798-1808. | 2011 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Pawlik, JR. 2011. The Chemical Ecology of Sponges on Caribbean Reefs: Natural Products Shape Natural Systems. Bioscience 61:888-898. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Rahman, MA; Fujimura, H; Shinjo, R; Oomori, T. 2011. Extracellular matrix protein in calcified endoskeleton: a potential additive for crystal growth and design. Journal of Crystal Growth 324:177-183. | 2011 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Naumann, MS; Orejas, C; Wild, C; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. First evidence for zooplankton feeding sustaining key physiological processes in a scleractinian cold-water coral. Journal of Experimental Biology 214:3570-3576. | 2011 | Lab Study | Complex Habitat & Resources; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Vijayanand, P; Anbalagan, T; Saravanan, R; Ammaiappan, V; Rajagopal, S. 2011. Diversity Of Wrasse Species Along Gulf Of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (South East Coast Of India). Thalassas 27:57-66. | 2011 | India | Index or Indicator | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Planktivorous Fish |
| Gondim, AI; Dias, TLP; Campos, FF; Alonso, C; Christoffersen, ML. 2011. Benthic macrofauna from Areia Vermelha Marine State Park, Cabedelo, Paraiba, Brazil. Biota Neotropica 11:75-86. | 2011 | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Hydrocoral; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Seastars; Tourism & Recreation |
| Anthony, K. R. N., J. A. Maynard, G. Diaz-Pulido, P. J. Mumby, P. A. Marshall, L. Coa, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2011. Ocean acidification and warming will lower coral reef resilience. Global Change Biology doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02364.x. | 2011 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Sondi, I; Salopek-Sondi, B; Skapin, SD; Segota, S; Jurina, I; Vukelic, B. 2011. Colloid-chemical processes in the growth and design of the bio-inorganic aragonite structure in the scleractinian coral Cladocora caespitosa. Journal Of Colloid And Interface Science 354:181-189. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | |
| Montagnon, T; Noutsias, D; Alexopoulou, I; Tofi, M; Vassilikogiannakis, G. 2011. Green oxidations of furans-initiated by molecular oxygen-that give key natural product motifs. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 9:2031-2039. | 2011 | Bivalves; Substrate | ||
| Lerman, A; Guidry, M; Andersson, AJ; Mackenzie, FT. 2011. Coastal Ocean Last Glacial Maximum to 2100 CO(2)-Carbonic Acid-Carbonate System: A Modeling Approach. Aquatic Geochemistry 17:749-773. | 2011 | Global | Model | CO2; Ocean Acidity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Kanamoto, H; Takemura, M; Ohyama, K. 2011. Identification of a cyclooxygenase gene from the red alga Gracilaria vermiculophylla and bioconversion of arachidonic acid to PGF(2 alpha) in engineered Escherichia coli. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 91:1121-1129. | 2011 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | |
| Hassan, HM; Elnagar, AY; Khanfar, MA; Sallam, AA; Mohammed, R; Shaala, LA; Youssef, DTA; Hifnawy, MS; El Sayed, KA. 2011. Design of semisynthetic analogues and 3D-QSAR study of eunicellin-based diterpenoids as prostate cancer migration and invasion inhibitors. European Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry 46:1122-1130. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Invasive Species; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Barbanti, SM; Moldowan, JM; Watt, DS; Kolaczkowska, E. 2011. New triaromatic steroids distinguish Paleozoic from Mesozoic oil. Organic Geochemistry 42:409-424. | 2011 | Global | Climate; Octocoral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cai, L; Wang, Q; Gu, CM; Wu, JG; Wang, J; Kang, N; Hu, JW; Xie, F; Yan, L; Liu, X; Cao, YL; Xiao, R. 2011. Vascular and micro-environmental influences on MSC-coral hydroxyapatite construct-based bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 32:8497-8505. | 2011 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Aragon, J; Gonzalez, R; Fuentes, G; Palin, L; Croce, G; Viterbo, D. 2011. Development and Characterization of a Novel Bioresorbable and Bioactive Biomaterial Based on Polyvinyl Acetate, Calcium Carbonate and Coralline Hydroxyapatite. Materials Research-Ibero-American Journal of Materials 14:25-30. | 2011 | Cuba | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | |
| Uda, K; Komeda, Y; Koyama, H; Koga, K; Fujita, T; Iwasaki, N; Suzuki, T. 2011. Complete mitochondrial genomes of two Japanese precious corals, Paracorallium japonicum and Corallium konojoi (Cnidaria, Octocorallia, Coralliidae): Notable differences in gene arrangement. Gene 476:27-37. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Taiwan | Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Stony Coral | |
| Navalgund, RR; Singh, RP. 2011. Climate Change Studies Using Space Based Observation. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing 39:281-295. | 2011 | Global; India | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Forestry; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Irrigation; Light; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Sarin, P; Lee, SJ; Apostolov, ZD; Kriven, WM. 2011. Porous Biphasic Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds from Cuttlefish Bone. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 94:2362-2370. | 2011 | Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Galkiewicz, JP; Pratte, ZA; Gray, MA; Kellogg, CA. 2011. Characterization of culturable bacteria isolated from the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 77:333-346. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Jones, AC; Monroe, EA; Podell, S; Hess, WR; Klages, S; Esquenazi, E; Niessen, S; Hoover, H; Rothmann, M; Lasken, RS; Yates, JR; Reinhardt, R; Kube, M; Burkart, MD; Allen, EE; Dorrestein, PC; Gerwick, WH; Gerwick, L. 2011. Genomic insights into the physiology and ecology of the marine filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108:8815-8820. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Anavi, Y; Avishai, G; Calderon, S; Allon, DM. 2011. Bone Remodeling in Onlay Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate and Coral Grafts to Rat Calvaria: Microcomputerized Tomography Analysis. Journal of Oral Implantology 37:379-386. | 2011 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Bivalves; Discharges; Fish; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pipelines; Salinity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation Policies; Waste Management; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. | 2011 | Aquaculture; Bivalves; Invasive Species; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | ||
| Schmitt, S; Deines, P; Behnam, F; Wagner, M; Taylor, MW. 2011. Chloroflexi bacteria are more diverse, abundant, and similar in high than in low microbial abundance sponges. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 78:497-510. | 2011 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Microorganisms; Ports & Harbors; Sponges | ||
| Minch, R; Es-Souni, M. 2011. A versatile approach to processing of high active area pillar coral- and sponge-like Pt-nanostructures. Application to electrocatalysis. Journal of Materials Chemistry 21:4182-4188. | 2011 | Sponges; Substrate | ||
| Goncalves, S; Nicolas, M; Maillos, P; Baati, R. 2011. Cationic cyclization of keto-epoxides mediated by zirconium(IV) tetrachloride: diastereoselective synthesis of cis-decalinols. Tetrahedron 67:8373-8382. | 2011 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Scott, A; Malcolm, HA; Damiano, C; Richardson, DL. 2011. Long-term increases in abundance of anemonefish and their host sea anemones in an Australian marine protected area. Marine and Freshwater Research 62:187-196. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Olivotto, I; Di Stefano, M; Rosetti, S; Cossignani, L; Pugnaloni, A; Giantomassi, F; Carnevali, O. 2011. Live prey enrichment, with particular emphasis on HUFAs, as limiting factor in false percula clownfish (Amphiprion ocellaris, Pomacentridae) larval development and metamorphosis: Molecular and biochemical implications. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A - Molecular and Integrative Physiology 159:207-218. | 2011 | Model | Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Mydlarz, LD; Palmer, CV. 2011. The presence of multiple phenoloxidases in Caribbean reef-building corals. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology A - Molecular and Integrative Physiology 159:372-378. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Pathogens; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Nordt, SP; Wu, J; Zahller, S; Clark, RF; Cantrell, FL. 2011. Palytoxin Poisoning After Dermal Contact With Zoanthid Coral. Journal of Emergency Medicine 40:397-399. | 2011 | Oman | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Wei, WC; Lin, SY; Chen, YJ; Wen, CC; Huang, CY; Palanisamy, A; Yang, NS; Sheu, JH. 2011. Topical application of marine briarane-type diterpenes effectively inhibits 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced inflammation and dermatitis in murine skin. Journal of Biomedical Science 18. | 2011 | China | Index or Indicator | Octocoral; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting |
| Li, CQ; Liu, WC; Zhu, P; Yang, JL; Cheng, KD. 2011. Phylogenetic Diversity of Bacteria Associated with the Marine Sponge Gelliodes carnosa Collected from the Hainan Island Coastal Waters of the South China Sea. Microbial Ecology 62:800-812. | 2011 | China | Cyanobacteria; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Stevenson, TC; Tissot, BN; Dierking, J. 2011. Fisher behaviour influences catch productivity and selectivity in West Hawaii's aquarium fishery. ICES Journal of Marine Science 68:813-822. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Yang, Y; Yao, QQ; Pu, XM; Hou, ZQ; Zhang, QQ. 2011. Biphasic calcium phosphate macroporous scaffolds derived from oyster shells for bone tissue engineering. Chemical Engineering Journal 173:837-845. | 2011 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Supova, M; Martynkova, GS; Sucharda, Z. 2011. Bioapatite Made From Chicken Femur Bone. Ceramics - Silikaty 55:256-260. | 2011 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Thurber, AR; Jones, WJ; Schnabel, K. 2011. Dancing for Food in the Deep Sea: Bacterial Farming by a New Species of Yeti Crab. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Traina, K; Henrist, C; Vertruyen, B; Cloots, R. 2011. Dense La(0.9)Sr(0.1)Ga(0.8)Mg(0.2)O(2.85) electrolyte for IT-SOFC's: Sintering study and electrochemical characterization. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 509:1493-1500. | 2011 | |||
| Gaitan, AS; Mora, PAR; Narvaez, DM; Moreno, LMM. 2011. Characterising structural, mechanical and cytotoxic properties of coral-based composite material intended for bone implant applications. Revista Ingenieria e Investigacion 31:135-141. | 2011 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Grkovic, T; Whitson, EL; Rabe, DC; Gardella, RS; Bottaro, DP; Linehan, WM; McMahon, JB; Gustafson, KR; McKee, TC. 2011. Identification and evaluation of soft coral diterpenes as inhibitors of HIF-2 alpha induced gene expression. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 21:2113-2115. | 2011 | Octocoral; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Stabili, L; Schirosi, R; Di Benedetto, A; Merendino, A; Villanova, L; Giangrande, A. 2011. First insights into the biochemistry of Sabella spallanzanii (Annelida: Polychaeta) mucus: a potentially unexplored resource for applicative purposes. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 91:199-208. | 2011 | Echinoderms; Marine Worms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Chen, MH; Sheu, SY; Chen, CA; Wang, JT; Chen, WM. 2011. Paracoccus isoporae sp nov., isolated from the reef-building coral Isopora palifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 61:1138-1143. | 2011 | Taiwan | Microorganisms; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Jokiel, P. 2011. Ocean acidification and control of reef coral calcification by boundary layer limitation of proton flux. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:639-657. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity | ||
| Sheu, SY; Jiang, SR; Chen, CA; Wang, JT; Chen, WM. 2011. Paracoccus stylophorae sp nov., isolated from the reef-building coral Stylophora pistillata. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 61:2221-2226. | 2011 | Taiwan | Stony Coral | |
| Kim, J; Roh, SW; Choi, JH; Jung, MJ; Nam, YD; Kim, MS; Park, EJ; Shin, KS; Bae, JW. 2011. Dietzia alimentaria sp nov., isolated from a traditional Korean food. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 61:2254-2258. | 2011 | Microorganisms | ||
| Koreny, L; Sobotka, R; Janouskovec, J; Keeling, PJ; Obornik, M. 2011. Tetrapyrrole Synthesis of Photosynthetic Chromerids Is Likely Homologous to the Unusual Pathway of Apicomplexan Parasites. Plant Cell 23:3454-3462. | 2011 | GIS & Maps | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Primary Production | |
| Mackenzie, FT; Andersson, AJ; Arvidson, RS; Guidry, MW; Lerman, A. 2011. Land-sea carbon and nutrient fluxes and coastal ocean CO(2) exchange and acidification: Past, present, and future. Applied Geochemistry 26:S298-S302. | 2011 | Model | CO2; Discharges; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Drahl, MA; Akhmedov, NG; Williams, LJ. 2011. Selective conversion of an enantioenriched cyclononadienone to the xeniolide, xenibellol, and florlide cores: an integrated routing strategy. Tetrahedron Letters 52:325-328. | 2011 | Florida | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Jokiel, PL. 2011. Ocean Acidification And Control Of Reef Coral Calcification By Boundary Layer Limitation Of Proton Flux. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:639-657. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | ||
| Lombardi, C; Cocito, S; Gambi, MC; Cisterna, B; Flach, F; Taylor, PD; Keltie, K; Freer, A; Cusack, M. 2011. Effects of ocean acidification on growth, organic tissue and protein profile of the Mediterranean bryozoan Myriapora truncata. Aquatic Biology 13:251-262. | 2011 | CO2; Ocean Acidity | ||
| Chen, MH; Sheu, SY; Chen, CA; Wang, JT; Chen, WM. 2011. Shimia isoporae sp. nov., isolated from the reef-building coral Isopora palifera. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 61:823-827. | 2011 | Taiwan | Docks & Marinas; Microorganisms; Stony Coral | |
| Marinha, D; Dessemond, L; Cronin, JS; Wilson, JR; Barnett, SA; Djurado, E. 2011. Microstructural 3D Reconstruction and Performance Evaluation of LSCF Cathodes Obtained by Electrostatic Spray Deposition. Chemistry of Materials 23:5340-5348. | 2011 | Model | Substrate | |
| Reveillaud, J; van Soest, R; Derycke, S; Picton, B; Rigaux, A; Vanreusel, A. 2011. Phylogenetic Relationships among NE Atlantic Plocamionida Topsent (1927) (Porifera, Poecilosclerida): Under-Estimated Diversity in Reef Ecosystems. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Sponges |
| Ernst, S; Janse, M; Renema, W; Kouwenhoven, T; Goudeau, ML; Reichart, GJ. 2011. Benthic Foraminifera In A Large Indo-Pacific Coral Reef Aquarium. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 41:101-113. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Java; Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock |
| Apprill, A; Rappe, MS. 2011. Response of the microbial community to coral spawning in lagoon and reef flat environments of Hawaii, USA. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 62:251-266. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Microorganisms; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Heal, Geoffrey. 2011. Sustainability and it's Measurement. NBER Working Paper No. 17008, National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, (MA, USA). | 2011 | Review | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Chou, JH; Ben-Nissan, B; Green, DW; Valenzuela, SM; Kohan, L. 2011. Targeting and Dissolution Characteristics of Bone Forming and Antibacterial Drugs by Harnessing the Structure of Microspherical Shells from Coral Beach Sand. Advanced Engineering Materials 13:93-99. | 2011 | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Liu, Y; Jiang, T; Zhou, Y; Zhang, Z; Wang, ZJ; Tong, H; Shen, XY; Wang, YN. 2011. Evaluation of the attachment, proliferation, and differentiation of osteoblast on a calcium carbonate coating on titanium surface. Materials Science and Engineering C 31:1055-1061. | 2011 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ramirez-Llodra, E., A. Brandt, R. Danovaro, B. De Mol, E. Escobar, C. R. German, L. A. Levin, P. M. Arbizu, L. Menot, P. Buhl-Mortensen, B. E. Narayanaswamy, C. R. Smith, D. P. Tittensor, P. A. Tyler, A. Vanreusel, and M. Vecchione. 2010. Deep, diverse and definitely different: unique attributes of the world's largest ecosystem. Biogeosciences 7:2851-2899. | 2010 | Global | Review | Finfish Harvest; Microorganisms; Primary Production |
| Kongkathip, B., A. Hasakunpaisarn, S. Boonananwong, and N. Kongkathip. 2010. Synthesis of cytotoxic novel 9,11-secosterol analogs: Structure/activity studies. Steroids 75:834-847. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Guest, M. A., A. J. Hirst, P. D. Nichols, and S. D. Frusher. 2010. Multi-scale spatial variation in stable isotope and fatty acid profiles amongst temperate reef species: implications for design and interpretation of trophic studies. Marine Ecology Progress Series 410:25-41. | 2010 | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Cantin, N. E., A. L. Cohen, K. B. Karnauskas, A. M. Tarrant, and D. C. McCorkle. 2010. Ocean Warming Slows Coral Growth in the Central Red Sea. Science 329:322-325. | 2010 | Model | Climate; Ocean Acidity; Stony Coral | |
| Yang, C. S., M. H. Chen, A. B. Arun, C. A. Chen, J. T. Wang, and W. M. Chen. 2010. Endozoicomonas montiporae sp nov., isolated from the encrusting pore coral Montipora aequituberculata. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 60:1158-1162. | 2010 | Taiwan | ||
| Vanreusel, A., G. Fonseca, R. Danovaro, M. C. da Silva, A. M. Esteves, T. Ferrero, G. Gad, V. Galtsova, C. Gambi, V. D. Genevois, J. Ingels, B. Ingole, N. Lampadariou, B. Merckx, D. Miljutin, M. Miljutina, A. Muthumbi, S. Netto, D. Portnova, T. Radziejewska, and Rae. 2010. The contribution of deep-sea macrohabitat heterogeneity to global nematode diversity. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 31:6-20. | 2010 | Global | Marine Worms; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Substrate | |
| Blunt, J. W., B. R. Copp, M. H. G. Munro, P. T. Northcote, and M. R. Prinsep. 2010. Marine natural products. Natural Product Reports 27:165-237. | 2010 | Review | Algae; Echinoderms; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Plankton; Sponges; Tunicates | |
| Ripamonti, U., R. M. Klar, L. F. Renton, and C. Ferretti. 2010. Synergistic induction of bone formation by hOP-1, hTGF-beta(3) and inhibition by zoledronate in macroporous coral-derived hydroxyapatites. Biomaterials 31:6400-6410. | 2010 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Huang, C. Y., J. H. Su, Y. C. Liu, Z. H. Wen, C. H. Hsu, M. Y. Chiang, and J. H. Sheu. 2010. Oppositane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from the Formosan Soft Coral Sinularia leptoclados. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan 83:678-682. | 2010 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Sutherland, K. R., L. P. Madina, and R. Stockerb. 2010. Filtration of submicrometer particles by pelagic tunicates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107:15129-15134. | 2010 | Model | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Plankton; Tunicates | |
| Messersmith, P. B. 2010. Holding on by a hard-shell thread. Science 328:180-181. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Rasala, B. A., M. Muto, P. A. Lee, M. Jager, R. M. R. Cardoso, C. A. Behnke, P. Kirk, C. A. Hokanson, R. Crea, M. Mendez, and S. P. Mayfield. 2010. Production of therapeutic proteins in algae, analysis of expression of seven human proteins in the chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Biotechnology 8:719-733. | 2010 | Algae; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Penesyan, A., S. Kjelleberg, and S. Egan. 2010. Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Marine Drugs 8:438-459. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Movassaghi, M., D. S. Siegel, and S. Han. 2010. Total synthesis of all (-)-agelastatin alkaloids. Chemical Science 1:561-566. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Rosenfelder, N., N. J. Van Zee, J. F. Mueller, C. Gaus, and W. Vetter. 2010. Gas Chromatography/Electron Ionization-Mass Spectrometry-Selected Ion Monitoring Screening Method for a Thorough Investigation of Polyhalogenated Compounds in Passive Sampler Extracts with Quadrupole Systems. Analytical Chemistry 82:9835-9842. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hunt, M. E., M. P. Scherrer, F. D. Ferrari, and M. V. Matz. 2010. Very Bright Green Fluorescent Proteins from the Pontellid Copepod Pontella mimocerami. PLoS One 5:e11517. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biomedical Research Policies; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| An, T. Y., J. Winshell, G. Scorzetti, J. W. Fell, and K. S. Rein. 2010. Identification of okadaic acid production in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymum from Florida Bay. Toxicon 55:653-657. | 2010 | Florida | ||
| DiMasi, J. A., L. Feldman, A. Seckler, and A. Wilson. 2010. Trends in risks associated with new drug development: success rates for investigational drugs. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 87:272-277. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Gray, D. L., R. Canessa, R. Rollins, C. P. Keller, and P. Dearden. 2010. Incorporating Recreational Users into Marine Protected Area Planning: A Study of Recreational Boating in British Columbia, Canada. Environmental Management 46:167-180. | 2010 | Columbia | Model | Aquaculture; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins |
| Harrington, M. J., A. Masic, N. Holten-Andersen, J. H. Waite, and P. Fratzl. 2010. Iron-clad fibers: a metal-based biological strategy for hard flexible coatings. Science 328:216-220. | 2010 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Wang, B. J., F. Q. Sun, Y. P. Du, X. P. Liu, G. Y. Li, Q. L. Lai, J. Luo, and Z. Z. Shao. 2010. Meridianimaribacter flavus gen. nov., sp nov., a member of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from marine sediment of the South China Sea. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 60:121-127. | 2010 | China | Microorganisms; Sediment | |
| Arai, M. and M. Kobayashi. 2010. Search for Medicinal Seeds from Marine Organisms. Journal Of Synthetic Organic Chemistry Japan 68:470-479. | 2010 | Japan; Indonesia | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Rastogi, R. P., Richa, R. P. Sinha, S. P. Singh, and D. P. Hader. 2010. Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. Journal Of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 37:537-558. | 2010 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Plankton | ||
| Saleh, M. B. and R. G. Kerr. 2010. Identification of the Cyclase Product and its First Oxidation Product in the Biosynthesis of Fuscol and Fuscosides. Australian Journal of Chemistry 63:901-906. | 2010 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Model | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Whalen, K. E., A. L. Lane, J. Kubanek, and M. E. Hahn. 2010. Biochemical Warfare on the Reef: The Role of Glutathione Transferases in Consumer Tolerance of Dietary Prostaglandins. PLoS One 5:e8537. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Lab Study | Octocoral; Snails & Conch; Substrate |
| Campbell, R. J., N. Ledesma, G. Zill, J. C. Herrera, and J. Leon. 2010. Collecting Pouterias (Pouteria spp.), Sapodilla (Manilkara zapota) and Caimito (Chrysophyllum cainito) for the Creation of New Markets. Journal Of The American Pomological Society 64:24-27. | 2010 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Nicaragua; Costa Rica | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Collaboration & Partnering; Landscaping & Household Services | |
| Sella, I. and Y. Benayahu. 2010. Rearing cuttings of the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum (Octocorallia, Alcyonacea): towards mass production in a closed seawater system. Aquaculture Research 41:1748-1758. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Salinity |
| Millero, F. J. and B. R. DiTrolio. 2010. Use of Thermodynamics in Examining the Effects of Ocean Acidification. Elements 6:299-303. | 2010 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Microorganisms; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Springer, Y. P., C. G. Hays, M. H. Carr, and M. R. Mackey. 2010. Toward Ecosystem-Based Management Of Marine Macroalgae-The Bull Kelp, Nereocystis Luetkeana. Pages 1-41 Oceanography And Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol 48. | 2010 | Review | Algae; Primary Production | |
| Tsounis, G., S. Rossi, R. Grigg, G. Santangelo, L. Bramanti, and J. M. Gili. 2010. The Exploitation And Conservation Of Precious Corals. Pages 161-211 Oceanography And Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Vol 48. | 2010 | Review | Fishing Sector; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Souvenir & Decorative Trade | |
| Lapointe, B. E. and B. J. Bedford. 2010. Ecology and nutrition of invasive Caulerpa brachypus f. parvifolia blooms on coral reefs off southeast Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 9:1-12. | 2010 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Knittweis, L. and M. Wolff. 2010. Live coral trade impacts on the mushroom coral Heliofungia actiniformis in Indonesia: Potential future management approaches. Biological Conservation 143:2722-2729. | 2010 | Indonesia | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Carpenter, L. W., M. R. Patterson, and E. S. Bromage. 2010. Water flow influences the spatiotemporal distribution of heat shock protein 70 within colonies of the scleractinian coral Montastrea annularis (Ellis and Solander, 1786) following heat stress: Implications for coral bleaching. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 387:52-59. | 2010 | Seawater Flow; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Cook, E. J., R. Shucksmith, H. Orr, G. V. Ashton, and J. Berge. 2010. Fatty acid composition as a dietary indicator of the invasive caprellid, Caprella mutica (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Marine Biology 157:19-27. | 2010 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Invasive Species |
| Armi, Z., S. Turki, E. Trabelsi, and N. Ben Maiz. 2010. First recorded proliferation of Coolia monotis (Meunier, 1919) in the North Lake of Tunis (Tunisia) correlation with environmental factors. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 164:423-433. | 2010 | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Gregati, R. A., V. Fransozo, L. S. Lopez-Greco, and M. L. Negreiros-Fransozo. 2010. Reproductive cycle and ovarian development of the marine ornamental shrimp Stenopus hispidus in captivity. Aquaculture 306:185-190. | 2010 | Cuba | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Salinity | |
| TEEB. 2010. Measuring biophysical quantities and the use of indicators. in P. Kumar, editor. The economics of ecosystems and biodiversity: ecological and economic foundations. Earthscan, United Kingdom. | 2010 | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Forestry | |
| Guzman, J. R., G. Espinosa-Paredes, J. L. Francois, C. Martin-Del-Campo, and A. Nunez-Carrera. 2010. Radiotoxicity of transuranics recycling in heterogeneous fuel assemblies for boiling water reactors. Progress In Nuclear Energy 52:698-706. | 2010 | Discharges | ||
| Arbuatti, A. and P. Lucidi. 2010. Poisonous ornamental fishes on free sale. Survey on envenomations by Pterois volitans. Sanitary and legislative aspects with reference to the Italian current regulations about dangerous animals. Veterinaria 24:37-41. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Special Use Permitting | |
| Justine, J. L., A. Grugeaud, F. Keller, and P. Leblanc. 2010. Two thousand parasites on a single ray: An infection with two species of skin monogeneans on a blotched fantail ray kept in an aquarium. Acta Parasitologica 55:286-290. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Taiwan | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Gergely, G., F. Weber, I. Lukacs, L. Illes, A. L. Toth, Z. E. Horvath, J. Mihaly, and C. Balazsi. 2010. Nano-hydroxyapatite preparation from biogenic raw materials. Central European Journal Of Chemistry 8:375-381. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Singh, S. P., A. Azua, A. Chaudhary, S. Khan, K. L. Willett, and P. R. Gardinali. 2010. Occurrence and distribution of steroids, hormones and selected pharmaceuticals in South Florida coastal environments. Ecotoxicology 19:338-350. | 2010 | Florida | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands | |
| Mckoy, H., D. M. Kennedy, and P. S. Kench. 2010. Sand cay evolution on reef platforms, Mamanuca Islands, Fiji. Marine Geology 269:61-73. | 2010 | Fiji | Climate; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Nayar, S., S. P. Sagar, and A. Guha. 2010. Non-destructive evaluation of mechanical properties of poly (vinyl) alcohol-hydroxyapatite nanocomposites. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 21:1099-1102. | 2010 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Chen, W. F., J. P. Wang, C. H. Hsu, J. Y. Jhan, H. S. Teng, and P. L. Kuo. 2010. Nanostructured Coral-like Carbon as Pt Support for Fuel Cells. Journal of Physical Chemistry C 114:6976-6982. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | ||
| Hou, Y. and L. Harinantenaina. 2010. New and Bioactive Natural Products Isolated from Madagascar Plants and Marine Organisms. Current Medicinal Chemistry 17:1191-1219. | 2010 | Madagascar | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Jackson, D. J., V. Thiel, and G. Worheide. 2010. An evolutionary fast-track to biocalcification. Geobiology 8:191-196. | 2010 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Special Use Permitting; Sponges | ||
| Lesser, M. P., M. Slattery, M. Stat, M. Ojimi, R. D. Gates, and A. Grottoli. 2010. Photoacclimatization by the coral Montastraea cavernosa in the mesophotic zone: light, food, and genetics. Ecology 91:990-1003. | 2010 | Bahamas | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Luna, G. M., L. Bongiorni, C. Gili, F. Biavasco, and R. Danovaro. 2010. Vibrio harveyi as a causative agent of the White Syndrome in tropical stony corals. Environmental Microbiology Reports 2:120-127. | 2010 | Indian Ocean; India; Indonesia | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Norse, E. A. 2010. Ecosystem-Based Spatial Planning And Management Of Marine Fisheries: Why And How? Bulletin of Marine Science 86:179-195. | 2010 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Colombo-Pallotta, M. F., A. Rodriguez-Roman, and R. Iglesias-Prieto. 2010. Calcification in bleached and unbleached Montastraea faveolata: evaluating the role of oxygen and glycerol. Coral Reefs 29:899-907. | 2010 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Niggl, W., M. S. Naumann, U. Struck, R. Manasrah, and C. Wild. 2010. Organic matter release by the benthic upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp fuels pelagic food webs in coral reefs. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 384:99-106. | 2010 | Cuba | Plankton | |
| Diaz, C., M. L. Valenzuela, A. Laguna, V. Lavayen, J. Jimenez, L. A. Power, and C. O'Dwyer. 2010. Metallophosphazene Precursor Routes to the Solid-State Deposition of Metallic and Dielectric Microstructures and Nanostructures on Si and SiO2. Langmuir 26:10223-10233. | 2010 | Substrate | ||
| Deeds, J. R. and M. D. Schwartz. 2010. Human risk associated with palytoxin exposure. Toxicon 56:150-162. | 2010 | Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Richlen, M. L., S. L. Morton, E. A. Jamali, A. Rajan, and D. M. Anderson. 2010. The catastrophic 2008-2009 red tide in the Arabian gulf region, with observations on the identification and phylogeny of the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 9:163-172. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Malaysia; United Arab Emirates; Oman; Mexico | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Stone, R., D. White, R. Guest, and B. Francis. 2009. The Virtual Scylla: An exploration of \serious games\", artificial life and simulation complexity". Virtual Reality 13:13-25. | 2009 | Europe; England | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Climate; Coastal Defense; Collaboration & Partnering; Military; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Baerga-Ortiz, A. 2009. Biotechnology and biochemistry of marine natural products. Marine Biotechnology 28:251-257. | 2009 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sheppard, B. J., D. Mahapatra, K. Reece, and J. K. Coleman. 2009. Exotic Perkinsus Sp Including Perkinsus Olseni Found In Ornamental Reef Clams, Tridacna Spp., Imported Into The Usa From The Indo-Pacific For Sale To The General Public. Journal of Shellfish Research 28:728-728. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Lin, M. Z., M. R. McKeown, H. L. Ng, T. A. Aguilera, N. C. Shaner, R. E. Campbell, S. R. Adams, L. A. Gross, W. Ma, T. Alber, and R. Y. Tsien. 2009. Autofluorescent Proteins with Excitation in the Optical Window for Intravital Imaging in Mammals. Chemistry & Biology 16:1169-1179. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biomedical Research Policies; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Raz-Bahat, M., H. Faibish, T. Mass, and B. Rinkevich. 2009. Three-dimensional laser scanning as an efficient tool for coral surface area measurements. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 7:657-663. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Smith, R. T., J. H. Pinzon, and T. C. LaJeunesse. 2009. Symbiodinium (Dinophyta) Diversity And Stability In Aquarium Corals. Journal of Phycology 45:1030-1036. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Collaboration & Partnering; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Pinon-Gimate, A., M. F. Soto-Jimenez, M. J. Ochoa-Izaguirre, E. Garcia-Pages, and F. Paez-Osuna. 2009. Macroalgae blooms and delta N-15 in subtropical coastal lagoons from the Southeastern Gulf of California: Discrimination among agricultural, shrimp farm and sewage effluents. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:1144-1151. | 2009 | Agriculture; Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Uemura, D., M. Kita, H. Arimoto, and M. Kitamura. 2009. Recent aspects of chemical ecology: Natural toxins, coral communities, and symbiotic relationships. Pure and Applied Chemistry 81:1093-1111. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Cheng, X. K., Q. J. He, J. Q. Li, Z. L. Huang, and R. A. Chi. 2009. Control of Pore Size of the Bubble-Template Porous Carbonated Hydroxyapatite Microsphere by Adjustable Pressure. Crystal Growth and Design 9:2770-2775. | 2009 | CO2; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Yamashita, T., Y. Nakao, S. Matsunaga, T. Oikawa, Y. Imahara, and N. Fusetani. 2009. A new antiangiogenic C-24 oxylipin from the soft coral Sinularia numerosa. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 17:2181-2184. | 2009 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Chouvelon, T., M. Warnau, C. Churlaud, and P. Bustamante. 2009. Hg concentrations and related risk assessment in coral reef crustaceans, molluscs and fish from New Caledonia. Environmental Pollution 157:331-340. | 2009 | New Caledonia | Fish; Marine Products; Molluscs | |
| Tans, P. 2009. An accounting of the observed increase in oceanic and atmospheric CO2 and an outlook for the future. Oceanography 22:26-35. | 2009 | CO2; Ocean Acidity | ||
| Berrue, F. and R. G. Kerr. 2009. Diterpenes from gorgonian corals. Natural Product Reports 26:681-710. | 2009 | Review | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Burford, M. A., P. C. Rothlisberg, and A. T. Revill. 2009. Sources of nutrients driving production in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia: a shallow tropical shelf system. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1044-1053. | 2009 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Qi, S.-H., G.-C. Su, Y.-F. Wang, Q.-Y. Liu, and C.-H. Gao. 2009. Alkaloids from the South China sea black coral antipathes dichotoma. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 57:87-88. | 2009 | Japan; China | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sashidhara, K. V., K. N. White, and P. Crews. 2009. A selective account of effective paradigms and significant outcomes in the discovery of inspirational marine natural products. Journal of Natural Products 72:588-603. | 2009 | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Suto, K., H. Masuda, Y. Takenaka, F. I. Tsuji, and H. Mizuno. 2009. Structural basis for red-shifted emission of a GFP-like protein from the marine copepod Chiridius poppei. Genes To Cells 14:727-737. | 2009 | |||
| Dubois, S., L. Barille, and B. Cognie. 2009. Feeding response of the polychaete Sabellaria alveolata (Sabellariidae) to changes in seston concentration. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 376:94-101. | 2009 | France | Algae; Bivalves; Marine Worms | |
| Wei, G., M. T. McCulloch, G. Mortimer, W. Deng, and L. Xie. 2009. Evidence for ocean acidification in the Great Barrier Reef of Australia. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73:2332-2346. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Non-point Source Runoff; Ocean Acidity; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Gross-Aviv, T. and R. Vago. 2009. The role of aragonite matrix surface chemistry on the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 30:770-779. | 2009 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | ||
| van Katwijk, M. M., A. R. Bos, V. N. de Jonge, L. S. A. M. Hanssen, D. C. R. Hermus, and D. J. de Jong. 2009. Guidelines for seagrass restoration: Importance of habitat selection and donor population, spreading of risks, and ecosystem engineering effects. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:179-188. | 2009 | Review | Seagrasses | |
| Chen, S.-P., J.-H. Su, H.-C. Yeh, A. F. Ahmed, C.-F. Dai, Y.-C. Wu, and J.-H. Sheu. 2009. Novel norhumulene and Xeniaphyllane-Derived terpenoids from a formosan soft coral sinularia gibberosa. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 57:162-166. | 2009 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Rossi, S. and J. M. Gili. 2009. Reproductive features and gonad development cycle of the soft bottom-gravel gorgonian Leptogorgia sarmentosa (Esper, 1791) in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Invertebrate Reproduction and Development 53:175-190. | 2009 | Octocoral | ||
