ReefLink Database
Nutrients
Nutrients are essential elements needed by plants and animals for growth and primarily include nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium, as well as minor nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, or zinc.
CMap
CMap Description
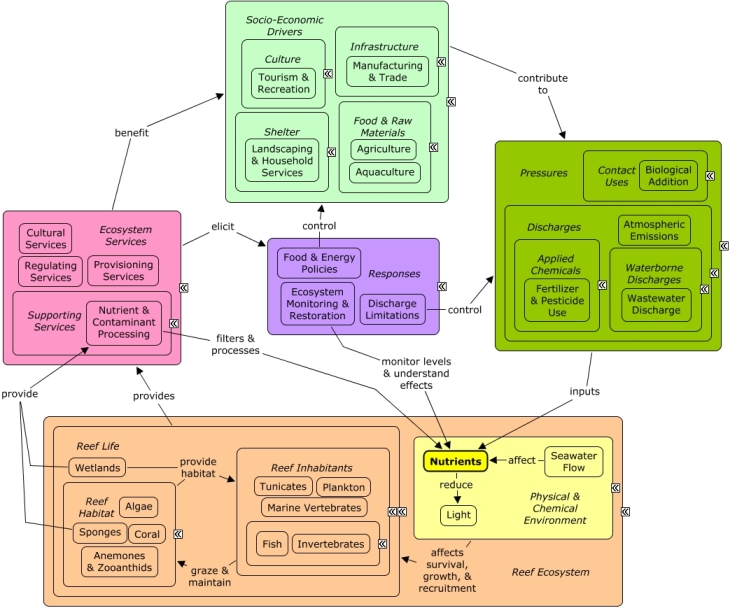
Excess nutrients can impact availability of light, affect the growth rates of reef species, and may also alter competitive interactions among algae and coral. Nutrients enter coastal waters from wastewater discharges and from non-point source runoff of fertilizers or animal waste from cities, agriculture, aquaculture, or landscaping activities. Nutrient and contaminant processing by sponges and wetlands can improve water quality. Wetlands also provide nutrients to reefs through the transport of materials, through fish or water movement between the ecosystems. Changes in reef condition can impact the availability of ecosystem services. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that create excess nutrients benefit indirectly from reef goods and services including fishing and recreational opportunities that contribute to the cultural identity of the local community. Monitoring and scientific research can be used to track nutrient levels, and to better understand the consequences for reef life. Agricultural practices and educational outreach can be implemented to reduce the over application of fertilizers. Point and non-point source controls can be implemented to reduce the intensity and frequency of nutrient loading. Ordinances can be adopted to mandate clean-up of pet or feral animal waste in cities.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011. Nonpoint Source Management Program 2010 Annual Report. Document # DEPLW-1205, Maine Department of Environmental Protection, Augusta, (Maine, USA). | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Housing; Impervious Surfaces; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Aboussalam, ZS; Becker, RT. 2011. The global Taghanic Biocrisis (Givetian) in the eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 304:136-164. | 2011 | Global; France; Germany | Climate; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Aeby, GS; Williams, GJ; Franklin, EC; Haapkyla, J; Harvell, CD; Neale, S; Page, CA; Raymundo, L; Vargas-Angel, B; Willis, BL; Work, TM; Davy, SK. 2011. Growth Anomalies on the Coral Genera Acropora and Porites Are Strongly Associated with Host Density and Human Population Size across the Indo-Pacific. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Global; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Climate; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Alvarez-Filip, L; Cote, IM; Gill, JA; Watkinson, AR; Dulvy, NK. 2011. Region-wide temporal and spatial variation in Caribbean reef architecture: is coral cover the whole story? Global Change Biology 17:2470-2477. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral |
| Anagnostou, E; Sherrell, RM; Gagnon, A; LaVigne, M; Field, MP; McDonough, WF. 2011. Seawater nutrient and carbonate ion concentrations recorded as P/Ca, Ba/Ca, and U/Ca in the deep-sea coral Desmophyllum dianthus. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75:2529-2543. | 2011 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Anthony, K. R. N., J. A. Maynard, G. Diaz-Pulido, P. J. Mumby, P. A. Marshall, L. Coa, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2011. Ocean acidification and warming will lower coral reef resilience. Global Change Biology doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02364.x. | 2011 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Anthony, KRN; Maynard, JA; Diaz-Pulido, G; Mumby, PJ; Marshall, PA; Cao, L; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 2011. Ocean acidification and warming will lower coral reef resilience. Global Change Biology 17:1798-1808. | 2011 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Baker, DM; Kim, K; Andras, JP; Sparks, JP. 2011. Light-mediated (15)N fractionation in Caribbean gorgonian octocorals: implications for pollution monitoring. Coral Reefs 30:709-717. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Bannister, RJ; Hoogenboom, MO; Anthony, KRN; Battershill, CN; Whalan, S; Webster, NS; de Nys, R. 2011. Incongruence between the distribution of a common coral reef sponge and photosynthesis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 423:95-100. | 2011 | Australia | Complex Habitat & Resources; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | |
| Bao, Y; Zhan, L; Wang, CX; Wang, YL; Qiao, WM; Ling, LC. 2011. Carbon foams used as packing media in a biological aerated filter system. Materials Letters 65:3154-3156. | 2011 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Barott, KL; Rodriguez-Brito, B; Janouskovec, J; Marhaver, KL; Smith, JE; Keeling, P; Rohwer, FL. 2011. Microbial diversity associated with four functional groups of benthic reef algae and the reef-building coral Montastraea annularis. Environmental Microbiology 13:1192-1204. | 2011 | Algae; Climate; Cyanobacteria; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | ||
| Bhattacharyya, J; Pal, S. 2011. Coexistence of competing predators in a coral reef ecosystem. Nonlinear Analysis - Real World Applications 12:965-978. | 2011 | Model | Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Blanco, AC; Watanabe, A; Nadaoka, K; Motooka, S; Herrera, EC; Yamamoto, T. 2011. Estimation of nearshore groundwater discharge and its potential effects on a fringing coral reef. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:770-785. | 2011 | Japan | Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Boehm, AB; Yamahara, KM; Walters, SP; Layton, BA; Keymer, DP; Thompson, RS; Knee, KL; Rosener, M. 2011. Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen, Soluble Reactive Phosphorous, and Microbial Pollutant Loading from Tropical Rural Watersheds in Hawai'i to the Coastal Ocean During Non-Storm Conditions. Estuaries and Coasts 34:925-936. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bouma, JA; Kuik, O; Dekker, AG. 2011. Assessing the value of Earth Observation for managing coral reefs: An example from the Great Barrier Reef. Science of the Total Environment 409:4497-4503. | 2011 | Global; Australia; Europe | Climate; Monetary Valuation; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Bover-Arnal, T; Salas, R; Martin-Closas, C; Schlagintweit, F; Moreno-Bedmar, JA. 2011. Expression Of An Oceanic Anoxic Event In A Neritic Setting: Lower Aptian Coral Rubble Deposits From The Western Maestrat Basin (Iberian Chain, Spain). Palaios 26:18-32. | 2011 | Global; Oman; Spain | Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Brodie, JE; Devlin, M; Haynes, D; Waterhouse, J. 2011. Assessment of the eutrophication status of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon (Australia). Biogeochemistry 106:281-302. | 2011 | Australia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bruno, JF; Ellner, SP; Vu, I; Kim, K; Harvell, CD. 2011. Impacts of aspergillosis on sea fan coral demography: modeling a moving target. Ecological Monographs 81:123-139. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; Mexico | Model | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens |
| Carricart-Ganivet, JP; Beltran-Torres, AU; Horta-Puga, G. 2011. Distribution and prevalence of coral diseases in the Veracruz Reef System, Southern Gulf of Mexico. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 95:181-187. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Castillo, KD; Ries, JB; Weiss, JM. 2011. Declining Coral Skeletal Extension for Forereef Colonies of Siderastrea siderea on the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, Southern Belize. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean | Climate; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Ceh, J; van Keulen, M; Bourne, DG. 2011. Coral-associated bacterial communities on Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 75:134-144. | 2011 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Chauvin, A; Denis, V; Cuet, P. 2011. Is the response of coral calcification to seawater acidification related to nutrient loading? Coral Reefs 30:911-923. | 2011 | Indian Ocean; Cuba; India | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Discharges; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae | |
| Chaves-Fonnegra, A; Zea, S. 2011. Coral colonization by the encrusting excavating Caribbean sponge Cliona delitrix. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 32:162-173. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Boring Sponges; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Chellaram, C; Anand, TP; Kesavan, D; Priya, G; Chandrika, M; Gladis, C. 2011. Enhanced cultivability of antagonistic bacterial strains from soft coral Sinularia sp., Gulf of Mannar, Southeastern India. African Journal Of Microbiology Research 5:1521-1526. | 2011 | India | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Chen, CP; Tseng, CH; Chen, CA; Tang, SL. 2011. The dynamics of microbial partnerships in the coral Isopora palifera. ISME Journal 5:728-740. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Collaboration & Partnering; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Chen, TR; Yu, KF. 2011. P/Ca in coral skeleton as a geochemical proxy for seawater phosphorus variation in Daya Bay, northern South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:2114-2121. | 2011 | China | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Cleveland, A; Verde, EA; Lee, RW. 2011. Nutritional exchange in a tropical tripartite symbiosis: direct evidence for the transfer of nutrients from anemonefish to host anemone and zooxanthellae. Marine Biology 158:589-602. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Collado-Vides, L; Mazzei, V; Thyberg, T; Lirman, D. 2011. Spatio-temporal patterns and nutrient status of macroalgae in a heavily managed region of Biscayne Bay, Florida, USA. Botanica Marina 54:377-390. | 2011 | Florida | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Corlett, H; Jones, B. 2011. Ecological controls on Devonian stromatoporoid-dominated and coral-dominated reef growth in the Mackenzie Basin, Northwest Territories, Canada. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 48:1543-1560. | 2011 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Cuet, P; Atkinson, MJ; Blanchot, J; Casareto, BE; Cordier, E; Falter, J; Frouin, P; Fujimura, H; Pierret, C; Susuki, Y; Tourrand, C. 2011. CNP budgets of a coral-dominated fringing reef at La Reunion, France: coupling of oceanic phosphate and groundwater nitrate. Coral Reefs 30:45-55. | 2011 | Australia; Reunion; France | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Cuet, P; Pierret, C; Cordier, E; Atkinson, MJ. 2011. Water velocity dependence of phosphate uptake on a coral-dominated fringing reef flat, La Reunion Island, Indian Ocean. Coral Reefs 30:37-43. | 2011 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Nutrients | |
| Dale, JJ; Wallsgrove, NJ; Popp, BN; Holland, KN. 2011. Nursery habitat use and foraging ecology of the brown stingray Dasyatis lata determined from stomach contents, bulk and amino acid stable isotopes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 433:221-236. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Apex Fish Predators; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting | |
| Dolenec, M; Zvab, P; Mihelcic, G; Belak, ZL; Lojen, S; Kniewald, G; Dolenec, T; Smuc, NR. 2011. Use of stable nitrogen isotope signatures of anthropogenic organic matter in the coastal environment: A case study of the Kosirina Bay (Murter Island, Croatia). Geologia Croatica 64:143-152. | 2011 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Downs, C. A., C. M. Woodley, J. E. Fauth, S. Knutson, M. M. Burtscher, L. A. May, A. R. Avadanei, J. L. Higgins, and G. K. Ostrander. 2011. A survey of environmental pollutants and cellular-stress markers of Porites astreoides at six sites in St. John, U.S. Virgin Islands. Ecotoxicology | 2011 | Global; US Virgin Islands | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Downs, CA; Woodley, CM; Fauth, JE; Knutson, S; Burtscher, MM; May, LA; Avadanei, AR; Higgins, JL; Ostrander, GK. 2011. A survey of environmental pollutants and cellular-stress markers of Porites astreoides at six sites in St. John, US Virgin Islands. Ecotoxicology 20:1914-1931. | 2011 | Global; Florida; US Virgin Islands | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Drupp, P; De Carlo, EH; Mackenzie, FT; Bienfang, P; Sabine, CL. 2011. Nutrient Inputs, Phytoplankton Response, and CO(2) Variations in a Semi-Enclosed Subtropical Embayment, Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Aquatic Geochemistry 17:473-498. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Engle, V. D. 2011. Estimating the provision of ecosystem services by Gulf of Mexico coastal wetlands. Wetlands DOI10.1007/s13157-010-0132-9. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Eynaud, Y; Nisbet, RM; Muller, EB. 2011. Impact of excess and harmful radiation on energy budgets in scleractinian corals. Ecological Modelling 222:1315-1322. | 2011 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Falter, JL; Atkinson, MJ; Schar, DW; Lowe, RJ; Monismith, SG. 2011. Short-term coherency between gross primary production and community respiration in an algal-dominated reef flat. Coral Reefs 30:53-58. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C; Peirano, A; Abbate, M; Cocito, S; Negri, A; Rottier, C; Riera, P; Rodolfo-Metalpa, R; Reynaud, S. 2011. Summer autotrophy and winter heterotrophy in the temperate symbiotic coral Cladocora caespitosa. Limnology and Oceanography 56:1429-1438. | 2011 | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Figueiredo, J; Pereira, HM. 2011. Regime shifts in a socio-ecological model of farmland abandonment. Landscape Ecology 26:737-749. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Nutrients | |
| Frank, N; Freiwald, A; Lopez Correa, M; Wienberg, C; Eisele, M; Hebbeln, D; Van Rooij, D; Henriet, JP; Colin, C; van Weering, T; de Haas, H; Buhl-Mortensen, P; Roberts, JM; De Mol, B; Douville, E; Blamart, D; Hatte, C. 2011. Northeastern Atlantic cold-water coral reefs and climate. Geology 39:743-746. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe | Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Freeman, CJ; Thacker, RW. 2011. Complex interactions between marine sponges and their symbiotic microbial communities. Limnology and Oceanography 56:1577-1586. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges; Zooxanthellae | |
| Fricke, A; Teichberg, M; Beilfuss, S; Bischof, K. 2011. Succession patterns in algal turf vegetation on a Caribbean coral reef. Botanica Marina 54:111-126. | 2011 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Turf Algae; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Fung, T; Seymour, RM; Johnson, CR. 2011. Alternative stable states and phase shifts in coral reefs under anthropogenic stress. Ecology 92:967-982. | 2011 | Florida | Model | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment |
| Gaidos, E; Rusch, A; Ilardo, M. 2011. Ribosomal tag pyrosequencing of DNA and RNA from benthic coral reef microbiota: community spatial structure, rare members and nitrogen-cycling guilds. Environmental Microbiology 13:1138-1152. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment | |
| Galkiewicz, JP; Pratte, ZA; Gray, MA; Kellogg, CA. 2011. Characterization of culturable bacteria isolated from the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 77:333-346. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Gates, RD; Ainsworth, TD. 2011. The nature and taxonomic composition of coral symbiomes as drivers of performance limits in scleractinian corals. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 408:94-101. | 2011 | Algae; Climate; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Seastars; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Godinot, C; Ferrier-Pages, C; Montagna, P; Grover, R. 2011. Tissue and skeletal changes in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata Esper 1797 under phosphate enrichment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 409:200-207. | 2011 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Godinot, C; Grover, R; Allemand, D; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. High phosphate uptake requirements of the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Biology 214:2749-2754. | 2011 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Godinot, C; Houlbreque, F; Grover, R; Ferrier-Pages, C. 2011. Coral Uptake of Inorganic Phosphorus and Nitrogen Negatively Affected by Simultaneous Changes in Temperature and pH. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Cuba | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Golberg, K; Eltzov, E; Shnit-Orland, M; Marks, RS; Kushmaro, A. 2011. Characterization of Quorum Sensing Signals in Coral-Associated Bacteria. Microbial Ecology 61:783-792. | 2011 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges; Stony Coral | ||
| Grol, MGG; Nagelkerken, I; Bosch, N; Meesters, EH. 2011. Preference of early juveniles of a coral reef fish for distinct lagoonal microhabitats is not related to common measures of structural complexity. Marine Ecology Progress Series 432:221-233. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Skeletal Coral | |
| Gutierrez-Ruiz, CV; Roman-Vives, MAM; Vergara, CH; Badano, EI. 2011. Impact of anthropogenic disturbances on the diversity of shallow stony corals in the Veracruz Reef System National Park. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad 82:249-260. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Haapkyla, J; Unsworth, RKF; Flavell, M; Bourne, DG; Schaffelke, B; Willis, BL. 2011. Seasonal Rainfall and Runoff Promote Coral Disease on an Inshore Reef. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Australia | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Haas, AF; Nelson, CE; Kelly, LW; Carlson, CA; Rohwer, F; Leichter, JJ; Wyatt, A; Smith, JE. 2011. Effects of Coral Reef Benthic Primary Producers on Dissolved Organic Carbon and Microbial Activity. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Australia; Cuba | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coralline Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | |
| Hata, H; Umezawa, Y. 2011. Food habits of the farmer damselfish Stegastes nigricans inferred by stomach content, stable isotope, and fatty acid composition analyses. Ecological Research 26:809-818. | 2011 | India; Japan | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Hearn, CJ. 2011. Perspectives in coral reef hydrodynamics. Coral Reefs 30:1-9. | 2011 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Guam | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients |
| Hedouin, L; Metian, M; Gates, RD. 2011. Ecotoxicological approach for assessing the contamination of a Hawaiian coral reef ecosystem (Honolua Bay, Maui) by metals and a metalloid. Marine Environmental Research 71:149-161. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Herbeck, LS; Unger, D; Krumme, U; Liu, SM; Jennerjahn, TC. 2011. Typhoon-induced precipitation impact on nutrient and suspended matter dynamics of a tropical estuary affected by human activities in Hainan, China. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 93:375-388. | 2011 | China | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hernandez-Terrones, L; Rebolledo-Vieyra, M; Merino-Ibarra, M; Soto, M; Le-Cossec, A; Monroy-Rios, E. 2011. Groundwater Pollution in a Karstic Region (NE Yucatan): Baseline Nutrient Content and Flux to Coastal Ecosystems. Water Air And Soil Pollution 218:517-528. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Discharges; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Holbrook, SJ; Schmitt, RJ; Brooks, AJ. 2011. Indirect effects of species interactions on habitat provisioning. Oecologia 166:739-749. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Seastars; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Howarth, R., F. Chan, D. J. Conley, J. Garnier, S. C. Doney, R. Marino, and G. Billen. 2011. Coupled biogeochemical cycles: eutrophication and hypoxia in temperate estuaries and coastal marine ecosystems. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 9:18-26. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Molluscs; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Salinity | |
| Huang, YCA; Hsieh, HJ; Huang, SC; Meng, PJ; Chen, YS; Keshavmurthy, S; Nozawa, Y; Chen, CA. 2011. Nutrient enrichment caused by marine cage culture and its influence on subtropical coral communities in turbid waters. Marine Ecology Progress Series 423:83-93. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Taiwan | Index or Indicator | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Stony Coral |
| Huang, Z; Brooke, BP; Harris, PT. 2011. A new approach to mapping marine benthic habitats using physical environmental data. Continental Shelf Research 31:S4-S16. | 2011 | Australia; Spain | GIS & Maps | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Isozaki, Y; Aljinovic, D; Kawahata, H. 2011. The Guadalupian (Permian) Kamura event in European Tethys. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 308:12-21. | 2011 | Global; Japan; China; Europe | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| James, NP; Jones, B; Nelson, CS; Campbell, HJ; Titjen, J. 2011. Cenozoic temperate and sub-tropical carbonate sedimentation on an oceanic volcano - Chatham Islands, New Zealand. Sedimentology 58:1007-1029. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jokela, Bill, Peter Kleinman, John Peters, and Ann Wolf,. 2011. Manure Spreader Calibration & Manure Testing. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Domestic Animal Waste; Nutrients | |
| Jones, AC; Monroe, EA; Podell, S; Hess, WR; Klages, S; Esquenazi, E; Niessen, S; Hoover, H; Rothmann, M; Lasken, RS; Yates, JR; Reinhardt, R; Kube, M; Burkart, MD; Allen, EE; Dorrestein, PC; Gerwick, WH; Gerwick, L. 2011. Genomic insights into the physiology and ecology of the marine filamentous cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108:8815-8820. | 2011 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Kaczmarsky, L; Richardson, LL. 2011. Do elevated nutrients and organic carbon on Philippine reefs increase the prevalence of coral disease? Coral Reefs 30:253-257. | 2011 | Philippines | Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Karnauskas, M; Cherubin, LM; Paris, CB. 2011. Adaptive Significance of the Formation of Multi-Species Fish Spawning Aggregations near Submerged Capes. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; Cayman Islands; Belize | Model | Fish; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish |
| Klemas, V. 2011. Remote Sensing Techniques for Studying Coastal Ecosystems: An Overview. Journal of Coastal Research 27:2-17. | 2011 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Salinity; Wetlands |
| Kolasinski, J; Rogers, K; Cuet, P; Barry, B; Frouin, P. 2011. Sources of particulate organic matter at the ecosystem scale: a stable isotope and trace element study in a tropical coral reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 443:77-93. | 2011 | Reunion; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kucken, M; Rinkevich, B; Shaish, L; Deutsch, A. 2011. Nutritional resources as positional information for morphogenesis in the stony coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Theoretical Biology 275:70-77. | 2011 | Model | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Lamb, JB; Willis, BL. 2011. Using Coral Disease Prevalence to Assess the Effects of Concentrating Tourism Activities on Offshore Reefs in a Tropical Marine Park. Conservation Biology 25:1044-1052. | 2011 | Australia | Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Lapointe, BE; Bedford, BJ. 2011. Stormwater nutrient inputs favor growth of non-native macroalgae (Rhodophyta) on O'ahu, Hawaiian Islands. Harmful Algae 10:310-318. | 2011 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Discharges; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lapointe, BE; Thacker, K; Hanson, C; Getten, L. 2011. Sewage pollution in Negril, Jamaica: effects on nutrition and ecology of coral reef macroalgae. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 29:775-789. | 2011 | Florida; Jamaica | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Lazar, KE; Frazer, TK; Jacoby, CA; St Mary, CM. 2011. Reproductive Strategy Of Siderastrea Radians In The St. Martins Keys, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:91-111. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Le Grand, HM; Fabricius, KE. 2011. Relationship of internal macrobioeroder densities in living massive Porites to turbidity and chlorophyll on the Australian Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 30:97-107. | 2011 | Australia; India | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Lentz, JA; Blackburn, JK; Curtis, AJ. 2011. Evaluating Patterns of a White-Band Disease (WBD) Outbreak in Acropora palmata Using Spatial Analysis: A Comparison of Transect and Colony Clustering. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Climate; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Lesser, MP; Slattery, M. 2011. Phase shift to algal dominated communities at mesophotic depths associated with lionfish (Pterois volitans) invasion on a Bahamian coral reef. Biological Invasions 13:1855-1868. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Caribbean | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Lin, HY; Wei, JD; Ou, CC; Lu, JW; Tsai, CY; Lee, MH. 2011. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of mesoporous zinc selenide agglomerates by nitrogen bubble templates. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 509:7009-7015. | 2011 | Nutrients | ||
| Lujan, NK; German, DP; Winemiller, KO. 2011. Do wood-grazing fishes partition their niche?: morphological and isotopic evidence for trophic segregation in Neotropical Loricariidae. Functional Ecology 25:1327-1338. | 2011 | Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Mackenzie, FT; Andersson, AJ; Arvidson, RS; Guidry, MW; Lerman, A. 2011. Land-sea carbon and nutrient fluxes and coastal ocean CO(2) exchange and acidification: Past, present, and future. Applied Geochemistry 26:S298-S302. | 2011 | Model | CO2; Discharges; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Maier, C; de Kluijver, A; Agis, M; Brussaard, CPD; van Duyl, FC; Weinbauer, MG. 2011. Dynamics of nutrients, total organic carbon, prokaryotes and viruses in onboard incubations of cold-water corals. Biogeosciences 8:2609-2620. | 2011 | Cuba | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Maina, J., T. R. McClanahan, V. Venus, M. Ateweberhan, and J. Madin. 2011. Global Gradients of Coral Exposure to Environmental Stresses and Implications for Local Management. PLoS One 6:1-14. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Middle East; Micronesia; Caribbean | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Maina, J; McClanahan, TR; Venus, V; Ateweberhan, M; Madin, J. 2011. Global Gradients of Coral Exposure to Environmental Stresses and Implications for Local Management. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; Chagos Archipelago; India; Middle East; Micronesia; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Mallela, J; Hermann, J; Rapp, RP; Eggins, SM. 2011. Fine-scale phosphorus distribution in coral skeletons: combining X-ray mapping by electronprobe microanalysis and LA-ICP-MS. Coral Reefs 30:813-818. | 2011 | GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Maloney, B; Iliffe, TM; Gelwick, F; Quigg, A. 2011. Effect of nutrient enrichment on naturally occurring macroalgal species in six cave pools in Bermuda. Phycologia 50:132-143. | 2011 | Florida; Bermuda | Index or Indicator | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Margreth, S; Gennari, G; Ruggeberg, A; Comas, MC; Pinheiro, LM; Spezzaferri, S. 2011. Growth and demise of cold-water coral ecosystems on mud volcanoes in the West Alboran Sea: The messages from the planktonic and benthic foraminifera. Marine Geology 282:26-39. | 2011 | Spain | Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Mason, HE; Montagna, P; Kubista, L; Taviani, M; McCulloch, M; Phillips, BL. 2011. Phosphate defects and apatite inclusions in coral skeletal aragonite revealed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 75:7446-7457. | 2011 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients | |
| Mayr, CC; Forsterra, G; Haussermann, V; Wunderlich, A; Grau, J; Zieringer, M; Altenbach, AV. 2011. Stable isotope variability in a Chilean fjord food web: implications for N- and C-cycles. Marine Ecology Progress Series 428:89-104. | 2011 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Marine Birds; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Salinity; Stony Coral | ||
| McAdoo, BG; Ah-Leong, JS; Bell, L; Ifopo, P; Ward, J; Lovell, E; Skelton, P. 2011. Coral reefs as buffers during the 2009 South Pacific tsunami, Upolu Island, Samoa. Earth-Science Reviews 107:147-155. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Samoa | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation |
| McMahon, KW; Berumen, ML; Mateo, I; Elsdon, TS; Thorrold, SR. 2011. Carbon isotopes in otolith amino acids identify residency of juvenile snapper (Family: Lutjanidae) in coastal nurseries. Coral Reefs 30:1135-1145. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Panama; Caribbean | Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Plankton; Seagrasses; Wetlands | |
| McMahon, KW; Fogel, ML; Johnson, BJ; Houghton, LA; Thorrold, SR. 2011. A new method to reconstruct fish diet and movement patterns from delta(13)C values in otolith amino acids. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 68:1330-1340. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fish; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Alino, PM; Geronimo, RC; Villanoy, CL; Gurney, GG. 2011. A multi-scale biophysical model to inform regional management of coral reefs in the western Philippines and South China Sea. Environmental Modelling & Software 26:66-82. | 2011 | China; Philippines | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Mitigation; Nutrients; Sea Urchins |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Fulton, EA. 2011. Characterizing sensitivity and uncertainty in a multiscale model of a complex coral reef system. Ecological Modelling 222:3320-3334. | 2011 | Model | Nutrients; Sea Urchins | |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Fulton, EA. 2011. Regional-scale scenario analysis for the Meso-American Reef system: Modelling coral reef futures under multiple stressors. Ecological Modelling 222:1756-1770. | 2011 | Global | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Decision Support; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Melbourne-Thomas, J; Johnson, CR; Fung, T; Seymour, RM; Cherubin, LM; Arias-Gonzalez, JE; Fulton, EA. 2011. Regional-scale scenario modeling for coral reefs: a decision support tool to inform management of a complex system. Ecological Applications 21:1380-1398. | 2011 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Decision Support; Fish; Nutrients; Physical Damage; Sea Urchins; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Morar, SR; Bury, SJ; Wilkinson, SP; Davy, SK. 2011. Sedimentary nitrogen uptake and assimilation in the temperate zooxanthellate sea anemone Anthopleura aureoradiata. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 399:110-119. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Bivalves; Discharges; Fish; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pipelines; Salinity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation Policies; Waste Management; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands | |
| Nelson, CE; Alldredge, AL; McCliment, EA; Amaral-Zettler, LA; Carlson, CA. 2011. Depleted dissolved organic carbon and distinct bacterial communities in the water column of a rapid-flushing coral reef ecosystem. ISME Journal 5:1374-1387. | 2011 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Okuku, EO; Ohowa, B; Mwangi, SN; Munga, D; Kiteresi, LI; Wanjeri, VO; Okumu, S; Kilonzo, J. 2011. Sewage pollution in the Coastal waters of Mombasa City, Kenya: A norm Rather than an Exception. International Journal Of Environmental Research 5:865-874. | 2011 | Kenya | Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Olivier, N; Colombie, C; Pittet, B; Lathuiliere, B. 2011. Microbial carbonates and corals on the marginal French Jura platform (Late Oxfordian, Molinges section). Facies 57:469-492. | 2011 | France; Germany | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Pandolfi, J. M., S. R. Connolly, D. J. Marshall, and A. L. Cohen. 2011. Projecting Coral Reef Futures Under Global Warming and Ocean Acidification. Science 333:418-422. | 2011 | Global | Climate; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity | |
| Patten, NL; Wyatt, ASJ; Lowe, RJ; Waite, AM. 2011. Uptake of picophytoplankton, bacterioplankton and virioplankton by a fringing coral reef community (Ningaloo Reef, Australia). Coral Reefs 30:555-567. | 2011 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Pauly, K; Jupp, BP; De Clerck, O. 2011. Modelling the distribution and ecology of Trichosolen blooms on coral reefs worldwide. Marine Biology 158:2239-2246. | 2011 | Global | Model; GIS & Maps | Nutrients |
| Peresypkin, VI; Smurov, AV; Shulga, NA; Safonova, ES; Smurova, TG; Bang, CV. 2011. Composition of the Organic Matter of the Water, Suspended Matter, and Bottom Sediments in Nha Trang Bay in Vietnam in the South China Sea. Oceanology 51:959-968. | 2011 | China; Vietnam | Nutrients; Sediment; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Pires, DO; Segal, B; Caparelli, AC. 2011. Reproductive effort of an endemic major reef builder along an inshore-offshore gradient in south-western Atlantic. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 91:1613-1616. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Pirlet, H; Colin, C; Thierens, M; Latruwe, K; Van Rooij, D; Foubert, A; Frank, N; Blamart, D; Huvenne, VAI; Swennen, R; Vanhaecke, F; Henriet, JP. 2011. The importance of the terrigenous fraction within a cold-water coral mound: A case study. Marine Geology 282:13-25. | 2011 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe; Iceland | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Retallack, GJ. 2011. Exceptional fossil preservation during CO(2) greenhouse crises? Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 307:59-74. | 2011 | Global; China | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands | |
| Reuter, M; Piller, WE. 2011. Volcaniclastic events in coral reef and seagrass environments: evidence for disturbance and recovery (Middle Miocene, Styrian Basin, Austria). Coral Reefs 30:889-899. | 2011 | Indonesia | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Reymond, CE; Uthicke, S; Pandolfi, JM. 2011. Inhibited growth in the photosymbiont-bearing foraminifer Marginopora vertebralis from the nearshore Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 435:97-U117. | 2011 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Climate; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Riaux-Gobin, C; Witkowski, A; Saenz-Agudelo, P; Neveux, J; Oriol, L; Vetion, G. 2011. Nutrient status in coral reefs of the Iles Eparses (Scattered Islands): comparison to nearby reefs subject to higher anthropogenic influences (Mozambique Channel and Mascarenes, Indian Ocean). Oceanological and Hyrdrobiological Studies 40:84-90. | 2011 | Indian Ocean; Mozambique; Mayotte; Reunion; India | Nutrients | |
| Rixen, T; Ramachandran, P; Lehnhoff, L; Dasbach, D; Gaye, B; Urban, B; Ramachandran, R; Ittekkot, V. 2011. Impact of monsoon-driven surface ocean processes on a coral off Port Blair on the Andaman Islands and their link to North Atlantic climate variations. Global and Planetary Change 75:1-13. | 2011 | Global; Indian Ocean; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; India; Thailand | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Roche, RC; Perry, CT; Johnson, KG; Sultana, K; Smithers, SG; Thompson, AA. 2011. Mid-Holocene coral community data as baselines for understanding contemporary reef ecological states. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 299:159-167. | 2011 | Australia; Europe | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Rochelle-Newall, EJ; Chu, VT; Pringault, O; Amouroux, D; Arfi, R; Bettarel, Y; Bouvier, T; Bouvier, C; Got, P; Nguyen, TMH; Mari, X; Navarro, P; Duong, TN; Cao, TTT; Pham, TT; Ouillon, S; Torreton, JP. 2011. Phytoplankton distribution and productivity in a highly turbid, tropical coastal system (Bach Dang Estuary, Vietnam). Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:2317-2329. | 2011 | Vietnam | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics | |
| Roder, C; Jantzen, C; Schmidt, GM; Kattner, G; Phongsuwan, N; Richter, C. 2011. Metabolic plasticity of the corals Porites lutea and Diploastrea heliopora exposed to large amplitude internal waves. Coral Reefs 30:57-69. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Thailand; Southeast Asia | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Roopin, M; Thornhill, DJ; Santos, SR; Chadwick, NE. 2011. Ammonia flux, physiological parameters, and Symbiodinium diversity in the anemonefish symbiosis on Red Sea coral reefs. Symbiosis 53:63-74. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Light; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Sawall, Y; Teichberg, MC; Seemann, J; Litaay, M; Jompa, J; Richter, C. 2011. Nutritional status and metabolism of the coral Stylophora subseriata along a eutrophication gradient in Spermonde Archipelago (Indonesia). Coral Reefs 30:841-853. | 2011 | Cuba; Indonesia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Schmidt, C; Heinz, P; Kucera, M; Uthicke, S. 2011. Temperature-induced stress leads to bleaching in larger benthic foraminifera hosting endosymbiotic diatoms. Limnology and Oceanography 56:1587-1602. | 2011 | Climate; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Schottner, S; Pfitzner, B; Grunke, S; Rasheed, M; Wild, C; Ramette, A. 2011. Drivers of bacterial diversity dynamics in permeable carbonate and silicate coral reef sands from the Red Sea. Environmental Microbiology 13:1815-1826. | 2011 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Senal, MIS; Jacinto, GS; San Diego-McGlone, ML; Siringan, F; Zamora, P; Soria, L; Cardenas, MB; Villanoy, C; Cabrera, O. 2011. Nutrient inputs from submarine groundwater discharge on the Santiago reef flat, Bolinao, Northwestern Philippines. Marine Pollution Bulletin 63:195-200. | 2011 | Florida; Philippines | GIS & Maps | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Shahhosseiny, MH; Mostafavi, PG; Fatemi, SMR; Karimi, E. 2011. Clade identification of symbiotic zooxanthellae of dominant sclerectinian coral species of intertidal pools in Hengam Island. African Journal of Biotechnology 10:1502-1506. | 2011 | Iran | Light; Nutrients; Salinity; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Shantz, AA; Stier, AC; Idjadi, JA. 2011. Coral density and predation affect growth of a reef-building coral. Coral Reefs 30:363-367. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Sherwood, OA; Lehmann, MF; Schubert, CJ; Scott, DB; McCarthy, MD. 2011. Nutrient regime shift in the western North Atlantic indicated by compound-specific delta(15)N of deep-sea gorgonian corals. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 108:1011-1015. | 2011 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Climate; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Simon, T; Pinheiro, HT; Joyeux, JC. 2011. Target fishes on artificial reefs: Evidences of impacts over nearby natural environments. Science of the Total Environment 409:4579-4584. | 2011 | Artificial Habitat; Commercial Fisheries; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Recreational Fishing; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Sjoo, GL; Mork, E; Andersson, S; Melander, I. 2011. Differences in top-down and bottom-up regulation of macroalgal communities between a reef crest and back reef habitat in Zanzibar. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 91:511-518. | 2011 | South & Central America; Tanzania; Caribbean | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Smith, SDA. 2011. Densities of the endolithic bivalve Lithophaga lessepsiana (Vaillant, 1865) in Pocillopora damicornis, Solitary Islands Marine Park, northern NSW, Australia. Molluscan Research 31:42-46. | 2011 | Australia | Bivalves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Sommer, B; Harrison, PL; Brooks, L; Scheffers, SR. 2011. Coral Community Decline At Bonaire, Southern Caribbean. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:541-565. | 2011 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Turf Algae | |
| Stokes, MD; Leichter, JJ; Wing, S; Frew, R. 2011. Temperature variability and algal isotopic heterogeneity on a Floridian coral reef. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 32:364-379. | 2011 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Salinity |
| Syahailatua, A; Taylor, MD; Suthers, IM. 2011. Growth variability and stable isotope composition of two larval carangid fishes in the East Australian Current: The role of upwelling in the separation zone. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 58:691-698. | 2011 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Tambutte, S; Holcomb, M; Ferrier-Pages, C; Reynaud, S; Tambutte, E; Zoccola, D; Allemand, D. 2011. Coral biomineralization: From the gene to the environment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 408:58-78. | 2011 | Global | Review; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Tanaka, K; Hanamura, Y; Chong, VC; Watanabe, S; Man, A; Kassim, FM; Kodama, M; Ichikawa, T. 2011. Stable isotope analysis reveals ontogenetic migration and the importance of a large mangrove estuary as a feeding ground for juvenile John's snapper Lutjanus johnii. Fisheries Science 77:809-816. | 2011 | Malaysia | Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Tanaka, Y; Miyajima, T; Watanabe, A; Nadaoka, K; Yamamoto, T; Ogawa, H. 2011. Distribution of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen in a coral reef. Coral Reefs 30:533-541. | 2011 | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | ||
| Tanaka, Y; Ogawa, H; Miyajima, T. 2011. Bacterial decomposition of coral mucus as evaluated by long-term and quantitative observation. Coral Reefs 30:443-449. | 2011 | Cuba | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Tanaka, Y; Ogawa, H; Miyajima, T. 2011. Production and bacterial decomposition of dissolved organic matter in a fringing coral reef. Journal of Oceanography 67:427-437. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Japan | Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Titlyanov, EA; Titlyanova, TV; Xia, BM; Bartsch, I. 2011. Checklist of marine benthic green algae (Chlorophyta) on Hainan, a subtropical island off the coast of China: comparisons between the 1930s and 1990-2009 reveal environmental changes. Botanica Marina 54:523-535. | 2011 | China | Algae; Aquaculture; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | |
| van Duyl, FC; Moodley, L; Nieuwland, G; van Ijzerloo, L; van Soest, RWM; Houtekamer, M; Meesters, EH; Middelburg, JJ. 2011. Coral cavity sponges depend on reef-derived food resources: stable isotope and fatty acid constraints. Marine Biology 158:1653-1666. | 2011 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Encrusting Sponges; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges; Substrate; Zooxanthellae |
| Velasquez, J; Lopez-Angarita, J; Sanchez, JA. 2011. Evaluation of the FORAM index in a case of conservation Benthic foraminifera as indicators of ecosystem resilience in protected and non-protected coral reefs of the southern caribbean. Biodiversity and Conservation 20:3591-3603. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Algae; Climate; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation |
| Verges, A; Vanderklift, MA; Doropoulos, C; Hyndes, GA. 2011. Spatial Patterns in Herbivory on a Coral Reef Are Influenced by Structural Complexity but Not by Algal Traits. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Australia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Vermeij, MJA; Dailer, ML; Smith, CM. 2011. Crustose coralline algae can suppress macroalgal growth and recruitment on Hawaiian coral reefs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 422:1-7. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| West, RR; McKinney, FK; Fagerstrom, JA; Vacelet, J. 2011. Biological interactions among extant and fossil clonal organisms. Facies 57:351-374. | 2011 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sponges | ||
| Whitall, D. R., B. M. Costa, L. J. Bauer, A. Dieppa, and S. D. Hile, editors. 2011. A Baseline Assessment of the Ecological Resources of Jobos Bay, Puerto Rico. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 133, NOAA, Silver Spring, (MD, USA). | 2011 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics |
| Wietz, M; Mansson, M; Gram, L. 2011. Chitin stimulates production of the antibiotic andrimid in a Vibrio coralliilyticus strain. Environmental Microbiology Reports 3:559-564. | 2011 | Model | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Wijgerde, T; Diantari, R; Lewaru, MW; Verreth, JAJ; Osinga, R. 2011. Extracoelenteric zooplankton feeding is a key mechanism of nutrient acquisition for the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Journal of Experimental Biology 214:3351-3357. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Witt, V; Wild, C; Uthicke, S. 2011. Effect of substrate type on bacterial community composition in biofilms from the Great Barrier Reef. FEMS Microbiology Letters 323:188-195. | 2011 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate |
| Xu, LQ; Liu, XD; Sun, LG; Yan, H; Liu, Y; Luo, YH; Huang, J. 2011. Geochemical evidence for the development of coral island ecosystem in the Xisha Archipelago of South China Sea from four ornithogenic sediment profiles. Chemical Geology 286:135-145. | 2011 | China | Marine Birds; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Yamazaki, A; Watanabe, T; Ogawa, NO; Ohkouchi, N; Shirai, K; Toratani, M; Uematsu, M. 2011. Seasonal variations in the nitrogen isotope composition of Okinotori coral in the tropical western Pacific: A new proxy for marine nitrate dynamics. Journal Of Geophysical Research-biogeosciences 116. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Zooxanthellae |
| Yamazaki, A; Watanabe, T; Tsunogai, U. 2011. Nitrogen isotopes of organic nitrogen in reef coral skeletons as a proxy of tropical nutrient dynamics. Geophysical Research Letters 38. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Yang, SL; Gao, RS; Niu, PL; Zou, ZY; Yu, RH. 2011. Arc Discharge Synthesis and Photoluminescence of 3D Feather-like AlN Nanostructures. Nanoscale Research Letters 6. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Discharges; Fish; Nutrients | |
| Yang, WF; Huang, YP; Chen, M; Qiu, YS; Li, HB; Zhang, L. 2011. A large excess of (210)Po in the overlying water of the Zhubi Coral Reef flat, in the South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:912-917. | 2011 | China | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Yang, WF; Huang, YP; Chen, M; Qiu, YS; Li, HB; Zhang, L. 2011. Carbon and nitrogen cycling in the Zhubi coral reef lagoon of the South China Sea as revealed by (210)Po and (210)Pb. Marine Pollution Bulletin 62:905-911. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Model | CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Yang, WF; Huang, YP; Chen, M; Qiu, YS; Li, HB; Zhang, L. 2011. Unusually high (210)Po activities in the surface water of the Zhubi Coral Reef Lagoon in the South China Sea. Science of the Total Environment 409:4612-4617. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Younesi, M; Javadpour, S; Bahrololoom, ME. 2011. Effect of Heat Treatment Temperature on Chemical Compositions of Extracted Hydroxyapatite from Bovine Bone Ash. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance 20:1484-1490. | 2011 | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Yu, HM; Huang, XX; Wen, GW; Zhang, T; Zhong, B; Bai, HW. 2011. A facile method for synthesis of novel coral-like boron nitride nanostructures. Materials Chemistry and Physics 129:30-34. | 2011 | Nutrients | ||
| Yuyama, I; Watanabe, T; Takei, Y. 2011. Profiling Differential Gene Expression of Symbiotic and Aposymbiotic Corals Using a High Coverage Gene Expression Profiling (HiCEP) Analysis. Marine Biotechnology 13:32-40. | 2011 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Zhang, ZL; Lowe, R; Falter, J; Ivey, G. 2011. A numerical model of wave- and current-driven nutrient uptake by coral reef communities. Ecological Modelling 222:1456-1470. | 2011 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment |
| Zhu, BH; Pan, KH; Wang, GC. 2011. Effects of host starvation on the symbiotic dinoflagellates from the sea anemone Stichodactyla mertensii. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 32:15-23. | 2011 | Index or Indicator | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| A. V. Borges and N. Gypens. 2010. Carbonate chemistry in the coastal zone responds more strongly to eutrophication than to ocean acidification. Limnology and Oceanography 55:346-353. | 2010 | Model | Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Abell, G. C. J., A. T. Revill, C. Smith, A. P. Bissett, J. K. Volkman, and S. S. Robert. 2010. Archaeal ammonia oxidizers and nirS-type denitrifiers dominate sediment nitrifying and denitrifying populations in a subtropical macrotidal estuary. ISME Journal 4:286-300. | 2010 | Australia | Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Armi, Z., S. Turki, E. Trabelsi, and N. Ben Maiz. 2010. First recorded proliferation of Coolia monotis (Meunier, 1919) in the North Lake of Tunis (Tunisia) correlation with environmental factors. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 164:423-433. | 2010 | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Baker, D. M., E. Jordan-Dahlgren, M. A. Maldonado, and C. D. Harvell. 2010. Sea fan corals provide a stable isotope baseline for assessing sewage pollution in the Mexican Caribbean. Limnology and Oceanography 55:2139-2149. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Infrastructure; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sewage Treatment; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies |
| Baker, D. M., K. L. Webster, and K. Kim. 2010. Caribbean octocorals record changing carbon and nitrogen sources from 1862 to 2005. Global Change Biology 16:2701-2710. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Model; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; CO2; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Octocoral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bartley, R., J. P. Corfield, B. N. Abbott, A. A. Hawdon, S. N. Wilkinson, and B. Nelson. 2010. Impacts of improved grazing land management on sediment yields, Part 1: Hills lope processes. Journal of Hydrology 389:237-248. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Littering; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bartley, R., S. N. Wilkinson, A. A. Hawdon, B. N. Abbott, and D. A. Post. 2010. Impacts of improved grazing land management on sediment yields. Part 2: Catchment response. Journal of Hydrology 389:249-259. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Batianoff, G. N., G. C. Naylor, R. J. Fensham, and V. J. Neldner. 2010. Characteristics of Coral Cay Soils at Coringa-Herald Coral Sea Islands, Australia. Pacific Science 64:335-347. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Marine Birds; Nutrients | |
| Bauman, A. G., J. A. Burt, D. A. Feary, E. Marquis, and P. Usseglio. 2010. Tropical harmful algal blooms: An emerging threat to coral reef communities? Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:2117-2122. | 2010 | Global; Indian Ocean; India; Oman | Ballast Discharge; Climate; Discharges; Fish; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Baums, I. B., M. E. Johnson, M. K. Devlin-Durante, and M. W. Miller. 2010. Host population genetic structure and zooxanthellae diversity of two reef-building coral species along the Florida Reef Tract and wider Caribbean. Coral Reefs 29:835-842. | 2010 | South & Central America; Florida; Bahamas; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bjerager, M., F. Surlyk, H. Lykke-Andersen, N. Thibault, and L. Stemmerik. 2010. Danian cool-water coral reefs in southern Scandinavia localised over seafloor highs. Marine and Petroleum Geology 27:455-466. | 2010 | Cuba; Norway | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Blanco, A. C., K. Nadaoka, T. Yamamoto, and K. Kinjo. 2010. Dynamic evolution of nutrient discharge under stormflow and baseflow conditions in a coastal agricultural watershed in Ishigaki Island, Okinawa, Japan. Hydrological Processes 24:2601-2616. | 2010 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Algae; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bourgeois, S., S. Hochard, and O. Pringault. 2010. Subtidal microphytobenthos: effects of inorganic and organic compound supplies on migration, production, and respiration in a tropical coastal environment. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 61:13-29. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Boyd, P. W., R. Strzepek, F. X. Fu, and D. A. Hutchins. 2010. Environmental control of open-ocean phytoplankton groups: Now and in the future. Limnology and Oceanography 55:1353-1376. | 2010 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Climate; CO2; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Brodie, J., T. Schroeder, K. Rohde, J. Faithful, B. Masters, A. Dekker, V. Brando, and M. Maughan. 2010. Dispersal of suspended sediments and nutrients in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon during river-discharge events: conclusions from satellite remote sensing and concurrent flood-plume sampling. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:651-664. | 2010 | Australia | Remote Sensing | Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Cadena, N. J., C. Rey, M. Hernandez-Hoyos, J. D. Sanchez, S. Teillaud, N. Ardila, and J. A. Sanchez. 2010. Linking local to global properties in branching modular networks: gorgonian coral colonies. Marine Biology 157:1003-1010. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Belize | Model | Nutrients; Octocoral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Cardenas-Palomo, N., J. Herrera-Silveira, and O. Reyes. 2010. Spatial and temporal distribution of physicochemical features in the habitat of whale shark Rhincodon typus (Orectolobiformes: Rhincodontidae) in the north of Mexican Caribbean. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:399-412. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Chemical Variables; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity |
| Charpy, L., K. A. Palinska, B. Casareto, M. J. Langlade, Y. Suzuki, R. M. M. Abed, and S. Golubic. 2010. Dinitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria in Microbial Mats of Two Shallow Coral Reef Ecosystems. Microbial Ecology 59:174-186. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; Reunion; India; Pacific Ocean | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Cheal, A. J., M. A. MacNeil, E. Cripps, M. J. Emslie, M. Jonker, B. Schaffelke, and H. Sweatman. 2010. Coral-macroalgal phase shifts or reef resilience: links with diversity and functional roles of herbivorous fishes on the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 29:1005-1015. | 2010 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Climate; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Chiang, C. J., P. T. Chen, and Y. P. Chao. 2010. Secreted Production of Renilla Luciferase in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnology Progress 26:589-594. | 2010 | Nutrients; Octocoral | ||
| Clavier, J. and L. Chauvaud. 2010. Biodeposit production by Bractechlamys vexillum (bivalve: pectinidae) in a tropical lagoon. Journal of Sea Research 64:231-240. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia | Bivalves; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan. 2010. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan: 2009 System Status Report. | 2010 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Infrastructure; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Dailer, M. L., R. S. Knox, J. E. Smith, M. Napier, and C. M. Smith. 2010. Using delta N-15 values in algal tissue to map locations and potential sources of anthropogenic nutrient inputs on the island of Maui, Hawai'i, USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:655-671. | 2010 | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Wastewater Discharge | |
| de Bello, F., S. Lavorel, S. Diaz, R. Harrington, J. H. C. Cornelissen, R. D. Bardgett, M. P. Berg, P. Cipriotti, C. K. Feld, D. Hering, P. M. da Silva, S. G. Potts, L. Sandin, J. P. Sousa, J. Storkey, D. A. Wardle, and P. A. Harrison. 2010. Towards an assessment of multiple ecosystem processes and services via functional traits. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2873-2893. | 2010 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invertebrates; Nutrients | |
| DeSalvo, M. K., S. Sunagawa, P. L. Fisher, C. R. Voolstra, R. Iglesias-Prieto, and M. Medina. 2010. Coral host transcriptomic states are correlated with Symbiodinium genotypes. Molecular Ecology 19:1174-1186. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Dewsbury, B. M. and J. W. Fourqurean. 2010. Artificial Reefs Concentrate Nutrients And Alter Benthic Community Structure In An Oligotrophic, Subtropical Estuary. Bulletin of Marine Science 86:813-829. | 2010 | Florida | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Douglas, G. B., M. Kuhnen, L. C. Radke, G. Hancock, B. Brooke, M. J. Palmer, T. Pietsch, P. W. Ford, M. G. Trefry, and R. Packett. 2010. Delineation of sediment sources to a coastal wetland in the Great Barrier Reef catchment: influence of climate variability and land clearing since European arrival. Environmental Chemistry 7:190-206. | 2010 | Australia; Europe | Agriculture; Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Edgar, G. J., A. Davey, G. Kelly, R. B. Mawbey, and K. Parsons. 2010. Biogeographical and ecological context for managing threats to coral and rocky reef communities in the Lord Howe Island Marine Park, south-western Pacific. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:378-396. | 2010 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Algae; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | |
| Edgar, G. J., P. R. Last, N. S. Barrett, K. Gowlett-Holmes, M. Driessen, and P. Mooney. 2010. Conservation of natural wilderness values in the Port Davey marine and estuarine protected area, south-western Tasmania. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:297-311. | 2010 | Global; Australia | Boating Activities; Climate; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Etiope, G., A. Savini, N. Lo Bue, P. Favali, and C. Corselli. 2010. Deep-sea survey for the detection of methane at the "Santa Maria di Leuca" cold-water coral mounds (Ionian Sea, South Italy). Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 57:431-440. | 2010 | Lab Study | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Fabricius, K. E., K. Okaji, and G. De'ath. 2010. Three lines of evidence to link outbreaks of the crown-of-thorns seastar Acanthaster planci to the release of larval food limitation. Coral Reefs 29:593-605. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Faure, V., C. Pinazo, J. P. Torreton, and P. Douillet. 2010. Modelling the spatial and temporal variability of the SW lagoon of New Caledonia II: Realistic 3D simulations compared with in situ data. Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:480-502. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Faure, V., C. Pinazo, J. P. Torreton, and S. Jacquet. 2010. Modelling the spatial and temporal variability of the SW lagoon of New Caledonia I: A new biogeochemical model based on microbial loop recycling. Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:465-479. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Faxneld, S., T. L. Jorgensen, and M. Tedengren. 2010. Effects of elevated water temperature, reduced salinity and nutrient enrichment on the metabolism of the coral Turbinaria mesenterina. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 88:482-487. | 2010 | Vietnam | Climate; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | |
| Fichez, R., S. Chifflet, P. Douillet, P. Gerard, F. Gutierrez, A. Jouon, S. Ouillon, and C. Grenz. 2010. Biogeochemical typology and temporal variability of lagoon waters in a coral reef ecosystem subject to terrigeneous and anthropogenic inputs (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:309-322. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients |
| Filatov, M. V., J. A. Kaandorp, M. Postma, R. van Liere, K. J. Kruszynski, M. J. A. Vermeij, G. J. Streekstra, and R. P. M. Bak. 2010. A comparison between coral colonies of the genus Madracis and simulated forms. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 277:3555-3561. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Fiore, C. L., J. K. Jarett, N. D. Olson, and M. P. Lesser. 2010. Nitrogen fixation and nitrogen transformations in marine symbioses. Trends in Microbiology 18:455-463. | 2010 | Review | Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Sponges | |
| Gavio, B., S. Palmer-Cantillo, and J. E. Mancera. 2010. Historical analysis (2000-2005) of the coastal water quality in San Andres Island, Sea Flower Biosphere Reserve, Caribbean Colombia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1018-1030. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Seagrasses |
| Gecek, S. and T. Legovic. 2010. Towards carrying capacity assessment for aquaculture in the Bolinao Bay, Philippines: A numerical study of tidal circulation. Ecological Modelling 221:1394-1412. | 2010 | Global; Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps | Aquaculture; Fish; Nutrients; Seawater Flow |
| Godiva, D., H. Evangelista, M. Kampel, M. V. Licinio, and C. Munita. 2010. Combined use of aerogammaspectrometry and geochemistry to access sediment sources in a shallow coral site at Armacao dos Buzios, Brazil. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 87:526-534. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Grenz, C., L. Denis, O. Pringault, and R. Fichez. 2010. Spatial and seasonal variability of sediment oxygen consumption and nutrient fluxes at the sediment water interface in a sub-tropical lagoon (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:399-412. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Guerra-Garcia, J. M., T. Ganesh, M. Jaikumar, and A. V. Raman. 2010. Caprellids (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from India. Helgoland Marine Research 64:297-310. | 2010 | India | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Guest, M. A., A. J. Hirst, P. D. Nichols, and S. D. Frusher. 2010. Multi-scale spatial variation in stable isotope and fatty acid profiles amongst temperate reef species: implications for design and interpretation of trophic studies. Marine Ecology Progress Series 410:25-41. | 2010 | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Haas, A. F. and C. Wild. 2010. Composition analysis of organic matter released by cosmopolitan coral reef-associated green algae. Aquatic Biology 10:131-138. | 2010 | Cuba | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| Haas, A. F., M. S. Naumann, U. Struck, C. Mayr, M. el-Zibdah, and C. Wild. 2010. Organic matter release by coral reef associated benthic algae in the Northern Red Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 389:53-60. | 2010 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Turf Algae; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Haas, A., M. el-Zibdah, and C. Wild. 2010. Seasonal monitoring of coral-algae interactions in fringing reefs of the Gulf of Aqaba, Northern Red Sea. Coral Reefs 29:93-103. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Hallegraeff, G. M. 2010. Ocean Climate Change, Phytoplankton Community Responses, And Harmful Algal Blooms: A Formidable Predictive Challenge. Journal of Phycology 46:220-235. | 2010 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Climate; CO2; Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hauri, C., K. E. Fabricius, B. Schaffelke, and C. Humphrey. 2010. Chemical and Physical Environmental Conditions Underneath Mat- and Canopy-Forming Macroalgae, and Their Effects on Understorey Corals. PLoS One 5:e12685. | 2010 | Australia; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Heindel, K., D. Birgel, J. Peckmann, H. Kuhnert, and H. Westphal. 2010. Formation Of Deglacial Microbialites In Coral Reefs Off Tahiti (Iodp 310) Involving Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Palaios 25:618-635. | 2010 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Holcomb, M., D. C. McCorkle, and A. L. Cohen. 2010. Long-term effects of nutrient and CO2 enrichment on the temperate coral Astrangia poculata (Ellis and Solander, 1786). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 386:27-33. | 2010 | Model | CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Stony Coral | |
| Holmes, G. and R. W. Johnstone. 2010. The role of coral mortality in nitrogen dynamics on coral reefs. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 387:1-8. | 2010 | Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate | ||
| Hoogenboom, M., R. Rodolfo-Metalpa, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2010. Co-variation between autotrophy and heterotrophy in the Mediterranean coral Cladocora caespitosa. Journal of Experimental Biology 213:2399-2409. | 2010 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Houk, P. and R. Camacho. 2010. Dynamics of seagrass and macroalgal assemblages in Saipan Lagoon, Western Pacific Ocean: disturbances, pollution, and seasonal cycles. Botanica Marina 53:205-212. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Jantzen, C., C. Wild, M. Rasheed, M. El-Zibdah, and C. Richter. 2010. Enhanced pore-water nutrient fluxes by the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp in a Red Sea coral reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 411:117-U162. | 2010 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Johnson, P. T. J., A. R. Townsend, C. C. Cleveland, P. M. Glibert, R. W. Howarth, V. J. McKenzie, E. Rejmankova, and M. H. Ward. 2010. Linking environmental nutrient enrichment and disease emergence in humans and wildlife. Ecological Applications 20:16-29. | 2010 | Global | Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Kasper-Zubillaga, J. J., L. Rosales-Hoz, and J. P. Bernal. 2010. Rare earth elements in corals from the Isla de Sacrificios Reef, Veracruz, Mexico. Chemie Der Erde-geochemistry 70:55-60. | 2010 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Kimes, N. E., J. D. Van Nostrand, E. Weil, J. Z. Zhou, and P. J. Morris. 2010. Microbial functional structure of Montastraea faveolata, an important Caribbean reef-building coral, differs between healthy and yellow-band diseased colonies. Environmental Microbiology 12:541-556. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Knee, K. L., J. H. Street, E. E. Grossman, A. B. Boehm, and A. Paytan. 2010. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean from submarine groundwater discharge in a groundwater-dominated system: Relation to land use (Kona coast, Hawaii, USA). Limnology and Oceanography 55:1105-1122. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Discharges; Golf Course Operations; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Komorita, T., R. Kajihara, H. Tsutsumi, S. Shibanuma, T. Yamada, N. Higaki, and S. Montani. 2010. Reevaluation of the nutrient mineralization process by infaunal bivalves (Ruditapes philippinarum) in a shallow lagoon in Hokkaido, Japan. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 383:8-16. | 2010 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Bivalves; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment |
| Lapointe, B. E. and B. J. Bedford. 2010. Ecology and nutrition of invasive Caulerpa brachypus f. parvifolia blooms on coral reefs off southeast Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 9:1-12. | 2010 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lapointe, B. E., R. Langton, B. J. Bedford, A. C. Potts, O. Day, and C. M. Hu. 2010. Land-based nutrient enrichment of the Buccoo Reef Complex and fringing coral reefs of Tobago, West Indies. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:334-343. | 2010 | Tobago | Remote Sensing | Algae; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| LaVigne, M., K. A. Matthews, A. G. Grottoli, K. M. Cobb, E. Anagnostou, G. Cabioch, and R. M. Sherrell. 2010. Coral skeleton P/Ca proxy for seawater phosphate: Multi-colony calibration with a contemporaneous seawater phosphate record. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 74:1282-1293. | 2010 | Panama | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Leigh, E. G. 2010. The evolution of mutualism. Journal of Evolutionary Biology 23:2507-2528. | 2010 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octopus & Squid | ||
| Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. | 2010 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Lemonnier, H., C. Courties, C. Mugnier, J. P. Torreton, and A. Herbland. 2010. Nutrient and microbial dynamics in eutrophying shrimp ponds affected or unaffected by vibriosis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:402-411. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Lenahan, M. J. and K. L. Bristow. 2010. Understanding sub-surface solute distributions and salinization mechanisms in a tropical coastal floodplain groundwater system. Journal of Hydrology 390:131-142. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Discharges; Irrigation; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Linan-Cabello, M. A., L. A. Flores-Ramirez, J. F. Cobo-Diaz, T. Zenteno-Savin, N. O. Olguin-Monroy, A. Olivos-Ortiz, and A. Tintos-Gomez. 2010. Response to short term ultraviolet stress in the reef-building coral Pocillopora capitata (Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:103-118. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and B. L. Brooks. 2010. The effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on algal community development: Artificial mini-reefs on the Belize Barrier Reef sedimentary lagoon. Harmful Algae 9:255-263. | 2010 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Looney, E. E., K. P. Sutherland, and E. K. Lipp. 2010. Effects of temperature, nutrients, organic matter and coral mucus on the survival of the coral pathogen, Serratia marcescens PDL100. Environmental Microbiology 12:2479-2485. | 2010 | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | ||