| Langhamer, O., D. Wilhelmsson, and J. Engstrom. 2009. Artificial reef effect and fouling impacts on offshore wave power foundations and buoys - a pilot study. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 82:426-432. | 2009 | Artificial Habitat; Invertebrates | ||
| Lee, O. O., P. Y. Chui, Y. H. Wong, J. R. Pawlik, and P. Y. Qian. 2009. Evidence for Vertical Transmission of Bacterial Symbionts from Adult to Embryo in the Caribbean Sponge Svenzea zeai. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 75:6147-6156. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Sponges | |
| Pazza, R., K. F. Kavalco, P. R. Penteado, S. A. F. Kavalco, and L. F. de Almeida-Toledo. 2009. Gene Mapping of 18S and 5S rDNA Genes in the Karyotype of the Three-Spot Gourami Trichogaster trichopterus (Perciformes, Osphronemidae). Zebrafish 6:219-222. | 2009 | GIS & Maps | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Ripamonti, U., J. Crooks, L. Khoali, and L. Roden. 2009. The induction of bone formation by coral-derived calcium carbonate/hydroxyapatite constructs. Biomaterials 30:1428-1439. | 2009 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sharp, K., K. E. Arthur, L. Gu, C. Ross, G. Harrison, S. P. Gunasekera, T. Meickle, S. Matthew, H. Luesch, R. W. Thacker, D. H. Sherman, and V. J. Paul. 2009. Phylogenetic and chemical diversity of three chemotypes of bloom-forming Lyngbya species (cyanobacteria: Oscillatoriales) from reefs of southeastern Florida. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 75:2879-2888. | 2009 | Florida | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Trost, B. M. and G. B. Dong. 2009. A Stereodivergent Strategy to Both Product Enantiomers from the Same Enantiomer of a Stereoinducing Catalyst: Agelastatin A. Chemistry-a European Journal 15:6910-6919. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hahn, Y. 2009. Molecular Evolution of TEPP Protein Genes in Metazoans. Pages 14-Jan Biochemical Genetics. | 2009 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Echinoderms; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Tunicates | ||
| Hii, Y. S., C. L. Soo, and H. C. Liew. 2009. Feeding of scleractinian coral, Galaxea fascicularis, on Artemia salina nauplii in captivity. Aquaculture International 17:363-376. | 2009 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | ||
| Freshwater, D. W., A. Hines, S. Parham, A. Wilbur, M. Sabaoun, J. Woodhead, L. Akins, B. Purdy, P. E. Whitfield, and C. B. Paris. 2009. Mitochondrial control region sequence analyses indicate dispersal from the US East Coast as the source of the invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans in the Bahamas. Marine Biology 156:1213-1221. | 2009 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Indonesia; Philippines | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Ivankovic, H., G. G. Ferrer, E. Tkalcec, S. Orlic, and M. Ivankovic. 2009. Preparation of highly porous hydroxyapatite from cuttlefish bone. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 20:1039-1046. | 2009 | Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Meirelles, M. E., M. Y. Tsuzuki, F. F. Ribeiro, R. C. Medeiros, and I. D. Silva. 2009. Reproduction, early development and larviculture of the barber goby, Elacatinus figaro (Sazima, Moura & Rosa 1997). Aquaculture Research 41:11-18. | 2009 | Cuba | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | |
| Kitson, R. R. A., A. Millemaggi, and R. J. K. Taylor. 2009. The Renaissance of alpha-Methylene-gamma-butyrolactones: New Synthetic Approaches. Angewandte Chemie-international Edition 48:9426-9451. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Haas, A., C. T. S. Little, H. Sahling, G. Bohrmann, T. Himmler, and J. Peckmann. 2009. Mineralization of vestimentiferan tubes at methane seeps on the Congo deep-sea fan. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 56:283-293. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Sediment |
| Philippot, R., F. Delangle, F.-X. Verdot, F. Farizon, and M.-H. Fessy. 2009. Femoral deficiency reconstruction using a hydroxyapatite-coated locked modular stem. A series of 43 total hip revisions. Orthopaedics and Traumatology: Surgery and Research 95:119-126. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Nakamura, K., M. Kitamura, and D. Uemura. 2009. Biologically active marine natural products. Heterocycles 78:17-Jan. | 2009 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Check, W. 2009. DNA sequencing grows virtuosic - And deep. Microbe 4:18-22. | 2009 | Biomedical Research Policies; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hutchins, D. A., M. R. Mulholland, and F. Fu. 2009. Nutrient cycles and marine microbes in a CO2-enriched ocean. Oceanography 22:128-145. | 2009 | Global | Review | CO2; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Substrate |
| Bell, J. D., E. Clua, C. A. Hair, R. Galzin, and P. J. Doherty. 2009. The Capture and Culture of Post-Larval Fish and Invertebrates for the Marine Ornamental Trade. Reviews in Fisheries Science 17:223-240. | 2009 | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Plankton; Substrate; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Kump, L. E., T. J. Bralower, and A. Ridgwell. 2009. Ocean acidification in deep time. Oceanography 22:94-107. | 2009 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Telles, C. A., L. A. Biasi, U. R. M. Neto, and C. Deschamps. 2009. Total phenols content, peroxidase activity and their relationship with the compatibility of the intergrafted seedlings of peach tree. Ciencia E Agrotecnologia 33:86-91. | 2009 | Japan | ||
| Sand, P. H. 2009. Diego Garcia: British-American legal black hole in the Indian ocean? Journal of Environmental Law 21:113-137. | 2009 | Global; Indian Ocean; Chagos Archipelago; India | Climate; Housing; Invasive Species; Military; Ocean Acidity | |
| Cooley, S. R. and S. C. Doney. 2009. Anticipating ocean acidification's economic consequences for commercial fisheries. Environmental Research Letters 4:24007. | 2009 | Review; Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fishing Sector; Molluscs; Ocean Acidity; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses | |
| Whittington, I. D. and G. C. Kearn. 2009. Two new species of entobdelline skin parasites (Monogenea, Capsalidae) from the blotched fantail ray, Taeniura meyeni, in the Pacific Ocean, with comments on spermatophores and the male copulatory apparatus. Acta Parasitologica 54:12-21. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean; Japan; Taiwan | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | |
| Vetter, W., N. Rosenfelder, J. F. Muller, C. Gaus, and N. J. Van Zee. 2009. CHED 128-Analysis of halogenated natural products in sediment and passive sampler samples from the Great Barrier Reef. Abstracts Of Papers Of The American Chemical Society 238. | 2009 | Australia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment | |
| Mooney, H., A. Larigauderie, M. Cesario, T. Elmquist, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, S. Lavorel, G. M. Mace, M. Palmer, R. Scholes, and T. Yahara. 2009. Biodiversity, climate change, and ecosystem services. Current Opinion In Environmental Sustainability 1:46-54. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kundzewicz, Z. W. and P. Doll. 2009. Will groundwater ease freshwater stress under climate change? Hydrological Sciences Journal-journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques 54:665-675. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Drinking Water Supply; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Vetter, W., P. Haase-Aschoff, N. Rosenfelder, T. Komarova, and J. F. Mueller. 2009. Determination of Halogenated Natural Products in Passive Samplers Deployed along the Great Barrier Reef, Queensland/Australia. Environmental Science and Technology 43:6131-6137. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| UNCWI. 2009. Healthy Watersheds through Healthy Forests. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Collaboration & Partnering; Drinking Water Supply; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2009. Rate and extent of decline in Corallium (pink and red coral) populations: existing data meet the requirements for a CITES Appendix II listing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 397:319-332. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Fishing Sector; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Special Use Permitting |
| Subach, F. V., V. N. Malashkevich, W. D. Zencheck, H. Xiao, G. S. Filonov, S. C. Almo, and V. V. Verkhusha. 2009. Photoactivation mechanism of PAmCherry based on crystal structures of the protein in the dark and fluorescent states. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:21097-21102. | 2009 | CO2 | ||
| Andersson, A. J., I. B. Kuffner, F. T. MacKenzie, P. L. Jokiel, K. S. Rodgers, and A. Tan. 2009. Net loss of CaCO3 from coral reef communities due to human induced seawater acidification. Biogeosciences Discussions 6:2163-2182. | 2009 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Ocean Acidity | |
| Monro, K. and A. G. B. Poore. 2009. The potential for evolutionary responses to cell-lineage selection on growth form and its plasticity in a red seaweed. American Naturalist 173:151-163. | 2009 | |||
| Dodds, W. K., W. A. Bouska, J. L. Eitzmann, T. J. Pilger, K. L. Pitts, A. J. Riley, J. T. Schloesser, and D. J. Thornbrugh. 2009. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environmental Science and Technology 43:13-19. | 2009 | Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Doney, S. C., V. J. Fabry, R.A. Feely, and J. A. Kleypas. 2009. Ocean acidification: the other CO2 problem. Annual Review of Marine Science 1:169-192. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Echinoderms; Ocean Acidity; Plankton | |
| Yampolsky, I. V., T. A. Balashova, and K. A. Lukyanov. 2009. Synthesis and Spectral and Chemical Properties of the Yellow Fluorescent Protein zFP538 Chromophore. Biochemistry 48:8077-8082. | 2009 | |||
| Levin, L. A., G. F. Mendoza, T. Konotchick, and R. Lee. 2009. Macrobenthos community structure and trophic relationships within active and inactive Pacific hydrothermal sediments. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 56:1632-1648. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Papua New Guinea | Field Study & Monitoring | Bivalves; Invertebrates; Marine Worms; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Kimura, A., E. Sakaguchi, and M. Nonaka. 2009. Multi-component complement system of Cnidaria: C3, Bf, and MASP genes expressed in the endodermal tissues of a sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis. Immunobiology 214:165-178. | 2009 | Anemones & Zooanthids | ||
| Williams, D. R., M. J. Walsh, and N. A. Miller. 2009. Studies for the Synthesis of Xenicane Diterpenes. A Stereocontrolled Total Synthesis of 4-Hydroxydictyolactone. Journal of the American Chemical Society 131:9038-9045. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Jones, R. W. 2009. Stratigraphy, palaeoenvironmental interpretation and uplift history of Barbados based on foraminiferal and other palaeontological evidence. Journal of Micropalaeontology 28:37-44. | 2009 | GIS & Maps | ||
| Xue, L. Y., X. C. Zhang, and W. Zhang. 2009. Larval release and settlement of the marine sponge Hymeniacidon perlevis (Porifera, Demospongiae) under controlled laboratory conditions. Aquaculture 290:132-139. | 2009 | Cuba | Lab Study; Model | Aquaculture; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. | 2009 | Southeast Asia; Europe | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Special Use Permitting; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Harrison, P. A. and the RUBICODE consortium. 2009. Conservation of biodiversity and ecosystem services in Europe: from threat to action. Pensoft. | 2009 | Europe | Review; Index or Indicator | Climate; Climate Regulation; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mitigation; Seawater Flow; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Gross-Aviv, T. and R. Vago. 2009. The role of aragonite matrix surface chemistry on the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 30:770-779. | 2009 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | ||
| Zajicek, P., S. Hardin, and C. Watson. 2009. A Florida marine ornamental pathway risk analysis. Reviews in Fisheries Science 17:156-169. | 2009 | Global; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species; Stony Coral; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Rhyne, A., R. Rotjan, A. Bruckner, and M. Tlusty. 2009. Crawling to Collapse: Ecologically Unsound Ornamental Invertebrate Fisheries. PLoS One 4:e8413. | 2009 | Florida | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Monetary Valuation | |
| Subramanian, S., M. Agarwal, T. Board, A. K. Gambhir, A. Hoad-Reddick, and M. Porter. 2009. Distally locked, fully hydroxyapatite coated modular long stems in salvage revision hip arthroplasty: a report of early experience. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Traumatology 0:5-Jan. | 2009 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sheppard, B. J. and C. F. Dungan. 2009. Exotic Perkinsus Sp Protozoa In An Imported Vietnamese Ornamental Clam (Tridacna Crocea) Maintained In A Home Aquarium. Journal of Zoo and Wildlife Medicine 40:140-146. | 2009 | Cuba; Vietnam | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Molluscs; Pathogens | |
| Steinke, D., T. S. Zemlak, and P. D. N. Hebert. 2009. Barcoding Nemo: DNA-Based Identifications for the Ornamental Fish Trade. PLoS One 4:e6300. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Special Use Permitting | |
| Harrington, M. 2009. Coral compound fights neuropathic pain. Lab Animal 38:280-280. | 2009 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources | ||
| Omann, I., A. Stocker, and J. Jager. 2009. Climate change as a threat to biodiversity: an application of the DPSIR approach. Ecological Economics 69:24-31. | 2009 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mitigation; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Viitala, R., V. Franklin, D. Green, C. Liu, A. Lloyd, and B. Tighe. 2009. Towards a synthetic osteo-odonto-keratoprosthesis. Acta Biomaterialia 5:438-452. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hoffmann, F., R. Radax, D. Woebken, M. Holtappels, G. Lavik, H. T. Rapp, M. L. Schlappy, C. Schleper, and M. M. M. Kuypers. 2009. Complex nitrogen cycling in the sponge Geodia barretti. Environmental Microbiology 11:2228-2243. | 2009 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges |
| Yuan, N., W. Tian, D. F. Chen, Y. G. Xing, D. He, D. F. Chen, L. Sun, and Z. Z. Gao. 2009. The research of degradability of a novel biodegradable coralline hydroxyapatite after implanted into rabbit. Journal Of Biomedical Materials Research Part A 741-746. | 2009 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Maehira, F., I. Miyagi, and Y. Eguchi. 2009. Effects of calcium sources and soluble silicate on bone metabolism and the related gene expression in mice. Nutrition 25:581-589. | 2009 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fish | |
| Graham, J. S., R. S. Stevenson, L. W. Mitcheltree, T. A. Hamilton, R. R. Deckert, R. B. Lee, and A. M. Schiavetta. 2009. Medical management of cutaneous sulfur mustard injuries. Toxicology 263:47-58. | 2009 | Florida | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Godbold, J. A., R. Rosenberg, and M. Solan. 2009. Species-Specific Traits Rather Than Resource Partitioning Mediate Diversity Effects on Resource Use. PLoS One 4:e7423. | 2009 | Echinoderms | ||
| Palmer, C. V., C. K. Modi, and L. D. Mydlarz. 2009. Coral Fluorescent Proteins as Antioxidants. PLoS One 4:e7298. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Kannan, R. and D. A. James. 2009. Effects of climate change on global biodiversity: A review of key literature. Tropical Ecology 50:31-39. | 2009 | Global; South & Central America | Review | Climate; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Pathogens |
| Purgley, H., J. Jewell, J. E. Deacon, R. M. Winokur, and V. M. Tripoli. 2009. Vitamin D-3 in Captive Green Sea Turtles (Chelonia mydas). Chelonian Conservation and Biology 8:161-167. | 2009 | Review | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Hotel & Food Services; Light; Sea Turtles | |
| Yamashita, T., Y. Nakao, S. Matsunaga, T. Oikawa, Y. Imahara, and N. Fusetani. 2009. A new antiangiogenic C24 oxylipin from the soft coral Sinularia numerosa. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 17:2181-2184. | 2009 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sauchyn, L. K. and R. E. Scheibling. 2009. Degradation of sea urchin feces in a rocky subtidal ecosystem: implications for nutrient cycling and energy flow. Aquatic Biology 6:99-108. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sea Urchins | |
| Fitt, W. K., R. D. Gates, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, J. C. Bythell, A. Jatkar, A. G. Grottoli, M. Gomez, P. Fisher, T. C. Lajuenesse, O. Pantos, R. Iglesias-Prieto, D. J. Franklin, L. J. Rodrigues, J. M. Torregiani, R. van Woesik, and M. P. Lesser. 2009. Response of two species of Indo-Pacific corals, Porites cylindrica and Stylophora pistillata, to short-term thermal stress: The host does matter in determining the tolerance of corals to bleaching. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373:102-110. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Roark, E. B., T. P. Guilderson, R. B. Dunbar, S. J. Fallon, and D. A. Mucciarone. 2009. Extreme longevity in proteinaceous deep-sea corals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:5204-5208. | 2009 | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Substrate | ||
| Ioannou, E., A. F. Abdel-Razik, X. Alexi, C. Vagias, M. N. Alexis, and V. Roussis. 2009. 9,11-Secosterols with antiproliferative activity from the gorgonian Eunicella cavolini. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 17:4537-4541. | 2009 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sakai, S., A. Kano, and K. Abe. 2009. Origin, glacial-interglacial responses, and controlling factors of a cold-water coral mound in NE Atlantic. Paleoceanography 24:PA2213. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sediment | |
| Parvatkar, R. R., C. D'Souza, A. Tripathi, and C. G. Naik. 2009. Aspernolides A and B, butenolides from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus. Phytochemistry 70:128-132. | 2009 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Philippot, R., F. Delangle, F. X. Verdot, F. Farizon, and M. H. Fessy. 2009. Femoral deficiency reconstruction using a hydroxyapatite-coated locked modular stem. A series of 43 total hip revisions. Orthopaedics & Traumatology-surgery & Research 95:119-126. | 2009 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Van Nguyen, L. and H. Kim Phan. 2008. Distribution and factors influencing on structure of reef fish communities in Nha Trang Bay Marine Protected Area, South-Central Vietnam. Environmental Biology of Fishes 82:309-324. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; China; Vietnam | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Fish; Hydrocoral; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Physical Variables; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Farina, O., R. Ramos, C. Bastidas, and E. Garcia. 2008. Biochemical responses of cnidarian larvae to mercury and benzo(a)pyrene exposure. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 81:553-557. | 2008 | Stony Coral; Toxics | ||
| Rhodes, K. L., M. H. Tupper, and C. B. Wichilmel. 2008. Characterization and management of the commercial sector of the Pohnpei coral reef fishery, Micronesia. Coral Reefs 27:443-454. | 2008 | Micronesia | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| McCauley, D. J., F. J. Joyce, and J. H. Lowenstein. 2008. Effects of the aquarium fish industry in costa rica on populations of the cortez rainbow wrasse thalassoma lucasanum [Efectos de la industria de peces ornamentales en costa rica sobre las poblacionesde la vieja de cortes thalassoma lucasanum]. Ciencias Marinas 34:445-451. | 2008 | Costa Rica | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Matsumoto, T., K. Yamano, M. Kitamura, and A. Hara. 2008. Ovarian follicle cells are the site of vitellogenin synthesis in the Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 149:293-298. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Bivalves; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Stony Coral | |
| Siddiq, A. and V. Dembitsky. 2008. Acetylenic anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry 8:132-170. | 2008 | Review | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges; Tunicates | |
| Suchitra, K. and M. Wanapat. 2008. Study on ruminal degradability of local plants by using nylon bag technique. Livestock Research for Rural Development 20. | 2008 | Cuba; Java | ||
| Goffredo, S. and H. R. Lasker. 2008. An adaptive management approach to an octocoral fishery based on the Beverton-Holt model. Coral Reefs 27:751-761. | 2008 | South & Central America; Bahamas; Caribbean | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Simmons, T. L. and W. H. Gerwick. 2008. Anticancer drugs of marine origin. Pages 431-452 in P. J. Walsh, S. L. Smith, L. E. Fleming, H. M. Solo-Gabriele, and W. H Gerwick, editors. Oceans and human health. Risks and remedies from the seas. Academic Press, San Diego. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Udwary, D. W., J. A. Kalaitzis, and B. S. Moore. 2008. Emerging marine biotechnologies: cloning of marine biosynthetic gene clusters. Pages 507-524 in P. J. Walsh, S. L. Smith, L. E. Fleming, H. M. Solo-Gabriele, and W. H. Gerwick, editors. Oceans and human health: risks and remedies from the seas. Academic Press, San Diego. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Kim, S.-K., Y. D. Ravichandran, S. B. Khan, and Y. T. Kim. 2008. Prospective of the cosmeceuticals derived from marine organisms. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering 13:511-523. | 2008 | Review | Algae; Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sussman, M., B. L. Willis, S. Victor, and D. G. Bourne. 2008. Coral pathogens identified for White Syndrome (WS) epizootics in the Indo-Pacific. PLoS One 3. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Palau; Marshall Islands | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Tang, Y., W. Tang, Y. Lin, J. Long, H. Wang, L. Liu, and W. Tian. 2008. Combination of bone tissue engineering and BMP-2 gene transfection promotes bone healing in osteoporotic rats. Cell Biology International 32:1150-1157. | 2008 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| DeBusk, B. C., M. Slattery, J.-S. Ki, J.-S. Lee, R. Aparicio-Fabre, and D. Schlenk. 2008. Species differences and effects of soft coral extracts from Sinnularia maximus on the expression of cytochrome P4501A and 2N in butterflyfishes (Chaetodon spp.). Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 34:483-492. | 2008 | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Medeiros, A. C., E. Vonallmen, M. Fukada, A. Samuelson, and T. Lau. 2008. Impact of the newly arrived seed-predating beetle Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) in Hawai'i. Pacific Conservation Biology 14:12-Jul. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Invasive Species; Ornamental Jewelry & Art | |
| Cuong, N. X., T. A. Tuan, P. Van Kiem, C. Van Minh, E. M. Choi, and Y. H. Kim. 2008. New cembranoid diterpenes from the Vietnamese soft coral Sarcophyton mililatensis stimulate osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 56:988-992. | 2008 | Japan; Vietnam | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| McNiven, I. J., J. Crouch, M. Weisler, N. Kemp, L. C. Martinez, J. Stanisic, M. Orr, L. Brady, S. Hocknull, and W. Boles. 2008. Tigershark Rockshelter (Baidamau Mudh): Seascape and settlement reconfigurations on the Sacred islet of Pulu, Western Zenadh Kes (Torres Strait). Australian Archaeology 66:15-32. | 2008 | Apex Fish Predators; Mangroves | ||
| Yuan, N., W. Tian, D.-F. Chen, Y.-G. Xing, D. He, D.-F. Chen, L. Sun, and Z.-Z. Gao. 2008. Degradation of degradable coral-hydroxyapatite after implanted into rabbit and its effect on bone healing. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:9614-9618. | 2008 | Medical Centers; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Zhang, H.-T., K. Liu, D.-Z. Cai, and Y.-J. Zeng. 2008. Effect of coral hydroxyapatite on the osteogenic property of platelet-rich plasma-induced human bone marrow stromal stem cells. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:8815-8818. | 2008 | Lab Study | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Slattery, M. and V. J. Paul. 2008. Indirect effects of bleaching on predator deterrence in the tropical Pacific soft coral Sinularia maxima. Marine Ecology Progress Series 354:169-179. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Octocoral; Sunscreen Use; Zooxanthellae |
| Rocha, L. A. and B. W. Bowen. 2008. Speciation in coral-reef fishes. Journal of Fish Biology 72:1101-1121. | 2008 | Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Poza, J. J., R. Fernandez, F. Reyes, J. Rodriguez, and C. Jimenez. 2008. Isolation, biological significance, synthesis, and cytotoxic evaluation of new natural parathiosteroids A-C and analogues from the soft coral Paragorgia sp. Journal of Organic Chemistry 73:7978-7984. | 2008 | Madagascar | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Timm, J. and M. Kochzius. 2008. Geological history and oceanography of the Indo-Malay Archipelago shape the genetic population structure in the false clown anemonefish (Amphiprion ocellaris). Molecular Ecology 17:3999-4014. | 2008 | Southeast Asia; Indonesia | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Plankton; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Zhong, W., C. Moya, R. S. Jacobs, and R. D. Little. 2008. Synthesis and an evaluation of the bioactivity of the C-glycoside of pseudopterosin a methyl ether. Journal of Organic Chemistry 73:7011-7016. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petrov, P., P. Mokreva, C. B. Tsvetanov, and L. Terlemezyan. 2008. Colloidal aqueous dispersion of polyaniline nanotubes grafted non-covalently with poly(ethylene oxide)-block-poly(acrylic acid) copolymer. Colloid and Polymer Science 286:691-697. | 2008 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Carson, M. T. 2008. Refining earliest settlement in remote oceania: Renewed archaeological investigation at Unai Bapot, Saipan. Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology 3:115-139. | 2008 | Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Huigens, R. W. III, L. Ma, C. Gambino, P. D. R. Moeller, A. Basso, J. Cavanagh, D. J. Wozniak, and C. Melander. 2008. Control of bacterial biofilms with marine alkaloid derivatives. Molecular BioSystems 4:614-621. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Nakajima, K. and I. Takeuchi. 2008. Rearing method for Caprella mutica (Malacostraca: Amphipoda) in an exhibition tank in the Port of Nagoya Public Aquarium, with notes on reproductive biology. Journal of Crustacean Biology 28:171-174. | 2008 | Japan | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Chockley, B. R., C. M. St Mary, and C. W. Osenberg. 2008. Population sinks in the Upper Florida Keys: The importance of demographic variation in population dynamics of the marine shrimp Stenopus hispidus. Marine Ecology Progress Series 360:135-145. | 2008 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| Boyer, C. R., G. B. Fain, C. H. Gilliam, T. V. Gallagher, H. A. Torbert, and J. L. Sibley. 2008. Clean chip residual: A substrate component for growing annuals. HortTechnology 18:423-432. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Forestry; Nutrients; Substrate |
| Jones, A. M., N. E. Cantin, R. Berkelmans, B. Sinclair, and A. P. Negri. 2008. A 3D modeling method to calculate the surface areas of coral branches. Coral Reefs 27:521-526. | 2008 | Model | Stony Coral | |
| Ellis, J. M. and M. T. Crimmins. 2008. Strategies for the total synthesis of C2-C11 cyclized cembranoids. Chemical Reviews 108:5278-5298. | 2008 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Zhang, J., J. Guo, S. Li, B. Song, and K. Yao. 2008. Synthesis of β-tricalcium phosphate using sol-gel self-propagating combustion method. Frontiers of Chemistry in China 3:451-453. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Intoh, M. 2008. Ongoing archaeological research on Fais Island, Micronesia. Asian Perspectives 47:121-138. | 2008 | Micronesia | ||
| Changyun, W., L. Haiyan, S. Changlun, W. Yanan, L. Liang, and G. Huashi. 2008. Chemical defensive substances of soft corals and gorgonians. Acta Ecologica Sinica 28:2320-2328. | 2008 | China | Review | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Casu, M., D. Casu, T. Lai, P. Cossu, and M. Curini-Galletti. 2008. A molecular tool for genetic surveys in the red coral (Corallium rubrum): An Inter-Simple Sequence Repeats (ISSRs) perspective. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 36:77-83. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Ornamental Jewelry & Art |
| Li, Y., A. M. Sierra, H.-W. Ai, and R. E. Campbell. 2008. Identification of sites within a monomeric red fluorescent protein that tolerate peptide insertion and testing of corresponding circular permutations. Photochemistry and Photobiology 84:111-119. | 2008 | |||
| Mangano, C., F. Mangano, A. Piattelli, A. Macchi, A. Mangano, and L. La Colla. 2008. Bone tissue engineering vs porous hydroxyapatite in maxillary sinus lift [Osso ingegnerizzato versus idrossiapatite porosa nel rialzo del seno mascellare]. Italian Oral Surgery 7:45-59. | 2008 | Germany | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Schroder, P., R. Herzig, B. Bojinov, A. Ruttens, E. Nehnevajova, S. Stamatiadis, A. Memon, A. Vassilev, M. Caviezel, and J. Vangronsveld. 2008. Bioenergy to save the world: Producing novel energy plants for growth on abandoned land. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 15:196-204. | 2008 | Global; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Climate; CO2; Domestic Animal Waste; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Hoover, C. A., M. Slattery, N. M. Targett, and A. G. Marsh. 2008. Transcriptome and metabolite responses to predation in a South Pacific soft coral. Biological Bulletin 214:319-328. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Lab Study; Model | Octocoral; Special Use Permitting |
| Lee, D.-S., P. Nioche, M. Hamberg, and C. S. Raman. 2008. Structural insights into the evolutionary paths of oxylipin biosynthetic enzymes. Nature 455:363-368. | 2008 | Microorganisms; Substrate | ||
| Feitosa, C. V., B. P. Ferreira, and M. Elisabeth De Araujo. 2008. A rapid new method for assessing sustainability of ornamental fish by-catch from coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 59:1092-1100. | 2008 | Index or Indicator | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Kurihara, H. 2008. Effects of CO2-driven ocean acidification on the early developmental stages of invertebrates. Marine Ecology Progress Series 373:275-284. | 2008 | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Echinoderms; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jankun, J., T. Doerks, A. M. Aleem, W. Lysiak-Szydlowska, and E. Skrzypczak-Jankun. 2008. Do Human lipoxygenases have a PDZ regulatory domain? Current Molecular Medicine 8:768-773. | 2008 | Review | Pathogens; Special Use Permitting | |
| Taylor, F. J. R., M. Hoppenrath, and J. F. Saldarriaga. 2008. Dinoflagellate diversity and distribution. Biodiversity and Conservation 17:407-418. | 2008 | Fish; Plankton; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Francois, J. L. and J. R. Guzman. 2008. BWR fuel design for actinide recycling. Pages 1486-1494 in Societe Francaise d'Energie Nucleaire - International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants - ICAPP 2007, \The Nuclear Renaissance at Work\"". | 2008 | Discharges | ||
| Blum, C., A. J. Meixner, and V. Subramaniam. 2008. Spectral versatility of single reef coral fluorescent proteins detected by spectrally-resolved single molecule spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 9:310-315. | 2008 | |||
| Hawdon, A. A., R. J. Keen, D. A. Post, and S. N. Wilkinson. 2008. Hydrological recovery of rangeland following cattle exclusion. IAHS-AISH Publication 532-539. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Laurent, D., A.-S. Kerbrat, H. T. Darius, E. Girard, S. Golubic, E. Benoit, M.-P. Sauviat, M. Chinain, J. Molgo, and S. Pauillac. 2008. Are cyanobacteria involved in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning-like outbreaks in New Caledonia? Harmful Algae 7:827-838. | 2008 | New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Microorganisms; Molluscs |
| Holt, G. E., J. L. Halpern, C. C. Lynch, C. J. Devin, and H. S. Schwartz. 2008. Imaging analysis of the in vivo bioreactor: A preliminary study. Pages 1890-1896 in Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. | 2008 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Jones, A. M., S. Gardner, and W. Sinclair. 2008. Losing 'Nemo': Bleaching and collection appear to reduce inshore populations of anemonefishes. Journal of Fish Biology 73:753-761. | 2008 | Australia | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Pongprayoon, C. 2008. Outcome of porous implants: incidence of complications, management, and morbidity. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet 0. | 2008 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Salisbury, J., M. Green, C. Hunt, and J. Campbell. 2008. Coastal Acidification by Rivers: A Threat to Shellfish? EOS Transactions 89:513-514. | 2008 | Global | Climate; CO2; Discharges; Ocean Acidity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hunter, H. M. and R. S. Walton. 2008. Land-use effects on fluxes of suspended sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus from a river catchment of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Journal of Hydrology 356:131-146. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Figueiredo, J., L. Narciso, R. Turingan, and J. Lin. 2008. Efficiency of using emerald crabs Mithraculus sculptus to control bubble alga Ventricaria ventricosa (syn. Valonia ventricosa) in aquaria habitats. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 88:95-101. | 2008 | United Kingdom | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| WBCSD, WRI, and Meridian Institute. 2008. The corporate ecosystem services review: guidelines for identifying business risks and opportunities arising from ecosystem change. World Resources Institute, Washington DC. | 2008 | Global | Review | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Climate; Corporate Responses; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Vago, R. 2008. Cnidarians biomineral in tissue engineering: A review. Marine Biotechnology 10:343-349. | 2008 | Review | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hecht, A. D., D. Shaw, R. Bruins, V. Dale, K. Kline, and A. Chen. 2008. Good policy follows good science: using criteria and indicators for assessing sustainable biofuel production. Ecotoxicology | 2008 | Model; Index or Indicator | ||
| Santos, P. R., N. Added, J. H. Aburaya, and M. A. Rizzutto. 2008. Measurements of Sr/Ca in bones to evaluate differences in temperature. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms 266:1616-1618. | 2008 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Isaac, J. L., L. E. Valentine, and B. A. Goodman. 2008. Demographic responses of an arboreal marsupial, the common brushtail possum (Trichosurus vulpecula), to a prescribed fire. Population Ecology 50:101-109. | 2008 | Australia | Model | |
| Peshut, P. J., R. J. Morrison, and B. A. Brooks. 2008. Arsenic speciation in marine fish and shellfish from American Samoa. Chemosphere 71:484-492. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Samoa; American Samoa | Fishing Sector; Molluscs | |
| Hu, Q.-L. 2008. Nano-hydroxyapatite/collagen composites imitating cancellous bone for repair of massive bone defects in rabbits. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:8935-8938. | 2008 | Lab Study | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Lei, Z.-M. and M. Zhang. 2008. Study of root canal filling in dogs by using compound coral paste. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:1983-1986. | 2008 | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Li, R.-Q., G.-P. Zhang, Z.-Y. Sha, H.-Y. Gao, L.-Z. Ren, W. Dong, F. Zhao, and W. Wang. 2008. Liquid nano-materials for bone repair. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:1915-1918. | 2008 | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Li, T., H.-M. Zang, and T.-S. Tang. 2008. 1, 25-(OH)2VitD3 promotes osteogenesis and vascularization of tissue-engineered bone. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:2001-2005. | 2008 | Cuba | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Tang, Y.-C., Y.-Q. Wang, and W. Tang. 2008. Repairing mandibular defect by gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells combined with coral hydroxyapatite scaffold in osteoporotic rats. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 12:2601-2605. | 2008 | Lab Study; Model | Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ortiz, D. M. and B. N. Tissot. 2008. Ontogenetic patterns of habitat use by reef-fish in a Marine Protected Area network: A multi-scaled remote sensing and in situ approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 365:217-232. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate |
| Guinotte, J. M. and V. J. Fabry. 2008. Ocean acidification and its potential effects on marine ecosystems. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1134:320-342. | 2008 | Review | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Coralline Algae; Echinoderms; Ocean Acidity; Seagrasses | |
| Padove Cohen, S. A., H. Hatt, J. Kubanek, and N. A. McCarty. 2008. Reconstitution of a chemical defense signaling pathway in a heterologous system. Journal of Experimental Biology 211:599-605. | 2008 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Fish; Sponges | ||
| Salvat, B., A. Aubanel, M. Adjeroud, P. Bouisset, D. Calmet, Y. Chancerelle, N. Cochennec, N. Davies, A. Fougerousse, R. Galzin, E. Lagouy, C. Lo, C. Monier, C. Ponsonnet, G. Remoissenet, D. Schneider, A. Stein, M. Tatarata, and L. Villiers. 2008. Monitoring of French Polynesia coral reefs and their recent development [Le suivi de l'etat des recifs coralliens de Polynesie francaise et leur recente evolution]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:145-177. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Molluscs; Nutrients; Seastars; Sewage Treatment; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies |
| Waller, R. G. and A. R. Baco. 2007. Reproductive morphology of three species of deep-water precious corals from the Hawaiian archipelago: Gerardia sp., Corallium secundum, and Corallium lauuense. Bulletin of Marine Science 81:533-542. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Anemones & Zooanthids; Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art | |
| Tang, M. and Y. Yue. 2007. Research on redispersible polymer powder-sulphate aluminium cement seawater resistant material. Shenyang Jianzhu Daxue Xuebao (Ziran Kexue Ban)/Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science) 23:438-442. | 2007 | Artificial Habitat; Forestry | ||
| DiMasi, J. A. and H. G. Grabowski. 2007. The cost of biopharmaceutical R&D: is biotech different? Managerial and Decision Economics 28:469-479. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Pecheva, E., P. Montgomery, D. Montaner, and L. Pramatarova. 2007. White light scanning interferometry adapted for large-area optical analysis of thick and rough hydroxyapatite layers. Langmuir 23:3912-3918. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Chen, B. and G. Q. Chen. 2007. Resource analysis of the Chinese society 1980-2002 based on exergy-Part 4: Fishery and rangeland. Energy Policy 35:2079-2086. | 2007 | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector | ||
| Andersson, A. J., N. R. Bates, and F. T. Mackenzie. 2007. Dissolution of carbonate sediments under rising pCO2 and ocean acidification: Observations from Devil's Hole, Bermuda. Aquatic Geochemistry 13:237-264. | 2007 | Global; Bermuda | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Ocean Acidity; Sediment | |
| Radjasa, O. K., S. I. O. Salasia, A. Sabdono, J. Weise, J. F. Imhoff, C. Lammler, and M. J. Risk. 2007. Antibacterial activity of marine bacterium pseudomonas sp. associated with soft coral Sinularia polydactyla against Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus. International Journal of Pharmacology 3:170-174. | 2007 | Java; Indonesia | Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Su, J.-H., C.-F. Dai, H.-H. Huang, Y.-C. Wu, P.-J. Sung, C.-H. Hsu, and J.-H. Sheu. 2007. Terpenoid-related metabolites from a formosan soft coral Nephthea chabrolii. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 55:594-597. | 2007 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sung, P.-J., L.-F. Chuang, J. Kuo, J.-J. Chen, T.-Y. Fan, J.-J. Li, L.-S. Fang, and W.-H. Wang. 2007. Rumphellolides A-F, six new caryophyllane-related derivatives from the Formosan gorgonian coral Rumphella antipathies. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 55:1296-1301. | 2007 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Dai, X., Z. Wan, R. G. Kerr, and H. M. L. Davies. 2007. Synthetic and isolation studies related to the marine natural products (+)-elisabethadione and (+)-elisabethamine. Journal of Organic Chemistry 72:1895-1900. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ibarra-Alvarado, C., J. Alejandro Garcia, M. B. Aguilar, A. Rojas, A. Falcon, and E. P. Heimer de la Cotera. 2007. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of toxins obtained from the fire coral Millepora complanata. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C 146:511-518. | 2007 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Hydrocoral | |
| Santiago-Vazquez, L. Z., T. B. Bruck, W. M. Bruck, A. P. Duque-Alarcon, P. J. McCarthy, and R. G. Kerr. 2007. The diversity of the bacterial communities associated with the azooxanthellate hexacoral Cirrhipathes lutkeni. ISME Journal 1:654-659. | 2007 | Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Costantini, F., C. Fauvelot, and M. Abbiati. 2007. Genetic structuring of the temperate gorgonian coral (Corallium rubrum) across the western Mediterranean Sea revealed by microsatellites and nuclear sequences. Molecular Ecology 16:5168-5182. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art | |
| Chao, C.-H., H.-C. Huang, Y.-C. Wu, C.-K. Lu, C.-F. Dai, and J.-H. Sheu. 2007. Glycolipids from the Formosan soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 55:1720-1723. | 2007 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Chen, S.-P., J.-H. Su, A. F. Ahmed, C.-F. Dai, Y.-C. Wu, and J.-H. Sheu. 2007. Xeniaphyllane-derived terpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 55:1471-1475. | 2007 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| El-Gamal, A. A. H., S.-K. Wang, and C.-Y. Duh. 2007. Prenylbicyclogermacrane diterpenoids from the formosan soft coral Nephthea elongata. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 55:890-893. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kalimutho, M., A. Ahmad, and Z. Kassim. 2007. Isolation, characterization and identification of bacteria associated with mucus of Acropora cervicornis coral from Bidong Island, Terengganu, Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Science 26:27-39. | 2007 | Malaysia | Stony Coral | |
| Yang, J.-C., Q.-S. Yin, J. Lin, J. Li, H. Y. Huang, and Y. Zhang. 2007. Anti-tumor activity of self-made composite anti-tumor coral hydroxyapatite: An in vitro study. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:3508-3511. | 2007 | Cuba; China | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Al-Sofyani, A. A. and G. R. Niaz. 2007. A comparative study of the components of the hard coral Seriatopora hystrix and the soft coral Xenia umbellata along the Jeddah coast, Saudi Arabia. Revista de Biologia Marina y Oceanografia 42:207-219. | 2007 | Saudi Arabia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Octocoral; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Yin, B., Y. Zhang, H.-B. Zhang, and Q.-S. Yin. 2007. Biocompatibility of coralline hydroxyapatite/bone morphogenic protein composite for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:191-193. | 2007 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Yu, Y.-X., Z.-S. Deng, B.-J. Li, S. L. Zhang, Q. Zhou, and W. F. Xiao. 2007. Influence of nano-hydroxyapatite on the bone regeneration of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:6183-6186. | 2007 | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment | |
| Zhang, D.-Q., X. Tang, and W.-G. Zhang. 2007. Co-culture of osteoblasts induced from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with coral hydroxyapatite and the function of basic fibroblast growth factor. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:3512-3516. | 2007 | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Zhu, W.-M., D.-P. Wang, and J.-Y. Xiong. 2007. Biological characteristics and clinical application of scaffold materials for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:9781-9784. | 2007 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Khalesi, M. K., H. H. Beeftink, and R. H. Wijffels. 2007. Flow-dependent growth in the zooxanthellate soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 351:106-113. | 2007 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Erlandson, J. M., M. H. Graham, B. J. Bourque, D. Corbett, J. A. Estes, and R. S. Steneck. 2007. The kelp highway hypothesis: Marine ecology, the coastal migration theory, and the peopling of the Americas. Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology 2:161-174. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Leibowitz, S. G., P. J. Wigington, and M. C. Rains. 2007. The effects of non-navigable streams and adjacent wetlands on navigable waters: an approach for addressing information needs following the US Supreme Court's Rapanos and Carabell decisions. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment [inpress]. | 2007 | Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | ||
| Oigman-Pszczol, S. S., A. E. S. Oliveira, and J. C. Creed. 2007. Perceptions of coral in a coastal tourist town in Brazil. Coral Reefs 26:667-670. | 2007 | Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Sea Urchins; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Singh, D., V. Choudhary, and V. Koul. 2007. Radiation synthesis of interpenetrating polymer networks based on N-vinyl pyrrolidone - Acrylic acid copolymer and Gelatin. I. Swelling, morphology, and thermal characterization for biomedical applications. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 104:1456-1463. | 2007 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sukarmi, and O. K. Radjasa. 2007. Bioethical consideration in the search for bioactive compounds from reef's invertebrates. Journal of Applied Sciences 7:1235-1238. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Lund, K. and A. R. Wilbur. 2007. Habitat classification feasibility study for coastal and marine environments in Massachusetts. Massachusetts Office of Coastal Zone Management, Boston, MA. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Wetlands | |
| Lewis, S. E., G. A. Shields, B. S. Kamber, and J. M. Lough. 2007. A multi-trace element coral record of land-use changes in the Burdekin River catchment, NE Australia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 246:471-487. | 2007 | Australia; Europe | Agriculture; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sahu, M. K., K. Sivakumar, and L. Kannan. 2007. Marine realm: A treasure house for bioprospecting. Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Environmental Sciences 9:191-196. | 2007 | Global | Algae; Echinoderms; Housing; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges; Tunicates | |
| Nunn, P. D., T. Ishimura, W. R. Dickinson, K. Katayama, F. Thomas, R. Kumar, S. Matararaba, J. Davidson, and T. Worthy. 2007. The Lapita occupation at Naitabale, Moturiki Island, central Fiji. Asian Perspectives 46:96-132. | 2007 | Oman; Fiji | Bivalves; Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish | |
| Thiel, M., E. C. Macaya, E. Acuna, W. E. Arntz, H. Bastias, K. Brokordt, P. A. Camus, J. C. Castilla, L. R. Castro, M. Cortes, C. P. Dumont, R. Escribano, M. Fernandez, J. A. Gajardo, C. F. Gaymer, I. Gomez, A. E. Gonzalez, H. E. Gonzalez, P. A. Haye, and J.-E. Illanes. 2007. The Humboldt Current System of northern and central Chile - Oceanographic processes, ecological interactions and socioeconomic feedback. Oceanography and Marine Biology 45:195-344. | 2007 | South & Central America | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| Kashman, Y., A. Rudi, and D. Pappo. 2007. Recent heterocyclic compounds from marine invertebrates: Structure and synthesis. Pure and Applied Chemistry 79:491-505. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Marine Products; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Maruska, K. P. and K. A. Peyton. 2007. Interspecific spawning between a recent immigrant and an endemic damselfish (Pisces: Pomacentridae) in the Hawaiian Islands. Pacific Science 61:211-221. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Morrison, A. E. and T. L. Hunt. 2007. Human impacts on the nearshore environment: An archaeological case study from Kaua'i, Hawaiian Islands. Pacific Science 61:325-345. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Molluscs | |
| Chou, J., B. Ben-Nissan, A. H. Choi, R. Wuhrer, and D. Green. 2007. Conversion of coral sand to calcium phosphate for biomedical applications. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society 43:44-48. | 2007 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Cuypers, E., A. Yanagihara, J. D. Rainier, and J. Tytgat. 2007. TRPV1 as a key determinant in ciguatera and neurotoxic shellfish poisoning. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 361:214-217. | 2007 | Pathogens | ||
| Paul, V. J., K. E. Arthur, R. Ritson-Williams, C. Ross, and K. Sharp. 2007. Chemical defenses: From compounds to communities. Biological Bulletin 213:226-251. | 2007 | Lab Study | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Su, J.-H., F.-Y. Lin, H.-C. Huang, C.-F. Dai, Y.-C. Wu, W.-P. Hu, C.-H. Hsu, and J.-H. Sheu. 2007. Novel steroids from the soft coral Nephthea chabrolii. Tetrahedron 63:703-707. | 2007 | Taiwan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sung, P.-J., M. Y. Chiang, W.-T. Tsai, J.-H. Su, Y.-M. Su, and Y.-C. Wu. 2007. Chlorinated briarane-type diterpenoids from the gorgonian coral Ellisella robusta (Ellisellidae). Tetrahedron 63:12860-12865. | 2007 | Taiwan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ronnback, P., B. Crona, and L. Ingwall. 2007. The return of ecosystem goods and services in replanted mangrove forests: Perspectives from local communities in Kenya. Environmental Conservation 34:313-324. | 2007 | Kenya | Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Valuation | |
| Liu, L., R. Chen, Y. Lin, G. Li, W. Tian, and S. Li. 2007. Comparison among four kinds of bone tissue engineering scaffold. Key Engineering Materials 963-966. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petersen, D., J. Falcato, P. Gilles, and R. Jones. 2007. Sexual reproduction of scleractinian corals in public aquariums: Current status and future perspectives. International Zoo Yearbook 41:122-137. | 2007 | Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Stony Coral |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Military; Mitigation; Schools & Colleges | |
| Palmtag, M. R. and G. J. Holt. 2007. Experimental studies to evaluate larval survival of the fire shrimp, Lysmata debelius, to the juvenile stage. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 38:102-113. | 2007 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | ||
| Zhang, Z., G. Li, L. Yang, and X. Ning. 2007. Bioremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil by novel bioactive mineral carriers. Pages 394-399 in Battelle Press - 9th International In Situ and On-Site Bioremediation Symposium 2007. | 2007 | Lab Study | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Remediation | |
| Chen, M.-X. and Y.-W. Lin. 2007. Artificial composite bone in repairing bone defects. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:9797-9800. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Livengood, E. J. and F. A Chapman. 2007. The ornamental fish trade: an introduction with perspectives for responsible aquarium fish ownership. University of Florida IFAS Extension FA. | 2007 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. | 2007 | Aquaculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | ||
| Yang, J. C., Q. S. Yin, J. Lin, H. Y. Huang, H. W. Ding, Y. Zhang, and J. Li. 2007. Preparation of cisplatin-impregnated coral hydroxyapatite drug delivery system. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = Journal of Southern Medical University 27:283-285. | 2007 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Choi, A. H. and B. Ben-Nissan. 2007. Sol-gel production of bioactive nanocoatings for medical applications. Part II: Current research and development. Nanomedicine 2:51-61. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Mitchelmore, C. L., E. A. Verde, and V. M. Weis. 2007. Uptake and partitioning of copper and cadmium in the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Aquatic Toxicology 85:48-56. | 2007 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Stony Coral | |
| Barron, M., L. Franklin, J. Woodall Jr., S. Wingerter, H. Benghuzzi, and M. Tucci. 2007. Comparison of osteoconductive materials on MG63 osteoblast cell function. Pages 248-253 in Biomedical Sciences Instrumentation. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Affonso, P. R. A. M. and P. M. Galetti Jr. 2007. Genetic diversity of three ornamental reef fishes (Families Pomacanthidae and Chaetodontidae) from the Brazilian coast. Brazilian Journal of Biology 67:925-933. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Tsounis, G., S. Rossi, J.-M. Gili, and W. E. Arntz. 2007. Red coral fishery at the costa brava (NW Mediterranean): Case study of an overharvested precious coral. Ecosystems 10:975-986. | 2007 | Cuba; Spain | Review; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Special Use Permitting |
| Biel, K. Y., R. D. Gates, and L. Muscatine. 2007. Effects of free amino acids on the photosynthetic carbon metabolism of symbiotic dinoflagellates. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 54:171-183. | 2007 | Cuba | Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Froukh, T. and M. Kochzius. 2007. Genetic population structure of the endemic fourline wrasse (Larabicus quadrilineatus) suggests limited larval dispersal distances in the Red Sea. Molecular Ecology 16:1359-1367. | 2007 | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Peltier, R. 2007. Cover Story: Gas-fired top plants: Tenaska Virginia Generating Station, Scottsville, Virginia. Power 151. | 2007 | Natural Gas & Electric Power; Wholesale & Retail Trade | ||
| Fu, Z.-H. and A.-M. Wang. 2007. Tissue-engineered bone grafts in the repair of bone defects in rabbits: Evaluation of radionuclide bone imaging. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:4500-4503. | 2007 | Medical Centers; Military; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Li, J., Q.-S. Yin, Y. Zhang, J. C. Yang, and H. W. Zhou. 2007. Biological properties of Ag-impregnated composite coralline hydroxyapatite. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:3472-3475. | 2007 | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Nassiri, N. 2007. Industry news: Biocoral wins French patent after three years. Pages 7-Jun Biomedical Materials. | 2007 | France | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Shih, W.-J., S.-H. Wang, W.-L. Li, M.-H. Hon, and M.-C. Wang. 2007. The phase transition of calcium phosphate coatings deposited on a Ti-6Al-4V substrate by an electrolytic method. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 0:693-696. | 2007 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Lirman, D., N. R. Gracias, B. E. Gintert, A. C. R. Gleason, R. P. Reid, S. Negahdaripour, and P. Kramer. 2007. Development and application of a video-mosaic survey technology to document the status of coral reef communities. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 125:59-73. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Nassiri, N. 2007. Materials: Coral bone substitute proves able to heal bone fast and effectively. Pages 3-Jan Biomedical Materials. | 2007 | Europe; France | Collaboration & Partnering; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Iwamaru, A., E. Iwado, S. Kondo, R. A. Newman, B. Vera, A. D. Rodriguez, and Y. Kondo. 2007. Eupalmerin acetate, a novel anticancer agent from Carribean gorgonian octocorals, induces apoptosis in malignat glioma cells via the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 6:184-192. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Sponges | |
| Thomas, F. R. 2007. The behavioral ecology of shellfish gathering in Western Kiribati, Micronesia 1: Prey choice. Human Ecology 35:179-194. | 2007 | Micronesia; Kiribati | Model | Invertebrates |
| Van Alstyne, K. L., P. Schupp, and M. Slattery. 2006. The distribution of dimethylsulfoniopropionate in tropical Pacific coral reef invertebrates. Coral Reefs 25:321-327. | 2006 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Climate; Climate Regulation; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting; Sponges; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gong, W., C. Xiao, M. Hu, Y. Li, and S. Liu. 2006. Facies and environments of Jurassic reef-bearing strata in Anduo-Baqing area, northern Xizang (Tibet). Scientia Geologica Sinica 41:479-488. | 2006 | Sediment | ||
| Gutierrez, J., A. Sorlozano, M. J. Soto, and G. Piedrola. 2006. Evaluation of two automated systems for detection of bacteriuria. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis 20:118-120. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Rahman, M. A., Y. Isa, and T. Uehara. 2006. Studies on two closely related species of octocorallians: Biochemical and molecular characteristics of the organic matrices of endoskeletal sclerites. Marine Biotechnology 8:415-424. | 2006 | Octocoral; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Kumar, R. and V. Lakshmi. 2006. Two new glycosides from the soft coral Sinularia firma. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54:1650-1652. | 2006 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Puthongking, P., C. Patarapanich, S. Amnuoypol, K. Suwanborirux, A. Kubo, and N. Saito. 2006. Chemistry of ecteinascidins. Part 2. Preparation of 6′-O-acyl derivatives of stable ecteinascidin and evaluation of cytotoxicity. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54:1010-1016. | 2006 | Japan | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Tunicates | |
| Johannesson, K. H., D. L. Hawkins Jr., and A. Cortes. 2006. Do Archean chemical sediments record ancient seawater rare earth element patterns? Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70:871-890. | 2006 | Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Zhang, W., Y.-W. Guo, and Y. Gu. 2006. Secondary metabolites from the South China Sea invertebrates: Chemistry and biological activity. Current Medicinal Chemistry 13:2041-2090. | 2006 | China | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Echinoderms; Invertebrates; Molluscs; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Downs, C. A., R. H. Richmond, W. J. Mendiola, L. Rougee, and G. K. Ostrander. 2006. Cellular physiological effects of the MV Kyowa Violet fuel-oil spill on the hard coral, Porites lobata. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 25:3171-3180. | 2006 | Micronesia | Model | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Mangroves; Petroleum Spills; Stony Coral |
| Sawant, S., D. Youssef, A. Mayer, P. Sylvester, V. Wali, M. Arant, and K. El Sayed. 2006. Anticancer and anti-inflammatory sulfur-containing semisynthetic derivatives of sarcophine. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54:1119-1123. | 2006 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Rossi, S., J.-M. Gili, R. Coma, C. Linares, A. Gori, and N. Vert. 2006. Temporal variation in protein, carbohydrate, and lipid concentrations in Paramuricea clavata (Anthozoa, Octocorallia): Evidence for summer-autumn feeding constraints. Marine Biology 149:643-651. | 2006 | Octocoral | ||
| Hawgood, B. J. 2006. The marine biologist-Bob Endean. Toxicon 48:768-779. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Discharges; Marine Protected Areas; Seastars; Snails & Conch |
| Santiago-Vazquez, L. Z., L. K. Ranzer, and R. G. Kerr. 2006. Comparison of two total RNA extraction protocols using the marine gorgonian coral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae and its symbiont Symbiodinium sp. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology 9:598-603. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biotechnology Research & Development; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Knackstedt, M. A., C. H. Arns, T. J. Senden, and K. Gross. 2006. Structure and properties of clinical coralline implants measured via 3D imaging and analysis. Biomaterials 27:2776-2786. | 2006 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Ai, H.-W., J. N. Henderson, S. J. Remington, and R. E. Campbell. 2006. Directed evolution of a monomeric, bright and photostable version of Clavularia cyan fluorescent protein: Structural characterization and applications in fluorescence imaging. Biochemical Journal 400:531-540. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Stony Coral | |
| Rougee, L., C. A. Downs, R. H. Richmond, and G. K. Ostrander. 2006. Alteration of normal cellular profiles in the scleractinian coral (Pocillopora damicornis) following laboratory exposure to fuel oil. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 25:3181-3187. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Petroleum Spills; Stony Coral | |
| Adams, C. P. and V. V. Brantner. 2006. Estimating the cost of new drug development: is it really $802 million? Health Affairs 25:420-428. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Davidson, E. H. and D. H. Erwin. 2006. Gene regulatory networks and the evolution of animal body plans. Science 311:796-800. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Ble, M. C., R. Arfi, A. F. Yeboua, and K. J. Diopoh. 2006. Food quality of the trophic sources provided by an acadja (Ebrie lagoon, Ivory Coast, West Africa) [Qualite nutritive des sources alimentaires au sein d'un Acadja (Lagune ebrie, Cote d'Ivoire, Afrique de L'Ouest)]. Vie et Milieu 56:255-264. | 2006 | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Housing; Sediment | ||
| Gullo, V. P., J. McAlpine, K. S. Lam, D. Baker, and F. Petersen. 2006. Drug discovery from natural products. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 33:523-531. | 2006 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Microorganisms; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hunt, B. and A. C. J. Vincent. 2006. Scale and sustainability of marine bioprospecting for pharmaceuticals. Ambio 35:57-64. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Coughlin, M. J., J. S. Grimes, and M. P. Kennedy. 2006. Coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitute in hindfoot surgery. Foot and Ankle International 27:19-22. | 2006 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Gross, H. and G. M. Konig. 2006. Terpenoids from marine organisms: Unique structures and their pharmacological potential. Phytochemistry Reviews 5:115-141. | 2006 | Algae; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Vita-Finzi, C. and F. Leaney. 2006. The direct absorption method of 14C assay-historical perspective and future potential. Quaternary Science Reviews 25:1073-1079. | 2006 | CO2; Molluscs; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Reed, J. K., D. C. Weaver, and S. A. Pomponi. 2006. Habitat and fauna of deep-water Lophelia pertusa coral reefs off the southeastern U.S.: Blake Plateau, Straits of Florida, and Gulf of Mexico. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:343-375. | 2006 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | GIS & Maps | Biomedical Research Policies; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Pipelines; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Warner, M. E. and S. Berry-Lowe. 2006. Differential xanothophyll cycling and photochemical activity in symbiotic dinoflagellates in multiple locations of three species of Caribbean coral. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 339:86-95. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Fleury, B., J. Coll, and P. Sammarco. 2006. Complementary (secondary) metabolites in a soft coral: Sex-specific variability, inter-clonal variability, and competition. Marine Ecology 27:204-218. | 2006 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Octocoral; Stony Coral |
| Chen, B., G.-X. Pei, K. Wang, D. Jin, and K.-H. Wei. 2006. Experimental study on the repair of goat tibia defects with revascularized tissue engineered bone. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 10:164-169. | 2006 | Index or Indicator | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Lindberg, W. J., T. K. Frazer, K. M. Portier, F. Vose, J. Loftin, D. J. Murie, D. M. Mason, B. Nagy, and M. K. Hart. 2006. Density-dependent habitat selection and performance by a large mobile reef fish. Ecological Applications 16:731-746. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Carballo, J. L., E. Zubia, and M. J. Ortega. 2006. Biological and chemical characterizations of three new species of Dysidea (Porifera: Demospongiae) from the Pacific Mexican coast. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 34:498-508. | 2006 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Mexico | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Radhika, P. 2006. Chemical constituents and biological activities of the soft corals of genus Cladiella: A review. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 34:781-789. | 2006 | Review | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kelley Hart. 2006. The upper Neuse Clean Water Iniative Conservation Plan. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Improved Technology; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Utilities Policies |
| Song, H., S. R. Kim, H. J. Kim, J. H. Hwang, W. T. Kwon, and Y. Kim. 2006. Preparation and characterization of porous hydroxyapatite block using a HHP method. Key Engineering Materials 1067-1070. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ehrlich, H., P. Etnoyer, S. D. Litvinov, M. M. Olennikova, H. Domaschke, T. Hanke, R. Born, H. Meissner, and H. Worch. 2006. Biomaterial structure in deep-sea bamboo coral (Anthozoa: Gorgonacea: Isididae): perspectives for the development of bone implants and templates for tissue engineering. Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik 37:552-557. | 2006 | Model | Molluscs; Sponges | |
| Martin, C., H. G. Deters, and T. W. Nattkemper. 2006. Fusing biomedical multi-modal data for exploratory data analysis. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics) 798-807. | 2006 | GIS & Maps | Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Lecchini, D., S. Polti, Y. Nakamura, P. Mosconi, M. Tsuchiya, G. Remoissenet, and S. Planes. 2006. New perspectives on aquarium fish trade. Fisheries Science 72:40-47. | 2006 | Agriculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fishing Sector | ||
| Levy, O., Y. Achituv, Y. Z. Yacobi, N. Stambler, and Z. Dubinsky. 2006. The impact of spectral composition and light periodicity on the activity of two antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) in the coral Favia favus. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 328:35-46. | 2006 | Lab Study | Algae; Light; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Liu, X. D., S. P. Zhao, L. G. Sun, H. H. Luo, X. B. Yin, Z. Q. Xie, Y. H. Wang, K. X. Liu, X. H. Wu, X. F. Ding, and D. P. Fu. 2006. Geochemical evidence for the variation of historical seabird population on Dongdao Island of the South China Sea. Journal of Paleolimnology 36:259-279. | 2006 | China | Marine Birds; Sediment | |
| Chen, B., G. X. Pei, K. Wang, and G. H. Tang. 2006. Long-term observation of large weight-bearing bone defect in goats repaired with tissue engineering technique. Nan fang yi ke da xue xue bao = Journal of Southern Medical University 26:770-773. | 2006 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Shrestha, S. and S. K. Deo. 2006. Anthozoa red fluorescent protein in biosensing. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry 386:515-524. | 2006 | Biomedical Research Policies; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petersen, D., M. Laterveer, D. Van Bergen, M. Hatta, R. Hebbinghaus, M. Janse, R. Jones, U. Richter, T. Ziegler, G. Visser, and H. Schuhmacher. 2006. The application of sexual coral recruits for the sustainable management of ex situ populations in public aquariums to promote coral reef conservation - SECORE Project. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16:167-179. | 2006 | Japan; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Stony Coral |
| Huettel, M., C. Wild, and S. Gonelli. 2006. Mucus trap in coral reefs: Formation and temporal evolution of particle aggregates caused by coral mucus. Marine Ecology Progress Series 307:69-84. | 2006 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Olson, D. W. 2006. Gemstones. Mining Engineering 58:31-32. | 2006 | Ornamental Jewelry & Art | ||
| Bybee, D. R., J. H. Bailey-Brock, and C. S. Tamaru. 2006. Larval development of Sabellastarte spectabilis (Grube, 1878) (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) in Hawaiian waters. Scientia Marina 70:279-286. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Marine Worms | |
| Calado, R. 2006. Marine ornamental species from European waters: A valuable overlooked resource or a future threat for the conservation of marine ecosystems? Scientia Marina 70:389-398. | 2006 | Europe | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Wholesale & Retail Trade | |
| Wells, R. M. G. and J. Baldwin. 2006. Plasma lactate and glucose flushes following burst swimming in silver trevally (Pseudocaranx dentex: Carangidae) support the \releaser\" hypothesis". Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 143:347-352. | 2006 | Australia | Fish | |
| Amaral, A. C. Z. and S. Jablonski. 2005. Conservation of marine and coastal biodiversity in Brazil. Conservation Biology 19:625-631. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Rinkevich, B. 2005. Conservation of coral reefs through active restoration measures: Recent approaches and last decade progress. Environmental Science and Technology 39:4333-4342. | 2005 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Substrate; Wetland & Reef Restoration | |
| Cuif, J.-P. and Y. Dauphin. 2005. The two-step mode of growth in the scleractinian coral skeletons from the micrometre to the overall scale. Journal of Structural Biology 150:319-331. | 2005 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | |
| Willmott, M. E., K. D. Clements, and R. M. G. Wells. 2005. The influence of diet and gastrointestinal fermentation on key enzymes of substrate utilization in marine teleost fishes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 317:97-108. | 2005 | Australia | Complex Habitat & Resources; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Kim, Y. H., H. Song, D. H. Riu, S. R. Kim, H. J. Kim, and J. H. Moon. 2005. Preparation of porous Si-incorporated hydroxyapatite. Current Applied Physics 5:538-541. | 2005 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Lin, Y.-C., Y.-L. Huang, A. T. Khalil, M.-H. Chen, and Y.-C. Shen. 2005. Juncenolides F and G, two new briarane diterpenoids from Taiwanese Gorgonian Junceella juncea. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 53:128-130. | 2005 | Japan; Taiwan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hofmann, G. E., J. L. Burnaford, and K. T. Fielman. 2005. Genomics-fueled approaches to current challenges in marine ecology. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 20:305-311. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Muralidhar, P., M. M. Kumar, N. Krishna, C. B. Rao, and D. V. Rao. 2005. New sphingolipids and a sterol from a Lobophytum species of the Indian Ocean. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 53:168-171. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India; Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Chan, G. L. 2005. A study of the effects of the San Francisco oil spill on marine organisms. Page 8142 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Lab Study | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Petroleum Spills; Snails & Conch | |
| Chan, G. L. 2005. The five-year recruitment of marine life after the 1971 San Francisco oil spill. Page 3151 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Seastars; Snails & Conch | ||
| Dhalin, J. and J. Michel. 2005. Resource response guides. Page 7035 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | GIS & Maps | Bivalves; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Birds; Octopus & Squid; Petroleum Spills; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Hunter Jr., M. L. 2005. A mesofilter conservation strategy to complement fine and coarse filters. Conservation Biology 19:1025-1029. | 2005 | Agriculture; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Gischler, E. and W. Oschmann. 2005. Historical climate variation in Belize (Central America) as recorded in scleractinian coral skeletons. Palaios 20:159-174. | 2005 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Belize | GIS & Maps | Climate; CO2; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Yan, X.-H. and Y.-W. Guo. 2005. A pharmaceutical perspective on soft coral: Chemistry and bioactivity. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines 3:65-73. | 2005 | Review | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Iskander, M. M., A. E. El-Anssary, M. M. A. El-Mooty, and H. M. Nagy. 2005. Simplified method to simulate wave transformations across coral reefs. AEJ - Alexandria Engineering Journal 44:79-89. | 2005 | Egypt | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Shoreline Protection |
| Mak, K. K. W., H. Yanase, and R. Renneberg. 2005. Cyanide fishing and cyanide detection in coral reef fish using chemical tests and biosensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 20:2581-2593. | 2005 | Philippines | Review | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish |
| O'Reagain, P. J., J. Brodie, G. Fraser, J. J. Bushell, C. H. Holloway, J. W. Faithful, and D. Haynes. 2005. Nutrient loss and water quality under extensive grazing in the upper Burdekin river catchment, North Queensland. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:37-50. | 2005 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Rickaby, R. E. M. and D. P. Schrag. 2005. Biogeochemistry of carbonates: Recorders of past oceans and climate. Metal Ions in Biological Systems 44:241-268. | 2005 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate | ||
| Aoki M, K., R. Encarnacion-Dimayuga, and A. R. Cortes A. 2005. Toxicological evaluation of natural products using microtechnics [Evaluacion toxicologica de productos naturales usando microtecnicas]. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Farmaceuticas 36:17-Nov. | 2005 | South & Central America; Mexico | Invertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hardin, M. P. and R. S. Legore. 2005. Development of management policy for the marine ornamental fish and invertebrate fishery in Puerto Rico: A case study. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:139-144. | 2005 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Resource Use Management | |
| Mansur, H. S., A. A. P. Mansur, and M. M. Pereira. 2005. XRD, SEM/EDX and FTIR characterization of Brazilian natural coral. Key Engineering Materials 43-46. | 2005 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Symons, L. C., R. Pavia, and M. Hodges. 2005. Emergency response in National Marine Sanctuaries. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Coastal Defense; Security Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Tripati, S., M. Sujatha, R. V. Rao, and K. S. Rao. 2005. Use of timber in shipbuilding industry: Identification and analysis of timber from shipwrecks off Goa coast, India. Current Science 89:1022-1027. | 2005 | India | Forestry | |
| LeGore, R. S., M. P. Hardin, and D. Ter-Ghazaryan. 2005. Organization and operation of the marine ornamental fish and invertebrate export fishery in Puerto Rico. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:145-153. | 2005 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Worms; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Snails & Conch | |
| Kibler, S. R., M. A. Faust, M. W. Vandersea, S. M. Varnam, R. W. Litaker, and P. A. Tester. 2005. Water column structure and circulation in the Main Channel, Twin Cays, Belize. Atoll Research Bulletin 133-156. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Wong, J. T. Y. and A. C. M. Kwok. 2005. Proliferation of dinoflagellates: Blooming or bleaching. BioEssays 27:730-740. | 2005 | Algae | ||
| Cuif, J. P. and Y. Dauphin. 2005. The Environment Recording Unit in coral skeletons - A synthesis of structural and chemical evidences for a biochemically driven, stepping-growth process in fibres. Biogeosciences 2:61-73. | 2005 | Global | Model | |
| Murugan, R. and S. Ramakrishna. 2005. Crystallographic study of hydroxyapatite bioceramics derived from various sources. Crystal Growth and Design 5:111-112. | 2005 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Gasparini, J. L., S. R. Floeter, C. E. L. Ferreira, and I. Sazima. 2005. Marine ornamental trade in Brazil. Biodiversity and Conservation 14:2883-2899. | 2005 | Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Molluscs; Stony Coral | |