| Lopez Correa, M., P. Montagna, B. Vendrell-Simon, M. McCulloch, and M. Taviani. 2010. Stable isotopes (delta O-18 and delta C-13), trace and minor element compositions of Recent scleractinians and Last Glacial bivalves at the Santa Maria di Leuca deep-water coral province, Ionian Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 57:471-486. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Lopez-Legentil, S., P. M. Erwin, J. R. Pawlik, and B. Song. 2010. Effects of Sponge Bleaching on Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea: Distribution and Relative Expression of Ammonia Monooxygenase Genes Associated with the Barrel Sponge Xestospongia muta. Microbial Ecology 60:561-571. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Sponges; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Maier, C., M. G. Weinbauer, and J. Patzold. 2010. Stable isotopes reveal limitations in C and N assimilation in the Caribbean reef corals Madracis auretenra, M. carmabi and M. formosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 412:103-112. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae | |
| Mass, T., A. Genin, U. Shavit, M. Grinstein, and D. Tchernov. 2010. Flow enhances photosynthesis in marine benthic autotrophs by increasing the efflux of oxygen from the organism to the water. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107:2527-2531. | 2010 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | ||
| Mayer, F. W. and C. Wild. 2010. Coral mucus release and following particle trapping contribute to rapid nutrient recycling in a Northern Red Sea fringing reef. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:1006-1014. | 2010 | Lab Study | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Mellin, C., C. J. A. Bradshaw, M. G. Meekan, and M. J. Caley. 2010. Environmental and spatial predictors of species richness and abundance in coral reef fishes. Global Ecology and Biogeography 19:212-222. | 2010 | Australia | Model | Fish; Nutrients; Salinity |
| Mendonca, V. M., M. M. Al Jabri, I. Al Ajmi, M. Al Muharrami, M. Al Areimi, and H. A. Al Aghbari. 2010. Persistent and Expanding Population Outbreaks of the Corallivorous Starfish Acanthaster planci in the Northwestern Indian Ocean: Are They Really a Consequence of Unsustainable Starfish Predator Removal through Overfishing in Coral Reefs, or a Response to. Zoological Studies 49:108-123. | 2010 | Indian Ocean; India; Oman | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars | |
| Mendoza-Carranza, M., D. J. Hoeinghaus, A. M. Garcia, and A. Romero-Rodriguez. 2010. Aquatic food webs in mangrove and seagrass habitats of Centla Wetland, a Biosphere Reserve in Southeastern Mexico. Neotropical Ichthyology 8:171-178. | 2010 | South & Central America; Mexico | Fish; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Wetlands | |
| Mohamed, N. M., K. Saito, Y. Tal, and R. T. Hill. 2010. Diversity of aerobic and anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in marine sponges. ISME Journal 4:38-48. | 2010 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Morimoto, N., Y. Furushima, M. Nagao, T. Irie, A. Iguchi, A. Suzuki, and K. Sakai. 2010. Water-Quality Variables across Sekisei Reef, A Large Reef Complex in Southwestern Japan. Pacific Science 64:113-123. | 2010 | Japan | Light; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seastars; Sediment | |
| Nagle, V. L., N. M. Mhalsekar, and T. G. Jagtap. 2010. Isolation, optimization and characterization of selected Cyanophycean members. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences 39:212-218. | 2010 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity | ||
| Naumann, M. S., A. Haas, U. Struck, C. Mayr, M. El-Zibdah, and C. Wild. 2010. Organic matter release by dominant hermatypic corals of the Northern Red Sea. Coral Reefs 29:649-659. | 2010 | Cuba | Lab Study | Hydrocoral; Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Naumann, M. S., C. Mayr, U. Struck, and C. Wild. 2010. Coral mucus stable isotope composition and labeling: experimental evidence for mucus uptake by epizoic acoelomorph worms. Marine Biology 157:2521-2531. | 2010 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Niggl, W. and C. Wild. 2010. Spatial distribution of the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp. within fringing coral reef environments of the Northern Red Sea: implications for its life cycle. Helgoland Marine Research 64:281-287. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Nishihara, G. N. and R. Terada. 2010. Spatial variations in nutrient supply to the red algae Eucheuma serra (J. Agardh) J. Agardh. Phycological Research 58:29-34. | 2010 | Model | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Nutzel, A., M. Joachimski, and M. Lopez Correa. 2010. Seasonal climatic fluctuations in the Late Triassic tropics-High-resolution oxygen isotope records from aragonitic bivalve shells (Cassian Formation, Northern Italy). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 285:194-204. | 2010 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Olsen, Y. S. and I. Valiela. 2010. Effect of Sediment Nutrient Enrichment and Grazing on Turtle Grass Thalassia testudinum in Jobos Bay, Puerto Rico. Estuaries and Coasts 33:769-783. | 2010 | Puerto Rico | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Osawa, Y., K. Fujita, Y. Umezawa, H. Kayanne, Y. Ide, T. Nagaoka, T. Miyajima, and H. Yamano. 2010. Human impacts on large benthic foraminifers near a densely populated area of Majuro Atoll, Marshall Islands. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1279-1287. | 2010 | Marshall Islands | Algae; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Parsons, M. L., C. J. Settlemier, and P. K. Bienfang. 2010. A simple model capable of simulating the population dynamics of Gambierdiscus, the benthic dinoflagellate responsible for ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 10:71-80. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Algae; Climate; Fish; Nutrients |
| Penesyan, A., S. Kjelleberg, and S. Egan. 2010. Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Marine Drugs 8:438-459. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Perez-Asensio, J. N. and J. Aguirre. 2010. Benthic Foraminiferal Assemblages In Temperate Coral-Bearing Deposits From The Late Pliocene. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 40:61-78. | 2010 | Spain | Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Radke, L. C., P. W. Ford, I. T. Webster, I. Atkinson, G. Douglas, K. Oubelkheir, J. Li, B. Robson, and B. Brooke. 2010. Biogeochemical Zones Within a Macrotidal, Dry-Tropical Fluvial-Marine Transition Area: A Dry-Season Perspective. Aquatic Geochemistry 16:1-29. | 2010 | Australia; Cuba | Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Rameil, N., A. Immenhauser, G. Warrlich, H. Hillgartner, and H. J. Droste. 2010. Morphological patterns of Aptian Lithocodium-Bacinella geobodies: relation to environment and scale. Sedimentology 57:883-911. | 2010 | Global; Oman | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Rastogi, R. P., Richa, R. P. Sinha, S. P. Singh, and D. P. Hader. 2010. Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. Journal Of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology 37:537-558. | 2010 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Plankton | ||
| Renema, W. 2010. Is increased calcarinid (foraminifera) abundance indicating a larger role for macro-algae in Indonesian Plio-Pleistocene coral reefs? Coral Reefs 29:165-173. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indonesia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients | |
| Richlen, M. L., S. L. Morton, E. A. Jamali, A. Rajan, and D. M. Anderson. 2010. The catastrophic 2008-2009 red tide in the Arabian gulf region, with observations on the identification and phylogeny of the fish-killing dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. Harmful Algae 9:163-172. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Malaysia; United Arab Emirates; Oman; Mexico | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Rivest, E. B., D. M. Baker, K. L. Rypien, and C. D. Harvell. 2010. Nitrogen source preference of Aspergillus sydowii, an infective agent associated with aspergillosis of sea fan corals. Limnology and Oceanography 55:386-392. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Santos, I. R., D. Erler, D. Tait, and B. D. Eyre. 2010. Breathing of a coral cay: Tracing tidally driven seawater recirculation in permeable coral reef sediments. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 115:C12010. | 2010 | Model | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Schmidt, S., K. Mackintosh, R. Gillett, A. Pudmenzky, D. E. Allen, H. Rennenberg, and J. F. Mueller. 2010. Atmospheric concentrations of ammonia and nitrogen dioxide at a tropical coral cay with high seabird density. Journal of Environmental Monitoring 12:460-465. | 2010 | Australia | Agriculture; Land & Air Transportation; Marine Birds; Nutrients | |
| Schutter, M., J. Crocker, A. Paijmans, M. Janse, R. Osinga, A. J. Verreth, and R. H. Wijffels. 2010. The effect of different flow regimes on the growth and metabolic rates of the scleractinian coral Galaxea fascicularis. Coral Reefs DOI10.1007/s00338-010-0617-2. | 2010 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral | ||
| Sere, M. G., L. M. Masse, R. Perissinotto, and M. H. Schleyer. 2010. Influence of heterotrophic feeding on the sexual reproduction of Pocillopora verrucosa in aquaria. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 395:63-71. | 2010 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Shen, P. P., Y. H. Tan, L. M. Huang, J. L. Zhang, and J. Q. Yin. 2010. Occurrence of brackish water phytoplankton species at a closed coral reef in Nansha Islands, South China Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1718-1725. | 2010 | China | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Shenton, W., B. T. Hart, and J. Brodie. 2010. A Bayesian network model linking nutrient management actions in the Tully catchment (northern Queensland) with Great Barrier Reef condition. Marine and Freshwater Research 61:587-595. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Algae; Decision Support; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Sherwood, O. A., B. E. Lapointe, M. J. Risk, and R. E. Jamieson. 2010. Nitrogen Isotopic Records of Terrestrial Pollution Encoded in Floridian and Bahamian Gorgonian Corals. Environmental Science and Technology 44:874-880. | 2010 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sea Turtles; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Shiell, G. R. and B. Knott. 2010. Aggregations and temporal changes in the activity and bioturbation contribution of the sea cucumber Holothuria whitmaei (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea). Marine Ecology Progress Series 415:127-139. | 2010 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Slater, M. J. and A. G. Carton. 2010. Sea cucumber habitat differentiation and site retention as determined by intraspecific stable isotope variation. Aquaculture Research 41:e695-e702. | 2010 | Agriculture; Bivalves; Complex Habitat & Resources; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Slater, M. J. and A. G. Jeffs. 2010. Do benthic sediment characteristics explain the distribution of juveniles of the deposit-feeding sea cucumber Australostichopus mollis? Journal of Sea Research 64:241-249. | 2010 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Smith, J. E., C. L. Hunter, and C. M. Smith. 2010. The effects of top-down versus bottom-up control on benthic coral reef community structure. Oecologia 163:497-507. | 2010 | Global | Algae; Climate; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Smith, J. E., C. L. Hunter, and C. M. Smith. 2010. The effects of top�down versus bottom�up control on benthic coral reef community structure. Oecologia 163:497-507. | 2010 | Global | Algae; Climate; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Smith, M. D., S. E. Goater, E. S. Reichwaldt, B. Knott, and A. Ghadouani. 2010. Effects of recent increases in salinity and nutrient concentrations on the microbialite community of Lake Clifton (Western Australia): are the thrombolites at risk? Hydrobiologia 649:207-216. | 2010 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Smith, T. B., P. Fong, R. Kennison, and J. Smith. 2010. Spatial refuges and associational defenses promote harmful blooms of the alga Caulerpa sertularioides onto coral reefs. Oecologia 164:1039-1048. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Sorokin, Y. I. and P. Y. Sorokin. 2010. Plankton of the central Great Barrier Reef: abundance, production and trophodynamic roles. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 90:1173-1187. | 2010 | Australia | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| Stier, A. C., C. S. McKeon, C. W. Osenberg, and J. S. Shima. 2010. Guard crabs alleviate deleterious effects of vermetid snails on a branching coral. Coral Reefs 29:1019-1022. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Seastars; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral | |
| Tanaka, Y., H. Ogawa, and T. Miyajima. 2010. Effects of nutrient enrichment on the release of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen by the scleractinian coral Montipora digitata. Coral Reefs 29:675-682. | 2010 | Cuba | Lab Study | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Thomas, Y., C. Courties, Y. El Helwe, A. Herbland, and H. Lemonnier. 2010. Spatial and temporal extension of eutrophication associated with shrimp farm wastewater discharges in the New Caledonia lagoon. Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:387-398. | 2010 | New Caledonia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Discharges; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Wastewater Discharge |
| Thomas, Y., P. Garen, C. Courties, and L. Charpy. 2010. Spatial and temporal variability of the pico- and nanophytoplankton and bacterioplankton in a deep Polynesian atoll lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 59:89-101. | 2010 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Titlyanov, E. A., S. I. Kiyashko, T. V. Titlyanova, and J. A. Raven. 2010. delta C-13 and delta N-15 in tissue of coral polyps and epilithic algae inhabiting damaged coral colonies under the influence of different light intensities. Aquatic Ecology 44:13-21. | 2010 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Todd, P. A., X. Y. Ong, and L. M. Chou. 2010. Impacts of pollution on marine life in Southeast Asia. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:1063-1082. | 2010 | Global; Southeast Asia; Philippines | Review | Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waterborne Discharges |
| Torreton, J. P., E. Rochelle-Newall, O. Pringault, S. Jacquet, V. Faure, and E. Briand. 2010. Variability of primary and bacterial production in a coral reef lagoon (New Caledonia). Marine Pollution Bulletin 61:335-348. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Trost, B. M., M. Osipov, and G. B. Dong. 2010. Palladium-Catalyzed Dynamic Kinetic Asymmetric Transformations of Vinyl Aziridines with Nitrogen Heterocycles: Rapid Access to Biologically Active Pyrroles and Indoles. Journal of the American Chemical Society 132:15800-15807. | 2010 | Nutrients | ||
| Ushie, H., H. Kawahata, A. Suzuki, S. Murayama, and M. Inoue. 2010. Enhanced riverine carbon flux from carbonate catchment to the ocean: A comparative hydrogeochemical study on Ishigaki and Iriomote islands, southwestern Japan. Journal Of Geophysical Research-biogeosciences 115:G02017. | 2010 | Japan | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Uthicke, S. and C. Altenrath. 2010. Water column nutrients control growth and C : N ratios of symbiont-bearing benthic foraminifera on the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Limnology and Oceanography 55:1681-1696. | 2010 | Australia | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting | |
| Uthicke, S., A. Thompson, and B. Schaffelke. 2010. y Effectiveness of benthic foraminiferal and coral assemblages as water quality indicators on inshore reefs of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 29:209-225. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Light; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seastars; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Van der Kooij, B., A. Immenhauser, T. Steuber, J. R. B. Rionda, and O. M. Tome. 2010. Controlling factors of volumetrically important marine carbonate cementation in deep slope settings. Sedimentology 57:1491-1525. | 2010 | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| van Dijk, J. K. and B. I. van Tussenbroek. 2010. Clonal diversity and structure related to habitat of the marine angiosperm Thalassia testudinum along the Atlantic coast of Mexico. Aquatic Botany 92:63-69. | 2010 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean; Mexico | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Wagner, D. E., P. Kramer, and R. van Woesik. 2010. Species composition, habitat, and water quality influence coral bleaching in southern Florida. Marine Ecology Progress Series 408:65-78. | 2010 | Florida | Discharges; Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Water Stewardship Inc. 2010. Beta Test Report: Process Development & Description of Findings. | 2010 | Agriculture; Nutrients | ||
| Webster, I. T. and P. W. Ford. 2010. Delivery, deposition and redistribution of fine sediments within macrotidal Fitzroy Estuary/Keppel Bay: Southern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Continental Shelf Research 30:793-805. | 2010 | Australia | Remote Sensing | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Weeks, S. J., A. Bakun, C. R. Steinberg, R. Brinkman, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2010. The Capricorn Eddy: a prominent driver of the ecology and future of the southern Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 29:975-985. | 2010 | Australia | Model | Climate; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Westphal, H., J. Halfar, and A. Freiwald. 2010. Heterozoan carbonates in subtropical to tropical settings in the present and past. International Journal of Earth Sciences 99:S153-S169. | 2010 | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | ||
| Westphal, H., K. Heindel, M. Brandano, and J. Peckmann. 2010. Genesis of microbialites as contemporaneous framework components of deglacial coral reefs, Tahiti (IODP 310). Facies 56:337-352. | 2010 | Algae; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Wild, C., W. Niggl, M. S. Naumann, and A. F. Haas. 2010. Organic matter release by Red Sea coral reef organisms-potential effects on microbial activity and in situ O-2 availability. Marine Ecology Progress Series 411:61-71. | 2010 | Cuba | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Williams, B. and A. G. Grottoli. 2010. Recent shoaling of the nutricline and thermocline in the western tropical Pacific. Geophysical Research Letters 37:L22601. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Palau | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients | |
| Williams, B. and A. G. Grottoli. 2010. Stable nitrogen and carbon isotope (delta N-15 and delta C-13) variability in shallow tropical Pacific soft coral and black coral taxa and implications for paleoceanographic reconstructions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 74:5280-5288. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Palau | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Octocoral |
| Wilson, B. 2010. Effect Of Hurricanes On Guilds Of Nearshore Epiphytal Foraminifera, Nevis, West Indies. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 40:327-343. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate |
| Wisshak, M., A. Form, J. Jakobsen, and A. Freiwald. 2010. Temperate carbonate cycling and water mass properties from intertidal to bathyal depths (Azores). Biogeosciences 7:2379-2396. | 2010 | Bahamas | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Light; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Wyatt, A. S. J., A. M. Waite, and S. Humphries. 2010. Variability in Isotope Discrimination Factors in Coral Reef Fishes: Implications for Diet and Food Web Reconstruction. PLoS One 5:e13682. | 2010 | Australia | Lab Study | Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Wyatt, A. S. J., R. J. Lowe, S. Humphries, and A. M. Waite. 2010. Particulate nutrient fluxes over a fringing coral reef: relevant scales of phytoplankton production and mechanisms of supply. Marine Ecology Progress Series 405:113-130. | 2010 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Xu, L. Q., X. D. Liu, L. G. Sun, H. Yan, Y. Liu, Y. H. Luo, J. Huang, and Y. H. Wang. 2010. Distribution of radionuclides in the guano sediments of Xisha Islands, South China Sea and its implication. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 101:362-368. | 2010 | China | Model | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Yeffet, D., A. Rudi, S. Ketzinel, Y. Benayahu, and Y. Kashman. 2010. Auroside, a Xylosyl-sterol, and Patusterol A and B, two Hydroxylated Sterols, from two Soft Corals Eleutherobia aurea and Lobophytum patulum. Natural Product Communications 5:205-210. | 2010 | Kenya; South Africa | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Yniguez, A. T., J. W. McManus, and L. Collado-Vides. 2010. Capturing the dynamics in benthic structures: environmental effects on morphology in the macroalgal genera Halimeda and Dictyota. Marine Ecology Progress Series 411:17-U40. | 2010 | Florida | Model; Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients |
| Zawada, D. G., G. A. Piniak, and C. J. Hearn. 2010. Topographic complexity and roughness of a tropical benthic seascape. Geophysical Research Letters 37:L14604. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Zeppelin, T. K. and A. J. Orr. 2010. Stable isotope and scat analyses indicate diet and habitat partitioning in northern fur seals Callorhinus ursinus across the eastern Pacific. Marine Ecology Progress Series 409:241-253. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients | |
| Alamaru, A., R. Yam, A. Shemesh, and Y. Loya. 2009. Trophic biology of stylophora pistillata larvae: Evidence from stable isotope analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 383:85-94. | 2009 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Alamaru, A., Y. Loya, E. Brokovich, R. Yam, and A. Shemesh. 2009. Carbon and nitrogen utilization in two species of Red Sea corals along a depth gradient: Insights from stable isotope analysis of total organic material and lipids. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73:5333-5342. | 2009 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Alvarado, J. J., C. Fernandez, and J. Cortes. 2009. Water quality conditions on coral reefs at the marino ballena national park, pacific costa RICA. Bulletin of Marine Science 84:137-152. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Appeldoorn, R. S., A. Aguilar-Perera, B. L. K. Bouwmeester, G. D. Dennis, R. L. Hill, W. Merten, C. W. Recksiek, and S. J. Williams. 2009. Movement of fishes (Grunts: Haemulidae) across the coral reef seascape: A review of scales, patterns and processes. Caribbean Journal of Science 45:304-316. | 2009 | Review; Model | Fish; Nutrients | |
| Armour, J. D., L. R. Hateley, and G. L. Pitt. 2009. Catchment modelling of sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient loads with SedNet/ANNEX in the Tully-Murray basin. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1091-1096. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Bainbridge, Z. T., J. E. Brodie, J. W. Faithful, D. A. Sydes, and S. E. Lewis. 2009. Identifying the land-based sources of suspended sediments, nutrients and pesticides discharged to the Great Barrier Reef from the Tully-Murray Basin, Queensland, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1081-1090. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Becker, E. L., E. E. Cordes, S. A. Macko, and C. R. Fisher. 2009. Importance of seep primary production to Lophelia pertusa and associated fauna in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 56:786-800. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Snails & Conch | |
| Ben-Dov, E., E. Kramarsky-Winter, and A. Kushmaro. 2009. An in situ method for cultivating microorganisms using a double encapsulation technique. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 68:363-371. | 2009 | Cuba; Europe | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Substrate |
| Bohlen, P. J., S. Lynch, L. Shabman, M. Clark, S. Shukla, and H. Swain. 2009. Paying for environmental services from agricultural lands: an example from the northern Everglades. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:46-55. | 2009 | Florida | Agriculture; Nutrients | |
| Bourillot, R., E. Vennin, C. Kolodka, J. M. Rouchy, A. Caruso, C. Durlet, C. Chaix, and V. Rommevaux. 2009. The role of topography and erosion in the development and architecture of shallow-water coral bioherms (Tortonian-Messinian, Cabo de Gata, SE Spain). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 281:92-114. | 2009 | Spain | Algae; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Boyer, J. N. and H. O. Briceno. 2009. 2009 annual report of the water quality monitoring project for the water quality protection program of the Florida Keys National Marine Sactuary. Florida International University, Miami, FL. | 2009 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Light; Nutrients; Salinity |
| Boyer, J. N., C. R. Kelble, P. B. Ortner, and D. T. Rudnick. 2009. Phytoplankton bloom status: Chlorophyll a biomass as an indicator of water quality condition in the southern estuaries of Florida, USA. Ecological Indicators 9:S56-S67. | 2009 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Brand, L. E. 2009. Human exposure to cyanobacteria and BMAA. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis 10:85-95. | 2009 | Florida | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Brandano, M., V. Frezza, L. Tomassetti, and M. Cuffaro. 2009. Heterozoan carbonates in oligotrophic tropical waters: The Attard member of the lower coralline limestone formation (Upper Oligocene, Malta). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 274:54-63. | 2009 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Brierley, A. S. and M. J. Kingsford. 2009. Impacts of Climate Change on Marine Organisms and Ecosystems. Current Biology 19:R602-R614. | 2009 | Global | Review | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Brodie, J., S. Lewis, Z. Bainbridge, A. Mitchell, J. Waterhouse, and F. Kroon. 2009. Target setting for pollutant discharge management of rivers in the Great Barrier Reef catchment area. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1141-1149. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Burford, M. A., P. C. Rothlisberg, and A. T. Revill. 2009. Sources of nutrients driving production in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia: a shallow tropical shelf system. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1044-1053. | 2009 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Burkepile, D. E. and M. E. Hay. 2009. Nutrient versus herbivore control of macroalgal community development and coral growth on a Caribbean reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 389:71-84. | 2009 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Coralline Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Cyanobacteria; Finfish Harvest; Large Herbivorous Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Carreiro-Silva, M., T. R. McClanahan, and W. E. Kiene. 2009. Effects of inorganic nutrients and organic matter on microbial euendolithic community composition and microbioerosion rates. Marine Ecology Progress Series 392:1-15. | 2009 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Casareto, B. E., M. P. Niraula, H. Fujimura, and Y. Suzuki. 2009. Effects of carbon dioxide on the coccolithophorid Pleurochrysis carterae in incubation experiments. Aquatic Biology 7:59-70. | 2009 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Chen, B.-Y., C.-Y. Yen, and C.-C. Hsueh. 2009. Cost-effective biostimulation strategy for wastewater decolorization using immobilized-cell systems. Bioresource Technology 100:2975-2981. | 2009 | Taiwan | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Cheng, Y. B., C. Y. Chen, Y. H. Kuo, and Y. C. Shen. 2009. New Nitrogen-Containing Sesquiterpenoids from the Taiwanese Soft Coral Cespitularia taeniata MAY. Chemistry & biodiversity 6:1266-1272. | 2009 | Taiwan | Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Clark, R. D., S. Pittman, C. Caldow, J. Christensen, B. Roque, R. S. Appeldoorn, and M. E. Monaco. 2009. Nocturnal fish movement and trophic flow across habitat boundaries in a coral reef ecosystem (SW Puerto Rico). Caribbean Journal of Science 45:282-303. | 2009 | Puerto Rico | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Molluscs; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Clements, K. D., D. Raubenheimer, and J. H. Choat. 2009. Nutritional ecology of marine herbivorous fishes: Ten years on. Functional Ecology 23:79-92. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Clode, P. L., M. Saunders, G. Maker, M. Ludwig, and C. A. Atkins. 2009. Uric acid deposits in symbiotic marine algae. Plant, Cell and Environment 32:170-177. | 2009 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Cohen, A. L. and M. Holcomb. 2009. Why Corals Care About Ocean Acidification: Uncovering the Mechanism. Oceanography 22:118-127. | 2009 | Global | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Contamin, R. and A. M. Ellison. 2009. Indicators of regime shifts in ecological systems: What do we need to know and when do we need to know it? Ecological Applications 19:799-816. | 2009 | Model; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Cooper, T. F. and K. E. Ulstrup. 2009. Mesoscale variation in the photophysiology of the reef building coral Pocillopora damicornis along an environmental gradient. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 83:186-196. | 2009 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Cooper, T. F., J. P. Gilmour, and K. E. Fabricius. 2009. Bioindicators of changes in water quality on coral reefs: review and recommendations for monitoring programmes. Coral Reefs 18-Jan. | 2009 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Cornelisen, C. D. and F. I. M. Thomas. 2009. Prediction and validation of flow-dependent uptake of ammonium over a seagrass-hardbottom community in Florida Bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 386:71-81. | 2009 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Skeletal Coral |
| De Goeij, J. M., A. De Kluijver, F. C. Van Duyl, J. Vacelet, R. H. Wijffels, A. F. P. M. De Goeij, J. P. M. Cleutjens, and B. Schutte. 2009. Cell kinetics of the marine sponge Halisarca caerulea reveal rapid cell turnover and shedding. Journal of Experimental Biology 212:3892-3900. | 2009 | Encrusting Sponges; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Sponges | ||
| Diaz-Pulido, G., L. J. McCook, S. Dove, R. Berkelmans, G. Roff, D. I. Kline, S. Weeks, R. D. Evans, D. H. Williamson, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2009. Doom and boom on a resilient reef: climate change, algal overgrowth and coral recovery. PLoS One 4. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Model | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Pathogens; Skeletal Coral |
| DiDonato, G. T., E. M. DiDonato, L. M. Smith, L. C. Harwell, and J. K. Summers. 2009. Assessing coastal waters of American Samoa: territory-wide water quality data provide a critical "big-picture" view for this tropical archipelago. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 150:157-165. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Samoa; American Samoa | Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria | |
| Dikou, A. 2009. Skeletal linear extension rates of the foliose scleractinian coral Merulina ampliata (Ellis & Solander, 1786) in a turbid environment. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 30:405-415. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Dikou, A., C. Ackerman, C. Banks, A. Dempsey, M. Fox, M. Gins, P. Hester, A. Parnes, S. Roach, J. Rohde, C. Spital, M. Tapleshay, and L. Thomas. 2009. Ecological assessment to detect imminent change in coral reefs of Admiral Cockburn Land and Sea National Park, Turks and Caicos Islands. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 30:425-436. | 2009 | South & Central America; Turks and Caicos; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation; Turf Algae |
| Dodds, W. K., W. A. Bouska, J. L. Eitzmann, T. J. Pilger, K. L. Pitts, A. J. Riley, J. T. Schloesser, and D. J. Thornbrugh. 2009. Eutrophication of U.S. freshwaters: analysis of potential economic damages. Environmental Science and Technology 43:13-19. | 2009 | Drinking Water Supply; Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Downs, C. A., E. Kramarsky-Winter, J. Martinez, A. Kushmaro, C. M. Woodley, Y. Loya, and G. K. Ostrander. 2009. Symbiophagy as a cellular mechanism for coral bleaching. Autophagy 5:211-216. | 2009 | Global | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Drinia, H. 2009. Foraminiferal biofacies and paleoenvironmental implications of the Early Tortonian deposits of Gavdos Island (Eastern Mediterranean). Revue de Micropaleontologie 52:15-29. | 2009 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Einbinder, S., T. Mass, E. Brokovich, Z. Dubinsky, J. Erez, and D. Tchernov. 2009. Changes in morphology and diet of the coral Stylophora pistillata along a depth gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 381:167-174. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Eklof, J. S., S. Frocklin, A. Lindvall, N. Stadlinger, A. Kimathi, J. N. Uku, and T. R. McClanahan. 2009. How effective are MPAs? Predation control and 'spill-in effects' in seagrass-coral reef lagoons under contrasting fishery management. Marine Ecology Progress Series 384:83-96. | 2009 | Kenya | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars | |
| Falcao, M., M. N. Santos, T. Drago, D. Serpa, and C. Monteiro. 2009. Effect of artificial reefs (southern Portugal) on sediment-water transport of nutrients: Importance of the hydrodynamic regime. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 83:451-459. | 2009 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Figueroa, F. L., B. Martinez, A. Israel, A. Neori, E. J. Malta, P. Ang, S. Inken, R. Marquardt, T. Rachamim, U. Arazi, S. Frenk, and N. Korbee. 2009. Acclimation of Red Sea macroalgae to solar radiation: photosynthesis and thallus absorptance. Aquatic Biology 7:159-172. | 2009 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Garren, M., L. Raymundo, J. Guest, C. D. Harvell, and F. Azam. 2009. Resilience of Coral-Associated Bacterial Communities Exposed to Fish Farm Effluent. PLoS One 4:e7319. | 2009 | Philippines | Aquaculture; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Genin, A., S. G. Monismith, M. A. Reidenbach, G. Yahel, and J. R. Koseff. 2009. Intense benthic grazing of phytoplankton in a coral reef. Limnology and Oceanography 54:938-951. | 2009 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Godinot, C. and N. E. Chadwick. 2009. Phosphate Excretion By Anemonefish And Uptake By Giant Sea Anemones: Demand Outstrips Supply. Bulletin of Marine Science 85:1-9. | 2009 | Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Granek, E. F., J. E. Compton, and D. L. Phillips. 2009. Mangrove-exported nutrient incorporation by sessile coral reef invertebrates. Ecosystems 12:462-472. | 2009 | Panama | Model | Algae; Bivalves; Mangroves; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates |
| Haas, A., M. Al-Zibdah, and C. Wild. 2009. Effect of inorganic and organic nutrient addition on coral-algae assemblages from the Northern Red Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 380:99-105. | 2009 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | ||
| Hadas, E., M. Shpigel, and M. Ilan. 2009. Particulate organic matter as a food source for a coral reef sponge. Journal of Experimental Biology 212:3643-3650. | 2009 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | ||
| Harii, S., N. Yasuda, M. Rodriguez-Lanetty, T. Irie, and M. Hidaka. 2009. Onset of symbiosis and distribution patterns of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the larvae of scleractinian corals. Marine Biology 156:1203-1212. | 2009 | Florida; China | Lab Study; Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral |
| Heindel, K., M. Wisshak, and H. Westphal. 2009. Microbioerosion in Tahitian reefs: a record of environmental change during the last deglacial sea-level rise (IODP 310). Lethaia 42:322-340. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coralline Algae; Light; Nutrients | |
| Hennige, S. J., D. J. Suggett, M. E. Warner, K. E. McDougall, and D. J. Smith. 2009. Photobiology of Symbiodinium revisited: Bio-physical and bio-optical signatures. Coral Reefs 28:179-195. | 2009 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Herrera-Silveira, J. A. and S. M. Morales-Ojeda. 2009. Evaluation of the health status of a coastal ecosystem in southeast Mexico: Assessment of water quality, phytoplankton and submerged aquatic vegetation. Marine Pollution Bulletin 59:72-86. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hii, Y. S., C. L. Soo, and H. C. Liew. 2009. Feeding of scleractinian coral, Galaxea fascicularis, on Artemia salina nauplii in captivity. Aquaculture International 17:363-376. | 2009 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | ||
| Ho, C. T., Y. C. Fu, C. L. Sun, S. J. Kao, and R. Q. Jan. 2009. Plasticity of Feeding Habits of Two Plectroglyphidodon Damselfishes on Coral Reefs in Southern Taiwan: Evidence from Stomach Content and Stable Isotope Analyses. Zoological Studies 48:649-656. | 2009 | Taiwan | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Hoffmann, F., R. Radax, D. Woebken, M. Holtappels, G. Lavik, H. T. Rapp, M. L. Schlappy, C. Schleper, and M. M. M. Kuypers. 2009. Complex nitrogen cycling in the sponge Geodia barretti. Environmental Microbiology 11:2228-2243. | 2009 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges |
| Holmes, G., J. C. Ortiz, and C. H. L. Schonberg. 2009. Bioerosion rates of the sponge Cliona orientalis Thiele, 1900: spatial variation over short distances. Facies 55:203-211. | 2009 | Australia | Boring Sponges; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Houlbreque, F. and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Heterotrophy in tropical scleractinian corals. Biological Review 84:17-Jan. | 2009 | Review | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Houlbreque, F. and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Heterotrophy in Tropical Scleractinian Corals. Biological Reviews 84:1-17. | 2009 | Review | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hutchins, D. A., M. R. Mulholland, and F. Fu. 2009. Nutrient cycles and marine microbes in a CO2-enriched ocean. Oceanography 22:128-145. | 2009 | Global | Review | CO2; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Plankton; Substrate |
| Ikeda, S., K. Osawa, and Y. Akamatsu. 2009. Sediment and nutrients transport in watershed and their impact on coastal environment. Proceedings Of The Japan Academy Series A-mathematical Sciences 85:374-390. | 2009 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Civil Engineering & Construction; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ikeda, S., K. Osawa, and Y. Akamatsu. 2009. Sediment and nutrients transport in watershed and their impact on coastal environment. Proceedings Of The Japan Academy Series B-physical And Biological Sciences 85:374-390. | 2009 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Civil Engineering & Construction; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Itoh, A., T. Ishigaki, T. Arakaki, A. Yamada, M. Yamaguchi, and N. Kabe. 2009. Determination of Trace Metals in Coastal Seawater around Okinawa and Its Multielement Profiling Analysis. Bunseki Kagaku 58:257-263. | 2009 | Japan | Nutrients | |
| Jan, S. and C. T. A. Chen. 2009. Potential biogeochemical effects from vigorous internal tides generated in Luzon Strait: A case study at the southernmost coast of Taiwan. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 114:C04021. | 2009 | Taiwan | Model | Nutrients |
| Jones, S. and R. L. Quinn. 2009. Prehistoric Fijian diet and subsistence: integration of faunal, ethnographic, and stable isotopic evidence from the Lau Island Group. Journal of Archaeological Science 36:2742-2754. | 2009 | Fiji | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Kamal, A. H. and M. A. A. Khan. 2009. Coastal and estuarine resources of Bangladesh: management conservation issues. Maejo International Journal Of Science And Technology 3:313-342. | 2009 | Discharges; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Keller, B. D., D. F. Gleason, E. McLeod, C. M. Woodley, S. Airame, B. D. Causey, A. M. Friedlander, R. Grober-Dunsmore, J. E. Johnson, S. L. Miller, and R. S. Steneck. 2009. Climate Change, Coral Reef Ecosystems, and Management Options for Marine Protected Areas. Environmental Management 44:1069-1088. | 2009 | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Kellogg, C. A., J. T. Lisle, and J. P. Galkiewicz. 2009. Culture-independent characterization of bacterial communities associated with the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 75:2294-2303. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients | |
| Khokiattiwong, S., N. Kornkanitnan, W. Goessler, S. Kokarnig, and K. A. Francesconi. 2009. Arsenic compounds in tropical marine ecosystems: similarities between mangrove forest and coral reef. Environmental Chemistry 6:226-234. | 2009 | Thailand | Algae; Fish; Mangroves; Molluscs; Nutrients | |
| Kiessling, W. 2009. Geologic and Biologic Controls on the Evolution of Reefs. Annual Review Of Ecology Evolution And Systematics 40:173-192. | 2009 | Climate; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients | ||
| Kragt, M. E., P. C. Roebeling, and A. Ruijs. 2009. Effects of Great Barrier Reef degradation on recreational reef-trip demand: A contingent behaviour approach. Australian Journal of Agricultural and Resource Economics 53:213-229. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Kramarsky-Winter, E., C. A. Downs, A. Downs, and Y. Loya. 2009. Cellular responses in the coral Stylophora pistillata exposed to eutrophication from fish mariculture. Evolutionary Ecology Research 11:381-401. | 2009 | Egypt | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Fish; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral |
| Kroon, F. J. and J. Brodie. 2009. Catchment management and health of coastal ecosystems: synthesis and future research. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1196-1200. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients |
| Larsen, M. C. and R. M. T. Webb. 2009. Potential effects of runoff, fluvial sediment, and nutrient discharges on the coral reefs of Puerto Rico. Journal of Coastal Research 25:189-208. | 2009 | Puerto Rico | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lartigue, J., E. L. E. Jester, R. W. Dickey, and T. A. Villareal. 2009. Nitrogen source effects on the growth and toxicity of two strains of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. Harmful Algae 8:781-791. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Lavaleye, M., G. Duineveld, T. Lundalv, M. White, D. Guihen, K. Kiriakoulakis, and G. A. Wolff. 2009. Cold-Water Corals On The Tisler Reef Preliminary Observations On The Dynamic Reef Environment. Oceanography 22:76-84. | 2009 | Global; Norway | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Liu, P. J., S. M. Lin, T. Y. Fan, P. J. Meng, K. T. Shao, and H. J. Lin. 2009. Rates of overgrowth by macroalgae and attack by sea anemones are greater for live coral than dead coral under conditions of nutrient enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 54:1167-1175. | 2009 | Taiwan | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| LoDuca, S. T. and E. R. Behringer. 2009. Functional morphology and evolution of early Paleozoic dasycladalean algae (Chlorophyta). Paleobiology 35:63-76. | 2009 | Model | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Lokier, S. W., M. E. J. Wilson, and L. M. Burton. 2009. Marine biota response to clastic sediment influx: A quantitative approach. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 281:25-42. | 2009 | Java; Spain | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coralline Algae; Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Lottermoser, B. G. 2009. Trace metal enrichment in sugarcane soils due to the long-term application of fertilisers, North Queensland, Australia: geochemical and Pb, Sr, and U isotopic compositions. Australian Journal of Soil Research 47:311-320. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Nutrients |
| Lourey, M. J. and H. Kirkman. 2009. Short-lived dissolved nitrate pulses in a shallow Western Australian coastal lagoon. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1068-1080. | 2009 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Maughan, M. and J. Brodie. 2009. Reef exposure to river-borne contaminants: a spatial model. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1132-1140. | 2009 | Australia; Europe | Model; GIS & Maps | Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| McClanahan, T. R., E. Weil, and J. Maina. 2009. Strong relationship between coral bleaching and growth anomalies in massive Porites. Global Change Biology 15:1804-1816. | 2009 | Kenya | Model | Algae; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Mendoza, W. G., R. G. Zika, J. E. Corredor, J. Morrel, D. S. Ko, and C. N. K. Mooers. 2009. Developmental strategy for effective sampling to detect possible nutrient fluxes in oligotrophic coastal reef waters in the Caribbean. Journal Of Operational Oceanography 2:35-47. | 2009 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Merino-Tome, O., J. R. Bahamonde, E. Samankassou, and E. Villa. 2009. The influence of terrestrial run off on marine biotic communities: An example from a thrust-top carbonate ramp (Upper Pennsylvanian foreland basin, Picos de Europa, NW Spain). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 278:23-Jan. | 2009 | Spain | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Metcalfe, J. Z., C. D. White, F. J. Longstaffe, G. Wrobel, D. C. Cook, and K. Anne Pyburn. 2009. Isotopic evidence for diet at Chau Hiix, Belize: Testing regional models of hierarchy and heterarchy. Latin American Antiquity 20:15-36. | 2009 | South & Central America; Belize | Model | Nutrients |
| Miguel, A. F. and A. Bejan. 2009. The principle that generates dissimilar patterns inside aggregates of organisms. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 388:727-731. | 2009 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Millero, F. J., R. Woosley, B. Ditrolio, and J. Waters. 2009. Effect of ocean acidification on the speciation of metals in seawater. Oceanography 22:72-85. | 2009 | Review | CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Primary Production | |
| Mitchell, A., J. Reghenzani, J. Faithful, M. Furnas, and J. Brodie. 2009. Relationships between land use and nutrient concentrations in streams draining a 'wet-tropics' catchment in northern Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1097-1108. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Miyajima, T., C. Yoshimizu, Y. Tsuboi, Y. Tanaka, I. Tayasu, T. Nagata, and I. Koike. 2009. Longitudinal distribution of nitrate delta N-15 and delta O-18 in two contrasting tropical rivers: implications for instream nitrogen cycling. Biogeochemistry 95:243-260. | 2009 | Southeast Asia | Model | Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics |
| Montagna, P., M. McCulloch, M. Taviani, J. Trotter, S. Silenzi, and C. Mazzoli. 2009. An improved sampling method for coral P/Ca as a nutrient proxy. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73:A895-A895. | 2009 | Nutrients | ||
| Mork, E., G. L. Sjoo, N. Kautsky, and T. R. McClanahan. 2009. Top-down and bottom-up regulation of macroalgal community structure on a Kenyan reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84:331-336. | 2009 | Kenya | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Muller, E. B., S. A. L. M. Kooijman, P. J. Edmunds, F. J. Doyle, and R. M. Nisbet. 2009. Dynamic energy budgets in syntrophic symbiotic relationships between heterotrophic hosts and photoautotrophic symbionts. Journal of Theoretical Biology 259:44-57. | 2009 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Nakajima, R., T. Yoshida, B. A. R. Azman, K. Zaleha, B. H. R. Othman, and T. Toda. 2009. In situ release of coral mucus by Acropora and its influence on the heterotrophic bacteria. Aquatic Ecology 43:815-823. | 2009 | Cuba; Malaysia; Oman | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Nelson, M., W. F. Dempster, and J. P. Allen. 2009. The water cycle in closed ecological systems: Perspectives from the Biosphere 2 and Laboratory Biosphere systems. Advances in Space Research 44:1404-1412. | 2009 | Global | Lab Study | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Irrigation; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| Nelson, S. G., E. P. Glenn, D. Moore, and B. Ambrose. 2009. Growth and Distribution of the Macroalgae Gracilaria salicornia and G-parvispora (Rhodophyta) Established from Aquaculture Introductions at Moloka'i, Hawai'i. Pacific Science 63:383-396. | 2009 | Algae; Aquaculture; Invasive Species; Nutrients | ||
| Nelson, W. A. 2009. Calcified macroalgae - critical to coastal ecosystems and vulnerable to change: a review. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:787-801. | 2009 | Global | Review | Agriculture; Algae; Aquaculture; CO2; Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Sediment |
| Nyunja, J., M. Ntiba, J. Onyari, K. Mavuti, K. Soetaert, and S. Bouillon. 2009. Carbon sources supporting a diverse fish community in a tropical coastal ecosystem (Gazi Bay, Kenya). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 83:333-341. | 2009 | Kenya | Algae; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Ohba, H., B. E. Casareto, and Y. Suzuki. 2009. Primary Producers And Nitrogen Fixers Colonizing Coral Rubble Of Coral Reefs At Ryukyus, Southern Japan. Phycologia 48. | 2009 | Japan | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral | |
| Oliver, L. M. and W. S. Fisher, editors. 2009. APM 289: Report on effects of UV radiation, temperature and nutrients on South Florida corals. US EPA Gulf Ecology Division, Gulf Breeze, (FL, USA). | 2009 | Global; Florida | Algae; Climate; Light; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Olson, N. D., T. D. Ainsworth, R. D. Gates, and M. Takabayashi. 2009. Diazotrophic bacteria associated with Hawaiian Montipora corals: Diversity and abundance in correlation with symbiotic dinoflagellates. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 371:140-146. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Cyanobacteria; Nutrients | |
| Otero, E. 2009. Spatial and temporal patterns of water quality indicators in reef systems of southwestern Puerto Rico. Caribbean Journal of Science 45:168-180. | 2009 | Puerto Rico | Model; Index or Indicator | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Oxford Economics. 2009. Valuing the effects of Great Barrier Reef bleaching. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Review | Climate; CO2; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Petkewich, R. 2009. Off-balance ocean. Chemical and Engineering News 87. | 2009 | Anemones & Zooanthids; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity | ||
| Pinon-Gimate, A., M. F. Soto-Jimenez, M. J. Ochoa-Izaguirre, E. Garcia-Pages, and F. Paez-Osuna. 2009. Macroalgae blooms and delta N-15 in subtropical coastal lagoons from the Southeastern Gulf of California: Discrimination among agricultural, shrimp farm and sewage effluents. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:1144-1151. | 2009 | Agriculture; Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Raina, J.-B., D. Tapiolas, B. L. Willis, and D. G. Bourne. 2009. Coral-associated bacteria and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of sulfur. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 75:3492-3501. | 2009 | Climate; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Rasheed, M., E. El-Hihi, S. Al-Rousan, and A. Abu-Hilal. 2009. Chemical evaluation of sand material sources for beach replenishment along the coast of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Chemistry and Ecology 25:371-384. | 2009 | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients | ||
| Renken, H. and P. J. Mumby. 2009. Modelling the dynamics of coral reef macroalgae using a Bayesian belief network approach. Ecological Modelling 220:1305-1314. | 2009 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins |
| Reopanichkul, P., T. A. Schlacher, R. W. Carter, and S. Worachananant. 2009. Sewage impacts coral reefs at multiple levels of ecological organization. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:1356-1362. | 2009 | Global; Thailand | Algae; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Revill, A. T., J. W. Young, and M. Lansdell. 2009. Stable isotopic evidence for trophic groupings and bio-regionalization of predators and their prey in oceanic waters off eastern Australia. Marine Biology 156:1241-1253. | 2009 | Australia | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Nutrients; Octopus & Squid | |
| Reynaud, S., P. Martinez, F. Houlbreque, I. Billy, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2009. Effect of light and feeding on the nitrogen isotopic composition of a zooxanthellate coral: role of nitrogen recycling. Marine Ecology Progress Series 392:103-110. | 2009 | Light; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Riegl, B., A. Bruckner, S. L. Coles, P. Renaud, and R. E. Dodge. 2009. Coral Reefs Threats and Conservation in an Era of Global Change. Pages 136-186 Year In Ecology And Conservation Biology 2009. | 2009 | Global; Florida | Climate; CO2; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Riegl, B., A. Bruckner, S. L. Coles, P. Renaud, and R. E. Dodge. 2009. Coral reefs: threats and conservation in an era of global change. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1162:136-186. | 2009 | Global; Florida | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Risk, M. 2009. The reef crisis and the reef science crisis: Nitrogen isotopic ratios as an objective indicator of stress. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:787-788. | 2009 | Index or Indicator | Nutrients | |
| Risk, M. J., B. E. Lapointe, O. A. Sherwood, and B. J. Bedford. 2009. The use of delta N-15 in assessing sewage stress on coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:793-802. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Bivalves; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment | |
| Risk, M. J., O. A. Sherwood, R. Nairn, and C. Gibbons. 2009. Tracking the record of sewage discharge off Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, since 1950, using stable isotope records from antipatharians. Marine Ecology Progress Series 397:219-226. | 2009 | Saudi Arabia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Wastewater Discharge |
| Risk, M.J., B.E. Lapointe, O.A. Sherwood, B.J. Bedford. 2009. The use of d15N in assessing sewage stress on coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:793-802. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Bivalves; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment | |
| Roark, A. M., K. A. Bjorndal, and A. B. Bolten. 2009. Compensatory responses to food restriction in juvenile green turtles (Chelonia mydas). Ecology 90:2524-2534. | 2009 | Nutrients; Sea Turtles | ||
| Rockstrom, J., W. Steffen, K. Noone, A. Persson, F. S. Chapin, E. Lambin, T. M. Lenton, M. Scheffer, C. Folke, H. J. Schellnhuber, B. Nykvist, C. A. de Wit, T. Hughes, S. van der Leeuw, H. Rodhe, S. Sorlin, P. K. Snyder, R. Costanza, U. Svedin, M. Falkenmark, and Karlbe. 2009. Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity. Ecology and Society 14:32. | 2009 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Toxics |
| Roder, C., J. Cortes, C. Jimenez, and R. Lara. 2009. Riverine input of particulate material and inorganic nutrients to a coastal reef ecosystem at the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:1937-1943. | 2009 | South & Central America; Costa Rica; Caribbean | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Roebeling, P. C., E. M. T. Hendrix, and M. E. van Grieken. 2009. Exploring industry specific social welfare maximizing rates of water pollution abatement in linked terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Journal of Coastal Research 1681-1685. | 2009 | Australia | Agriculture; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Roebeling, P. C., M. E. van Grieken, A. J. Webster, J. Biggs, and P. Thorburn. 2009. Cost-effective water quality improvement in linked terrestrial and marine ecosystems: a spatial environmental-economic modelling approach. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1150-1158. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges |
| Roopin, M. and N. E. Chadwick. 2009. Benefits to host sea anemones from ammonia contributions of resident anemonefish. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 370:27-34. | 2009 | Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Rosales-Hoz, L., A. Carranza-Edwards, L. Sanvicente-Anorve, M. A. Alatorre-Mendieta, and F. Rivera-Ramirez. 2009. Distribution of Dissolved Trace Metals Around the Sacrificos Coral Reef Island, in the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 83:713-719. | 2009 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies | |
| Rusch, A., A. K. Hannides, and E. Gaidos. 2009. Diverse communities of active Bacteria and Archaea along oxygen gradients in coral reef sediments. Coral Reefs 28:15-26. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Russell, B. D., J. A. I. Thompson, L. J. Falkenberg, and S. D. Connell. 2009. Synergistic effects of climate change and local stressors: CO2 and nutrient-driven change in subtidal rocky habitats. Global Change Biology 15:2153-2162. | 2009 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Coralline Algae; Economic Markets & Policies; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Sattler, U., A. Immenhauser, W. Schlager, and V. Zampetti. 2009. Drowning history of a Miocene carbonate platform (Zhujiang Formation, South China Sea). Sedimentary Geology 219:318-331. | 2009 | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
| Sauchyn, L. K. and R. E. Scheibling. 2009. Degradation of sea urchin feces in a rocky subtidal ecosystem: implications for nutrient cycling and energy flow. Aquatic Biology 6:99-108. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sea Urchins | |
| Shafir, S., S. Abady, and B. Rinkevich. 2009. Improved sustainable maintenance for mid-water coral nursery by the application of an anti-fouling agent. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 368:124-128. | 2009 | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Wetland & Reef Restoration | ||
| Sheaves, M. 2009. Consequences of ecological connectivity: the coastal ecosystem mosaic. Marine Ecology Progress Series 391:107-115. | 2009 | Nutrients; Wetlands | ||
| Shima, J. S. and S. E. Swearer. 2009. Larval quality is shaped by matrix effects: Implications for connectivity in a marine metapopulation. Ecology 90:1255-1267. | 2009 | Fish; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors | ||
| Singh, S., W. G. L. Aalbersberg, and R. J. Morrison. 2009. Nutrient Pollution in Laucala Bay, Fiji Islands. Water Air And Soil Pollution 204:363-372. | 2009 | Fiji | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies | |
| Sisma-Ventura, G., B. Guzner, R. Yam, M. Fine, and A. Shemesh. 2009. The reef builder gastropod Dendropoma petreaum - A proxy of short and long term climatic events in the Eastern Mediterranean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73:4376-4383. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sotka, E. E. and M. E. Hay. 2009. Effects of herbivores, nutrient enrichment, and their interactions on macroalgal proliferation and coral growth. Coral Reefs 28:555-568. | 2009 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral |
| Steele-Petrovich, H. M. 2009. The biological reconstruction of Tetradium Dana, 1846. Lethaia 42:297-311. | 2009 | Model | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, Y. Umezawa, T. Hayashibara, H. Ogawa, and I. Koike. 2009. Net release of dissolved organic matter by the scleractinian coral Acropora pulchra. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 377:101-106. | 2009 | Cuba | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Thresher, R. E., C. M. MacRae, N. C. Wilson, and S. Fallon. 2009. Feasibility of age determination of deep-water bamboo corals (Gorgonacea; Isididae) from annual cycles in skeletal composition. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 56:442-449. | 2009 | Nutrients; Octocoral | ||
| Thurber, R. V., D. Willner-Hall, B. Rodriguez-Mueller, C. Desnues, R. A. Edwards, F. Angly, E. Dinsdale, L. Kelly, and F. Rohwer. 2009. Metagenomic analysis of stressed coral holobionts. Environmental Microbiology 11:2148-2163. | 2009 | Cyanobacteria; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Titlyanov, E. A., S. I. Kiyashko, T. V. Titlyanova, and J. A. Raven. 2009. δ13C and δ15N in tissue of coral polyps and epilithic algae inhabiting damaged coral colonies under the influence of different light intensities. Aquatic Ecology 9-Jan. | 2009 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Uthicke, S., B. Schaffelke, and M. Byrne. 2009. A boom-bust phylum? Ecological and evolutionary consequences of density variations in echinoderms. Ecological Monographs 79:3-24. | 2009 | Global | Review; Model | Echinoderms; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Sea Urchins; Seastars |
| Uthicke, S., L. Llewellyn, and F. Eder. 2009. Fluorescent lectin assay to quantify particulate marine polysaccharides on 96-well filtration plates. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 7:449-458. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Vermeij, M. J. A., M. L. Dailer, and C. M. Smith. 2009. Nutrient enrichment promotes survival and dispersal of drifting fragments in an invasive tropical macroalga. Coral Reefs 7-Jan. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Vermeij, M. J. A., T. B. Smith, M. L. Dailer, and C. M. Smith. 2009. Release from native herbivores facilitates the persistence of invasive marine algae: a biogeographical comparison of the relative contribution of nutrients and herbivory to invasion success. Biological Invasions 11:1463-1474. | 2009 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Algae; Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Wallace, B. P., L. Avens, J. Braun-McNeill, and C. M. McClellan. 2009. The diet composition of immature loggerheads: Insights on trophic niche, growth rates, and fisheries interactions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 373:50-57. | 2009 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Wallace, J., L. Stewart, A. Hawdon, R. Keen, F. Karim, and J. Kemei. 2009. Flood water quality and marine sediment and nutrient loads from the Tully and Murray catchments in north Queensland, Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1123-1131. | 2009 | Australia | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Walton, R. S. and H. M. Hunter. 2009. Isolating the water quality responses of multiple land uses from stream monitoring data through model calibration. Journal of Hydrology 378:29-45. | 2009 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short, and S. L. Williams. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:12377-12381. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Coastal Development; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Webster, A. J., P. J. Thorburn, P. C. Roebeling, H. L. Horan, and J. S. Biggs. 2009. The expected impact of climate change on nitrogen losses from wet tropical sugarcane production in the Great Barrier Reef region. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1159-1164. | 2009 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wild, C., M. S. Naumann, A. Haas, U. Struck, F. W. Mayer, M. Y. Rasheed, and M. Huettel. 2009. Coral sand O-2 uptake and pelagic-benthic coupling in a subtropical fringing reef, Aqaba, Red Sea. Aquatic Biology 6:133-142. | 2009 | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Williams, J. S., C. D. White, and F. J. Longstaffe. 2009. Maya marine subsistence: Isotopic evidence from Marco Gonzalez and San Pedro, Belize. Latin American Antiquity 20:37-56. | 2009 | South & Central America; Belize | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Winters, G., S. Beer, B. Ben Zvi, I. Brickner, and Y. Loya. 2009. Spatial and temporal photoacclimation of Stylophora pistillata: zooxanthella size, pigmentation, location and clade. Marine Ecology Progress Series 384:107-119. | 2009 | Light; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Wolanski, E., J. A. Martinez, and R. H. Richmond. 2009. Quantifying the impact of watershed urbanization on a coral reef: Maunalua Bay, Hawaii. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 84:259-268. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-Monetary Valuation; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wooldridge, S. A. 2009. Water quality and coral bleaching thresholds: Formalising the linkage for the inshore reefs of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:745-751. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Model | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wooldridge, S. A. and T. J. Done. 2009. Improved water quality can ameliorate effects of climate change on corals. Ecological Applications 19:1492-1499. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Climate; CO2; Collaboration & Partnering; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures | |
| Yamamoto, N., A. Kitamura, A. Ohmori, Y. Morishima, T. Toyofuku, and S. Ohashi. 2009. Long-term changes in sediment type and cavernicolous bivalve assemblages in Daidokutsu submarine cave, Okinawa Islands: evidence from a new core extending over the past 7,000 years. Coral Reefs 28:967-976. | 2009 | Japan | Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection | |
| Yuen, Y. S., S. S. Yamazaki, T. Nakamura, G. Tokuda, and H. Yamasaki. 2009. Effects of live rock on the reef-building coral Acropora digitifera cultured with high levels of nitrogenous compounds. Aquacultural Engineering 41:35-43. | 2009 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | ||
| Zamagni, J., A. Kosir, and M. Mutti. 2009. The first microbialite - coral mounds in the Cenozoic (Uppermost Paleocene) from the Northern Tethys (Slovenia): Environmentally-triggered phase shifts preceding the PETM? Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 274:17-Jan. | 2009 | Model | Climate; Nutrients | |
| Zamagni, J., A. Kosir, and M. Mutti. 2009. The first microbialite-coral mounds in the Cenozoic (Uppermost Paleocene) from the Northern Tethys (Slovenia): Environmentally-triggered phase shifts preceding the PETM? Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 274:1-17. | 2009 | Model | Climate; Nutrients | |
| Acker, J., G. Leptoukh, S. Shen, T. Zhu, and S. Kempler. 2008. Remotely-sensed chlorophyll a observations of the northern Red Sea indicate seasonal variability and influence of coastal reefs. Journal of Marine Systems 69:191-204. | 2008 | Middle East | Model; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Aguilar, C., G. Gonzalez-Sanson, I. Faloh, and R. A. Curry. 2008. Spatial variation in stable isotopes (δ13C and δ 15N) in marine fish along the coast of Havana City: Evidence of human impacts from harbor and river waters. Journal of Coastal Research 24:1281-1288. | 2008 | South & Central America; Cuba; Caribbean | Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Ports & Harbors; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Aguirre-Macedo, M. L., V. M. Vidal-Martinez, J. A.Herrera-Silveira, D. S. Valdes-Lozano, M. Herrera-Rodriguez, and M. A. Olvera-Novoa. 2008. Ballast water as a vector of coral pathogens in the Gulf of Mexico: The case of the Cayo Arcas coral reef. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:1570-1577. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pathogens; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Albert, S., J. Udy, and I. R. Tibbetts. 2008. Responses of algal communities to gradients in herbivore biomass and water quality in Marovo Lagoon, Solomon Islands. Coral Reefs 27:73-82. | 2008 | Solomon Islands | Index or Indicator | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Alibert, C. and L. Kinsley. 2008. A 170-year Sr/Ca and Ba/Ca coral record from the western Pacific warm pool: 1. What can we learn from an unusual coral record? Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 113. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Papua New Guinea | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Alibert, C. and L. Kinsley. 2008. A 170-year Sr/Ca and Ba/Ca coral record from the western Pacific warm pool: 2. A window into variability of the New Ireland Coastal Undercurrent. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 113. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Aline, T. 2008. Dissolution of dead corals by euendolithic microorganisms across the northern Great Barrier Reef (Australia). Microbial Ecology 55:569-580. | 2008 | Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Alongi, D. M. 2008. Mangrove forests: resilience, protection from tsunamis, and responses to global climate change. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 76:1-13. | 2008 | Global | Review; Model | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Mangroves; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Alongi, D. M., L. A. Trott, Rachmansyah, F. Tirendi, A. D. McKinnon, and M. C. Undu. 2008. Growth and development of mangrove forests overlying smothered coral reefs, Sulawesi and Sumatra, Indonesia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 370:97-109. | 2008 | Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mangroves; Nutrients |
| Alongi, D. M., L. A. Trott, and J. Pfitzner. 2008. Biogeochemistry of inter-reef sediments on the northern and central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 27:407-420. | 2008 | Australia; Cuba | Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Barton, D. N., T. Saloranta, S.J. Moe, H.O. Eggestad, and S. Kuikka. 2008. Bayesian belief networks as a meta-modelling tool in integrated river basin management Pros and cons in evaluating nutrient abatement decisions under uncertainty in a Norwegian river basin. Ecological Economics 66:91-104. | 2008 | Norway | Review; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Recreational Opportunities; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation |
| Bell, J. J. 2008. The functional roles of marine sponges. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 79:341-353. | 2008 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Biegala, I. C. and P. Raimbault. 2008. High abundance of diazotrophic picocyanobacteria (<3 μm) in a Southwest Pacific coral lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 51:45-53. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Blanco, A. C., K. Nadaoka, and T. Yamamoto. 2008. Planktonic and benthic microalgal community composition as indicators of terrestrial influence on a fringing reef in Ishigaki Island, Southwest Japan. Marine Environmental Research 66:520-535. | 2008 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Algae; Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Borell, E. M. and K. Bischof. 2008. Feeding sustains photosynthetic quantum yield of a scleractinian coral during thermal stress. Oecologia 157:593-601. | 2008 | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bouchon, C., P. Portillo, M. Louis, F. Mazeas, and Y. Bouchon-Navaro. 2008. Recent evolution of the coral reefs of Guadeloupe and Saint- Barthelemy Islands [evolution recente des recifs coralliens des îles de la Guadeloupe et de Saint-Barthelemy]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:45-65. | 2008 | Antilles | Field Study & Monitoring | Chemical Use Regulations; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Wastewater Discharge |
| Boyer, C. R., G. B. Fain, C. H. Gilliam, T. V. Gallagher, H. A. Torbert, and J. L. Sibley. 2008. Clean chip residual: A substrate component for growing annuals. HortTechnology 18:423-432. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Forestry; Nutrients; Substrate |
| Broderick, E., K. Bushaw-Newton, J. Santangelo, and K. Kim. 2008. Role of the coral surface microbiota in disease: an in situ test using the Gorgonia-Aspergillus pathosystem. Pages 242-246 in Proceedings of the 11th International Coral Reef Symposium, Ft. Lauderdale, Florida. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Bruschetti, M., T. Luppi, E. Fanjul, A. Rosenthal, and O. Iribarne. 2008. Grazing effect of the invasive reef-forming polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus (Fauvel) on phytoplankton biomass in a SW Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 354:212-219. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seawater Flow | |
| Burns, K. A., G. Brunskill, D. Brinkman, and I. Zagorskis. 2008. Organic carbon and nutrient fluxes to the coastal zone from the Sepik River outflow. Continental Shelf Research 28:283-301. | 2008 | Papua New Guinea | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Capper, A. and V. J. Paul. 2008. Grazer interactions with four species of Lyngbya in southeast Florida. Harmful Algae 7:717-728. | 2008 | Florida | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Carassou, L., M. Kulbicki, T. J. R. Nicola, and N. V. C. Polunin. 2008. Assessment of fish trophic status and relationships by stable isotope data in the coral reef lagoon of New Caledonia, southwest Pacific. Aquatic Living Resource 21:12-Jan. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; New Caledonia | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Cardona-Maldonado, M. A. 2008. Assessment of coral reef community structure using water optical properties. Masters Thesis. University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez (Puerto Rico). | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Sediment; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Cebrian, J., C. D. Foster, R. Plutchak, K. L. Sheehan, M.-E.C. Miller, A. Anton, K. Major, K. L. Heck Jr., and S. P. Powers. 2008. The impact of Hurricane Ivan on the primary productivity and metabolism of marsh tidal creeks in the NorthCentral Gulf of Mexico. Aquatic Ecology 42:391-404. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. | 2008 | Puerto Rico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Improved Technology; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Charlier, R. H., P. Morand, and C. W. Finkl. 2008. How Brittany and Florida coasts cope with green tides. International Journal of Environmental Studies 65:191-208. | 2008 | Florida; France | Agriculture; Algae; Beaches & Nature Parks; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Chazottes, V., J. J. G. Reijmer, and E. Cordier. 2008. Sediment characteristics in reef areas influenced by eutrophication-related alterations of benthic communities and bioerosion processes. Marine Geology 250:114-127. | 2008 | Reunion | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Chimetto, L. A., M. Brocchi, C. C. Thompson, R. C. R. Martins, H. R. Ramos, and F. L. Thompson. 2008. Vibrios dominate as culturable nitrogen-fixing bacteria of the Brazilian coral Mussismilia hispida. Systematic and Applied Microbiology 31:312-319. | 2008 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Costa, O. S., Jr., M. Nimmo, and M. J. Attrill. 2008. Coastal nutrification in Brazil: A review of the role of nutrient excess on coral reef demise. Journal of South American Earth Sciences 25:257-270. | 2008 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Review | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Couch, C. S., L. D. Mydlarz, C. D. Harvell, and N. L. Douglas. 2008. Variation in measures of immunocompetence of sea fan coral, Gorgonia ventalina, in the Florida Keys. Marine Biology 155:281-292. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Davey, M., G. Holmes, and R. Johnstone. 2008. High rates of nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) on coral skeletons following bleaching mortality. Coral Reefs 27:227-236. | 2008 | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | ||
| Davies, A. J., M. Wisshak, J. C. Orr, and J. Murray Roberts. 2008. Predicting suitable habitat for the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia). Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 55:1048-1062. | 2008 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Salinity; Stony Coral |
| De Goeij, J. M., H. Van Den Berg, M. M. Van Oostveen, E. H. G. Epping, and F. C. Van Duyl. 2008. Major bulk dissolved organic carbon (DOC) removal by encrusting coral reef cavity sponges. Marine Ecology Progress Series 357:139-151. | 2008 | South & Central America; Antilles; Cuba; Caribbean | Encrusting Sponges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | |
| de Paula Silva, P. H., S. McBride, R. de Nys, and N. A. Paul. 2008. Integrating filamentous 'green tide' algae into tropical pond-based aquaculture. Aquaculture 284:74-80. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Aquaculture; Nutrients; Remediation; Salinity; Special Use Permitting | |
| DeMartini, E. E., A. M. Friedlander, S. A. Sandin, and E. Sala. 2008. Differences in fish-assemblage structure between fished and unfished atolls in the northern Line Islands, central Pacific. Marine Ecology Progress Series 365:199-215. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Index or Indicator | Apex Fish Predators; Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish |
| Demopoulos, A. W. J., N. Cormier, K. C. Ewel, and B. Fry. 2008. Use of multiple chemical tracers to define habitat use of Indo-Pacific mangrove crab, Scylla serrata (Decapoda: Portunidae). Estuaries and Coasts 31:371-381. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Micronesia | Model | Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Dong, J., Y. Zhang, Y. Wang, S. Zhang, and H. Wang. 2008. Spatial and seasonal variations of cyanobacteria and their nitrogen fixation rates in Sanya Bay, South China Sea. Scientia Marina 72:239-251. | 2008 | China | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Forsterra, G. and V. Haussermann. 2008. Unusual symbiotic relationships between microendolithic phototrophic organisms and azooxanthellate cold-water corals from Chilean fjords. Marine Ecology Progress Series 370:121-125. | 2008 | Nutrients | ||
| Furman, B. T. and K. L. Heck, Jr. 2008. Effects of nutrient enrichment and grazers on coral reefs: an experimental assessment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 363:89-101. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Coralline Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Gaino, E. and F. Scoccia. 2008. Female gametes of the black coral Cirrhipathes cfr. anguina (Anthozoa, Antipatharia) from the Indonesian Marine Park of Bunaken. Invertebrate Reproduction and Development 51:119-126. | 2008 | Indonesia | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients | |
| Gao, Q.-F., P. K. S. Shin, W. Z. Xu, and S. G. Cheung. 2008. Amelioration of marine farming impact on the benthic environment using artificial reefs as biofilters. Marine Pollution Bulletin 57:652-661. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Gao, Q.-F., W.-Z. Xu, X.-S. Liu, S. G. Cheung, and P. K. S. Shin. 2008. Seasonal changes in C, N and P budgets of green-lipped mussels Perna viridis and removal of nutrients from fish farming in Hong Kong. Marine Ecology Progress Series 353:137-146. | 2008 | Southeast Asia | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Nutrients | |
| Garren, M., S. Smriga, and F. Azam. 2008. Gradients of coastal fish farm effluents and their effect on coral reef microbes. Environmental Microbiology 10:2299-2312. | 2008 | Philippines | Aquaculture; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Gibson, P. J., J. N. Boyer, and N. P. Smith. 2008. Nutrient mass flux between Florida Bay and the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Estuaries and Coasts 31:21-32. | 2008 | Florida | Discharges; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Gibson. T., H. Wanless, J. Klaus, P. Foster-Turley, K. Florini, T. Olson. 2008. Corals and Climate Change: Florida�s Natural Treasures at Risk. Environmental Defense Fund. | 2008 | Global; Florida | Climate; CO2; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Recreational Fishing; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Gopinath, A., N. Chandramohanakumar, D. Padmalal, and S. M. Nair. 2008. Distributional characteristics in fractionation of phosphorus in a coral reef sedimentary environment. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability 20:149-159. | 2008 | Indian Ocean; India | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Granek, E. and B. I. Ruttenberg. 2008. Changes in biotic and abiotic processes following mangrove clearing. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 80:555-562. | 2008 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Greenslade, P. 2008. Climate variability, biological control and an insect pest outbreak on Australia's Coral Sea islets: Lessons for invertebrate conservation. Journal of Insect Conservation 12:333-342. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; Seychelles; India; Samoa; Palmyra Atoll | Climate; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Marine Birds; Nutrients | |
| Grover, R., J.-F. Maguer, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2008. Uptake of dissolved free amino acids by the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Biology 211:860-865. | 2008 | Cuba | Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Gruner, D. S., J. E. Smith, E. W. Seabloom, S. A. Sandin, J. T. Ngai, H. Hillebrand, W. S. Harpole, J. J. Elser, E. E. Cleland, M. E. S. Bracken, E. T. Borer, and B. M. Bolker. 2008. A cross-system synthesis of consumer and nutrient resource control on producer biomass. Ecology Letters 11:740-755. | 2008 | Review; Model | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Guerry, A. D. 2008. Interactive effects of grazing and enrichment on diversity; Conceptual implications of a rocky intertidal experiment. Oikos 117:1185-1196. | 2008 | Model | Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Guest, J. 2008. Ecology: How reefs respond to mass coral spawning. Science 320:621-623. | 2008 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Guttal, V. and C. Jayaprakash. 2008. Changing skewness: an early warning signal of regime shifts in ecosystems. Ecology Letters 11:450-460. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Climate; Nutrients | |
| Hii, Y.-S., C.-L. Soo, and H.-C. Liew. 2008. Feeding of scleractinian coral, Galaxea fascicularis, on Artemia salina nauplii in captivity. Pages 14-Jan Aquaculture International. | 2008 | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | ||
| Hoch, MA TT HE W. P., K. S. Dillon, R. B. Coffin, and L. A. Cifuentes. 2008. Sensitivity of bacterioplankton nitrogen metabolism to eutrophication in sub-tropical coastal waters of Key West, Florida. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:913-926. | 2008 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Holbrook, S. J., A. J. Brooks, R. J. Schmitt, and H. L. Stewart. 2008. Effects of sheltering fish on growth of their host corals. Marine Biology 155:521-530. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Holt, B. G., B. C. Emerson, J. Newton, M. J. G. Gage, and I. M. Cote. 2008. Stable isotope analysis of the Hypoplectrus species complex reveals no evidence for dietary niche divergence. Marine Ecology Progress Series 357:283-289. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Fish; Nutrients | |
| Humphrey, C., M. Weber, C. Lott, T. Cooper, K. Fabricius. 2008. Effects of suspended sediments, dissolved inorganic nutrients and salinity on fertilisation and embryo development in the coral Acropora millepora (Ehrenberg, 1834). Coral Reefs 27:837-850. | 2008 | Australia | Lab Study | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hunter, H. M. and R. S. Walton. 2008. Land-use effects on fluxes of suspended sediment, nitrogen and phosphorus from a river catchment of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Journal of Hydrology 356:131-146. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Hunting, E. R., R. W. M. Van Soest, H. G. Van Der Geest, A. Vos, and A. O. Debrot. 2008. Diversity and spatial heterogeneity of mangrove associated sponges of Curacao and Aruba. Contributions to Zoology 77:205-215. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | |
| Jackson, J. B. C. 2008. Ecological extinction and evolution in the brave new ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105:11458-11465. | 2008 | Global | Agriculture; Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Jupiter, S., G. Roff, G. Marion, M. Henderson, V. Schrameyer, M. McCulloch, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2008. Linkages between coral assemblages and coral proxies of terrestrial exposure along a cross-shelf gradient on the southern Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 27:887-903. | 2008 | Australia | Agriculture; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kannapiran, E., L. Kannan, A. Purushothaman, and T. Thangarajdou. 2008. Physico-chemical and microbial characteristics of the coral reef environment of the Gulf of Mannar marine biosphere reserve, India. Journal of Environmental Biology 29:215-222. | 2008 | India | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Kim, W. K., Y. S. Son, J. H. Lee, J. P. Hong, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee, and Q. Jo. 2008. Macrobenthic community at type and age-different artificial reefs located along the Korean coast of the East Sea. Journal of Environmental Biology 29:501-505. | 2008 | India; Japan | Artificial Habitat; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Tunicates | |
| Knee, K. L., B. A. Layton, J. H. Street, A. B. Boehm, and A. Paytan. 2008. Sources of nutrients and fecal indicator bacteria to nearshore waters on the north shore of Kaua'i (Hawai'i, USA). Estuaries and Coasts 31:607-622. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Beaches & Nature Parks; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kolasinski, J., K. Rogers, and P. Frouin. 2008. Effects of acidification on carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of benthic macrofauna from a tropical coral reef. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 22:2955-2960. | 2008 | Review | Arthropods; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Molluscs; Nutrients | |
| Kroeger, K. D. and M. A. Charette. 2008. Nitrogen biogeochemistry of submarine groundwater discharge. Limnology and Oceanography 53:1025-1039. | 2008 | Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Lamb, K. and P. K. Swart. 2008. The carbon and nitrogen isotopic values of particulate organic material from the Florida Keys: A temporal and spatial study. Coral Reefs 27:351-362. | 2008 | Florida | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses | |
| Lampert-Karako, S., N. Stambler, D. J. Katcoff, Y. Achituv, Z. Dubinsky, and N. Simon-Blecher. 2008. Effects of depth and eutrophication on the zooxanthella cludes of Stylophora pistillata from the Gulf of Eilat (Red Sea). Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:1039-1045. | 2008 | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| LaVigne, M., M. P. Field, E. Anagnostou, A. G. Grottoli, G. M. Wellington, and R. M. Sherrell. 2008. Skeletal P/Ca tracks upwelling in Gulf of Panama coral: Evidence for a new seawater phosphate proxy. Geophysical Research Letters 35. | 2008 | Panama | Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Leao, Z. M. A. N., R. K. P. De Kikuchi, and M. D. D. M. De Oliveira. 2008. Coral bleaching in Bahia reefs and its relation with sea surface temperatura anomalies [Branqueamento de corais nos recifes da Bahia e sua relacão com eventos de anomalias termicas nas aguas superficiais do oceano]. Biota Neotropica 8:69-82. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Leichter, J. J., M. D. Stokes, and S. J. Genovese. 2008. Deep water macroalgal communities adjacent to the Florida Keys reef tract. Marine Ecology Progress Series 356:123-138. | 2008 | Florida; Cuba | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Lubeseder, S. 2008. Palaeozoic low-oxygen, high-latitude carbonates: Silurian and Lower Devonian nautiloid and scyphocrinoid limestones of the Anti-Atlas (Morocco). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 264:195-209. | 2008 | Global | Model | Nutrients |
| Manzello, D. P., J. A. Kleypas, D. A. Budd, C. M. Eakin, P. W. Glynn, and C. Langdon. 2008. Poorly cemented coral reefs of the eastern tropical Pacific: Possible insights into reef development in a high-CO2 world. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105:10450-10455. | 2008 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity |
| Marynowski, L., P. Filipiak, and A. Pisarzowska. 2008. Organic geochemistry and palynofacies of the Early-Middle Frasnian transition (Late Devonian) of the Holy Cross Mountains, Southern Poland. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 269:152-165. | 2008 | Poland | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Mayor, D. 2008. Acid oceans. Planet Earth 22-23. | 2008 | Global | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity | |
| Meng, P.-J., H.-J. Lee, J.-T. Wang, C.-C. Chen, H.-J. Lin, K. S. Tew, and W.-J. Hsieh. 2008. A long-term survey on anthropogenic impacts to the water quality of coral reefs, southern Taiwan. Environmental Pollution 156:67-75. | 2008 | Taiwan | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Mohamed, N. M., A. S. Colman, Y. Tal, and R. T. Hill. 2008. Diversity and expression of nitrogen fixation genes in bacterial symbionts of marine sponges. Environmental Microbiology 10:2910-2921. | 2008 | Florida | Cyanobacteria; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Nakajima, R., T. Yoshida, B. A. R. Azman, K. Zaleha, B. H. R. Othman, and T. Toda. 2008. In situ release of coral mucus by Acropora and its influence on the heterotrophic bacteria. Aquatic Ecology 9-Jan. | 2008 | Cuba; Malaysia; Oman | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Noe, S. U., L. Lembke-Jene, and W.-Chr. Dullo. 2008. Varying growth rates in bamboo corals: Sclerochronology and radiocarbon dating of a mid-Holocene deep-water gorgonian skeleton (Keratoisis sp.: Octocorallia) from Chatham Rise (New Zealand). Facies 54:151-166. | 2008 | Nutrients; Octocoral; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Olivier, N., B. Pittet, W. Werner, P. Hantzpergue, and C. Gaillard. 2008. Facies distribution and coral-microbialite reef development on a low-energy carbonate ramp (Chay Peninsula, Kimmeridgian, western France). Sedimentary Geology 205:14-33. | 2008 | France | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Ouillon, S., P. Douillet, A. Petrenko, J. Neveux, C. Dupouy, J.-M. Froidefond, S. Andrefouet, and A. Munoz-Caravaca. 2008. Optical algorithms at satellite wavelengths for total suspended matter in tropical coastal waters. Sensors 8:4165-4185. | 2008 | Global; Cuba; New Caledonia; Fiji | Model; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Paerl, R. W., R. A. Foster, B. D. Jenkins, J. P. Montoya, and J. P. Zehr. 2008. Phylogenetic diversity of cyanobacterial narB genes from various marine habitats. Environmental Microbiology 10:3377-3387. | 2008 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Pacific Ocean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Page, H. M., D. C. Reed, M. A. Brzezinski, J. M. Melack, and J. E. Dugan. 2008. Assessing the importance of land and marine sources of organic matter to kelp forest food webs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 360:47-62. | 2008 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Sea Urchins | ||
| Pan, Y., X.-W. Li, L. Rong, W.-Y. Yuan, and J. Wang. 2008. Root nodulation of young Alnus formosana on forest lands converted from agricultural lands. Chinese Journal of Ecology 27:1482-1486. | 2008 | Agriculture; Nutrients | ||
| Paris, C. B. and L. M. Cherubin. 2008. River-reef connectivity in the Meso-American Region. Coral Reefs 27:773-781. | 2008 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras | Model | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Parsons, M. L., W. J. Walsh, C. J. Settlemier, D. J. White, J. M. Ballauer, P. M. Ayotte, K. M. Osada, and B. Carman. 2008. A multivariate assessment of the coral ecosystem health of two embayments on the lee of the island of Hawai'i. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:1138-1149. | 2008 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral | ||
| Patten, N. L., J. G. Mitchell, M. Middelboe, B. D. Eyre, L. Seuront, P. L. Harrison, and R. N. Glud. 2008. Bacterial and viral dynamics during a mass coral spawning period on the Great Barrier Reef. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 50:209-220. | 2008 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Paul, N. A. and R. de Nys. 2008. Promise and pitfalls of locally abundant seaweeds as biofilters for integrated aquaculture. Aquaculture 281:49-55. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Aquaculture; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Remediation | |
| Payros, A. and V. Pujalte. 2008. Calciclastic submarine fans: An integrated overview. Earth-Science Reviews 86:203-246. | 2008 | Review; Model | Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Perry, C. T., S. G. Smithers, S. E. Palmer, P. Larcombe, and K. G. Johnson. 2008. 1200 year paleoecological record of coral community development from the terrigenous inner shelf of the Great barrier reef. Geology 36:691-694. | 2008 | Australia; Europe | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Pomar, L. and P. Hallock. 2008. Carbonate factories: A conundrum in sedimentary geology. Earth-Science Reviews 87:134-169. | 2008 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Przeslawski, R., S. Ahyong, M. Byrne, G. Worheide, and P. Hutchings. 2008. Beyond corals and fish: The effects of climate change on noncoral benthic invertebrates of tropical reefs. Global Change Biology 14:2773-2795. | 2008 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Review | Climate; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Salinity; Sediment; Special Use Permitting |
| Reid, C. M., N. P. James, T. K. Kyser, N. Barrett, and A. J. Hirst. 2008. Modern estuarine siliceous spiculites, Tasmania, Australia: A non-polar link to phanerozoic spiculitic cherts. Geology 36:107-110. | 2008 | Australia | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Reitzel, A. M., J. C. Sullivan, N. Traylor-Knowles, and J. R. Finnerty. 2008. Genomic survey of candidate stress-response genes in the estuarine anemone Nematostella vectensis. Biological Bulletin 214:233-254. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Salinity; Stony Coral | |
| Renema, W. 2008. Habitat selective factors influencing the distribution of larger benthic foraminiferal assemblages over the Kepulauan Seribu. Marine Micropaleontology 68:286-298. | 2008 | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients | ||
| Riegel, W. 2008. The Late Palaeozoic phytoplankton blackout - Artefact or evidence of global change? Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology 148:73-90. | 2008 | Global | Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Rochelle-Newall, E. J., J.-P. Torreton, X. Mari, and O. Pringault. 2008. Phytoplankton-bacterioplankton coupling in a subtropical South Pacific coral reef lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 50:221-229. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Cuba; New Caledonia | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Rodriguez, M. V. 2008. ESTIMATING PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY OF RED MANGROVES IN SOUTHWESTERN PUERTO RICO FROM REMOTE SENSING AND FIELD MEASUREMENTS. Masters Thesis. University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez (Puerto Rico). | 2008 | Global; Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Climate; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity |
| Rodriguez, S. and A. Croquer. 2008. Dynamics of Black Band Disease in a Diploria strigosa population subjected to annual upwelling on the northeastern coast of Venezuela. Coral Reefs 27:381-388. | 2008 | South & Central America; Venezuela; Caribbean | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Roopin, M., R. P. Henry, and N. E. Chadwick. 2008. Nutrient transfer in a marine mutualism: Patterns of ammonia excretion by anemonefish and uptake by giant sea anemones. Marine Biology 154:547-556. | 2008 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Salerno, C. 2008. Stromatoporoid fauna, facies and palaeoecology of carbonate platforms from the Lower Givetian of the Eifel (Devon, Rhenish Slate Mountains) [Stromatoporen-fauna, Fazies und Palaookologie von Plattformkarbonaten aus dem Unter-givetium der Eifel (Devon, R. Zitteliana Reihe B: Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Staatssammlung fur Palaontologie und Geologie 27:3-129. | 2008 | Europe | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Salvat, B., A. Aubanel, M. Adjeroud, P. Bouisset, D. Calmet, Y. Chancerelle, N. Cochennec, N. Davies, A. Fougerousse, R. Galzin, E. Lagouy, C. Lo, C. Monier, C. Ponsonnet, G. Remoissenet, D. Schneider, A. Stein, M. Tatarata, and L. Villiers. 2008. Monitoring of French Polynesia coral reefs and their recent development [Le suivi de l'etat des recifs coralliens de Polynesie francaise et leur recente evolution]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:145-177. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Molluscs; Nutrients; Seastars; Sewage Treatment; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies |
| Sammarco, P. W. 2008. Crises on coral reefs and in coral reef science in the 21st century: The need for a new peer-review system. Ethics in Science and Environmental Politics 8:109-119. | 2008 | Global | Review; Index or Indicator | Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Pathogens |
| Sandin, S. A., E. M. Sampayo, and M. J. A. Vermeij. 2008. Coral reef fish and benthic community structure of bonaire and Curacao, Netherlands Antilles. Caribbean Journal of Science 44:137-144. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Algae; Apex Fish Predators; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Turf Algae | |
| Scheibner, C. and R. P. Speijer. 2008. Late Paleocene-early Eocene Tethyan carbonate platform evolution - A response to long- and short-term paleoclimatic change. Earth-Science Reviews 90:71-102. | 2008 | Global; Egypt; Spain | CO2; Nutrients | |
| Schroder, P., R. Herzig, B. Bojinov, A. Ruttens, E. Nehnevajova, S. Stamatiadis, A. Memon, A. Vassilev, M. Caviezel, and J. Vangronsveld. 2008. Bioenergy to save the world: Producing novel energy plants for growth on abandoned land. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 15:196-204. | 2008 | Global; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Climate; CO2; Domestic Animal Waste; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Schueth, J. D. and T. D. Frank. 2008. Reef foraminifera as bioindicators of coral reef health: Low Isles Reef, Northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 38:22-Nov. | 2008 | South & Central America; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Sekar, R., L. T. Kaczmarsky, and L. L. Richardson. 2008. Microbial community composition of black band disease on the coral host Siderastrea siderea from three regions of the wider Caribbean. Marine Ecology Progress Series 362:85-98. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Bahamas; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Sharon, G. and E. Rosenberg. 2008. Bacterial growth on coral mucus. Current Microbiology 56:481-488. | 2008 | Cuba | Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Shaw, E. C., A. J. Gabric, and G. H. McTainsh. 2008. Impacts of aeolian dust deposition on phytoplankton dynamics in Queensland coastal waters. Marine and Freshwater Research 59:951-962. | 2008 | Australia | Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Shenkar, N., O. Bronstein, and Y. Loya. 2008. Population dynamics of a coral reef ascidian in a deteriorating environment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 367:163-171. | 2008 | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tunicates | ||
| Siboni, N., E. Ben-Dov, A. Sivan, and A. Kushmaro. 2008. Global distribution and diversity of coral-associated Archaea and their possible role in the coral holobiont nitrogen cycle. Environmental Microbiology 10:2979-2990. | 2008 | Global; US Virgin Islands; Australia | Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Smith, L. W., H. H. Wirshing, A. C. Baker, and C. Birkeland. 2008. Environmental versus genetic influences on growth rates of the corals Pocillopora eydouxi and Porites lobata (Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Pacific Science 62:57-69. | 2008 | Samoa; American Samoa | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Southwell, M. W., B. N. Popp, and C. S. Martens. 2008. Nitrification controls on fluxes and isotopic composition of nitrate from Florida Keys sponges. Marine Chemistry 108:96-108. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges |
| Southwell, M. W., J. B. Weisz, C. S. Martens, and N. Lindquist. 2008. In situ fluxes of dissolved inorganic nitrogen from the sponge community on Conch Reef, Key Largo, Florida. Limnology and Oceanography 53:986-996. | 2008 | Florida; Cuba | Encrusting Sponges; Nutrients; Sponges; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Stat, M., E. Morris, and R. D. Gates. 2008. Functional diversity in coral-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105:9256-9261. | 2008 | Nutrients; Pathogens | ||
| Storlazzi, C. D. and B. E. Jaffe. 2008. The relative contribution of processes driving variability in flow, shear, and turbidity over a fringing coral reef: West Maui, Hawaii. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 77:549-564. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Street, J. H., K. L. Knee, E. E. Grossman, and A. Paytan. 2008. Submarine groundwater discharge and nutrient addition to the coastal zone and coral reefs of leeward Hawai'i. Marine Chemistry 109:355-376. | 2008 | Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Sun, D., R. Su, T. A. McConnaughey, and J. Bloemendal. 2008. Variability of skeletal growth and δ13C in massive corals from the South China Sea: Effects of photosynthesis, respiration and human activities. Chemical Geology 255:414-425. | 2008 | China | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Sunagawa, S., J. Cortes, C. Jimenez, and R. Lara. 2008. Variation in cell densities and pigment concentrations of symbiotic dinoflagellates in the coral Pavona clavus in the eastern Pacific (Costa Rica) [Variacion en la densidad de celulas y en las concentraciones de pigmentos de los dinosflagelados simbiot. Ciencias Marinas 34:113-123. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica | Light; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Zooxanthellae | |
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, I. Koike, T. Hayashibara, and H. Ogawa. 2008. Production of dissolved and particulate organic matter by the reef-building corals Porites cylindrica and Acropora pulchra. Bulletin of Marine Science 82:237-245. | 2008 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Terrados, J., P. Ramirez-Garcia, O. Hernandez-Martinez, K. Pedraza, and A. Quiroz. 2008. State of Thalassia testudinum Banks ex Konig meadows in the Veracruz Reef System, Veracruz, Mexico. Aquatic Botany 88:17-26. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Titlyanov, E. A., S. I. Kiyashko, T. V. Titlyanova, T. L. Kalita, and J. A. Raven. 2008. δ13C and δ15N values in reef corals Porites lutea and P. cylindrica and in their epilithic and endolithic algae. Marine Biology 155:353-361. | 2008 | Japan | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Tomas, S., H. Loser, and R. Salas. 2008. Low-light and nutrient-rich coral assemblages in an Upper Aptian carbonate platform of the southern Maestrat Basin (Iberian Chain, eastern Spain). Cretaceous Research 29:509-534. | 2008 | Spain | Model | Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment |
| Uchida, A., M. Nishizawa, K. Shirai, H. Iijma, H. Kayanne, N. Takahata, and Y. Sano. 2008. High sensitivity measurements of nitrogen isotopic ratios in coral skeletons from Palau, western Pacific: Temporal resolution and seasonal variation of nitrogen sources. Geochemical Journal 42:255-262. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Palau | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Umezawa, Y., T. Miyajima, and I. Koike. 2008. Stable nitrogen isotope composition in sedimentary organic matter as a potential proxy of nitrogen sources for primary producers at a fringing coral reef. Journal of Oceanography 64:899-909. | 2008 | Japan | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Uthicke, S. and K. Nobes. 2008. Benthic Foraminifera as ecological indicators for water quality on the Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 78:763-773. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Vabrit, S., E. Leedu, K. Suigusaar, and I. Bender. 2008. Effect of sewage sludge and pig manure compost on the ornamental quality of impatiens 'candy coral bee' container grown plants. Pages 637-642 in Acta Horticulturae. | 2008 | Domestic Animal Waste; Nutrients; Substrate | ||
| Vega Thurber, R. L., K. L. Barott, D. Hall, H. Liu, B. Rodriguez-Mueller, C. Desnues, R. A. Edwards, M. Haynes, F. E. Angly, L. Wegley, and F. L. Rohwer. 2008. Metagenomic analysis indicates that stressors induce production of herpes-like viruses in the coral Porites compressa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105:18413-18418. | 2008 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | ||
| Venn, A. A., J. E. Loram, and A. E. Douglas. 2008. Photosynthetic symbioses in animals. Pages 1069-1080 in Journal of Experimental Botany. | 2008 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Verweij, M. C., I. Nagelkerken, I. Hans, S. M. Ruseler, and P. R. D. Mason. 2008. Seagrass nurseries contribute to coral reef fish populations. Limnology and Oceanography 53:1540-1547. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Vicente, M., M. Falcao, M. N. Santos, M. Caetano, D. Serpa, C. Vale, and C. Monteiro. 2008. Environmental assessment of two artificial reef systems off southern Portugal (Faro and Olhão): A question of location. Continental Shelf Research 28:839-847. | 2008 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Wagner, D., E. Mielbrecht, and R. Van Woesik. 2008. Application of landscape ecology to spatial variance of water-quality parameters along the Florida Keys reef tract. Bulletin of Marine Science 83:553-569. | 2008 | Global; Florida | GIS & Maps | Nutrients; Salinity; Substrate |
| Wells, R. J. D., J. H. Cowan Jr., and B. Fry. 2008. Feeding ecology of red snapper Lutjanus campechanus in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Marine Ecology Progress Series 361:213-225. | 2008 | South & Central America; Mexico | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Plankton | |
| Wernberg, T., M. White, and M. A. Vanderklift. 2008. Population structure of turbinid gastropods on wave-exposed subtidal reefs: Effects of density, body size and algae on grazing behaviour. Marine Ecology Progress Series 362:169-179. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Werner, U., A. Blazejak, P. Bird, G. Eickert, R. Schoon, R. M. M. Abed, A. Bissett, and D. de Beer. 2008. Microbial photosynthesis in coral reef sediments (Heron Reef, Australia). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 76:876-888. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Wild, C., C. Jantzen, U. Struck, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, and M. Huettel. 2008. Biogeochemical responses following coral mass spawning on the Great Barrier Reef: Pelagic-benthic coupling. Coral Reefs 27:123-132. | 2008 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Wild, C., C. Mayr, L. Wehrmann, S. Schottner, M. Naumann, F. Hoffmann, and H. T. Rapp. 2008. Organic matter release by cold water corals and its implication for fauna-microbe interaction. Marine Ecology Progress Series 372:67-75. | 2008 | Norway | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Wilson, B. 2008. Late Quaternary benthonic foraminifera in a bathyal core from the Leeward Islands, Lesser Antilles, NE Caribbean Sea. Journal of Micropalaeontology 27:177-188. | 2008 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Wilson, B. 2008. Population structures among epiphytal foraminiferal communities, Nevis, West Indies. Journal of Micropalaeontology 27:63-73. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Wilson, M. E. J. 2008. Global and regional influences on equatorial shallow-marine carbonates during the Cenozoic. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 265:262-274. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India; Caribbean | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Wolanski, E., K. E. Fabricius, T. F. Cooper, and C. Humphrey. 2008. Wet season fine sediment dynamics on the inner shelf of the Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 77:755-762. | 2008 | Australia | Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Yellowlees, D., T. A. V. Rees, and W. Leggat. 2008. Metabolic interactions between algal symbionts and invertebrate hosts. Plant, Cell and Environment 31:679-694. | 2008 | Global | Algae; Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Yniguez, A. T., J. W. McManus, and D. L. DeAngelis. 2008. Allowing macroalgae growth forms to emerge: Use of an agent-based model to understand the growth and spread of macroalgae in Florida coral reefs, with emphasis on Halimeda tuna. Ecological Modelling 216:60-74. | 2008 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients |
| Zhang, S. Y., L. Wang, and W. D. Wang. 2008. Algal communities at Gouqi Island in the Zhoushan archipelago, China. Journal of Applied Phycology 20:853-861. | 2008 | China | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Zhang, W., N. Travitzky, and P. Greil. 2008. Formation of NbAl3/Al2O3 composites by pressureless reactive infiltration. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 91:3117-3120. | 2008 | Nutrients | ||
| Zvuloni, A., R. Armoza-Zvuloni, and Y. Loya. 2008. Structural deformation of branching corals associated with the vermetid gastropod Dendropoma maxima. Marine Ecology Progress Series 363:103-108. | 2008 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Aburto-Oropeza, O., E. Sala, G. Paredes, A. Mendoza, and E. Ballesteros. 2007. Predictability of reef fish recruitment in a highly variable nursery habitat. Ecology 88:2220-2228. | 2007 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Climate; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish |
| Alongi, D. M., L. A. Trott, and J. Pfitzner. 2007. Deposition, mineralization, and storage of carbon and nitrogen in sediments of the far northern and northern Great Barrier Reef shelf. Continental Shelf Research 27:2595-2622. | 2007 | Australia; Cuba; Europe | CO2; Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Amar, K. O. and B. Rinkevich. 2007. A floating mid-water coral nursery as larval dispersion hub: Testing an idea. Marine Biology 151:713-718. | 2007 | Global | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Bachar, A., Y. Achituv, Z. Pasternak, and Z. Dubinsky. 2007. Autotrophy versus heterotrophy: The origin of carbon determines its fate in a symbiotic sea anemone. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 349:295-298. | 2007 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Baker, D. M., S. E. MacAvoy, and K. Kim. 2007. Relationship between water quality, δ15N, and aspergillosis of Caribbean sea fan corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 343:123-130. | 2007 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Agriculture; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Bartley, R., A. Hawdon, D. A. Post, and C. H. Roth. 2007. A sediment budget for a grazed semi-arid catchment in the Burdekin basin, Australia. Geomorphology 87:302-321. | 2007 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bell, P. R. F., B. E. Lapointe, and I. Elmetri. 2007. Reevaluation of ENCORE: Support for the eutrophication threshold model for coral reefs. Ambio 36:416-424. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Nutrients |
| Bondarenko, O., S. Kininmonth, and M. Kingsford. 2007. Coral reef sensor network deployment for collecting real time 3-D temperature data with correlation to plankton assemblages. Pages 204-209 in 2007 International Conference on Sensor Technologies and Applications, SENSORCOMM 2007, Proceedings. | 2007 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Bondarenko, O., S. Kininmonth, and M. Kingsford. 2007. Underwater sensor networks, oceanography and plankton assemblages. Pages 657-662 in Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information Processing, ISSNIP. | 2007 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Brandano, M., G. Vannucci, and G. Mateu-Vicens. 2007. Calcareous red algae as paleoenvironmental indicators: The example of the Latium-Abruzzi carbonate ramp (Burdigalian, Central Appennines) [Le alghe rosse calcaree come indicatori paleoambientali: L'esempio della rampa carbonatica Laziale-Abruzzese (Burdig. Bollettino della Societa Geologica Italiana 126:55-69. | 2007 | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Brando, V. E., B. J. Robson, N. R. C. Cherukuru, A. G. Dekker, and I. T. Webster. 2007. Towards assimilation of ocean colour satellite observation into coastal ocean biogeochemical models: The tropical Fitzroy River Estuary case study. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 6685. | 2007 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Brodie, J., G. De'ath, M. Devlin, M. Furnas, and M. Wright. 2007. Spatial and temporal patterns of near-surface chlorophyll a in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Marine and Freshwater Research 58:342-353. | 2007 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Cardona, L., M. Sales, and D. Lopez. 2007. Changes in fish abundance do not cascade to sea urchins and erect algae in one of the most oligotrophic parts of the Mediterranean. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 72:273-282. | 2007 | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrates; Invertivorous Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Celliers, L., B. Q. Mann, A. H. H. Macdonald, and M. H. Schleyer. 2007. A benthic survey of the rocky reefs off Pondoland, South Africa. African Journal of Marine Science 29:65-77. | 2007 | South Africa | GIS & Maps | Algae; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Charpy, L., R. Alliod, M. Rodier, and S. Golubic. 2007. Benthic nitrogen fixation in the SW New Caledonia lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 47:73-81. | 2007 | New Caledonia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Chen, B.-Y. 2007. Revealing threshold criteria of biostimulation for dye-laden wastewater treatment using immobilized cell systems. Process Biochemistry 42:158-166. | 2007 | Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Chung, I.-C., R.-L. Hwang, S.-H. Lin, T.-M. Wu, J.-Y. Wu, S.-W. Su, C.-S. Chen, and T.-M. Lee. 2007. Nutrients, temperature, and salinity as primary factors influencing the temporal dynamics of macroalgal abundance and assemblage structure on a reef of Du-Lang Bay in Taitung in southeastern Taiwan. Botanical Studies 48:419-433. | 2007 | Taiwan | Algae; Nutrients; Salinity; Sponges | |
| Claro, R., K. Cantelar, F. P. Amargos, and J. P. Garcia-Arteaga. 2007. Changes in fish communities of coral reefs at Sabana-Camaguey Archipelago, Cuba [Cambios en las comunidades de peces de los arrecifes coralinos del Archipielago Sabana-Camaguey, Cuba]. Revista de Biologia Tropical 55:537-547. | 2007 | Cuba | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Collado-Vides, L., V. G. Caccia, J. N. Boyer, and J. W. Fourqurean. 2007. Tropical seagrass-associated macroalgae distributions and trends relative to water quality. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 73:680-694. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Cooper, T. F., S. Uthicke, C. Humphrey, and K. E. Fabricius. 2007. Gradients in water column nutrients, sediment parameters, irradiance and coral reef development in the Whitsunday Region, central Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 74:458-470. | 2007 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Cramer, B. D. and M. R. Saltzman. 2007. Fluctuations in epeiric sea carbonate production during Silurian positive carbon isotope excursions: A review of proposed paleoceanographic models. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 245:37-45. | 2007 | Global | Review; Model | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Cunningham, K. J., J. K. Rigby, M. A. Wacker, and H. A. Curran. 2007. First documentation of tidal-channel sponge biostromes (upper Pleistocene, southeastern Florida). Geology 35:475-478. | 2007 | Florida | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Derse, E., K. L. Knee, S. D. Wankel, C. Kendall, C. J. Berg Jr., and A. Paytan. 2007. Identifying sources of nitrogen to Hanalei Bay, Kauai, utilizing the nitrogen isotope signature of macroalgae. Environmental Science and Technology 41:5217-5223. | 2007 | Algae; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Remediation; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Diez, B., K. Bauer, and B. Bergman. 2007. Epilithic cyanobacterial communities of a marine tropical beach rock (Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef): Diversity and diazotrophy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73:3656-3668. | 2007 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Nutrients | |
| Dominici, S. and T. Kowalke. 2007. Depositional dynamics and the record of ecosystem stability: Early Eocene faunal gradients in the Pyrenean foreland, Spain. Palaios 22:268-284. | 2007 | Spain | Model | Climate; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Done, T., E. Turak, M. Wakeford, L. DeVantier, A. McDonald, and D. Fisk. 2007. Decadal changes in turbid-water coral communities at Pandora Reef: Loss of resilience or too soon to tell? Coral Reefs 26:789-805. | 2007 | Global; Australia; Europe | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Dragastan, O. N. and H.-G. Herbig. 2007. Halimeda (green siphonous algae) from the Paleogene of (Morocco) - Taxonomy, phylogeny and paleoenvironment. Micropaleontology 53:Jan-72. | 2007 | Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Duchamp-Alphonse, S., S. Gardin, N. Fiet, A. Bartolini, D. Blamart, and M. Pagel. 2007. Fertilization of the northwestern Tethys (Vocontian basin, SE France) during the Valanginian carbon isotope perturbation: Evidence from calcareous nannofossils and trace element data. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 243:132-151. | 2007 | Global; France | Index or Indicator | CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ellner, S. P., L. E. Jones, L. D. Mydlarz, and C. D. Harvell. 2007. Within-host disease ecology in the sea fan Gorgonia ventalina: Modeling the spatial immunodynamics of a coral-pathogen interaction. American Naturalist 170. | 2007 | Model | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Enpu, G., E. Samankassou, G. Changqing, Z. Yongli, and S. Baoliang. 2007. Paleoecology of Pennsylvanian phylloid algal buildups in south Guizhou, China. Facies 53:615-623. | 2007 | Australia; Bahamas; China; Java | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. | 2007 | Aquaculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | ||
| Fagan, K. E. and F. T. Mackenzie. 2007. Air-sea CO2 exchange in a subtropical estuarine-coral reef system, Kaneohe Bay, Oahu, Hawaii. Marine Chemistry 106:174-191. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Falcao, M., M. N. Santos, M. Vicente, and C. C. Monteiro. 2007. Biogeochemical processes and nutrient cycling within an artificial reef off Southern Portugal. Marine Environmental Research 63:429-444. | 2007 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Frisk, A. M. and J. Ormo. 2007. Facies distribution of post-impact sediments in the Ordovician Lockne and Tvaren impact craters: Indications for unique impact-generated environments. Pages 1971-1984 in Meteoritics and Planetary Science. | 2007 | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Fu, Z.-H. and A.-M. Wang. 2007. Tissue-engineered bone grafts in the repair of bone defects in rabbits: Evaluation of radionuclide bone imaging. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research 11:4500-4503. | 2007 | Medical Centers; Military; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Furnas, M. 2007. Intra-seasonal and inter-annual variations in phytoplankton biomass, primary production and bacterial production at North West Cape, Western Australia: Links to the 1997-1998 El Nino event. Continental Shelf Research 27:958-980. | 2007 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Indonesia | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Garrison, V., K. Kroeger, D. Fenner, and P. Craig. 2007. Identifying nutrient sources to three lagoons at Ofu and Olosega, American Samoa using δ15N of benthic macroalgae. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:1830-1838. | 2007 | Samoa; American Samoa | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Gordon, I. J. 2007. Linking land to ocean: Feedbacks in the management of socio-ecological systems in the Great Barrier Reef catchments. Hydrobiologia 591:25-33. | 2007 | Australia | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Gottschalk, S., S. Uthicke, and K. Heimann. 2007. Benthic diatom community composition in three regions of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 26:345-357. | 2007 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Graham, M. H., B. P. Kinlan, L. D. Druehl, L. E. Garske, and S. Banks. 2007. Deep-water kelp refugia as potential hotspots of tropical marine diversity and productivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104:16576-16580. | 2007 | Model | Climate; Light; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Guo, Q., Z.-H. Wu, M.-L. Qian, and B. Gu. 2007. The roles of porous coral sands in initial enrichment of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. TheScientificWorldJournal 7:525-532. | 2007 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Substrate | ||
| Harvell, D., E. Jord�n-Dahlgren, S. Merkel, E. Rosenberg, L. Raymundo, G. Smith, E. Weil and B. Willis. 2007. Coral disease, environmental drivers, and the balance between coral and microbial associates. Oceanography 20:172-195. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Philippines; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hayashi, I., H. Mizuno, K. I. Tong, T. Furuta, F. Tanaka, M. Yoshimura, A. Miyawaki, and M. Ikura. 2007. Crystallographic Evidence for Water-assisted Photo-induced Peptide Cleavage in the Stony Coral Fluorescent Protein Kaede. Journal of Molecular Biology 372:918-926. | 2007 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Haynes, D., J. Brodie, J. Waterhouse, Z. Bainbridge, D. Bass, and B. Hart. 2007. Assessment of the water quality and ecosystem health of the Great Barrier Reef (Australia): Conceptual models. Environmental Management 40:993-1003. | 2007 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Heck Jr., K. L. and J. F. Valentine. 2007. The primacy of top-down effects in shallow benthic ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 30:371-381. | 2007 | Review | Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Helson, J. G., S. Pledger, and J. P. A. Gardner. 2007. Does differential particulate food supply explain the presence of mussels in Wellington Harbour (New Zealand) and their absence on neighbouring Cook Strait shores? Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 72:223-234. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Herr, A. and P. M. Kuhnert. 2007. Assesment of uncertainty in Great Barrier Reef catchment models. Water Science and Technology 56:181-188. | 2007 | Australia | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| Hewson, I. and J. A. Fuhrman. 2007. Covariation of viral parameters with bacterial assemblage richness and diversity in the water column and sediments. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 54:811-830. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Mexico | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hewson, I., P. H. Moisander, A. E. Morrison, and J. P. Zehr. 2007. Diazotrophic bacterioplankton in a coral reef lagoon: Phylogeny, diel nitrogenase expression and response to phosphate enrichment. ISME Journal 1:78-91. | 2007 | Australia; Cuba | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Hiratsuka, Y. and T. Uehara. 2007. Feeding rates and absorption efficiencies of four species of sea urchins (genus Echinometra) fed a prepared diet. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 148:223-229. | 2007 | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Turf Algae | |
| Jegatheesan, V., C. Zeng, L. Shu, C. Manicom, and C. Steicke. 2007. Technological advances in aquaculture farms for minimal effluent discharge to oceans. Journal of Cleaner Production 15:1535-1544. | 2007 | Australia | Aquaculture; Discharges; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jones, G., M. Curran, A. Broadbent, S. King, E. Fischer, and R. Jones. 2007. Factors affecting the cycling of dimethylsulfide and dimethylsulfoniopropionate in coral reef waters of the great barrier reef. Environmental Chemistry 4:310-322. | 2007 | Australia | Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kashman, Y., A. Rudi, and D. Pappo. 2007. Recent heterocyclic compounds from marine invertebrates: Structure and synthesis. Pure and Applied Chemistry 79:491-505. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Marine Products; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges |
| Kneip, C., P. Lockhart, C. Voss, and U.-G. Maier. 2007. Nitrogen fixation in eukaryotes - New models for symbiosis. BMC Evolutionary Biology 7. | 2007 | Review; Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Lapointe, B. E. and B. J. Bedford. 2007. Drift rhodophyte blooms emerge in Lee County, Florida, USA: Evidence of escalating coastal eutrophication. Harmful Algae 6:421-437. | 2007 | Global; Florida | Agriculture; Algae; Artificial Habitat; Beaches & Nature Parks; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Lasemi, Y. and H. Amin-Rasouli. 2007. Archaeocyathan buildups within an entirely siliciclastic succession: New discovery in the Toyonian Lalun Formation of northern Iran, the Proto-Paleotethys passive margin of northern Gondwana. Sedimentary Geology 201:302-320. | 2007 | Iran | Nutrients; Salinity; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Leichter, J. J., A. Paytan, S. Wankel, K. Hanson, S. Miller, and M. A. Altabet. 2007. Nitrogen and oxygen isotopic signatures of subsurface nitrate seaward of the Florida Keys reef tract. Limnology and Oceanography 52:1258-1267. | 2007 | Florida | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lesser, M. P., L. I. Falcon, A. Rodriguez-Roman, S. Enriquez, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, and R. Iglesias-Prieto. 2007. Nitrogen fixation by symbiotic cyanobacteria provides a source of nitrogen for the scleractinian coral Montastraea cavernosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 346:143-152. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Lin, H.-J., C.-Y. Wu, S.-J. Kao, W.-Y. Kao, and P.-J. Meng. 2007. Mapping anthropogenic nitrogen through point sources in coral reefs using δ15N in macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 335:95-109. | 2007 | Taiwan | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Algae; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Tourism & Recreation |
| Lirman, D. and P. Fong. 2007. Is proximity to land-based sources of coral stressors an appropriate measure of risk to coral reefs? An example from the Florida Reef Tract. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:779-791. | 2007 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler. 2007. Assessment of coral reefs using herbivory/nutrient assays and indicator groups of benthic primary producers: A critical synthesis, proposed protocols, and critique of management strategies. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 17:195-215. | 2007 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Algae; Coralline Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | |
| Luick, J. L., L. Mason, T. Hardy, and M. J. Furnas. 2007. Circulation in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon using numerical tracers and in situ data. Continental Shelf Research 27:757-778. | 2007 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Maier, K. L., J. S. Klaus, D. F. McNeill, and A. F. Budd. 2007. A late Miocene low-nutrient window for Caribbean reef formation? Coral Reefs 26:635-639. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; Dominican Republic; Caribbean | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Marques, F. A., M. R. Ribeiro, S. M. B. Bittar, A. N. T. Filho, and J. F. W. F. Lima. 2007. Characterization and classification ofneosols on the Fernando de Noronha island, Pernambuco, Brazil [Caracterizacão e classificacão de neossolos da Ilha de Fernando de Noronha (PE)]. Revista Brasileira de Ciencia do Solo 31:1553-1562. | 2007 | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| McClanahan, T. R., M. Carreiro-Silva, and M. DiLorenzo. 2007. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorous, and their interaction on coral reef algal succession in Glover's Reef, Belize. Marine Pollution Bulletin 54:1947-1957. | 2007 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Turf Algae | |
| McPhee-Shaw, E. E., D. A. Siegel, L. Washburn, M. A. Brzezinski, J. L. Jones, A. Leydecker, and J. Melack. 2007. Mechanisms for nutrient delivery to the inner shelf: Observations from the Santa Barbara Channel. Limnology and Oceanography 52:1748-1766. | 2007 | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Migon, C., S. Ouillon, X. Mari, and E. Nicolas. 2007. Geochemical and hydrodynamic constraints on the distribution of trace metal concentrations in the lagoon of Noumea, New Caledonia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 74:657-666. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Miyajima, T., H. Hata, Y. Umezawa, H. Kayanne, and I. Koike. 2007. Distribution and partitioning of nitrogen and phosphorus in a fringing reef lagoon of Ishigaki Island, northwestern Pacific. Marine Ecology Progress Series 341:45-57. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Moissette, P., A. Dulai, G. Escarguel, M. Kazmer, P. Muller, and J.-P. Saint Martin. 2007. Mosaic of environments recorded by bryozoan faunas from the Middle Miocene of Hungary. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 252:530-556. | 2007 | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Monbet, PH ., G. J. Brunskill, I. Zagorskis, and J. Pfitzner. 2007. Phosphorus speciation in the sediment and mass balance for the central region of the Great Barrier Reef continental shelf (Australia)>. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 71:2762-2779. | 2007 | Australia | Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Monismith, S.G. 2007. Hydrodynamics of coral reefs. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 39:37-55. | 2007 | Review | Coastal Engineering; Nutrients | |
| Mutchler, T., K. H. Dunton, A. Townsend-Small, S. Fredriksen, and M. K. Rasser. 2007. Isotopic and elemental indicators of nutrient sources and status of coastal habitats in the Caribbean Sea, Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 74:449-457. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| Nicoletti, L., S. Marzialetti, D. Paganelli, and G. D. Ardizzone. 2007. Long-term changes in a benthic assemblage associated with artificial reefs. Hydrobiologia 580:233-240. | 2007 | Cuba | Index or Indicator | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Novotny, V. 2007. Diffuse pollution from agriculture: Ecological sustainability or food production or both. Pages 52-59 Water 21. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Olivier, N., B. Pittet, C. Gaillard, and P. Hantzpergue. 2007. High-frequency palaeoenvironmental fluctuations recorded in Jurassic coral- and sponge-microbialite bioconstructions. Comptes Rendus - Palevol 6:21-36. | 2007 | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Oren, A. and N. Gunde-Cimerman. 2007. Mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids: UV protectants or multipurpose secondary metabolites? FEMS Microbiology Letters 269:10-Jan. | 2007 | Europe | Review | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sunscreen Use |
| Pait, A. S., D. R. Whitall, C. F. G. Jeffrey, C. Caldow, A. L. Mason, J. D. Christensen, M. E. Monaco, and J. Ramirez. 2007. An Assessment of Chemical Contaminants in the Marine Sediments of Southwest Puerto Rico. NOAA/NOS/Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment, Silver Spring, MD. | 2007 | Puerto Rico | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Sediment; Toxics | |
| Peretz, H., A. E. Talpalar, R. Vago, and D. Baranes. 2007. Superior survival and durability of neurons and astrocytes on 3-dimensional aragonite biomatrices. Tissue Engineering 13:461-472. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Perez-Matus, A., L. A. Ferry-Graham, A. Cea, and J. A. Vasquez. 2007. Community structure of temperate reef fishes in kelp-dominated subtidal habitats of northern Chile. Marine and Freshwater Research 58:1069-1085. | 2007 | Algae; Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients | ||
| Perry, C. 2007. Tropical coastal environments: coral reefs and mangroves. in C. Perry and K. Taylor, editors. Environmental sedimentology. Blackwell Publishing, Malden, MA. | 2007 | Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Picciano, M. and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2007. Ingestion of pico- and nanoplankton by the Mediterranean red coral Corallium rubrum. Marine Biology 150:773-782. | 2007 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Reid, C. M., N. P. James, B. Beauchamp, and T. K. Kyser. 2007. Faunal turnover and changing oceanography: Late Palaeozoic warm-to-cool water carbonates, Sverdrup Basin, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 249:128-159. | 2007 | Europe | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Ribes, M. and M. J. Atkinson. 2007. Effects of water velocity on picoplankton uptake by coral reef communities. Coral Reefs 26:413-421. | 2007 | Bivalves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Seawater Flow; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | ||
| Rosenberg, E., O. Koren, L. Reshef, R. Efrony, and I. Zilber-Rosenberg. 2007. The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nature Reviews Microbiology 5:355-362. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production | |
| Santiago-Vazquez, L. Z., N. C. Newberger, and R. G. Kerr. 2007. Cryopreservation of the dinoflagellate symbiont of the octocoral Pseudopterogorgia elisabethae. Marine Biology 152:549-556. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Scaps, P. and V. Denis. 2007. Association between the scallop, pedum spondyloideum, (bivalvia: Pteriomorphia: Pectinidae) and scleractinian corals from the Wakatobi marine national park (southeastern Sulawesi, Indonesia). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 55:371-380. | 2007 | Indonesia | Bivalves; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Seaman, W. 2007. Artificial habitats and the restoration of degraded marine ecosystems and fisheries. Hydrobiologia 580:143-155. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Cuba; Pacific Ocean; Japan; Mexico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mitigation; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Shen, Y.-C., Y.-B. Cheng, J. Kobayashi, T. Kubota, Y. Takahashi, Y. Mikami, J. Ito, and Y.-S. Lin. 2007. Nitrogen-containing verticillene diterpenoids from the Taiwanese soft coral Cespitularia taeniata. Journal of Natural Products 70:1961-1965. | 2007 | Taiwan | Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Sherman, B. S., J. Brodie, L. Cogle, and C. Carroll. 2007. Appropriate use of catchment models for water-quality target setting and land-use management. IAHS-AISH Publication 239-250. | 2007 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps | Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Silverman, J., B. Lazar, and J. Erez. 2007. Community metabolism of a coral reef exposed to naturally varying dissolved inorganic nutrient loads. Biogeochemistry 84:67-82. | 2007 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Silverman, J., B. Lazar, and J. Erez. 2007. Effect of aragonite saturation, temperature, and nutrients on the community calcification rate of a coral reef. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 112. | 2007 | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity | |
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, I. Koike, T. Hayashibara, and H. Ogawa. 2007. Imbalanced coral growth between organic tissue and carbonate skeleton caused by nutrient enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography 52:1139-1146. | 2007 | Cuba | Lab Study | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| The coral disease working group of the global environmental facility coral reef targeted research program. 2007. Coral disease, environmental drivers, and the balance between coral and microbial associates. Oceanography 20:172-195. | 2007 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Philippines; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Thiel, M., E. C. Macaya, E. Acuna, W. E. Arntz, H. Bastias, K. Brokordt, P. A. Camus, J. C. Castilla, L. R. Castro, M. Cortes, C. P. Dumont, R. Escribano, M. Fernandez, J. A. Gajardo, C. F. Gaymer, I. Gomez, A. E. Gonzalez, H. E. Gonzalez, P. A. Haye, and J.-E. Illanes. 2007. The Humboldt Current System of northern and central Chile - Oceanographic processes, ecological interactions and socioeconomic feedback. Oceanography and Marine Biology 45:195-344. | 2007 | South & Central America | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Decision Support; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins |
| Torreton, J.-P., E. Rochelle-Newall, A. Jouon, V. Faure, S. Jacquet, and P. Douillet. 2007. Correspondence between the distribution of hydrodynamic time parameters and the distribution of biological and chemical variables in a semi-enclosed coral reef lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 74:667-677. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia | Model; Index or Indicator | Chemical Variables; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Traina, K., M. C. Steil, J. P. Pirard, C. Henrist, A. Rulmont, R. Cloots, and B. Vertruyen. 2007. Synthesis of La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O2.85 by successive freeze-drying and self-ignition of a hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose solution. Journal of the European Ceramic Society 27:3469-3474. | 2007 | Nutrients; Toxics | ||
| Tribollet, A. D. and P. S. Vroom. 2007. Temporal and spatial comparison of the relative abundance of macroalgae across the Mariana Archipelago between 2003 and 2005. Phycologia 46:187-197. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Turf Algae |
| Tsai, C.-C., J.-H. Liao, H.-H. Wang, and Z.-Y. Hseu. 2007. Effects of typhoon disturbances on soil microbial activities in an uplifted coral reef tropical forest, Southern Taiwan. Taiwan Journal of Forest Science 22:265-279. | 2007 | Taiwan | Field Study & Monitoring | CO2; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Umezawa, Y., T. Miyajima, Y. Tanaka, I. Koike, and T. Hayashibara. 2007. Variation in internal δ15N and δ13C distributions and their bulk values in the brown macroalga Padina australis growing in subtropical oligotrophic waters. Journal of Phycology 43:437-448. | 2007 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrients |
| Unrine, J. M., W. A. Hopkins, C. S. Romanek, and B. P. Jackson. 2007. Bioaccumulation of trace elements in omnivorous amphibian larvae: Implications for amphibian health and contaminant transport. Environmental Pollution 149:182-192. | 2007 | Nutrients; Wetlands | ||
| Visser, F., C. H. Roth, R. Wasson, and G. Govers. 2007. A sediment budget for a cultivated floodplain in tropical North Queensland, Australia. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 32:1475-1490. | 2007 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Voss, J. D., D. K. Mills, J. L. Myers, E. R. Remily, and L. L. Richardson. 2007. Black band disease microbial community variation on corals in three regions of the wider Caribbean. Microbial Ecology 54:730-739. | 2007 | South & Central America; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Bahamas; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Wang, Y., Y. J. Chen, J. H. Cho, J. S. Yoo, Q. Wang, Y. Huang, H. J. Kim, and I. H. Kim. 2007. The effects of dietary herbs and coral mineral complex on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, blood characteristics and meat quality in finishing pigs. Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences 16:397-407. | 2007 | Nutrients | ||