| Zaffe, D. 2005. Some considerations on biomaterials and bone. Micron 36:583-592. | 2005 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Radhika, P., P. R. Rao, J. Archana, and N. K. Rao. 2005. Anti-inflammatory activity of a new sphingosine derivative and cembrenoid diterpene (lobohedleolide) isolated from marine soft corals of Sinularia crassa Tixier-Durivault and Lobophytum species of the andaman and nicobar islands. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 28:1311-1313. | 2005 | Japan | Model | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Salin, K. R., T. M. Yohannan, and C. Mohanakumaran Nair. 2005. Fisheries and trade of seahorses, Hippocampus spp., in southern India. Fisheries Management and Ecology 12:269-273. | 2005 | India; Malaysia; United Arab Emirates | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Sponges; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Tanaka, J., M. Kuniyoshi, C. Tanaka, H. H. Issa, W. Balansa, M. Otsuka, W. P. Githige, and T. Higa. 2005. Diverse metabolites of coral reef organisms. Pure and Applied Chemistry 77:83-89. | 2005 | Oman | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Octocoral; Sponges | |
| Wacnik, P. W., C. M. Baker, M. J. Herron, B. T. Kren, B. R. Blazar, G. L. Wilcox, M. K. Hordinsky, A. J. Beitz, and M. E. Ericson. 2005. Tumor-induced mechanical hyperalgesia involves CGRP receptors and altered innervation and vascularization of DsRed2 fluorescent hindpaw tumors. Pain 115:95-106. | 2005 | Model | ||
| Nowak, D., M. Florek, J. Nowak, W. Kwiatek, J. Lekki, E. Zieba, P. G. Romero, B. Ben-Nissan, and A. Kuczumow. 2005. Micro-spectrometric investigations of inorganic components of the black corals for biomedical applications. Key Engineering Materials 297-300. | 2005 | GIS & Maps | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Badran, M. I., M. Rasheed, R. Manasrah, and T. Al-Najjar. 2005. Nutrient flux fuels the summer primary productivity in the oligotrophic waters of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Oceanologia 47:47-60. | 2005 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, M. M. Littler, D. S. Littler, B. J. Bedford, and C. Gasque. 2005. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: I. Nutrient stoichiometry of the invasive green alga Codium isthmocladum in the wider Caribbean indicates nutrient enrichment. Harmful Algae 4:1092-1105. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Kundu, B., M. K. Sinha, S. Mitra, and D. Basu. 2005. Synthetic hydroxyapatite-based integrated orbital implants: A human pilot trial. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology 53:235-241. | 2005 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Guilderson, T. P., J. E. Cole, and J. R. Southon. 2005. Pre-bomb Δ14C variability and the Suess effect in Cariaco Basin surface waters as recorded in hermatypic corals. Radiocarbon 47:57-65. | 2005 | CO2; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Shuman, C. S., G. Hodgson, and R. F. Ambrose. 2005. Population impacts of collecting sea anemones and anemonefish for the marine aquarium trade in the Philippines. Coral Reefs 24:564-573. | 2005 | Philippines | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector | |
| Jeyasekaran, G., K. Maheswari, P. Ganesan, R. J. Shakila, and D. Sukumar. 2005. Quality changes in ice-stored tropical wire-netting reef cod (Epinephelus merra). Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 29:165-182. | 2005 | Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Work, T. M. and R. A. Rameyer. 2005. Coral Reefs 24:384-390. | 2005 | Samoa; American Samoa | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Zooxanthellae |
| Bensaid, W., K. Oudina, V. Viateau, E. Potier, V. Bousson, C. Blanchat, L. Sedel, G. Guillemin, and H. Petite. 2005. De Novo reconstruction of functional bone by tissue engineering in the metatarsal sheep model. Tissue Engineering 11:814-824. | 2005 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Pramatarova, L., E. Pecheva, R. Presker, M. T. Pham, M. F. Maitz, and M. Stutzmann. 2005. Hydroxyapatite growth induced by native extracellular matrix deposition on solid surfaces. European Cells and Materials 9:12-Sep. | 2005 | Molluscs; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Watters, M. R. 2005. Tropical marine neurotoxins: Venoms to drugs. Seminars in Neurology 25:278-289. | 2005 | Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Invertivorous Fish; Microorganisms; Octopus & Squid; Snails & Conch | |
| Bruckner, A. W. 2005. The importance of the marine ornamental reef fish trade in the wider Caribbean. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:127-137. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Maldives; Sri Lanka; India; Japan; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Caribbean; Europe | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Corallivorous Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Zhang, K., L. F. Francis, H. Yan, and A. Stein. 2005. Apatite converted from 3-D ordered macroporous sol-gel bioactive glass (3DOM-BG) particles. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 88:587-592. | 2005 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Bongiorni, L. and B. Rinkevich. 2005. The pink-blue spot syndrome in Acropora eurystoma (Eilat, Red Sea): A possible marker of stress? Zoology 108:247-256. | 2005 | Lab Study | Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Bender, K. and R. Taylor. 2005. Oil spill contingency planning in Thailand. Page 5512 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | Thailand | Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Petroleum Spills; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bennett, V. and D. Noviello. 2005. Response to the grounding of the F/V Ei Jyu Maru No. 21. Page 7183 in 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Palau; Guam | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Coastal Defense; Finfish Harvest; Infrastructure; Petroleum Spills | |
| Kamel, H. N. and M. Slattery. 2005. Terpenoids of Sinularia: Chemistry and biomedical applications. Pharmaceutical Biology 43:253-269. | 2005 | Review | Biotechnology Research & Development; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Puverel, S., E. Tambutte, L. Pereira-Mouries, D. Zoccola, D. Allemand, and S. Tambutte. 2005. Soluble organic matrix of two Scleractinian corals: Partial and comparative analysis. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 141:480-487. | 2005 | Molluscs; Stony Coral | ||
| Lindquist, N., P. H. Barber, and J. B. Weisz. 2005. Episymbiotic microbes as food and defence for marine isopods: Unique symbioses in a hostile environment. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 272:1209-1216. | 2005 | Papua New Guinea | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Substrate | |
| [No author name available]. 2005. News: Mock ship grounding and oil spill in Florida keys National Marine Sanctuary. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50. | 2005 | Florida | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Complex Habitat & Resources; Petroleum Spills; Security Policies | |
| Holt, G. E., J. L. Halpern, T. T. Dovan, D. Hamming, and H. S. Schwartz. 2005. Evolution of an in vivo bioreactor. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 23:916-923. | 2005 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Andrefouet, S., M. Zubia, and C. Payri. 2004. Mapping and biomass estimation of the invasive brown algae Turbinaria ornata (Turner) J. Agardh and Sargassum mangarevense (Grunow) Setchell on heterogeneous Tahitian coral reefs using 4-meter resolution IKONOS satellite data. Coral Reefs 23:26-38. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Algae; Biotechnology Research & Development; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Seagrasses |
| Lunn, K. E. and M.-A. Moreau. 2004. Unmonitored trade in marine ornamental fishes: The case of Indonesia's Banggai cardinalfish (Pterapogon kauderni). Coral Reefs 23:344-351. | 2004 | Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector |
| 2004. Collaborative Network of Facilities for Science. US Environmental Protection Agency. | 2004 | Collaboration & Partnering | ||
| Prioli, G. 2004. Shellfish farming: Technologies and production. Veterinary Research Communications 28:51-56. | 2004 | Aquaculture | ||
| Beck, M. W., T. D. Marsh, S. E. Reisewitz, and M. L. Bortman. 2004. New tools for marine conservation: The leasing and ownership of submerged lands. Conservation Biology 18:1214-1223. | 2004 | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Bivalves; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Ashworth, J. S., R. F. G. Ormond, and H. T. Sturrock. 2004. Effects of reef-top gathering and fishing on invertebrate abundance across take and no-take zones. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 303:221-242. | 2004 | Egypt | Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Sea Urchins | |
| Grigg, R. W. 2004. Harvesting impacts and invasion by an Alien species decrease estimates of black coral yield off Maui, Hawai'i. Pacific Science 58:6-Jan. | 2004 | Fishing Sector; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Kolian, S. and A. Walker. 2004. Louisiana is losing critical reef habitat and job opportunities. Sea Technology 45:31-34. | 2004 | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing Sector; Oil & Gas Rigs; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Pipelines; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Tibbetts, J. 2004. The state of the oceans, part 2: delving deeper into the sea's bounty. Environmental Health Perspectives 112:A472-481. | 2004 | Global | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Biomedical Research Policies; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Tibbetts, J. 2004. The state of the oceans, part 1: eating away at a global food source. Environmental Health Perspectives 112:A282-A291. | 2004 | Global | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Pathogens | |
| Radhika, P., V. L. Rao, and H. Laatsch. 2004. Chemical constituents of a marine soft coral of the genus Lobophytum. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 52:1345-1348. | 2004 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sung, P.-J., M.-R. Lin, and L.-S. Fang. 2004. Briarane diterpenoids from the Formosan gorgonian coral Junceella fragilis. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 52:1504-1506. | 2004 | Taiwan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Yakovleva, I. and M. Hidaka. 2004. Diel fluctuations of mycosporine-like amino acids in shallow-water scleractinian corals. Marine Biology 145:863-873. | 2004 | Japan | Algae; Light; Stony Coral; Sunscreen Use | |
| Semmens, B. X., E. R. Buhle, A. K. Salomon, and C. V. Pattengill-Semmens. 2004. A hotspot of non-native marine fishes: Evidence for the aquarium trade as an invasion pathway. Marine Ecology Progress Series 266:239-244. | 2004 | Florida | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Ballast Discharge; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fish; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Social Organizations | |
| Nowak, R. 2004. Sewage nutrients fuel coral disease. New Scientist 181:13-Dec. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Agriculture; Algae; Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Avasthi, A. 2004. Releasing Nemo proves a disaster for native fish. New Scientist 183:13. | 2004 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Ballast Discharge; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species | ||
| Wiedenmann, J., S. Ivanchenko, F. Oswald, F. Schmitt, C. Rocker, A. Salih, K.-D. Spindler, and G. U. Nienhaus. 2004. EosFP, a fluorescent marker protein with UV-inducible green-to-red fluorescence conversion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101:15905-15910. | 2004 | Stony Coral | ||
| Salih, A., A. Larkum, T. Cronin, J. Wiedenmann, R. Szymczak, and G. Cox. 2004. Biological properties of coral GFP-type proteins provide clues for engineering novel optical probes and biosensors. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 5329:61-72. | 2004 | Australia | Sunscreen Use | |
| 2004. U.S. Ocean Action Plan: The Bush Administration�s Response to the U.S. Ocean Commission on Policy. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Pacific Ocean; Mexico | Climate; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Epstein, P. R. and C. Rogers, editors. 2004. INSIDE THE GREENHOUSE THE IMPACTS OF CO2 AND CLIMATE CHANGE ON PUBLIC HEALTH IN THE INNER CITY. Center for Health and the Global Environment Harvard Medical School, Boston, (MA, USA). | 2004 | Climate; CO2; Microorganisms; Pathogens | ||
| Sawant, S. S., P. W. Sylvester, M. A. Avery, P. Desai, D. T. A. Youssef, and K. A. El Sayed. 2004. Bioactive rearranged and halogenated semisynthetic derivatives of the marine natural product sarcophine. Journal of Natural Products 67:2017-2023. | 2004 | Model | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Guillaume, M. M. M. 2004. Corals and coral trade [Les coraux et leur commerce]. Bulletin de la Societe Zoologique de France 129:28-Nov. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Solomon Islands; Vanuatu; Fiji; Indonesia; Philippines; Taiwan; Europe; Spain; France | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Hydrocoral; Monetary Valuation; Octocoral; Ornamental Jewelry & Art |
| Iliescu, M., V. Nelea, J. Werckmann, I. N. Mihailescu, G. Socol, A. Bigi, and B. Bracci. 2004. Electron microscopy studies of octa-calcium phosphate thin films obtained by pulsed laser deposition. Pages 157-161 Thin Solid Films. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Shick, J. M. 2004. The continuity and intensity of ultraviolet irradiation affect the kinetics of biosynthesis, accumulation, and conversion of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in the coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnology and Oceanography 49:442-458. | 2004 | Lab Study | Light; Special Use Permitting; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kashman, Y. and A. Rudi. 2004. On the biogenesis of marine isoprenoids. Phytochemistry Reviews 3:309-323. | 2004 | Algae; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Ben-Nissan, B., A. Milev, and R. Vago. 2004. Morphology of sol-gel derived nano-coated coralline hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials 25:4971-4975. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ben-Nissan, B., A. Milev, R. Vago, M. Conway, and A. Diwan. 2004. Sol-Gel Derived Nano-Coated Coralline Hydroxyapatite for Load Bearing Applications. Key Engineering Materials 301-304. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Kamel, H. N., F. R. Fronczek, N. H. Fischer, and M. Slattery. 2004. A novel metabolite from the hybrid soft coral Sinularia maxima x Sinularia polydactyla: A biosynthetically mixed skeleton linking cembrane and africanane terpenoids. Tetrahedron Letters 45:1995-1997. | 2004 | Guam | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Blake, D. 2004. Biodiscovery - From reef to outback. Nature 429. | 2004 | Australia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kiriakoulakis, K., B. J. Bett, M. White, and G. A. Wolff. 2004. Organic biogeochemistry of the Darwin Mounds, a deep-water coral ecosystem, of the NE Atlantic. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 51:1937-1954. | 2004 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Plankton; Sediment | |
| McCutcheon, A. L., G. S. K. Kannangara, M. A. Wilson, and B. Ben-Nissan. 2004. Preliminary analysis of pore distributions using NMR in natural coral and hydrothermally prepared hydroxyapatite. Journal of Materials Science 39:5711-5717. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Toxics |
| Schellmann, G. and U. Radtke. 2004. A revised morpho- and chronostratigraphy of the Late and Middle Pleistocene coral reef terraces on Southern Barbados (West Indies). Earth-Science Reviews 64:157-187. | 2004 | Model | Beach & Land Formation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Sun, W. H., J. B. Lo, F. M. Robert, C. Ray, and C.-S. Tang. 2004. Phytoremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in tropical coastal soils: I. Selection of promising woody plants. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 11:260-266. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Military; Remediation; Salinity; Sediment |
| Piniak, G. A. and F. Lipschultz. 2004. Effects of nutritional history on nitrogen assimilation in congeneric temperate and tropical scleractinian corals. Marine Biology 145:1085-1096. | 2004 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Berlinck, R. G. S., E. Hajdu, R. M. Da Rocha, J. H. H. L. De Oliveira, I. L. C. Hernandez, M. H. R. Seleghim, A. C. Granato, E. V. R. De Almeida, C. V. Nunez, G. Muricy, S. Peixinho, C. Pessoa, M. O. Moraes, B. C. Cavalcanti, G. G. F. Nascimento, O. Thiemann, M. Silva, A. O. Souza, C. L. Silva, and P. R. Minarini. 2004. Challenges and Rewards of Research in Marine Natural Products Chemistry in Brazil. Journal of Natural Products 67:510-522. | 2004 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Collaboration & Partnering; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Molinski, T. F. 2004. Antifungal compounds from marine organisms. Current Medicinal Chemistry: Anti-Infective Agents 3:197-220. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Review | Invertebrates; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Severance, E. G., A. M. Szmant, and S. A. Karl. 2004. Single-copy gene markers isolated from the Caribbean coral, Montastraea annularis. Molecular Ecology Notes 4:167-169. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Stony Coral | |
| Bath, A., B. Shackleton, and C. Botica. 2004. Development of temperature criteria for marine discharge from a large industrial seawater supplies project in Western Australia. Water SA 30:648-654. | 2004 | Australia | Discharges; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pipelines; Water | |
| Verkhusha, V. V. and K. A. Lukyanov. 2004. The molecular properties and applications of Anthozoa fluorescent proteins and chromoproteins. Nature Biotechnology 22:289-296. | 2004 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | ||
| Petchey, F., M. Phelan, and J. P. White. 2004. New ΔR values for the southwest Pacific Ocean. Radiocarbon 46:1005-1014. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Sediment | |
| Kim, S. R., S. J. Jung, Y. J. Lee, H. Song, and Y. H. Kim. 2004. Silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite derived from coral. Key Engineering Materials 1941-1944. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Kim, S. R., J. H. Lee, Y. T. Kim, S. J. Jung, Y. J. Lee, H. Song, and Y. H. Kim. 2004. Bioactive Behaviors of Porous Si-Substituted Hydroxyapatite Derived from Coral. Key Engineering Materials 969-972. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Shipp, R. L. 2004. Harvest benefits: Marine reserves or traditional fishery management tools. Pages 125-131 in American Fisheries Society Symposium. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector |
| Wei, X., A. D. Rodriguez, P. Baran, R. G. Raptis, J. A. Sanchez, E. Ortega-Barria, and J. Gonzalez. 2004. Antiplasmodial cembradiene diterpenoids from a Southwestern Caribbean gorgonian octocoral of the genus Eunicea. Tetrahedron 60:11813-11819. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Shuman, C. S., G. Hodgson, and R. F. Ambrose. 2004. Managing the marine aquarium trade: Is eco-certification the answer? Environmental Conservation 31:339-348. | 2004 | Global; Indonesia; Philippines | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector |
| Marrero, J., A. D. Rodriguez, P. Baran, and R. G. Raptis. 2004. Ciereszkolide: Isolation and structure characterization of a novel rearranged cembrane from the Caribbean sea plume pseudopterogorgia kallos. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2004:3909-3912. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Germany | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Najafpour, H. D., A. H. Suzina, A. Nizam, and A. R. Samsudin. 2004. A comparative study of osseointegration phenomenon in coated and non-coated NiTi implants in a rabbit model. The Medical journal of Malaysia 121-122. | 2004 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Rosdan, S., K. A. Al-Salihi, A. H. Suzina, and A. R. Samsudin. 2004. In vivo study of CORAGRAF: a preliminary results. The Medical journal of Malaysia 111-112. | 2004 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | |
| Shamsuria, O., A. S. Fadilah, A. B. Asiah, M. R. Rodiah, A. H. Suzina, and A. R. Samsudin. 2004. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of biomaterials on human osteoblast cells CRL-1543; hydroxyapatite, natural coral and polyhydroxybutarate. The Medical journal of Malaysia 174-175. | 2004 | Cuba; Malaysia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| [No author name available]. 2004. Proceedings of SPIE - Genetically Engineered and Optical Probes for Biomedical Applications II. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 5329. | 2004 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Tissot, B. N., W. J. Walsh, and L. E. Hallacher. 2004. Evaluating effectiveness of a marine protected area network in West Hawai'i to increase productivity of an aquarium fishery. Pacific Science 58:175-188. | 2004 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Harris, C. T. and L. F. Cooper. 2004. Comparison of bone graft matrices for human mesenchymal stem cell-directed osteogenesis. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 68:747-755. | 2004 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ren, G.-H., X.-J. Liu, and G.-X. Pei. 2004. Biocompatibility of coral hydroxyapatite and adult human osteoblasts derived from bone marrow. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 8:4883-4885. | 2004 | Lab Study | Medical Centers; Military; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Harvey, L. D. D. 2004. Declining temporal effectiveness of carbon sequestration: Implications for compliance with the united national framework convention on climate change. Climatic change 63:259-290. | 2004 | Model | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Sun, Y., E. W. Castner Jr., C. L. Lawson, and P. G. Falkowski. 2004. Biophysical characterization of natural and mutant fluorescent proteins cloned from zooxanthellate corals. FEBS Letters 570:175-183. | 2004 | Europe | ||
| Moreira, S. M., M. Moreira-Santos, R. Ribeiro, and L. Guilhermino. 2004. The 'Coral Bulker' fuel oil spill on the north coast of portugal: Spatial and temporal biomarker responses in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicology 13:619-630. | 2004 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Petroleum Spills; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Devecioglu, D., T. F. Tozum, D. Sengun, and R. M. Nohutcu. 2004. Biomaterials in periodontal regenerative surgery: Effects of cryopreserved bone, commercially available coral, demineralized freeze-dried dentin, and cementum on periodontal ligament fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Journal of Biomaterials Applications 19:107-120. | 2004 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petersen, D., M. Laterveer, D. Van Bergen, and M. Kuenen. 2004. Transportation techniques for massive scleractinian corals. Zoo Biology 23:165-176. | 2004 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Pathogens; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Stony Coral |
| Kurata, M., T. Inoue, J. Serp, M. Ougier, and J.-P. Glatz. 2004. Electro-chemical reduction of MOX in LiCl. Journal of Nuclear Materials 328:97-102. | 2004 | |||
| Caldeira, K. and M. E. Wickett. 2003. Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 425:365. | 2003 | CO2 | ||
| Kolm, N. and A. Berglund. 2003. Wild populations of a reef fish suffer from the \nondestructive\" aquarium trade fishery". Conservation Biology 17:910-914. | 2003 | Japan; Indonesia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Sea Urchins |
| Johnson, J. E. and R. T. Hill. 2003. Sediment microbes of deep-sea bioherms on the northwest shelf of Australia. Microbial Ecology 46:55-61. | 2003 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Remediation; Sediment |
| Merkx, M. A. W., J. C. Maltha, and P. J. W. Stoelinga. 2003. Assessment of the value of anorganic bone additives in sinus floor augmentation: A review of clinical reports. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 32:6-Jan. | 2003 | South Africa | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Dubois, S., L. Barille, and C. Retiere. 2003. Efficiency of particle retention and clearance rate in the polychaete Sabellaria alveolata L. Comptes Rendus - Biologies 326:413-421. | 2003 | France | Algae; Aquaculture; Marine Worms | |
| Kim, Y. H., S. R. Kim, S. J. Jung, Y. J. Lee, and H. Song. 2003. Porous Hydroxyapatite Containing Silicon derived from Natural Coral. Pages 45-52 in Ceramic Transactions. | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ojika, M., M. K. Islam, T. Shintani, Y. Zhang, T. Okamoto, and Y. Sakagami. 2003. Three new cytotoxic acylspermidines from the soft coral, Sinularia sp. Bioscience, Biotechnology and Biochemistry 67:1410-1412. | 2003 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| [No author name available]. 2003. Bioceramics: Materials and Applications IV, Proceedings. in Ceramic Transactions. | 2003 | Biotechnology Research & Development; Manufacturing & Trade; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Karr, J. R. and D. N. Kimberling. 2003. A terrestrial arthropod index of biological integrity for shrub-steppe landscapes. Northwest Science 77:202-213. | 2003 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Arthropods; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Toxics | |
| Mahler, S. M., D. Y. Chin, and D. D. Van Dyk. 2003. The application of emerging technologies in genomics and proteomics to drug development. Journal of Pharmacy Practice and Research 33:11-Jul. | 2003 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Clarke, P. J., T. Komatsu, J. D. Bell, F. Lasi, C. P. Oengpepa, and J. Leqata. 2003. Combined culture of Trochus niloticus and giant clams (Tridacnidae): Benefits for restocking and farming. Aquaculture 215:123-144. | 2003 | Solomon Islands | Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Marine Protected Areas; Sediment | |
| DiMasi, J. A., R. W. Hansen, and H. G Grabowski. 2003. The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs. Journal of Health Economics 22:151-185. | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Calado, R., J. Lin, A. L. Rhyne, R. Araujo, and L. Narciso. 2003. Marine ornamental decapods - Popular, pricey, and poorly studied. Journal of Crustacean Biology 23:963-973. | 2003 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Seastars | ||
| Chockley, B. R. and C. M. St. Mary. 2003. Effects of body size on growth, survivorship, and reproduction in the banded coral shrimp, Stenopus hispidus. Journal of Crustacean Biology 23:836-848. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| [No author name available]. 2003. Key engineering materials: Bioceramics 15. Key Engineering Materials | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ho, K. T., A. Kuhn, R. M. Burgess, M. Pelletier, D. G. McGovern, J. Charles, and L. Patton. 2003. Use of marine toxicity identification and evaluation methods in determining causes of toxicity to fish in a marine aquarium facility. North American Journal of Aquaculture 65:14-20. | 2003 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | ||
| Tissot, B. N. and L. E. Hallacher. 2003. Effects of Aquarium Collectors on Coral Reef Fishes in Kona, Hawaii. Conservation Biology 17:1759-1768. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Tourism & Recreation; Travel Services & Tour Operators | |
| Olivotto, I., M. Cardinali, L. Barbaresi, F. Maradonna, and O. Carnevali. 2003. Coral reef fish breeding: The secrets of each species. Aquaculture 224:69-78. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Chen, B., G. X. Pei, K. Wang, D. Jin, K. H. Wei, and G. H. Ren. 2003. The method of accelerating osteanagenesis and revascularization of tissue engineered bone in big animal in vivo. Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan xue bao. Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae 25:26-31. | 2003 | Model; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Gilger, B. C., S. Pizzirani, L. C. Johnston, and N. R. Urdiales. 2003. Use of a hydroxyapatite orbital implant in a cosmetic corneoscleral prosthesis after enucleation in a horse. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 222:343-345+316. | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Pomponi, S. A., A. E. Wright, and J. K. Reed. 2003. Exploration in the South Atlantic bight: Discovery of new resources with pharmaceutical potential. Pages 1283-1284 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2003 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Smith, L. D., A. P. Negri, E. Philipp, N. S. Webster, and A. J. Heyward. 2003. The effects of antifoulant-paint-contaminated sediments on coral recruits and branchlets. Marine Biology 143:651-657. | 2003 | Australia | Lab Study | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Marine Protected Areas; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Hamann, M. T. 2003. Enhancing marine natural product structural diversity and bioactivity through semisynthesis and biocatalysis. Current Pharmaceutical Design 9:879-889. | 2003 | Review | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Borelli, G., N. Mayer-Gostan, P. L. Merle, H. De Pontual, G. Boeuf, D. Allemand, and P. Payan. 2003. Composition of biomineral organic matrices with special emphasis on turbot (Psetta maxima) otolith and endolymph. Calcified Tissue International 72:717-725. | 2003 | Sea Urchins; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Moberg, F. and P. Ronnback. 2003. Ecosystem services of the tropical seascape: Interactions, substitutions and restoration. Ocean and Coastal Management 46:27-46. | 2003 | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Mangroves; Seagrasses | ||
| Innes, J. K., R. Vago, and B. Ben-Nissan. 2003. Hydrothermal conversion and sol-gel coating of Red Sea coral. Key Engineering Materials 43-46. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Biotechnology Research & Development; Hydrocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ferraris, J. and P. Cayre. 2003. The reef fisheries of the South Pacific: Intuitive management versus an ecosystem management [Les pecheries recifales dans le Pacifique sud: D'une gestion intuitive vers une gestion ecosystemique raisonnee]. Oceanis 29:397-414. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation |
| Brooke, B. P., C. D. Woodroffe, C. V. Murray-Wallace, H. Heijnis, and B. G. Jones. 2003. Quaternary calcarenite stratigraphy on Lord Howe Island, southwestern Pacific Ocean and the record of coastal carbonate deposition. Quaternary Science Reviews 22:859-880. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Beach & Land Formation; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Pepponi, L. C. 2003. A voyage through the ocean depths [Un viaggio attraverso le profondità oceaniche]. Industria Italiana del Cemento 73:148-159. | 2003 | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Walsh, W. R., P. J. Chapman-Sheath, S. Cain, J. Debes, W. J. M. Bruce, M. J. Svehla, and R. M. Gillies. 2003. A resorbable porous ceramic composite bone graft substitute in a rabbit metaphyseal defect model. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21:655-661. | 2003 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Monzon, J. E. 2003. Coral and its role in Latin America over the last decade. Pages 3454-3456 in Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology - Proceedings. | 2003 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Legros, E. J. 2003. Exploration-Production. The day when peak production will come... [Exploration-Production. Le jour où le pic viendra...]. Pages 57-59 in Petrole et Gaz Informations. | 2003 | Global; Middle East; Saudi Arabia; Iran; Oman; Europe | Schools & Colleges | |
| Lam, K. K. Y. 2003. Coral recruitment onto an experimental pulverised fuel ash-concrete artificial reef. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:642-653. | 2003 | Artificial Habitat; Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral | ||
| Rezanka, T. and V. M. Dembitsky. 2003. Brominated oxylipins and oxylipin glycosides from red sea corals. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2003:309-316. | 2003 | Germany | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sea Urchins | |
| Zhukova, N. V. and E. A. Titlyanov. 2003. Fatty acid variations in symbiotic dinoflagellates from Okinawan corals. Phytochemistry 62:191-195. | 2003 | Japan | Hydrocoral; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| de Macedo, N. L., L. G. de Macedo, F. S. Matuda, S. M. Ouchi, A. S. Monteiro, and Y. R. Carvalho. 2003. Guided bone regeneration with subperiosteal implants of PTFE and hydroxyapatite physical barriers in rats. Brazilian dental journal 14:119-124. | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Moreira-Gonzalez, A., I. T. Jackson, T. Miyawaki, V. DiNick, and R. Yavuzer. 2003. Augmentation of the craniomaxillofacial region using porous hydroxyapatite granules. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 111:1808-1817. | 2003 | Review | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Thomas, F. R. 2003. Shellfish gathering in Kiribati, micronesia: Nutritional microbiological, and toxicological aspects. Ecology of Food and Nutrition 42:91-127. | 2003 | Micronesia; Kiribati | Bivalves; Invertebrates | |
| Zhao, L., T. Mao, F. Chen, K. Tao, L. Ma, S. Chen, and Z. Gao. 2003. Comparative study of three kinds of scaffold materials for bone tissue engineering. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 7:548-549. | 2003 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Amos, M. J. and S. W. Purcell. 2003. Evaluation of strategies for intermediate culture of Trochus niloticus (Gastropoda) in sea cages for restocking. Aquaculture 218:235-249. | 2003 | Vanuatu | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Molluscs | |
| McLaughlin, R. J. 2003. Foreign access to shared marine genetic materials: Management options for a quasi-fugacious resource. Ocean Development and International Law 34:297-348. | 2003 | Global | Model | Biochemical & Genetic Resources |
| Cuif, J. P., Y. YA NN IC KE Dauphin, J. Doucet, M. Salome, and J. Susini. 2003. XANES mapping of organic sulfate in three scleractinian coral skeletons. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 67:75-83. | 2003 | GIS & Maps | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | |
| Watanabe, T., I. Fukuda, K. China, and Y. Isa. 2003. Molecular analyses of protein components of the organic matrix in the exoskeleton of two scleractinian coral species. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 136:767-774. | 2003 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Stony Coral | ||
| Watanabe, K., M. Sekine, and K. Iguchi. 2003. Isolation of three marine prostanoids, possible biosynthetic intermediates for Clavulones, from the Okinawan soft coral Clavularia viridis. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 51:909-913. | 2003 | Japan | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Zhang, W., W. K. Liu, and C.-T. Che. 2003. Polyhydroxylated steroids and other constituents of the soft coral Nephthea chabroli. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 51:1009-1011. | 2003 | Japan; China | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ganesan, S., J. Felo, M. Saldana, V. F. Kalasinsky, M. R. Lewin-Smith, and J. F. Tomashefski Jr. 2003. Embolized crospovidone (poly[N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone]) in the lungs of intravenous drug users. Modern Pathology 16:286-292. | 2003 | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Abramovitch-Gottlib, L., D. Katoshevski, and R. Vago. 2002. A computerized tank system for studying the effect of temperature on calcification of reef organisms. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods 50:245-252. | 2002 | Global | Lab Study | Hydrocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Zooxanthellae |
| Gullstrom, M., M. De La Torre Castro, S. O. Bandeira, M. Bjork, M. Dahlberg, N. Kautsky, P. Ronnback, and M. C. Ohman. 2002. Seagrass ecosystems in the Western Indian Ocean. Ambio 31:588-596. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; Tanzania; Mozambique; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius; Reunion; India; South Africa; France | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Velasco, D., E. Gil, P. Garcia, and A. Guerrero. 2002. Efficacy of two semiautomatic methods for bacteriuria detection [Eficacia de dos metodos semiautomaticos para la exclusion de bacteriuria]. Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiologia Clinica 20:22-24. | 2002 | Medical Centers; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Seigler, D. S. 2002. Plant secondary metabolism. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA. | 2002 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Buckley, R. 2002. Surf tourism and sustainable development in Indo-Pacific Islands. I. The industry and the islands. Journal of Sustainable Tourism 10:405-424. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Cultural Policies; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Textiles & Apparel; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Alam, N., J. Hong, C.-O. Lee, J. S. Choi, K. S. Im, and J. H. Jung. 2002. Additional cytotoxic diacetylenes from the stony coral Montipora sp. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 50:661-662. | 2002 | Japan | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | |
| Schwartz, S. E. 2002. Challenges in EPA's coastal and ocean programs. Sea Technology 43:33-37. | 2002 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins |
| Vago, R., D. Plotquin, A. Bunin, I. Sinelnikov, D. Atar, and D. Itzhak. 2002. Hard tissue remodeling using biofabricated coralline biomaterials. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods 50:253-259. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Biotechnology Research & Development; Hydrocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Negri, A. P., L. D. Smith, N. S. Webster, and A. J. Heyward. 2002. Understanding ship-grounding impacts on a coral reef: Potential effects of anti-foulant paint contamination on coral recruitment. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:111-117. | 2002 | Australia | Lab Study | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Yamada, Y. 2002. Studies on discovery and synthesis of bioactive marine organic molecules. Yakugaku Zasshi 122:727-743. | 2002 | Japan | Lab Study | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Grabowski, H. G., J. Vernon, and J. A. DiMasi. 2002. Returns on research and development for the 1990s new drug introductions. PharmacoEconomics 20:11-29. | 2002 | Monetary Valuation; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Rosenberg, E. and Y. Ben-Haim. 2002. Microbial diseases of corals and global warming. Environmental Microbiology 4:318-326. | 2002 | Global | Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Oku, H., H. Yamashiro, K. Onaga, H. Iwasaki, and K. Takara. 2002. Lipid distribution in branching coral Montipora digitata. Fisheries Science 68:517-522. | 2002 | Stony Coral | ||
| Urban, K. 2002. Use of bioactive glass-ceramics in the management of tibial plateau fractures [Použiti bioaktivni sklokeramiky v lečeni zlomenin tibialniho plata]. Acta Chirurgiae Orthopaedicae et Traumatologiae Cechoslovaca 69:295-301. | 2002 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ben-Nissan, B., A. Milev, D. Green, M. Conway, R. Vago, and W. Walsh. 2002. Mechanical properties and characterisation of sol-gel coated coralline hydroxyapatite. Key Engineering Materials 379-382. | 2002 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Taberner, C., J. D. Marshall, J. P. Hendry, C. Pierre, and M. F. Thrilwall. 2002. Celestite formation, bacterial sulphate reduction and carbonate cementation of Eocene reefs and basinal sediments (Igualada, NE Spain). Sedimentology 49:171-190. | 2002 | Spain | Index or Indicator | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Rojas, A., M. Torres, J. I. Rojas, A. Feregrino, and E. P. Heimer-De La Cotera. 2002. Calcium-dependent smooth muscle excitatory effect elicited by the venom of the hydrocoral Millepora complanata. Toxicon 40:777-785. | 2002 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Hydrocoral | |
| Sung, P.-J. and M.-C. Chen. 2002. The heterocyclic natural products of gorgonian corals of genus Briareum exclusive of briarane-type diterpenoids. Heterocycles 57:1705-1715. | 2002 | Review | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Grigg, R. W. 2002. Precious corals in Hawaii: Discovery of a new bed and revised management measures for existing beds. Marine Fisheries Review 64:13-20. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fishing Sector; Ornamental Jewelry & Art | |
| [No author name available]. 2002. World's largest fuel cell installation at Verizon switching center. Fuel Cells Bulletin 2002:4-Mar. | 2002 | Internet & Telecommunications | ||
| Cebrian, J. 2002. Variability and control of carbon consumption, export, and accumulation in marine communities. Limnology and Oceanography 47:22-Nov. | 2002 | Mangroves; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses | ||
| Hooper, J. N. A. and J. A. Kennedy. 2002. Small-scale patterns of sponge biodiversity (Porifera) on Sunshine Coast reefs, eastern Australia. Invertebrate Systematics 16:637-653. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Sponges | |
| Samkutty, P. J. and R. H. Gough. 2002. Filtration treatment of dairy processing wastewater. Journal of Environmental Science and Health - Part A Toxic/Hazardous Substances and Environmental Engineering 37:195-199. | 2002 | Lab Study | Wastewater Discharge | |
| Visser, N. V., M. A. Hink, J. W. Borst, G. N. M. Van der Krogt, and A. J. W. G. Visser. 2002. Circular dichroism spectroscopy of fluorescent proteins. FEBS Letters 521:31-35. | 2002 | Europe | Stony Coral | |
| Kim, J. and E. J. Park. 2002. Cytotoxic anticancer candidates from natural resources. Current Medicinal Chemistry - Anti-Cancer Agents 2:485-537. | 2002 | Review | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Michaelis, W., R. Seifert, K. Nauhaus, T. Treude, V. Thiel, M. Blumenberg, K. Knittel, A. Gieseke, K. Peterknecht, T. Pape, A. Boetius, R. Amann, B. B. Jorgensen, F. Widdel, J. Peckmann, N. V. Pimenov, and M. B. Gulin. 2002. Microbial reefs in the black sea fueled by anaerobic oxidation of methane. Science 297:1013-1015. | 2002 | Cuba | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Microorganisms | |
| Burnett, J. W. and R. Pfau. 2002. Aquatic antagonists: Catalaphyllia jardinei sting. Cutis 70:27-28. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Seychelles; Japan; Vanuatu | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Octocoral | |
| Munday, P. L. and B. W. Molony. 2002. The energetic cost of protogynous versus protandrous sex change in the bi-directional sex-changing fish Gobiodon histrio. Marine Biology 141:1011-1017. | 2002 | Fish | ||
| Jinawath, S., D. Polchai, and M. Yoshimura. 2002. Low-temperature, hydrothermal transformation of aragonite to hydroxyapatite. Materials Science and Engineering C 22:35-39. | 2002 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Serumgard, J. R. 2002. Issues in scrap tire management. Technology 8:299-300. | 2002 | Civil Engineering & Construction; Fish; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Shoreline Protection | ||
| Straub, J. O. 2002. Coral gardener of the maldives. Biologist 49:53-57. | 2002 | Maldives | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Reckhow, Kenneth H.; Stow, Craig A.; Borsuk, Mark E. 2002. Uncertainty Between The Criterion And The Designated Use: Implications For Standards And Tmdl Margin Of Safety. Pages 1223-1228 in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | Model; Index or Indicator | Designated Uses; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Water | |
| Brown, B. E., C. A. Downs, R. P. Dunne, and S. W. Gibb. 2002. Preliminary evidence for tissue retraction as a factor in photoprotection of corals incapable of xanthophyll cycling. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 277:129-144. | 2002 | Algae; Light | ||
| Chen, B., G. X. Pei, K. Wang, Y. X. Fan, H. Wang, D. Jin, and K. H. Wei. 2002. Repair of tibial defect with tissue-engineered bone graft and radionuclide bone imaging in goats. Di yi jun yi da xue xue bao = Academic journal of the First Medical College of PLA 22:966-969. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ren, G. H., G. X. Pei, L. Q. Gu, K. Wang, D. Jin, K. H. Wei, B. Chen, and X. H. Mo. 2002. Biocompatibility of adult human osteoblasts with coral-derived hydroxyapatite in vitro. Di yi jun yi da xue xue bao = Academic journal of the First Medical College of PLA 22:974-978. | 2002 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ortega, M. J., E. Zubia, S. Rodriguez, J. L. Carballo, and J. Salva. 2002. Muricenones A and B: New degraded pregnanes from a gorgonian of the genus Muricea. European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2002:3250-3253. | 2002 | Germany | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sliwonik, I. 2002. Development of parietal bone based on ossification in the fetus [Rozwoj kości ciemieniowej kostniejacej na podłozu łacznotkankowym u płodow ludzkich w świetle badań anatomicznych, radiologicznych i biochemicznych.]. Annales Academiae Medicae Stetinensis 48:145-162. | 2002 | |||
| Mayer, A. 2002. Current marine pharmacology contributions to new drug development in the biopharmaceutical industry. Pharmaceutical News 9:479-482. | 2002 | Florida; Spain | Review | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Sacchetti, A., V. Subramaniam, T. M. Jovin, and S. Alberti. 2002. Oligomerization of DsRed is required for the generation of a functional red fluorescent chromophore. FEBS Letters 525:13-19. | 2002 | Europe | ||
| Shick, J. M. and W. C. Dunlap. 2002. Mycosporine-like amino acids and related gadusols: Biosynthesis, accumulation, and UV-protective functions in aquatic organisms. Annual Review of Physiology 64:223-262. | 2002 | Review | Algae; Light; Microorganisms; Special Use Permitting; Sunscreen Use | |
| Papina, M., Y. Sakihama, C. Bena, R. Van Woesik, and H. Yamasaki. 2002. Separation of highly fluorescent proteins by SDS-PAGE in Acroporidae corals. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 131:767-774. | 2002 | Light; Stony Coral | ||
| Al-Lihaibi, S. S., A. Al-Sofyani, G. R. Niaz, V. U. Ahmad, M. Noorwala, and F. Vali Mohammad. 2002. Long-chain wax esters and diphenylamine in fire coral Millepora dichotoma and Millepora platyphylla from Saudi Red Sea Coast. Scientia Marina 66:95-102. | 2002 | Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Osenberg, C. W., C. M. St. Mary, J. A. Wilson, and W. J. Lindberg. 2002. A quantitative framework to evaluate the attraction-production controversy. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat | |
| Sivakumar, M., I. Manjubala, and K. Panduranga Rao. 2002. Preparation, characterization and in-vitro release of gentamicin from coralline hydroxyapatite-chitosan composite microspheres. Carbohydrate Polymers 49:281-288. | 2002 | India | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Dahlhoff, E. P., B. A. Buckley, and B. A. Menge. 2001. Physiology of the rocky intertidal predator Nucella ostrina along an environmental stress gradient. Ecology 82:2816-2829. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Invertebrates; Snails & Conch | |
| Kim, C. G. 2001. Artificial reefs in Korea. Fisheries 26:15-18. | 2001 | Artificial Habitat; Fishing Sector; Substrate | ||
| Burja, A. M. and R. T. Hill. 2001. Microbial symbionts of the Australian Great Barrier Reef sponge, Candidaspongia flabellata. Hydrobiologia 461:41-47. | 2001 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Sponges | |
| Morrison, R. J., S. P. Narayan, and P. Gangaiya. 2001. Trace element studies in Laucala Bay, Suva, Fiji. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:397-404. | 2001 | Fiji | Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Daw, T. M., G. C. C. Rogers, P. Mapson, and J. E. Kynoch. 2001. Structure and management issues of the emerging ornamental fish trade in Eritrea. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:53-64. | 2001 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Collaboration & Partnering; Corallivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Ikeguchi, A. 2001. Fishing ground use and shellfish collecting activity in a diving fishery: A case study in Wagu, Shima, mie prefecture. Human Geography 53:66-81. | 2001 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| DiMasi, J. A. 2001. New drug development in the United States from 1963 to 1999. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 69:286-296. | 2001 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| DiMasi, J. A. 2001. Risks in new drug development: approval success rates for investigational drugs. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics 69:297-307. | 2001 | Model | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Borneman, E. H. and J. Lowrie. 2001. Advances in captive husbandry and propagation: An easily utilized reef replenishment means from the private sector? Bulletin of Marine Science 69:897-913. | 2001 | Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Octocoral; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Widdig, A. and D. Schlichter. 2001. Phytoplankton: A significant trophic source for soft corals? Helgoland Marine Research 55:198-211. | 2001 | Cuba | Algae; Octocoral; Plankton | |
| Ostrowski, A. C. and C. W. Laidley. 2001. Application of marine foodfish techniques in marine ornamental aquaculture: Reproduction and larval first feeding. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:191-204. | 2001 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | ||
| Rubec, P. J., F. Cruz, V. Pratt, R. Oellers, B. McCullough, and F. Lallo. 2001. Cyanide-free net-caught fish for the marine aquarium trade. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:37-51. | 2001 | Indonesia; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Rubec, P. J., V. R. Pratt, and F. Cruz. 2001. Territorial use rights in fisheries to manage areas for farming coral reef fish and invertebrates for the aquarium trade. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:119-134. | 2001 | Southeast Asia; Philippines | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management | |
| Salafsky, N., H. Cauley, G. Balachander, B. Cordes, J. Parks, C. Margoluis, S. Bhatt, C. Encarnacion, D. Russell, and R. Margoluis. 2001. A systematic test of an enterprise strategy for community-based biodiversity conservation. Conservation Biology 15:1585-1595. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Wilson, J., C. W. Osenberg, C. M. St. Mary, C. A. Watson, and W. J. Lindberg. 2001. Artificial reefs, the attraction-production issue, and density dependence in marine ornamental fishes. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:95-105. | 2001 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Fish | |
| Wood, E. 2001. Global advances in conservation and management of marine ornamental resources. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 3:65-77. | 2001 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artificial Habitat; Fish; Fishing Sector |
| Dubinsky, Z. and I. Berman-Frank. 2001. Uncoupling primary production from population growth in photosynthesizing organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic Science 63:17-Apr. | 2001 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Stolarski, J. and E. Roniewicz. 2001. Towards a new synthesis of evolutionary relationships and classification of Scleractinia. Journal of Paleontology 75:1090-1108. | 2001 | |||
| Dong, S. K., J. M. Wen, and J. Bi. 2001. Ectopic osteogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells induced by bone morphogenetic protein. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi = Zhongguo xiufu chongjian waike zazhi = Chinese journal of reparative and reconstructive surgery 15:17-20. | 2001 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Barnes, D. J. and R. B. Taylor. 2001. On the nature and causes of luminescent lines and bands in coral skeletons. Coral Reefs 19:221-230. | 2001 | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Salinity | |
| Sivakumar, M. and I. Manjubala. 2001. Preparation of hydroxyapatite/fluoroapatite-zirconia composites using Indian corals for biomedical applications. Materials Letters 50:199-205. | 2001 | India | Field Study & Monitoring | Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Halim, A. 2001. Grouper culture: An option for grouper management in Indonesia. Coastal Management 29:319-326. | 2001 | Indonesia | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Live Collection; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Pena, J., R. Z. LeGeros, R. Rohanizadeh, and J. P. LeGeros. 2001. CaCO3/Ca-P biphasic materials prepared by microwave processing of natural aragonite and calcite. Key Engineering Materials 267-270. | 2001 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| [No author name available]. 2001. Reef quest and daydream express. Work Boat World 20:37-38. | 2001 | Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Druffel, E. R. M., S. Griffin, T. P. Guilderson, M. Kashgarian, J. Southon, and D. P. Schrag. 2001. Changes of subtropical North Pacific radiocarbon and correlation with climate variability. Radiocarbon 43:15-25. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; CO2; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lange, R., M. Bergbauer, U. Szewzyk, and J. Reitner. 2001. Soluble proteins control growth of skeleton crystals in three coralline demosponges. Facies 195-202. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sponges | |
| Chen, C.-T., C.-H. Wang, K.-Y. Soong, and B.-J. Wang. 2001. Water temperature records from corals near the nuclear power plant in southern Taiwan. Science in China, Series D: Earth Sciences 44:356-362. | 2001 | China; Taiwan | ||
| Ben-Nissan, B., J. J. Russell, J. Hu, A. Milev, D. Green, R. Vago, W. Walsh, and R. M. Conway. 2001. Comparison of surface morphology in sol-gel treated coralline hydroxyapatite structures for implant purposes. Key Engineering Materials 959-962. | 2001 | Australia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Michalek-Wagner, K. and B. L. Willis. 2001. Impacts of bleaching on the soft coral Lobophytum compactum. Ii. Biochemical changes in adults and their eggs. Coral Reefs 19:240-246. | 2001 | Octocoral | ||
| Petersen, D. and R. Tollrian. 2001. Methods to enhance sexual recruitment for restoration of damaged reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:989-1000. | 2001 | Florida | Lab Study | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Castillo, I., C. Lodeiros, M. Nunez, and I. Campos. 2001. Evaluacion in vitro de sustancias antibacterianas producidas por bacterias aisladas de diferentes organismos marinos. Revista de Biologia Tropical 49:1213-1222. | 2001 | Bivalves; Boring Sponges; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Pathogens; Sponges; Stony Coral | ||
| Michalek-Wagner, K. 2001. Seasonal and sex-specific variations in levels of photo-protecting mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in soft corals. Marine Biology 139:651-660. | 2001 | Light; Octocoral | ||
| Fonseca, M. S. 2001. Comparative analysis of the functioning of disturbed and undisturbed coral reef and seagrass ecosystems in the Tortugas: phase I- establishing a baseline. Center for Coastal Fisheries and Habitat Research, Beaufort, North Carolina. | 2001 | Florida | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Complex Habitat & Resources; Plankton; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wulff, J. 2001. Assessing and monitoring coral reef sponges: Why and how? Bulletin of Marine Science 69:831-846. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | |
| Paulay, G. 2001. Benthic ecology and biota of Tarawa Atoll Lagoon: Influence of equatorial upwelling, circulation, and human harvest. Atoll Research Bulletin Jan-33. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch | |
| Dove, S.G., O. Hoegh-Guldberg, S. Ranganathan. 2001. Major colour patterns of reef-building corals are due to a family of GFP-like proteins. Coral Reefs 19:197-204. | 2001 | Model | Light; Stony Coral | |
| Faulkner, D. J. 2000. Marine pharmacology. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 77:135-145. | 2000 | Review | Aquaculture; Biotechnology Research & Development; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| World Conservation Monitoring, CE NT RE. 2000. Coral reefs and mangroves of the world from the World Conservation Monitoring Centre (WCMC). Coral reefs and mangroves of the world from the World Conservation Monitoring Centre (WCMC). | 2000 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Forestry; Mangroves |
| Esslemont, G., V. J. Harriott, and D. M. McConchie. 2000. Variability of trace-metal concentrations within and between colonies of Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:637-642. | 2000 | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Stony Coral | |
| Koh, E. G. L. and H. Sweatman. 2000. Chemical warfare among scleractinians: Bioactive natural products from Tubastraea faulkneri Wells kill larvae of potential competitors. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 251:141-160. | 2000 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Perry, C. T. 2000. Factors controlling sediment preservation on a north Jamaican fringing reef: A process-based approach to microfacies analysis. Journal of Sedimentary Research 70:633-648. | 2000 | Jamaica | Calcareous Macroalgae; Sediment | |
| Gautret, P. 2000. Intraskeletal organic matrices from reefal scleractiman corals: Early diagenetic transformations of biochemical characters and consequences for cementing processes [Matrices organiques intrasquelettiques des scleractiniaires recifaux: evolution diagen. Geobios 33:73-78. | 2000 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sponges; Stony Coral; Substrate | ||
| Lindel, T., H. Hoffmann, M. Hochgurtel, and J. R. Pawlik. 2000. Structure-activity relationship of inhibition of fish feeding by sponge- derived and synthetic pyrrole-imidazole alkaloids. Journal of Chemical Ecology 26:1477-1496. | 2000 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Moore, M. D., C. D. Charles, J. L. Rubenstone, and R. G. Fairbanks. 2000. U/Th-dated sclerosponges from the Indonesian Seaway record subsurface adjustments to west Pacific winds. Paleoceanography 15:404-416. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Solomon Islands; Indonesia | Model | Sponges |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hormansdorfer, S., H. Wentges, K. Neugebaur-Buchler, and J. Bauer. 2000. Isolation of Vibrio alginolyticus from seawater aquaria. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health 203:169-175. | 2000 | Model | Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Edgar, G. J. and N. S. Barrett. 2000. Impact of the Iron Baron oil spill on subtidal reef assemblages in Tasmania. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:36-49. | 2000 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Invertebrates; Petroleum Spills | |
| Maloney, K. A., L. A. Maguire, and E. A. Lind. 2000. NEUSE RIVER ESTUARY MODELING AND MONITORING PROJECT STAGE 1: ASSESSMENT OF STAKEHOLDER INTEREST AND CONCERNS TO INFORM LONG-TERM MODELING. 50237, Fuqua School of Business, Duke University, Durham, (NC, USA). | 2000 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Croteau, R., T. M. Kutchan, and N. G. Lewis. 2000. Natural products (secondary metabolites). Pages 1250-1318 in B. B. Buchanan, W.Gruissem, and R. Jones, editors. Biochemistry & molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, MD. | 2000 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Goldsworthy, S. D., R. P. Gales, M. Giese, and N. Brothers. 2000. Effects of the Iron Baron oil spill on little penguins (Eudyptula minor). I. Estimates of mortality. Wildlife Research 27:559-571. | 2000 | Australia | Petroleum Spills; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Chan, T.T.C. and Y. Sadovy. 2000. Profile of the marine aquarium fish trade in Hong Kong. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 2:197-213. | 2000 | Global | Review | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Designate Protected Species; Invertivorous Fish; Live Collection; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Labrosse, P., R. Fichez, R. Farman, and T. Adams. 2000. New Caledonia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 723-736. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Europe; France | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Sea Turtles; Special Use Permitting; Valuation | |
| Maragos, J. E. 2000. Hawaiian Islands (U.S.A.). Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 791-812. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Military; Pathogens; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Oakley, S., N. Pilcher, and E. Wood. 2000. Borneo. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 361-379. | 2000 | Global; Malaysia; Indonesia | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Forestry; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Sediment; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Cervi, G. A. 2000. War wrecks and the environment: Who's responsible for the legacy of war? A case study: Solomon Islands and the United States. Journal of Environmental Law and Litigation 14:351-399. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Japan; Solomon Islands | Finfish Harvest; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ten-Hage, L., N. Delaunay, V. Pichon, A. Coute, S. Puiseux-Dao, and J. Turquet. 2000. Okadaic acid production from the marine benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum arenarium Faust (Dinophyceae) isolated from Europa Island coral reef ecosystem (SW Indian Ocean). Toxicon 38:1043-1054. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Pathogens | |
| Richardson, B. J., P. K. S. Lam, and R. S. S. Wu. 2000. Hong Kong. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 535-547. | 2000 | China | Beaches & Nature Parks; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Land & Air Transportation; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Rajasuriya, A. and A. Premaratne. 2000. Sri Lanka. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 175-187. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Cuba; Sri Lanka; India | Agriculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Echinoderms; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Wetlands | |
| Wong, P. P. 2000. Malacca Strait including Singapore and Johore Straits. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 331-344. | 2000 | Thailand; Malaysia; Southeast Asia; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Commercial Fisheries; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands | |
| Zann, L. P. 2000. Northeastern Australia: The Great Barrier Reef region. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 611-628. | 2000 | Australia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Manjubala, I., M. Sivakumar, T. S. Sampath Kumar, and K. Panduranga Rao. 2000. Synthesis and characterization of functional gradient materials using Indian corals. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 11:705-709. | 2000 | India | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Miyaoka, H., H. Mitome, M. Nakano, and Y. Yamada. 2000. Xeniaoxolane: A new xenicane-type diterpenoid from the Okinawan soft coral, Xenia sp.; Absolute configurations of xeniaoxolane, xeniolide-A and xenialactol. Tetrahedron 56:7737-7740. | 2000 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. | 2000 | Global | Agriculture; Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fishing Sector; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral | |
| Ben-David-Zaslow, R. and Y. Benayahu. 2000. Biochemical composition, metabolism, and amino acid transport in planula-larvae of the soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens. Journal of Experimental Zoology 287:401-412. | 2000 | Nutrients; Octocoral | ||
| Lam, K. K. Y. 2000. Early growth of a pioneer recruited coral Oulastrea crispata (Scleractinia, Faviidae) on PFA-concrete blocks in a marine park in Hong Kong, China. Marine Ecology Progress Series 205:113-121. | 2000 | China | Artificial Habitat; Stony Coral | |
| Lam, K. K. Y. 2000. Sexual reproduction of a low-temperature tolerant coral Oulastrea crispata (Scleractinia, Faviidae) in Hong Kong, China. Marine Ecology Progress Series 205:101-111. | 2000 | China | Artificial Habitat; Marine Protected Areas; Stony Coral | |
| Chapman, F. A. 2000. Ornamental fish culture, freshwater. Pages 602-610 in Stickney, R. R., editor. Encyclopedia of aquaculture. John Wiley & Sons, York, NY. | 2000 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | ||
| U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. | 2000 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Palop del Rio, A., C. Labayru Echeverria, L. Lopez-Urrutia Lorente, C. Avellaneda Martinez, and A. Gomez Nieto. 2000. Application of bioluminescence for bacteriuria screening [Bioluminiscencia aplicada al cribado de bacteriuria]. Quimica Clinica 19:395-398. | 2000 | Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment | ||
| Regus, R. R. 2000. Ciguatera: A seafood poisoning caused by marine biotoxins [La ciguatera: Intoxicacion por biotoxinas marinas]. Anales de la Real Academia de Farmacia 66:433-447. | 2000 | Algae; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Hodgson, G. and J. A. Dixon. 2000. El Nido revisited: ecotourism, logging and fisheries. Pages 55-68 in H. S. J. Cesar, editor. Collected essays on the economics of coral reefs. CORDIO, Kalmar, Sweden. | 2000 | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Gautret, P., J.-P. Cuif, and J. Stolarski. 2000. Organic components of the skeleton of scleractinian corals - evidence from in situ acridine orange staining. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 45:107-118. | 2000 | Poland | Stony Coral | |
| Gordon, M. S., J. R. Hove, P. W. Webb, and D. Weihs. 2000. Boxfishes as unusually well-controlled autonomous underwater vehicles. Pages 663-671 in Physiological and Biochemical Zoology. | 2000 | Model | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Koslow, J. A., G. W. Boehlert, J. D. M. Gordon, R. L. Haedrich, P. Lorance, and N. Parin. 2000. Continental slope and deep-sea fisheries: Implications for a fragile ecosystem. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57:548-557. | 2000 | Global | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Fradkov, A. F., Y. Chen, L. Ding, E. V. Barsova, M. V. Matz, and S. A. Lukyanov. 2000. Novel fluorescent protein from Discosoma coral and its mutants possesses a unique far-red fluorescence. FEBS Letters 479:127-130. | 2000 | Europe | ||
| Gagan, M. K., L. K. Ayliffe, J. W. Beck, J. E. Cole, E. R. M. Druffel, R. B. Dunbar, and D. P. Schrag. 2000. New views of tropical paleoclimates from corals. Quaternary Science Reviews 19:45-64. | 2000 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia | Model | Climate; CO2; Sea Temperatures; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Morrall, C. E., T. S. Galloway, H. G. Trapido-Rosenthal, and M. H. Depledge. 2000. Characterisation of nitric oxide synthase activity in the tropical sea anemone Aiptasia pallida. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 125:483-491. | 2000 | Anemones & Zooanthids | ||
| Rice, M. A., A. Valliere, and A. Caporelli. 2000. A review of shellfish restoration and management projects in Rhode Island. Journal of Shellfish Research 19:401-408. | 2000 | Review | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Petroleum Spills; Ports & Harbors; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hajkowicz, S., M. Young, S. Wheeler, D. MacDonald, and D. Young. 2000. Supporting Decisions: Understanding Natural Resource Management Assessment Techniques - A report to the Land and Water Resources Research and Development Corporation. Primary Industries and Resources SA, Adelaide (South Australia). | 2000 | Australia | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Resource Use Management; Salinity | |
| MacMillan, J. B. and T. F. Molinski. 2000. Herbacic acid, a simple prototype of 5,5,5-trichloroleucine metabolites from the sponge Dysidea herbacea. Journal of Natural Products 63:155-157. | 2000 | Australia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Jakobs, S., V. Subramaniam, A. Schonle, T. M. Jovin, and S. W. Hell. 2000. EGFP and DsRed expressing cultures of Escherichia coli imaged by confocal, two-photon and fluorescence lifetime microscopy. FEBS Letters 479:131-135. | 2000 | Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms |
| Vrzheshch, P. V., N. A. Akovbian, S. D. Varfolomeyev, and V. V. Verkhusha. 2000. Denaturation and partial renaturation of a tightly tetramerized DsRed protein under mildly acidic conditions. FEBS Letters 487:203-208. | 2000 | Europe | ||
| Adey, H. W. 2000. Coral reef ecosystems and human health: Biodiversity counts! Ecosystem Health 6:227-236. | 2000 | Global | Monetary Valuation; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Adey, W. H., T. A. McConnaughey, A. M. Small, and D. M. Spoon. 2000. Coral reefs: Endangered, biodiverse, genetic resources. Pages 33-42 Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 3. | 2000 | Global | Lab Study | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Duguy, N., H. Petite, and E. Arnaud. 2000. Biomaterials and osseous regeneration [Biomateriaux et regeneration osseuse]. Annales de Chirurgie Plastique et Esthetique 45:364-376. | 2000 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hamel, E., D. L. Sackett, D. Vourloumis, and K. C. Nicolaou. 1999. The coral-derived natural products eleutherobin and sarcodictyins A and B: Effects on the assembly of purified tubulin with and without microtubule- associated proteins and binding at the polymer taxoid site. Biochemistry 38:5490-5498. | 1999 | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ronnback, P. 1999. The ecological basis for economic value of seafood production supported by mangrove ecosystems. Ecological Economics 29:235-252. | 1999 | Review | Aquaculture; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Molluscs; Monetary Valuation; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Seagrasses | |
| Weisler, M. I. 1999. The Antiquity of Aroid Pit Agriculture and Significance of Buried a Horizons on Pacific Atolls. Geoarchaeology - An International Journal 14:621-654. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Marshall Islands | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Sediment; Snails & Conch |
| Volkman, J. K. 1999. Australasian research on marine natural products: Chemistry, bioactivity and ecology. Marine and Freshwater Research 50:761-779. | 1999 | Australia | Review | Algae; Fish; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges; Sunscreen Use |
| Powis, T. G., N. Stanchly, C. D. White, P. F. Healy, J. J. Awe, and F. Longstaffe. 1999. A reconstruction of Middle Preclassic Maya subsistence economy at Cahal Pech, Belize. Antiquity 73:364-376. | 1999 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Agriculture; Corallivorous Fish; Land & Air Transportation; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Woodroffe, C. D., R. F. McLean, S. G. Smithers, and E. M. Lawson. 1999. Atoll reef-island formation and response to sea-level change: West Island, Cocos (Keeling) Islands. Marine Geology 160:85-104. | 1999 | Model; Index or Indicator | Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Al-Awadhi, F. M. A. 1999. The Year of the Ocean and its crucial importance to the Gulf. Desalination 123:127-133. | 1999 | Global | Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Littering; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waste Management Policies | |
| Druffel, E. R. M. and S. Griffin. 1999. Variability of surface ocean radiocarbon and stable isotopes in the southwestern Pacific. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 104:23607-23613. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | CO2; Salinity | |
| National Research Council (NRC). 1999. Part II: value of marine biodiversity to biomedicine. Pages 71-111 From monsoons to microbes. understanding the ocean�s role in human ealth. National Research Council, Commission on Geosciences, Environment, and Resources, Ocean Studies Board, Committee on the Ocean�s Role in Human Health, Washington, D.C. | 1999 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Rao, M. R., U. Venkatesham, M. V. R. Reddy, and Y. Venkateswarlu. 1999. Erratum: An unusual novel C29 steroid from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum (Journal of Natural Products (1999) 62 (785)). Journal of Natural Products 62:1352. | 1999 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Cuif, J. P., Y. Dauphin, A. Freiwald, P. Gautret, and H. Zibrowius. 1999. Biochemical markers of zooxanthellae symbiosis in soluble matrices of skeleton of 24 Scleractinia species. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 123:269-278. | 1999 | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Ruitenbeek, J. and C. Cartier. 1999. Issues in applied coral reef biodiversity valuation: results for Montego Bay, Jamaica. World Bank Research Committee Project RPO# 682-22. | 1999 | Jamaica | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Fishing Sector; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Merticaru, A. R. and V. Moagar-Poladian. 1999. Hollow glass for insulating layers. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 3680:440-446. | 1999 | Model | Sponges | |
| Boelen, P., I. Obernosterer, A. A. Vink, and A. G. J. Buma. 1999. Attenuation of biologically effective UV radiation in tropical atlantic waters measured with a biochemical DNA dosimeter. Photochemistry and Photobiology 69:34-40. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Cuba | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Boller, P. C. 1999. Home range size, movement behavior and habitat utilization in juvenile white-tailed deer on Webb Wildlife Center. Pages 41-42 NCASI Technical Bulletin. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Forestry | |
| Zeng, L. 1999. Search for new compounds and biologically active substances from Chinese marine organisms. Pure and Applied Chemistry 71:1147-1151. | 1999 | China | Algae; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Miyaoka, H., M. Nakano, K. Iguchi, and Y. Yamada. 1999. Three new xenicane diterpenoids from Okinawan soft coral of the genus, Xenia. Tetrahedron 55:12977-12982. | 1999 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Ben-David-Zaslow, R. and Y. Benayahu. 1999. Temporal variation in lipid, protein and carbohydrate content in the Red Sea soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 79:1001-1006. | 1999 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Morrison, R. J. and M. R. Naqasima. 1999. Fiji's Great Astrolabe Lagoon: Baseline study and management issues for a pristine marine environment. Ocean and Coastal Management 42:617-636. | 1999 | Fiji | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation |
| Dunlap, W. C. 1999. Sunscreens, oxidative stress and antioxidant functions in marine organisms of the Great Barrier Reef. Redox Report 4:304-306. | 1999 | Australia | Microorganisms; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Sunscreen Use | |
| Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 1999. Climate change, coral bleaching and the future of the world's coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 50:839-866. | 1999 | Global | Model | Climate; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Konig, G. M. and A. D. Wright. 1999. Cymbastela hooperi and Amphimedon terpenensis: Where do they really belong? Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 44:281-288. | 1999 | Australia | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Snails & Conch; Sponges | |
| Southgate, P. C. and K. Kavanagh. 1999. The effect of dietary n-3 highly unsaturated fatty acids on growth, survival and biochemical composition of the coral reef damselfish Acanthochromis polyacanthus. Aquatic Living Resource 12:31-36. | 1999 | Lab Study | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Fish; Octopus & Squid; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Albisetti, W., C. Sala, M. Corbella, A. Aloja, and F. Angaroni. 1999. Chondrocyte transplants. Growth and biointegration in bone graft substitute: Coralline hydroxyapatite. A preliminary study [Trapianti condrocitari. Crescita e biointegrazione in sostituti dell'osso: Esoscheletro di carbonato di calcio di corallo: Studio p. Minerva Ortopedica e Traumatologica 50:6-Jan. | 1999 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Pusceddu, A., G. Sara, M. Armeni, M. Fabiano, and A. Mazzola. 1999. Seasonal and spatial changes in the sediment organic matter of a semi-enclosed marine system (W-Mediterranean Sea). Hydrobiologia 397:59-70. | 1999 | Algae; Plankton; Sediment | ||
| Camoin, G. F., P. Gautret, L. F. Montaggioni, and G. Cabioch. 1999. Nature and environmental significance of microbialites in Quaternary reefs: The Tahiti paradox. Sedimentary Geology 126:271-304. | 1999 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Snedaker, S. C., R. J. Araujo, A. A. Capin, M. D. Hearon, and E. A. Ofengand. 1999. Organochlorine compounds in subtropical and tropical marine organisms: A meta-analysis. Pages 214-230 in Toxicology and Industrial Health. | 1999 | Algae; Octocoral; Seagrasses; Sponges | ||