| Wang, Y.-H., C.-F. Dai, and Y.-Y. Chen. 2007. Physical and ecological processes of internal waves on an isolated reef ecosystem in the South China Sea. Geophysical Research Letters 34. | 2007 | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Wegley, L., R. Edwards, B. Rodriguez-Brito, H. Liu, and F. Rohwer. 2007. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides. Environmental Microbiology 9:2707-2719. | 2007 | Algae; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Cyanobacteria; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Weidlich, O. 2007. Permian reef and shelf carbonates of the Arabian platform and Neo-Tethys as recorders of climatic and oceanographic changes. Geological Society Special Publication 229-253. | 2007 | Oman | Model | Algae; Climate; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges |
| Weisz, J. B., U. Hentschel, N. Lindquist, and C. S. Martens. 2007. Linking abundance and diversity of sponge-associated microbial communities to metabolic differences in host sponges. Marine Biology 152:475-483. | 2007 | Florida | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Wilson, B. 2007. Guilds among epiphytal foraminifera on fibrous substrates, Nevis, West Indies. Marine Micropaleontology 63:18-Jan. | 2007 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Xu, D.-X. and G.-X. Zhang. 2007. Impact of human activities on coastal wetlands in China. Wetland Science 5:282-298. | 2007 | China | Agriculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Nutrients; Scientific Research; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| [No author name available]. 2006. Drilling & Production - Quick takes: Michigan reef due portable N-CO2 flood. Oil and Gas Journal 104:9-Aug. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring | CO2; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients | |
| Alongi, D. M., J. Pfitzner, and L. A. Trott. 2006. Deposition and cycling of carbon and nitrogen in carbonate mud of the lagoons of Arlington and Sudbury Reefs, Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 25:123-143. | 2006 | Australia; Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Altieri, A. H. and J. D. Witman. 2006. Local extinction of a foundation species in a hypoxic estuary: Integrating individuals to ecosystem. Ecology 87:717-730. | 2006 | Model | Bivalves; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars | |
| Armitage, A. R. and J. W. Fourqurean. 2006. The short-term influence of herbivory near patch reefs varies between seagrass species. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 339:65-74. | 2006 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Baisre, J. A. and Z. Arboleya. 2006. Going against the flow: Effects of river damming in Cuban fisheries. Fisheries Research 81:283-292. | 2006 | Cuba | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Beach, K. S., L. J. Walters, and H. B. Borgeas. 2006. Irradiance and nutrient limitation of Dicytota spp. populations on Conch Reef, Florida Keys, USA. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 329:101-112. | 2006 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Fleshy Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Bishop, G. A. and B. T. Palmer Sr. 2006. A new genus and species of crab from the bryozoan bioherms of the Eocene Santee Limestone; South Carolina, USA. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geologicas 23:334-337. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | |
| Bosellini, F. R. 2006. Biotic changes and their control on Oligocene-Miocene reefs: A case study from the Apulia Platform margin (southern Italy). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 241:393-409. | 2006 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Substrate | ||
| Boyer, J. N. 2006. Shifting N and P limitation along a north-south gradient of mangrove eestuaries in South Florida. Hydrobiologia 569:167-177. | 2006 | Florida | Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Brachert, T. C., M. Reuter, K. F. Kroeger, and J. M. Lough. 2006. Coral growth bands: A new and easy to use paleothermometer in paleoenvironment analysis and paleoceanography (late Miocene, Greece). Paleoceanography 21. | 2006 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Light; Nutrients | |
| Brock, J. C., K. K. Yates, R. B. Halley, I. B. Kuffner, C. W. Wright, and B. G. Hatcher. 2006. Northern Florida reef tract benthic metabolism scaled by remote sensing. Marine Ecology Progress Series 312:123-139. | 2006 | Florida; Cuba | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Bulleri, F. 2006. Duration of overgrowth affects survival of encrusting coralline algae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 321:79-85. | 2006 | Florida | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients |
| Burke, L. and Z. Sugg. 2006. Hydrologic Modeling of Watersheds Discharging Adjacent to the Mesoamerican Reef. World Resource Institute. | 2006 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Burkepile, D. E. and M. E. Hay. 2006. Herbivore vs. nutrient control of marine primary producers: Context-dependent effects. Ecology 87:3128-3139. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Cabioch, G., G. Camoin, G. E. Webb, F. Le Cornec, M. Garcia Molina, C. Pierre, and M. M. Joachimski. 2006. Contribution of microbialites to the development of coral reefs during the last deglacial period: Case study from Vanuatu (South-West Pacific). Sedimentary Geology 185:297-318. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Vanuatu | Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Camoin, G., G. Cabioch, A. Eisenhauer, J.-C. Braga, B. Hamelin, and G. Lericolais. 2006. Environmental significance of microbialites in reef environments during the last deglaciation. Sedimentary Geology 185:277-295. | 2006 | Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Carpenter, S. R. and W. A. Brock. 2006. Rising variance: a leading indicator of ecological transition. Ecology Letters 9:311-318. | 2006 | Model; Index or Indicator | Climate; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Carr, A., I. R. Tibbetts, A. Kemp, R. Truss, and J. Drennan. 2006. Inferring parrotfish (Teleostei: Scaridae) pharyngeal mill function from dental morphology, wear, and microstructure. Journal of Morphology 267:1147-1156. | 2006 | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients | ||
| Carter, R. M. 2006. Great news for the Great Barrier Reef: Tully River water quality. Energy and Environment 17:527-548. | 2006 | Australia | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Costa Jr., O. S., M. J. Attrill, and M. Nimmo. 2006. Seasonal and spatial controls on the delivery of excess nutrients to nearshore and offshore coral reefs of Brazil. Journal of Marine Systems 60:63-74. | 2006 | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Davy, S. K., K. J. T. Withers, and R. Hinde. 2006. Effects of host nutritional status and seasonality on the nitrogen status of zooxanthellae in the temperate coral Plesiastrea versipora (Lamarck). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 335:256-265. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Day-Lewis, F. D., E. A. White, C. D. Johnson, J. W. Lane, and M. Belaval. 2006. Continuous resistivity profiling to delineate submarine groundwater discharge - Examples and limitations. Leading Edge (Tulsa, OK) 25:724-728. | 2006 | Discharges; Nutrients; Resource Use Management; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Dolenec, T., S. Lojen, Z. Lambasa, and M. Dolenec. 2006. Effects of fish farm loading on sea grass Posidonia oceanica at Vrgada Island (Central Adriatic): A nitrogen stable isotope study. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies 42:77-85. | 2006 | Aquaculture; Nutrients | ||
| Douglas, G. B., P. W. Ford, M. Palmer, R. M. Noble, and R. Packett. 2006. Fitzroy River Basin, Queensland, Australia. I. Identification of sediment sources in impoundments and flood events. Environmental Chemistry 3:364-376. | 2006 | Australia | Model | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Esselman, P. C., M. C. Freeman, and C. M. Pringle. 2006. Fish-assemblage variation between geologically defined regions and across a longitudinal gradient in the Monkey River Basin, Belize. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25:142-156. | 2006 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fabricius, K. E. 2006. Effects of irradiance, flow, and colony pigmentation on the temperature microenvironment around corals: Implications for coral bleaching? Limnology and Oceanography 51:30-37. | 2006 | Light; Nutrients; Seawater Flow | ||
| Fabricius, K. E. and D. McCorry. 2006. Changes in octocoral communities and benthic cover along a water quality gradient in the reefs of Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin 52:22-33. | 2006 | China | Index or Indicator | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Flemer, D. A. and M. A. Champ. 2006. What is the future fate of estuaries given nutrient over-enrichment, freshwater diversion and low flows? Marine Pollution Bulletin 52:247-258. | 2006 | Discharges; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Wetlands | ||
| Fong, P., T. B. Smith, and M. J. Wartian. 2006. Epiphytic cyanobacteria maintain shifts to macroalgal dominance on coral reefs following ENSO disturbance. Ecology 87:1162-1168. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Frankovich, T. A., E. E. Gaiser, J. C. Zieman, and A. H. Wachnicka. 2006. Spatial and temporal distributions of epiphytic diatoms growing on Thalassia testudinum Banks ex Konig: Relationships to water quality. Hydrobiologia 569:259-271. | 2006 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Salinity |
| Gaston, T. F., T. A. Schlacher, and R. M. Connolly. 2006. Flood discharges of a small river into open coastal waters: Plume traits and material fate. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 69:9-Apr. | 2006 | Australia | Model | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Georgiades, E. T., A. Temara, and D. A. Holdway. 2006. The reproductive cycle of the asteroid Coscinasterias muricata in Port Phillip Bay, Victoria, Australia. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 332:188-197. | 2006 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Echinoderms; Nutrients |
| Gil-Agudelo, D. L., C. Myers, G. W. Smith, and K. Kim. 2006. Changes in the microbial communities associated with Gorgonia ventalina during aspergillosis infection. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 69:89-94. | 2006 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | ||
| Gobler, C. J., D. B. Thibault, T. W. Davis, P. B. Curran, B. J. Peterson, and L. B. Liddle. 2006. Algal assemblages associated with Stegastes sp. territories on Indo-Pacific coral reefs: Characterization of diversity and controls on growth. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 336:135-145. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Solomon Islands; Fiji; Tonga | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Turf Algae | |
| Goni, M. A., N. Monacci, R. Gisewhite, A. Ogston, J. Crockett, and C. Nittrouer. 2006. Distribution and sources of particulate organic matter in the water column and sediments of the Fly River Delta, Gulf of Papua (Papua New Guinea). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 69:225-245. | 2006 | Papua New Guinea | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Grover, R., J.-F. Maguer, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2006. Urea uptake by the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 332:216-225. | 2006 | Cuba | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hadas, E., D. Marie, M. Shpigel, and M. Ilan. 2006. Virus predation by sponges is a new nutrient-flow pathway in coral reef food webs. Limnology and Oceanography 51:1548-1550. | 2006 | Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Halfar, J., L. Godinez-Orta, M. Mutti, J. E. Valdez-Holguin, and J. M. Borges. 2006. Carbonates calibrated against oceanographic parameters along a latitudinal transect in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Sedimentology 53:297-320. | 2006 | Global; South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Halpern, B.S., K. Cottenie, B.R. Broitman. 2006. Strong Top-Down Control in Southern California Kelp Forest Ecosystems. Science 312:1230-1232. | 2006 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Special Use Permitting | |
| Hase, C., M. Al-Qutob, Z. Dubinsky, E. A. Ibrahim, B. Lazar, N. Stambler, and M. M. Tilzer. 2006. A system in balance? - Implications of deep vertical mixing for the nitrogen budget in the northern Red Sea, including the Gulf of Aqaba (Eilat). Biogeosciences Discussions 3:383-408. | 2006 | Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Hewson, I. and J. A. Fuhrman. 2006. Spatial and vertical biogeography of coral reef sediment bacterial and diazotroph communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 306:79-86. | 2006 | Global | Index or Indicator | Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Houlbreque, F., B. Delesalle, J. Blanchot, Y. Montel, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2006. Picoplankton removal by the coral reef community of La Prevoyante, Mayotte Island. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 44:59-70. | 2006 | Mayotte | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Huettel, M., C. Wild, and S. Gonelli. 2006. Mucus trap in coral reefs: Formation and temporal evolution of particle aggregates caused by coral mucus. Marine Ecology Progress Series 307:69-84. | 2006 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Imamverdiyev, S. B., T. A. Talibov, and V. Y. Abdurrahimova. 2006. Surgical treatment of coral-like and multiple nephrolithiasis in children. Azerbaijan Medical Journal 1:13-17. | 2006 | Nutrients | ||
| Jacquet, S., B. Delesalle, J.-P. Torreton, and J. Blanchot. 2006. Response of phytoplankton communities to increased anthropogenic influences (southwestern lagoon, New Caledonia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 320:65-78. | 2006 | New Caledonia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Jost, C. H. and S. Andrefouet. 2006. Long-term natural and human perturbations and current status of Clipperton Atoll, a remote island of the Eastern Pacific. Pacific Conservation Biology 12:207-217. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review; Remote Sensing | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Nutrients |
| Kahn, A. E. and M. J. Durako. 2006. Thalassia testudinum seedling responses to changes in salinity and nitrogen levels. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 335:12-Jan. | 2006 | Florida | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting | |
| Kline, D. I., N. M. Kuntz, M. Breitbart, N. Knowlton, and F. Rohwer. 2006. Role of elevated organic carbon levels and microbial activity in coral mortality. Marine Ecology Progress Series 314:119-125. | 2006 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Kunkel, C. M., R. W. Hallberg, and M. Oppenheimer. 2006. Coral reefs reduce tsunami impact in model simulations. Geophysical Research Letters 33:L23612. | 2006 | Global; Indian Ocean; India | Model | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Lapointe, B. E., B. J. Bedford, and R. Baumberger. 2006. Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne remove blooms of the invasive green alga Caulerpa brachypus forma parvifolia (Harvey) cribb from coral reefs off northern Palm Beach County, Florida. Estuaries and Coasts 29:966-971. | 2006 | Florida; France | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Lee, J. J. 2006. Algal symbiosis in larger foraminifera. Symbiosis 42:63-75. | 2006 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Primary Production |
| Liao, J.-H., H.-H. Wang, C.-C. Tsai, and Z.-Y. Hseu. 2006. Litter production, decomposition and nutrient return of uplifted coral reef tropical forest. Forest Ecology and Management 235:174-185. | 2006 | Java; Taiwan | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Lidz, B. H. 2006. Pleistocene corals of the Florida keys: Architects of imposing reefs - Why? Journal of Coastal Research 22:750-759. | 2006 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Nutrients; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and B. L. Brooks. 2006. Harmful algae on tropical coral reefs: Bottom-up eutrophication and top-down herbivory. Harmful Algae 5:565-585. | 2006 | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, B. L. Brooks, and B. E. Lapointe. 2006. Nutrient manipulation methods for coral reef studies: A critical review and experimental field data. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 336:242-253. | 2006 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Madin, J. S., K. P. Black, and S. R. Connolly. 2006. Scaling water motion on coral reefs: From regional to organismal scales. Coral Reefs 25:635-644. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients | |
| Meekan, M. G., J. H. Carleton, C. R. Steinberg, A. D. Mckinnon, R. Brinkman, P. J. Doherty, A. Halford, S. Duggan, and L. Mason. 2006. Turbulent mixing and mesoscale distributions of late-stage fish larvae on the NW Shelf of Western Australia. Fisheries Oceanography 15:44-59. | 2006 | Australia | Model | Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Messie, M. and M.-H. Radenac. 2006. Seasonal variability of the surface chlorophyll in the western tropical Pacific from SeaWiFS data. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 53:1581-1600. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Messie, M., M.-H. Radenac, and J. Lefevre. 2006. Chlorophyll bloom in the western equatorial Pacific during the 1998 El Nino / La Nina transition: The role of Kiribati Islands as seen from satellite, In-situ data, and a high-resolution simulation. European Space Agency, (Special Publication) ESA SP | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients |
| Miguel, A. F. 2006. Constructal pattern formation in stony corals, bacterial colonies and plant roots under different hydrodynamics conditions. Journal of Theoretical Biology 242:954-961. | 2006 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Montaggioni, L. F., F. Le Cornec, T. Correge, and G. Cabioch. 2006. Coral barium/calcium record of mid-Holocene upwelling activity in New Caledonia, South-West Pacific. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 237:436-455. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia | Climate; Nutrients; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Montagna, P., M. McCulloch, M. Taviani, C. Mazzoli, and B. Vendrell. 2006. Phosphorus in cold-water corals as a proxy for seawater nutrient chemistry. Science 312:1788-1791. | 2006 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Nagelkerken, I. 2006. Relationship between anthropogenic impacts and bleaching-associated tissue mortality of corals in Curacao (Netherlands Antilles). Revista de Biologia Tropical 54:31-43. | 2006 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Oak, T. and R. E. Scheibling. 2006. Tidal activity pattern and feeding behaviour of the ophiuroid Ophiocoma scolopendrina on a Kenyan reef flat. Coral Reefs 25:213-222. | 2006 | Kenya | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Olivier, N., B. Lathuiliere, and P. Thiry-Bastien. 2006. Growth models of Bajocian coral-microbialite reefs of Chargey-les-Port (eastern France): Palaeoenvironmental interpretations. Facies 52:113-127. | 2006 | France | Model | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Palardy, J. E., A. G. Grottoli, and K. A. Matthews. 2006. Effect of naturally changing zooplankton concentrations on feeding rates of two coral species in the Eastern Pacific. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 331:99-107. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Paytan, A., G. G. Shellenbarger, J. H. Street, M. E. Gonneea, K. Davis, M. B. Young, and W. S. Moore. 2006. Submarine groundwater discharge: An important source of new inorganic nitrogen to coral reef ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 51:343-348. | 2006 | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Pinnegar, J. K. and N. V. C. Polunin. 2006. Planktivorous damselfish support significant nitrogen and phosphorus fluxes to Mediterranean reefs. Marine Biology 148:1089-1099. | 2006 | Fish; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Plankton; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Pisarzowska, A., M. Sobstel, and G. Racki. 2006. Conodont-based event stratigraphy of the Early-Middle Frasnian transition on the South Polish carbonate shelf. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 51:609-646. | 2006 | Global; Poland | Model; Index or Indicator | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Echinoderms; Nutrients |
| Puthongking, P., C. Patarapanich, S. Amnuoypol, K. Suwanborirux, A. Kubo, and N. Saito. 2006. Chemistry of ecteinascidins. Part 2. Preparation of 6′-O-acyl derivatives of stable ecteinascidin and evaluation of cytotoxicity. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 54:1010-1016. | 2006 | Japan | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Tunicates | |
| Raina, S., W. P. Kang, J. L. Davidson, A. B. Bonds, D. E. Cliffel, and M. Howell. 2006. A novel \coral\" carbon microprobe with and without N2 incorporation". Diamond and Related Materials 15:1844-1848. | 2006 | Nutrients | ||
| Rasheed, M., C. Wild, C. Jantzen, and M. Badran. 2006. Mineralization of particulate organic matter derived from coral-reef organisms in reef sediments of the Gulf of Aqaba. Chemistry and Ecology 22:13-20. | 2006 | Cuba | Lab Study; Model | Nutrients; Sediment; Zooxanthellae |
| Rayment, G. E. and P. M. Bloesch. 2006. Phosphorus fertility assessment of intensively farmed areas of catchments draining to the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area; 1: Soil phosphorus status. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 37:2249-2264. | 2006 | Australia | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients | |
| Reuter, M., T. C. Brachert, and K. F. Kroeger. 2006. Shallow-marine carbonates of the tropical-temperate transition zone: Effects of hinterland climate and basin physiography (late Miocene, Crete, Greece). Geological Society Special Publication 157-178. | 2006 | Climate; Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Richardson, S. L. 2006. Response of epiphytic foraminiferal communities to natural eutrophication in seagrass habitats off Man O'War Cay, Belize. Marine Ecology 27:404-416. | 2006 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Mangroves; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Rilov, G. and D. R. Schiel. 2006. Trophic linkages across seascapes: Subtidal predators limit effective mussel recruitment in rocky intertidal communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 327:83-93. | 2006 | Fish; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Roberts, D. E., A. R. Davis, and S. P. Cummins. 2006. Experimental manipulation of shade, silt, nutrients and salinity on the temperate reef sponge Cymbastela concentrica. Marine Ecology Progress Series 307:143-154. | 2006 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Sponges | |
| Rodrigues, L. J. and A. G. Grottoli. 2006. Calcification rate and the stable carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen isotopes in the skeleton, host tissue, and zooxanthellae of bleached and recovering Hawaiian corals. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70:2781-2789. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Roelfsema, C. M., S. R. Phinn, W. C. Dennison, A. G. Dekker, and V. E. Brando. 2006. Monitoring toxic cyanobacteria Lyngbya majuscula (Gomont) in Moreton Bay, Australia by integrating satellite image data and field mapping. Harmful Algae 5:45-56. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Substrate |
| Scavia, D. and S. B. Bricker. 2006. Coastal eutrophication assessment in the United States. Biogeochemistry 79:187-208. | 2006 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients |
| Shafir, S., J. Van Rijn, and B. Rinkevich. 2006. Steps in the construction of underwater coral nursery, an essential component in reef restoration acts. Marine Biology 149:679-687. | 2006 | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Wetland & Reef Restoration | ||
| Shellenbarger, G. G., S. G. Monismith, A. Genin, and A. Paytan. 2006. The importance of submarine groundwater discharge to the nearshore nutrient supply in the Gulf of Aqaba (Israel). Limnology and Oceanography 51:1876-1886. | 2006 | Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Sobstel, M., M. Makowska-Haftka, and G. Racki. 2006. Conodont ecology in the Early-Middle Frasnian transition on the South Polish carbonate shelf. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 51:719-746. | 2006 | Global; Oman; Europe; Poland | Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Stamski, R. E. and M. E. Field. 2006. Characterization of sediment trapped by macroalgae on a Hawaiian reef flat. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 66:211-216. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Stewart, L. K., P. B. Charlesworth, K. L. Bristow, and P. J. Thorburn. 2006. Estimating deep drainage and nitrate leaching from the root zone under sugarcane using APSIM-SWIM. Agricultural Water Management 81:315-334. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Storlazzi, C. D., M. A. McManus, J. B. Logan, and B. E. McLaughlin. 2006. Cross-shore velocity shear, eddies and heterogeneity in water column properties over fringing coral reefs: West Maui, Hawaii. Continental Shelf Research 26:401-421. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment |
| Sumathi, J. C., S. Raghukumar, D. P. Kasbekar, and C. Raghukumar. 2006. Molecular Evidence of Fungal Signatures in the Marine Protist Corallochytrium limacisporum and its Implications in the Evolution of Animals and Fungi. Protist 157:363-376. | 2006 | Nutrients | ||
| Tanaka, Y., T. Miyajima, I. Koike, T. Hayashibara, and H. Ogawa. 2006. Translocation and conservation of organic nitrogen within the coral-zooxanthella symbiotic system of Acropora pulchra, as demonstrated by dual isotope-labeling techniques. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 336:110-119. | 2006 | Cuba | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Todd, B. D., D. J. Thornhill, and W. K. Fitt. 2006. Patterns of inorganic phosphate uptake in Cassiopea xamachana: A bioindicator species. Marine Pollution Bulletin 52:515-521. | 2006 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Tsemel, A., E. Spanier, and D. L. Angel. 2006. Benthic communities of artificial structures: Effects of mariculture in the gulf of Aqaba (Eilat) on development and bioaccumulation. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:103-113. | 2006 | Aquaculture; Nutrients | ||
| Uthicke, S. 2006. Photosynthetic efficiency and rapid light curves of sediment-biofilms along a water quality gradient in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 322:61-73. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment |
| van de Flierdt, T., L. F. Robinson, J. F. Adkins, S. R. Hemming, and S. L. Goldstein. 2006. Temporal stability of the neodymium isotope signature of the Holocene to glacial North Atlantic. Paleoceanography 21. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; England | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Nutrients |
| Van Duyl, F. C., S. R. Scheffers, F. I. M. Thomas, and M. Driscoll. 2006. The effect of water exchange on bacterioplankton depletion and inorganic nutrient dynamics in coral reef cavities. Coral Reefs 25:23-36. | 2006 | Antilles | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Vattakaven, T., P. Bond, G. Bradley, and C. B. Munn. 2006. Differential effects of temperature and starvation on induction of the viable-but-nonculturable state in the coral pathogens Vibrio shiloi and vibrio tasmaniensis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 72:6508-6513. | 2006 | Cuba | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens | |
| Villanueva, R. D., H. T. Yap, and M. N. E. Montano. 2006. Intensive fish farming in the Philippines is detrimental to the reef-building coral Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 316:165-174. | 2006 | Philippines | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Vimala, A., C. C. Rath, A. Sree, and S. Patanayak. 2006. Biodiversity and antimicrobial properties of cultivable microbial association of marine sessiler organisms of Orissa coast (Bay of Bengal). Asian Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Environmental Sciences 8:17-22. | 2006 | Aquaculture; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sponges | ||
| Voss, J. D. and L. L. Richardson. 2006. Nutrient enrichment enhances black band disease progression in corals. Coral Reefs 25:569-576. | 2006 | Lab Study | Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Wakibia, J. G., J. J. Bolton, D. W. Keats, and L. M. Raitt. 2006. Factors influencing the growth rates of three commercial eucheumoids at coastal sites in southern Kenya. Journal of Applied Phycology 18:565-573. | 2006 | Kenya | Aquaculture; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Weber, M., C. Lott, K.E. Fabricius. 2006. Sedimentation stress in a scleractinian coral exposed to terrestrial and marine sediments with contrasting physical, organic and geochemical properties. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 336:18-32. | 2006 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Wielgus, J., D. Glassom, and N. E. Chadwick. 2006. Patterns of polychaete worm infestation of stony corals in the Northern Red Sea and relationships to water chemistry. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:377-388. | 2006 | Discharges; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Williams, B., M. J. Risk, S. W. Ross, and K. J. Sulak. 2006. Deep-water antipatharians: Proxies of environmental change. Geology 34:773-776. | 2006 | South & Central America; Mexico | Nutrients | |
| Wooldridge, S., J. Brodie, and M. Furnas. 2006. Exposure of inner-shelf reefs to nutrient enriched runoff entering the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon: Post-European changes and the design of water quality targets. Marine Pollution Bulletin 52:1467-1479. | 2006 | Australia; Europe | Model | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Yahel, G., T. Zalogin, R. Yahel, and A. Genin. 2006. Phytoplankton grazing by epi- and infauna inhabiting exposed rocks in coral reefs. Coral Reefs 25:153-163. | 2006 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Zhao, M.-X., K.-F. Yu, and Q.-M. Zhang. 2006. Review on coral reefs biodiversity and ecological function. Acta Ecologica Sinica 26:186-194. | 2006 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); China | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Salinity; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Abelson, A., R. Olinky, S. Gaines. 2005. Coral recruitment to the reefs of Eilat, Red Sea: temporal and spatial variation, and possible effects of anthropogenic disturbances. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:576-582. | 2005 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Abramovitch-Gottlib, L., T. Gross, D. Naveh, S. Geresh, S. Rosenwaks, I. Bar, and R. Vago. 2005. Low level laser irradiation stimulates osteogenic phenotype of mesenchymal stem cells seeded on a three-dimensional biomatrix. Lasers in Medical Science 20:138-146. | 2005 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Albert, S., J.M. O'Neil, J.W. Udy, K.S. Ahern, C.M. O'Sullivan, W.C. Dennison. 2005. Blooms of the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula in coastal Queensland, Australia: disparate sites, common factors. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:428-437. | 2005 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Cyanobacteria; Marine Birds; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients |
| Alongi, D.M., A.D. McKinnon. 2005. The cycling and fate of terrestrially-derived sediments and nutrients in the coastal zone of the Great Barrier Reef shelf. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:239-252. | 2005 | Australia; Europe | Cyanobacteria; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Al-Rousan, S. A., M. Y. Rasheed, M. A. Khalaf, and M. I. Badran. 2005. Ecological and geochemical characteristics of bottom habitats at the northern Jordanian coast of the Gulf of Aqaba. Chemistry and Ecology 21:227-239. | 2005 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Echinoderms; Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | ||
| Andersson, A. J., F. T. MacKenzie, and A. Lerman. 2005. Coastal ocean and carbonate systems in the high CO2 world of the anthropocene. American Journal of Science 305:875-918. | 2005 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Arce, J. A. 2005. REMOTE SENSING OF BENTHIC HABITATS IN SOUTHWESTERN PUERTO RICO. Master's Thesis. University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez, Puerto Rico. | 2005 | Puerto Rico | Remote Sensing | Climate; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Badran, M. I. and M. K. Al Zibdah. 2005. Environmental quality of Jordanian coastal surface sediment, Gulf of Aqaba, red sea. Ambio 34:615-620. | 2005 | Beaches & Nature Parks; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Complex Habitat & Resources; Discharges; Hotel & Food Services; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Badran, M. I., M. Rasheed, R. Manasrah, and T. Al-Najjar. 2005. Nutrient flux fuels the summer primary productivity in the oligotrophic waters of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Oceanologia 47:47-60. | 2005 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Baird, A. H., S. J. Campbell, A. W. Anggoro, R. L. Ardiwijaya, N. Fadli, Y. Herdiana, T. Kartawijaya, D. Mahyiddin, A. Mukminin, S. T. Pardede, M. S. Pratchett, E. Rudi, and A. M. Siregar. 2005. Acehnese reefs in the wake of the Asian tsunami. Current Biology 15:1926-1930. | 2005 | Indonesia | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection | |
| Balasubramanian, R. and L. Kannan. 2005. Physico-chemical characteristics of the coral reef environs of the Gulf of Mannar biosphere reserve, India. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences 31:265-271. | 2005 | India | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Barile, P. J. and B. E. Lapointe. 2005. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition from a remote source enriches macroalgae in coral reef ecosystems near Green Turtle Cay, Abacos, Bahamas. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:1262-1272. | 2005 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Nutrients; Sea Turtles | |
| Bell, P. R. F. and F.-X. Fu. 2005. Effect of light on growth, pigmentation and N2 fixation of cultured Trichodesmium sp. from the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Hydrobiologia 543:25-35. | 2005 | Australia | Lab Study | Nutrients |
| Bell, P. R. F., P. J. R. Uwins, I. Elmetri, J. A. Phillips, F.-X. Fu, and A. J. E. Yago. 2005. Laboratory culture studies of Trichodesmium isolated from the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon, Australia. Hydrobiologia 532:21-Sep. | 2005 | Australia; Cuba | Lab Study | Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity |
| Boulon, R., M. Chiappone, R. Halley, W. Jaap, B. Keller, B. Kruczynski, M. Miller, and C. Rogers. 2005. Atlantic Acropora Status Review. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Jamaica; Belize; Caribbean; Mexico | Review | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Coastal Development; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Zooxanthellae |
| Brodie, J., K. Fabricus, G. De'ath, and K. Okaji. 2005. Are increased nutrient inputs responsible for more outbreaks of crown-of-thorn starfish? An appraisal of the evidence. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:266-278. | 2005 | Australia | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bymers, L., E. P. Glenn, S. G. Nelson, and K. Fitzsimmons. 2005. Diversity and biomass dynamics of marine algae in Biosphere II's tropical reef macrocosm. Ecological Engineering 25:442-456. | 2005 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Wetland & Reef Restoration | ||
| Carreiro-Silva, M., T. R. McClanahan, and W. E. Kiene. 2005. The role of inorganic nutrients and herbivory in controlling microbioerosion of carbonate substratum. Coral Reefs 24:214-221. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Cyanobacteria; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Carruthers, T. J. B., B. I. Van Tussenbroek, and W. C. Dennison. 2005. Influence of submarine springs and wastewater on nutrient dynamics of Caribbean seagrass meadows. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 64:191-199. | 2005 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Hotel & Food Services; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Charpy, L. 2005. Importance of photosynthetic picoplankton in coral reef ecosystems. Vie et Milieu 55:217-223. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Fiji | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Charpy-Roubaud, C. and A. W. D. Larkum. 2005. Dinitrogen fixation by exposed communities on the rim of Tikehau atoll (Tuamotu Archipelago, French Polynesia). Coral Reefs 24:622-628. | 2005 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Chong, Jo. 2005. Protective values of mangrove and coral ecosystems: a review of methods and evidence. IUCN. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Recreational Opportunities; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Civitelli, G. and M. Brandano. 2005. The «Calcari a Briozoi e Litotamni» in the Latium-Abruzzi carbonate platform (Central Apennines, Italy): Atlas of the lithofacies and depositional model [Atlante delle litofacies e modello deposizionale dei Calcari a Briozoi e Litotamni nella Piattaform. Bollettino della Societa Geologica Italiana 124:611-643. | 2005 | Global; Europe | Model | Algae; Climate; Coralline Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Clavier, J., G. Boucher, L. Chauvaud, R. Fichez, and S. Chifflet. 2005. Benthic response to ammonium pulses in a tropical lagoon: Implications for coastal environmental processes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 316:231-241. | 2005 | New Caledonia | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Cohen, B. L. 2005. Not armour, but biomechanics, ecological opportunity and increased fecundity as keys to the origin and expansion of the mineralized benthic metazoan fauna. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 85:483-490. | 2005 | Nutrients | ||
| Costanzo, S. D., J. Udy, B. Longstaff, and A. Jones. 2005. Using nitrogen stable isotope ratios of macroalgae to determine the effectiveness of sewage upgrades: changes in the extent of sewage plumes over four years in Moreton Bay, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:212-217. | 2005 | Australia; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Algae; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies |
| Crigger, D. K., G. A. Graves, and D. L. Fike. 2005. Lake Worth Lagoon conceptual ecological model. Wetlands 25:943-954. | 2005 | Florida | Model | Boating Activities; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrates; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Crossman, D. J., J. H. Choat, and K. D. Clements. 2005. Nutritional ecology of nominally herbivorous fishes on coral reefs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 296:129-142. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Davies, P.L., B.D. Eyre. 2005. Estuarine modification of nutrient and sediment exports to the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park from the Daintree and Annan River catchments. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:174-185. | 2005 | Australia | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| D'Croz, L., J. B. del Rosario, and P. Gondola. 2005. The effect of fresh water runoff on the distribution of dissolved inorganic nutrients and plankton in the Bocas del Toro Archipelago, Caribbean Panama. Caribbean Journal of Science 41:414-429. | 2005 | South & Central America; Panama; Iran; Caribbean | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity | |
| Devlin, M.J., J. Brodie. 2005. Terrestrial discharge into the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon: nutrient behavior in coastal waters. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:9-22. | 2005 | Australia; Europe | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Diaz-Pulido, G. and L. J. McCook. 2005. Effects of nutrient enhancement on the fecundity of a coral reef macroalga. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 317:13-24. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Dizon, R. M. and H. T. Yap. 2005. Coral responses in single- and mixed-species plots to nutrient disturbance. Marine Ecology Progress Series 296:165-172. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Duke, N. C., A. M. Bell, D. K. Pederson, C. M. Roelfsema, and S. B. Nash. 2005. Herbicides implicated as the cause of severe mangrove dieback in the Mackay region, NE Australia: Consequences for marine plant habitats of the GBR World Heritage Area. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:308-324. | 2005 | Australia | Review | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fabricius, K. E. 2005. Effects of terrestrial runoff on the ecology of corals and coral reefs: Review and synthesis. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:125-146. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coralline Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Fabricius, K., G. De'ath, L. McCook, E. Turak, and D. MC B. Williams. 2005. Changes in algal, coral and fish assemblages along water quality gradients on the inshore Great Barrier Reef. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:384-398. | 2005 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Faithful, J., W. Finlayson. 2005. Water quality assessment for sustainable agriculture in the Wet Tropics - A community-assisted approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:99-112. | 2005 | Agriculture; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Falter, J. L., M. J. Atkinson, and C. F. M. Coimbra. 2005. Effects of surface roughness and oscillatory flow on the dissolution of plaster forms: Evidence for nutrient mass transfer to coral reef communities. Limnology and Oceanography 50:246-254. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients | |
| Faust, M. A., R. W. Litaker, M. W. Vandersea, S. R. Kibler, and P. A. Tester. 2005. Dinoflagellate diversity and abundance in two Belizean coral-reef mangrove lagoons: A test of Margalef's mandala. Atoll Research Bulletin 103-131. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., F. Houlbreque, E. Wyse, C. Richard, D. Allemand, and F. Boisson. 2005. Bioaccumulation of zinc in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Coral Reefs 24:636-645. | 2005 | Cuba | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Fichez, R., M. Adjeroud, Y.-M. Bozec, L. Breau, Y. Chancerelle, C. Chevillon, P. Douillet, J.-M. Fernandez, P. Frouin, M. Kulbicki, B. Moreton, S. Ouillon, C. Payri, T. Perez, P. Sasal, and J. Thebault. 2005. A review of selected indicators of particle, nutrient and metal inputs in coral reef lagoon systems. Aquatic Living Resource 18:125-147. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Finkl, C. W., R. H. Charlier, and S. L. Krupa. 2005. Vulnerability of coastal environments to land use and abuse: The example of southeast Florida. International Journal of Environmental Studies 62:535-554. | 2005 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Floros, C. D., M. J. Samways, and B. Armstrong. 2005. Polychaete (Spirobranchus giganteus) loading on South African corals. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 15:289-298. | 2005 | Global; South Africa | Climate; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral | |
| Fournier, F., J. Borgomano, and L. F. Montaggioni. 2005. Development patterns and controlling factors of Tertiary carbonate buildups: Insights from high-resolution 3D seismic and well data in the Malampaya gas field (Offshore Palawan, Philippines). Sedimentary Geology 175:189-215. | 2005 | Philippines | Nutrients | |
| Furnas, M., A. Mitchell, M. Skuza, and J. Brodie. 2005. In the other 90%: Phytoplankton responses to enhanced nutrient availability in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:253-265. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Fursich, F. T., I. B. Singh, M. Joachimski, S. Krumm, M. Schlirf, and S. Schlirf. 2005. Palaeoclimate reconstructions of the Middle Jurassic of Kachchh (western India): An integrated approach based on palaeoecological, oxygen isotopic, and clay mineralogical data. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 217:289-309. | 2005 | India | Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Gopinath, A., N. C. Kumar, K. V. Jayalakshmi, D. Padmalal, and S. M. Nair. 2005. A predictive regression model for the geochemical variability of iron and manganese in a coral reef ecosystem. Environmental Forensics 6:301-310. | 2005 | Model | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Gotz, S., H. Loser, and D. U. Schmid. 2005. Reef development on a deepening platform: Two Early Cretaceous coralgal patch reefs (Cati, Llàcova Formation, eastern Spain) compared. Cretaceous Research 26:864-881. | 2005 | Oman; Spain | Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Greiner, R., A. Herr, J. Brodie, and D. Haynes. 2005. A multi-criteria approach to Great Barrier Reef catchment (Queensland, Australia) diffuse-source pollution problem. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:128-137. | 2005 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Guerra-Garcia, J. M. and M. S. Koonjul. 2005. Metaprotella sandalensis (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Caprellidae): A bioindicator of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs? Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 104:353-367. | 2005 | Mauritius | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation |
| Halfar, J. and M. Mutti. 2005. Global dominance of coralline red-algal facies: A response to Miocene oceanographic events. Geology 33:481-484. | 2005 | Global | Index or Indicator | Algae; Climate; Nutrients |
| Halfar, J., L. Godinez-Orta, B. Riegl, J. E. Valdez-Holguin, and J. M. Borges. 2005. Living on the edge: High-latitude Porites carbonate production under temperate eutrophic conditions. Coral Reefs 24:582-592. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Mexico | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Hallock, P. 2005. Global change and modern coral reefs: New opportunities to understand shallow-water carbonate depositional processes. Sedimentary Geology 175:19-33. | 2005 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Cyanobacteria; Finfish Harvest; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Sunscreen Use; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics | |
| Harrington, L., K. Fabricius, G. Eaglesham, and A. Negri. 2005. Synergistic effects of diuron and sedimentation on photosynthesis and survival of crustose coralline algae. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:415-427. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Hitchcock, G. L., T. N. Lee, P. B. Ortner, S. Cummings, C. Kelble, and E. Williams. 2005. Property fields in a Tortugas Eddy in the southern straits of Florida. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 52:2195-2213. | 2005 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ismail, M., T. Kimura, Y. Suzuki, and M. Tsuchiya. 2005. Seasonal and spatial variations of total mass flux around coral reefs in the Southern Ryukyus, Japan. Journal of Oceanography 61:631-644. | 2005 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Discharges; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Jarrett, B. D., A. C. Hine, R. B. Halley, D. F. Naar, S. D. Locker, A. C. Neumann, D. Twichell, C. Hu, B. T. Donahue, W. C. Jaap, D. Palandro, and K. Ciembronowicz. 2005. Strange bedfellows - A deep-water hermatypic coral reef superimposed on a drowned barrier island; Southern Pulley Ridge, SW Florida platform margin. Marine Geology 214:295-307. | 2005 | Florida | Algae; Coralline Algae; Light; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Jeyasekaran, G., K. Maheswari, P. Ganesan, R. J. Shakila, and D. Sukumar. 2005. Quality changes in ice-stored tropical wire-netting reef cod (Epinephelus merra). Journal of Food Processing and Preservation 29:165-182. | 2005 | Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Juman, R. A. 2005. The structure and productivity of the Thalassia testudinum community in Bon Accord Lagoon, Tobago. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:219-227. | 2005 | South & Central America; Tobago; Caribbean | Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Kayanne, H., M. Hirota, M. Yamamuro, and I. Koike. 2005. Nitrogen fixation of filamentous cyanobacteria in a coral reef measured using three different methods. Coral Reefs 24:197-200. | 2005 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Kibler, S. R., M. A. Faust, M. W. Vandersea, S. M. Varnam, R. W. Litaker, and P. A. Tester. 2005. Water column structure and circulation in the Main Channel, Twin Cays, Belize. Atoll Research Bulletin 133-156. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Klaus, J. S., J. Frias-Lopez, G. T. Bonheyo, J. M. Heikoop, and B. W. Fouke. 2005. Bacterial communities inhabiting the healthy tissues of two Caribbean reef corals: Interspecific and spatial variation. Coral Reefs 24:129-137. | 2005 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Kuntz, N. M., D. I. Kline, S. A. Sandin, and F. Rohwer. 2005. Pathologies and mortality rates caused by organic carbon and nutrient stressors in three Caribbean coral species. Marine Ecology Progress Series 294:173-180. | 2005 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Langdon, C. and M. J. Atkinson. 2005. Effect of elevated pCO2 on photosynthesis and calcification of corals and interactions with seasonal change in temperature/ irradiance and nutrient enrichment. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 110:16-Jan. | 2005 | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, M. M. Littler, and D. S. Littler. 2005. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: II. Cross-shelf discrimination of nitrogen sources indicates widespread assimilation of sewage nitrogen. Harmful Algae 4:1106-1122. | 2005 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, M. M. Littler, D. S. Littler, B. J. Bedford, and C. Gasque. 2005. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: I. Nutrient stoichiometry of the invasive green alga Codium isthmocladum in the wider Caribbean indicates nutrient enrichment. Harmful Algae 4:1092-1105. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Leletkin, V. A. 2005. Nitrogen and photosynthetic function of hermatypic corals. Oxygen exchange of Stylophora pistillata coral under artificial feeding. Zhurnal Obshchei Biologii 66:164-169. | 2005 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Marion, G. S., R. B. Dunbar, D. A. Mucciarone, J. N. Kremer, J. S. Lansing, and A. Arthawiguna. 2005. Coral skeletal δ15N reveals isotopic traces of an agricultural revolution. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:931-944. | 2005 | Indonesia | Agriculture; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Wastewater Discharge | |
| McClanahan, T. R., R. S. Steneck, D. Pietri, B. Cokos, and S. Jones. 2005. Interaction between inorganic nutrients and organic matter in controlling coral reef communities in Glovers Reef Belize. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:566-575. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Coralline Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae | |
| McKergow, L. A., I. P. Prosser, A. O. Hughes, and J. Brodie. 2005. Regional scale nutrient modelling: Exports to the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:186-199. | 2005 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Mellors, J., M. Waycott, and H. Marsh. 2005. Variation in biogeochemical parameters across intertidal seagrass meadows in the central Great Barrier Reef region. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:335-342. | 2005 | Global; Australia | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Mitchell, C., J. Brodie, and I. White. 2005. Sediments, nutrients and pesticide residues in event flow conditions in streams of the Mackay Whitsunday Region, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:23-36. | 2005 | Australia | Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Miyajima, T., Y. Tanaka, and I. Koike. 2005. Determining 15N enrichment of dissolved organic nitrogen in environmental waters by gas chromatography/negative-ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 3:164-173. | 2005 | Cuba | Nutrients | |
| Montaggioni, L. F. 2005. History of Indo-Pacific coral reef systems since the last glaciation: Development patterns and controlling factors. Earth-Science Reviews 71:Jan-75. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India; Pacific Ocean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; CO2; Coralline Algae; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Moss, A., J. Brodie, and M. Furnas. 2005. Water quality guidelines for the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area: A basis for development and preliminary values. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:76-88. | 2005 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Muscatine, L., C. Goiran, L. Land, J. Jaubert, J.-P. Cuif, and D. Allemand. 2005. Stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) of organic matrix from coral skeleton. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102:1525-1530. | 2005 | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients | ||
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. | 2005 | Improved Technology; Nutrients; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| O'Reagain, P. J., J. Brodie, G. Fraser, J. J. Bushell, C. H. Holloway, J. W. Faithful, and D. Haynes. 2005. Nutrient loss and water quality under extensive grazing in the upper Burdekin river catchment, North Queensland. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:37-50. | 2005 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Otero, E. and K. K. Carbery. 2005. Chlorophyll a and turbidity patterns over coral reefs systems of La Parguera Natural Reserve, Puerto Rico. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:25-32. | 2005 | Puerto Rico | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment |
| Peirano, A., M. Abbate, G. Cerrati, V. Difesca, C. Peroni, and R. Rodolfo-Metalpa. 2005. Monthly variations in calix growth, polyp tissue, and density banding of the Mediterranean scleractinian Cladocora caespitosa (L.). Coral Reefs 24:404-409. | 2005 | Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Perna, C. and D. Burrows. 2005. Improved dissolved oxygen status following removal of exotic weed mats in important fish habitat lagoons of the tropical Burdekin River floodplain, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:138-148. | 2005 | Australia | Agriculture; Fish; Irrigation; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Porat, D. and N. E. Chadwick-Furman. 2005. Effects of anemonefish on giant sea anemones: Ammonium uptake, zooxanthella content and tissue regeneration. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology 38:43-51. | 2005 | Lab Study | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Fish; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Raja, R., P. K. Saraswati, K. Rogers, and K. Iwao. 2005. Magnesium and strontium compositions of recent symbiont-bearing benthic foraminifera. Marine Micropaleontology 58:31-44. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India; Japan | Climate; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Raubenheimer, D., W. L. Zemke-White, R. J. Phillips, and K. D. Clements. 2005. Algal macronutrients and food selection by the omnivorous marine fish Girella tricuspidata. Ecology 86:2601-2610. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | |
| Renegar, D. A. and B. M. Riegl. 2005. Effect of nutrient enrichment and elevated CO2 partial pressure on growth rate of Atlantic scleractinian coral Acropora cervicornis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 293:69-76. | 2005 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Lab Study | CO2; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Rex, M. A., J. A. Crame, C. T. Stuart, and A. Clarke. 2005. Large-scale biogeographic patterns in marine mollusks: A confluence of history and productivity? Ecology 86:2288-2297. | 2005 | Nutrients | ||
| Ribes, M., R. Coma, M. J. Atkinson, and R. A. Kinzie III. 2005. Sponges and ascidians control removal of particulate organic nitrogen from coral reef water. Limnology and Oceanography 50:1480-1489. | 2005 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | ||
| Rinkevich, B. 2005. Nutrient enrichment and coral reproduction between truth and repose (a critique of Loya et al.). Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:111-113. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Rinkevich, B., Y. Loya, M. Rosenfeld, and E. Kramarsky-Winter. 2005. Nutrient enrichment and coral reproduction: Between truth and repose (a critique of Loya et al.) [2] (multiple letters). Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:111-118. | 2005 | Nutrients; Waterborne Discharges | ||
| Sakas, C. J. 2005. Rivers to reefs - Watersheds affect ocean reefs oceans 2005 MTS/IEEE. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sanders, D. and R. C. Baron-Szabo. 2005. Scleractinian assemblages under sediment input: Their characteristics and relation to the nutrient input concept. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 216:139-181. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Schaffelke, B., J. Mellors, and N. C. Duke. 2005. Water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: Responses of mangrove, seagrass and macroalgal communities. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:279-296. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Scheffers, S. R., R. P. M. Bak, and F. C. Van Duyl. 2005. Why is bacterioplankton growth in coral reef framework cavities enhanced? Marine Ecology Progress Series 299:89-99. | 2005 | Antilles | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Scheibner, C., R. P. Speijer, and A. M. Marzouk. 2005. Turnover of larger foraminifera during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum and paleoclimatic control on the evolution of platform ecosystems. Geology 33:493-496. | 2005 | Global; Egypt | Climate; Nutrients | |
| Seymour, J. R., N. Patten, D. G. Bourne, and J. G. Mitchell. 2005. Spatial dynamics of virus-like particles and heterotrophic bacteria within a shallow coral reef system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 288:8-Jan. | 2005 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Shen, J.-W. and G. E. Webb. 2005. Metazoan-microbial framework fabrics in a Mississippian (Carboniferous) coral-sponge-microbial reef, Monto, Queensland, Australia. Sedimentary Geology 178:113-133. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Salinity; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Sherwood, O. A., J. M. Heikoop, D. B. Scott, M. J. Risk, T. P. Guilderson, and R. A. McKinney. 2005. Stable isotopic composition of deep-sea gorgonian corals Primnoa spp.: A new archive of surface processes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 301:135-148. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Pacific Ocean; Japan | Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Smith, J. E., J. W. Runcie, and C. M. Smith. 2005. Characterization of a large-scale ephemeral bloom of the green alga Cladophora sericea on the coral reefs of West Maui, Hawai'i. Marine Ecology Progress Series 302:77-91. | 2005 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Spencer, T., A. S. Laughton, and N. C. Flemming. 2005. Variability, interaction and change in the atmosphere-ocean-ecology system of the Western Indian Ocean. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 363:13-Mar. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India | Agriculture; Climate; Nutrients | |
| Stadelmaier, M., M. Nose, A. May, C. Salerno, S. Schroder, and R. R. Leinfelder. 2005. Middle Devonian branching tabulate coral community of Sotenicher Mulde (Eifel): [Ästige tabulate Korallen-Gemeinschaften aus dem Mitteldevon der Sotenicher Mulde (Eifel): Faunenzusammensetzung und fazielles Umfeld]. Zitteliana Reihe B: Abhandlungen der Bayerischen Staatssammlung fur Palaontologie und Geologie 25:May-38. | 2005 | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment | ||
| Sunda, W. G., R. W. Litaker, D. R. Hardison, and P. A. Tester. 2005. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) and its relation to algal pigments in diverse waters of the Belize coastal lagoon and barrier reef system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 287:22-Nov. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Cyanobacteria; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Tomasko, D. A., C. A. Corbett, H. S. Greening, and G. E. Raulerson. 2005. Spatial and temporal variation in seagrass coverage in Southwest Florida: assessing the relative effects of anthropogenic nutrient load reductions and rainfall in four contiguous estuaries. Marine Pollution Bulletin 50:797-805. | 2005 | Florida | Nutrients; Plankton; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Tsai, C.-C., J.-S. Chang, F. Sheu, Y.-T. Shyu, A.Y.-C. Yu, S.-L. Wong, C.-F. Dai, and T.-M. Lee. 2005. Seasonal growth dynamics of Laurencia papillosa and Gracilaria coronopifolia from a highly eutrophic reef in southern Taiwan: Temperature limitation and nutrient availability. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 315:49-69. | 2005 | Taiwan | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Nutrients |
| van Nes, E. H. and M. Scheffer. 2005. Implications of spatial heterogeneity for catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems. Ecology 87:1797-1807. | 2005 | Global | Model | Nutrients |
| Villanueva, R. D., Yap, Helen T., Montano, Marco Nemesio E. 2005. Survivorship of coral juveniles in a fish farm environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:580-589. | 2005 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Ward-Paige, C. A., M. J. Risk, and O. A. Sherwood. 2005. Reconstruction of nitrogen sources on coral reefs: δ15N and δ13C in gorgonians from Florida Reef Tract. Marine Ecology Progress Series 296:155-163. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Belize; Mexico | Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Ward-Paige, C. A., M. J. Risk, and O. A. Sherwood. 2005. Reconstruction of nitrogen sources on coral reefs: d15N and d13C in gorgonians from Florida Reef Tract. Marine Ecology Progress Series 296:155-263. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Belize; Mexico | Nutrients; Octocoral | |
| Ward-Paige, C. A., M. J. Risk, O. A. Sherwood, and W. C. Jaap. 2005. Clionid sponge surveys on the Florida Reef Tract suggest land-based nutrient inputs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:570-579. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Belize | Boring Sponges; Nutrients; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Warne, A. G., R. M. T. Webb, and M. C. Larsen. 2005. Water, sediment, and nutrient discharge characteristics of rivers in Puerto Rico, and their potential influence on coral reefs. Scientific Investigations Report 2005-5206, U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, Virginia. | 2005 | Puerto Rico | Agriculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Waycott, M., B. J. Longstaff, and J. Mellors. 2005. Seagrass population dynamics and water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: A review and future research directions. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:343-350. | 2005 | Australia | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Toxics |
| Webster, I. T., P. W. Ford, and P. Tillman. 2005. Estimating nutrient budgets in tropical estuaries subject to episodic flows. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:165-173. | 2005 | Australia | Model | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Whitney, F., K. Conway, R. Thomson, V. Barrie, M. Krautter, and G. Mungov. 2005. Oceanographic habitat of sponge reefs on the Western Canadian Continental Shelf. Continental Shelf Research 25:211-226. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Wild, C., H. Woyt, and M. Huettel. 2005. Influence of coral mucus on nutrient fluxes in carbonate sands. Marine Ecology Progress Series 287:87-98. | 2005 | Australia; Cuba | Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wilson, M. E. J. 2005. Development of equatorial delta-front patch reefs during the Neogene, Borneo. Journal of Sedimentary Research 75:114-133. | 2005 | Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Xie, Z., L. Sun, P. Zhang, S. Zhao, X. Yin, X. Liu, and B. Cheng. 2005. Preliminary geochemical evidence of groundwater contamination in coral islands of Xi-Sha, South China Sea. Applied Geochemistry 20:1848-1856. | 2005 | China | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| [No author name available]. 2004. Nutrient pollution aggravates coral diseases. Water Environment and Technology 16:10. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Agriculture; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| [No author name available]. 2004. Wastewater, polluted runoff may cause coral reef destruction. Water Environment and Technology 16:8. | 2004 | Florida | Agriculture; Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Snails & Conch; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Al-Rousan, S., M. Rasheed, and M. Badran. 2004. Nutrient diffusive fluxes from sediments in the northern Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Scientia Marina 68:483-490. | 2004 | Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Baird, M. E., M. Roughan, R. W. Brander, J. H. Middleton, and G. J. Nippard. 2004. Mass-transfer-limited nitrate uptake on a coral reef flat, Warraber Island, Torres Strait, Australia. Coral Reefs 23:386-396. | 2004 | Australia | Climate; Nutrients | |
| Barile, P. J. 2004. Evidence of anthropogenic nitrogen enrichment of the littoral waters of east central Florida. Journal of Coastal Research 20:1237-1245. | 2004 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); India | Index or Indicator | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Improved Technology; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Boyer, K. E., P. Fong, A. R. Armitage, and R. A. Cohen. 2004. Elevated nutrient content of tropical macroalgae increases rates of herbivory in coral, seagrass, and mangrove habitats. Coral Reefs 23:530-538. | 2004 | Honduras | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Bracken, M. E. S. and K. J. Nielsen. 2004. Diversity of intertidal macroalgae increases with nitrogen loading by invertebrates. Ecology 85:2828-2836. | 2004 | Algae; Invertebrates; Nutrients | ||
| Burns, K. A., P. Greenwood, R. Benner, D. Brinkman, G. Brunskill, S. Codi, and I. Zagorskis. 2004. Organic biomarkers for tracing carbon cycling in the Gulf of Papua (Papua New Guinea). Continental Shelf Research 24:2373-2394. | 2004 | Papua New Guinea | Carbon Storage & Cycling; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Cosgrove, J., D. Walker, P. Morrison, and K. Hillman. 2004. Periphyton indicate effects of wastewater discharge in the near-coastal zone, Perth (Western Australia). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 61:331-338. | 2004 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Wastewater Discharge |
| Davies, P. 2004. Nutrient processes and chlorophyll in the estuaries and plume of the Gulf of Papua. Continental Shelf Research 24:2317-2341. | 2004 | Remote Sensing | Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Fabricius, K. E. and G. De'ath. 2004. Identifying ecological change and its causes: A case study on coral reefs. Ecological Applications 14:1448-1465. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Falter, J. L., M. J. Atkinson, and M. A. Merrifield. 2004. Mass-transfer limitation of nutrient uptake by a wave-dominated reef flat community. Limnology and Oceanography 49:1820-1831. | 2004 | Nutrients; Shoreline Protection | ||
| Fleury, B. G., J. C. Coll, P. W. Sammarco, E. Tentori, and S. Duquesne. 2004. Complementary (secondary) metabolites in an octocoral competing with a scleractinian coral: Effects of varying nutrient regimes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 303:115-131. | 2004 | Australia | Nutrients; Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Gaston, T. F. and I. M. Suthers. 2004. Spatial variation in δ13C and δ15N of liver, muscle and bone in a rocky reef planktivorous fish: The relative contribution of sewage. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 304:17-33. | 2004 | Australia | Discharges; Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Gaston, T. F., A. Kostoglidis, and I. M. Suthers. 2004. The 13C, 15N and 34S signatures of a rocky reef planktivorous fish indicate different coastal discharges of sewage. Marine and Freshwater Research 55:689-699. | 2004 | Discharges; Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies | ||
| Genovese, S. J. and J. D. Witman. 2004. Wind-mediated diel variation in flow speed in a Jamaican back reef environment: Effects on ecological processes. Bulletin of Marine Science 75:281-293. | 2004 | Global; Jamaica | Algae; Climate; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Seawater Flow | |
| Gopinath, A., N. C. Kumar, and S. M. Nair. 2004. An introductory study on the biogeochemical features of the coral sediments of the Minicoy Island, Lakshadweep. Indian Journal of Environmental Protection 24:113-120. | 2004 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Gopinath, A., N. C. Kumar, D. Padmalal, and S. M. Nair. 2004. Speciation of nitrogen in the coral reef sedimentary environment of Lakshadweep Archipelago, Indian Ocean. Chemistry and Ecology 20:267-278. | 2004 | Indian Ocean; India | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Goreau, T. J., J. M. Cervino, and R. Pollina. 2004. Increased zooxanthellae numbers and mitotic index in electrically stimulated corals. Symbiosis 37:107-120. | 2004 | Global; Indonesia | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Halfar, J., L. Godinez-Orta, M. Mutti, J. E. Valdez-Holguin, and J. M. Borges. 2004. Nutrient and temperature controls on modern carbonate production: An example from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Geology 32:213-216. | 2004 | South & Central America; Mexico | Lab Study | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Heil, C. A., K. Chaston, A. Jones, P. Bird, B. Longstaff, S. Costanzo, and W. C. Dennison. 2004. Benthic microalgae in coral reef sediments of the southern Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 23:336-343. | 2004 | Australia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 2004. Coral reefs in a century of rapid environmental change. Symbiosis 37:31-Jan. | 2004 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral |
| Hoegh-Guldberg, O., L. Muscatine, C. Goiran, D. Siggaard, and G. Marion. 2004. Nutrient-induced perturbations to δ13C and δ15N in symbiotic dinoflagellates and their coral hosts. Marine Ecology Progress Series 280:105-114. | 2004 | Australia | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Hohenegger, J. 2004. Depth coenoclines and environmental considerations of Western Pacific larger foraminifera. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 34:Sep-33. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Climate; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Hotinski, R. M., L. R. Kump, and M. A. Arthur. 2004. The effectiveness of the Paleoproterozoic biological pump: A δ13C gradient from platform carbonates of the Pethei Group (Great Slave Lake Supergroup, NWT). Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 116:539-554. | 2004 | Global | Model | CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Houlbreque, F., E. Tambutte, C. Richard, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2004. Importance of a micro-diet for scleractinian corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 282:151-160. | 2004 | Cuba | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Hwang, R.-L., C.-C. Tsai, and T.-M. Lee. 2004. Assessment of temperature and nutrient limitation on seasonal dynamics among species of Sargassum from a coral reef in southern Taiwan. Journal of Phycology 40:463-473. | 2004 | Taiwan | Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| James, N. P., D. A. Feary, C. Betzler, Y. Bone, A. E. Holbourn, Q. Li, H. Machiyama, J. A. T. Simo, and F. Surlyk. 2004. Origin of Late Pleistocene bryozoan reef mounds; Great Australian Bight. Journal of Sedimentary Research 74:20-48. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Sponges; Tunicates |
| James, N. P., Y. Bone, T. K. Kyser, G. R. Dix, and L. B. Collins. 2004. The importance of changing oceanography in controlling late Quaternary carbonate sedimentation on a high-energy, tropical, oceanic ramp: North-western Australia. Sedimentology 51:1179-1205. | 2004 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Index or Indicator | Algae; Climate; Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Jameson, S. C., R. A. Kelty. 2004. A review of indicators of land-based pollution stress on coral reefs. Honolulu, HI. | 2004 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Special Use Permitting | |
| Jokiel, P.L. 2004. Temperature Stress and Coral Bleaching. Pages 401-425 in Rosenberg, E., Y. Loya, editor. Coral Health and Disease. | 2004 | Algae; Nutrients; Pathogens; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Kaljo, D. 2004. Diversity of late Ordovician rugose corals in Baltoscandia: Role of environmental changes and comparison with other areas [Baltoskandia Hilisordoviitsiumi rugooside mitmekesisus: Keskkonnamuutuste roll ja võrdlus teiste aladega]. Proceedings of the Estonian Academy of Sciences: Geology 53:233-245. | 2004 | Climate; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Kieckbusch, D. K., M. S. Koch, J. E. Serafy, and W. T. Anderson. 2004. Trophic linkages among primary producers and consumers in fringing mangroves of subtropical lagoons. Bulletin of Marine Science 74:271-285. | 2004 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Caribbean | Algae; Invertebrates; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Substrate | |
| Kuguru, B. L., Y. D. Mgaya, M. C. Ohman, and G. M. Wagner. 2004. The reef environment and competitive success in the Corallimorpharia. Marine Biology 145:875-884. | 2004 | Tanzania | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, and W. R. Matzie. 2004. Anthropogenic nutrient enrichment of seagrass and coral reef communities in the Lower Florida Keys: Discrimination of local versus regional nitrogen sources. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 308:23-58. | 2004 | Global; Florida | Agriculture; Algae; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, C. S. Yentsch, M. M. Littler, D. S. Littler, and B. Kakuk. 2004. The relative importance of nutrient enrichment and herbivory on macroalgal communities near Norman's Pond Cay, Exumas Cays, Bahamas: A \natural\" enrichment experiment". Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 298:275-301. | 2004 | Bahamas | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Latypov, YU .Y A. 2004. Reef-building corals and reefs of Vietnam: 2. The Gulf of Tonkin. Russian Journal of Marine Biology 29. | 2004 | Vietnam | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Laws, E. A., D. Brown, and C. Peace. 2004. Coastal water quality in the Kihei and Lahaina districts of the island of Maui, Hawaiian Islands. Impacts from physical habitat and groundwater seepage: Implications for water quality standards. International Journal of Environment and Pollution 22:531-546. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Beaches & Nature Parks; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Lesser, M. P., C. H. Mazel, M. Y. Gorbunov, and P. G. Falkowski. 2004. Discovery of symbiotic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria in corals. Science 305:997-1000. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and B. L. Brooks. 2004. Extraordinary mound-building forms of Avrainvillea (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta): Their experimental taxonomy, comparative functional morphology and ecological strategies. Atoll Research Bulletin 26-Jan. | 2004 | South & Central America; Belize | Mangroves; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Loya, Y. 2004. Coral Reef Health and Diease. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. | 2004 | Review | Aquaculture; Discharges; Nutrients; Petroleum Spills; Stony Coral | |
| Loya, Y., H. Lubinevsky, M. Rosenfeld, and E. Kramarsky-Winter. 2004. Nutrient enrichment caused by in situ fish farms at Eilat, Red Sea is detrimental to coral reproduction. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49:344-353. | 2004 | Aquaculture; Nutrients | ||
| Mallela, J., C. T. Perry, and M. P. Haley. 2004. Reef morphology and community structure along a fluvial gradient, Rio Bueno, Jamaica. Caribbean Journal of Science 40:299-311. | 2004 | Jamaica | Discharges; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Martina, M., D. W. Hutmacher, and S. Valiyaveettil. 2004. Developing natural hard tissue as scaffolds for tissue repairs. Page 1024 in Transactions - 7th World Biomaterials Congress. | 2004 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Seastars | ||
| McClanahan, T. R., E. Sala, P. J. Mumby, and S. Jones. 2004. Phosphorus and nitrogen enrichment do not enhance brown frondose \macroalgae\" [2]". Marine Pollution Bulletin 48:196-199. | 2004 | Algae; Nutrients | ||
| McManus, J. W. and J. F. Polsenberg. 2004. Coral-algal phase shifts on coral reefs: Ecological and environmental aspects. Progress in Oceanography 60:263-279. | 2004 | Review; Model | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Mills, M. M. and K. P. Sebens. 2004. Ingestion and assimilation of nitrogen from benthic sediments by three species of coral. Marine Biology 145:1097-1106. | 2004 | Jamaica | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Mills, M. M., F. Lipschultz, and K. P. Sebens. 2004. Particulate matter ingestion and associated nitrogen uptake by four species of scleractinian corals. Coral Reefs 23:311-323. | 2004 | Cuba; Bermuda | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Munday, P. L. 2004. Habitat loss, resource specialization, and extinction on coral reefs. Global Change Biology 10:1642-1647. | 2004 | Global; Papua New Guinea | Coastal Development; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Nagelkerken, I. and G. Van Der Velde. 2004. Are Caribbean mangroves important feeding grounds for juvenile reef fish from adjacent seagrass beds? Marine Ecology Progress Series 274:143-151. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Antilles; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Nowak, R. 2004. Sewage nutrients fuel coral disease. New Scientist 181:13-Dec. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Agriculture; Algae; Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Okey, T.A., G.A. Vargo, S. Mackinson, M. Vasconcellos, B. Mahmoudie, and C.A. Meyer. 2004. Simulating community effects of sea floor shading by plankton blooms over the West Florida Shelf. Ecological Modelling 172:339-359. | 2004 | Florida | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invertebrates; Light; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production |
| Olivier, N., C. Carpentier, B. Martin-Garin, B. Lathuiliere, C. Gaillard, S. Ferry, P. Hantzpergue, and J. Geister. 2004. Coral-microbialite reefs in pure carbonate versus mixed carbonate-siliciclastic depositional environments: The example of the Pagny-sur-Meuse section (Upper Jurassic, northeastern France). Facies 50:229-255. | 2004 | France | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Palfalvi, S. 2004. Palaeoenvironments on a Middle Eocene carbonate ramp in the Vertes Mountains, Hungary. Hantkeniana 4:63-81. | 2004 | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | ||
| Pinazo, C., S. Bujan, P. Douillet, R. Fichez, C. Grenz, and A. Maurin. 2004. Impact of wind and freshwater inputs on phytoplankton biomass in the coral reef lagoon of New Caledonia during the summer cyclonic period: A coupled three-dimensional biogeochemical modeling approach. Coral Reefs 23:281-296. | 2004 | New Caledonia | Model | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Piniak, G. A. and F. Lipschultz. 2004. Effects of nutritional history on nitrogen assimilation in congeneric temperate and tropical scleractinian corals. Marine Biology 145:1085-1096. | 2004 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Rasheed, M., C. Wild, U. Franke, and M. Huettel. 2004. Benthic photosynthesis and oxygen consumption in permeable carbonate sediments at Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 59:139-150. | 2004 | Australia | Lab Study | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Reif, J. S., A. Bachand, A. A. Aguirre, D. L. Borjesson, L. Kashinsky, R. Braun, and G. Antonelis. 2004. Morphometry, hematology, and serum chemistry in the Hawaiian monk seal (Monachus schauinslandi). Marine Mammal Science 20:851-860. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
| Rodriguez, W. and I. C. Feller. 2004. Mangrove landscape characterization and change in Twin Cays, Belize using aerial photography and IKONOS satellite data. Atoll Research Bulletin 22-Jan. | 2004 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Nutrients |
| Scheffers, S. R., G. Nieuwland, R. P. M. Bak, and F. C. Van Duyl. 2004. Removal of bacteria and nutrient dynamics within the coral reef framework of Curacao (Netherlands Antilles). Coral Reefs 23:413-422. | 2004 | Antilles | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | |
| Schmidt, S., W. C. Dennison, G. J. Moss, and G. R. Stewart. 2004. Nitrogen ecophysiology of Heron Island, a subtropical coral cay of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Functional Plant Biology 31:517-528. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Algae; Marine Birds; Nutrients |
| Schrimm, M., R. Buscail, and M. Adjeroud. 2004. Spatial variability of the biogeochemical composition of surface sediments in an insular coral reef ecosystem: Moorea, French Polynesia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 60:515-528. | 2004 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Schwindt, E., C. G. De Francesco, and O. O. Iribarne. 2004. Individual and reef growth of the invasive reef-building polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus in a south-western Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 84:987-993. | 2004 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Sealey, K. S. 2004. Large-scale ecological impacts of development on tropical islands systems: Comparison of developed and undeveloped islands in the central Bahamas. Bulletin of Marine Science 75:295-320. | 2004 | Bahamas | Algae; Coastal Development; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Smith, J. E., C. M. Smith, P. S. Vroom, K. L. Beach, and S. Miller. 2004. Nutrient and growth dynamics of Halimeda tuna on Conch Reef, Florida Keys: Possible influence of internal tides on nutrient status and physiology. Limnology and Oceanography 49:1923-1936. | 2004 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients |
| Stambler, N. and Z. Dubinsky. 2004. Stress effects on metabolism and photosynthesis of hermatypic corals. Pages 195-215 in E. Rosenberg and Y. Loya, editors. Coral health and disease. Springer, Berlin, Germany. | 2004 | Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Stiger, V., E. Deslandes, and C. E. Payri. 2004. Phenolic contents of two brown algae, Turbinaria ornata and Sargassum mangarevense on Tahiti (French Polynesia): Interspecific, ontogenic and spatio-temporal variations. Botanica Marina 47:402-409. | 2004 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | ||
| Sutherland, K. P., J. W. Porter, and C. Torres. 2004. Disease and immunity in Caribbean and Indo-Pacific zooxanthellate corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 266:273-302. | 2004 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Review | Cyanobacteria; Invertebrates; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Tibbetts, J. 2004. The state of the oceans, part 2: delving deeper into the sea's bounty. Environmental Health Perspectives 112:A472-481. | 2004 | Global | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Biomedical Research Policies; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Uthicke, S., D. Welch, and J. A. H. Benzie. 2004. Slow growth and lack of recovery in overfished holothurians on the Great Barrier Reef: Evidence from DNA fingerprints and repeated large-scale surveys. Conservation Biology 18:1395-1404. | 2004 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Echinoderms; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Nutrients |
| van Beukering, P. J. H. and H. S. J. Cesar. 2004. Ecological economic modeling of coral reefs: Evaluating tourist overuse at Hanauma Bay and algae blooms at the Kīhei Coast, Hawai'i. Pacific Science 58:243-260. | 2004 | Model | Algae; Discharges; Hotel & Food Services; Mitigation; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Vennin, E., J.-M. Rouchy, C. Chaix, M.-M. Blanc-Valleron, A. Caruso, and V. Rommevau. 2004. Paleoecological constraints on reef-coral morphologies in the Tortonian - Early Messinian of the Lorca Basin, SE Spain. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 213:163-185. | 2004 | Global; Spain | Algae; Coralline Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Wielgus, J., N. E. Chadwick-Furman, and Z. Dubinsky. 2004. Coral cover and partial mortality on anthropogenically impacted coral reefs at Eilat, northern Red Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 48:248-253. | 2004 | Cuba | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Wild, C., M. Huettel, A. Klueter, S. G. Kremb, M. Y. M. Rasheed, and B. B. Jorgensen. 2004. Coral mucus functions as an energy carrier and particle trap in the reef ecosystem. Nature 428:66-70. | 2004 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wild, C., R. Tollrian, and M. Huettel. 2004. Rapid recycling of coral mass-spawning products in permeable reef sediments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 271:159-166. | 2004 | Australia | Lab Study | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Yang, Z. B. and I. J. Hodgkiss. 2004. Hong Kong's worst \red tide\" - Causative factors reflected in a phytoplankton study at Port Shelter station in 1998". Harmful Algae 3:149-161. | 2004 | China | Climate; Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Yentsch, C. S., C. M. Yentsch, D. A. Phinney, B. E. Lapointe, and S. F. W. Yentsch. 2004. The odyssey of new production. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 300:15-30. | 2004 | Florida; Bahamas | Lab Study; Remote Sensing | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Zooxanthellae |
| Zabielski, R. 2004. Reefs in experimental gastroenterology--cyclic activities of the gastrointestinal tract. Journal of physiology and pharmacology : an official journal of the Polish Physiological Society 0:19-32. | 2004 | Nutrients | ||
| Allen, J. P., M. Nelson, and A. Alling. 2003. The legacy of biosphere 2 for the study of biospherics and closed ecological systems. Advances in Space Research 31:1629-1639. | 2003 | Global; Columbia | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Model | Agriculture; Artificial Habitat; CO2; Nutrients; Pathogens; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge |
| Barker, S., J. A. Higgins, H. Elderfield, I. N. McCave, and J. G. Shepherd. 2003. The future of the carbon cycle: Review, calcification response, ballast and feedback on atmospheric CO2. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 361:1977-1999. | 2003 | Review; Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Barr, N. G. and T. A. V. Rees. 2003. Nitrogen status and metabolism in the green seaweed Enteromorpha intestinalis: An examination of three natural populations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 249:133-144. | 2003 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Nutrients | |
| Bassim, K. M. and P. W. Sammarco. 2003. Effects of temperature and ammonium on larval development and survivorship in a scleractinian coral (Diploria strigosa). Marine Biology 142:241-252. | 2003 | Florida | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Batabyal, A. A., J. R. Kahn, and R. V. O�Neill. 2003. On the scarcity value of ecosystem services. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management 46:334-352. | 2003 | Nutrients | ||
| Beach, K., L. Walters, P. Vroom, C. Smith, J. Coyer, and C. Hunter. 2003. Variability in the ecophysiology of Halimeda spp. (Chlorophyta, bryopsidales) on Conch Reef, Florida Keys, USA. Journal of Phycology 39:633-643. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Bongiorni, L., S. Shafir, and B. Rinkevich. 2003. Effects of particulate matter released by a fish farm (Eilat, Red Sea) on survival and growth of Stylophora pistillata coral nubbins. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:1120-1124. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Bongiorni, L., S. Shafir, D. Angel, and B. Rinkevich. 2003. Survival, growth and gonad development of two hermatypic corals subjected to in situ fish-farm nutrient enrichment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 253:137-144. | 2003 | Aquaculture; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Bruno, J. F., L. E. Petes, C. D. Harvell, and A. Hettinger. 2003. Nutrient enrichment can increase the severity of coral diseases. Ecology Letters 6:1056-1061. | 2003 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Stony Coral |
| Cheevaporn, V. and P. Menasveta. 2003. Water pollution and habitat degradation in the Gulf of Thailand. Marine Pollution Bulletin 47:43-51. | 2003 | Thailand | Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Plankton; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Chen, B., G. X. Pei, K. Wang, D. Jin, K. H. Wei, and G. H. Ren. 2003. The method of accelerating osteanagenesis and revascularization of tissue engineered bone in big animal in vivo. Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan xue bao. Acta Academiae Medicinae Sinicae 25:26-31. | 2003 | Model; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Cleveland, A. and W. L. Montgomery. 2003. Gut characteristics and assimilation efficiencies in two species of herbivorous damselfishes (Pomacentridae: Stegastes dorsopunicans and S. planifrons). Marine Biology 142:35-44. | 2003 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Corda, L. and M. Brandano. 2003. Aphotic zone carbonate production on a Miocene ramp, Central Apennines, Italy. Sedimentary Geology 161:55-70. | 2003 | Model | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Cruz-Pinon, G., J. P. Carricart-Ganivet, and J. Espinoza-Avalos. 2003. Monthly skeletal extension rates of the hermatypic corals Montastraea annularis and Montastraea faveolata : biological and environmental controls. Marine Biology 143:491-500. | 2003 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Daby, D. 2003. Some quantitative aspects of seagrass ecology in a coastal lagoon of Mauritius. Marine Biology 142:193-203. | 2003 | Mauritius | GIS & Maps | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Davidson, K., M. Hamnett, and C. Minato. 2003. The first four years: Hawaii Coral Reef Initiative Research Program. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients |
| Della Porta, G., J. A. M. Kenter, J. R. Bahamonde, A. Immenhauser, and E. Villa. 2003. Microbial boundstone dominated carbonate slope (Upper Carboniferous, N Spain): Microfacies, Lithofacies distribution and stratal geometry. Facies 175-208. | 2003 | Japan; Spain | Model | Algae; Nutrients; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Diaz-Pulido, G. and L. J. McCook. 2003. Relative roles of herbivory and nutrients in the recruitment of coral-reef seaweeds. Ecology 84:2026-2033. | 2003 | Australia | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| Dizon, R. M. and H. T. Yap. 2003. Metabolic changes and compositional shifts in nutrient-enriched tropical reef sediment communities [Cambios metabolicos y de composicion en comunidades de sedimentos de arrecife tropical enriquecidos con nutrientes]. Scientia Marina 67:117-127. | 2003 | Philippines | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Finkl, C. W. and R. H. Charlier. 2003. Sustainability of Subtropical Coastal Zones in Southeastern Florida: Challenges for Urbanized Coastal Environments Threatened by Development, Pollution, Water Supply, and Storm Hazards. Journal of Coastal Research 19:934-943. | 2003 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Cuba | Model | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Remediation; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water; Wetlands |
| Fourqurean, J. W., J. N. Boyer, M. J. Durako, L. N. Hefty, and B. J. Peterson. 2003. Forecasting response of seagrass distributions to changing water quality using monitoring data. Ecological Applications 13:474-489. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fu, F.-X. and P. R. F. Bell. 2003. Effect of salinity on growth, pigmentation, N2 fixation and alkaline phosphatase activity of cultured Trichodesmium sp. Marine Ecology Progress Series 257:69-76. | 2003 | Australia | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Fu, F.-X. and P. R. F. Bell. 2003. Factors affecting N2 fixation by the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium sp. GBRTRLI101. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 45:203-209. | 2003 | Australia; Europe | Nutrients | |
| Garrison, V. H., E. A. Shinn, W. T. Foreman, D. W. Griffin, C. W. Holmes, C. A. Kellogg, M. S. Majewski, L. L. Richardson, K. B. Ritchie, and G. W. Smith. 2003. African and Asian dust: From desert soils to coral reefs. Bioscience 53:469-480. | 2003 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens | ||
| Greenstein, B. J. and J. M. Pandolfi. 2003. Taphonomic alteration of reef corals: Effects of reef environment and coral growth form II: The Florida Keys. Palaios 18:495-509. | 2003 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Index or Indicator | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Grenz, C., L. Denis, G. Boucher, L. Chauvaud, J. Clavier, R. Fichez, and O. Pringault. 2003. Spatial variability in Sediment Oxygen Consumption under winter conditions in a lagoonal system in New Caledonia (South Pacific). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 33-47. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Cuba; New Caledonia | Lab Study | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Griggs, E. M., L. R. Kump, and J. K. Bohlke. 2003. The fate of wastewater-derived nitrate in the subsurface of the Florida Keys: Key Colony Beach, Florida. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 58:517-539. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| Gross, E. M. 2003. Allelopathy of aquatic autotrophs. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 22:313-339. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| Grover, R., J.-F. Maguer, D. Allemand, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2003. Nitrate uptake in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnology and Oceanography 48:2266-2274. | 2003 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Gupta, L. P. and H. Kawahata. 2003. Biogeochemical processes and labile composition of settling particulate organic matter in the south-west Pacific Ocean. Marine and Freshwater Research 54:259-270. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Hoitink, A. J. F. 2003. Physics of coral reef systems in a shallow tidal embayment. Nederlandse Geografische Studies 313:11-141. | 2003 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Discharges; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Salinity; Sediment; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hovland, M. and M. Risk. 2003. Do Norwegian deep-water coral reefs rely on seeping fluids? Marine Geology 198:83-96. | 2003 | Norway | Index or Indicator | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Howarth, R. W., R. Marino, and D. Scavia. 2003. Nutrient pollution in coastal waters: priority topics for an integrated national research program for the United States. | 2003 | Nutrients | ||
| Huang, L., Y. Tan, X. Song, X. Huang, H. Wang, S. Zhang, J. Dong, and R. Chen. 2003. The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin 47:180-186. | 2003 | China | Fish; Mangroves; Molluscs; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Plankton; Shoreline Protection; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Jimenez, C. and J. Cortes. 2003. Growth of seven species of scleractinian corals in an upwelling environment of the eastern Pacific (Golfo de Papagayo, Costa Rica). Bulletin of Marine Science 72:187-198. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica | Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Johnson, J. E. and R. T. Hill. 2003. Sediment microbes of deep-sea bioherms on the northwest shelf of Australia. Microbial Ecology 46:55-61. | 2003 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Remediation; Sediment |
| Kemp, A. E. S., D. N. Langhorne, I. J. Fairchild, T. S. Schmitt, and E. G. Nisbet. 2003. Evidence for abrupt climate changes in annually laminated marine sediments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 361:1851-1870. | 2003 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Kirke, B. 2003. Enhancing fish stocks with wave-powered artificial upwelling. Ocean and Coastal Management 46:901-915. | 2003 | Australia | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton; Shoreline Protection | |
| Kirkland, D. W. 2003. An explanation for the varves of the Castile evaporites (Upper Permian), Texas and New Mexico, USA. Sedimentology 50:899-920. | 2003 | South & Central America; Mexico | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Lane, P. V. Z., S. L. Smith, H. C. Graber, and G. L. Hitchcock. 2003. Mesoscale circulation and the surface distribution of copepods near the South Florida Keys. Bulletin of Marine Science 72:18-Jan. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Langdon, C., W. S. Broecker, D. E. Hammond, E. Glenn, K. Fitzsimmons, S. G. Nelson, T.-H. Peng, I. Hajdas, and G. Bonani. 2003. Effect of elevated CO2 on the community metabolism of an experimental coral beef. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 17:1-Nov. | 2003 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | ||
| Langer, M. R. and J. H. Lipps. 2003. Foraminiferal distribution and diversity, Madang Reef and Lagoon, Papua New Guinea. Coral Reefs 22:143-154. | 2003 | Papua New Guinea | Index or Indicator | Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Leichter, J.J., H.L. Stewart, S. Miller. 2003. Episodic nutrient transport to Florida coral reefs. Limnology and Oceanography 48:1394-1407. | 2003 | Florida | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Lemmens, S. 2003. Periphyton collectors as a tool to measure environmental performance of ocean outlets. Water Science and Technology 47:125-131. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Chemical Use Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Wastewater Discharge |
| Linton, D. M. and G. F. Warner. 2003. Biological indicators in the Caribbean coastal zone and their role in integrated coastal management. Ocean and Coastal Management 46:261-276. | 2003 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Review; Index or Indicator | Climate; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Mitigation; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Loya, Y. and E. Kramarsky-Winter. 2003. In situ eutrophication caused by fish farms in the nothern Gulf of Eilat (Aqaba) is benificial for its coral reefs: A critique. Marine Ecology Progress Series 261:299-303. | 2003 | Aquaculture; Nutrients | ||
| McClanahan, T. R., E. Sala, P. A. Stickels, B. A. Cokos, A. C. Baker, C. J. Starger, and S. H. Jones IV. 2003. Interaction between nutrients and herbivory in controlling algal communities and coral condition on Glover's Reef, Belize. Marine Ecology Progress Series 261:135-147. | 2003 | South & Central America; Belize | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Turf Algae |
| McLaughlin, C. J., C. A. Smith, R. W. Buddemeier, J. D. Bartley, and B. A. Maxwell. 2003. Rivers, runoff, and reefs. Global and Planetary Change 39:191-199. | 2003 | Global | GIS & Maps | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Merks, R., A. Hoekstra, J. Kaandorp, and P. Sloot. 2003. Models of coral growth: Spontaneous branching, compactification and the Laplacian growth assumption. Journal of Theoretical Biology 224:153-166. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Meyer, C. P. 2003. Molecular systematics of cowries (Gastropoda: Cypraeidae) and diversification patterns in the tropics. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 79:401-459. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Mizuno, H., T. K. Mal, K. I. Tong, R. Ando, T. Furuta, M. Ikura, and A. Miyawaki. 2003. Photo-induced peptide cleavage in the green-to-red conversion of a fluorescent protein. Molecular Cell 12:1051-1058. | 2003 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Muslim, I. and G. Jones. 2003. The seasonal variation of dissolved nutrients, chlorophyll a and suspended sediments at Nelly Bay, Magnetic Island. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 57:445-455. | 2003 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Nordemar, I., M. Nystrom, and R. Dizon. 2003. Effects of elevated seawater temperature and nitrate enrichment on the branching coral Porites cylindrica in the absence of particulate food. Marine Biology 142:669-677. | 2003 | Global | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Pile, A. J., A. Grant, R. Hinde, and M. A. Borowitzka. 2003. Heterotrophy on ultraplankton communities is an important source of nitrogen for a sponge-rhodophyte symbiosis. Journal of Experimental Biology 206:4533-4538. | 2003 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | ||
| Piniak, G. A., F. Lipschultz, and J. McClelland. 2003. Assimilation and partitioning of prey nitrogen within two anthozoans and their endosymbiotic zooxanthellae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 262:125-136. | 2003 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Rao, V. P., L. Montaggioni, K. H. Vora, F. Almeida, K. M. Rao, and G. Rajagopalan. 2003. Significance of relic carbonate deposits along the central and southwestern margin of India for late Quaternary environmental and sea level changes. Sedimentary Geology 159:95-111. | 2003 | India | Index or Indicator | Algae; Coralline Algae; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Rasheed, M., M. I. Badran, and M. Huettel. 2003. Particulate matter filtration and seasonal nutrient dynamics in permeable carbonate and silicate sands of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Coral Reefs 22:167-177. | 2003 | Cuba | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Rayment, G. E. 2003. Water quality in sugar catchments of Queensland. Water Science and Technology 48:35-47. | 2003 | Australia | Review; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ribes, M., R. Coma, M. J. Atkinson, and R. A. Kinzie III. 2003. Particle removal by coral reef communities: Picoplankton is a major source of nitrogen. Marine Ecology Progress Series 257:13-23. | 2003 | Nutrients; Plankton; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | ||
| Richardson, L. L. and K. G. Kuta. 2003. Ecological physiology of the black band disease cyanobacterium Phormidium corallyticum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 43:287-298. | 2003 | Europe | Lab Study | Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production |
| Rollon, R. N., E. D. De Ruyter Van Steveninck, and W. Van Vierssen. 2003. Spatio-temporal variation in sexual reproduction of the tropical seagrass Enhalus acoroides (L.f.) Royle in Cape Bolinao, NW Philippines. Aquatic Botany 76:339-354. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Philippines | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Saadoun, M., B. Bessais, N. Mliki, M. Ferid, H. Ezzaouia, and R. Bennaceur. 2003. Formation of luminescent (NH4)2SiF6 phase from vapour etching-based porous silicon. Applied Surface Science 210:240-248. | 2003 | Nutrients; Substrate | ||
| Steven, A. D. L. and M. J. Atkinson. 2003. Nutrient uptake by coral-reef microatolls. Coral Reefs 22:197-204. | 2003 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Stow, C. A., C. Roessler, M. E. Borsuk, J. D. Bowen, and K. H. Reckhow. 2003. Comparison of Estuarine Water Quality Models for Total Maximum Daily Load Development in Neuse River Estuary. Journal of Water Resources Planning and Management 307-314. | 2003 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Tada, K., K. Sakai, Y. Nakano, A. Takemura, and S. Montani. 2003. Size-fractionated phytoplankton biomass in coral reef waters off Sesoko Island, Okinawa, Japan. Journal of Plankton Research 25:991-997. | 2003 | Japan | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Thattai, D. V. and B. Kjerfve. 2003. Numerical modeling of tidal and wind-driven circulation in the Meso-American barrier reef lagoon, Western Caribbean. in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2003 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Model | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Thattai, D., B. Kjerfve, and W. D. Heyman. 2003. Hydrometeorology and variability of water discharge and sediment load in the inner gulf of Honduras, western Caribbean. Journal of Hydrometeorology 4:985-995. | 2003 | South & Central America; Honduras; Caribbean | Model; Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Thorburn, P. J., J. S. Biggs, K. L. Weier, and B. A. Keating. 2003. Nitrate in groundwaters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal Northeastern Australia. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 94:49-58. | 2003 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Van De Schootbrugge, B., O. Kuhn, T. Adatte, P. Steinmann, and K. Follmi. 2003. Decoupling of P- And Corg-burial following Early Cretaceous (Valanginian-Hauterivian) platform drowning along the NW Tethyan margin. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 199:315-331. | 2003 | Global | GIS & Maps | Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Van Trump, J. 2003. Protecting the 'rainforests of the sea': Creating the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands coral reef ecosystem reserve by executive order. Penn State Environmental Law Review 11:273-293. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Versteegh, E. 2003. Migrations in tropical reef fish. | 2003 | Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | ||
| Vroom, P. S., C. M. Smith, J. A. Coyer, L. J. Walters, C. L. Hunter, K. S. Beach, and J. E. Smith. 2003. Field biology of Halimeda tuna (Bryopsidales, Chlorophyta) across a depth gradient: Comparative growth, survivorship, recruitment, and reproduction. Hydrobiologia 501:149-166. | 2003 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients |
| Wielgus, J., D. Glassom, and L. Fishelson. 2003. Long-term persistence of low coral cover and abundance on a disturbed coral reef flat in the northern Red Sea. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 297:31-41. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring | Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Wilson, G., A. R. G. Price, T. Huntington, and S. C. Wilson. 2003. Environmental status of Yemen's Gulf of Aden coast determined from rapid field assessment and satellite imagery. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 6:119-129. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Seagrasses | |
| Yamamuro, M., H. Kayanne, H. Yamano. 2003. N of seagrass leaves for monitoring anthropogenic nutrient increases in coral reef ecosystems. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:452-458. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Yap, H. T. and R. A. Molina. 2003. Comparison of coral growth and survival under enclosed, semi-natural conditions and in the field. Marine Pollution Bulletin 46:858-864. | 2003 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Young, G. C. and I. C. Potter. 2003. Do the characteristics of the ichthyoplankton in an artificial and a natural entrance channel of a large estuary differ? Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 56:765-779. | 2003 | Australia | Fish; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Aleksandrov, B. G., G. G. Minicheva, and T. V. Strikalenko. 2002. Ecological aspects of artificial reef construction using scrap tires. Russian Journal of Marine Biology 28:120-126. | 2002 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Plankton; Substrate | ||
| Al-Lihaibi, S. S., A. Al-Sofyani, G. R. Niaz, V. U. Ahmad, M. Noorwala, and F. Vali Mohammad. 2002. Long-chain wax esters and diphenylamine in fire coral Millepora dichotoma and Millepora platyphylla from Saudi Red Sea Coast. Scientia Marina 66:95-102. | 2002 | Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Stony Coral | ||
| Angel, D. L., N. Eden, S. Breitstein, A. Yurman, T. Katz, and E. Spanier. 2002. In situ biofiltration: A means to limit the dispersal of effluents from marine finfish cage aquaculture. Hydrobiologia 469:10-Jan. | 2002 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Bivalves; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Sponges; Tunicates | ||
| Annis, E. R. and C. B. Cook. 2002. Alkaline phosphatase activity in symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae) as a biological indicator of environmental phosphate exposure. Marine Ecology Progress Series 245:20-Nov. | 2002 | Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Belliveau, S. A. and V. J. Paul. 2002. Effects of herbivory and nutrients on the early colonization of crustose coralline and fleshy algae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 232:105-114. | 2002 | Guam | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Benayahu, Y., T. Yosief, and M. H. Schleyer. 2002. Soft corals (octocorallia, alcyonacea) of the southern Red Sea. Israel Journal of Zoology 48:273-283. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Octocoral; Salinity |
| Buck, B. H., H. Rosenthal, and U. Saint-Paul. 2002. Effect of increased irradiance and thermal stress on the symbiosis of Symbiodinium microadriaticum and Tridacna gigas. Aquatic Living Resource 15:107-117. | 2002 | Australia | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Carruthers, T. J. B., W. C. Dennison, B. J. Longstaff, M. Waycott, E. G. Abal, L. J. McKenzie, and W. J. Lee Long. 2002. Seagrass habitats of northeast Australia: Models of key processes and controls. Bulletin of Marine Science 71:1153-1169. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Chabanet, P., E. Tessier, P. Durville, T. Mulochau, and F. Rene. 2002. Fish communities of Geyser and Zelee coral banks (Western Indian Ocean) [Peuplement ichtyologique des bancs de Geyser et Zelee (Ocean Indien Occidental)]. Cybium 26:26-Nov. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Mozambique; India | Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Chazottes, V., T. Le Campion-Alsumard, M. Peyrot-Clausade, and P. Cuet. 2002. The effects of eutrophication-related alterations to coral reef communities on agents and rates of bioerosion (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean). Coral Reefs 21:375-390. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral | |
| Coutis, P. F. and J. H. Middleton. 2002. The physical and biological impact of a small island wake in the deep ocean. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 49:1341-1361. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Cox, E. F. and S. Ward. 2002. Impact of elevated ammonium on reproduction in two Hawaiian scleractinian corals with different life history patterns. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:1230-1235. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Danovaro, R., C. Gambi, A. Mazzola, and S. Mirto. 2002. Influence of artificial reefs on the surrounding infauna: Analysis of meiofauna. ICES Journal of Marine Science 59. | 2002 | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Davis, R. A., A. R. Carroll, and R. J. Quinn. 2002. Lepadins F-H, new cis-decahydroquinoline alkaloids from the Australian ascidian Aplidium tabascum. Journal of Natural Products 65:454-457. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Nutrients |
| Davy, S. K., D. A. Trautman, M. A. Borowitzka, and R. Hinde. 2002. Ammonium excretion by a symbiotic sponge supplies the nitrogen requirements of its rhodophyte partner. Journal of Experimental Biology 205:3505-3511. | 2002 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| De Loma, T. L., C. Conand, M. Harmelin-Vivien, and E. Ballesteros. 2002. Food selectivity of Tripneustes gratilla (L.) (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) in oligotrophic and nutrient-enriched coral reefs at La Reunion (Indian Ocean). Bulletin of Marine Science 70:927-938. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sea Urchins |
| De Mol, B., P. Van Rensbergen, S. Pillen, K. Van Herreweghe, D. Van Rooij, A. McDonnell, V. Huvenne, M. Ivanov, R. Swennen, and J. P. Henriet. 2002. Large deep-water coral banks in the Porcupine Basin, southwest of Ireland. Marine Geology 188:193-231. | 2002 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Diaz-Pulido, G. and J. Garzon-Ferreira. 2002. Seasonality in algal assemblages on upwelling-influenced coral reefs in the Colombian Caribbean. Botanica Marina 45:284-292. | 2002 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Turf Algae | |
| Diekmann, O. E., R. P. M. Bak, L. Tonk, W. T. Stam, and J. L. Olsen. 2002. No habitat correlation of zooxanthellae in the coral genus Madracis on a Curacao reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 227:221-232. | 2002 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Review | Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Dovlatian, A. A. 2002. Surgical treatment of complicated forms of coral-like nephrolithiasis [Operativnoe lechenie oslozhnennykh form korallovidnogo nefrolitiaza.]. Urologiia (Moscow, Russia : 1999) 4:23-27. | 2002 | Nutrients | ||
| Drexler, J. Z. and E. W. De Carlo. 2002. Source water partitioning as a means of characterizing hydrologic function in mangroves. Wetlands Ecology and Management 10:103-113. | 2002 | Micronesia | Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Dunne Jr., W. M. 2002. Bacterial adhesion: Seen any good biofilms lately? Clinical Microbiology Reviews 15:155-166. | 2002 | Model | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Plankton | |
| Dupraz, C. and A. Strasser. 2002. Nutritional modes in coral-microbialite reefs (Jurassic, Oxfordian, Switzerland): Evolution of trophic structure as a response to environmental change. Palaios 17:449-471. | 2002 | Model | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Edinger, E. N., P. Copper, M. J. Risk, and W. Atmojo. 2002. Oceanography and reefs of recent and Paleozoic tropical epeiric seas. Facies 127-150. | 2002 | Java | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Fourqurean, J.W., J.C. Zieman. 2002. Nutrient Content of the Seagrass Thalassia Testudinum Reveals Regional Patterns of Relative Availability of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Florida Keys USA. Biogeochemistry 61:229-245. | 2002 | Florida | Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Freitas, C. E. C., M. Petrere Jr, and M. A. P. Abuabara. 2002. Artificial reefs and their effects on fish assemblages in a Brazilian reservoir and Tailrace. Ecohydrology and Hydrobiology 2:305-313. | 2002 | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Gartner, A., P. Lavery, and A. J. Smit. 2002. Use of δ15N signatures of different functional forms of macroalgae and filter-feeders to reveal temporal and spatial patterns in sewage dispersal. Marine Ecology Progress Series 235:63-73. | 2002 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Sponges; Wastewater Discharge |
| George, A. D. and N. Chow. 2002. The depositional record of the Frasnian/Famennian boundary interval in a fore-reef succession, Canning Basin, western Australia. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 181:347-374. | 2002 | Global; Australia | Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Gleason, S. M. and K. C. Ewel. 2002. Organic matter dynamics on the forest floor of a Micronesian mangrove forest: An investigation of species composition shifts. Biotropica 34:190-198. | 2002 | Micronesia | Mangroves; Nutrients | |
| Gong, Y., B. Li, Y. Si, and Y. Wu. 2002. Late Devonian red tide and mass extinction. Chinese Science Bulletin 47:1138-1144. | 2002 | China | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Grottoli, A. G. 2002. Effect of light and brine shrimp on skeletal δ13C in the Hawaiian coral Porites compressa: A tank experiment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 66:1955-1967. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Grover, R., J.-F. Maguer, S. Reynaud-Vaganay, and C. Ferrier-Pages. 2002. Uptake of ammonium by the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: Effect of feeding, light, and ammonium concentrations. Limnology and Oceanography 47:782-790. | 2002 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Gullstrom, M., M. De La Torre Castro, S. O. Bandeira, M. Bjork, M. Dahlberg, N. Kautsky, P. Ronnback, and M. C. Ohman. 2002. Seagrass ecosystems in the Western Indian Ocean. Ambio 31:588-596. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; Tanzania; Mozambique; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius; Reunion; India; South Africa; France | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Hearn, C. J., M. J. Atkinson, and J. L. Falter. 2002. Response to the comment by G. Symonds, K.P. Black, and I.R. Young on \A physical derivation of nutrient-uptake rates in coral reefs: Effects of roughness and waves\"". Coral Reefs 21:319-321. | 2002 | Nutrients | ||
| Heikoop, J. M., D. D. Hickmott, M. J. Risk, C. K. Shearer, and V. Atudorei. 2002. Potential climate signals from the deep-sea gorgonian coral Primnoa resedaeformis. Hydrobiologia 471:117-124. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sea Temperatures | |
| Houghton, R.A. 2002. Magnitude, distribution and causes of terrestrial carbon sinks and some implications for policy. Climate Policy 2:71-88. | 2002 | Review | Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hovland, M., S. Vasshus, A. Indreeide, L. Austdal, and O. Nilsen. 2002. Mapping and imaging deep-sea coral reefs off Norway, 1982-2000. Hydrobiologia 471:13-17. | 2002 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Norway | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pipelines; Sediment |
| Hutchings, P. A. and M. Peyrot-Clausade. 2002. The distribution and abundance of boring species of polychaetes and sipunculans in coral substrates in French Polynesia. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 269:101-121. | 2002 | Algae; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Substrate | ||
| Jompa, J. and L. J. McCook. 2002. The effects of nutrients and herbivory on competition between a hard coral (Porites cylindrica) and a brown alga (Lobophora variegata). Limnology and Oceanography 47:527-534. | 2002 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Kaiser, M. J., J. S. Collie, S. J. Hall, S. Jennings, and I. R. Poiner. 2002. Modification of marine habitats by trawling activities: Prognosis and solutions. Fish and Fisheries 3:114-136. | 2002 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Kamermans, P., M. A. Hemminga, J. F. Tack, M. A. Mateo, N. Marba, M. Mtolera, J. Stapel, A. Verheyden, and T. Van Daele. 2002. Groundwater effects on diversity and abundance of lagoonal seagrasses in Kenya and on Zanzibar Island (East Africa). Marine Ecology Progress Series 231:75-83. | 2002 | Kenya | Model | Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Kamp-Nielsen, L., J. E. Vermaat, I. Wesseling, J. Borum, and O. Geertz-Hansen. 2002. Sediment properties along gradients of siltation in south-east Asia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 54:127-138. | 2002 | Thailand; China; Philippines | Index or Indicator | Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Lambert, G. 2002. Nonindigenous Ascidians in tropical waters. Pacific Science 56:291-298. | 2002 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Palau; Guam; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Ballast Discharge; Coastal Defense; Docks & Marinas; Invasive Species; Military; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Rigs; Plankton; Ports & Harbors; Salinity |
| Lee, S. Y., C. J. Kwon, K.-S. Lee, and C. I. Choi. 2002. Distribution of eelgrass, Zostera marina L. on coasts of the Korean Peninsula: Preliminary study for eelgrass restoration. Ocean and Polar Research 24:55-61. | 2002 | Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Lescinsky, H. L., E. Edinger, and M. J. Risk. 2002. Mollusc shell encrustation and bioerosion rates in a modern Epeiric Sea: Taphonomy experiments in the Java Sea, Indonesia. Palaios 17:171-191. | 2002 | Java; Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Lison de Loma, T. and M. L. Harmelin-Vivien. 2002. Summer fluxes of organic carbon and nitrogen through a damselfish resident, Stegastes nigricans (Lacepede, 1803), on a coral reef flat at La Reunion (Indian Ocean). Marine and Freshwater Research 53:169-174. | 2002 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Discharges; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Marnane, M. J. and D. R. Bellwood. 2002. Diet and nocturnal foraging in cardinalfishes (Apogonidae) at One Tree Reef, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 231:261-268. | 2002 | Australia | Fish; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Marshall, J. F. and M. T. McCulloch. 2002. An assessment of the Sr/Ca ratio in shallow water hermatypic corals as a proxy for sea surface temperature. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 66:3263-3280. | 2002 | Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Mastandrea, A., F. Muto, C. Neri, C. A. Papazzoni, E. Perri, and F. Russo. 2002. Deep-water coral banks: An example from the \Calcare di Mendicino\" (Upper Miocene, Northern Calabria, Italy)". Facies 27-42. | 2002 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| McClanahan, T. R. 2002. The near future of coral reefs. Environmental Conservation 29:460-483. | 2002 | Global | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Resource Use Management; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae | |
| McClanahan, T. R., B. A. Cokos, and E. Sala. 2002. Algal growth and species composition under experimental control of herbivory, phosphorus and coral abundance in Glovers Reef, Belize. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:441-451. | 2002 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| McClanahan, T., N. Polunin, and T. Done. 2002. Ecological states and the resilience of coral reefs. Conservation Ecology 6. | 2002 | Global | Review | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Mellors, J., H. Marsh, T. J. B. Carruthers, and M. Waycott. 2002. Testing the sediment-trapping paradigm of seagrass: Do seagrasses influence nutrient status and sediment structure in tropical intertidal environments? Bulletin of Marine Science 71:1215-1226. | 2002 | Australia | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Mitchell, S. F. 2002. Palaeoecology of corals and rudists in mixed volcaniclastic-carbonate small-scale rhythms (Upper Cretaceous, Jamaica). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 186:237-259. | 2002 | Jamaica | Algae; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Muhando, C. A., B. L. Kuguru, G. M. Wagner, N. E. Mbije, and M. C. Ohman. 2002. Environmental effects on the distribution of corallimorpharians in Tanzania. Ambio 31:558-561. | 2002 | Tanzania | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Mwashote, B. M. and I. O. Jumba. 2002. Quantitative aspects of inorganic nutrient fluxes in the Gazi Bay (Kenya): Implications for coastal ecosystems. Marine Pollution Bulletin 44:1194-1205. | 2002 | Kenya | Discharges; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Neil, D. T., A. R. Orpin, P. V. Ridd, and B. Yu. 2002. Sediment yield and impacts from river catchments to the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Marine and Freshwater Research 53:733-752. | 2002 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Pari, N., M. Peyrot-Clausade, and P. A. Hutchings. 2002. Bioerosion of experimental substrates on high islands and atoll lagoons (French Polynesia) during 5 years of exposure. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 276:109-127. | 2002 | Boring Sponges; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Substrate | ||
| Petrichtcheva, N. V., C. Duque, A. Duenas, S. Zea, N. Hara, and Y. Fujimoto. 2002. New nitrogenous eudesmane-type compounds isolated from the Caribbean sponge Axinyssa ambrosia. Journal of Natural Products 65:851-855. | 2002 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Poff, N. L., M. M. Brinson, and J. W. Day. 2002. Aquatic ecosystems & global climate change. | 2002 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Fish; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Pomar, L., A. Obrador, and H. Westphal. 2002. Sub-wavebase cross-bedded grainstones on a distally steepened carbonate ramp, Upper Miocene, Menorca, Spain. Sedimentology 49:139-169. | 2002 | Spain | Algae; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Precht, W. F., A. W. Bruckner, R. B. Aronson, and R. J. Bruckner. 2002. Endangered acroporid corals of the Caribbean. Coral Reefs 21:41-42. | 2002 | South & Central America; Florida; Bahamas; Caribbean | Algae; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Regulations; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Racki, G., M. Racka, H. Matyja, and X. Devleeschouwer. 2002. The Frasnian/Famennian boundary interval in the South Polish-Moravian shelf basins: Integrated event-stratigraphical approach. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 181:251-297. | 2002 | Poland | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Rasheed, M., M. I. Badran, C. Richter, and M. Huettel. 2002. Effect of reef framework and bottom sediment on nutrient enrichment in a coral reef of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 239:277-285. | 2002 | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Reckhow, Kenneth H.; Borsuk, Mark E.; Stow, Craig A. 2002. Adaptive Implementation Of Tmdls Using Bayesian Analysis. in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients |
| Reckhow, Kenneth H.; Stow, Craig A.; Borsuk, Mark E. 2002. Uncertainty Between The Criterion And The Designated Use: Implications For Standards And Tmdl Margin Of Safety. Pages 1223-1228 in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | Model; Index or Indicator | Designated Uses; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Water | |
| Reyes Bonilla, H. and G. Cruz Pinon. 2002. Influence of temperature and nutrients on species richness of deep water corals from the western coast of the Americas. Hydrobiologia 471:35-41. | 2002 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Riding, R. 2002. Biofilm architecture of Phanerozoic cryptic carbonate marine veneers. Geology 30:31-34. | 2002 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Salvat, B. and A. Aubanel. 2002. The management of coral reefs of French Polynesia [La gestion des recifs coralliens de Polynesie francaise]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 57:193-251. | 2002 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; France | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Aquaculture; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Echinoderms; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Molluscs; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation |
| Scavia, D., J. C. Field, D. F. Boesch, R. W. Buddemeier, V. Burkett, D. R. Cayan, M. Fogarty, M. A. Harwell, R. W. Howarth, C. Mason, D. J. Reed, T. C. Royer, A. H. Sallenger, and J. G. Titus. 2002. Climate change impacts on U.S. coastal and marine ecosystems. Estuaries 25:149-164. | 2002 | Global | Review | Climate; CO2; Coastal Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Soreghan, G. S. and M. J. Soreghan. 2002. Atmospheric dust and algal dominance in the late Paleozoic: A hypothesis. Journal of Sedimentary Research 72:457-461. | 2002 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Symonds, G., K. P. Black, and I. R. Young. 2002. A comment on \A physical derivation of nutrient-uptake rates in coral reefs: Effects of roughness and waves\" by C.J. Hearn, M.J. Atkinson, and J.L. Falter". Coral Reefs 21:317-318. | 2002 | Nutrients | ||
| Szmant, A. M. 2002. Nutrient enrichment on coral reefs: Is it a major cause of coral reef decline? Estuaries 25:743-766. | 2002 | Nutrients | ||
| Tabeta, S., I. S. F. Jones, and M. L. Heron. 2002. Modelling and observation of tropical river inflow to the coastal ocean. Pages 2025-2030 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2002 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Todd, J. A., J. B. C. Jackson, K. G. Johnson, H. M. Fortunato, A. Heitz, M. Alvarez, and P. Jung. 2002. The ecology of extinction: Molluscan feeding and faunal turnover in the Caribbean Neogene. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 269:571-577. | 2002 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Bivalves; Molluscs; Nutrients | |
| Torreton, J.-P., J. Pages, and V. Talbot. 2002. Relationships between bacterioplankton and phytoplankton biomass, production and turnover rate in Tuamotu atoll lagoons. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 28:267-277. | 2002 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Turley, C. M. and J. L. Dixon. 2002. Bacterial numbers and growth in surficial deep-sea sediments and phytodetritus in the NE Atlantic: Relationships with particulate organic carbon and total nitrogen. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 49:815-826. | 2002 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Umezawa, Y., T. Miyajima, H. Kayanne, and I. Koike. 2002. Significance of groundwater nitrogen discharge into coral reefs at ishigaki island, southwest of Japan. Coral Reefs 21:346-356. | 2002 | Japan | Discharges; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Umezawa, Y., T. Miyajima, M. Yamamuro, H. Kayanne, and I. Koike. 2002. Fine-scale mapping of land-derived nitrogen in coral reefs by δ15N in macroalgae. Limnology and Oceanography 47:1405-1416. | 2002 | Japan | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients |
| Underwood, G. J. C. 2002. Adaptations of tropical marine microphytobenthic assemblages along a gradient of light and nutrient availability in Suva Lagoon, Fiji. European Journal of Phycology 37:449-462. | 2002 | Fiji | Climate; Light; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| van Dam, A. A., M. C. M. Beveridge, M. E. Azim, and M. C. J. Verdegem. 2002. The potential of fish production based on periphyton. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 12:31-Jan. | 2002 | Review; Model | Algae; Aquaculture; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Substrate; Supplemental Feeding | |
| Van Duyl, F. C., G. J. Gast, W. Steinhoff, S. Kloff, M. J. W. Veldhuis, and R. P. M. Bak. 2002. Factors influencing the short-term variation in phytoplankton composition and biomass in coral reef waters. Coral Reefs 21:293-306. | 2002 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Whalen, M. T., J. Day, G. P. Eberli, and P. W. Homewood. 2002. Microbial carbonates as indicators of environmental change and biotic crises in carbonate systems: Examples from the Late Devonian, Alberta basin, Canada. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 181:127-151. | 2002 | Index or Indicator | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Wilson, M. E. J. and S. W. Lokier. 2002. Siliciclastic and volcaniclastic influences on equatorial carbonates: Insights from the Neogene of Indonesia. Sedimentology 49:583-601. | 2002 | Java; Indonesia | Algae; Coralline Algae; Echinoderms; Light; Molluscs; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Yentsch, C.S., C.M. Yentsch, J.J. Cullen, B. Lapointe, D.A. Phinney, S.W. Yentsch. 2002. Sunlight and water transparency: cornerstones in coral research. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 268:171-183. | 2002 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Primary Production; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Zemke-White, W. L., J. H. Choat, and K. D. Clements. 2002. A re-evaluation of the diel feeding hypothesis for marine herbivorous fishes. Marine Biology 141:571-579. | 2002 | Australia | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Allmon, W. D. 2001. Nutrients, temperature, disturbance, and evolution: A model for the late Cenozoic marine record of the western Atlantic. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 166:26-Sep. | 2001 | Global; South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Review; Model | Marine Birds; Nutrients; Whales & Dolphins |
| Aronson, R.B. and W. F. Precht. 2001. White-band disease and the changing face of Caribbean coral reefs. Hydrobiologia 460:25-38. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Atkinson, M., J. Falter, and C. Hearn. 2001. Nutrient dynamics in the Biosphere 2 coral reef mesocosm: Water velocity controls NH4 and PO4 uptake. Coral Reefs 20:341-346. | 2001 | Nutrients | ||
| Barber, R. T., A. K. Hilting, and M. L. Hayes. 2001. The changing health of coral reefs. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 7:1255-1270. | 2001 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Climate; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Brodie, J., C. Christie, M. Devlin, D. Haynes, S. Morris, M. Ramsay, J. Waterhouse, and H. Yorkston. 2001. Catchment management and the Great Barrier Reef. Water Science and Technology 43:203-211. | 2001 | Australia | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Campbell, S. 2001. Ammonnium requirements of fast-growing ephemeral macroalgae in a nutrient-enriched marine embayment (Port Phillip Bay, Australia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 209:99-107. | 2001 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Charpy, L. 2001. Phosphorus supply for atoll biological productivity. Coral Reefs 20:357-360. | 2001 | Nutrients | ||
| Chaston, K.A.V. 2001. Sediment Nutrient Bioavailability in a Sub-tropical Catchment Dominated by Agriculture: The transition from Land to Sea. PhD Thesis. University of Queensland. | 2001 | Australia | Agriculture; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Crosbie, N. D. and M. J. Furnas. 2001. Net growth rates of picocyanobacteria and nano-/microphytoplankton inhabiting shelf waters of the central (17° S) and southern (20° S) Great Barrier Reef. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 24:209-224. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Davy, S. K. and C. B. Cook. 2001. The influence of 'host release factor' on carbon release by zooxanthellae isolated from fed and starved Aiptasia pallida (Verrill). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 129:487-494. | 2001 | Cuba | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Devlin, M., J. Waterhouse, and J. Brodie. 2001. Community and connectivity: Summary of a community based monitoring program set up to assess the movement of nutrients and sediments into the Great Barrier Reef during high flow events. Water Science and Technology 43:121-131. | 2001 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Social Organizations; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Diaz, M.C., K. Rutzler. 2001. Sponges: an essential component of caribbean coral reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:535-546. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges |
| Dubinsky, Z. and I. Berman-Frank. 2001. Uncoupling primary production from population growth in photosynthesizing organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Aquatic Science 63:17-Apr. | 2001 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Dy, D. T. and H. T. Yap. 2001. Surge ammonium uptake of the cultured seaweed, Kappaphycus alvarezii (doty) doty (rhodophyta: gigartinales). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 265:89-100. | 2001 | Cuba; Philippines | Nutrients | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C. and P. Furla. 2001. Pico- and nanoplankton biomass and production in the two largest atoll lagoons of French Polynesia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 211:63-76. | 2001 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Ferrier-Pages, C., V. Schoelzke, J. Jaubert, L. Muscatine, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 2001. Response of a scleractinian coral, Stylophora pistillata, to iron and nitrate enrichment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 259:249-261. | 2001 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Fitt, W. K. and C. B. Cook. 2001. The effects of feeding or addition of dissolved inorganic nutrients in maintaining the symbiosis between dinoflagellates and a tropical marine cnidarian. Marine Biology 139:507-517. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Fong, P., K. Kamer, K. E. Boyer, and K. A. Boyle. 2001. Nutrient content of macroalgae with differing morphologies may indicate sources of nutrients for tropical marine systems. Marine Ecology Progress Series 220:137-152. | 2001 | Puerto Rico | Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Fursich, F. T., R. Berndt, T. Scheuer, and M. Gahr. 2001. Comparative ecological analysis of Toarcian (Lower Jurassic)benthic faunas from southern France and east-central Spain. Lethaia 34:169-202. | 2001 | Spain; France | Bivalves; Climate; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Harrison, P. L. and S. Ward. 2001. Elevated levels of nitrogen and phosphorus reduce fertilisation success of gametes from scleractinian reef corals. Marine Biology 139:1057-1068. | 2001 | Australia | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Hayes, M. L., J. Bonaventura, T. P. Mitchell, J. M. Prospero, E. A. Shinn, F. Van Dolah, and R. T. Barber. 2001. How are climate and marine biological outbreaks functionally linked? Hydrobiologia 460:213-220. | 2001 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Climate; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Hearn, C., M. Atkinson, and J. Falter. 2001. A physical derivation of nutrient-uptake rates in coral reefs: Effects of roughness and waves. Coral Reefs 20:347-356. | 2001 | Model | Nutrients; Shoreline Protection | |
| Hicklenton, P. R., V. Rodd, and P. R. Warman. 2001. The effectiveness and consistency of source-separated municipal solid waste and bark composts as components of container growing media. Scientia Horticulturae 91:365-378. | 2001 | Nutrients; Substrate | ||
| Isern, A. R., F. S. Anselmetti, and P. Blum. 2001. ODP Leg 194: Sea level magnitudes recorded by continental margin sequences on the Marion Plateau, northeast Australia. JOIDES Journal 27:11-Jul. | 2001 | Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Jackson, J. B. C. 2001. What was natural in the coastal oceans? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98:5411-5418. | 2001 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sponges | |
| Job, S. D. and J. Shand. 2001. Spectral sensitivity of larval and juvenile coral reef fishes: Implications for feeding in a variable light environment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 214:267-277. | 2001 | Model | Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Keim, L., R. Brandner, L. Krystyn, and W. Mette. 2001. Termination of carbonate slope progradation: An example from the Carnian of the Dolomites, Northern Italy. Sedimentary Geology 143:303-323. | 2001 | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Kleemann, K. 2001. The Pectinid bivalve Pedum spondyloideum (Gmelin 1791): Amount of surface and volume occupied in host corals from the red sea. Marine Ecology 22:111-133. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients | |
| Knowlton, N. 2001. The future of coral reefs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98:5419-5425. | 2001 | Global | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Temperatures | |
| Koop, K., A. Steven, R. Mcgill, E. Drew, and B. Macdonald. 2001. Use of a telemetered dispensing system for controlling nutrient additions to experimental patch reefs in the ENCORE Study at One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:121-126. | 2001 | Australia; Cuba | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients | |
| Koop, K., D. Booth, A. Broadbents, J. Brodie, D. Bucher, D. Capone, J. Coll, W. Dennison, M. Erdmann, P. Harrison, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, P. Hutchings, G. B. Jones, A. W. D. Larkum, J. O'Neil, A. Steven, E. Tentori, S. Ward, J. Williamson, and D. Yellowless. 2001. ENCORE: The effect of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs. Synthesis of results and conculsions. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:91-120. | 2001 | Nutrients | ||