| Burja, A. M., N. S. Webster, P. T. Murphy, and R. T. Hill. 1999. Microbial symbionts of Great Barrier Reef sponges. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 44:63-75. | 1999 | Australia | Algae; Microorganisms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Yamashiro, H., H. Oku, H. Higa, I. Chinen, and K. Sakai. 1999. Composition of lipids, fatty acids and sterols in Okinawan corals. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 122:397-407. | 1999 | Japan | Anemones & Zooanthids; Hydrocoral; Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Cragg, G. M. and D. J. Newman. 1999. Discovery and development of antineoplastic agents from natural sources. Cancer Investigation 17:153-163. | 1999 | Collaboration & Partnering; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Jordan, D. R., S. Gilberg, L. Mawn, S. Brownstein, and S. Z. Grahovac. 1998. The synthetic hydroxyapatite implant: A report on 65 patients. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 14:250-255. | 1998 | France | Index or Indicator | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Pitt, R.; Robertson, B.; and Field, R. 1998. Innovative Multi-Chambered Stormwater Control Device for Critical Source Areas. Proc. Adv. in Urban Wet Weather Pollut. Reduction , Cleveland, Ohio, WEF (CP3805), 141. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Carew, J. L., J. E. Mylroie, and S. J. Schwabe. 1998. The geology of South Andros Island, Bahamas: A reconnaissance report. Cave and Karst Science 25:57-66. | 1998 | Bahamas | Beach & Land Formation; Sediment | |
| Mayer, A. M. S., P. B. Jacobson, W. Fenical, R. S. Jacobs, and K. B. Glaser. 1998. Pharmacological characterization of the pseudopterosins: Novel anti- inflammatory natural products isolated from the caribbean soft coral, Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Life Sciences 62:401-407. | 1998 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| NEPA. 1998. MARICULTURE DRAFT POLICY AND REGULATION NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION AUTHORITY COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT DIVISION. National Environment & Planning agency. | 1998 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands | |
| Fleischer, R. C., C. E. McIntosh, and C. L. Tarr. 1998. Evolution on a volcanic conveyor belt: Using phylogeographic reconstructions and K-Ar-based ages of the Hawaiian Islands to estimate molecular evolutionary rates. Molecular Ecology 7:533-545. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii | ||
| Crow, G. L., M. J. Atkinson, B. Ron, S. Atkinson, A. D. K. Skillman, and G. T. F. Wong. 1998. Relationship of water chemistry to serum thyroid hormones in captive sharks with goitres. Aquatic Geochemistry 4:469-480. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Henning, G., D. K. Hofmann, and Y. Benayahu. 1998. Metamorphic processes in the soft corals Heteroxenia fuscescens and Xenia umbellata: The effect of protein kinase C activators and inhibitors. Invertebrate Reproduction and Development 34:35-45. | 1998 | Octocoral; Plankton | ||
| El Sayed, K. A., M. T. Hamann, C. A. Waddling, C. Jensen, S. Lee Kook, C. A. Dunstan, and J. M. Pezzuto. 1998. Structurally novel bioconversion products of the marine natural product sarcophine effectively inhibit JB6 cell transformation. Journal of Organic Chemistry 63:7449-7455. | 1998 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Wilcox, T. P. 1998. Large-Subunit Ribosomal RNA Systematics of Symbiotic Dinoflagellates: Morphology Does Not Recapitulate Phylogeny. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 10:436-448. | 1998 | Stony Coral | ||
| Carpenter, S. R., N. F. Caraco, D. L. Correll, R. W. Howarth, A. N. Sharpley, and V. H. Smith. 1998. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications 8:559-568. | 1998 | Review | Agriculture; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Hower Amy, E. 1998. Combining wave energy and artificial reef technology for sustainable coastal resource development. Pages 1691-1695 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1998 | Review | Artificial Habitat; Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Drinking Water Supply; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Vose, F. E. and W. G. Nelson. 1998. An assessment of the use of stabilized coal and oil ash for construction of artificial fishing reefs: Comparison of fishes observed on small ash and concrete reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 36:980-988. | 1998 | Florida | Artificial Habitat; Coal Mining; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Garson, M. J., A. E. Flowers, R. I. Webb, R. D. Charan, and E. J. McCaffrey. 1998. A sponge/dinoflagellate association in the haplosclerid sponge Haliclona sp.: Cellular origin of cytotoxic alkaloids by Percoll density gradient fractionation. Cell and Tissue Research 293:365-373. | 1998 | Australia | Sponges; Substrate | |
| Sheu, J.-H., P.-J. Sung, M.-C. Cheng, H.-Y. Liu, L.-S. Fang, C.-Y. Duh, and M. Y. Chiang. 1998. Novel cytotoxic diterpenes, excavatolides A-E, isolated from the Formosan gorgonian Briareum excavatum. Journal of Natural Products 61:602-608. | 1998 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Takahashi, S. and H. Wada. 1998. Radiocarbon age determination at Shizuoka University (2). Geoscience Reports of the Shizuoka University 25:19-29. | 1998 | Snails & Conch | ||
| De la Caffiniere, J.-Y., E. Viehweger, and A. Worcel. 1998. Radiological evolution of coral substitute implanted into lower limb cancellous bone madreporic coral versus coralline hydroxyapatite [Evolution radiologique a long terme du corail implante en os spongieux au membre inferieur: Corail madreporique versus h. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopedique et Reparatrice de l'Appareil Moteur 84:501-507. | 1998 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Barnes, D. K. A., A. Corrie, M. Whittington, M. A. Carvalho, and F. Gell. 1998. Coastal shellfish resource use in the Quirimba Archipelago, Mozambique. Journal of Shellfish Research 17:51-58. | 1998 | Mozambique | Bivalves; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Seagrasses; Skeletal Coral | |
| Lewis, AL AN. 1998. National Marine Aquarium, Plymouth. 32:22-23. | 1998 | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Docks & Marinas | ||
| Negri, A. and L. Llewellyn. 1998. Comparative analyses by HPLC and the sodium channel and saxiphilin 3H- saxitoxin receptor assays for paralytic shellfish toxins in crustaceans and molluscs from tropical North West Australia. Toxicon 36:283-298. | 1998 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs | |
| Rinkevich, B. and S. Shafir. 1998. Ex situ culture of colonial marine ornamental invertebrates: Concepts for domestication. Aquarium Sciences and Conservation 2:237-250. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Schools & Colleges; Tunicates | |
| Schlichter, D. and H. Brendelberger. 1998. Plasticity of the scleractinian body plan: Functional morphology and trophic specialization of Mycedium elephantotus (Pallas, 1766). Facies 227-242. | 1998 | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Nesheiwat, F., W. M. Brown, and K. M. Healey. 1998. Post-traumatic first metatarsal reconstruction using coralline hydroxyapatite. Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association 88:130-134. | 1998 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Adey, Walter H. 1998. Coral reefs: conservation by valuation and the utilization of pharmaceutical potential. Pages 72-5 in Coral Reefs: Challenges and Opportunities for Sustainable Management; Proceedings of an Associated Event of the Fifth Annual World Bank Conference on Environmentally and Socially Sustainable Development, World Bank, Washington, DC October 9-11,. | 1998 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Valuation | ||
| Duan, Y., J. Song, M. Cui, and B. Luo. 1998. Organic geochemical studies of sinking particulate material in China sea area (I) - Organic matter fluxes and distributional features of hydrocarbon compounds and fatty acids. Science in China, Series D: Earth Sciences 41:208-214. | 1998 | China | Plankton; Sediment | |
| Swetnam, T. W. and J. L. Betancourt. 1998. Mesoscale disturbance and ecological response to decadal climatic variability in the American Southwest. Journal of Climate 11:3128-3147. | 1998 | Climate | ||
| Nicolaou, K. C., N. Winssinger, D. Vourloumis, T. Ohshima, S. Kim, J. Pfefferkorn, J.-Y. Xu, and T. Li. 1998. Solid and solution phase synthesis and biological evaluation of combinatorial sarcodictyin libraries. Journal of the American Chemical Society 120:10814-10826. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Francesconi, K. A., K. L. Pedersen, and P. Hojrup. 1998. Sex-specific accumulation of Cd-metallothionein in the abdominal muscle of the coral prawn Metapenaeopsis crassissima from a natural population. Marine Environmental Research 46:541-544. | 1998 | Australia | Lab Study | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| Worheide, G. 1998. The reef cave dwelling ultraconservative coralline demosponge Astrosclera willeyana Lister 1900 from the Indo-Pacific. Facies 38:Jan-88. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Microorganisms; Special Use Permitting; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lindel, T. 1998. From D-arabinose to the marine natural product eleutherobin. Angewandte Chemie - International Edition 37:774-776. | 1998 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Dunlap, W. C., B. E. Chalker, W. M. Bandaranayake, and J. J. Wu Won. 1998. Nature's sunscreen from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Pages 41-51 in International Journal of Cosmetic Science. | 1998 | Australia | Light; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral; Sunscreen Use | |
| Falcon-Lang, H. 1998. The impact of wildfire on an early carboniferous coastal environment, North Mayo, Ireland. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 139:121-138. | 1998 | Algae; Discharges; Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Cavenagh, A. 1997. Greenpeace tries to obstruct oil licences. Engineer 285:14-15. | 1997 | Review | ||
| Jones, R. J. 1997. Zooxanthellae loss as a bioassay for assessing stress in corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 149:163-171. | 1997 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Druffel, E. R. M. 1997. Pulses of rapid ventilation in the North Atlantic surface ocean during the past century. Science 275:1454-1457. | 1997 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Melezhik, V. A., A. E. Fallick, and T. Clark. 1997. Two billion year old isotopically heavy carbon: Evidence from the Labrador Trough, Canada. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 34:271-285. | 1997 | Australia; Europe | Sediment | |
| Mines, D., S. Stahmer, and S. M. Shepherd. 1997. Poisonings: Food, fish, shellfish. Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America 15:157-177. | 1997 | Invertivorous Fish; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Chanas, B., J. R. Pawlik, T. Lindel, and W. Fenical. 1997. Chemical defense of the Caribbean sponge Agelas clathrodes (Schmidt). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 208:185-196. | 1997 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Jackson, J. B. C. 1997. Reefs since Columbus. Coral Reefs 16. | 1997 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Duckworth, A. R., C. N. Battershill, and P. R. Bergquist. 1997. Influence of explant procedures and environmental factors on culture success of three sponges. Aquaculture 156:251-267. | 1997 | Aquaculture; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Daily, G. C., S. Alexander, P. R. Ehrlich, L. Goulder, J. Lubchenco, P. A. Matson, H. A. Mooney, S. Postel, S. H. Schneider, D.Tilman, and G. M. Woodwell. 1997. Ecosystem services: benefits supplied to human societies by natural ecosystems. Issues in Ecology 1:1-18. | 1997 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Climate; Economic Markets & Policies; Forestry; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting |
| Gautret, P., J.-P. Cuif, and A. Freiwald. 1997. Composition of soluble mineralizing matrices in zooxanthellate and non-zooxanthellate scleractinian corals: Biochemical assessment of photosynthetic metabolism through the study of a skeletal feature. Facies 188-194. | 1997 | Stony Coral | ||
| Cuif, J.-P., Y. Dauphin, and P. Gautret. 1997. Biomineralization features in scleractinian coral skeletons: source of new taxonomic criteria. Boletin - Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural: Seccion Geologica 92:129-141. | 1997 | Stony Coral | ||
| White, E. W. 1997. Biomaterials innovation: It's a long road to the operating room. Materials Research Innovations 1:57-63. | 1997 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Zhang, D., J. Lin, and R. L. Creswell. 1997. Effect of eyestalk ablation on molt cycle and reproduction in the banded coral shrimp, Stenopus hispidus (Oliver). Journal of Shellfish Research 16:363-366. | 1997 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | ||
| Dvorak, J. 1997. Geology of palaeozoic sediments in the surroundings of Ostrov u Macochy (Moravian Karst, Moravia) [Geologie paleozoika v okoli Ostrova u Macochy (Moravský kras, Morava)]. Journal of the Czech Geological Society 42:105-110. | 1997 | Drinking Water Supply; Sediment | ||
| Ohgushi, H. 1997. Coral derived porous framework having different chemical compositions as a scaffold for osteoblastic differentiation. Materials Science Forum 250:209-220. | 1997 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. | 1997 | Global; Tanzania; Maldives; Fiji; Papua New Guinea; Southeast Asia; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Germany | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Health Policies; Live Collection; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Vallejo, B.M. Jr. 1997. An overview of the Philippine marine aquarium fish industry. Pages 1981-6 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1997 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | ||
| Gaillard, S., P. Pellerin, P. Dhellemmes, B. Pertuzon, J.-P. Lejeune, and J.-L. Christiaens. 1997. Strategy of craniofacial reconstruction after resection of spheno- orbital 'en plaque' meningiomas. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 100:1113-1120. | 1997 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| McCormick, M. I. and B. A. Kerrigan. 1996. Predation and its influence on the condition of a newly settled tropical demersal fish. Marine and Freshwater Research 47:557-562. | 1996 | Lab Study | Fish; Invertivorous Fish | |
| Perry, C. T. 1996. The rapid response of reef sediments to changes in community composition: Implications for time averaging and sediment accumulation. Journal of Sedimentary Research 66:459-467. | 1996 | Jamaica | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Molluscs; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Jensen, S. S., M. Aaboe, E. M. Pinholt, E. Hjorting-Hansen, F. Melsen, and I. Eystein Ruyter. 1996. Tissue Reaction and Material Characteristics of Four Bone Substitutes. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 11:55-66. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Poulsen, A. L. 1996. Coral reef gastropods - A sustainable resource? Pacific Conservation Biology 2:142-145. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Commercial Fisheries; Molluscs; Resource Use Management | |
| Magan, A. and U. Ripamonti. 1996. Geometry of porous hydroxyapatite implants influences osteogenesis in baboons (Papio ursinus). Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 7:71-78. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sivakumar, M., T. S. Sampath Kumar, K. L. Shantha, and K. Panduranga Rao. 1996. Development of hydroxyapatite derived from Indian coral. Biomaterials 17:1709-1714. | 1996 | India | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| De Peretti, F., C. Trojani, P. M. Cambas, R. Loubiere, and C. Argenson. 1996. Coral Graft As Support In The Surgical Treatment Of Articular Traumatic Depression [Le Corail Comme Soutien D'Un Enfoncement Articulaire Traumatique. Etude Prospective Au Membre Inferieur De 23 Cas]. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopedique et Reparatrice de l'Appareil Moteur 82:234-240. | 1996 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Evans, C. R., A. P. M. Lockwood, and A. J. Evans. 1996. Field Studies of the Population Dynamics of the Spotted Spiny Lobster Panulirus guttatus (Latreille) at Bermuda. Gulf of Mexico Science 14:55-64. | 1996 | Bermuda | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp |
| Walters, L. J., M. G. Hadfield, and C. M. Smith. 1996. Waterborne chemical compounds in tropical macroalgae: Positive and negative cues for larval settlement. Marine Biology 126:383-393. | 1996 | Algae; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrates; Marine Worms | ||
| Bohm, F., M. M. Joachimski, H. Lehnert, G. Morgenroth, W. Kretschmer, J. Vacelet, and W.-Chr. Dullo. 1996. Carbon isotope records from extant Caribbean and South Pacific sponges: Evolution of δ13C in surface water DIC. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 139:291-303. | 1996 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Caribbean | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Bandaranayake, W. M. and W. A. Wickramasinghe. 1996. Benzylmercaptan (benzylthiol) and dibenzyldisulphide from the marine sponge Crella spinulata, (Hentschel)(Poecilosclerida: Crellidae). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 113:499-502. | 1996 | Australia | Sponges | |
| Flathman Paul, E., L. Laski Mary, R. Trausch Jason, H. Carson Jr. John, M. Woodhull Patrick, E. Jerger Douglas, and R. Lear Paul. 1996. Effect of micronutrient addition on the bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon (PHC)-contaminated coral sand at a U.S. Navy facility on Midway Island in the Pacific. in Proceedings of the Air & Waste Management Association's Annual Meeting & Exhibition. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Coastal Defense; Military; Nutrients; Remediation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Richards, R. P., D. B. Baker, N. L. Creamer, J. W. Kramer, D. E. Ewing, B. J. Merryfield, and L. K. Wallrabenstein. 1996. Well water quality, well vulnerability, and agricultural contamination in the midwestern United States. Journal of Environmental Quality 25:389-402. | 1996 | India | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Cultural Protections; Drinking Water Supply; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Muller-Mai, C., C. Voigt, S. R. De Almeida Reis, H. Herbst, and U. M. Gross. 1996. Substitution of natural coral by cortical bone and bone marrow in the rat femur. Part II SEM, TEM, and in situ hybridization. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 7:479-488. | 1996 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Petite, H., K. Kacem, and J. T. Triffitt. 1996. Adhesion, growth and differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells on non-porous calcium carbonate and plastic substrata: Effects of dexamethasone and 1,25dihydroxyvitamin D3. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 7:665-671. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | ||
| Swart, P. K., R. E. Dodge, and H. J. Hudson. 1996. A 240-year stable oxygen and carbon isotopic record in a coral from South Florida: implications for the prediction of precipitation in Southern Florida. Palaios 11:362-375. | 1996 | Florida | CO2 | |
| Carte, B. K. 1996. Biomedical Potential of Marine Natural Products. Bioscience 46:271-286. | 1996 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Invertebrates; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sammarco, P. W. 1996. Comments on coral reef regeneration, bioerosion, biogeography, and chemical ecology: Future directions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 200:135-168. | 1996 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Review | Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment |
| Chen, L., W. Klaes, and S. Assenmacher. 1996. A comparative morphometric and histologic study of five bone substitute materials. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 76:527-530. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Vuola, J., H. Goransson, T. Bohling, and S. Asko-Seljavaara. 1996. Bone marrow induced osteogenesis in hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate implants. Biomaterials 17:1761-1766. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Gardner, G. 1996. Gribble in the greenheart. New Civil Engineer (NCE) 1171:18-19. | 1996 | Artificial Habitat; Forestry | ||
| Gao, T., T. S. Lindholm, A. Marttinen, and M. R. Urist. 1996. Composites of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and type IV collagen, coral-derived coral hydroxyapatite, and tricalcium phosphate ceramics. International Orthopaedics 20:321-325. | 1996 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Smith, J. M. B. 1996. Notes on coral-trees (Erythrina) in Australia with particular reference to E. crista-galli L. in New South Wales. Australian Geographical Studies 34:225-236. | 1996 | South & Central America; Australia | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Invasive Species | |
| Senderowicz, A. M., G. Kaur, E. Saina, C. Lang, W. D. Inman, J. Rodriguez, P. Crews, L. Malspeis, M. R. Grever, E. A. Sausville, and K. L. K. Duncan. 1995. Jasplakinolide�s inhibition of the growth of prostate carcinoma cells in vitro with disruption of the actin cytoskeleton. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 87:46-51. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Huang, H. and C. J. Forsyth. 1995. Anti selective spirocarbomercuration: Synthesis and stereochemistry of the spirobicyclic sesquiterpenes spirojatamol and erythrodiene. Journal of Organic Chemistry 60:2773-2779. | 1995 | South & Central America; India; Caribbean | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Brockman, Dieter, and Alf Jacob Nilsen. 1995. A critical comparison of methods for dosing calcium in sea aquariums, Part 2. Aquarium Frontiers 2:2-27. | 1995 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Chen, K. M. 1995. Disappearance of ALS from Guam: Implications for exogenous causes. Pages 1549-1553 in Clinical Neurology. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Guam | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Housing; Military; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Brockman, Dieter, and Alf Jacob Nilsen. 1995. A critical comparison of methods for dosing calcium in sea aquariums, Part 1. Aquarium Frontiers 2:2-25. | 1995 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Park, D. L. 1995. Prediction of aquatic biotoxin potential in fish and shellfish harvesting areas: ciguatera and diarrheic shellfish poisoning. Pages 271-282 in Coastal ocean space utilization III. Proc. symposium, Genoa, 1993. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Finfish Harvest | |
| Genin, A., B. Lazar, and S. Brenner. 1995. Vertical mixing and coral death in the Red Sea following the eruption of Mount Pinatubo. Nature 377:507-510. | 1995 | Middle East; Philippines | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Sampath Kumar, T. S., M. Sivakumar, N. P. Kumar, K. S. Selvi, and K. P. Rao. 1995. Synthesis and characterization of bioactive hydroxyapatite/fluoroapatite solid solutions using corals. Bulletin of Materials Science 18:955-961. | 1995 | India | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Fukuhara, T., H. Inomata, and H. Wada. 1995. Benzene synthesis for radiocarbon dating at Shizuoka University. Geoscience Reports of the Shizuoka University 22:47-58. | 1995 | CO2 | ||
| Spotte, S. and P. M. Bubucis. 1995. Visual censusing of two coral fishes important to the marine aquarium trade. Conservation Biology 9:1304-1306. | 1995 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Kumar, T. S. SA MP AT H, M. Sivakumar, N. PR AS AN TH Kumar, K. SE NT HA MI L Selvi, and K. Panduranga Rao. 1995. Preparation and properties of bioactive coralline hydroxyapatite/fluoroapatite - zirconia composites. in IEEE/ Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Annual Conference. | 1995 | India | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Levine, D. Z. 1995. Ciguatera: Current concepts. Journal of the American Osteopathic Association 95:193-198. | 1995 | Review | Microorganisms | |
| Catena John, G. 1995. World prodigy oil spill restoration planning. Pages 92-93 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Tambutte, E., D. Allemand, I. Bourge, J.-P. Gattuso, and J. Jaubert. 1995. An improved 45Ca protocol for investigating physiological mechanisms in coral calcification. Marine Biology 122:453-459. | 1995 | Cuba | Lab Study | Stony Coral |
| Mora, F. and J. P. Ouhayoun. 1995. Clinical evaluation of natural coral and porous hydroxyapatite implants in periodontal bone lesions: results of a 1-year follow-up. Journal of clinical periodontology 22:877-884. | 1995 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Klein, B. Y., S. Jaber, M. Liebergall, H. Ben-Bassat, and I. Leichter. 1995. Mineral composition analysis by Fourier transform infrared in coral bone implants. European Journal of Experimental Musculoskeletal Research 4:21-26. | 1995 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Leitha, T., A. Staudenherz, and U. Scholz. 1995. Three-phase hone scintigraphy of hydroxyapatite ocular implants. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine 22:308-314. | 1995 | Model | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | |
| Kangas, P., M. Shave, and P. Shave. 1995. Economics of an ecotouriasm in Belize. Environmental Management 19:669-673. | 1995 | South & Central America; Belize | Funding & Donations; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ates, Ron. 1995. Colonial anemones - Zoantharia: a review for the seriously interested marine aquarist. Aquarium Frontiers 2:10-13. | 1995 | Review | Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | |
| Lodde, J.-P. 1995. Biomaterials In Plastic And Maxillofacial Surgery [Les Biomateriaux En Chirurgie Plastique Et Maxillo-Faciale]. Annales de Chirurgie Plastique et Esthetique 40:676-689. | 1995 | Field Study & Monitoring | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Collins, K. J., A. C. Jensen, A. P. M. Lockwood, and S. J. Lockwood. 1994. Coastal structures, waste materials and fishery enhancement. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:1240-1250. | 1994 | Review | Agriculture; Coal Mining; Coastal Defense; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fishing Sector; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Waste Management Policies | |
| Lesser, M. P., V. M. Weis, M. R. Patterson, and P. L. Jokiel. 1994. EfTects of morphology and water motion on carbon delivery and productivity in the reef coral, Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus): Diffusion barriers, inorganic carbon limitation, and biochemical plasticity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 176:153-179. | 1994 | Stony Coral | ||
| Meesters, E.H., M. Noordeloos, R. P.M. Bak. 1994. Damage and regeneration: links to growth in the reef-building coral Montastraea annularis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 112:119-128. | 1994 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Light; Physical Damage; Stony Coral | |
| Slegrist, R. L., T. J. Phelps, N. E. Korte, and D. A. Pickering. 1994. Characterization and biotreatability of petroleum contaminated soils in a coral Atoll in the Pacific Ocean. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 1:757-773. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Marshall Islands | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Remediation; Sediment |
| Delbeek, J.C., J. Sprung. 1994. Alternative Filtration Systems. Pages 142-147 The Reef Aquarium: A Comprehensive Guide to the Identification and Care of Tropical Marine Invertebrates. Ricordea Publishing. | 1994 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Invertebrates | ||
| Su,. 1994. Erratum: Lobocalone: A novel secondary metabolite from the soft coral Lobophytum caledonense (Journal of Natural Products (Lloydia) (1993) 56 (279)). Journal of Natural Products (Lloydia) 57:1765. | 1994 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Grace, K. J. S., D. Zavortink, and R. S. Jacobs. 1994. Inactivation of bee venom phospholipase A2 by a sesquiterpene furanoic acid marine natural product. Biochemical Pharmacology 47:1427-1434. | 1994 | Cuba | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Substrate | |
| Proksch, P. 1994. Defensive roles for secondary metabolites from marine sponges and sponge-feeding nudibranchs. Toxicon 32:639-655. | 1994 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Martin, G. R. and G. Katzir. 1994. Visual fields and eye movements in herons (Ardeidae). Brain, Behavior and Evolution 44:74-85. | 1994 | Field Study & Monitoring | ||
| Damien, C. J., J. L. Ricci, P. Christel, H. Alexander, and J.-L. Patat. 1994. Formation of a calcium phosphate-rich layer on absorbable calcium carbonate bone graft substitutes. Calcified Tissue International 55:151-158. | 1994 | Europe | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Scheuer, P. J. 1994. From the rainforest to the reef: Searching for bioactive natural products in the mid-pacific. Medicinal Research Reviews 14:487-503. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Bernier, P., C. Gaillard, G. Barale, J.-P. Bourseau, E. Buffetaut, J.-C. Gall, and S. Wenz. 1994. The underlying substrate ofthe Cerin Lithographic Limestones. Geobios 27:13-24. | 1994 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Sediment; Substrate | ||
| Marin, F. and P. Gautret. 1994. Acidic amino acid contents in soluble organic matrices of sponges and corals calcareous skeletons: a possible implication in their diagenetic change [Les teneurs en acides amines acides des matrices organiques solubles associees aux squelettes calcaires d. Bulletin - Societe Geologique de France 165:77-84. | 1994 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Konig, G. M., A. D. Wright, O. Sticher, C. K. Angerhofer, and J. M. Pezzuto. 1994. Biological activities of selected marine natural products. Planta Medica 60:532-537. | 1994 | Algae; Molluscs; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Shields, C. L., J. A. Shields, P. De Potter, and A. D. Singh. 1994. Problems with the hydroxyapatite orbital implant: Experience with 250 consecutive cases. British Journal of Ophthalmology 78:702-706. | 1994 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hallegraeff, G. M. 1993. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32:79-99. | 1993 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton; Tourism & Recreation |
| Landing, E. 1993. In situ earliest Cambrian tube worms and the oldest metazoan- constructed biostrome (Placentian Series, southeastern Newfoundland). Journal of Paleontology 67:333-342. | 1993 | Marine Worms; Snails & Conch | ||
| Rodier-Bruant, C., A. Wilk, D. Herman, and A. Manunta. 1993. Use of a new malleable implant as a bone substitute in maxillofacial surgery. Advances in Therapy 10:142-150. | 1993 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Matthews, W. S., A. E. van Wyk, and G. J. Bredenkamp. 1993. Endemic flora of the north-eastern Transvaal Escarpment, South Africa. Biological Conservation 63:83-94. | 1993 | South Africa | Forestry; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Substrate | |
| Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. | 1993 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Docks & Marinas; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Prins, H. H. T. and J. Wind. 1993. Research for nature conservation in south-east Asia. Biological Conservation 63:43-46. | 1993 | Indonesia | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Wetlands | |
| Brickner, I., E. Kramarskywinter, O. Mokady, and Y. Loya. 1993. Speciation in the coral boring bivalve Lithophaga purpurea - Evidence from ecological, biochemical and SEM analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 101:139-146. | 1993 | Bivalves | ||
| Khavari, F. and P. K. Bajpai. 1993. Coralline-sulfate bone substitutes. Pages 65-69 in Biomedical Sciences Instrumentation. | 1993 | Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Nunn, P. D. 1993. Oceanic islands. Oceanic islands. | 1993 | Model | Climate | |
| Danilowicz, B. S. and C. L. Brown. 1992. Rearing methods for two damselfish species: Dascyllus albisella (Gill) and D. aruanus (L.). Aquaculture 106:141-149. | 1992 | Algae; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Plankton; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Oda, S. 1992. Prehistoric culture in the region washed by the Kuroshio Current. Quaternary Research (Tokyo) 31:409-420. | 1992 | Japan; Taiwan | Finfish Harvest; Snails & Conch | |
| Weindling, S. M., C. L. Robinette, and R. E. Wesley. 1992. Porous hydroxyapatite in orbital reconstructive surgery, radiologic recognition of coral bone grafts. American Journal of Neuroradiology 13:239-240. | 1992 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Paul, Valerie J. 1992. Chemical defenses of benthic marine invertebrates. Pages 164-89 in Valerie J Paul, editor. Ecological Roles of Marine Natural Products. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca. | 1992 | Invertebrates; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Pawlik, Joseph R. 1992. Induction of marine invertebrate larval settlement: evidence for chemical cues. Pages 189-237 in Valerie J Paul, editor. Ecological Roles of Marine Natural Products. Comstock Publishing Associates, Ithaca. | 1992 | Invertebrates; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Collins, K. J., A. C. Jensen, and A. P. M. Lockwood. 1992. Stability of a coal waste artificial reef. Chemistry & Ecology 6:79-93. | 1992 | Artificial Habitat; Coal Mining; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs | ||
| Pitcher, C. R., T. D. Skewes, D. M. Dennis, and J. H. Prescott. 1992. Estimation of the abundance of the tropical lobster Panulirus ornatus in Torres Strait, using visual transect-survey methods. Marine Biology 113:57-64. | 1992 | GIS & Maps | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| McCormick, M. I. and B. W. Molony. 1992. Effects of feeding history on the growth characteristics of a reef fish at settlement. Marine Biology 114:165-173. | 1992 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invertivorous Fish |
| Ware, J. R., S. V. Smith, and M. L. Reaka-Kudla. 1992. Coral reefs: sources or sinks of atmospheric CO2? Coral Reefs 11:127-130. | 1992 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2 | |
| Pajaro, M. 1992. Alternatives to cyanide use in aquarium fish collection: A community based approach. Pages 1039-40 in Proceedings of the 7th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1992 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish | ||
| Ripamonti, U., S.-S. Ma, and A. H. Reddi. 1992. Induction of bone in composites of osteogenin and porous hydroxyapatite in baboons. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 89:731-739. | 1992 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Goreau, T. J. 1992. Control of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Global Environmental Change 2:11-May. | 1992 | Climate; CO2 | ||
| Edwards, A. J. and A. D. Shepherd. 1992. Environmental implications of aquarium-fish collection in the Maldives, with proposals for regulation. Environmental Conservation 19:61-72. | 1992 | Maldives | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| McCallum, H. 1992. Completing the circle: stock-recruitment relationships and Acanthaster. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 43:653-662. | 1992 | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Seastars | ||
| Uchio, Y., M. Kodama, S. Usui, and Y. Fukuzawa. 1992. Three new eunicellin-based diterpenoids from an Okinawan Cladiella species of soft coral. Tetrahedron Letters 33:1317-1320. | 1992 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Kvitek, R. G. 1991. Paralytic shellfish toxins by bivalves as a defense against siphon-nipping fish. Marine Biology 111:369-374. | 1991 | Bivalves | ||
| Karr, J. R. 1991. Biological integrity: a long-neglected aspect of water resource management. Ecological Applications 1:66-84. | 1991 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Resource Use Management; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Ripamonti, U. 1991. The morphogenesis of bone in replicas of porous hydroxyapatite obtained from conversion of calcium carbonate exoskeletons of coral. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series A 73:692-706. | 1991 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Adey, W. H. and K. Loveland. 1991. Dynamic aquaria: building living ecosystems. Dynamic aquaria: building living ecosystems. | 1991 | Australia | Model | Domestic Animal Waste; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Wetlands |
| [No author name available]. 1991. Our living oceans. The first annual report on the status of US living marine resources. in [No source information available]. | 1991 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Fishing Sector; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Light, M. and I. O. Kanat. 1991. The possible use of coralline hydroxyapatite as a bone implant. Journal of Foot Surgery 30:472-476. | 1991 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Smart, P. L. 1991. Electron spin resonance (ESR) dating. Pages 128-160 Quaternary dating methods - a user's guide. | 1991 | Molluscs; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment | ||
| Aharon, P. 1991. Recorders of reef environment histories: stable isotopes in corals, giant clams, and calcareous algae. Coral Reefs 10:71-90. | 1991 | Australia; Java | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Ahmed, F. E. 1991. Naturally occurring seafood toxins. Journal of Toxicology - Toxin Reviews 10:263-287. | 1991 | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Kobayashi, M., M. Hori, K. Kan, T. Yasuzawa, M. Matsui, S. Suzuki, and I. Kitagawa. 1991. Marine natural products. XXVII. Distribution of lanostane-type triterpene oligoglycosides in ten kinds of Okinawan sea cucumbers. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 39:2282-2287. | 1991 | Japan | Echinoderms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Ehrhardt, M. G. 1990. Petroleum-derived dissolved organic compounds concentrated from inshore waters in Burmuda. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 138:35-47. | 1990 | Bermuda | ||
| Fagoonee, I. 1990. Coastal marine ecosystems of Mauritius. Hydrobiologia 208:55-62. | 1990 | Indian Ocean; Mauritius; India | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Wetlands | |
| Coffroth, M. A. 1990. Mucous sheet formation on poritid corals: An evaluation of coral mucus as a nutrient source on reefs. Marine Biology 105:39-49. | 1990 | Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Panama | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wisniewski, John. 1990. "Fireworms in the Marine Aquarium". Marine Fish Monthly 22. | 1990 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Marine Worms | ||
| Sindermann, C. J. 1990. Principal diseases of marine fish and shellfish. Academic Press, Inc., New York. | 1990 | Pathogens | ||
| Guerriero,. 1990. Erratum: Hydroxyicosatetraenoic, hydroxyicosapentaenoic, hydroxydocosapentaenoic, and hydroxydocosahexaenoic acids from the sponge Echinochalina mollis of the coral sea (Journal of natural products (1990) 53, (57-61)). Journal of Natural Products 53:1181. | 1990 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Garrity, S. D. and S. C. Levings. 1990. Effects of an oil spill on the gastropods of a tropical intertidal reef flat. Marine Environmental Research 30:119-153. | 1990 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Molluscs; Petroleum Spills; Snails & Conch | |
| Delbeek, J. Charles. 1990. Stocking the reef aquarium: Coral compatibility. Aquarium Fish | 1990 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Delbeek, J. Charles. 1990. Reef aquariums part 6: coral aggression. Aquarium Fish 2:26-32. | 1990 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Matson, E. A. 1989. Biogeochemistry of Mariana Islands coastal sediments: terrestrial influence on /gd13, Ash, CaCO3, Al, Fe, Si and P. Coral Reefs 7:153-160. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Guam | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Non-point Source Runoff; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Hatcher, A. 1989. RQ of benthic marine invertebrates. Marine Biology 102:445-452. | 1989 | Australia; Cuba | Index or Indicator | CO2; Invertebrates; Substrate |
| Dunlap, W. C., D. MC B. Williams, B. E. Chalker, and A. T. Banaszak. 1989. Biochemical photoadaptation in vision: U.V.-absorbing pigments in fish eye tissues. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B 93:601-607. | 1989 | Australia | Fish; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Buddemeier, R. W. and S. V. Smith. 1988. Coral reef growth in an era of rapidly rising sea level: predictions and suggestions for long-term research. Coral Reefs 7:51-56. | 1988 | Global | Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Morse, D. E., N. Hooker, A. N. C. Morse, and R. A. Jensen. 1988. Control of larval metamorphosis and recruitment in sympatric agariciid corals. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 116:193-217. | 1988 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Plankton; Stony Coral | ||
| Perez-Rosas, N. and T. C. Hazen. 1988. In situ survival of vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli in tropical coral reefs. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54:9-Jan. | 1988 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Sediment |
| Tencer, A. F., P. L. Woodard, J. Swenson, and K. L. Brown. 1988. Mechanical and bone ingrowth properties of a polymer-coated, porous, synthetic, coralline hydroxyapatite bone-graft material. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 523:157-172. | 1988 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Anon,. 1988. American Pavilion Mimics The Oceans|. Indian Concrete Journal 62:114-115. | 1988 | Florida | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Plankton | |
| Morrissey, J., M.S. Jones, and V. Harriot. 1988. Nutrient cycling in the Great Barrier Reef Aquarium. Pages 563-7 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | Australia | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Nutrients | |
| Kyle, D. 1987. The biochemical basis for photoinhibition fo photosystem II. Pages 197-226 Topics in photosynthesis, volume 9. Elsevier, Amsterdam. | 1987 | Primary Production | ||
| Richards, W. J. and K. C. Lindeman. 1987. Recruitment dynamics of reef fishes: planktonic processes, settlement and demersal ecologies, and fishery analysis. Bulletin of Marine Science 41:392-410. | 1987 | Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Plankton | ||
| Zimmer-Faust, R. K. and E. Spanier. 1987. Gregariousness and sociality in spiny lobsters: implications for den habitation. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 105:57-71. | 1987 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Mann, K. and M. Florence. 1987. Toxicity of oil shale waste waters to marine algae. Fuel 66:404. | 1987 | Australia | Model | Algae; Nutrients; Wastewater Discharge |
| Driessen Paul, K. 1987. Oil Rigs: Biology, Mariculture, Drilling Muds, Rigs-To-Reefs. Pages 3605-3620 in [No source information available]. | 1987 | South & Central America; Mexico | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Oil & Gas Rigs; Substrate | |
| Shen, G. T. and E. A. Boyle. 1987. Lead in corals: reconstruction of historical industrial fluxes to the surface ocean. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 82:289-304. | 1987 | Global; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda; Mauritius; India; Fiji | Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hughes, DO NA LD. 1987. Briny Deep Comes Ashore. Civil engineering New York, N.Y57:50-52. | 1987 | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Plankton | ||
| Dunlap, W. C., B. E. Chalker, and J. K. Oliver. 1986. Bathymetric adaptations of reef-building corals at Davies Reef, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. III. UV-B absorbing compounds. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 104:239-248. | 1986 | Australia | Light; Stony Coral | |
| Holmes, R. E., R. W. Bucholz, and V. Mooney. 1986. Porous hydroxyapatite as a bone-graft substitute in metaphyseal defects. A histometric study. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery - Series A 68:904-911. | 1986 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | |
| Anon,. 1986. Amazone, First Cutter Suction Dredger Completed By Boelwerf, Belgium. Holland Shipbuilding 35:39-41. | 1986 | Beach & Land Formation; Dredging, Draining, & Filling | ||
| Coll, John C., et. al. 1986. Studies of Australian soft corals - The natural products chemistry of Alcyonacean soft corals with special reference to the. Bulletin des Societes Chimiques Belges 95:815-34. | 1986 | Australia | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kaul, P. N. and P. Daftari. 1986. Marine pharmacology: bioactive molecules from the sea. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 26:117-142. | 1986 | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| White, E. and E. C. Shors. 1986. Biomaterial aspects of Interpore-200 porous hydroxyapatite. Dental clinics of North America 30:49-67. | 1986 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sartoris, D. J., D. H. Gershuni, and W. H. Akeson. 1986. Coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitutes: Preliminary report of radiographic evaluation. Radiology 159:133-137. | 1986 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sartoris, D. J., R. E. Holmes, R. W. Bucholz, and D. Resnick. 1986. Coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitutes in a canine diaphyseal defect model: Radiographic features of failed and successful union. Skeletal Radiology 15:642-647. | 1986 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Sartoris, D. J., R. E. Holmes, and A. F. Tencer. 1986. Coralline hydroxyapatite bone graft substitutes in a canine metaphyseal defect model: Radiographic-biomechanical correlation. Skeletal Radiology 15:635-641. | 1986 | Model | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kuo Shu, T., I. H. Su, C. Hsu Chan, and P. Chen Ming. 1985. Solidification Of Fly Ash With Other Industrial Waste Material. Pages 402-417 in United States Department of Energy, Morgantown Energy Technology Center (Report) DOE/METC. | 1985 | |||
| Pfeffer, R. A. and G. W. Tribble. 1985. Hurricane effects on an aquarium fish fishery in the Hawaiian Islands. in IN: PROC. FIFTH INT. CORAL REEF CONGRESS, (MOOREA, FRENCH POLYNESIA: MAY 27-JUN. 1, 1985). | 1985 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Skeletal Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Ryan, J. J. 1985. Investigation, design and construction of submarine ocean outfall pipeline off ninety mile beach, Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. Water Science and Technology 17:1465-1467. | 1985 | Australia | Discharges; Forestry; Pipelines; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| [No author name available]. 1985. Another port for Florida? PORT DEV. INT3:-22. | 1985 | Florida | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fish; Forestry | |
| Tencer, A. F., V. Mooney, K. L. Brown, and P. A. Silva. 1985. Compressive properties of polymer coated synthetic hydroxyapatite for bone grafting. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 19:957-969. | 1985 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Sakai, IT SU O, NO BU O Takai, and TA KE O Kondo. 1985. Improvement And Construction Of Coastal Fishing Grounds In Japan. Pages 2239-2248 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1985 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Products |
| Sheehy Daniel, J. and F. Vik Susan. 1985. Designed Reefs For Habitat Loss Compensation. Pages 1439-1450 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1985 | Artificial Habitat; Finfish & Shellfish Stock | ||
| Hine, A. C. and J. C. Steinmetz. 1984. Cay Sal Bank, Bahamas - A partially drowned carbonate platform. Marine Geology 59. | 1984 | Bahamas; Cuba | Beach & Land Formation; Calcareous Macroalgae; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Huxley, A. 1984. Green inheritance: the world wildlife fund book of plants. Collins/Harvill, London. | 1984 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Mehta, G. and A. N. Murty. 1984. Total synthesis of the marine natural product (±)-precapnelladiene. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications 16:1058-1060. | 1984 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Entsch, B., R. G. Sim, and B. G. Hatcher. 1983. Indications from photosynthetic components that iron is a limiting nutrient in primary producers on coral reefs. Marine Biology 73:17-30. | 1983 | Australia | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae |
| Finn, D. 1983. Land use and abuse in the East African region. Ambio 12:296-301. | 1983 | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Deforestation & Devegetation; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Fisher, W. S. 1983. Eggs of Palaemon macrodactylus: II. association with aquatic bacteria. Biological Bulletin 162:201-213. | 1983 | Lab Study | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Fisher, W. S. 1983. Eggs of Palaemon macrodactylus: III. infection by the fungus, Lagenidium callinectes. Biological Bulletin 162:214-226. | 1983 | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Fisher, W. S. and W. H. Clark Jr. 1983. Eggs of Palaemon macrodactylus: I. attachment to the pleopods and formation of the outer investment coat. Biological Bulletin 162:189-200. | 1983 | Cuba | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Raj, U., Y. Oshima, and T. Yasumoto. 1983. The occurrence of paralytic shellfish toxins in two species of xanthid crab from Suva barrier reef, Fiji Islands. Toxicon 21:547-551. | 1983 | Fiji | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp | |
| Hayakaya, Y. 1983. Land use for agriculture and flora in the Nansei Islands classified by ecological geography. The relationship between beef cattle raising and establishment of subclimax grasslands or arable land. Bulletin - Kyushu National Agricultural Experiment Station 22:605-665. | 1983 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture |
| Polunin, N. V. C. 1983. Marine 'genetic resources' and the potential role of protected areas in conserving them. Environmental Conservation 10:31-41. | 1983 | Review | Aquaculture; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kingston, J. F., N. Ang Ser, G. Gallacher, and A. G. Fallis. 1983. Studies in marine organic chemistry: marine natural products from invertebrates found in newfoundland waters and approaches to the total synthesis of sinularene and 12-acetoxysinularene. Marine Chemistry 12:147-157. | 1983 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Rapson, A. M. 1983. Economic management of lagoons. Ocean Management 8:297-304. | 1983 | Australia | Agriculture; Molluscs; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Peters, E. C., P. A. Meyers, P. P. Yevich, and N. J. Blake. 1981. Bioaccumulation and histopathological effects of oil on a stony coral. Marine Pollution Bulletin 12:333-339. | 1981 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Davis, B. J., E. E. De Martini, and K. McGee. 1981. Gene flow among population of a teleost (painted greenling, Oxylebius pictus) from Puget Sound to southern California. Marine Biology 65:17-23. | 1981 | Fish | ||
| Sadati, S.-M. 1981. The hohe wand: An upper triassic lagoonal reef at the Eastern Margin of the Northern Calcareous Alps (Lower Austria) [Die Hohe Wand: Ein obertriadisches Lagunen-Riff am Ostende der Nordlichen Kalkalpen (Niederosterreich)]. Facies 5:191-263. | 1981 | Model | Algae; Arthropods; Cyanobacteria; Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Falkowski, P. G. and Z. Dubinsky. 1981. Light-shade adaptation of Stylophora pistillata, a hermatypic coral from the Gulf of Eilat. Nature 289:172-174. | 1981 | Algae; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Szmant-Froelich, A. 1981. Coral nutrition: Comparison of the fate of 14C from ingested labeled brine shrimp and from the uptake of NaH14CO3 by its zooxanthellae. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 55:133-144. | 1981 | Cuba | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Keith, R. E. 1981. Loss of therapeutic copper in closed marine systems. Aquaculture 24:355-362. | 1981 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock | ||
| Daumas, Raoul. Robert Galois, and Bernard A. Thomassin. 1981. Biochemical composition of soft and hard coral mucus on a New Caledonian lagoonal reef. Pages 59-67 in Proceedings of the 4th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1981 | New Caledonia | Stony Coral | |
| Dollar, S. J. and R. W. Grigg. 1981. Impact of a kaolin clay spill on a coral reef in Hawaii. Marine Biology 65:269-276. | 1981 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Stony Coral |
| Murtland, W. O. 1981. Current Trends In Scrap Rubber Recycling. Elastomerics 113:13-16. | 1981 | Fish | ||
| Yamada, Y., S. Suzuki, K. Iguchi, H. Kikuchi, Yasumasa, Tsukitani, H. Horiai, and F. Shibayama. 1980. Studies on marine natural products. IV The stereochemistry of 13-membered carbocyclic cembranolide diterpenes from the soft coral lobophytum pauciflorum (Ehrenberg). Tetrahedron Letters 21:3911-3914. | 1980 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Szmant-Froelich, A. and M. E. Q. Pilson. 1980. The effects of feeding frequency and symbiosis with zooxanthellae on the biochemical composition of Astrangia Danae Milne Edwards & Haime 1849. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 48:85-97. | 1980 | Lab Study | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Zooxanthellae | |
| Prota, Giuseppe. 1980. Nitrogenous pigments in marine invertebrates. Pages 141-80 in Paul J Scheuer, editor. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological perspectives, Vol III,. Academic Press, New York. | 1980 | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Yamada, Y., S. Suzuki, and K. Iguchi. 1980. Studies on marine natural products. II. New polyhydroxylated sterols from the soft coral Lobophytum pauciflorum (Ehrenberg). Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 28:473-478. | 1980 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hildemann, W. H., C. H. Bigger, and I. S. Johnston. 1979. Histoincompatibility reactions and allogeneic polymorphism among invertebrates. Pages 1136-1142 in Transplantation Proceedings. | 1979 | Echinoderms; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Holmes, R. E. 1979. Bone regeneration within a coralline hydroxyapatite implant. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 63:626-633. | 1979 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Fenical, William. 1978. Diterpenoids. Pages 173-246 in Paul J Scheuer, editor. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological perspectives, Vol II. Academic Press, London. | 1978 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Vanderah, D. J., N. Rutledge, F. J. Schmitz, and L. S. Ciereszko. 1978. Marine natural products: Cembrene-A and cembrene-C from a soft coral, Nephthea sp. Journal of Organic Chemistry 43:1614-1616. | 1978 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Liaaen-Jensen, Synnove. 1978. Marine carotenoids. Pages 2-70 in Paul J Scheuer, editor. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological Perspectives, Vol II. Academic Press, New York. | 1978 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Tursch, B., et. al. 1978. Terpenoids from coelenterates. Pages 247-95 in Paul J Scheuer, editor. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological Perspectives, Vol II,. Academic Press, New York. | 1978 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Chan Gordon, L. 1977. Five-Year Recruitment Of Marine Life After The 1971 San Francisco Oil Spill. Pages 543-545 in [No source information available]. | 1977 | Invertebrates; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Vanderah, D. J., P. A. Steudler, L. S. Ciereszko, F. J. Schmitz, J. D. Ekstrand, and D. Van Der Helm. 1977. Marine natural products. Xenicin: A diterpenoid possessing a nine-membered ring from the soft coral, Xenia elongata. Journal of the American Chemical Society 99:5780-5784. | 1977 | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Hanscomb, N. J., J. P. Bennett, and G. Harper. 1976. Biochemical stimuli for feeding in Acanthaster planci (L.). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 22:193-197. | 1976 | Seastars; Stony Coral | ||
| Rahaman, M. M., M. M. Khan, and K. M. S. Aziz. 1975. An outbreak of dysentery caused by Shigella dysenteriae type 1 on a coral island in the Bay of Bengal. Journal of Infectious Diseases 132:15-19. | 1975 | Drinking Water Supply; Pathogens; Water Utilities Policies | ||
| Collins, A. R. S. 1975. Biochemical investigation of two responses involved in the feeding behaviour of Acanthaster planci (L.). II. Isolation and characterization of chemical stimuli. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 17:69-86. | 1975 | Seastars | ||
| Collins, A. R. S. 1975. Biochemical investigation of two responses involved in the feeding behaviour of Acanthaster planci (L.). III. Food preferences. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 17:87-94. | 1975 | Seastars | ||
| Lubbock, H. R. and N. V. C. Polunin. 1975. Conservation and the tropical marine aquarium trade. Environmental Conservation 2:229-232. | 1975 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Kenya; Mauritius; Sri Lanka; Thailand; Saudi Arabia; Japan; Indonesia; Philippines; Taiwan; Caribbean; France; Germany | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species | |
| Chiroff, R. T., E. W. White, J. N. Weber, and D. M. Roy. 1975. Tissue ingrowth of Replamineform implants. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 9:29-45. | 1975 | Manufacturing & Trade; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| White, E. W., J. N. Weber, and D. M. Roy. 1975. Replamineform porous biomaterials for hard tissue implant applications. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research 9:23-27. | 1975 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Beckman, J. A., G. Crane, E. L. Kay, and J. R. Laman. 1974. Scrap tire disposal. Rubber Chemistry and Technology 47:597-624. | 1974 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Petroleum Spills; Shoreline Protection | |
| Roy, D. M. and S. K. Linnehan. 1974. Hydroxyapatite formed from coral skeletal carbonate by hydrothermal exchange. Nature 247:220-222. | 1974 | Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| collins, A. R. S. 1974. Biochemical investigation of two responses involved in the feeding behaviour of Acanthaster planci (L). I. Assay methods and preliminary results. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 15:173-184. | 1974 | Seastars | ||
| Carlton, J. M. 1974. Land-building and stabilization by mangroves. Environmental Conservation 1:285-294. | 1974 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Housing; Mangroves; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Substrate |
| Schmitz, F. J., D. J. Vanderah, and L. S. Ciereszko. 1974. Marine natural products: Nephthenol and epoxynephthenol acetate, cembrene derivatives from a soft coral. Journal of the Chemical Society, Chemical Communications 10:407-408. | 1974 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hildemann, W. H. and A. L. Reddy. 1973. Phylogeny of immune responsiveness: marine invertebrates. Pages 2188-2194 in Federation Proceedings. | 1973 | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Echinoderms; Octocoral; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates | |
| Johannes, R. E. 1972. Coral Reefs And Pollution [Marine Pollution And Sea Life]. Pages 364-375 FISHING NEWS LTD., SURREY. | 1972 | Review | Algae; Chemical Use Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Salinity; Seastars; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Bergmann, W., M. J. McLean, and D. Lester. 1943. Contributions to the study of marine products. XIII. Sterols from various marine invertebrates. Journal of Organic Chemistry 8:271-282. | 1943 | Boring Sponges; Echinoderms; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Octocoral; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Tunicates | ||
| Malcohn, E., Bentham Paulos, Andrew Stoeckle, Herbert Han-Pu Wang, and Julie Lynch. Determinants of Effectiveness for Environmental Certification and Labeling Programs. EPA-742-R-94-001, US EPA, Washington, DC. | Review | Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade | ||
| Folmer, F., M. Jaspars, G. Solano, S. Cristofanon, E. Henry, J. Tabudravu, K. Black, D. H. Green, F. C. Kupper, W. Aalbersberg, K. Feussner, M. Dicato, and M. Diederich. The inhibition of TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation by marine natural products. Biochemical Pharmacology. | Oman; Fiji | Echinoderms; Octocoral; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | ||
| Barthelemy, D. Chapter 37: Progress in sexual coral reproduction at Oceanopolis. Pages 339-346 in Leewis, R. J., and M. Janse, editors. Advances in Coral Husbandry in Public Aquariums. Public Aquarium Husbandry Series. Vol 2. Burgers' Zoo, Arnhem, the Netherlands. | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Stony Coral | |||
| Jalal, K. F. Regional water resources situation: quantitative and qualitative aspects. in [No source information available]. | Drinking Water Supply; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Bivalve Aquaculture Biofouling Control | These management options reduce, clean or remove biofouling organisms and other waste from bivalve production areas while minimizing environmental risk. Aquaculture shellfish production requires adequate food availability and water of dependable quantity and quality. Aquaculture operations and gear must have a minimal adverse impact on the surrounding water, plant, animal and human resources. Biofouling is detrimental to shellfish production, increasing exposure to pathogens, reducing the available food stuffs, and increasing organic loading. Only environmentally appropriate biofoul control methods should be used, and fouling organisms and algae should be disposed of appropriately to avoid local degradation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. |
Algae; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Improved Technology; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Octopus & Squid; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Snails & Conch; Supplemental Feeding |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Waterspreading | This management option uses a system of dams, dikes, ditches, or other means of diverting or collecting runoff from natural channels, gullies, or streams and spreading it over relatively flat areas. Waterspreading differs from irrigation in that applications are timed by the availability of natural runoff flow rather than scheduled to meet plant needs. Waterspreading is most beneficial in areas with an average annual precipitation of 8 to 25 inches. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Landuse Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Resources |
| Corporate Response: Invest & Co-finance Projects | Investing and co-financing projects that aim to conserve or restore habitats can be an effective means to preserving reef habitats as well as establishing positive working relationships between organizations. Investing in private sector projects will promote desired businesses and business practices, reducing barriers to entry and competitiveness as compared to traditional businesses and business practices to counterbalance advantages from undesired externalities. | World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. |
Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Shipping Businesses | This option requires the sanctuary to continue to alert shipping businesses about sanctuary regulations. Such regulations may include vessel waste discharge, ATBA, PSSA, etc. The targeted audiences will include importers, exporters, port authorities, commercial fishing companies, ship insurers. This information can be provided to the audience through NOAA nautical charts, trade publications, newsletters, trade shows, and direct mailings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finance & Insurance; Infrastructural Policies; Insurance; Manufacturing & Trade; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Increase Public Grounding Notification | Public notification of groundings can be increased through more centralized, accessible notification methods, and public education and outreach. Notification methods could include creating a �grounding hotline� with a central government agency as the enforcement dispatch center. By centralizing notification methods, public confusion over what agency to contact can be reduced. Education and outreach efforts should focus on the importance of grounding notification and awareness of notification methods (i.e. the hotline). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels | Semi- permanent/permanent vessels can have a negative impact on the surrounding local environment both due to the effects of shade and from the direct contact with the substrate. Sunken vessels that cannot be seen from the surface may present a danger to navigation. Derelict vessels that do not remain stationary may cause harm in multiple locations before becoming stationary. If fishing gear is still intact, it may cause further biological damage through "ghost fishing� (#283). Early response, creating mooring fields, pump-out stations, and providing support for removing derelict vessels, reduces the impact of these vessels. Also, the removal of intrusive vessels will help contribute to the restoration of reef areas to previous conditions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Military; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Stony Coral; Substrate; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Large Vessel Achoring | Damage from freighter anchor is extreme due to the mere weight and size of the anchor and chain. The chain can even be more damaging as it drags along the benthic environment leaving behind catastrophic ruin. This management response would encourage the creation of restoration and monitoring methodologies in shallow reef areas as well as at greater depths. If unacceptable damages are occurring restrictions and regulations prohibiting the use of anchors in high risk areas should be instituted. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Cruise Ships; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Large Ships; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Transportation; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Operating Permits for Towing & Salvage Professionals | This management option evaluates the need for a permitting system for all towing and salvage operations. This type of permit would require salvage operators to notify injury response when there are groundings. The permit program would also reduce impacts by ensuring operators know the proper practices and use the proper equipment to most effectively minimize damage to the operating area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Water Transportation |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Develop Chain of Notification for Grounding Incidents | This option advocates coordinating with other agencies such as FWC, NOAA, and local coral managers to determine the standard protocol and responsibilities when there are groundings. Through coordination, these agencies can determine threshold levels of damage for different responses and for notifying other agencies higher up the chain. Enhancing inter-agency coordination will be beneficial in terms of dealing with groundings because it will allow the problem to be fixed in a more time-efficient manner. Having a centralized grounding notification system is the first step of this management option, as it ensures all incidents pass through a single agency to determine further actions. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Vessel Grounding Database | This management approach would involve refining and maintaining a vessel grounding database and adequate staffing for on-going management, GIS processing of archived data, creating products for management case tracking, and developing a database that is user-friendly and useful. If previously established, the management option #165, will allow this data to be combined with similar data from other inventory management options such as #95, and future integration into larger databases, such as that in the management option #85. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop and Maintain Database for Tracking Restoration, Repairs, and Monitoring Activities | This response involves adapting NOAA�s Damage Assessment Center�s seagrass injury assessment team component to local management areas. If previously established, the management option # 165, will allow this data to be compared to previously collected baseline data such as that collected with management option #164. This would also allow for comparisons across different types of data, such as use changes, that would be contained in a #166. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Physical Damage; Pressures; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Dissemination of Findings: Distribute Periodic Sanctuary Health Reports | The management option involves creating monitoring/condition reports on the health of the sanctuary and reef that is released for the public. The findings can be released through newsletters, presentations, reports, publications, and other written and oral methods. Criteria reported on typically include water quality, critical habitats, and species of particular interest. These reports will ultimately help reveal the effectiveness of marine protections and policies based on the conditions researched. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Protections; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Regulate International Trade of Reef Species | Many coral reef species are harvested internationally for a variety of markets including the aquarium trade, food, curios, jewelry and pharmaceuticals. The US is the largest importer for many of these markets. The US strictly limits extraction of stony coral and many reef species in its waters; but as a major importer and consumer of coral reef species, more actions can be taken to decrease the demand on international imports. Setting and enforcing regulations on what can be imported (such as Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species CITES) is one approach that has been taken. More information is needed, leaving room to collect trade data and assess the impacts of extraction techniques to find sustainable methods. Demand for species collected this way will be increased with greater transparency to consumers, which can be accomplished through certifications for environmentally cognoscente collectors and those using alternatives like aquaculture and coral farming. Continued participation in Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) is also beneficial. | U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Live Collection; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Political Pressure; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Sponges; Stony Coral; Toxics; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig Maintenance and Use Regulations | There are regulated procedures and documentation required during production operations to prevent major incidents that may harm workers or the environment. A major part of incident prevention is inspection and maintenance. | Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies | |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Offshore Wind and Hydrokinetic Alternative Energies | Policies encouraging or authorizing construction of offshore facilities are evolving, and there are many sides to the issue of how to best manage them. Alternative energies are desirable and would reduce the dependence on fossil fuel resources. However, hydrokinetic technologies are just becoming viable, meaning long term impacts are still unknown. Facilitative policies reduce barriers for alternative energy development or increase barriers or costs for incumbent technologies. These include research and innovation policies, technology improvement subsidies, market based policies that internalize externalities, and regulatory changes that simplify the permitting process. | Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. Portman, M.E. 2010. Marine Renewable Energy Policy: Some US and International Perspectices Compared. Oceanography 23:98-105. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Seawater Flow; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig Construction Regulations | The Minerals Management Service (MMS) has several requirements for leasing and permits for construction of new drilling rigs and platforms. Placement is very important so as to not interfere with other uses or the environment. These permits also cover exploratory structures for research and test sites. | Minerals Management Service. 2006. Leasing Oil and Natural Gas Resources. U.S. Department of the Interior. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Energy Policy & Development: Pipeline Maintenance Requirements | The best way to ensure a high level of safety and reliability in operation of pipelines is to have a maintenance and inspection plan in place that targets damage, degradation or defects before they lead to failures. Economically, expenditures for maintenance and inspection are significantly less than those for emergency service in reaction to unforeseen situations. However, legislative requirements for plans, procedures and documentation ensures compliance with these best management practices. | Environmental Protection Agency. 2008. Pipeline Maintenance Best Practices: Lessons Learned from the Natural Gas STAR Program. Charlotte (North Carolina). United Kingdom Onshore Pipeline Operators� Association. 2006. UKOPA Recommendations for Pipeline Maintenance and Inspection. UKOPA/06/0032, |
Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Cable and Pipeline Construction Assessments | Pre-assessments must be conducted to ensure pipelines and cables buried on the ocean floor will not disrupt or destroy natural or cultural resources. | Reach Networks Hong Kong Ltd. 2007. Project Profile: Asia-America Gateway (AAG) Cable Network, South Lantau. Wanchai, Hong Kong SAR. |
Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Forestry Policy: Forest Chemical Management | Pesticides and fertilizers are commonly used in forestry to reduce mortality of desired trees, improve forest production, and ease harvest/extraction. The rate of application is typically very low, but given the overall area covered, pesticides can still accumulate within watersheds. Some forest management chemical use considerations to reduce nonpoint source pollution impacts include: Develop an effective spill contingency plan to contain spills, and immediately report accidental spills into surface waters to the appropriate State agency. Prior to application, inspect the mixing and loading process and the calibration of equipment, and identify the appropriate weather conditions, the spray area, and buffer areas for surface waters. Buffer areas for surface waters are especially important for aerial applications. Carefully prescribe the type and amount of pesticides appropriate for the insect, fungus, or herbaceous species. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Provisioning Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Water Resources; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Marine Zoning: Ecological Reserves (ERs) | Ecological Reserves set aside areas with minimal human interference. These reserves aim to enhance and protect biodiversity through encompassing large, contiguous habitats. The goal of ecological reserves is to encourage spawning, nurseries, and residence areas that contribute to genetic protection of fish and marine life. Ecological Reserves can be achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Special Use Areas | Special use areas are set aside for specific scientific or educational purposes. This is in order to encourage the recovery or restoration of injured or degraded resources. Also, the areas may be designated to facilitate access to, or use of, resources, and prevent other user conflicts. Special-use areas are achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts; and determining/establishing appropriate zones for high-impact or user-conflict activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Biomedical Research Policies; Complex Habitat & Resources; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Marine Zoning: Develop Baseline Data | Baseline surveys of existing resources need to be conducted before monitoring can begin. The surveys must be conducted in Ecological Reserves, Sanctuary Preservation Areas, and Special-Use Areas to characterize the status of important marine species and their habitats. Establishing baseline data allows for later comparisons to monitoring data to gauge changes over time and revaluate current management actions being taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Use Patterns on Artificial and Natural Reefs | This management option seeks to provide data for decisions concerning creating new artificial reefs. Use data is important because justification for artificial reefs extends from their ability to shift use pressures (diving, fishing, etc.) from natural reefs. Once an artificial reef is decided on there is much more data to collect and factors to consider when deciding where the artificial reef (#189). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Defense; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Military; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Sanctuary Use Patterns and Resource Value | This management option seeks to provide data and analysis of consumptive and non-consumptive use of all natural resources within sanctuary borders. Special emphasis is to be placed on artificial and natural reef resources used by residents and visitors. Wherever possible, market and non-market values of these resources should be elicited as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Services; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Monitor & Research: Research Artificial Reef Siting, Size, and Materials Impact for Future Management Decisions | The effects of artificial reefs on fish and invertebrate abundance and community composition and on other sanctuary resources need to be assessed. Siting and size considerations should include spatial components such as nearest natural reef, species connectivity, currents, distance to shore, expected use, hurricane occurances, etc. The longevity of artificial reefs composed of different materials needs to be evaluated and considered heavily. | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Debris; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Water Resources; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Monitor & Research: Fisheries Sampling | Improved fisheries sampling programs require improving the spatial resolution of commercial and recreation fisheries-dependent and fisheries-independent sampling programs to provide statistics on catch and effort. Improved sampling can be achieved through evaluating and enhancing census programs by using smaller sampling areas. Also, fishery pre-recruitment monitoring efforts should be continued for long-term prediction of fishery stocks. Last, investigating life histories of fishery species needs to be conducted because it is currently a gap. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Utilize Managed Areas for Socioeconomic Research | Data are needed to test hypotheses about the socioeconomic impact of marine zoning and user-group perceptions about changes in natural resources within the sanctuary area. User-group perception of changes in natural resources can be compared with quantitative ecological data to identify misconceptions and knowledge gaps. Providing funding opportunities for external scientists to conduct research in the managed area is another option. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Raw Materials; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Permitting & Zoning; Provisioning Services; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Valuation |
| Monitor & Research: Research Queen Conch Reproduction and Restoration | Inshore Queen Conch may be experiencing reproductive failure. Research on various snails in other parts of the world has shown that snails are susceptible to endocrine disruption caused by various anthropogenic contaminants. This activity will determine the cause of reproductive failure, possibly by endocrine disruption, of queen conch in reef areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Applied Chemicals; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Molluscs; Recreational Fishing; Reef Inhabitants; Snails & Conch; Waterborne Discharges |
| Public Participation: Assist Seafood Watch | Assist Seafood Watch and other sustainable seafood consumption initiatives, in their efforts to educate the public and promote sustainable seafood. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. SeafoodWatch. 2005. Sustainable Seafood Business Practices. Monteray Bay. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Sectors Filling Human Needs |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Consider Regulations for Catch & Release Trolling | This plan seeks to reduce or eliminate catch-and-release fishing in many fragile areas. First an assessment must be conducted to measure the effects of catch-and -release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Bait Fishing and/or Catch & Release Trolling Regulations | This option seeks to reduce or eliminate bait fishing, and catch & release trolling in fragile areas. First assessments must be conducted to measure the effects of bait fishing and catch & release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Spearfishing Regulations | Spearfishing is already prohibited in ecological reserves, sanctuary preservation areas, management areas, and special-use areas. There are additional considerations to be made to see if restrictions need to be extended in high priority areas. There may also be need to be further scientific study on the impacts of spearfishing. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Dredging Regulations | Dredging is oftentimes prohibited with certain exceptions. Dredging regulation often falls under other controls over the alteration of the seabed, discharging or depositing materials. At times dredging is necessary for navigation or other activities, necessitating .permitting mechanisms for allowing otherwise prohibited activities. Revising the regulations to help eliminate negative dredge-and-fill activities within a certain distance of corals would be beneficial because it would help promote the reestablishment of sensitive benthic communities. Reservoirs may require periodic dredging to remove sediment that may have collected. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sand & Rock Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Transportation; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Channel & Reef Navigation Markers | This option would evaluate the need for proper marking to ensure better navigation. There are many types of markers, including buoys, charts, beacons, and GPS mapping. Such markers can also be used to advocate prohibition on vessel speeds greater than idle speed in areas designated as idle-speed only/no-wake and around shallow reef locations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beach & Land Formation; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Live Collection Regulations | Live collection is often more destructive than capture of food fishes because of the destructive methods used to remove live fish and invertebrates from the reef habitat. These methods include use of cyanide and explosives. Current methods should be assessed and alternatives should be developed or collection prohibited. | World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Regulations for Sponge Fisheries | Sponges play a vital role on reefs, providing structure, food and filtration. Depending on the method of removal, this process can be very destructive to other reef fauna and habitat. Research is needed to compare impacts of different sponge fishing methods in different areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boring Sponges; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Educational & Research Opportunities; Encrusting Sponges; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Resource Use Management: Designated Uses | The water quality standards regulation requires that States and Tribes specify appropriate water uses to be achieved and protected. Appropriate uses are identified by taking into consideration the use and value of the water body for public water supply, for protection of fish, shellfish, and wildlife, and for recreational, agricultural, industrial, and navigational purposes. In designating uses for a water body, States and Tribes examine the suitability of a water body for the uses based on the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the water body, its geographical setting and scenic qualities, and economic considerations. Each water body does not necessarily require a unique set of uses. Instead, the characteristics necessary to support a use can be identified so that water bodies having those characteristics can be grouped together as supporting particular uses. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. Environmental Protection Agency. What are Water Quality Standards? Designated Uses. Water: Water Quality Standards Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Marine Products; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Water Efficiency Initiatives | Reducing water use through cost effective water efficiency improvements can be beneficial as it reduces pressure on water as a finite resource and saves money. There are several ways water efficiency can be promoted. Some Water Efficiency BMPs recommended by the EPA include: Water Management Planning; Information and Education Programs; Distribution System Audits, Leak Detection and Repair; Water-Efficient Landscaping, Water-Efficient Irrigation; Toilets and Urinals; Faucets and Showerheads; Boiler/Steam Systems; Single-Pass Cooling Equipment; Cooling Tower Management; Commercial Kitchen Equipment; Laboratory/ Medical Equipment; Other Water Intensive Processes; Alternative Water Sources. One of the ways the US government has promoted Water Efficiency Initiatives is through Executive order 13123 which places certain water use reduction requirements on Federal Agencies. There are also existing funding and incentives for non-government sectors. Project funding comes in many forms, such as appropriations, energy savings performance contract (ESPC) and Utility Energy Service Contract (UESCs) programs; ratepayer incentive programs such as rebates from public benefit funds or utilities; and the retention of energy and water cost savings. | US Department of Energy. 2008. Establishing Baseline and Meeting Water Conservation Goals of Executive Order 13423. Environmental Protection Agency. Federal Water Efficiency Best Management Practices. Federal Energy Management Program Accessed 7/12/2011. |
Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Designated Uses; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Resource Use Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Textiles & Apparel; Utilities; Utility Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Restoration: Beach Renourishment and Nourishment | Beaches are subject to natural accretion and erosion. Tourism is often best supported by wide, accessible, public sandy beaches. Beaches can be restored to counteract natural erosion by transporting large quantities of sand onto the beach. This sand often comes from nearby dredging. Caution should be used when restoring long sections of beaches, as often the area above the mean high tide line is littoral, or privately owned, and restoration of these beaches can impact these property rights, see "Stop the Beach Renourishment, Inc. v. Florida Department of Environmental Protection (2010) U.S. Supreme Court decision." Beach protection or nourishment offers an alternative to this often expensive and abrupt type of renourishment, nourishment involves practices which encourage coastal accretion and discourage erosional forces. See "Florida's Beach and Shore Preservation Act" for some restrictions on this. | NOAA Coastal Services Center. Beach Nourishment: A Guide for Local Government Officials. Coastal Services Center Accessed 6/17/2011. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Culture; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Recreational Opportunities; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation |
| Transportation Policy: Airline Carbon Policy | Civil aviation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, and this contribution has grown as the industry has grown. Some regions are implementing policies such as cap and trade that apply to the airline industry. | Bruce Duguid. 2009. Fasten Your Seat Belt: Airlines and cap-and-trade. CTC764, Carbon Trust, United Kingdom. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Political Pressure; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Supporting Services; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Transportation Policy: Corporate Average Fuel Economy Standards | The purpose of Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAF�) standards is to reduce fuel consumption by increasing the fuel economy of cars and light trucks. NHTSA sets fuel economy standards for cars and light trucks sold in the US while EPA calculates the average fuel economy for each manufacturer. Since the standard only dictates the average fuel economy, manufacturers can sell vehicles with higher or lower fuel economy than the standard. | National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE). Accessed 8/11/2011. |
Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Food & Energy Policies; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Industry; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Supporting Services; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Water Quality Management: Water Quality Standards | Water Quality Standards are the foundation of the water quality-based pollution control program mandated by the Clean Water Act. Water Quality Standards define the goals for a waterbody by establishing Designated Uses (#279), setting baseline waterbody minimum criteria to protect those uses, and establishing provisions that regulate Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards (#280). Since the baseline water quality standards are for the waterbody in its entirety, there is some flexibility on how that minimum criterion is accomplished. In some cases, Remediation (#281) may be preferable to more stringent effluent standards. The criteria include specific biochemical and ecological measures that would be good indicators of ecological health, including Biocriteria (#282). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biocriteria; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Toxics |
| Water Quality Management: Pet Waste Cleanup Ordinance & Education | In residential areas, pet waste can contributes to the large amount of nutrients and pathogens that enter the water through stormwater runoff. This is especially useful in regions such as Gu�nica, Puerto Rico where there are a lot of stray dogs. Education for pet-owners and possible ordinance would help decrease harmful pathogens reaching corals through stormwater runoff and reduce eutrophication. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Animal Waste Collection. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Clary, J., Leisenring, M., and Jeray, J. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Pollutant Category Summary: Fecal Indicator Bacteria. Wright Water Engineers. |
Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Domestic Animal Waste; Environmental Education & Outreach; Health; Health Policies; Invasive Species; Landscaping & Household Services; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Stormwater Management; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Aquatic Organism Passage | This management action allows for upstream and downstream passage for fish and other aquatic organisms. The passage of these organisms is often restricted by barriers which must be modified, removed, or worked around with fishways. Sites should be evaluated for variations in discharge, tidal influence, hydraulics, geomorphic impacts, sediment transport and continuity, and organic debris movement. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Water Resources |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Waterway Management/Marking Plan | Proper waterway markings provide coherent guidance for boats. Clearly-marked waterway exits and entrances reduce the probability of damage to reefs from boat gear damage, boat movement, trampling, and ballast discharge. Waterway marking can be achieved through surveying damage from propeller scarring and vessel groundings, enhancing channel marking aids, assessing the effectiveness of channel marking, and through removing waterway obstructions. "Hotspots" where many incidents have been reported should be considered for further marking, especially those that are in high use areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Trampling; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Mooring Buoy Management | Installing mooring buoys is encouraged in order to prevent damage to corals from anchors. Areas that experience a lot of traffic from recreation and fishing will experience damage from vessel groundings and boat gear. Mooring buoys help to minimize damage to corals and at the same time provide access to water resources. Mooring buoys protect as well as lower resource-use conflicts. Mooring buoy management is achieved through maintaining existing mooring buoys; assessing current buoy technology; reviewing visitor-use and boating data; developing sitting criteria; recommending new sites; conducting site assessments; installing additional buoys; and implementing vessel size limits in high-use and sensitive areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Altmeier, Bernie. FKNMS Mooring Buoy Mainenance. NOAA: FKNMS Mooring Buoy Manual Accessed 3/23/2011. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amendment to the U.S. Caribbean Fishery Management Plans, Code of Federal Regulations § 600 and 622. | NMFS issues this final rule to implement a comprehensive amendment prepared by the Caribbean Fishery Management Council (Council) to amend its Reef Fish, Spiny Lobster, Queen Conch, and Coral Fishery Management Plans (FMPs). The comprehensive amendment is designed to ensure the FMPs are fully compliant with the provisions of the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (Magnuson-Stevens Act). This final rule redefines the fishery management units for the FMPs; establishes seasonal closures; imposes gear restrictions and requirements; revises requirements for marking pots and traps; and prohibits the filleting of fish at sea. In addition, the comprehensive amendment establishes biological reference points and stock status criteria; establishes rebuilding schedules and strategies to end overfishing and rebuild overfished stocks; provides for standardized collection of bycatch data; minimizes bycatch and bycatch mortality to the extent practicable; designates essential fish habitat (EFH) and EFH habitat areas of particular concern (HAPCs); and minimizes adverse impacts on such habitat to the extent practicable. The intended effect of this final rule is to achieve optimum yield in the fisheries and provide social and economic benefits associated with maintaining healthy stocks. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects coral reefs in the USVI and Puerto Rico from overfishing reef resources, specifically reef fish, lobster, and queen conch taking. It establishs seasonal closures, restrictions on the gear used, lists areas of specific biological reference points, and has a schedule and strategy for restocking fishery resources. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Recreational Fishing; Reef Inhabitants |
| Anadromous Fish Conservation Act of 1965, as amended, 16 United States Code § 757. | The Act is intended to conserve anadromous fish. It authorizes the Secretatries of Interior and Commerce to enter into cooperatve agreements with states and other non-federal interests for conservation, development and enhancement of anadromous fish and contribute up to fifty percent as the federal share of the cost of carrying out such agreements. Reclamation construction projects for water resource projects needed solely for such fish are also authorized. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Projects are for conservation, development, and enhancement on fisheries. Comments: |
Department of Interior/Department of Commerce Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 17: Oil soil prevention and pollution control, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Prohibits the discharge of oil, petroleum products or their by-products, and other pollutants into or upon any coastal waters, estuaries, tidal flats, beaches, and land adjoining the seacoast of the Territory. Requires prompt containment and removal of petroleum. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects ecosystems, including coral reefs, from petroleum spills and provides for cleanup. Legislative Actions:Established the Virgin Island Coastal Protection Fund of $1,000,000 for cleanup response. Prohibits derilict vessels upon any public waters or ports. Provides for civil penaltiesup to $50,000per day. Requires a National Contingency Plan. Comments:Because it is the intent of this chapter to provide the means for rapid and effective cleanup and to minimize damages, any licensee and its agents or servants, including vessels destined for or leaving a licensee's terminal facility, who permits or suffers a prohibited discharge or other polluting condition to take place within territorial boundaries shall be liable to the territory for all costs of cleanup or other damage incurred by the territory and for damages resulting from injury to others. The territory shall have an absolute maritime lien which shall attach to any vessel and its freight on behalf of the territory or any person injured, for all costs of cleanup and other damages incurred as a result of a prohibited discharge. In any suit to enforce claims of the territory under this chapter, it shall not be necessary for the territory to plead or prove negligence in any form or manner on the part of the licensee or any vessel. If the territory is damaged by a discharge prohibited by this chapter it need only plead and prove the fact of the prohibited discharge or other polluting condition and that it occurred. In addition to the civil penalty, the pilot and the master of any vessel or person in charge of any licensee's terminal facility who fails to give immediate notification of a discharge to the harbor master and nearest U.S. Coast Guard station shall be guilty of a misdemeanor and fined not less than $5,000 nor more than $10,000. The Department shall, by rules and regulations, require that the licensee designate a person at the terminal facility who shall be the person in charge of that facility for the purposes specified by this section. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Collaboration & Partnering; Mangroves; Oil & Gas Tankers; Petroleum Spills; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Water Resources |
| Chapter 2: Protection of indigenous, endangered and threatened fish, wildlife and plants, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates activities, including scientific research, that could affect indigenous species and species considered at risk (threatened) or endangered, establishes species of special concern and habitats that should be protected, requires permits for trimming mangroves Application to Coral Reefs:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Legislative Actions:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Delineation of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters, 62-340 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2000). | The Rule's intent is to provide a unified statewide methodology for the delineation of the extent of wetlands to satisfy the mandate of Section 373.421, F. S. Application to Coral Reefs:Preservation of wetlands will allow them to continue to function as buffers for sediment and contaminant control keeping them from reaching estuarine and marine waters and eventually habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative and methodological for delineation purposes. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Energy Policy & Development; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Environmental resource permitting procedures, 62-343 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2003). | The rule provides the procedural requirements for processing environmental resource permits and obtaining formal determinations of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring permits for projects related to environmental resources will indirectly protect environmental habitats. The permits are related to stormwater managemnt systems including discharges to wetlands. The permit conditions can limit toxics, nutrients and sediment that would be discharged to the environment if the rule were not in place. Legislative Actions:The rule is procedural and does not have fines or penalties. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Permitting & Zoning; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| Exec. Order No. 12962, Recreational Fisheries, 60 Federal Register (1995). | Federal agencies are directed to improve the quantity, function, sustainable productivity, and distribution of U.S. aquatic resources for increased recreational fishing opportunities in cooperation with states and tribes. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | To provide financial and technical assistance to the states for development, revision and implementation of conservation plans and programs for nongame fish and wildlife, and to encourage federal agencies to utilize their statutory and administrative authority to conserve and to promote the conservation of nongame fish and wildlife and their habitats. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Incentives; Microorganisms; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Anchoring on Tortugas Bank, Federal Register § Volume 63, Number 158 (1998). | The regulation reinstates and makes permanent the temporary prohibition on anchoring by vessels 50 meters or greater in registered length on the Tortugas Bank west of the Dry Tortugas National Park within the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition on anchoring protects coral reefs and benthic habitats from physical damage. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Identification of impaired surface waters, 62-303 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2002). | The Chapter established a methodology to identify surface waters of the state that will be included on the state's planning list of waters that will be assessed pursuant to subsections 403.067(2) and (3), Florida Statutes. It also establishes a methodology to identify impaired waters based on representative data that will be included on the state's verified list of impaired waters, for which the Department will calculate Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDLs), pursuant to subsection 403.067(4), F.S., and which will be submitted to the United States Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to paragraph 303(d)(1) of the Clean Water Act (CWA). Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Microorganisms; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Lacey Act, 16 United States Code §§ 3372 et seq. | The Act provides that it is unlawful for any person to import, export, transport, sell, receive, acquire, or purchase any fish or wildlifeor plant taken, possessed, transported, or sold in violation of any law, treaty, or regulation of the United States or in violation of any Indian tribal law whether in interstate or foreign commerce. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act makes possession, selling, transporting, importing, exporting, receiving, acquiring, and purchasing illegal under specific cases. Corals would be included. Legislative Actions:Civil Penalties up to $10,000 per each violation or maximum criminal sanctions of $20,000 in fines and/or up to five years imprisonment. All plants and animals taken in violation of the Act are subject to forfeiture as well as all vessels, vehicles, aircraft, and other equipment used to aid in the importing, exporting, transporting, selling, receiving, acquiring, or purchasing of fish and wildlife or plants in a criminal violation for which a felony conviction is obtained where the owner should have known of the illegal transgression. Comments: |
US Department of Agriculture/Us Border Patrol Jurisdiction: United States |
Aquarium Stock; Coral; Improved Technology; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Reauthorization Act as amended through January 2007, Statutes at Large §§ 94-265. | National program for the conservation and management of fishery resources of the US to prevent overfishing, to rebuild overfished stocks, to facilitate the long-term protection of essential fish habitat, and to realize the full potential of the Nation's fishery resources. Application to Coral Reefs:Promote the protection of essential fish habitat in the review of projects conducted under federal permits, licenses, or other authorities that effct or have the potential to affect such habitats. The amendments of 2006 specifically require the protection of deep sea coral habitats. Legislative Actions:Requires government observers on board a certain number of fishing vessels. The Act provides for criminal and civil penalties dependent on the sections of the Act under which violations occured. Criminal penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $50,000 and not more than one year in prison. Civil penalties may be imposed including seizure, forfeiture, and condemnation of property. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Economic Markets & Policies; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Oil Pollution Act of 1990, 33 United States Code §§ 2701 et seq. | Established limitations on liability for damages resulting from oil pollution, established a fund for the payment of compensation for such damages, mandated the National Oil and Hazardous Substance Contingency Plan to provide organizational structure and procedures for responding to spills. Application to Coral Reefs:In the event of an oil spill that contaminates a coral reef, the Act could be used to determine liability and provide funds for rapid cleanup. Legislative Actions:Can provide fines for failing to notify the appropriate federal agency of a maximum of $250,000 per day for an individual and a maximum of $500,000 for an organization. Civil penalties are authorized at $25,000 per day of violation or $1,000 per barrel of oil discharged. Prison sentences up to a maximum of fifteen years can be imposed on violators. Comments:The Act was signed in 1990, largely in response to rising public concern following the Exxon Valdex incident. The Act improved the nation's ability to prevent and respond to oil spills by establishing provisions that expand the federal government's ability, and and provided the money and resources necessary, to respond to oil spills. The Oil Spill Liability Trust Fund was established and provided up to one billion dollars per spill incident. |
US Coast Guard/US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters |
Chemical Variables; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Funding & Incentives; Mangroves; Non-point Source Controls; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Environment; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Toxics; Wetlands |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proposed Coral Reef Conservation Act Amendments of 2005, 2007 and 2009,. | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:When passed, the Amendments, among other issues, would reauthorize the Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000 and authorize appropriations through fiscal 2012 for the coral reef conservation program and community- based planning grants. Will authorize activities designed to minimize the likelihood of vessel impacts or other physical dammage to coral reefs, including activities to identify certain at-risk coral reefs. Promote international cooperation, codify the US Coral Reef Task Force. Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The amendments would not add regulations to the Act. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; CO2; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 include (1) Coastal Barrier Improvement Act of 1990, (2) Coastal Barrier Resources Reauthorization Act of 2000, (3) Coastal Barriers Resources Reauthorization Act of 2005,. | (1) Added additional areas along the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, the Florida Keys and the Virgin Islands and established "Otherwise Protected Areas OPAs); (2) amended the guidelines for making recommendations regarding additions to the CBRS and reqired a pilot digital mapping project; (3) reauthorized CBRA and required the submission of the final digital mapping pilot project. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restricted most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Forestry; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Sovereign submerged lands management, 18-21 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | To manage, protect, and enhance sovereignty lands so that the public may continue to enjoy traditional uses, including, but not limited to, navigation, fishing and swimming, public drinking water supply, shellfish harvesting, public recreation, and fish and wildlife propagation and management. Application to Coral Reefs:Permitting activities on submerged lands owned by Florida will improve water quality which will indirectly protect reef systems. Legislative Actions:These rules are to implement the administration and management responsibilities of the board and department regarding sovereign submerged lands. Responsibility for environmental permitting of activities and water quality protection on sovereign lands is vested with the Department of Environmental Protection. These rules are considered cumulative. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Energy Policy & Development; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Surface water quality standards in table format, 62.302.500 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | This section of Chapter 62-302 presents the water quality standards in a tabular format for each class of waters of the State. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| The Sustainable Fisheries Act, 23 §§ 104-297 (1996). | To amend the Magnuson Fisheries Conservation and Management Act to authorize appropriations, to provide for sustainable fisheries, and for other purposes. Application to Coral Reefs:The law recogonizes that direct and indirect habitat losses have resulted in a diminshed capacity to support existing fish levels. Habitat considerations should receive increased attention for conservation and management of fishery resources in the United States. Therefore, the Act encourages, though not indirectly, the protection of coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Commercial Fisheries; Economic Markets & Policies; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Seagrasses |
| Total maximum daily loads, 62-304 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | The Chapter establishes Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), and their allocations, for waters that have been verified to be impaired by a pollutant pursuant to Chapter 62-303. F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Envitonmental Protection Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Biomedical Research Policies; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Impervious Surfaces; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Uniform Mitigation Assessment Method, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-345 (2005). | Establishes a methodology that provides a standard procedure for assessing the functions provided by wetlands and other surface waters, the amount that those functions are reduced by a proposed impact, and the amount of mitigation necessary to offset that loss. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting wetlands provides wetland areas that can act as buffers against nutrients, pollutants and contaminants from reaching habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is administrative and provides methods to assess wetland value and appropriate mitigation to offset impact. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Water quality based effluent limitations, 62-650 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To implement the provisions of Section 403.051, 403.085 through 403.088 concerning the development of effluent limitations for wastewater facilities. Application to Coral Reefs:The Florida Air and Water Pollution Act establishes that no wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessay to protect the beneficial uses of such water. Requiring treatment of industrial and domestic waste water indirectly protects adjoining ecosystem, such as reefs, by limiting the pollutant that reach these other systems. Legislative Actions:The Department shall not issue a permit for a discharge to waters of the state, unless the Department has established an efflent limit for those pollutants in the discharge that are present in quantities or concentrations which can be reasonably expected to cause or contribute, directly or indirectly, to a violation of any water quality standard established in rule 62-302. The effluent limit may be a technology based effluent limit (TBEL), a water quality based effluent limit (WQBEL) determined by a Level 1 process, or where applicable, a WQBEL determined by a Level 2 process. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Domestic Animal Waste; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water Resource Implementation Rule, 62-40 Florida Administrative Code (2006). | The Chapter is intended to provide water resouirce implementation goals, objectives and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources. A goal of the Chapter is to coordinate the management of water and land resources. It is the objective of the State to protect the functions of the entire ecological systems, as developed and defined in the programs, rules, and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is a goal of the Chapter that sufficient water be available for all existing and future reasonable-beneficial uses and the natural systems and that adverse effects of competition for water supplies be avoided. Application to Coral Reefs:By protecting the functions of entire aquatic ecological systems, those waters will contain less contaminants when they are discharged and meet other natural water bodies including marine ecosystems. Cleaner water will result in less ecological strees to marine ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This Chapter is intended to provide water resource implementation goals, objectives, and guidance for the development and review of programs, rules, and plans relating to water resources, based on statutory policies and directives in Chapters 187, 373, and 403, Florida Statutes. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Education & Outreach; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Waste Management Policies |
| Wetland applications, 62-611 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To provide qualitative and quantitative design criteria discharge limits, permitting requirements, and monitoring requirements for wetlands, man-made and natural, receiving domestic wastewater. Application to Coral Reefs:Because wetlands act as buffers and remove nutrients from contaminated water, in many case the nutrients will not reach the estuarine and marine environments and potentially have an adverse effect on coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative in nature and specific pollutant limits and monitoring requirements are specified in individual permits Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Education & Outreach; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