| Kuffner, I. B. and V. J. Paul. 2001. Effects of nitrate, phosphate and iron on the growth of macroalgae and benthic cyanobacteria from cocos lagoon, guam. Marine Ecology Progress Series 222:63-72. | 2001 | Guam | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Cyanobacteria; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Lourey, M. J., D. M. Alongi, D. A. J. Ryan, and M. J. Devlin. 2001. Variability of nutrient regeneration rates and nutrient concentrations in surface sediments of the northern Great Barrier Reef shelf. Continental Shelf Research 21:145-155. | 2001 | Australia | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Masse, J. P. and L. F. Montaggioni. 2001. Growth history of shallow-water carbonates: Control of accommodation on ecological and depositional processes. International Journal of Earth Sciences 90:452-469. | 2001 | Model | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| McCook, L. J. 2001. Competition between corals and algal turfs along a gradient of terrestrial influence in the nearshore central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 19:419-425. | 2001 | Australia | Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Mitchell, A. W., J. R. Reghenzani, and M. J. Furnas. 2001. Nitrogen levels in the Tully River - A long-term view. Water Science and Technology 43:99-105. | 2001 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Miyajima, T., M. Suzumura, Y. Umezawa, and I. Koike. 2001. Microbiological nitrogen transformation in carbonate sediments of a coral-reef lagoon and associated seagrass beds. Marine Ecology Progress Series 217:273-286. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Algae; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Montgomery, P., M. R. Farr, E. K. Franseen, and R. H. Goldstein. 2001. Constraining controls on carbonate sequences with high-resolution chronostratigraphy: Upper Miocene, Cabo de Gata region, SE Spain. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 176:Nov-45. | 2001 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Spain | Field Study & Monitoring | Calcareous Macroalgae; Climate; Nutrients |
| Morelock, J., W. R. Ram�rez, A. W. Bruckner, and M. Carlo. 2001. Status of coral reefs southwest Puerto Rico. Caribbean Journal of Science pp.57. | 2001 | Puerto Rico | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Muller-Parker, G. and J. Cortes. 2001. Spatial distribution of light and nutrients in some coral reefs of Costa Rica during January 1997. Revista de Biologia Tropical 49:251-263. | 2001 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica; Pacific Ocean; Caribbean | Coastal Development; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Obura, D. O. 2001. Kenya. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1264-1278. | 2001 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Parkhill, J.-P., G. Maillet, and J. J. Cullen. 2001. Fluorescence-based maximal quantum yielf for PSII as a diagnostic or nutrient stress. Journal of Phycology 37:517-529. | 2001 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Paulay, G. 2001. Benthic ecology and biota of Tarawa Atoll Lagoon: Influence of equatorial upwelling, circulation, and human harvest. Atoll Research Bulletin Jan-33. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Kiribati | Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch | |
| Pedersen, M. and P. Snoeijs. 2001. Patterns of macroalgal diversity, community composition and long-term changes along the swedish west coast. Hydrobiologia 459:83-102. | 2001 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Algae; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Pomar, L. 2001. Ecological control of sedimentary accommodation: Evolution from a carbonate ramp to rimmed shelf, Upper Miocene, Balearic Islands. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 175:249-272. | 2001 | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Purcell, S. W. and D. R. Bellwood. 2001. Spatial patterns of epilithic algal and detrital resources on a windward coral reef. Coral Reefs 20:117-125. | 2001 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Richter, C., M. Wunsch, M. Rasheed, I. Kotter, and M. I. Badran. 2001. Endoscopic exploration of Red Sea coral reefs reveals dense populations of cavity-dwelling sponges. Nature 413:726-730. | 2001 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Plankton; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | ||
| Risk, M. J., J. M. Heikoop, E. N. Edinger, and M. V. Erdmann. 2001. The assessment 'toolbox': Community-based reef evaluation methods coupled with geochemical techniques to identify sources of stress. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:443-458. | 2001 | Indonesia | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Discharges; Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral |
| Roberts, J. M., L. M. Fixter, and P. S. Davies. 2001. Ammonium metabolism in the symbiotic sea anemone Anemonia viridis. Hydrobiologia 461:25-35. | 2001 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Schaffelke, B. 2001. Surface alkaline phosphatase activities of macroalgae on coral reefs of the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Coral Reefs 19:310-317. | 2001 | Global; Australia | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| Scheffer, M., S. Carpenter, J. A. Foley, C. Folke, and B. Walker. 2001. Catastrophic shifts in ecosystems. Nature 413:591-596. | 2001 | Climate; Nutrients | ||
| Smith, J. E., C. M. Smith, and C. L. Hunter. 2001. An experimental analysis of the effects of herbivory and nutrient enrichment on benthic community dynamics on a Hawaiian reef. Coral Reefs 19:332-342. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Sprachta, S., G. Camoin, S. Golubic, and TH . Le Campion. 2001. Microbialites in a modern lagoonal environment: Nature and distribution, Tikehau atoll (French Polynesia). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 175:103-124. | 2001 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Stimson, J., S. T. Larned, and E. Conklin. 2001. Effects of herbivory, nutrient levels, and introduced algae on the distribution and abundance of the invasive macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 19:343-357. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Discharges; Fish; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Suchy, D. R. and R. R. West. 2001. Chaetetid buildups in a Westphalian (Desmoinesian) Cyclothem in Southeastern Kansas. Palaios 16:425-443. | 2001 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Tarrant, A. M., M. J. Atkinson, and S. Atkinson. 2001. Uptake of estrone from the water column by a coral community. Marine Biology 139:321-325. | 2001 | Cuba | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | |
| Thacker, R. W. and V. J. Paul. 2001. Are benthic cyanobacteria indicators of nutrient enrichment? Relationships between cyanobacterial abundance and environmental factors on the reef flats of Guam. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:497-508. | 2001 | Guam | Index or Indicator | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity; Shoreline Protection |
| Thacker, R. W., D. W. Ginsburg, and V. J. Paul. 2001. Effects of herbivore exclusion and nutrient enrichment on coral reef macroalgae and cyanobacteria. Coral Reefs 19:318-329. | 2001 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens | ||
| Uthicke, S. 2001. Interactions between sediment-feeders and microalgae on coral reefs: Grazing losses versus production enhancement. Marine Ecology Progress Series 210:125-138. | 2001 | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | ||
| Uthicke, S. 2001. Nutrient regeneration by abundant coral reef holothurians. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 265:153-170. | 2001 | Australia | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Van Duyl, F. C. and G. J. Gast. 2001. Linkage of small-scale spatial variations in DOC, inorganic nutrients and bacterioplankton growth with different coral reef water types. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 24:17-26. | 2001 | Antilles | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Substrate | |
| Webster, N. S. and R. T. Hill. 2001. The culturable microbial community of the great barrier reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is dominated by an α-Proteobacterium. Marine Biology 138:843-851. | 2001 | Australia | Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Williams, I. D., N. V. C. Polunin, and V. J. Hendrick. 2001. Limits to grazing by herbivorous fishes and the impact of low coral cover on macroalgal abundance on a coral reef in Belize. Marine Ecology Progress Series 222:187-196. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Wilson, S., K. Burns, and S. Codi. 2001. Identifying sources of organic matter in sediments from a detritivorous coral reef fish territory. Organic Geochemistry 32:1257-1269. | 2001 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | ||
| Wood, R. 2001. Are reefs and mud mounds really so different? Sedimentary Geology 145:161-171. | 2001 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Wulff, J. 2001. Assessing and monitoring coral reef sponges: Why and how? Bulletin of Marine Science 69:831-846. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | |
| Yamamoto, M., H. Kayanne, and M. Yamamuro. 2001. Characteristics of organic matter in lagoonal sediments from the great barrier reef. Geochemical Journal 35:385-401. | 2001 | Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Zubia, M. and M. Peyrot-Clausade. 2001. Internal bioerosion of Acropora formosa in Reunion (Indian Ocean): Microborer and macroborer activities. Oceanologica Acta 24:251-262. | 2001 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fish; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Zuschin, M., J. Hohenegger, and F. F. Steininger. 2001. Molluscan assemblages on coral reefs and associated hard substrata in the northern red sea. Coral Reefs 20:107-116. | 2001 | Bivalves; Hydrocoral; Molluscs; Nutrients; Physical Damage; Skeletal Coral; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral; Substrate | ||
| Adey, W. H., T. A. McConnaughey, A. M. Small, and D. M. Spoon. 2000. Coral reefs: Endangered, biodiverse, genetic resources. Pages 33-42 Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 3. | 2000 | Global | Lab Study | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Agard, J. B. R. and J. F. Gobin. 2000. The Lesser Antilles, Trinidad and Tobago. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 627-641. | 2000 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Antilles; British Virgin Islands; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Martinique; Venezuela; Guyana; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Deforestation & Devegetation; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Land & Air Transportation; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Apte, S., B. S. Holland, L. S. Godwin, and J. P. A. Gardner. 2000. Jumping ship: A stepping stone event mediating transfer of a non-indigenous species via a potentially unsuitable environment. Biological Invasions 2:75-79. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Molluscs; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Aronson, R. B. and W. F. Precht. 2000. Herbivory and algal dynamics on the coral reef at Discovery Bay, Jamaica. Limnology and Oceanography 45:251-255. | 2000 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Algae; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Ben-David-Zaslow, R. and Y. Benayahu. 2000. Biochemical composition, metabolism, and amino acid transport in planula-larvae of the soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens. Journal of Experimental Zoology 287:401-412. | 2000 | Nutrients; Octocoral | ||
| Bourge, I. and M. Frankignoulle. 2000. Measurement of photosynthetic parameters in benthic organisms in situ using a SCUBA-based fast repetition rate fluorometer. Limnology and Oceanography 45:242-245. | 2000 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Light; Nutrients |
| Boyer, J. N., P. Sterling, and R. D. Jones. 2000. Maximizing information from a water quality monitoring network through visualization techniques. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 50:39-48. | 2000 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Salinity |
| Brown, B. E. 2000. Significance of pollution in eliciting the 'bleaching' response in symbiotic cnidarians. International Journal of Environment and Pollution 13:392-415. | 2000 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Light; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Chen, Y., H. Arakawa, J. Ohta, and T. Morinaga. 2000. Effect of nutrient salts eluted from hedoro blocks on growth and survival rate of gametophyte and juvenile Eisenia bicyclis. Fisheries Science 66:1001-1005. | 2000 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Chesney, E. J., D. M. Baltz, and R. G. Thomas. 2000. Louisiana estuarine and coastal fisheries and habitats: Perspectives from a fish's eye view. Ecological Applications 10:350-366. | 2000 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Cooke, A., O. Ratomahenina, E. Ranaivoson, and H. Razafindrainibe. 2000. Madagascar. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 113-131. | 2000 | Mozambique; Madagascar | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Aquaculture; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Special Use Permitting |
| Costa O.S., JR ., Z. M. A. N. Leao, M. Nimmo, and M. J. Attrill. 2000. Nutrification impacts on coral reefs from northern Bahia, Brazil. Hydrobiologia 440:307-315. | 2000 | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Costanzo, S. D., M. J. O'Donohue, and W. C. Dennison. 2000. Gracilaria edulis (Rhodophyta) as a biological indicator of pulsed nutrients in oligotrophic waters. Journal of Phycology 36:680-685. | 2000 | Australia; Cuba | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Discharges; Nutrients |
| Cresswell, G. R. and K. A. Badcock. 2000. Tidal mixing near the Kimberley coast of NW Australia. Marine and Freshwater Research 51:641-646. | 2000 | Australia | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Debrot, A. O. and J. Sybesma. 2000. The Dutch Antilles. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 595-614. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Health Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Dustan, P. 2000. Florida Keys. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 405-414. | 2000 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Pipelines; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation |
| Dy, D. T. and H. T. Yap. 2000. Ammonium and phosphate excretion in three common echinoderms from Philippine coral reefs. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 251:227-238. | 2000 | Cuba | Lab Study | Echinoderms; Nutrients |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Edinger, E. N., G. V. Limmon, J. Jompa, W. Widjatmoko, J. M. Heikoop, and M. J. Risk. 2000. Normal coral growth rates on dying reefs: Are coral growth rates good indicators of reef health? Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:404-425. | 2000 | Java; Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Fabricius, K. E. and E. Wolanski. 2000. Rapid Smothering of Coral Reef Organisms by Muddy Marine Snow. 50:115-120. | 2000 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Fabricius, K. E. and M. Dommisse. 2000. Depletion of suspended particulate matter over coastal reef communities dominated by zooxanthellate soft corals. Marine Ecology Progress Series 196:157-167. | 2000 | Algae; Bivalves; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sponges; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tunicates; Turf Algae | ||
| Ferrier-Pages, C., J.-P. Gattuso, S. Dallot, and J. Jaubert. 2000. Effect of nutrient enrichment on growth and photosynthesis of the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata. Coral Reefs 19:103-113. | 2000 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Ferrier-Pages, C., N. Leclercq, J. Jaubert, and S. P. Pelegri. 2000. Enhancement of pico- and nanoplankton growth by coral exudates. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 21:203-209. | 2000 | Cuba | Lab Study | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Fleury, B. G., J. C. Coll, E. Tentori, S. Duquesne, and L. Figueiredo. 2000. Effect of nutrient enrichment on the complementary (secondary) metabolite composition of the soft coral Sarcophyton ebrenbergi (Cnidaria: Octocorallia: Alcyonaceae) of the Great Barrier Reef. Marine Biology 136:63-68. | 2000 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Octocoral; Stony Coral |
| Gosmano, J. and D. Pike. 2000. Crowded energy e-trading arena grows with TradeSpark offering. Natural Gas Week 16:2. | 2000 | Internet & Telecommunications; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Toxics | ||
| Gross, L. A., G. S. Baird, R. C. Hoffman, K. K. Baldridge, and R. Y. Tsien. 2000. The structure of the chromophore within DsRed, a red fluorescent protein from coral. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 97:11990-11995. | 2000 | Nutrients | ||
| Hallock, P. 2000. Symbiont-bearing foraminifera: Harbingers of global change? Micropaleontology 46:95-104. | 2000 | Global | CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Light; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Haynes, D. and K. Michalek-Wagner. 2000. Water quality in the Great Barrier Reef World Heritage Area: Past perspectives, current issues and new research directions. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41:428-434. | 2000 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Toxics |
| Heikoop, J. M., J. J. Dunn, M. J. Risk, T. Tomascik, H. P. Schwarcz, I. M. Sandeman, and P. W. Sammarco. 2000. δ15 N and δ13 C of coral tissue show significant inter-reef variation. Coral Reefs 19:189-193. | 2000 | Nutrients | ||
| Heikoop, J. M., M. J. Risk, A. V. Lazier, E. N. Edinger, J. Jompa, G. V. Limmon, J. J. Dunn, D. R. Browne, and H. P. Schwarez. 2000. Nitrogen-15 signals of anthropogenic nutrient loading in reef corals. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:628-363. | 2000 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Wastewater Discharge; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Holmes, K. E. 2000. Effects of eutrophication on bioeroding sponge communities with the description of new West Indian sponges, Cliona spp. (Porifera: Hadromerida: Clionidae). Invertebrate Biology 119:125-138. | 2000 | India | Boring Sponges; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Holmes, K. E., E. N. Edinger, Hariyadi, G. V. Limmon, and M. J. Risk. 2000. Bioerosion of live massive corals and branching coral rubble on Indonesian coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:606-617. | 2000 | Java; Indonesia | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral |
| Ibrahim, Z. Z., A. Arshad, L. S. Chong, J. S. Bujang, L. A. Theem, N. M. R. Abdullah, and M. M. Marghany. 2000. East Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 345-359. | 2000 | Malaysia; China | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Ichiki, S., H. Mizuta, and H. Yamamoto. 2000. Effects of irradiance, water temperature and nutrients on the growth of sporelings of the crustose coralline alga Lithophyllum yessoense Foslie (Corallinales, Rhodophyceae). Phycological Research 48:115-120. | 2000 | Japan | Light; Nutrients | |
| Iizumi, H. and M. Yamamuro. 2000. Nitrogen fixation activity by periphytic blue-green algae in a seagrass bed on the great barrier reef. Japan Agricultural Research Quarterly 34:69-73. | 2000 | Australia; Fiji | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses |
| Jacinto, G. S., P. M. Alino, C. L. Villanoy, L. Talaue-McManus, and E. D. Gomez. 2000. The Philippines. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 405-423. | 2000 | Philippines | Chemical Use Regulations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jean-Baptiste, P. and A. M. Leclerc. 2000. Self-limiting geothermal convection in marine carbonate platforms. Geophysical Research Letters 27:743-746. | 2000 | Model | Nutrients | |
| Kawahata, H., I. Yukino, and A. Suzuki. 2000. Terrestrial influences on the Shiraho fringing reef, Ishigaki Island, Japan: High carbon input relative to phosphate. Coral Reefs 19:172-178. | 2000 | Japan | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kiessling, W., E. Flugel, and J. Golonka. 2000. Fluctuations in the carbonate production of Phanerozoic reefs. Geological Society Special Publication 191-215. | 2000 | Global | CO2; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Knap, A. H., D. P. Connelly, and J. N. Butler. 2000. The Sargasso Sea and Bermuda. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 221-231. | 2000 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Kuta, K. 2000. Black band disease of corals: Ecology and physiology of Phormidium corallyticum. Florida International University, Miami. | 2000 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Octocoral; Pathogens; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Langdon, C., T. Takahashi, C. Sweeney, D. Chipman, J. Goddard, F. Marubini, H. Aceves, H. Barnett, and M. J. Atkinson. 2000. Effect of calcium carbonate saturation state on the calcification rate of an experimental coral reef. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 14:639-654. | 2000 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Chemical Variables; CO2; Nutrients; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Lehane, L. and R. J. Lewis. 2000. Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. International Journal of Food Microbiology 61:91-125. | 2000 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Indian Ocean; India; Caribbean | Algae; Docks & Marinas; Fish; Nutrients; Pathogens; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Lidz, B. H. and P. Hallock. 2000. Sedimentary petrology of a declining reef ecosystem, Florida reef tract (U.S.A.). Journal of Coastal Research 16:675-697. | 2000 | Florida | Model; Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Molluscs; Nutrients; Pathogens; Plankton; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Lison De Loma, T., M. Harmelin-Vivien, O. Naim, and M.-F. Fontaine. 2000. Algal food processing by stegastes nigricans, an herbivorous damselfish: Differences between an undisturbed and a disturbed coral reef site (La Reunion, Indian Ocean). Oceanologica Acta 23:793-804. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Maloney, K. A., L. A. Maguire, and E. A. Lind. 2000. NEUSE RIVER ESTUARY MODELING AND MONITORING PROJECT STAGE 1: ASSESSMENT OF STAKEHOLDER INTEREST AND CONCERNS TO INFORM LONG-TERM MODELING. 50237, Fuqua School of Business, Duke University, Durham, (NC, USA). | 2000 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Marnane, M. J. 2000. Site fidelity and homing behaviour in coral reef cardinalfishes. Journal of Fish Biology 57:1590-1600. | 2000 | Fish; Nutrients | ||
| Marrugo-Gonzalez, A. J., R. Fernandez-Maestre, and A. A. Alm. 2000. The Pacific coast of Colombia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 677-686. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Beaches & Nature Parks; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| McConnaughey, T. A., W. H. Adey, and A. M. Small. 2000. Community and environmental influences on reef coral calcification. Limnology and Oceanography 45:1667-1671. | 2000 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| McManus, J. W., L. A. B. Menez, K. N. Kesner-Reyes, S. G. Vergara, and S. M. C. Ablan. 2000. Coral reef fishing and coral-algal phase shifts: Implications for global reef status. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57:572-578. | 2000 | Global | Remote Sensing | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral |
| Mitchell, S., S. Khan, R. Maharaj, and E. Robinson. 2000. Carbonate beach sediment composition at a tourist beach, Negril, Jamaica. Pages 204-217 in Carbonate Beaches 2000. | 2000 | Jamaica | Algae; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Montaggioni, L. 2000. Postglacial reef growth. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie de Sciences - Serie IIa: Sciences de la Terre et des Planetes 331:319-330. | 2000 | Model | Nutrients; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Montaggioni, L. F. 2000. The reef phenomenon: Geological aspects [Le phenomene recifal: Aspects geologiques]. Oceanis 26:147-266. | 2000 | Global | Index or Indicator | CO2; Nutrients; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Morelock, J., J. Capella, J. Garcia, and M. Barreto. 2000. Puerto Rico. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 575-585. | 2000 | Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection | |
| Murphy, A. E., B. B. Sageman, and D. J. Hollander. 2000. Eutrophication by decoupling of the marine biogeochemical cycles of C, N, and P: A mechanism for the Late Devonian mass extinction. Geology 28:427-430. | 2000 | Global | Model | Nutrients |
| O'Hara, T. D. 2000. Victoria province, Australia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 661-671. | 2000 | Australia; Europe | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Commercial Fisheries; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wetlands | |
| Payri, C. E. 2000. Primary production and calcification of coral reef benthic algae [Production primaire et calcification des algues benthiques en milieu corallien]. Oceanis 26:427-463. | 2000 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Penchaszadeh, P. E., C. A. Leon, H. Alvarez, D. Bone, P. Castellano, M. M. Castillo, Y. Diaz, M. P. Garcia, M. Lemus, F. Losada, A. Martin, P. Miloslavich, C. Paredes, D. Perez, M. Sebastiani, D. Stecconi, V. Roa, and A. Villamizar. 2000. Venezuela. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 643-661. | 2000 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Venezuela; Caribbean | Beaches & Nature Parks; Bivalves; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Molluscs; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Perry, C. T. and M. Bertling. 2000. Spatial and temporal patterns of macroboring within Mesozoic and Cenozoic coral reef systems. Geological Society Special Publication 33-50. | 2000 | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Substrate | ||
| Rao, D. V. S. and F. Al-Yamani. 2000. The Arabian Gulf. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 16-Jan. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Fish; Invasive Species; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Plankton; Scientific Research; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Richardson, B. J., P. K. S. Lam, and R. S. S. Wu. 2000. Hong Kong. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 535-547. | 2000 | China | Beaches & Nature Parks; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Land & Air Transportation; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Riegl, B. and W. E. Piller. 2000. Mapping of benthic habitats in northern Safaga Bay (Red Sea, Egypt): A tool for proactive management. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 10:127-140. | 2000 | Egypt | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Risk, M. J., M. V. Erdmann. 2000. Isotopic composition of nitrogen in stomatopod (Crustacea) tissues as an indicator of human sewage impacts on Indonesian coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 40:50-58. | 2000 | Indonesia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Rutzler, K., M. C. Diaz, R. W. M. Van Soest, S. Zea, K. P. Smith, B. Alvarez, and J. Wulff. 2000. Diversity of sponge fauna in mangrove ponds, Pelican Cays, Belize. Atoll Research Bulletin 231-248. | 2000 | South & Central America; Belize | Boating Activities; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Sakami, T. 2000. Effects of temperature, irradiance, salinity and inorganic nitrogen concentration on coral zooxanthellae in culture. Fisheries Science 66:1006-1013. | 2000 | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Sakka, A., L. Legendre, M. Gosselin, and B. Delesalle. 2000. Structure of the oligotrophic planktonic food web under low grazing of heterotrophic bacteria: Takapoto Atoll, French Polynesia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 197:17-Jan. | 2000 | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Samtleben, C., A. Munnecke, and T. Bickert. 2000. Development of facies and C/O-isotopes in transects through the Ludlow of Gotland: Evidence for global and local influences on a shallow-marine environment. Facies Jan-38. | 2000 | Global | GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Sheppard, C. R. C. 2000. The Red Sea. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 35-45. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waste Management Policies | |
| Shyka, T. A. and K. P. Sebens. 2000. Community structure, water column nutrients and water flow in two Pelican Cays ponds, Belize. Atoll Research Bulletin 107-121. | 2000 | South & Central America; Belize | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow | |
| Stimson, J. and S. T. Larned. 2000. Nitrogen efflux from the sediments of a subtropical bay and the potential contribution to macroalgal nutrient requirements. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 252:159-180. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Swart, P. K., G. Ellis, P. Milne. 2000. The Impact of Sewage-Derived Nutrients on the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. University of Miami, Miami, FL. | 2000 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Titlyanov, E. A., V. A. Leletkin, and Z. Dubinsky. 2000. Autotrophy and predation in the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata in different light habitats. Symbiosis 29:263-281. | 2000 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae |
| Titlyanov, E., K. Bil', I. Fomina, T. Titlyanova, V. Leletkin, N. Eden, A. Malkin, and Z. Dubinsky. 2000. Effects of dissolved ammonium addition and host feeding with Artemia salina on photoacclimation of the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata. Marine Biology 137:463-472. | 2000 | Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | CO2; Light; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Torreton, J.-P. 2000. Importance of bacterioplankton in the transformation and fate of organic matter in coral reef environments [Importance du bacterioplancton dans la transformation et le devenir de la matiere organique en milieu corallien]. Oceanis 26:389-425. | 2000 | Review | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Van Tussenbroek, B. I., C. A. Galindo, and J. Marquez. 2000. Dormancy and foliar density regulation in Thalassia testudinum. Aquatic Botany 68:281-295. | 2000 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting | |
| Vierros, M. 2000. Jamaica. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 559-574. | 2000 | Jamaica | Algae; Beaches & Nature Parks; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Viles, H. A., T. Spencer, K. Teleki, and C. Cox. 2000. Observations on 16 years of microfloral recolonization data from limestone surfaces, Aldabra Atoll, Indian ocean: Implications for biological weathering. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 25:1355-1370. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Vogel, K., M. Gektidis, S. Golubic, W. E. Kiene, and G. Radtke. 2000. Experimental studies on microbial bioerosion at Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas and One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia: Implications for paleoecological reconstructions. Lethaia 33:190-204. | 2000 | Australia; Bahamas | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Vuki, V. C., L. P. Zann, M. Naqasima, and M. Vuki. 2000. The Fiji Islands. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 751-764. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Fiji | Corallivorous Fish; Echinoderms; Finfish Harvest; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seastars; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Vuki, V. C., S. Appana, M. R. Naqasima, and M. Vuki. 2000. Vanuatu. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 737-749. | 2000 | Vanuatu | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Beaches & Nature Parks; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Forestry; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies |
| Ward, S. and P. Harrison. 2000. Changes in gametogenesis and fecundity of acroporid corals that were exposed to elevated nitrogen and phosphorus during the ENCORE experiment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 246:179-221. | 2000 | Australia | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Wong, P. P. 2000. Malacca Strait including Singapore and Johore Straits. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 331-344. | 2000 | Thailand; Malaysia; Southeast Asia; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Commercial Fisheries; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands | |
| Zann, L. P. 2000. Northeastern Australia: The Great Barrier Reef region. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 611-628. | 2000 | Australia | Model | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Zann, L. P. 2000. The Australian Region: An overview. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 579-592. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Al-Jufaili, S., M. Al-Jabri, A. Al-Baluchi, R. M. Baldwin, S. G. Wilson, F. West, and A. D. Matthews. 1999. Human impacts on coral reefs in the Sultanate of Oman. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 49:65-74. | 1999 | Oman | Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Pathogens; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Ambariyanto, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1999. Influence of field-based nutrient enrichment on the photobiology of the giant clam Tridacna maxima. Marine Biology 133:659-664. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Ambariyanto, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1999. Net uptake of dissolved free amino acids by the giant clam, Tridacna maxima: Alternative sources of energy and nitrogen? Coral Reefs 18:91-96. | 1999 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
| Anthony, K. R. N. 1999. Coral suspension feeding on fine particulate matter. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 232:85-106. | 1999 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral |
| Atkinson, M. J., H. Barnett, H. Aceves, C. Langdon, S. J. Carpenter, T. McConnaughey, E. Hochberg, M. Smith, and B. D. V. Marino. 1999. The Biosphere 2 coral reef biome. Ecological Engineering 13:147-171. | 1999 | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Fish; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sponges | ||
| Bak, R. P. M. and E. H. Meesters. 1999. Population structure as a response of coral communities to global change. American Zoologist 39:56-65. | 1999 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Barrie Pnrock, A. 1999. Coral reefs and environmental change: Adaptation to what? American Zoologist 39:29-Oct. | 1999 | Global | Climate; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Salinity; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bell, P. R. F., I. Elmetri, and P. Uwins. 1999. Nitrogen fixation by Trichodesmium spp. in the Central and Northern Great Barrier Reef Lagoon: Relative importance of the fixed-nitrogen load. Marine Ecology Progress Series 186:119-126. | 1999 | Australia | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Ben-David-Zaslow, R. and Y. Benayahu. 1999. Temporal variation in lipid, protein and carbohydrate content in the Red Sea soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 79:1001-1006. | 1999 | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Ben-David-Zaslow, R., G. Henning, D. K. Hofmann, and Y. Benayahu. 1999. Reproduction in the Red Sea soft coral Heteroxenia fuscescens: Seasonality and long-term record (1991 to 1997). Marine Biology 133:553-559. | 1999 | Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bett, B. J. 1999. RRS Charles Darwin Cruise 112C, 19 May-24 Jun 1998. Atlantic Margin Environmental Survey: Seabed survey of deep-water areas (17(th) round tranches) to the north and west of Scotland. Cruise Report of the Southampton Oceanography Centre 25:1-171. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Britain | Field Study & Monitoring | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Boelen, P., I. Obernosterer, A. A. Vink, and A. G. J. Buma. 1999. Attenuation of biologically effective UV radiation in tropical atlantic waters measured with a biochemical DNA dosimeter. Photochemistry and Photobiology 69:34-40. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Cuba | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Bright, C. 1999. The nemesis effect. Pages 23-Dec World watch. | 1999 | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Light; Nutrients; Pathogens | ||
| Brown, B. E., R. P. Dunne, I. Ambarsari, M. D. A. Le Tissier, and U. Satapoomin. 1999. Seasonal fluctuations in environmental factors and variations in symbiotic algae and chlorophyll pigments in four Indo-Pacific coral species. Marine Ecology Progress Series 191:53-69. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Thailand | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cabioch, G., F. W. Taylor, T. Correge, J. Recy, L. R. Edwards, G. S. Burr, F. Le Cornec, and K. A. Banks. 1999. Occurrence and significance of microbialites in the uplifted Tasmaloum reef (SW Espiritu Santo, SW Pacific). Sedimentary Geology 126:305-316. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Vanuatu | Nutrients; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Camoin, G. F., P. Gautret, L. F. Montaggioni, and G. Cabioch. 1999. Nature and environmental significance of microbialites in Quaternary reefs: The Tahiti paradox. Sedimentary Geology 126:271-304. | 1999 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Cavicchioli, R., F. Fegatella, M. Ostrowski, M. Eguchi, and J. Gottschal. 1999. Sphingomonads from marine environments. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 23:268-272. | 1999 | Review | Nutrients | |
| Chandrasena, N. and R. Sim. 1999. Managing entrenched weed problems in botany wetlands - An urban stormwater basin in Sydney. Pages 313-319 in Water Supply. | 1999 | Chemical Use Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Valuation; Water; Wetlands | ||
| Cirilli, S., A. Iannace, F. Jadoul, and V. Zamparelli. 1999. Microbial-serpulid build-ups in the Norian-Rhaetian of the western Mediterranean area: Ecological response of shelf margin communities to stressed environments. Terra Nova 11:195-202. | 1999 | Australia | Climate; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Clarke, R. D. 1999. Diets and metabolic rates of four caribbean tube blennies, genus Acanthemblemaria (teleostei: Chaenopsidae). Bulletin of Marine Science 65:185-199. | 1999 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Dawes, C. J., C. Uranowski, J. Andorfer, and B. Teasdale. 1999. Changes in the macroalga taxa and zonation at the content keys, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 64:95-102. | 1999 | Florida | Algae; Nutrients | |
| D'Croz, L., D. R. Robertson, and J. A. Martinez. 1999. Cross-shelf distribution of nutrients, plankton, and fish larvae in the San Blas Archipelago, Caribbean Panama. Revista de Biologia Tropical 47:203-215. | 1999 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Fish; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| De Voogd, S. N. J., R. W. M. Van Soest, and B. W. Hoeksema. 1999. Cross-shelf distribution of southwest sulawesi reef. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 44:147-154. | 1999 | Indonesia | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Diaz-Castaneda, V. and C. Almeda-Jauregui. 1999. Early benthic organism colonization on a Caribbean coral reef (Barbados, West Indies): A plate experimental approach. Marine Ecology 20:197-220. | 1999 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients | |
| Dizon, R. M. and H. T. Yap. 1999. Short-term responses of coral reef microphytobenthic communities to inorganic nutrient loading. Limnology and Oceanography 44:1259-1267. | 1999 | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Downing, J. A., M. McClain, R. Twilley, J. M. Melack, J. Elser, N. N. Rabalais, W. M. Lewis Jr., R. E. Turner, J. Corredor, D. Soto, A. Yanez-Arancibia, J. A. Kopaska, and R. W. Howarth. 1999. The impact of accelerating land-use change on the N-cycle of tropical aquatic ecosystems: Current conditions and projected changes. Biogeochemistry 46:109-148. | 1999 | Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Dupraz, C. and A. Strasser. 1999. Microbialites and micro-encrusters in shallow coral bioherms (Middle to Late Oxfordian, Swiss Jura Mountains). Facies 101-130. | 1999 | Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Gast, G. J., P. J. Jonkers, F. C. Van Duyl, and R. P. M. Bak. 1999. Bacteria, flagellates and nutrients in island fringing coral reef waters: Influence of the ocean, the reef and eutrophication. Bulletin of Marine Science 65:523-538. | 1999 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Discharges; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Glenn, E. P., D. Moore, M. Akutagawa, A. Himler, T. Walsh, and S. G. Nelson. 1999. Correlation between Gracilaria parvispora (Rhodophyta) biomass production and water quality factors on a tropical reef in Hawaii. Aquaculture 178:323-331. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Haberstroh, P. R. and F. J. Sansone. 1999. Reef framework diagenesis across wave-flushed oxic-suboxic-anoxic transition zones. Coral Reefs 18:229-240. | 1999 | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | ||
| Hall, L. W., J. M. Giddings, K. R. Solomon, and R. Balcomb. 1999. An ecological risk assessment for the use of Irgarol 1051 as an algaecide for antifoulant paints. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 29:367-437. | 1999 | Europe | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Boating Regulations; Chemical Use Regulations; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Primary Production; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hanisak, M. D. 1999. Algal Tissue Nutrients as Indicators of Nutrient Enrichment in the Florida Keys. Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution. | 1999 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients |
| Hawaii Institute of Marine, BI OL OG Y. 1999. Kaneohe Bay monitoring project from the University of Hawaii. Kaneohe Bay monitoring project from the University of Hawaii. | 1999 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Remote Sensing | Light; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Hoegh-Guldberg, O. and J. Williamson. 1999. Availability of two forms of dissolved nitrogen to the coral Pocillopora damicornis and its symbiotic zooxanthellae. Marine Biology 133:561-570. | 1999 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| James, N. P., L. B. Collins, Y. Bone, and P. Hallock. 1999. Subtropical carbonates in a temperate realm: Modern sediments on the southwest australian shelf. Journal of Sedimentary Research 69:1297-1321. | 1999 | Global; Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Molluscs; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Jenkyns, H. C. and P. A. Wilson. 1999. Stratigraphy, paleoceanography, and evolution of Cretaceous Pacific guyots: Relics from a greenhouse Earth. American Journal of Science 299:341-392. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Oman | CO2; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Jesinghaus, J. and R. Montgomery. 1999. Towards environmental pressure indicators for the EU. | 1999 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Johnson, A. K. L., S. P. Ebert, and A. E. Murray. 1999. Distribution of coastal freshwater wetlands and riparian forests in the Herbert River catchment and implications for management of catchments adjacent the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Environmental Conservation 26:229-235. | 1999 | Australia; Europe | GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Kleypas, J. A., J. W. McManu, and L. A. B. Mene. 1999. Environmental limits to coral reef development: Where do we draw the line? American Zoologist 39:146-159. | 1999 | Global | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Kline Jr., T. C. and R. A. Lewin. 1999. Natural 15N/14N abundance as evidence for N2 fixation by Prochloron (Prochlorophyta) endosymbiotic with didemnid ascidians. Symbiosis 26:193-198. | 1999 | Palau | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Knoppers, B., M. Meyerhofer, E. Marone, J. Dutz, R. Lopes, T. Leipe, and R. De Camargo. 1999. Compartments of the pelagic system and material exchange at the Abrolhos bank coral reefs, Brazil. Archive of Fishery and Marine Research 47:285-306. | 1999 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Kunzmann, A. 1999. Korallen, Fischer und Touristen. Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 51:25-32. | 1999 | Global; Philippines | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Kurosawa, K. and Y. Suzuki. 1999. Nitrogen-phosphorous coupling model combined with circulation in coral reef. Geoscience Reports of the Shizuoka University 26:61-69. | 1999 | Model | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Leclerc, A.-M., P. Jean-Baptiste, D. Texier, and D. Broc. 1999. Density-induced water circulations in atoll coral reefs: A numerical study. Limnology and Oceanography 44:1268-1281. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lee Long, W. J., R. G. Coles, and L. J. McKenzie. 1999. Issues for seagrass conservation management in Queensland. Pacific Conservation Biology 5:321-328. | 1999 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Leichter, J. J. and S. L. Miller. 1999. Predicting high-frequency upwelling: Spatial and temporal patterns of temperature anomalies on a Florida coral reef. Continental Shelf Research 19:911-928. | 1999 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Maldonado, M., M. Carmona, M. J. Uriz, and A. Cruzado. 1999. Decline in Mesozoic reef-building sponges explained by silicon limitation. Nature 401:785-788. | 1999 | Nutrients; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Marubini, F. and M. J. Atkinson. 1999. Effects of lowered pH and elevated nitrate on coral calcification. Marine Ecology Progress Series 188:117-121. | 1999 | CO2; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Mason, C. 1999. The ocean's role in climate variability and change and the resulting impacts on coasts. Natural Resources Forum 23:123-134. | 1999 | Global | Climate; CO2; Fishing Sector; Housing; Light; Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands | |
| McCook, L. J. 1999. Macroalgae, nutrients and phase shifts on coral reefs: Scientific issues and management consequences for the Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 18:357-367. | 1999 | Australia | Review; Index or Indicator | Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Miller, M. W., M. E. Hay, S. L. Miller, D. Malone, E. E. Sotka, and A. M. Szmant. 1999. Effects of nutrients versus herbivores on reef algae: A new method for manipulating nutrients on coral reefs. Limnology and Oceanography 44:1847-1861. | 1999 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Large Herbivorous Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate |
| Mioche, D. and P. Cuet. 1999. Carbon, carbonate and nutrient fluxes in summer on a fringing reef subject to anthropogenic pressure (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean) [Metabolisme du carbone, des carbonates et des sels nutritifs en saison chaude, sur un recif frangeant soumis a une pressio. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie de Sciences - Serie IIa: Sciences de la Terre et des Planetes 329:53-59. | 1999 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Morrison, R. J. and M. R. Naqasima. 1999. Fiji's Great Astrolabe Lagoon: Baseline study and management issues for a pristine marine environment. Ocean and Coastal Management 42:617-636. | 1999 | Fiji | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation |
| Ochieng, C. A. and P. L. A. Erftemeijer. 1999. Accumulation of seagrass beach cast along the Kenyan coast: A quantitative assessment. Aquatic Botany 65:221-238. | 1999 | Kenya | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Fleshy Macroalgae; Littering; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses |
| Ohde, S. and R. Van Woesik. 1999. Carbon dioxide flux and metabolic processes of a coral reef, Okinawa. Bulletin of Marine Science 65:559-576. | 1999 | Japan | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Ovalle, A. R. C., C. E. Rezende, C. E. V. Carvalho, T. C. Jennerjahn, and V. Ittekkot. 1999. Biogeochemical characteristics of coastal waters adjacent to small river-mangrove systems, East Brazil. Geo-Marine Letters 19:179-185. | 1999 | CO2; Complex Habitat & Resources; Mangroves; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Patzkowsky, M. E. and S. M. Holland. 1999. Biofacies replacement in a sequence stratigraphie framework: Middle and upper ordovician of the Nashville Dome, Tennessee, USA. Palaios 14:301-323. | 1999 | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Porter, J. W., S. K. Lewis, and K. G. Porter. 1999. The effect of multiple stressors on the Florida Keys coral reef ecosystem: A landscape hypothesis and a physiological test. Limnology and Oceanography 44:941-949. | 1999 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Model | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seawater Flow |
| Raghukumar, C., T. M. D'Souza, R. G. Thorn, and C. A. Reddy. 1999. Lignin-modifying enzymes of Flavodon flavus, a basidiomycete isolated from a coastal marine environment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 65:2103-2111. | 1999 | India | CO2; Nutrients; Remediation; Substrate | |
| Reckhow, K. H. 1999. Water quality prediction and probability network models. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56:1150-1158. | 1999 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Model | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Rees, J. G., D. Setiapermana, V. A. Sharp, J. M. Weeks, and T. M. Williams. 1999. Evaluation of the impacts of land-based contaminants on the benthic faunas of Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. Oceanologica Acta 22:627-640. | 1999 | Java; Indonesia | Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Risk, M. J. 1999. Paradise lost: How marine science failed the world's coral reefs. Marine and Freshwater Research 50:831-837. | 1999 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mitigation; Nutrients |
| Ruitenbeek, J., M. Ridgley, S. Dollar, and R. Huber. 1999. Optimization of economic policies and investment projects using a fuzzy logic based cost-effectiveness model of coral reef quality: Empirical results for Montego Bay, Jamaica. Coral Reefs 18:381-392. | 1999 | Jamaica | Model | Economic Markets & Policies; Mitigation; Nutrients; Physical Damage; Sediment |
| Russ, G. R. and L. J. McCook. 1999. Potential effects of a cyclone on benthic algal production and yield to grazers on coral reefs across the central Great Barrier Reef. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 235:237-254. | 1999 | Australia | Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sammarco, P. W., M. J. Risk, H. P. Schwarcz, and J. M. Heikoop. 1999. Cross-continental shelf trends in coral δ15N on the Great Barrier Reef: Further consideration of the reef nutrient paradox. Marine Ecology Progress Series 180:131-138. | 1999 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Schaffelke, B. 1999. Particulate organic matter as an alternative nutrient source for tropical Sargassum species (Fucales, Phaeophyceae). Journal of Phycology 35:1150-1157. | 1999 | Australia | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients | |
| Schaffelke, B. 1999. Short-term nutrient pulses as tools to assess responses of coral reef macroalgae to enhanced nutrient availability. Marine Ecology Progress Series 182:305-310. | 1999 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Schmidt, S. and G. R. Stewart. 1999. Glycine metabolism by plant roots and its occurrence in Australian plant communities. Functional Plant Biology 26:253-264. | 1999 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
| Schuhmacher, H. 1999. Korallenriffe-Bedrohungen, Schutzkonzepte und Rehabilitationsmaßnahmen. Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 51:17-23. | 1999 | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Sterr, H., V. Ittekkot, and R. J. T. Klein. 1999. Oceans and coasts responding to future climatic change [Weltmeere und kusten im wandel des klimas]. Petermanns Geographische Mitteilungen 143:24-31. | 1999 | Global | Climate; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Mangroves; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Swart, P. K., G. Healy, L. Greer, M. Lutz, A. Saied, D. Anderegg, R. E. Dodge, and D. Rudnick. 1999. The use of proxy chemical records in coral skeletons to ascertain past environmental conditions in Florida Bay. Estuaries 22:384-397. | 1999 | Florida | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Stony Coral |
| Swearer, S. E., J. E. Caselle, D. W. Lea, and R. R. Warner. 1999. Larval retention and recruitment in an island population of a coral-reef fish. Nature 402:799-802. | 1999 | Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Nutrients | ||
| Tarasov, V. G., A. V. Gebruk, V. M. Shulkin, G. M. Kamenev, V. I. Fadeev, V. N. Kosmynin, V. V. Malakhov, D. A. Starynin, and A. I. Obzhirov. 1999. Effect of shallow-water hydrothermal venting on the biota of Matupi Harbour (Rabaul Caldera, New Britain Island, Papua New Guinea). Continental Shelf Research 19:79-116. | 1999 | Papua New Guinea; Britain | Model | Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges |
| Udy, J. W., W. C. Dennison, W. J. Lee Long, and L. J. McKenzie. 1999. Responses of seagrass to nutrients in the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 185:257-271. | 1999 | Australia | GIS & Maps | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Vinithkumar, N. V., S. Kumaresan, M. Manjusha, and T. Balasubramanian. 1999. Organic matter, nutrients and major ions in the sediments of coral reefs and seagrass beds of Gulf of Mannar biosphere reserve, southeast coast of India. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences 28:383-393. | 1999 | India | Molluscs; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Wilkinson, C. R., R. E. Summons, and E. Evans. 1999. Nitrogen fixation in symbiotic marine sponges: Ecological significance and difficulties in detection. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum 44:667-673. | 1999 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Zeng, L. 1999. Search for new compounds and biologically active substances from Chinese marine organisms. Pure and Applied Chemistry 71:1147-1151. | 1999 | China | Algae; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sponges | |
| Adjeroud, M., Y. Letourneur, M. Porcher, and B. Salvat. 1998. Factors influencing spatial distribution of fish communities on a fringing reef at Mauritius, S.W. Indian Ocean. Environmental Biology of Fishes 53:169-182. | 1998 | Indian Ocean; Mauritius; India | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Echinoderms; Fish; Molluscs; Nutrients | |
| Adkins, J. F., H. Cheng, E. A. Boyle, E. R. M. Druffel, and R. L. Edwards. 1998. Deep-sea coral evidence for rapid change in ventilation of the deep North Atlantic 15,400 years ago. Science 280:725-728. | 1998 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Algeo, T. J. 1998. Terrestrial-marine teleconnections in the devonian: Links between the evolution of land plants, weathering processes, and marine anoxic events. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 353:113-130. | 1998 | Global | Model | Climate; CO2; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ayukai, T., D. Miller, E. Wolanski, and S. Spagnol. 1998. Fluxes of nutrients and dissolved and particulate organic carbon in two mangrove creeks in northeastern Australia. Mangroves and Salt Marshes 2:223-230. | 1998 | Australia | Mangroves; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Bach Hanne, K., KO CK Rasmussen Erik, and TO M Foster. 1998. Eutrophication modelling of a tidally influenced mangrove area in Bali subject to major dredging and reclamation activities. Pages 251-261 in International Conference on Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions. | 1998 | Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hotel & Food Services; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Baird, M. E. and M. J. Atkinson. 1998. Measurement and prediction of mass transfer to experimental coral reef communities. Limnology and Oceanography 42:1685-1693. | 1998 | Nutrients | ||
| Bak, R. P. M., M. Joenje, I. De Jong, D. Y. M. Lambrechts, and G. Nieuwland. 1998. Bacterial suspension feeding by coral reef benthic organisms. Marine Ecology Progress Series 175:285-288. | 1998 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Basillais, E. 1998. Functional role of the fractal morphology of corals: A full model of the nutrient turbulent diffusion fluxes to a coral reef [ROLE FONCTIONNEL DE LA MORPHOLOGIE FRACTALE DE CORAUX. MODELE COMPLET DES FLUX DE NUTRIMENTS PAR DIFFUSION TURBULENTE VERS UN REC. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie des Sciences - Serie III 321:295-298. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Light; Nutrients | |
| Belda-Baillie, C. A., W. Leggat, and D. Yellowlees. 1998. Growth and metabolic responses of the giant clamzooxanthellae symbiosis in a reef-fertilisation experiment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 170:131-141. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Bergstrom, D. M. and C. E. Tweedie. 1998. A conceptual model for integrative studies of epiphytes: Nitrogen utilisation, a case study. Australian Journal of Botany 46:273-280. | 1998 | Model | Nutrients | |
| Bertling, M. and E. Insalaco. 1998. Late jurassic coral/microbial reefs from the northern Paris basin - Facies, palaeoecology and palaeobiogeography. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 139:139-175. | 1998 | France | Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Sponges | |
| Breitburg, D. L. 1998. Scaling eutrophication effects between species and ecosystems: The importance of variation and similarity among species with similar functional roles. Austral Ecology 23:280-286. | 1998 | Fish; Nutrients | ||
| Bucher, D. J., V. J. Harriott, and L. G. Roberts. 1998. Skeletal micro-density, porosity and bulk density of acroporid corals. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 228:117-136. | 1998 | Australia | Lab Study | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Carpenter, S. R., N. F. Caraco, D. L. Correll, R. W. Howarth, A. N. Sharpley, and V. H. Smith. 1998. Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications 8:559-568. | 1998 | Review | Agriculture; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Charpy, L., C. Charpy-Roubaud, and P. Buat. 1998. Excess primary production, calcification and nutrient fluxes of a patch reef (Tikehau atoll, French Polynesia). Marine Ecology Progress Series 173:139-147. | 1998 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Done, T. 1998. Science for management of the Great Barrier Reef. Nature and Resources 34:16-29. | 1998 | Australia | Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Duwig, C., T. Becquer, B. E. Clothier, and M. Vauclin. 1998. Nitrate leaching through oxisols of the Loyalty Islands (New Caledonia) under intensified agricultural practices. Geoderma 84:29-43. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; New Caledonia | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Elias, R. J. and G. A. Young. 1998. Coral diversity, ecology, and provincial structure during a time of crisis: The latest Ordovician to earliest Silurian Edgewood Province in Laurentia. Palaios 13:98-112. | 1998 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | ||
| Falcon-Lang, H. 1998. The impact of wildfire on an early carboniferous coastal environment, North Mayo, Ireland. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 139:121-138. | 1998 | Algae; Discharges; Fish; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Feldmann, M. and J. A. McKenzie. 1998. Stromatolite-thrombolite associations in a modern environment, Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas. Palaios 13:201-212. | 1998 | Bahamas | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Felis, T., J. Patzold, Y. Loya, and G. Wefer. 1998. Vertical water mass mixing and plankton blooms recorded in skeletal stable carbon isotopes of a Red Sea coral. Journal of Geophysical Research C: Oceans 103:30731-30739. | 1998 | Middle East | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Ferrier-Pages, C. and J.-P. Gattuso. 1998. Biomass, production and grazing rates of pico- and nanoplankton in coral reef waters (Miyako Island, Japan). Microbial Ecology 35:46-57. | 1998 | Japan | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., D. Allemand, J.-P. Gattuso, J. Jaubert, and F. Rassoulzadegan. 1998. Microheterotrophy in the zooxanthellate coral Stylophora pistillata: Effects of light and ciliate density. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1639-1648. | 1998 | Cuba | Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Ferrier-Pages, C., J.-P. Gattuso, G. Cauwet, J. Jaubert, and D. Allemand. 1998. Release of dissolved organic carbon and nitrogen by the zooxanthellate coral Galaxea fascicularis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 172:265-274. | 1998 | Lab Study | Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| France, R., J. Holmquist, M. Chandler, and A. Cattaneo. 1998. δ15N evidence for nitrogen fixation associated with macroalgae from a seagrass-mangrove-coral reef system. Marine Ecology Progress Series 167:297-299. | 1998 | Puerto Rico | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Gast, G. J., S. Wiegman, E. Wieringa, F. C. Van Duyl, and R. P. M. Bak. 1998. Bacteria in coral reef water types: Removal of cells, stimulation of growth and mineralization. Marine Ecology Progress Series 167:37-45. | 1998 | Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Gattuso, J.-P., M. Frankignoulle, and R. Wollast. 1998. Carbon and carbonate metabolism in coastal aquatic ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 29:405-434. | 1998 | Global | Review | Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Hader, D.-P., H. D. Kumar, R. C. Smith, and R. C. Worrest. 1998. Effects on aquatic ecosystems. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 46:53-68. | 1998 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Europe | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Climate; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Wetlands |
| Hammer, O. 1998. Regulation of astogeny in halysitid tabulates. Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 43:635-651. | 1998 | Model | Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Sponges | |
| Hata, H., A. Suzuki, T. Maruyama, N. Kurano, S. Miyachi, Y. Ikeda, and H. Kayanne. 1998. Carbon flux by suspended and sinking particles around the barrier reef of Palau, western Pacific. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1883-1893. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Palau | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Heikoop, J. M., J. J. Dunn, M. J. Risk, I. M. Sandeman, H. P. Schwarcz, and N. Waltho. 1998. Relationship between light and the δ15N of coral tissue: Examples from Jamaica and Zanzibar. Limnology and Oceanography 43:909-920. | 1998 | Jamaica | Algae; Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hu, C. and K. J. Voss. 1998. Measurement of solar-stimulated fluorescence in natural waters. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1198-1206. | 1998 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
| Jameson, S. C. 1998. Rapid ecological assessment of the Cayos Miskitos Marine Reserve with notes on the shallow-water stony corals from Nicaragua. Atoll Research Bulletin 15-Jan. | 1998 | South & Central America; Nicaragua; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Kump, L. R. 1998. Wastewater Nutrients in Groundwaters of the Florida Keys. United States Environmental Protection Agency Cooperative Agreement #X994870-96-0. | 1998 | Florida | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Larned, S. T. 1998. Nitrogen- versus phosphorus-limited growth and sources of nutrients for coral reef macroalgae. Marine Biology 132:409-421. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Le Bris, S., T. Le Campion-Alsumard, and J.-C. Romano. 1998. Characteristics of epilithic and endolithic algal turf exposed to different levels of bioerosion in French Polynesian coral reefs [Caracteristiques du feutrage algal des recifs coralliens de Polynesie francaise soumis a differentes intensites de bioerosio. Oceanologica Acta 21:695-708. | 1998 | Global | Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Corallivorous Fish; Cyanobacteria; Large Herbivorous Fish; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Lin, H.-J. and K.-T. Shao. 1998. Temporal changes in the abundance and growth of intertidal Thalassia hemprichii seagrass beds in southern Taiwan. Botanical Bulletin of Academia Sinica 39:191-198. | 1998 | Taiwan | Climate; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Littlewood, I. G., C. D. Watts, and J. M. Custance. 1998. Systematic application of United Kingdom river flow and quality databases for estimating annual river mass loads (1975-1994). Science of the Total Environment 21-40. | 1998 | Europe; Britain; United Kingdom | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Lugo-Fernandez, A. 1998. Ecological implications of hydrography and circulation to the Flower Garden Banks, northwest Gulf of Mexico. Gulf of Mexico Science 16:144-160. | 1998 | South & Central America; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| McClanahan, T. R. and N. A. Muthiga. 1998. An ecological shift in a remote coral atoll of Belize over 25 years. Environmental Conservation 25:122-130. | 1998 | Global; South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Meester, E.H., R.P.M. Bak, S. Westmacott, M. Ridgley, and S. Dollar. 1998. A Fuzzy Logic Model to Predict Coral Reef Development under Nutrient and Sediment Stress. Conservation Biology 12:957-965. | 1998 | Antilles | Model | Nutrients; Sediment |
| Miyajima, T., I. Koike, H. Yamano, and H. Iizumi. 1998. Accumulation and transport of seagrass-derived organic matter in reef flat sediment of Green Island, Great Barrier Reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 175:251-259. | 1998 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Mokady, O., Y. Loya, and B. Lazar. 1998. Ammonium contribution from boring bivalves to their coral host - A mutualistic symbiosis? Marine Ecology Progress Series 169:295-301. | 1998 | Lab Study | Algae; Bivalves; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Morris, G.L., Fan, J. 1998. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. Ver. 1.04 edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY. | 1998 | Puerto Rico; Costa Rica; Venezuela; India | Model | Agriculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Forestry; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrients; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Special Use Permitting; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water |
| Muscatine, L., C. Ferrier-Pages, A. Blackburn, R. D. Gates, G. Baghdasarian, and D. Allemand. 1998. Cell-specific density of symbiotic dinoflagellates in tropical anthozoans. Coral Reefs 17:329-337. | 1998 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Jamaica | Index or Indicator | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Substrate |
| Pari, N., M. Peyrot-Clausade, T. Le Campion-Alsumard, P. Hutchings, V. Chazottes, S. Golubic, J. Le Campion, and M. F. Fontaine. 1998. Bioerosion of experimental substrates on high islands and on atoll lagoons (French Polynesia) after two years of exposure. Marine Ecology Progress Series 166:119-130. | 1998 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate | ||
| Payne, T. E., R. Szymczak, and T. D. Waite. 1998. Interaction between dissolved phosphorus and suspended sediments in a tropical estuary. Pages 219-230 in International Conference on Environmental Problems in Coastal Regions. | 1998 | Australia | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Pitt, R.; Robertson, B.; and Field, R. 1998. Innovative Multi-Chambered Stormwater Control Device for Critical Source Areas. Proc. Adv. in Urban Wet Weather Pollut. Reduction , Cleveland, Ohio, WEF (CP3805), 141. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Pugliese, R. 1998. Final habitat plan for the South Atlantic Region. South Atlantic Fishery Management Council, Charleston, SC. | 1998 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Agriculture; Aquaculture; Commercial Fisheries; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Piscivorous Fish; Recreational Fishing; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Ribes, M., R. Coma, and J.-M. Gili. 1998. Heterotrophic feeding by gorgonian corals with symbiotic zooxanthella. Limnology and Oceanography 43:1170-1179. | 1998 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Zooxanthellae | |
| Richardson, L. L. 1998. Coral diseases: what is really known? Trends in Ecology and Evolution 13:438-443. | 1998 | Global | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Pathogens | |
| Robertson, A. I., P. Dixon, and D. M. Alongi. 1998. The influence of fluvial discharge on pelagic production in the Gulf of Papua, Northern Coral Sea. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 46:319-331. | 1998 | Papua New Guinea | Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Schaffelke, B. and D. W. Klumpp. 1998. Nutrient-limited growth of the coral reef macroalga Sargassum baccularia and experimental growth enhancement by nutrient addition in continuous flow culture. Marine Ecology Progress Series 164:199-211. | 1998 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate |
| Schaffelke, B. and D. W. Klumpp. 1998. Short-term nutrient pulses enhance growth and photosynthesis of the coral reef macroalga Sargassum baccularia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 170:95-105. | 1998 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Stambler, N. 1998. Effects of light intensity and ammonium enrichment on the hermatypic coral Stylophora pistillata and its zooxanthellae. Symbiosis 24:127-146. | 1998 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Uthicke, S. and D. W. Klumpp. 1998. Microphytobenthos community production at a near-shore coral reef: Seasonal variation and response to ammonium recycled by holothurians. Marine Ecology Progress Series 169:11-Jan. | 1998 | Australia | Algae; Echinoderms; Light; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Vacelet, E., A. Arnoux, B. A. Thomassin, and M. Travers. 1998. Influence of freshwater and terrigenous material on nutrients, bacteria and phytoplankton in a high island lagoon: Mayotte, Comoro Archipelago, Indian Ocean. Hydrobiologia 380:165-178. | 1998 | Indian Ocean; Mayotte; India | Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Wang, J.-T. and A. E. Douglas. 1998. Nitrogen recycling or nitrogen conservation in an alga-invertebrate symbiosis? Journal of Experimental Biology 201:2445-2453. | 1998 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Domestic Animal Waste; Nutrients | ||
| Whitman, W. B., D. C. Coleman, and W. J. Wiebe. 1998. Prokaryotes: The unseen majority. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95:6578-6583. | 1998 | Global | Model | Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources |
| Williams, S. L. and R. C. Carpenter. 1998. Effects of unidirectional and oscillatory water flow on nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) in coral reef algal turfs, Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 226:293-316. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow |
| Zhao, HU AN TI NG. 1998. Type and evolution of landscapes of Nansha Islands. Chinese Geographical Science 8:144-151. | 1998 | Model | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Abou-Aisha, K. H. M., E. F. Shabana, M. S. El-Abyad, I. A. Kobbia, and F. Schanz. 1997. Seasonal changes in Cystoseira myrica and phosphorus input at two sites of the Red Sea Egyptian coast. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 93:199-211. | 1997 | Egypt | Nutrients | |
| Ambariyanto, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. 1997. Effect of nutrient enrichment in the field on the biomass, growth and calcification of the giant clam Tridacna maxima. Marine Biology 129:635-642. | 1997 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Baron-Szabo, R. C. 1997. The coral facies of the eastern alpine Cretaceous (Helveticum: allgau Schrattenkalk; Calcaceous, Alps: Brandenberger Gosau): taxonomy and palaeoecology [Die Korallenfazies der ostalpinen Kreide (Helvetikum: Allgauer Schrattenkalk; Nordliche Kalkalpen: Bra. Zitteliana 21:Mar-97. | 1997 | Europe | Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Barry, G. A. and G. E. Rayment. 1997. Heavy metals and nutrients in soils and sediments of Raine Island, Great Barrier Reef. Pages 281-285 in Land Contamination and Reclamation. | 1997 | Australia; Papua New Guinea | Agriculture; Landscape Changes; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Birkeland, C. 1997. Symbiosis, fisheries and economic development on coral reefs. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 12:364-367. | 1997 | Palau | Commercial Fisheries; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Resource Use Management | |
| Bouvy, M., R. Arfi, and M. Troussellier. 1997. Taxonomic characterization of pelagic and periphytic heterotrophic bacteria isolated from the tropical Ebrie lagoon, Cote d'lvoire. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 140:393-409. | 1997 | Index or Indicator | Artificial Habitat; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Brand, L. 1997. Semi-Synoptic Sampling of Phytoplankton in Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. University of Miami. | 1997 | Florida | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Carrera, M. G. 1997. The evolution and turnover of the Ordovician sponge and bryozoan faunas in the Argentine Precordillera [Evolucion y recambio de las faunas de poriferos y briozoos en el Ordovicico de la Precordillera Argentina]. Ameghiniana 34:295-308. | 1997 | Global | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Cook, C. B., E. M. Mueller, M. D. Ferrier. 1997. Reef Corals and Their Symbiotic Algae as Indicators of Nutrient Exposure. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency / South Florida Water Management District. | 1997 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Cortes, J. 1997. Biology and geology of eastern Pacific coral reefs. Coral Reefs 16. | 1997 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Review; Lab Study | Nutrients; Salinity |
| Daily, G. C., S. Alexander, P. R. Ehrlich, L. Goulder, J. Lubchenco, P. A. Matson, H. A. Mooney, S. Postel, S. H. Schneider, D.Tilman, and G. M. Woodwell. 1997. Ecosystem services: benefits supplied to human societies by natural ecosystems. Issues in Ecology 1:1-18. | 1997 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Climate; Economic Markets & Policies; Forestry; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Special Use Permitting |
| Diaz, M. C. and B. B. Ward. 1997. Sponge-mediated nitrification in tropical benthic communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 156:97-107. | 1997 | South & Central America; Cuba; Belize; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sponges; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges | |
| Hantoro, W. S. 1997. Quaternary sea level variations in the Pacific-Indian Ocean gateways: Response and impact. Quaternary International 37:73-80. | 1997 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; India; Pacific Ocean; Indonesia | Climate; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Hoegh-Guldberg, Ove, Misaki Takabayashi and Guillermo Moreno. 1997. The impact of long-term nutrient enrichment on coral calcification and growth. Pages 861-6 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1997 | Nutrients | ||
| Holmes, N. J., V. J. Harriott, and S. A. Banks. 1997. Latitudinal variation in patterns of colonisation of cryptic calcareous marine organisms. Marine Ecology Progress Series 155:103-113. | 1997 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Hunter, D. J., L. G. G. Yapa, and N. V. Hue. 1997. Effects of green manure and coral lime on corn growth and chemical properties of an acid Oxisol in Western Samoa. Biology and Fertility of Soils 24:266-273. | 1997 | Samoa | Agriculture; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients | |
| Hussner, H. and J. Roessler. 1997. Mathematical modelling and numerical simulation of reefs. CFS Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg 225-235. | 1997 | Model | Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Jennings, S., O. Renones, B. Morales-Nin, N. V. C. Polunin, J. Moranta, and J. Coll. 1997. Spatial variation in the 15N and 13C stable isotope composition of plants, invertebrates and fishes on Mediterranean reefs: Implications for the study of trophic pathways. Marine Ecology Progress Series 146:109-116. | 1997 | Spain | Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Jones, R. J. and D. Yellowlees. 1997. Regulation and control of intracellular algae ( = zooxanthellae) in hard corals. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 352:457-468. | 1997 | Model; Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kleypas, J. A. 1997. Modeled estimates of global reef habitat and carbonate production since the last glacial maximum. Paleoceanography 12:533-545. | 1997 | Global | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Complex Habitat & Resources; Light; Nutrients; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Komatsu, T. 1997. Long-term changes in the Zostera bed area in the Seto Inland Sea (Japan), especially along the coast of the Okayama Prefecture. Oceanologica Acta 20:209-216. | 1997 | Japan | Review | Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development; Nutrients |
| Kump, L. R. 1997. Fate of Wastewater nutrients in Florida Keys Groundwater. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency #x98429297-0-PA. | 1997 | Florida | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Lapointe, B. E. 1997. Nutrient thresholds for bottom-up control of macroalgal blooms on coral reefs in Jamaica and southeast Florida. Limnology and Oceanography 42:1119-1131. | 1997 | South & Central America; Florida; Jamaica; Caribbean | Algae; Discharges; Light; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Lapointe, B. E., W. R. Matzie. 1997. High Frequency Monitoring of Wastewater Nutrient Discharges and Their Ecological Effects in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution. | 1997 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Discharges; Nutrients; Wastewater Discharge |
| Larned, S. T. and M. J. Atkinson. 1997. Effects of water velocity on NH4 and PO4 uptake and nutrient-limited growth in the macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa. Marine Ecology Progress Series 157:295-302. | 1997 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Lewis, J. B. 1997. Abundance, distribution and partial mortality of the massive coral Siderastrea siderea on degrading coral reefs at Barbados, West Indies. Marine Pollution Bulletin 34:622-627. | 1997 | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral | ||
| Littler, D. S. and M. M. Littler. 1997. An illustrated marine flora of the Pelican Cays, Belize. Bulletin - Biological Society of Washington 9:149. | 1997 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Nutrients; Physical Damage | |
| Marguillier, S., G. Van Der Velde, F. Dehairs, M. A. Hemminga, and S. Rajagopal. 1997. Trophic relationships in an interlinked mangrove-seagrass ecosystem as traced by δ13C and δ15N. Marine Ecology Progress Series 151:115-121. | 1997 | Kenya | Algae; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses | |
| Mate, T., L. Juan. 1997. Experimental responses of Panamanian reef corals to high temperature and nutrients. Pages 515-20 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1997 | Panama | Nutrients | |
| McClanahan, T. R. 1997. Primary succession of coral-reef algae: Differing patterns on fished versus unfished reefs. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 218:77-102. | 1997 | Model | Algae; Coralline Algae; Discharges; Fish; Light; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| McClanahan, T. R., D. Obura. 1997. Sedimentation effects on shallow coral communities in Kenya. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 209:103-122. | 1997 | Kenya | Algae; Discharges; Hydrocoral; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| McConnaughey, T. A. and J. F. Whelan. 1997. Calcification generates protons for nutrient and bicarbonate uptake. Earth-Science Reviews 42:95-117. | 1997 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Neuman, B. E. E. 1997. Evaluation of rugose coral potentials as index fossils. Boletin - Real Sociedad Espanola de Historia Natural: Seccion Geologica 92:303-309. | 1997 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Ohowa, B. O., B. M. Mwashote, and W. S. Shimbira. 1997. Dissolved inorganic nutrient fluxes from two seasonal rivers into Gazi Bay, Kenya. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 45:189-195. | 1997 | Kenya | Discharges; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Pandey, J. S. and P. Khanna. 1997. Sensitivity analysis of a mangrove ecosystem model. Journal of Environmental Systems 26:57-72. | 1997 | Model | Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients | |
| Pisera, A. 1997. Upper Jurassic siliceous sponges from the Swabian Alb: taxonomy and paleoecology. Palaeontologia Polonica 57:216. | 1997 | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Rendell, P. S. and T. R. Pritchard. 1997. Physicochemical conditions in coastal waters off Sydney, Central NSW, Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 33:132-139. | 1997 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Rissik, D., I. M. Suthers, and C. T. Taggart. 1997. Enhanced zooplankton abundance in the lee of an isolated reef in the south Coral Sea: The role of flow disturbance. Journal of Plankton Research 19:1347-1368. | 1997 | Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Rosenthal, Y., E. A. Boyle, and N. Slowey. 1997. Temperature control on the incorporation of magnesium, strontium, fluorine, and cadmium into benthic foraminiferal shells from Little Bahama Bank: Prospects for thermocline paleoceanography. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 61:3633-3643. | 1997 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Rougerie, F., C. Jehl, and J. Trichet. 1997. Phosphorus pathways in atolls: Interstitial nutrient pool, cyanobacterial accumulation and Carbonate-Fluoro-Apatite (CFA) precipitation. Marine Geology 139:201-217. | 1997 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Semple, S. 1997. Algal growth on two sections of a fringing coral reef subject to different levels of eutrophication in Reunion Island. Oceanologica Acta 20:851-861. | 1997 | Reunion | Algae; Nutrients | |
| Sharpies, J. M. and J. W. G. Cairney. 1997. Organic nitrogen utilization by an unidentified mycobiont isolated from mycorrhizas of Pisonia grandis. Mycological Research 101:315-318. | 1997 | Nutrients | ||
| Stapel, J., R. Manuntun, and M. A. Hemminga. 1997. Biomass loss and nutrient redistribution in an Indonesian Thalassia hemprichii seagrass bed following seasonal low tide exposure during daylight. Marine Ecology Progress Series 148:251-262. | 1997 | Indonesia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Steven, Andrew D.L., and Andrew D. Broadbent. 1997. Growth and metabolic responses of Acropora palifera to long term nutrient enrichment. Pages 867-72 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1997 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Stimson, J. 1997. The annual cycle of density of zooxanthellae in the tissues of field and laboratory-held Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 214:35-48. | 1997 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Szmant, A.M. 1997. Nutrient effects on coral reefs: a hypothesis on the importance of topographic and trophic complexity to reef nutrient dyna. Pages 1527-32 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Symp. | 1997 | Nutrients | ||
| Tentori, E., J.C. Coll, and B. Fleury. 1997. ENCORE: Effects of elevated nutrients on the C:N:P ratios of Sarcophyton sp (Alcyonacea). Pages 885-90 in Proceedings of the 8th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1997 | Nutrients | ||
| Williams, S. L. and R. C. Carpenter. 1997. Grazing effects on nitrogen fixation in coral reef algal turfs. Marine Biology 130:223-231. | 1997 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Wilson, S. and D. R. Bellwood. 1997. Cryptic dietary components of territorial damselfishes (Pomacentridae, Labroidei). Marine Ecology Progress Series 153:299-310. | 1997 | Algae; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Alongi, D. M. 1996. The dynamics of benthic nutrient pools and fluxes in tropical mangrove forests. Journal of Marine Research 54:123-148. | 1996 | Australia | Forestry; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Arias, C., J.-P. Masse, and L. Vilas. 1996. Hauterivian shallow marine calcareous biogenic mounds: S.E. Spain. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 119:17-Mar. | 1996 | Spain | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Burrage, D. M., C. R. Steinberg, W. J. Skirving, and J. A. Kleypas. 1996. Mesoscale circulation features of the great barrier reef region inferred from NOAA satellite imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment 56:21-41. | 1996 | Australia | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Chazottes, V. 1996. Experimental study of bioerosion and sedimentogenesis in a reefal environment: Eutrophication effects (Reunion Island, Indian Ocean) [Etude experimentale de la bioerosion et de la sedimentogenese en milieu recifal: Effets de Feutrophisation (île de. Comptes Rendus de l'Academie de Sciences - Serie IIa: Sciences de la Terre et des Planetes 323:787-794. | 1996 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India; France | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Cockey, E., P. Hallock, and B. H. Lidz. 1996. Decadal-scale changes in benthic foraminiferal assemblages off Key Largo, Florida. Coral Reefs 15:237-248. | 1996 | Florida | Nutrients; Pathogens; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Coultas, C. L., T. J. Post, J. B. Jones Jr., and Y. P. Hsieh. 1996. Use of velvet bean to improve soil fertility and weed control in corn production in Northern Belize. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis 27:2171-2196. | 1996 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients |
| Dubinsky, Z. and N. Stambler. 1996. Marine pollution and coral reefs. Global Change Biology 2:511-526. | 1996 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Edinger, E. N. and M. J. Risk. 1996. Sponge borehole size as a relative measure of bioerosion and paleoproductivity. Lethaia 29:275-286. | 1996 | Puerto Rico; Australia | Index or Indicator | Boring Sponges; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Sponges |
| Fabricius, T. E. 1996. Ecosystem recovery after episodic disturbance: Resilience of some coral reefs after Acanthaster outbreaks. Senckenbergiana Maritima 27:227-235. | 1996 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Octocoral; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates |
| Flathman Paul, E., L. Laski Mary, R. Trausch Jason, H. Carson Jr. John, M. Woodhull Patrick, E. Jerger Douglas, and R. Lear Paul. 1996. Effect of micronutrient addition on the bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon (PHC)-contaminated coral sand at a U.S. Navy facility on Midway Island in the Pacific. in Proceedings of the Air & Waste Management Association's Annual Meeting & Exhibition. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Coastal Defense; Military; Nutrients; Remediation; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Freiwald, A. and J. Schonfeld. 1996. Substrate pitting and boring pattern of Hyrrokkin sarcophaga Cedhagen, 1994 (foraminifera) in a modem deep-water coral reef mound. Marine Micropaleontology 28:199-207. | 1996 | Bivalves; Nutrients; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Furnas, M. J. and A. W. Mitchell. 1996. Nutrient inputs into the central Great Barrier Reef (Australia) from subsurface intrusions of Coral Sea waters: A two-dimensional displacement model. Continental Shelf Research 16:1127-1148. | 1996 | Australia | Model | Nutrients |
| Hicklenton, P. R. and K. G. Cairns. 1996. Plant water relations and mineral nutrition of containerized nursery plants in relation to irrigation method. Canadian Journal of Plant Science 76:155-160. | 1996 | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Irrigation; Nutrients | ||
| Homewood, P. W. 1996. The carbonate feedback system: Interaction between stratigraphic accommodation, ecological succession and the carbonate factory [Le systeme de feed-back des carbonate: Une interaction entre accommodation stratigraphique, succession ecologique et l'usine. Bulletin de la Societe Geologique de France 167:701-715. | 1996 | Oman; France | Model | Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Insalaco, E. 1996. Upper jurassic microsolenid biostromes of northern and central Europe: Facies and depositional environment. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 121:169-194. | 1996 | Europe | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges |
| Kaandorp, J. A., C. P. Lowe, D. Frenkel, and P. M. A. Sloot. 1996. Effect of nutrient diffusion and flow on coral morphology. Physical Review Letters 77:2328-2331. | 1996 | Model | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Katz, M. 1996. The Florida Keys ecosystem monitoring integration project. Earth System Monitor 6:13-Dec. | 1996 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Internet & Telecommunications; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins |
| Kitheka, J. U. 1996. Water circulation and coastal trapping of brackish water in a tropical mangrove-dominated bay in Kenya. Limnology and Oceanography 41:169-176. | 1996 | Kenya | Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kitheka, J. U., B. O. Ohowa, B. M. Mwashote, W. S. Shimbira, J. M. Mwaluma, and J. M. Kazungu. 1996. Water circulation dynamics, water column nutrients and plankton productivity in a well-flushed tropical bay in Kenya. Journal of Sea Research 35:257-268. | 1996 | Kenya | Discharges; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kudo, I., H. Kokubun, and K. Matsunaga. 1996. Cadmium in the southwest Pacific Ocean two factors significantly affecting the Cd-PO4 relationship in the ocean. Marine Chemistry 54:55-67. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Model | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Lapointe, B. E. and W. R. Matzie. 1996. Effects of stormwater nutrient discharges on eutrophication processes in nearshore waters of the Florida Keys. Estuaries 19:422-435. | 1996 | Florida | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Larned, S. T. and J. Stimson. 1996. Nitrogen-limited growth in the coral reef chlorophyte Dictyosphaeria cavernosa, and the effect of exposure to sediment-derived nitrogen on growth. Marine Ecology Progress Series 145:95-108. | 1996 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral | |
| Laws, E. A. and C. B. Allen. 1996. Water quality in a subtropical embayment more than a decade after diversion of sewage discharges. Pacific Science 50:194-210. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Leichter, J. J., S. R. Wing, S. L. Miller, and M. W. Denny. 1996. Pulsed delivery of subthermocline water to Conch Reef (Florida Keys) by internal tidal bores. Limnology and Oceanography 41:1490-1501. | 1996 | Florida | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Letourneur, Y. 1996. Dynamics of fish communities on Reunion fringing reefs, Indian Ocean. II. Patterns of temporal fluctuations. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 195:31-52. | 1996 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Fish; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Marks, A. D. and T. L. Fallowfield. 1996. A retrospective study of decompression illness in recreational scuba divers and scuba instructors in Queensland. South Pacific Underwater Medicine Society Journal 26:119-123. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Cuba; Papua New Guinea | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Marubini, F. and P. S. Davies. 1996. Nitrate increases zooxanthellae population density and reduces skeletogenesis in corals. Marine Biology 127:319-328. | 1996 | Cuba | Lab Study; Model | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| McConnaughey, T.A., and J.F. Whelan. 1996. Calification generates protons for nutrient and bicarbonate uptake. Earth Science Reviews 967:1-23. | 1996 | Nutrients | ||
| McCook, L. J. 1996. Effects of herbivores and water quality on Sargassum distribution on the central Great Barrier Reef: Cross-shelf transplants. Marine Ecology Progress Series 139:179-192. | 1996 | Australia | Algae; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Middelburg, J. J., J. Nieuwenhuize, F. J. Slim, and B. Ohowa. 1996. Sediment biogeochemistry in an east African mangrove forest (Gazi Bay, Kenya). Biogeochemistry 34:133-155. | 1996 | Kenya | Carbon Storage & Cycling; CO2; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Millhr, M. W. and M. E. Hay. 1996. Coral-seaweed-grazer-nutrient interactions on temperate reefs. Ecological Monographs 66:323-344. | 1996 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients |
| O'Neil, J. M., P. M. Metzler, and P. M. Glibert. 1996. Ingestion of 15N2-labelled Trichodesmium spp. and ammonium regeneration by the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis. Marine Biology 125:89-96. | 1996 | South & Central America; Australia; Cuba; Caribbean | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Pedley, M. 1996. Miocene reef distributions and their associations in the central Mediterranean region: an overview. Models for carbonate stratigraphy from Miocene reef complexes of Mediterranean regions 73-87. | 1996 | Review | Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Perez-Espana, H. and L. A. Abitia-Cardenas. 1996. Description of the digestive tract and feeding habits of the king angelfish and the Cortes angelfish. Journal of Fish Biology 48:807-817. | 1996 | Fish; Invertivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Pickard, N. A. H. 1996. Evidence for microbial influence on the development of Lower Carboniferous buildups. Geological Society Special Publication 65-82. | 1996 | Europe | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Sammarco, P. W. 1996. Comments on coral reef regeneration, bioerosion, biogeography, and chemical ecology: Future directions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 200:135-168. | 1996 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Review | Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment |
| Scott, R. W. 1996. Global environmental controls on Cretaceous reefal ecosystems. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 119:187-199. | 1996 | Global | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Shulman, M. J. and D. R. Robertson. 1996. Changes in the coral reefs of San Bias, Caribbean Panama: 1983 to 1990. Coral Reefs 15:231-236. | 1996 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Spokes, Lucinda J. and Peter S. Liss. 1996. Photochemically induced redox reactions in seawater II Nitrogen and iodine. Marine Chemistry 54:1-10. | 1996 | Nutrients | ||
| Spotte, S. 1996. Supply of regenerated nitrogen to sea anemones by their symbiotic shrimp. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 198:27-36. | 1996 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Stimson, J., S. Larned, and K. McDermid. 1996. Seasonal growth of the coral reef macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa (Forskal) Borgesen and the effects of nutrient availability, temperature and herbivory on growth rate. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 196:53-77. | 1996 | Lab Study | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Light; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Swart, P. K., G. F. Healy, R. E. Dodge, P. Kramer, J. H. Hudson, R. B. Halley, and M. B. Robblee. 1996. The stable oxygen and carbon isotopic record from a coral growing in Florida Bay: A 160 year record of climatic and anthropogenic influence. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 123:219-237. | 1996 | South & Central America; Florida; Mexico | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Szmant, A. M. and A. Forrester. 1996. Water column and sediment nitrogen and phosphorus distribution patterns in the Florida Keys, USA. Coral Reefs 15:21-41. | 1996 | Florida | Docks & Marinas; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Torreton, J.-P. and P. Dufour. 1996. Temporal and spatial stability of bacterioplankton biomass and productivity in an atoll lagoon. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 11:251-261. | 1996 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Turnbull, M. H., S. Schmidt, P. D. Erskine, S. Richards, and G. R. Stewart. 1996. Root adaptation and nitrogen source acquisition in natural ecosystems. Tree Physiology 16:941-948. | 1996 | Australia | Mangroves; Nutrients | |
| Wright, J. K. 1996. The depositional history of the hackness coral-sponge bed and its associated sediments within the passage beds member of the coralline oolite formation (corallian group; oxfordian) of north yorkshire. Proceedings of the Yorkshire Geological Society 49:155-168. | 1996 | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Zann, L. P. 1996. The state of the Marine Environment Report for Australia (SOMER): Process, findings and perspectives. Ocean and Coastal Management 33:63-86. | 1996 | Global; Australia | Invasive Species; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Zhuravlev, A. Y. 1996. Reef ecosystem recovery after the early Cambrian extinction. Pages 79-96 Biotic recovery from mass extinction events. | 1996 | Nutrients; Plankton; Sponges | ||
| Atkinson, M. J., B. Carlson, and G. L. Crow. 1995. Coral growth in high-nutrient, low-pH seawater: a case study of corals cultured at the Waikiki Aquarium, Honolulu, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 14:215-223. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | CO2; Nutrients |
| Bell, P. R. and I. Elmetri. 1995. Ecological indicators of large-scale eutrophication in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Ambio 24:208-215. | 1995 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Nutrients |
| Bilger, R. W. and M. J. Atkinson. 1995. Effects of nutrient loading on mass-transfer rates to a coral-reef community. Limnology and Oceanography 40:279-289. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| Bjork, M., S. M. Mohammed, M. Bjorklund, and A. Semesi. 1995. Coralline algae, important coral-reef builders threatened by pollution. Ambio 24:502-505. | 1995 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Light; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Bridges, P. H., P. Gutteridge, and N. A. H. Pickard. 1995. The environmental setting of Early Carboniferous mud-mounds. Pages 171-190 Carbonate mud-mounds: their origin and evolution. | 1995 | Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Clavier, J., P. Chardy, and C. Chevillon. 1995. Sedimentation of particulate matter in the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia: Spatial and temporal patterns. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 40:281-294. | 1995 | New Caledonia | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | |
| Crossland, C.J. 1995. Dissolved nutrients in coral reef waters. Pages 56-69 in DJ Barnes, editor. Perspectives on Coral Reefs. AIMS, Brian Clouston Publisher. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| Dullo, W.-C., M. Gektidis, S. Golubic, G. A. Heiss, H. Kampmann, W. Kiene, D. K. Kroll, M. L. Kuhrau, G. Radtke, J. G. Reijmer, G. B. Reinicke, D. Schlichter, H. Schuhmacher, and K. Vogel. 1995. Factors controlling holocene reef growth: An interdisciplinary approach. Facies 32:145-188. | 1995 | Global; Bahamas; Egypt; Sudan; Djibouti | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Cyanobacteria; Light; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae |
| Farmer, A. M. 1995. Soil chemistry change in a lowland English deciduous woodland 1974-1991. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 85:677-682. | 1995 | England | Nutrients | |
| Gates, R. D., O. Hoegh-Guldberg, M. J. McFall-Ngai, K. Y. Bil, and L. Muscatine. 1995. Free amino acids exhibit anthozoan 'host factor' activity: They induce the release of photosynthate from symbiotic dinoflagellates in vitro. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92:7430-7434. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Primary Production; Stony Coral | |
| Genin, A., B. Lazar, and S. Brenner. 1995. Vertical mixing and coral death in the Red Sea following the eruption of Mount Pinatubo. Nature 377:507-510. | 1995 | Middle East; Philippines | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Iryu, Y., T. Nakamori, S. Matsuda, and O. Abe. 1995. Distribution of marine organisms and its geological significance in the modern reef complex of the Ryukyu Islands. Sedimentary Geology 99:243-258. | 1995 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Coralline Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Skeletal Coral | ||
| Janson, S., A. N. Rai, and B. Bergman. 1995. Intracellular cyanobiont Richelia intracellularis: ultrastructure and immuno-localisation of phycoerythrin, nitrogenase, Rubisco and glutamine synthetase. Marine Biology 124:39821. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| Li, S., R. R. Manory, and J. H. Hensler. 1995. Compound layer growth and compound layer porosity of austenite plasma nitrocarburised non-alloyed steel. Surface and Coatings Technology 71:112-120. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| McAuley, P. J. and V. J. Smith. 1995. Effect of diel photoperiod on nitrogen metabolism of cultured and symbiotic zooxanthellae. Marine Biology 123:145-152. | 1995 | Cuba | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ndaro, S. G. M., S. Sjoling, and E. Olafsson. 1995. Small-scale variation in major meiofaunal taxa and sediment chemistry in tropical sediments. Ambio 24:470-474. | 1995 | Mangroves; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Rougerie, F. 1995. Nature and functioning of the atolls of Tuamotu archipelago, French Polynesia [Nature et fonctionnement des atolls des Tuamotu (Polynesie Francaise)]. Oceanologica Acta 18:61-78. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | CO2; Nutrients; Salinity |
| San Diego-McGlone, M. L., C. L. Villanoy, and P. M. Alino. 1995. Nutrient mediated stress on the marine communities of a coastal lagoon (Puerto Galera, Philippines). Marine Pollution Bulletin 31:355-366. | 1995 | Philippines | Index or Indicator | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Staunton Smith, J. and C. R. Johnson. 1995. Nutrient inputs from seabirds and humans on a populated coral cay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 124:189-200. | 1995 | Australia | Marine Birds; Nutrients | |
| Suzuki, Y., N. Nakashima, K. Yoshida, B. Casareto, M. Taki, T. Hiraga, T. Okabayashi, H. Ito, and K. Yamada. 1995. The important role of organic matter cycling for the biological fixation of CO2 in coral reefs. Energy Conversion and Management 36:737-740. | 1995 | Japan | CO2; Nutrients | |
| Tegner, M. J., P. K. Dayton, P. B. Edwards, K. L. Riser, D. B. Chadwick, T. A. Dean, and L. Deysher. 1995. Effects of a large sewage spill on a kelp forest community: Catastrophe or disturbance? Marine Environmental Research 40:181-224. | 1995 | Light; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Wolanski, E. and B. Delesalle. 1995. Upwelling by internal waves, Tahiti, French Polynesia. Continental Shelf Research 15:357-368. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| Yamamuro, M., H. Kayanne, and M. Minagawa. 1995. Carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of primary producers in coral reef ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography 40:617-621. | 1995 | Nutrients | ||
| Bell, P. R. F. and T. Tomascik. 1994. The demise of the fringing coral reefs of Barbados and of regions in the Great Barrier Reef (GBR) lagoon - impacts of eutrophication. Pages 319-325 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Agriculture; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bishop, J. W. and J. G. Greenwood. 1994. Nitrogen excretion by some demersal macrozooplankton in Heron and One Tree Reefs, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Marine Biology 120:447-454. | 1994 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Burke, Maria. 1994. Phosphorous fingered as coral killer. Science 263:1086. | 1994 | Nutrients | ||
| Chansang, H. and N. Phongsuwan. 1994. Health of fringing reefs of Asia through a decade of change: a case history from Phuket Island, Thailand. Pages 286-292 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; Thailand | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Seastars; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Chong, CA LV IN and R. A. Cline. 1994. Response of container-grown nursery crops to raw and composted paper mill sludges. Compost Science and Utilization 2:90-96. | 1994 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Cook, C. B., G. Mullerparker, and C. D. Orlandini. 1994. Ammonium enhancement of dark carbon fixation and nitrogen limitation in zooxanthellae symbiotic with the reef corals Madracis mirabilis and Montastrea annularis. Marine Biology 118:157-166. | 1994 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| De Sylva, D. P. 1994. Distribution and ecology of ciguatera fish poisoning in Florida, with emphasis on the Florida Keys. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:944-954. | 1994 | Global; Florida | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fish; Nutrients | |
| Dubinsky, Z., and P.L. Jokiel. 1994. Ratio of energy and nutrient fluxes regulates symbiosis between zooxanthellae and corals. Pacific Science 48:313-24. | 1994 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Edinger, E. N. and M. J. Risk. 1994. Oligocene-Miocene extinction and geographic restriction of Caribbean corals: roles of turbidity, temperature, and nutrients. Palaios 9:576-598. | 1994 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Erftemeijer, P. L. A. 1994. Differences in nutrient concentrations and resources between seagrass communities on carbonate and terrigenous sediments in South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:403-419. | 1994 | Indonesia | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Eyre, B. 1994. Nutrient biogeochemistry in the tropical Moresby River estuary system North Queensland, Australia. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 39:15-32. | 1994 | Australia | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Fautin, D. G., D. J. Futuyma, and F. C. James. 1994. Annual review of ecology and systematic. Volume 25. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics | 1994 | Review; Model | Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Snails & Conch; Stony Coral; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Fong, P. and M. A. Harwell. 1994. Modeling seagrass communities in tropical and subtropical bays and estuaries: a mathematical model synthesis of current hypothesis. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:757-781. | 1994 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Galetto, M. J. and D. R. Bellwood. 1994. Digestion of algae by Stegastes nigricans and Amphiprion akindynos (Pisces: Pomacentridae), with an evaluation of methods used in digestibility studies. Journal of Fish Biology 44:415-428. | 1994 | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Ginsburg, R. N. and E. A. Shinn. 1994. Preferential distribution of reefs in the Florida reef tract: the past is the key to the present. Pages 21-26 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; Florida; Bahamas | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Gischler, E., K.-U. Grafe, and J. Wiedmann. 1994. The upper cretaceous Lacazina limestone in the Basco-Cantabrian and Iberian basins of northern Spain: Cold-water grain associations in warm-water environments. Facies 30:209-245. | 1994 | Oman; Spain | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Haroun, R. J. 1994. Environmental description of an artificial reef site in Gran Canaria (Canary Islands, Spain) prior to reef placement. Bulletin of Marine Science 55:932-938. | 1994 | Spain | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Invertebrates; Nutrients | |
| Hovland, M., P. F. Croker, and M. Martin. 1994. Fault-associated seabed mounds (carbonate knolls?) off western Ireland and north-west Australia. Marine and Petroleum Geology 11:232-246. | 1994 | Australia | Calcareous Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Huber, M. E. 1994. An assessment of the status of the coral reefs of Papua New Guinea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:69-73. | 1994 | Global; Papua New Guinea | Agriculture; Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Hudson, J. H., K. J. Hanson, R. B. Halley, and J. L. Kindinger. 1994. Environmental implications of growth rate changes in Montastrea annularis: Biscayne National Park, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:647-669. | 1994 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Hunter, C. L. and C. W. Evans. 1994. Reefs in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii: two centuries of western influence and two decades of data. Pages 339-345 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Hutchings, P. 1994. The Pacific reefs: a paradise lost? Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:1-140. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Sediment |
| Intes, A. 1994. Tikehau: an atoll of the Tuamotu Archipelago (French Polynesia). Atoll Research Bulletin | 1994 | Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Jokiel, P. L. 1994. Nutrient limitation in the symbiotic association between zooxanthellae and reef-building corals: a United States-Israel workshop, Coconut Island, Hawaii, August 1991. Pacific Science 48:213-324. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Lapointe, B. E., D. A. Tomasko, and W. R. Matzie. 1994. Eutrophication and Tropic State Classification of Seagrass Communities in the Florida Keys. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:696-717. | 1994 | Florida | Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Lapointe, B. E., W. R. Matzie, and M. W. Clark. 1994. Phosphorus inputs and eutrophication on the Florida reef tract. Pages 106-112 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; Mexico | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Larkum, A. W. D. and A. D. L. Steven. 1994. ENCORE: The Effect of Nutrient Enrichment on Coral Reefs. 1. Experimental design and research programme. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:112-120. | 1994 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients |
| Lobban, C. S. and P. J. Harrison. 1994. Seaweed ecology and physiology. Seaweed ecology and physiology. | 1994 | Review | Algae; Aquaculture; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Seagrasses | |
| Mann, G. S. 1994. Distribution, Abundance and Life History of the Reef Coral Favia fragum (Espter) in Barbados: Effects of Eutrophication and of the Black Sea Urchin Diadema antillarum (Philippi). McGill University, Montreal, Quebec. | 1994 | Nutrients; Sea Urchins | ||
| Martin, JO SM . and J. C. Braga. 1994. Messinian events in the Sorbas Basin in southeastern Spain and their implications in the recent history of the Mediterranean. Sedimentary Geology 90:257-268. | 1994 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Spain | Calcareous Macroalgae; Climate; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Montaggioni, L. F., P. Cuet, and O. Naim. 1994. Effect of nutrient excess on a modern fringing reef (Reunion Island, western Indian Ocean). Geological implications. Pages 397-403 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Algae; Boring Sponges; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Salinity; Sponges | |
| Ogden, J. C., J. W. Porter, N. P. Smith, A. M. Szmant, W. C. Jaap, and D. Forcucci. 1994. A long-term interdisciplinary study of the Florida Keys seascape. Bulletin of Marine Science 54:1059-1071. | 1994 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Piot, BE RN AR D, RE MI Ferriere, and BE RN AR D Fraboulet. 1994. Unique experience with foamed cement. Pages 127-142 in European Petroleum Conference - Proceedings. | 1994 | Europe | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Nutrients; Special Use Permitting |
| Prove, B. G., T. J. McShane, J. R. Reghenzani, J. D. Armour, S. Sen, and P. W. Moody. 1994. Nutrient loss via drainage from the major agricultural industries on the wet tropical coast of Queensland. in National Conference Publication - Institution of Engineers, Australia. | 1994 | Australia | Agriculture; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Risk, M. J., J. J. Dunn, W. R. Allison, and C. Horrill. 1994. Reef monitoring in Maldives and Zanzibar: low-tech and high-tech science. Pages 66-72 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; Maldives | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Nutrients |
| Rougerie, F. and J. Rancher. 1994. The Polynesian South Ocean: Features and circulation. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:14-25. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Scoffin, T. P. 1994. History of a fringing reef on the west coast of Barbados 1974-1992. Pages 273-278 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global | Algae; Coralline Algae; Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Sebens K.P. 1994. Biodiversity of coral reefs: what are we losing and why? American Zoologist 34:115-133. | 1994 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Seastars; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Shashar, N., T. Feldstein, Y. Cohen, and Y. Loya. 1994. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) on a coral reef. Coral Reefs 13:171-174. | 1994 | Nutrients | ||
| Shashar, N., Y. Cohen, Y. Loya, and N. Sar. 1994. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) in stony corals - Evidence for coral-bacteria interactions. Marine Ecology Progress Series 111:259-264. | 1994 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Shinn, E. A., R. S. Reese, and C. D. Reich. 1994. Fate and pathways of injection-well effluent in the Florida Keys. | 1994 | Florida | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Slegrist, R. L., T. J. Phelps, N. E. Korte, and D. A. Pickering. 1994. Characterization and biotreatability of petroleum contaminated soils in a coral Atoll in the Pacific Ocean. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 1:757-773. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Marshall Islands | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Remediation; Sediment |
| Smith, S. R. 1994. Status and recent history of coral reefs at the CARICOMP network of Caribbean marine laboratories. Pages 73-79 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Lab Study | Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation |
| Snidvongs, A. and R. A. Kinzie III. 1994. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichement on in vivo symbiotic zooxanthellae of Pocillopora damicornis. Marine Biology 118:705-711. | 1994 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Thomas, P. M. E. 1994. Everglades nutrient removal project. Pages 27-Nov in Proc. conference on explosives and blasting technique, Austin Texas, 1994. | 1994 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Stony Coral |
| Tomascik, T., Suharsono, and A. J. Mah. 1994. Case histories: a historical perspective of the natural and anthropogenic impacts in the Indonesian Archipelago with a focus on the Kepulauan Seribu, Java Sea. Pages 304-310 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; Java; Indonesia | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Veron, J. E. N. 1994. Biodiversity of reef corals: is there a problem in the Indo-Pacific centre of diversity? Pages 365-370 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Japan; Indonesia | Finfish Harvest; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients | |
| Young, I. R., K. P. Black, and M. L. Heron. 1994. Circulation in the Ribbon Reef Region of the Great Barrier Reef. Continental Shelf Research 14:117-142. | 1994 | Australia | Model | Nutrients |
| Zann, L. P. 1994. The status of coral reefs in South Western Pacific Islands. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:52-61. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Fiji; Tonga; Samoa | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Seastars; Sediment | |
| Ayukai, T. 1993. Temporal variability of the nutrient environment on Davies Reef in the central Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Pacific Science 47:171-179. | 1993 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Bekkaoui, A. and E. Thibout. 1993. Role of the cocoon of Acrolepiopsis assectella (Lep., Hyponomeutoidae) in host recognition by the parasitoid Diadromus pulchellus (Hym., Ichneumonidae). Entomophaga 38:101-113. | 1993 | Nutrients | ||
| Boreen, T., N. James, C. Wilson, and D. Heggie. 1993. Surficial cool-water carbonate sediments on the Otway continental margin, southeastern Australia. Marine Geology 112:35-56. | 1993 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | |
| Brasier, M. D. and O. R. Green. 1993. Winners and losers: stable isotopes and microhabitats of living Archaiadae and Eocene Nummulites (larger foraminifera). Marine Micropaleontology 20:267-276. | 1993 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean; England | Nutrients | |
| Caus, E., A. Gomez-Garrido, A. Simo, and K. Sofiano. 1993. Cenomanian-Turonian platform to basin integrated stratigraphy in the South Pyrenees (Spain). Cretaceous Research 14:531-551. | 1993 | Oman; Spain | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Champalbert, G. 1993. Plankton inhabiting the surface layer of the southern and southwestern lagoon of New Caledonia. Marine Biology 115:223-228. | 1993 | New Caledonia | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Fitt, W. K., H. J. Spero, J. Halas, M. W. White, J. W. Porter. 1993. Recovery of the coral Montastrea annularis in the Florida Keys after the 1987 Caribbean "bleaching event". Coral Reefs 12:57-64. | 1993 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Freiwald, A. 1993. Coralline algal maerl frameworks-Islands within the phaeophytic kelp belt. Facies 29:133-148. | 1993 | Global; Norway | Algae; Coralline Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Gabric, A. J. and P. R. F. Bell. 1993. Review of the effects of non-point nutrient loading on coastal ecosystems. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 44:261-283. | 1993 | Review | Discharges; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Remediation; Seagrasses; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Hallegraeff, G. M. 1993. A review of harmful algal blooms and their apparent global increase. Phycologia 32:79-99. | 1993 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Plankton; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hallock, P., F. E. Muller-Karger, and J. C. Halas. 1993. Coral Reef Decline: Anthropogenic nutrients and the degradation of Western Atlantic and Caribbean coral reefs. National Geographic 9:358-378. | 1993 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Nutrients | |
| Hands, M. R., J. R. French, and A. O'Neill. 1993. Reef stress at Cahuita Point, Costa Rica: anthropogenically enhanced sediment influx or natural geomorphic change? Journal of Coastal Research 9:25-Nov. | 1993 | Costa Rica | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Hughes, T. 1993. Disturbance: effects on coral reef dynamics. Coral Reefs 12:117-233. | 1993 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Review; Model | Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Lapointe, B. E., W. R. Matzie, and M. W. Clark. 1993. Phosporus inputs and eutrophication on the Florida reef tract. Pages 106-112 Miami, FL. | 1993 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Leinfelder, R. R., M. Nose, D. U. Schmid, and W. Werner. 1993. Microbial crusts of the late jurassic: Composition, palaeoecological significance and importance in reef construction. Facies 29:195-229. | 1993 | Spain; Germany | Algae; Bivalves; Climate; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| McMinn, A. 1993. Quaternary dinoflagellate cyst distribution at Site 820, Great Barrier Reef. Proc., scientific results, ODP, Leg 133, northeast Australian margin 93-95. | 1993 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Montgomery, W. L. and R. Galzin. 1993. Seasonality in gonads, fat deposits and condition of tropical surgeonfishes (Teleostei: Acanthuridae). Marine Biology 115:529-536. | 1993 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Morell, J. M. and J. E. Corredor. 1993. Sediment Nitrogen Trapping in a Mangrove Lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 37:203-212. | 1993 | Puerto Rico | Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Moriarty, D. J. W. and M. J. O'Donohue. 1993. Nitrogen fixation in seagrass communities during summer in the Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 44:117-125. | 1993 | Australia | Mangroves; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Morris, R. C. 1993. Genetic modelling for banded iron-formation of the Hamersley Group, Pilbara Craton, Western Australia. Precambrian Research 60:243-286. | 1993 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Naim, O. 1993. Seasonal responses of a fringing reef community to eutrophication (Reunion Island, western Indian Ocean). Marine Ecology Progress Series 99:137-151. | 1993 | Indian Ocean; Reunion; India | Algae; Coralline Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Pailles, C., D. M. McConchie, A. V. Arakel, and P. Saenger. 1993. The distribution of phosphate in sediments of the Johnstone Rivers catchment-estuary system, North Queensland, Australia. Sedimentary Geology 85:253-269. | 1993 | Australia | Agriculture; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Renon, J.-P. 1993. Geographic distribution of the planktonic copepod Undinula vulgaris (Dana) in three types of coral reef environments [Repartition du copepode planctonique Undinula vulgaris (Dana) dans trois types de milieux coralliens]. Annales - Institut Oceanographique, Paris 69:239-247. | 1993 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Saudi Arabia | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Robert Pitt and K. Dunkers. 1993. Lake Water Quality Improvements from Treatment of Stormwater Using the Flow Balancing Method, 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. Anaheim, CA. October 1993.; Detecting Water Quality Trends from Stormwater Discharge Reductions, Engineerin. in 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. | 1993 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Algae; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Rougerie, F. and B. Wauthy. 1993. The endo-upwelling concept: from geothermal convection to reef construction. Coral Reefs 12:19-30. | 1993 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity |
| Steven, A. and T. Larkum. 1993. ENCORE: the effect of nutrient enrichment on coral reefs. Search 24:216-219. | 1993 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Wood, R. 1993. Nutrients, predation and the history of reef-building. Palaios 8:526-543. | 1993 | Global | Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Yamamuro, M., I. Koike, and H. Iizumi. 1993. Partitioning of the nitrogen stock in the vicinity of a Fijian seagrass bed dominated by Syringodium isoetifolium (Ascherson) Dandy. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 44:101-115. | 1993 | Fiji | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Zempolich, W. G. 1993. The drowning succession in Jurassic carbonates of the Venetian Alps, Italy: a record of supercontinent breakup, gradual eustatic rise, and eutrophication of shallow-water environments. Pages 63-105 Carbonate sequence stratigraphy: recent developments and applications. | 1993 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Alino, P. M., P. W. Sammarco, and J. C. Coll. 1992. Competitive strategies in soft corals (Coelenterata, Octocorallia). IV. Environmentally induced reversals in competitive superiority. Marine Ecology Progress Series 81:129-145. | 1992 | Australia | Nutrients; Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Alongi, D. M., P. Christoffersen, F. Tirendi, and A. I. Robertson. 1992. The influence of freshwater and material export on sedimentary facies and benthic processes within the Fly Delta and adjacent Gulf of Papua (Papua New Guinea). Continental Shelf Research 12:287-326. | 1992 | Australia; Papua New Guinea; China | Model | Echinoderms; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Antonelli, P. L. and P. W. Sammarco. 1992. Allelochemic interactions on pandora reef - The great barrier reef: Stabilizing weak chaos in production. Open Systems and Information Dynamics 1:207-215. | 1992 | Australia | Model | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Octocoral; Stony Coral |
| Baarli, B. G., M. E. Johnson, and H. B. Keilen. 1992. Size and shape distribution of level-bottom tabulate corals and stromatoporoids (Silurian). Lethaia 25:269-282. | 1992 | Norway | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Bell, P. R. F. 1992. Eutrophication and coral reefs - Some examples in the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Water Research 26:553-568. | 1992 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Algae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Seastars; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Berland, B., D. Grzebyk, and B. A. Thomassin. 1992. Benthic dinoflagellates from the coral reef lagoon of Mayotte Island (S-W Indian Ocean); identification, toxicity and preliminary ecophysiological study. Bulletin de la Societe de pathologie exotique (1990) 85:453-456. | 1992 | Indian Ocean; Mayotte; India | Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Braley, R. D., D. Sutton, S. S. M. Mingoa, and P. C. Southgate. 1992. Passive greenhouse heating, recirculation, and nutrient addition for nursery phase Tridacna gigas: growth boost during winter months. Aquaculture 108:29-50. | 1992 | Australia | Index or Indicator | Bivalves; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae |
| Brodie, J. E. 1992. Enhancement of larval and juvenile survival and recruitment in Acanthaster planci from the effects of terrestrial runoff: a review. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 43:539-554. | 1992 | Australia | Review | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Seastars |
| Capone, D. G., S. E. Dunham, S. G. Horrigan, and L. E. Duguay. 1992. Microbial nitrogen transformations in unconsolidated coral reef sediments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 80:75-88. | 1992 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Carpenter, E. J., D. G. Capone, and J. G. Rueter. 1992. Marine pelagic cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and other diazotrophs. Marine pelagic cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and other diazotrophs. | 1992 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Thailand; Caribbean; Germany | Remote Sensing | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Special Use Permitting |
| Cook, C.B., G. Muller-Parker, and C.F. D'Elia. 1992. Factors affecting nutrient sufficiency for symbiotic zooxanthellae. Pages 379-80 in Proceedings of the 7th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1992 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Delesalle, B. and A. Sournia. 1992. Residence time of water and phytoplankton biomass in coral reef lagoons. Continental Shelf Research 12:939-949. | 1992 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Edsall, T. A., C. L. Brown, G. W. Kennedy, and T. P. Poe. 1992. Lake trout spawning habitat in the Six Fathom Bank-Yankee Reef lake trout sanctuary, Lake Huron. Journal of Great Lakes Research 18:70-90. | 1992 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Erez, J., et. al. 1992. Plankton is a major source of nutrients in coral reef ecosystems. Page 345 in Proceedings of the 7th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1992 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Gersekowski, J. N. 1992. Sewage treatment on green island. Pages 175-179 in National Conference Publication - Institution of Engineers, Australia. | 1992 | Australia | Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Goreau, T. J. 1992. Bleaching and reef community change in Jamaica: 1951-1991. American Zoologist 32:683-695. | 1992 | Jamaica | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Hansen, U., G. Patzold, and R. Sachse. 1992. Deep chlorophyll a maxima in the Red Sea observed by in-vivo flash fluorometry. Hydrobiologia 238:183-188. | 1992 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Hunte, W. and M. Wittenberg. 1992. Effects of eutrophication and sedimentation on juvenile corals - II. Settlement. Marine Biology 114:625-631. | 1992 | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate | ||
| Johnson, K. G. 1992. Population dynamics of a free-living coral: Recruitment, growth and survivorship of Manicina areolata (Linnaeus) on the Caribbean coast of Panama. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 164:171-191. | 1992 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Mangroves; Nutrients | |
| Klumpp, D. W. 1992. Nutrition of the giant clam Tridacna gigas (L.) I. Contribution of filter feeding and photosynthates to respiration and growth. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 155:105-122. | 1992 | Australia | Bivalves; Nutrients | |
| Krol, A., M. Noordink, J. Jell, and D. Chen. 1992. Heron island groundwater project. Pages 181-185 in National Conference Publication - Institution of Engineers, Australia. | 1992 | Australia | Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lao, Y., R. F. Anderson, W. S. Broecker, S. E. Trumbore, H. J. Hofmann, and W. Wolfli. 1992. Increased production of cosmogenic 10Be during the Last Glacial Maximum. Nature 357:576-578. | 1992 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Lapointe, B. D. and M. Clarke. 1992. Watershed nutrient inputs and coastal eutrophication in the Florida Keys. Estuaries and Coasts | 1992 | Florida | Nutrients | |
| Lapointe, B. E. and M. W. Clark. 1992. Nutrient inputs from the watershed and coastal eutrophication in the Florida Keys. Estuaries 15:465-476. | 1992 | Florida | Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Lee, T. N., C. Rooth, E. Williams, M. McGowan, A. F. Szmant, and M. E. Clarke. 1992. Influence of Florida Current, gyres and wind-driven circulation on transport of larvae and recruitment in the Florida Keys coral reefs. Continental Shelf Research 12:971-1002. | 1992 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler. 1992. Results of the USSR-USA expedition in marine biology to the Seychelles Islands. Atoll Research Bulletin | 1992 | Indian Ocean; Seychelles; India | Algae; Invertebrates; Light; Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Primary Production; Seagrasses; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| McClanahan, T. R. 1992. Epibenthic gastropods of the middle Florida keys: The role of habitat and environmental stress on assemblage composition. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 160:169-190. | 1992 | Florida | Fish; Nutrients; Salinity; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses | |
| Ramaiah, N. and D. Chandramohan. 1992. Densities, cellulases, alginate and pectin lyases of luminous and other heterotrophic bacteria associated with marine algae. Aquatic Botany 44:71-81. | 1992 | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Roberts, H. H., P. A. Wilson, and A. Lugo-Fernandez. 1992. Biologic and geologic responses to physical processes: examples from modern reef systems of the Caribbean-Atlantic region. Continental Shelf Research 12:809-834. | 1992 | South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Bermuda; Nicaragua; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Robison, W. L. and E. L. Stone. 1992. The effect of potassium on the uptake of 137Cs in food crops grown on coral soils: Coconut at Bikini Atoll. Health Physics 62:496-511. | 1992 | Nutrients | ||
| Rougerie, F. and R. Bagnis. 1992. Bursts of ciguatera and endo-upwelling process on coral reef. Bulletin de la Societe de pathologie exotique (1990) 85:464-466. | 1992 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Rougerie, F., B. Wauthy, and J. Rancher. 1992. The drowned barrier reef and the island effect by endo-upwelling in Marquesas Archipelago [Le recif barriere ennoye des Iles marquises et l'effet d'ile par endo-upwelling]. Comptes Rendus - Academie des Sciences, Serie II 315:677-682. | 1992 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Rougerie, F., J. A. Fagerstrom, and C. Andrie. 1992. Geothermal endo-upwelling: a solution to the reef nutrient paradox? Continental Shelf Research 12:785-798. | 1992 | Model | Nutrients | |
| Stambler, N., and Z. Dubinsky. 1992. Effects of light and eutrophication on coral-algae association. Page 347 in Proceedings of the 7th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1992 | Algae; Nutrients | ||
| Wittenberg, M., Hunte, W. 1992. Effects of eutrophication and sedimentation on juvenile corals. Marine Biology 112:131-138. | 1992 | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | ||
| [No author name available]. 1991. The natural release of amino acids from the symbiotic coral Heteroxenia fuscescens (Ehrb.) as a function of photosynthesis. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 150:83-90. | 1991 | Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Adey, W. H. and K. Loveland. 1991. Dynamic aquaria: building living ecosystems. Dynamic aquaria: building living ecosystems. | 1991 | Australia | Model | Domestic Animal Waste; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Wetlands |
| Bell, P. R. F. 1991. Status of eutrophication in the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. Marine Pollution Bulletin 23:89-93. | 1991 | Australia | Review | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Bronck, D. A. and P. M. Glibert. 1991. A 15N tracer method for the measurement of dissolved organic nitrogen release by phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 77:171-182. | 1991 | Nutrients; Plankton | ||
| Carpenter, R. C., J. M. Hackney, and W. H. Adey. 1991. Measurements of primary productivity and nitrogenase activity of coral reef algae in a chamber incorporating oscillatory flow. Limnology and Oceanography 36:40-49. | 1991 | Algae; Nutrients; Seawater Flow | ||
| Chisholm, J. R. M. and J.-P. Gattuso. 1991. Validation of the alkalinity anomaly technique for investigating calcification and photosynthesis in coral reef communities. Limnology and Oceanography 36:1232-1239. | 1991 | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral | ||
| Conway, K. W., J. V. Barrie, W. C. Austin, and J. L. Luternauer. 1991. Holocene sponge bioherms on the western Canadian continental shelf. Continental Shelf Research 11:771-790. | 1991 | Columbia | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Ferrier, M. D. 1991. Net uptake of dissolved free amino acids by four scleractinian corals. Coral Reefs 10:183-187. | 1991 | Cuba | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Guilcher, A. 1991. Progress and problems in knowledge of coral lagoon topography and its origin in the South Pacific, by way of pinnacle study. Pages 173-188 From shoreline to abyss: contributions in marine geology in honor of Francis Parker Shepard. | 1991 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Nutrients | |
| Hatcher, B. G. 1991. Coral reefs in the Leeuwin Current - an ecological perspective. Journal - Royal Society of Western Australia 74:115-127. | 1991 | Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Nutrients; Plankton; Sea Temperatures | |
| Hawker, D. W., and D. W. Connell. 1991. Standards and criteria for pollution control in coral reef areas. Pages 169-188 Pollution in Tropical Aquatic Systems. CRC, Boca Raton, FL. | 1991 | Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment | ||
| Hawkins, J. P., C. M. Roberts, and T. Adamson. 1991. Effects of a phosphate ship grounding on a Red Sea coral reef. Marine Pollution Bulletin 22:538-542. | 1991 | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Herndl, G. J. 1991. Microbial biomass dynamics along a trophic gradient at the Atlantic Barrier Reef off Belize (Central America). Marine Ecology 12:41-51. | 1991 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Belize | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Hollibaugh, J. T., R. W. Buddemeier, and S. V. Smith. 1991. Contributions of colloidal and high molecular weight dissolved material to alkalinity and nutrient concentrations in shallow marine and estuarine systems. Marine Chemistry 34:27-Jan. | 1991 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Hopkinson Jr, C. S., R. D. Fallon, B.-O. Jansson, and J. P. Schubauer. 1991. Community metabolism and nutrient cycling at Gray's Reef, a hard bottom habitat in the Georgia Bight. Marine Ecology Progress Series 73:105-120. | 1991 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Houghton, S. D. and M. V. S. Guptha. 1991. Monsoonal and fertility controls on Recent marginal sea and continental shelf coccolith assemblages from the western Pacific and northern Indian oceans. Marine Geology 97:251-259. | 1991 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Indian Ocean; India | Nutrients | |
| Kinsey, Donald W. 1991. Can we resolve the nutrient issue for the reef. 22:119-21. | 1991 | Nutrients | ||
| Konan, A. A., B. Soulemane, and J. Abe. 1991. Sediments of fish artifical habitats (acadja-enclos) in a tropical lagoon [Sediments d'habitats artificiels pour poissons (acadja-enclos) dans une lagune tropicale]. Bulletin - Institut de Geologie du Bassin d'Aquitaine 50:79-91. | 1991 | Artificial Habitat; Fish; Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Lindo, M. K. 1991. The effect of Kingston Harbour outflow on the zooplankton populations of Hellshire, south-east coast, Jamaica. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 32:597-608. | 1991 | Jamaica | Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and E. A. Titlyanov. 1991. Comparisons of N- and P-limited productivity between high granitic islands versus low carbonate atolls in the Seychelles Archipelago: a test of the relative-dominance paradigm. Coral Reefs 10:199-209. | 1991 | Seychelles | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Marine Birds; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Littler, M. M., D. S. Littler, and E. A. Titlyanov. 1991. Producers of organic matter on tropical reefs and their relative dominance. Biologiya Morya (Vladivostok) 6:14-Mar. | 1991 | Algae; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Stony Coral | ||
| Rothans, T. C. and A. C. Miller. 1991. A link between biologically imported particulate organic nutrients and the detritus food web in reef communities. Marine Biology 110:145-150. | 1991 | US Virgin Islands | Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish | |
| Stambler, N., N. Popper, Z. Dubinsky, and J. Stimson. 1991. Effects of nutrient enrichment and water motion on the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Pacific Science 45:299-307. | 1991 | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Stimson, J. 1991. The temporal pattern and rate of release of zooxanthellae from the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus) under nitrogen-enrichment and control conditions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 153:63-74. | 1991 | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Stimson, John, and Robert A. Kinzie. 1991. The temporal pattern and rate of release of zooxanthellae from the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaues) under nitrogen-enrichment and control conditions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 153:63-74. | 1991 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Sullivan, P. K. and V. Dayananda. 1991. Engineering management considerations in coastal development. Page 1430 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1991 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients | |
| Tomascik, T. 1991. Settlement patterns of Caribbean scleractinian corals on artificial substrata along a eutrophication gradient, Barbados, West Indies. Marine Ecology Progress Series 77:261-269. | 1991 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Wylie Poag, C. 1991. Rise and demise of the Bahama-Grand Banks gigaplatform, northern margin of the Jurassic proto-Atlantic seaway. Marine Geology 102:63-130. | 1991 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas | GIS & Maps | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment |
| Yoshinaga, I., K. Fukami, and Y. Ishida. 1991. Comparison of DNA and protein synthesis rates of bacterial assemblages between coral reef waters and pelagic waters in tropical ocean. Marine Ecology Progress Series 76:167-174. | 1991 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Alongi, D. M. 1990. Effect of mangrove detrital outwelling on nutrient regeneration and oxygen fluxes in coastal sediments of the central Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 31:581-598. | 1990 | Australia; Cuba | Lab Study | Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment |
| Black, K. P., S. L. Gay, and J. C. Andrews. 1990. Residence times of neutrally-buoyant matter such as larvae, sewage or nutrients on coral reefs. Coral Reefs 9:105-114. | 1990 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Blythell, J. C. 1990. Nutrient uptake in the reef-building coral Acropora palmata at natural environmental concentrations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 68:65-69. | 1990 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Charpy-Roubaud, C. J., L. Charpy, and J. L. Cremoux. 1990. Nutrient budget of the lagoonal waters in an open central South Pacific atoll (Tikehau, Tuamotu, French Polynesia). Marine Biology 107:67-73. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Coffroth, M. A. 1990. Mucous sheet formation on poritid corals: An evaluation of coral mucus as a nutrient source on reefs. Marine Biology 105:39-49. | 1990 | Florida; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Panama | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Davidson, R. J. 1990. Pre-burial adsorption model for the genesis of gold in the Witwatersrand. Journal of The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 90:53-57. | 1990 | Model | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production; Substrate | |
| D'Elia, C.F., and W.J. Wiebe. 1990. Biogeochemical nutrient cycles in coral-reef ecosystems. Pages 49-74 in Z Dubinsky, editor. Coral Reefs: Ecosystems of the World Vol 25. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co Inc New York:. | 1990 | Nutrients | ||
| Dubinsky, Z., N. Stambler, M. Ben-Zion, L. R. McCloskey, L. Muscatine, and P. G. Falkowski. 1990. The effect of external nutrient resources on the optical properties and photosynthetic efficiency of Stylophora pistillata. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 239:231-246. | 1990 | Algae; CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Gabric, A. J., P. Hoffenberg, and W. Boughton. 1990. Spatio-temporal variability in surface chlorophyll distribution in the central Great Barrier Reef as derived from CZCS imagery. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 41:313-324. | 1990 | Australia | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Glenn, E. P. and M. S. Doty. 1990. Growth of the seaweeds Kappaphycus alvarezii, K. striatum and Eucheuma denticulatum as affected by environment in Hawaii. Aquaculture 84:245-255. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Philippines | Agriculture; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Glynn, P. W. 1990. Coral mortality and disturbances to coral reefs in the tropical eastern Pacific. Pages 55-126 Global ecological consequences of the 1982-83 El Nino-Southern Oscillation. | 1990 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica; Panama | Algae; Fish; Molluscs; Nutrients; Plankton; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hatcher, B. G. 1990. Coral reef primary productivity: A hierarchy of pattern and process. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 5:149-155. | 1990 | Nutrients; Primary Production | ||
| Jackson, A. E. and D. Yellowlees. 1990. Phosphate uptake by zooxanthellae isolated from corals. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 242:201-204. | 1990 | Cuba | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Kazmer, M. 1990. Birth, life and death of the Pannonian Lake. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 79:171-188. | 1990 | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Molluscs; Nutrients; Plankton; Salinity; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Keupp, H., R. Koch, R. Leinfelder, W. Bausch, R. Huttner, H.-P. Luterbacher, R. K. F. Meyer, U. Rehfeld, J. Schroeder, and F. Wurm. 1990. Controlling processes in the development of Upper Jurassic spongiolites in Southern Germany: State of the art, problems and perspectives [Steuerungsprozesse der Entwicklung von Oberjura-Spongiolithen Suddeutschlands: Kenntnisstand, Probleme und Perspekti. Facies 23:141-173. | 1990 | Germany | Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Lewis, J. B. and P. V. R. Snelgrove. 1990. Corallum morphology and composition of crustacean cryptofauna of the hermatypic coral Madracis mirabilis. Marine Biology 106:267-272. | 1990 | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients | ||
| Littler, M. M. and D. S. Littler. 1990. Productivity and nutrient relationships in psammophytic versus epilithic forms of Bryopsidales (Chlorophyta): comparisons based on a short-term physiological assay. Hydrobiologia 49-55. | 1990 | Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Muckelbauer, G. 1990. The shelf of Cozumel, Mexico: Topography and organisms. Facies 23:185-200. | 1990 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment; Sponges; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Reichelt, R. E., R. H. Bradbury, and P. J. Moran. 1990. The crown-of-thorns starfish, Acanthaster planci, on the great barrier reef. Mathematical and Computer Modelling 13:45-60. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars; Stony Coral |
| Schroder-Adams, C. J., F. E. Cole, F. S. Medioli, P. J. Mudie, D. B. Scott, and L. Dobbin. 1990. Recent Arctic shelf Foraminifera: seasonally ice covered vs. perennially ice covered areas. Journal of Foraminiferal Research 20:Aug-36. | 1990 | Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Sponges | ||
| Szmant A.M. and N. J. Gassman. 1990. The effects of prolonged \bleaching\" on the tissue biomass and reproduction of the reef coral Montastrea annularis". Coral Reefs 8:217-224. | 1990 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Szmant, A. M., L. M. Ferrer, and L. M. FitzGerald. 1990. Nitrogen excretion and O:N ratios in reef corals: Evidence for conservation of nitrogen. Marine Biology 104:119-127. | 1990 | Bahamas | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae |
| Ten Lohuis, M., P. Alderslade, and D. J. Miller. 1990. Isolation and cloning of DNA from somatic tissue of soft corals (Cnidaria: Octocorallia). Marine Biology 104:489-492. | 1990 | Nutrients; Octocoral | ||
| Tomascik, T. 1990. Growth rates of two morphotypes of Montastrea annularis along a eutrophication gradient, Barbados, W.I. Marine Pollution Bulletin 21:376-381. | 1990 | Nutrients | ||
| Tribble, G. W., F. J. Sansone, and S. V. Smith. 1990. Stoichiometric modeling of carbon diagenesis within a coral reef framework. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 54:2439-2449. | 1990 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients |
| Williams, S. L. 1990. Experimental studies of Caribbean seagrass bed development. Ecological Monographs 60:449-469. | 1990 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Model | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment |
| Alongi, D. M. 1989. Benthic processes across mixed terrigenous-carbonate sedimentary facies on the central Great Barrier Reef continental shelf. Continental Shelf Research 9:629-663. | 1989 | Australia; Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Baldwin, C. L. 1989. Water quality and management in the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park. Water Science and Technology 21:267-272. | 1989 | Australia | Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bell, P. R. F., P. F. Greenfield, D. Hawker, and D. Connell. 1989. The impact of waste discharges on coral reef regions. Water Science and Technology 21:121-130. | 1989 | Discharges; Hotel & Food Services; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Bonvallot, J., F. Rougerie, and B. Wauthy. 1989. Geomorphology and functioning of an atoll: the example of Tikehau, Tuamotu, French Polynesia [Geomorphologie et fonctionnement d'un atoll: l'exemple de Tikehau, Tuamotu, Polynesie francaise]. Bulletin - Centre de Geomorphologie du CNRS, Caen 36:145-148. | 1989 | Nutrients | ||
| Esry, D.H., and D.J. Cairns. 1989. Overview of the Lake Jackson Restoration Project with Artificially Created Wetlands for Treatment of Urban Runoff. p. 247-257 m: D.W. Fisk (ed.), Wetlands, Concerns and Successes. Proceedings, American Water Resources Association. | 1989 | Field Study & Monitoring | Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Wetlands | |
| Klumpp, D. W. and N. V. C. Polunin. 1989. Partitioning among grazers of food resources within damselfish territories on a coral reef. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 125:145-169. | 1989 | Australia | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Le Borgne, R., J. Blanchot, and L. Charpy. 1989. Zooplankton of tikehau atoll (Tuamotu archipelago) and its relationship to particulate matter. Marine Biology 102:341-353. | 1989 | Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Lea, D. W., G. T. Shen, and E. A. Boyle. 1989. Coralline barium records temporal variability in equatorial Pacific upwelling. Nature 340:373-376. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Maristany, A.E. and Bartel, R.L. 1989. �Wetlands and Stormwater Management: A Case Study of Lake Munson, Part I: Long-Term Treatment Efficiencies�, in: Fisk, D.W. (Ed.) Proceedings of the Symposium on Wetlands: Concerns and Successes, AWRA, Tampa, FL, pp. 215-229 (1989). | 1989 | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands | ||
| Meiorin, E.C. 1989. �Urban Runoff Treatment in a Fresh/Brackish Water Marsh in Fremont, California�, in: Hammer, D.A. (Ed.) Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: Municipal, Industrial, and Agricultural, Lewis Publishers, Inc., Chelsea, pp. 677-685. | 1989 | Agriculture; Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands | ||
| Miller, D.J., and D. Yellowlees. 1989. Inorganic nitrogen uptake by symbiotic marine cnidarians: a critical review. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B 237:109-25. | 1989 | Review | Nutrients | |
| Montgomery, W. L., A. A. Myrberg Jr., and L. Fishelson. 1989. Feeding ecology of surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae) in the northern Red Sea, with particular reference to Acanthurus nigrofuscus (Forsskål). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 132:179-207. | 1989 | Algae; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Muscatine, L., P. G. Falkowski, Z. Dubinsky, P. A. Cook, and L. R. McCloskey. 1989. The effect of external nutrient resources on the population dynamics of zooxanthellae in a reef coral. Pages 311-324 in Proceedings - Royal Society of London, B. | 1989 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Nienhuis, P. H., J. Coosen, and W. Kiswara. 1989. Community structure and biomass distribution of seagrasses and macrofauna in the flores sea, Indonesia. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 23:197-214. | 1989 | Indonesia | Model; Index or Indicator | Mangroves; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Substrate |
| Phillips, JD. 1989. An evaluation of the factors determining the effectiveness of water quality buffer zones., J. HYDROL. (AMST.)., vol. 107, no. 1-4, pp. 133-145, 1989. | 1989 | Field Study & Monitoring | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Pilkey, O., D. Heron, W. Harbridge, J. Kamens, F. Keer, and S. Thornton. 1989. The sedimentology of three Tunisian lagoons. Marine Geology 88:285-301. | 1989 | Climate; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Polunin, N. V. C. and E. B. Brothers. 1989. Low efficiency of dietary carbon and nitrogen conversion to growth in an herbivorous coral-reef fish in the wild. Journal of Fish Biology 35:869-879. | 1989 | Papua New Guinea | Fish; Nutrients; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Snelgrove, P. V. R. and J. B. Lewis. 1989. Response of a coral-associated crustacean community to eutrophication. Marine Biology 101:249-257. | 1989 | Index or Indicator | Nutrients | |
| Van Der Land, J. 1989. The need for new concepts in reef biology. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 23:231-238. | 1989 | Indonesia | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sponges | |
| Vogt, P. R. 1989. Volcanogenic upwelling of anoxic, nutrient-rich water: a possible factor in carbonate-bank/reef demise and benthic faunal extinctions? Geological Society of America Bulletin 101:1225-1245. | 1989 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Nutrients | |
| Wilkinson, C. R. and A. C. Cheshire. 1989. Patterns in the distribution of sponge populations across the central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 8:127-134. | 1989 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Wilkinson, C. R. and E. Evans. 1989. Sponge distribution across Davies Reef, Great Barrier Reef, relative to location, depth, and water movement. Coral Reefs 8:7-Jan. | 1989 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Anon,. 1988. Heap Leaching For Uranium. Canadian Mining Journal 109. | 1988 | Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Bethoux, J. P. 1988. Red Sea geochemical budgets and exchanges with the Indian Ocean. Marine Chemistry 24:83-92. | 1988 | Global; Indian Ocean; India | Discharges; Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Bray, R. N., A. C. Miller, S. Johnson, P. R. Krause, D. L. Robertson, and A. M. Westcott. 1988. Ammonium excretion by macroinvertebrates and fishes on a subtidal rocky reef in southern California. Marine Biology 100:21-30. | 1988 | Cuba | Lab Study | Algae; Fish; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Bythell, J.C. 1988. A total nitrogen and carbon budget for the elkhorn coral Acropora palmata. Pages 535-40 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Carannante, G., M. Esteban, J. D. Milliman, and L. Simone. 1988. Carbonate lithofacies as paleolatitude indicators: problems and limitations. Sedimentary Geology 60:333-346. | 1988 | Index or Indicator | Algae; Coralline Algae; Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| D'Elia, C. F. 1988. The cycling of essential elements in coral reefs. Pages 195-230 Concepts of ecosystem ecology. | 1988 | Review | Nutrients | |
| D'Elia, C. F. and C. B. Cook. 1988. Methylamine uptake by zooxanthellae-invertebrate symbioses: insights into host ammonium environment and nutrition. Limnology and Oceanography 33:1153-1165. | 1988 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Disalvo, L. H., J. E. Randall, and A. Cea. 1988. Ecological reconnaissance of the Easter Island sublittoral marine environment. National Geographic Research 4:451-473. | 1988 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Echinoderms; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Drew, E. A. and K. M. Abel. 1988. Studies on Halimeda - I. The distribution and species composition of Halimeda meadows throughout the Great Barrier Reef Province. Coral Reefs 6:195-205. | 1988 | Australia | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Ferrer, L.M. and A.M. Szmant. 1988. Nutrient regeneration by the endolithic community in coral skeletons. Pages 1-4 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | Nutrients | ||
| Fitzgerald, L.M., and A.M. Szmant. 1988. Amino acid metabolism: adaptations to low nutrient conditions? Pages 5-9 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | Nutrients | ||
| Gunnersen, J., D. Yellowlees, and D. J. Miller. 1988. The ammonium/methylammonium uptake system of Symbiodinium microadriaticum. Marine Biology 97:593-596. | 1988 | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Hallock, P. 1988. The role of nutrient availability in bioerosion: Consequences to carbonate buildups. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 63:275-291. | 1988 | Oman | Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Fleshy Macroalgae; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Hay, M. E., V. J. Paul, S. M. Lewis, K. Gustafson, J. Tucker, and R. N. Trindell. 1988. Can tropical seaweeds reduce herbivory by growing at night? Diel patterns of growth, nitrogen content, herbivory, and chemical versus morphological defenses. Oecologia 75:233-245. | 1988 | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Primary Production; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Hinde, Rosalind. 1988. Symbiotic nutrition and nutrient limitation. Pages 199-204 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sy. | 1988 | Nutrients | ||
| Kuhlmann, D. H. H. 1988. The sensitivity of coral reefs to environmental pollution. Ambio 17:13-21. | 1988 | Japan | Agriculture; Algae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Larkum, A. W. D. 1988. High rates of nitrogen fixation on coral skeletons after predation by the crown of thorns starfish Acanthaster planci. Marine Biology 97:503-506. | 1988 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Seastars | |
| Larkum, A. W. D., I. R. Kennedy, and W. J. Muller. 1988. Nitrogen fixation on a coral reef. Marine Biology 98:143-155. | 1988 | Australia | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Marshall, J. F. and P. J. Davies. 1988. Halimeda bioherms of the northern Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 6:139-148. | 1988 | Australia; Cuba | Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Morrissey, J., M.S. Jones, and V. Harriot. 1988. Nutrient cycling in the Great Barrier Reef Aquarium. Pages 563-7 in Proceedings of the 6th Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1988 | Australia | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Nutrients | |
| Nelson, S. G. and S. DE C. Wilkins. 1988. Sediment processing by the surgeonfish Ctenochaetus striatus at Moorea, French Polynesia. Journal of Fish Biology 32:817-824. | 1988 | Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish | ||
| Oberts, G; Osgood, R. 1988. The effectiveness of a detention/wetland treatment system and its effect on an urban lake., 8. ANNUAL INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON LAKE AND WATERSHED MANAGEMENT., 1988., p. 29. | 1988 | Field Study & Monitoring | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Roberts, H. H., P. Aharon, and C. V. Phipps. 1988. Morphology and sedimentology of Halimeda bioherms from the eastern Java Sea (Indonesia). Coral Reefs 6:161-172. | 1988 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Java; Indonesia | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Rosen, B. R. 1988. Progress, problems and patterns in the biogeography of reef corals and other tropical marine organisms. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 42:269-301. | 1988 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Review | Nutrients |
| Sandstrom, M. W. 1988. Aliphatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the North Queensland coast and Great Barrier Reef: Effects of tropical cyclone Winifred. Organic Geochemistry 12:445-454. | 1988 | Australia | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sassi, R., M. B. B. Kutner, and G. F. Moura. 1988. Studies on the decomposition of drift seaweed from the northeast Brazilian coastal reefs. Hydrobiologia 157:187-192. | 1988 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Schubauer, J. P. 1988. Metabolism and Nutrient Cycling By Marine Sponges. University of Georgia, Athens. | 1988 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Scott, P. J. B., K. A. Moser, and M. J. Risk. 1988. Bioerosion of concrete and limestone by marine organisms: A 13 year experiment from Jamaica. Marine Pollution Bulletin 19:219-222. | 1988 | Global; Jamaica | Bivalves; Boring Sponges; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Skeletal Coral; Sponges; Substrate | |
| Shen, G. T., E. A. Boyle, and D. W. Lea. 1988. Cadmium in corals as a tracer of historical upwelling and industrial fallout. Nature 328:794-796. | 1988 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bermuda | Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Stevenson, J. C. 1988. Comparative ecology of submersed grass beds in freshwater, estuarine, and marine environments. Limnology and Oceanography 33:867-893. | 1988 | Global; South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | CO2; Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Sediment | |
| Wilkinson, C. R. 1988. Foliose Dictyoceratida of the Australian Great Barrier Reef. II. Ecology and distribution of these prevalent sponges. Marine Ecology 9:321-327. | 1988 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Wolanski, E., E. Drew, K. M. Abel, and J. O'Brien. 1988. Tidal jets, nutrient upwelling and their influence on the productivity of the alga Halimeda in the Ribbon Reefs, Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 26:169-201. | 1988 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Calcareous Macroalgae; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Alongi, D. M. 1987. The distribution and composition of deep-sea microbenthos in a bathyal region of the western Coral Sea. Deep Sea Research Part A, Oceanographic Research Papers 34:1245-1254. | 1987 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Anderson, S. L. and J. E. Burris. 1987. Role of glutamine synthetase in ammonia assimilation by symbiotic marine dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae). Marine Biology 94:451-458. | 1987 | Nutrients; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Bhavsar, R. D., M. Ghoreshy, and R. W. Smith. 1987. Graphite Morphology In Vacuum-Treated Fe-C-Si Alloys. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Metals 28:808-818. | 1987 | Nutrients | ||
| Catmull, J., D. Yellowlees, and D. J. Miller. 1987. NADP+-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase from Acropora formosa: purification and properties. Marine Biology 95:559-563. | 1987 | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Cook, Clayton B., and Christopher F. D'Elia. 1987. Are natural populations of zooxanthellae ever nutrient-limited? Symbiosis 4:199-212. | 1987 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Hansen, L. A., D. M. Alongi, D. J. W. Moriarty, and P. C. Pollard. 1987. The dynamics of benthic microbial communities at Davies Reef, central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 6:63-70. | 1987 | Australia | Algae; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Hatcher, B. G., H. Kirkman, and W. F. Wood. 1987. Growth of the kelp Ecklonia radiata near the northern limit of its range in Western Australia. Marine Biology 95:63-73. | 1987 | Australia | Nutrients; Sea Temperatures | |
| Hulsman, K. 1987. Resource partitioning among sympatric species of tern. Ardea 75:255-262. | 1987 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Koop, K. and A. W. D. Larkum. 1987. Deposition of organic material in a coral reef lagoon, One Tree Island, Great Barrier Reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 25:9-Jan. | 1987 | Australia | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment; Turf Algae | |
| Lapointe, B. E., M. M. Littler, and D. S. Littler. 1987. A comparison of nutrient-limited productivity in macroalgae from a Caribbean barrier reef and from a mangrove ecosystem. Aquatic Botany 28:243-255. | 1987 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Mangroves; Nutrients | |
| Lewis, J. B. 1987. Measurements of groundwater seepage flux onto a coral reef: spatial and temporal variations ( Barbados). Limnology and Oceanography 32:1165-1169. | 1987 | Model | Discharges; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Mann, K. and M. Florence. 1987. Toxicity of oil shale waste waters to marine algae. Fuel 66:404. | 1987 | Australia | Model | Algae; Nutrients; Wastewater Discharge |
| Nair, S. and U. Simidu. 1987. Distribution and significance of heterotrophic marine bacteria with antibacterial activity. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 53:2957-2962. | 1987 | Taiwan | Nutrients; Octocoral; Plankton; Sediment; Sponges | |
| Polunin, N. V. C. and I. Koike. 1987. Temporal focusing of nitrogen release by a periodically feeding herbivorous reef fish. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 111:285-296. | 1987 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Striegl, R.G.; Cowan, E.A. 1987. Relations Between Quality of Urban Runoff and Quality of Lake Ellyn at Glen Ellyn, Illinois. Available from Books and Open-File Reports Section, USGS, Box 25425, Denver, CO 80225. USGS Water-Supply Paper 2301, 1987. 59p, 27 fig, 20 tab, 60 ref. | 1987 | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Tomascik, T. and F. Sander. 1987. Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals - II. Structure of scleractinian coral communities on fringing reefs, Barbados, West Indies. Marine Biology 94:53-75. | 1987 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Tomascik, T. and F. Sander. 1987. Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals - III. Reproduction of the reef-building coral Porites porites. Marine Biology 94:77-94. | 1987 | Index or Indicator | Light; Nutrients; Primary Production; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Ullman, W. J. and M. W. Sandstrom. 1987. Dissolved nutrient fluxes from the nearshore sediments of Bowling Green Bay, central Great Barrier Reef Lagoon (Australia). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 24:289-303. | 1987 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Welborn, C.T.; Veenhuis, J.E. 1987. Effects of Runoff Controls on the Quantity and Quality of Urban Runoff at Two Locations in Austin, Texas., Available from OFSS, USGS, Box 25425, Denver, CO 80225. USGS Water-Resources Investigations Report 87-4004, 1987. 101p, 51 fig, 14 tab, 13 ref. | 1987 | Discharges; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Williams, W. M., A. B. Viner, and W. J. Broughton. 1987. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with the living coral Acropora variabilis. Marine Biology 94:531-535. | 1987 | Cuba; Malaysia | CO2; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Woodroffe, C. D. 1987. Pacific Island mangroves: distribution and environmental settings. Pacific Science 41:166-185. | 1987 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Yousef, YA; Hvitved-Jacobsen, T; Wanielista, MP; Harper, HH; Hamilton, RS; Harrison, RM. (eds). 1987. Removal of contaminants in highway runoff flowing through swales, SPECIAL ISSUE: HIGHWAY POLLUTION. PROCEEDINGS OF THE SECOND INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM, LONDON, UNITED KINGDOM, 7-11 JULY 1986., 1987., pp. 391-399, SCI. TOTAL ENVIRON., vol. 59. | 1987 | Florida; United Kingdom | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Zann, L. P. 1987. A review of macrosymbiosis in the coral reef ecosystem. International Journal for Parasitology 17:399-405. | 1987 | Review | Nutrients; Plankton; Seastars | |
| Airey, D. 1986. The entrainment of nutrients from below the thermocline in the coral sea into the great barrier reef lagoon via cook's passage. Science of the Total Environment 49:147-161. | 1986 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Boon, P. I. 1986. Uptake and release of nitrogen compounds in coral reef and seagrass, Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb.) Aschers., bed sediments at Lizard Island, Queensland. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 37:19-Nov. | 1986 | Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment | ||
| Bray, R. N., L. J. Purcell, and A. C. Miller. 1986. Ammonium excretion in a temperate-reef community by a planktivorous fish, Chromis punctipinnis (Pomacentridae), and potential uptake by young giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera (Laminariales). Marine Biology 90:327-334. | 1986 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Fish; Nutrients; Planktivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Fries, B.M. 1986. Fate of Phosphorus from Residential Stormwater Runoff in a Southern Hardwood Wetland, Thesis, Master of Science in Engineering, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL. | 1986 | Florida | Discharges; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Furnas, M. J. and A. W. Mitchell. 1986. Phytoplankton dynamics in the central Great Barrier Reef-I. Seasonal changes in biomass and community structure and their relation to intrusive activity. Continental Shelf Research 6:363-384. | 1986 | Australia | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton | |
| Hallock, P. and W. Schlager. 1986. Nutrient excess and the demise of coral reefs and carbonate platforms. Palaios 1:389-398. | 1986 | Nutrients | ||
| Littler, M. M., P. R. Taylor, and D. S. Littler. 1986. Plant defense associations in the marine environment. Coral Reefs 5:63-71. | 1986 | South & Central America; Belize | Model | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Corallivorous Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| McFadden, C. S. 1986. Colony fission increases particle capture rates of a soft coral: Advantages of being a small colony. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 103:20-Jan. | 1986 | Lab Study | Nutrients; Octocoral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Oberdorfer, J. A. and R. W. Buddemeier. 1986. Coral-reef hydrology: field studies of water movement within a barrier reef. Coral Reefs 5:12-Jul. | 1986 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral |
| Wilkerson, F. P. and R. K. Trench. 1986. Uptake of dissolved inorganic nitrogen by the symbiotic clam Tridacna gigas and the coral Acropora sp. Marine Biology 93:237-246. | 1986 | Micronesia | Nutrients; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Adey, W. H. and R. S. Steneck. 1985. Highly productive eastern caribbean reefs: synergistic effects of biological, chemical, physical, and geological factors. Pages 163-187 | 1985 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seawater Flow; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Turf Algae; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Aharon, P. 1985. Carbon isotope record of late Quaternary coral reefs: possible index of sea surface paleoproductivity. Pages 343-355 in The carbon cycle and atmospheric CO2: natural variations Archean to present. Chapman conference papers, 1984. | 1985 | Index or Indicator | CO2; Nutrients | |
| Antonius, A. 1985. Coral diseases in the Indo-Pacific: a first record. Marine Ecology 6:197-218. | 1985 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Philippines | Nutrients; Pathogens; Stony Coral | |
| Archer, E. 1985. Emerging environmental problems in a tourist zone: the case of Barbados. Caribbean Geography 2:45-55. | 1985 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Nutrients; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Birkeland, C. and D. Grosenbaugh. 1985. Ecological interactions between tropical coastal ecosytems. UNEP regional seas reports and studies No. 73. UNEP. | 1985 | Mangroves; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection | ||
| Corredor, J. E. and J. Morell. 1985. Inorganic nitrogen in coral reef sediments. Marine Chemistry 16:379-384. | 1985 | Nutrients; Sediment | ||
| Evans, C., J. E. Maragos, and P. Holtus. 1985. Reef corals in Kaneohe Bay six years before and after termination of sewage discharges (Oahu, Hawaiian Archipelago). Pages 189-194 in Proceedings of the fifth international coral reef congress. Tahiti. | 1985 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Algae; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Military; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Froelich, Alina Szmant. 1985. The Ecology of Coral Reefs: Symposia Series for Undersea Research. NOAA. | 1985 | Nutrients | ||
| Gray, J. S. 1985. Nitrogenous excretion by meiofauna from coral reef sediments: Mecor 5. Marine Biology 89:31-35. | 1985 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Hammond, L. S. and C. R. Wilkinson. 1985. Exploitation of sponge exudates by coral reef holothuroids. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 94:9-Jan. | 1985 | Model | Echinoderms; Nutrients; Sponges | |
| Hatcher, A. I. and C. A. Frith. 1985. The control of nitrate and ammonium concentrations in a coral reef lagoon. Coral Reefs 4:101-110. | 1985 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Nutrients | |
| Littler, M. M., P. R. Taylor, D. S. Littler, R. H. Sims, and J. N. Norris. 1985. The distribution, abundance and primary productivity of submerged macrophytes in a Belize barrier-reef mangrove system. Atoll Research Bulletin | 1985 | South & Central America; Belize | Index or Indicator | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses |
| Meyer, J.L, E.T. Schultz. 1985. Tissue Condition and Growth Rate of Corals Associated with Schooling Fish. Limnology and Oceanography 30:157-166. | 1985 | US Virgin Islands | Light; Nutrients; Stony Coral | |
| Moriarty, D. J. W., P. C. Pollard, and W. G. Hunt. 1985. Temporal and spatial variation in bacterial production in the water column over a coral reef. Marine Biology 85:285-292. | 1985 | Australia | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Seagrasses | |
| Pastorok, R. A., G. R. Bilyard. 1985. Effects of sewage pollution on coral-reef communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 21:175-189. | 1985 | Algae; Nutrients; Primary Production; Sediment | ||
| Tomascik, T. and F. Sander. 1985. Effects of eutrophication on reef-building corals. I. Growth rate of the reef-building coral Montastrea annularis. Marine Biology 87:143-155. | 1985 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Walton, RA YM ON D, W. MA RT IN Williams, P. Wang Ming, and A. Roesner Larry. 1985. Coral Reef Modeling: Key Largo Case Study. Pages 2420-2438 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1985 | Florida | Model; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | CO2; Nutrients; Primary Production |
| Domotor, S. L. and C. F. D'Elia. 1984. Nutrient uptake kinetics and growth of zooxanthellae maintained in laboratory culture. Marine Biology 80:93-101. | 1984 | Lab Study | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Grigg, R. W., J. J. Polovina, and M. J. Atkinson. 1984. Model of a coral reef ecosystem - III. Resource limitation, community regulation, fisheries yield and resource management. Coral Reefs 3:23-27. | 1984 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting | |
| Hottinger, L. 1984. Les organismes constructeurs sur la plate-forme du golfe d'aqaba (mer Rouge) et les mecanismes regissant leur repartition. Geobios 17:241-249. | 1984 | Nutrients; Sediment; Substrate | ||
| Lawrence, J. M. and P. W. Glynn. 1984. Absorption of nutrients from the coral Pocillopora damicornis (L.) by the echinoid Eucidaris thouarsii (val.). Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A 77:111-112. | 1984 | Nutrients; Stony Coral | ||
| Lipps, J. H. and K. P. Severin. 1984. Alveolinella quoyi, a living fusiform foraminifera, at Motupore Island, Papua New Guinea. Science in New Guinea 11:126-137. | 1984 | Papua New Guinea | Nutrients; Skeletal Coral | |
| Paerl, H. W. 1984. N2 fixation (nitrogenase activity) attributable to a specific Prochloron (Prochlorophyta)-ascidian association in Palau, Micronesia. Marine Biology 81:251-254. | 1984 | Palau; Micronesia | Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients | |
| Rayner, R. F. and E. A. Drew. 1984. Nutrient concentrations and primary productivity at the Peros Banhos and Salomon atolls in the Chagos Archipelago. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 18:121-132. | 1984 | Chagos Archipelago | Nutrients; Primary Production | |
| Smith, S.V. 1984. Phosphorous versus nitrogen limitation in the marine environment. Limnology and Oceanography 29:1149-60. | 1984 | Nutrients | ||
| Szmant-Froelich, A. and M. E. Q. Pilson. 1984. Effects of feeding frequency and symbiosis with zooxanthellae on nitrogen metabolism and respiration of the coral Astrangia danae. Marine Biology 81:153-162. | 1984 | Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Szmant-Froelich, A., and M.E.Q. Pilson. 1984. Effects of feeding frequency and symbiosis with zooxanthellae on nitrogen metabolism and respiration of the coral Astrangia. Marine Biology 81:153-62. | 1984 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Theil, H. and H. Weikert. 1984. Biological oceanography of the red oceanic system. Deep Sea Research Part A, Oceanographic Research Papers 31:829-831. | 1984 | Indian Ocean; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; India; Sudan | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Thomson Richard, E. and J. Wolanski Eric. 1984. Tidal Period Upwelling Within Raine Island Entrance Great Barrier Reef. Journal of Marine Research 42:787-808. | 1984 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Wilkinson, C. R., D. M. Williams, P. W. Sammarco, R. W. Hogg, and L. A. Trott. 1984. Rates of nitrogen fixation on coral reefs across the continental shelf of the central Great Barrier Reef. Marine Biology 80:255-262. | 1984 | Australia | Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Small Herbivorous Fish; Substrate | |
| Andrews, J. C. 1983. Water masses, nutrient levels and seasonal drift on the outer central Queensland Shelf ( Great Barrier Reef). Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 34:821-834. | 1983 | Australia | Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Brock, R. E. and S. V. Smith. 1983. Response of coral reef cryptofaunal communities to food and space. Coral Reefs 1:179-183. | 1983 | Nutrients | ||
| Burris, R. H. 1983. Uptake and assimilation of 15NH4+ by a variety of corals. Marine Biology 75:151-155. | 1983 | Australia | Nutrients; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Cowen, R. 1983. Algal symbiosis and its recognition in the fossil record. Pages 431-478 Biotic interactions in Recent and fossil benthic communities. | 1983 | Review | Nutrients | |
| Crossland, C. J. and D. J. Barnes. 1983. Dissolved nutrients and organic particulates in water flowing over coral reefs at Lizard Island. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 34:835-844. | 1983 | Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| D'Elia, C. F., S. L. Domotor, and K. L. Webb. 1983. Nutrient uptake kinetics of freshly isolated zooxanthellae. Marine Biology 75:157-167. | 1983 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Pacific Ocean; Caribbean | Algae; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Entsch, B., K. G. Boto, R. G. Sim, and J. T. Wellington. 1983. Phosphorus and nitrogen in coral reef sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 28:465-476. | 1983 | Australia | Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Entsch, B., R. G. Sim, and B. G. Hatcher. 1983. Indications from photosynthetic components that iron is a limiting nutrient in primary producers on coral reefs. Marine Biology 73:17-30. | 1983 | Australia | Lab Study | Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Primary Production; Sediment; Zooxanthellae |
| Fisher, W. S. 1983. Eggs of Palaemon macrodactylus: II. association with aquatic bacteria. Biological Bulletin 162:201-213. | 1983 | Lab Study | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Fisher, W. S. 1983. Eggs of Palaemon macrodactylus: III. infection by the fungus, Lagenidium callinectes. Biological Bulletin 162:214-226. | 1983 | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Gottfried, M. and M. R. Roman. 1983. Ingestion and incorporation of coral-mucus detritus by reef zooplankton. Marine Biology 72:211-218. | 1983 | Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Substrate | ||
| Hatcher, B. G. and A. W. D. Larkum. 1983. An experimental analysis of factors controlling the standing crop of the epilithic algal community on a coral reef. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 69:61-84. | 1983 | Australia | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Nutrients | |
| Kiefer, D. A. and B. G. Mitchell. 1983. A simple, steady state description of phytoplankton growth based on absorption cross section and quantum efficiency. Limnology and Oceanography 28:770-776. | 1983 | Model | Light; Nutrients; Plankton; Special Use Permitting | |
| Meyer, J. L., E. T. Schultz, and G. S. Helfman. 1983. Fish schools: An asset to corals. Science 220:1047-1049. | 1983 | Fish; Nutrients | ||
| Milbrink, G. 1983. An improved environmental index based on the relative abundance of oligochaete species. Hydrobiologia 102:89-97. | 1983 | Europe | Index or Indicator | Nutrients |
| Risk, M. J. and H. R. Muller. 1983. Porewater in coral heads: Evidence for nutrient regeneration. Limnology and Oceanography 28:1004-1008. | 1983 | Nutrients | ||
| Schoeninger, M. J. and M. DeNiro. 1983. Stable nitrogen isotope ratios of bone collagen reflect marine and terrestrial components of prehistoric human diet. Science 220:1381-1383. | 1983 | Bahamas; India | Agriculture; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients | |
| Bellamy, N. and M. J. Risk. 1982. Coral gas: Oxygen production in Millepora on the great barrier reef. Science 216:1618-1619. | 1982 | Australia | Algae; CO2; Hydrocoral; Nutrients; Substrate | |
| Campbell, I. B. 1982. Soils of Atiu, Cook Islands. New Zealand Soil Survey Report 54. | 1982 | Cook Islands | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Nutrients |
| Ikeda, T., J. H. Carleton, A. W. Mitchell, and P. Dixon. 1982. Ammonia and phosphate excretion by zooplankton from the inshore waters of the Great Barrier Reef. II. Their in situ contributions to nutrient regeneration. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33:683-698. | 1982 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Laws, E. A. and D. G. Redalje. 1982. Sewaged diversion effects on the water column of a subtropical estuary. Marine Environmental Research 6:265-279. | 1982 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Index or Indicator | Discharges; Nutrients; Plankton |
| Moriarty, D. J. W. 1982. Feeding of Holothuria atra and Stichopus chloronotus on bacteria, organic carbon and organic nitrogen in sediments of the Great Barrier Reef. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33:255-263. | 1982 | Australia | Echinoderms; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Schlichter, Dietrich. 1982. Nutritional strategies of cnidarians: the absorption, translocation and utilization of dissolved nutrients by Heteroxenia f. American Zoologist 22:659-69. | 1982 | Nutrients | ||
| Wellington, G. M. 1982. An experimental analysis of the effects of light and zooplankton on coral zonation. Oecologia 52:311-320. | 1982 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Nutrients; Plankton; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Goldstein, Alan. 1981. Upland Detention/Retention Demonstration Project. | 1981 | Florida | Agriculture; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Johnston Jr., S. A. 1981. Estuarine dredge and fill activities: A review of impacts. Environmental Management 5:427-440. | 1981 | Review | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Nutrients; Sediment; Wetlands | |
| Mullins, H. T., C. R. Newton, K. Heath, and H. M. Vanburen. 1981. Modern deep-water coral mounds north of Little Bahama Bank: criteria for recognition of deep-water coral bioherms in the rock record. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 51:999-1014. | 1981 | Algae; Nutrients; Octocoral; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Pugh, D. T. and R. F. Rayner. 1981. The tidal regimes of three indian ocean atolls and some ecological implications. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 13:389-407. | 1981 | Indian Ocean; India | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sander, F. 1981. A preliminary assessment of the main causative mechanisms of the \island mass\" effect of Barbados". Marine Biology 64:199-205. | 1981 | Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity | ||
| Walker, T. A. and G. O'Donnell. 1981. Observations on nitrate, phosphate and silicate in Cleveland Bay, northern Queensland. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 32:877-887. | 1981 | Australia | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Collins, N. 1980. Population ecology of Ephydra cinerea Jones (Diptera: Ephydridae), the only benthic metazoan of the Great Salt Lake, U.S.A. Hydrobiologia 68:99-112. | 1980 | Algae; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Salinity; Special Use Permitting; Substrate | ||
| Keene Jr., W. C. 1980. The importance of a reef-forming polychaete, Mercierella enigmatica Fauvel, in the oxygen and nutrient dynamics of a hypereutrophic subtropical lagoon. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 11:167-178. | 1980 | Marine Worms; Nutrients | ||
| Prota, Giuseppe. 1980. Nitrogenous pigments in marine invertebrates. Pages 141-80 in Paul J Scheuer, editor. Marine Natural Products: Chemical and Biological perspectives, Vol III,. Academic Press, New York. | 1980 | Invertebrates; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | ||
| Kinsey, D. W. and P. J. Davies. 1979. Effects of elevated nitrogen and phosphorus on coral reef growth. Limnology and Oceanography 24:935-940. | 1979 | Australia | Nutrients | |
| Lee, J. J., M. E. McEnery, M. Shilo, and Z. Reiss. 1979. Isolation and cultivation of diatom symbionts from larger Foraminifera (Protozoa) [12]. Nature 280:57-58. | 1979 | Algae; Nutrients | ||
| Levanon-Spanier, I., E. Padan, and Z. Reiss. 1979. Primary production in a desert-enclosed sea- the Gulf of Elat (Aqaba), Red Sea. Deep Sea Research Part A, Oceanographic Research Papers 26:673-685. | 1979 | Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production | ||
| Shanks, Alan L., and Jonathan D. Trent. 1979. Marine snow: microscale nutrient patches. Limnology and Oceanography 24:850-4. | 1979 | Nutrients | ||
| Wilkinson, C. R. and P. Fay. 1979. Nitrogen fixation in coral reef sponges with symbiotic cyanobacteria. Nature 279:527-529. | 1979 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Emery, A. R. 1978. The basis of fish community structure: marine and freshwater comparisons. Environmental Biology of Fishes 3:33-47. | 1978 | Fish; Light; Nutrients | ||
| Webb, K. L. and W. J. Wiebe. 1978. The kinetics and possible significance of nitrate uptake by several algal-invertebrate symbioses. Marine Biology 47:21-27. | 1978 | Australia | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | |
| Wilkinson, C. R. 1978. Microbial associations in sponges. III. Ultrastructure of the in situ associations in coral reef sponges. Marine Biology 49:177-185. | 1978 | Cyanobacteria; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Sponges | ||
| Brawley, S. H. and W. H. Adey. 1977. Territorial behavior of threespot damselfish (Eupomacentrus planifrons) increases reef algal biomass and productivity. Environmental Biology of Fishes 2:45-51. | 1977 | Jamaica | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Capone, D. G., D. L. Taylor, and B. F. Taylor. 1977. Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with macroalgae in a coral-reef community in the Bahamas. Marine Biology 40:29-32. | 1977 | Bahamas | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Microorganisms; Nutrients | |
| Connor, J. L. and W. H. Adey. 1977. The benthic algal composition, standing crop, and productivity of a caribbean algal ridge. | 1977 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Algae; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invertebrates; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection | |
| D'Elia, C.F. and K.L. Webb. 1977. The dissolved nitrogen flux of reef corals. Pages 325-30 in Proceedings of the 3rd Int Coral Reef Sym. | 1977 | Nutrients | ||
| D'Elia, Christopher F. 1977. The uptake and release of dissolved phosphorous by reef corals. Limnology and Oceanography 22:301-15. | 1977 | Nutrients | ||
| Evans III, E. C. 1977. Microcosm responses to environmental perturbants - An extension of baseline field survey. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 30:178-191. | 1977 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Substrate |
| Hanson, R. B. and K. Gundersen. 1977. Relationship between nitrogen fixation (Acetylene reduction) and the C:N ratio in a polluted coral reef ecosystem, Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 5:437-444. | 1977 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Skeletal Coral | |
| Muscatine, L. and J. W. Porter. 1977. Reef corals: mutualistic symbiosis adapted to nutrient-poor environments. Bioscience 27:454-460. | 1977 | Nutrients; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Por, F. D., I. Dor, and A. Amir. 1977. The mangal of Sinai: Limits of an ecosystem. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen 30:295-314. | 1977 | Model | Algae; Mangroves; Nutrients; Primary Production; Salinity; Sediment | |
| Potts, D. C. 1977. Suppression of coral populations by filamentous algae within damselfish territories. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 28:207-216. | 1977 | Algae; Fish; Nutrients; Sediment; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | ||
| Sebens, K. P. and K. DeRiemer. 1977. Diel cycles of expansion and contraction in coral reef anthozoans. Marine Biology 43:247-256. | 1977 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Anemones & Zooanthids; Nutrients; Primary Production; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hanson, R. B. and K. Gundersen. 1976. Influence of sewage discharge on nitrogen fixation and nitrogen flux from coral reefs in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 31:942-948. | 1976 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Discharges; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Plankton; Skeletal Coral | |
| Harbridge, W., O. H. Pilkey, P. Whaling, and P. Swetland. 1976. Sedimentation in the Lake of Tunis: A lagoon strongly influenced by man. Environmental Geology 1:215-225. | 1976 | Oman | Fish; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Moore, E. and F. Sander. 1976. Quantitative and qualitative aspects of the zooplankton and breeding patterns of copepods at two Caribbean coral reef stations. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 4:589-607. | 1976 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Nutrients; Plankton |
| Loya, Y. 1975. Possible effects of water pollution on the community structure of Red Sea corals. Marine Biology 29:177-185. | 1975 | Nutrients; Petroleum Spills; Waterborne Discharges | ||
| Wiebe, W. J., R. E. Johannes, and K. L. Webb. 1975. Nitrogen fixation in a coral reef community. Science 188:257-259. | 1975 | Marshall Islands | Agriculture; Nutrients | |
| Crossland, C. J. and D. J. Barnes. 1974. The role of metabolic nitrogen in coral calcification. Marine Biology 28:325-332. | 1974 | Cuba | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Nutrients; Stony Coral; Substrate; Zooxanthellae | |
| Hickel, W. 1974. Seston composition of the bottom waters of Great Lameshur Bay, St. John, US Virgin Islands. Marine Biology 24:125-130. | 1974 | US Virgin Islands | Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment | |
| Nedwell, D. B. 1974. Sewage treatment and discharge into tropical coastal waters. Search 5:187-190. | 1974 | Discharges; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies | ||
| Dugan, G. L. and R. H. F. Young. 1973. Effects of coastal water disposal in Hawaii. Pages 691-701 in J.ENVIRONM.ENGN DIV.PROC.ASCE. | 1973 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Agriculture; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment | |
| Fishelson, L. 1973. Ecology of coral reefs in the Gulf of Aqaba (Red Sea) influenced by pollution. Oecologia 12:55-67. | 1973 | Algae; Nutrients; Petroleum Spills; Stony Coral | ||
| Godfrey, J. S. 1973. Comparison of the east australian current with the western boundary flow in Bryan and Cox's (1968) numerical model ocean. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts 20:1059-1076. | 1973 | Australia | Model | Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Green, J. H. 1973. The study of metal organic complexes as pollutants in marine plants and animals. Pages 99-104 in PROC.ROY.SOC.QUEENSLAND. | 1973 | Review | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seastars; Toxics | |
| Littler, M. M. 1973. The population and community structure of Hawaiian fringing-reef crustose Corallinaceae (Rhodophyta, Cryptonemiales). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 11:103-120. | 1973 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Coralline Algae; Nutrients | |
| Sorokin, Y. I. 1973. Trophical role of bacteria in the ecosystem of the Coral Reef. Nature 242:415-417. | 1973 | Microorganisms; Nutrients | ||
| Farr, E. and L. V. Vaidyanathan. 1972. The supply of nutrient ions by diffusion to plant roots in soil - IV. Direct measurement of changes in labile phosphate content in soil near absorbing roots. Plant and Soil 37:609-616. | 1972 | Nutrients | ||
| Gundersen, K. and P. Bienfang. 1972. Thermal Pollution: Use Of Deep, Cold, Nutrient Rich Sea Water For Power Plant Cooling And Subsequent Aquaculture In Hawaii [Marine Pollution And Sea Life]. Pages 513-516 FISHING NEWS. | 1972 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Light; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Primary Production; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Johannes, R.E., et. al. 1972. The metabolism of some coral reef communities: a team study of nutrient and energy flux at Eniwetok. Bioscience 22:541-3.. | 1972 | Nutrients | ||
| Bunt, J. S., K. E. Cooksey, M. A. Heeb, C. C. Lee, and B. F. Taylor. 1970. Assay of algal nitrogen fixation in the marine subtropics by acetylene reduction. Nature 227:1163-1164. | 1970 | Florida; Bahamas; Cuba | Algae; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Drew, M. C. and P. H. Nye. 1970. The supply of nutrient ions by diffusion to plant roots in soil - III. Uptake of phosphate by roots of onion, leek, and rye-grass. Plant and Soil 33:545-563. | 1970 | Model | Nutrients | |
| POTTER, JL. 1969. Use Pollution To Benefit Mankind. Ocean Industry 4:94-97. | 1969 | Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Petroleum Spills | ||
| Rotschi, H. 1961. Oxygene, phosphate et gaz carbonique total en Mer de Corail. Deep Sea Research (1953) 8:181-195. | 1961 | US Pacific & Hawaii | CO2; Nutrients | |
| Burkholder, P. R., L. M. Burkholder, and J. A. Rivero. 1959. Chlorophyll a in some corals and marine plants. Nature 183:1338-1339. | 1959 | Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; CO2; Fish; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses | ||
| Becker, E. L., E. E. Cordes, S. A. Macko, and C. R. Fisher. Importance of seep primary production to Lophelia pertusa and associated fauna in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers | South & Central America; Mexico | Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Primary Production; Snails & Conch | ||
| Erickson, K. L., S. A. Macko, and C. L. Van Dover. Evidence for a chemoautotrophically based food web at inactive hydrothermal vents (Manus Basin). Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography | US Pacific & Hawaii; Papua New Guinea | Nutrients; Primary Production; Sponges | ||
| Falcao, M., M. N. Santos, T. Drago, D. Serpa, and C. Monteiro. Effect of artificial reefs (southern Portugal) on sediment-water transport of nutrients: Importance of the hydrodynamic regime. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science | Artificial Habitat; Nutrients; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes | |||
| Herrera-Silveira, J. A. and S. M. Morales-Ojeda. Evaluation of the health status of a coastal ecosystem in southeast Mexico: Assessment of water quality, phytoplankton and submerged aquatic vegetation. Marine Pollution Bulletin | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Mork, E., G. L. Sjoo, N. Kautsky, and T. R. McClanahan. Top-down and bottom-up regulation of macroalgal community structure on a Kenyan reef. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science | Kenya | Algae; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Ogden, J. V. and E. H. Gladfelter, editors. Coral reefs, seagrass beds and mangroves: their interactions in the coastal zones of the Caribbean. UNESCO Reports in Marine Science, vol. 23, Paris. | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; Tobago; Nicaragua; Costa Rica; Panama; Venezuela; Caribbean; Mexico | Mangroves; Nutrients; Plankton; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Peddicord, R. K. Impacts of open-water dredged material discharge. in [No source information available]. | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Military; Nutrients | ||
| Risk, M. J., B. E. Lapointe, O. A. Sherwood, and B. J. Bedford. The use of δ 15N in assessing sewage stress on coral reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Bivalves; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Octocoral; Sediment | ||
| Sattler, U., A. Immenhauser, W. Schlager, and V. Zampetti. Drowning history of a Miocene carbonate platform (Zhujiang Formation, South China Sea). Sedimentary Geology | China | Field Study & Monitoring | Nutrients |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Livestock Waste Storage and Utilization | Confined animal facilities often produce large amounts of animal waste. This waste can be stored and disposed of in a variety of ways, and it is important to consider how rainwater may carry these wastes in groundwater. Wastes can be kept in temporary storage ponds, storage structures, or treatment lagoons. Once composted, these wastes may be applied to agricultural land in an environmentally acceptable manner in place of other fertilizers. Site selection, timing of application and rate of application must be properly managed to reduce the potential for degradation of ground water. Additionally, this practice may increase microbial action in the soil surface, which helps keep pesticides and other pollutants in place. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Food & Raw Materials; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Contour Farming | Contour Farming involves sloping land in such a way that field preparation, planting and cultivating are done on the contour. This includes following established grades of terraces or diversions. During heavy rains the crop rows formed slow water runoff reducing erosion and water runoff of non-point source pollutants such as agricultural herbicides and fertilizers. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Fertilizer Application Management | This agricultural best management practice involves the development, implementation and periodic update of nutrient management plans. Nutrient management plans are used to efficiently apply nutrients at appropriate rates so as to still achieve desired crop yields. There are several important measures and considerations that must be taken before developing the nutrient plan. Farm and field maps, yield expectations, nutrient resources, and geologic field limitations are all important. Some crops fix nitrogen, such as legumes, and have a nitrogen credit that must be factored. Field limitations include shallow aquifers, nearby surface water, sinkholes, and highly erodible soils. If the nutrients to be applied aren�t commercial they must be assessed to determine the nutrient value and the rate of availability of the nutrients. The nutrient plan�s timing and application methods should use the limiting nutrient concept and avoid applications to frozen soil and during periods of leaching or runoff. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Jokela, Bill, Peter Kleinman, John Peters, and Ann Wolf,. 2011. Manure Spreader Calibration & Manure Testing. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Grazing Land Management | This management option protects range, pasture and other types of grazing lands for agricultural animals. Special actions should be taken to protect sensitive areas such as streams, wetlands and estuaries if livestock is to have access to these areas. Grazing management practices can be categorized into four types, vegetative stabilization, grazing management systems, access limitations and alternative water supplies. Vegetative stabilization involves reestablishing the vegetative cover on ranges after it has been removed by grazing to reduce erosion rates. Grazing management systems typically reduce the time livestock spend in each pasture to increase the quantity and quality of vegetation in those pastures. Grazing frequency, timing, duration, area allocation, and livestock distribution kind, class, distribution and stocking rates should all be considered in the management system to ensure adequate pasture rehabilitation. Access limitations, such as fencing and stream crossings are used to herd and control livestock movement. Physical disturbance from livestock can increase erosion, so crossings and watering access points should be hardened. Alternative water supplies are an alternative to more sensitive water sources that may be vulnerable to erosion and discharges from grazing areas. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Composting | Composting involves the controlled aerobic decomposition of manure or other organic material by micro-organisms into a biologically stable organic material that is suitable for use as a soil supplement. Composting should be part of nutrient management plans because it reduces the pollution potential of organic wastes. Smaller scale household composting may reduce the amount of material that enters the waste stream, where again it may have greater pollution potential. Larger volumes of material may require construction of containment facilities to ensure pollutants aren't able to enter runoff water in high concentrations. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Landscaping & Household Services; Littering; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Pond Sealing | Waste treatment ponds and pits are useful methods of treatment, but premature seepage from these storage impoundments would also have negative impacts. Bentonite Liner Treatment, Compacted Clay Treatment, Flexible membrane, and Soil Dispersant Treatment are all options for sealing treatment impoundments, depending on the specific soil suitability and other criteria. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Remediation; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Discharge Controls: Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards | Effluent Toxicity is considered the aggregate toxic effect to aquatic organisms from all pollutants contained in a facility's wastewater (effluent). It is one part of the Water Quality Standards (#22) that prohibits the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts. Numerical criteria can be adopted from the Clean Water Act of based on scientifically-defensible methods. In addition to setting this numerical criteria, enforcement of the standards requires inspection programs and monitoring. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Improved Technology; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Management Planning | There are many aspects to properly managing forestry sites to reduce point source and non-point source pollutants. Forestry activities can degrade water quality with several types of pollutants and impacts, including: sediment, nutrients, forest chemicals like pesticides, organic debris from tree litter, increased water temperature and increased streamflow. The Forestry management plan and practices include, but are not limited to: pre-harvest planning, road construction and use, prescribed burning and fire management, brush management, timber harvest, regeneration, and application of forest chemicals. Wetlands Forest Management has additional best practices. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Biological Harvest; Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Forestry Policy: Forest Chemical Management | Pesticides and fertilizers are commonly used in forestry to reduce mortality of desired trees, improve forest production, and ease harvest/extraction. The rate of application is typically very low, but given the overall area covered, pesticides can still accumulate within watersheds. Some forest management chemical use considerations to reduce nonpoint source pollution impacts include: Develop an effective spill contingency plan to contain spills, and immediately report accidental spills into surface waters to the appropriate State agency. Prior to application, inspect the mixing and loading process and the calibration of equipment, and identify the appropriate weather conditions, the spray area, and buffer areas for surface waters. Buffer areas for surface waters are especially important for aerial applications. Carefully prescribe the type and amount of pesticides appropriate for the insect, fungus, or herbaceous species. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Provisioning Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Water Resources; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Landuse Management: Household Landscaping Best Management Practices | Homeowners manipulate the visible features of the land surrounding their home through landscaping. This includes flora, fauna, and terrain. Best Management Practices (BMPs) for landscaping include selection of indigenous flora and fauna, landscape irrigation (sprinkler systems etc), stormwater runoff BMPs, reducing water use, integrated pest management, composting, and incorporation of permeable surfaces. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Addition; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shelter; Supplemental Feeding; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Research and Monitor Wetlands | This management option involves monitoring and research of mangroves, both for biotic and abiotic factors. Some biotic factors include disease, species, invasive species, abundance, age and leaf litter. Important abiotic factors include sedimentation rates, types and causes of turbidity, and soil chemistry. The activity would document changes to the extent of mangrove vegetation by using historical aerial photography and other records. Wetland nutrient and contaminant processing productivity depends on maintaining a balance and not exceeding thresholds. There remain many unknowns in wetland restoration as to optimal capacity and how to achieve this. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Primary Production; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Water Quality Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term, comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of water quality parameters. Parameters that should be measured include temperature, salinity, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, relative fluorescence, light attenuation, nutrients, chlorophyll, and alkaline phosphatase activity. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate; Climate Regulation; CO2; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Regulating Services; Salinity; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Supporting Services; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Develop Innovative Monitoring Tools | This management option calls for identifying and evaluating monitoring tools and methodologies used to detect pollutants and identify cause-and-effect relationships among water quality and biological resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Chemical Variables; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Scientific Research; Toxics |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Wastewater Pollutants Impacts: Wastewater Pollutant Monitoring and Impact Studies | Potential approaches to this management option include experimental studies, eutrophication gradient studies, comparative studies of impacted and non-impacted sites, historical studies, geography comparison, use of biochemical and ecological indicators, use of sewage tracers, and high-frequency and spatially intensive water quality sampling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Infrastructure; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Public Administration; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Utilities; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Reduce Pollution & Discharges from Marinas & Live-Aboards | This management option strives to reduce and eliminate the discharge of wastewater and pollution within zones near corals. In many instances, "no-discharge" zones already exist and are simply poorly enforced. In other instances the discharge limits are not stringent enough. Successful regulation requires marinas to be equipped with the proper infrastructure to support transfer of wastewater from vessels to shore-side for treatment. This infrastructure includes: pump-out facilities and mobile pump-out services. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Health; Health Policies; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Treating Effluent Water Through Wetlands | Additional treatment of sewage is often a necessary management option because secondary treatment alone leaves 20,000 times more nutrients in the water than the safe limit for corals. High concentrations of nutrients in the water leads to eutrophication, and coral reefs are more sensitive to nutrient enrichment than any other coastal system. Wetlands are extremely successful at reducing nitrogen levels in water. Using natural wetlands or "living machines" to perform this task can actually be more cost effective than further sewage treatment. Each successive wetland treatment cell of the series can provide incredible levels of denitrification, and thus protect corals from nutrient enrichment. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2003. Waste Treatment Lagoon. CODE 359. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Water Quality Management: Landfill & Solid Waste Disposal Site Assessment Strategy | This option seeks to reduce/eliminate pollution from leaching at landfill sites. High risk, old landfill sites that may have hazardous waste must be identified. Once identified, monitoring at these landfills should be intensified to insure leaching does not occur into marine systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health; Health Policies; Littering; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Remediation; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Water Quality Management: Wastewater Management System Standards | This management option involves reducing the amount of pollutants entering groundwater by enforcing existing standards. Inspection and compliance programs for cesspits, Onsite Sewage Treatment and Disposal Systems (OSTDS) and septic tanks are necessary to do this. Municipal sewage treatment plants have a variety of means to meet these standards, including improving management of current treatment systems or upgrading treatment systems with newer technology. Some of these technologies include: Continuous-Flow, Suspended-Growth Aerobic Systems (CFSGAS), Fixed-film, Sequencing batch reactor systems, Stabilization ponds, FWS constructed wetlands, and other aquatic systems (#2), Enhanced nutrient removal: phosphorus & nitrogen, Recirculating sand/media filters and Land treatment systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Center for Watershed Protection. 2004. Illicit Discharge Detection and Elimination. US EPA. US Environmental Protection Agency. 2002. Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. EPA/625/R-00/008, US EPA. |
Chemical Variables; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Water Quality Standards | Water Quality Standards are the foundation of the water quality-based pollution control program mandated by the Clean Water Act. Water Quality Standards define the goals for a waterbody by establishing Designated Uses (#279), setting baseline waterbody minimum criteria to protect those uses, and establishing provisions that regulate Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards (#280). Since the baseline water quality standards are for the waterbody in its entirety, there is some flexibility on how that minimum criterion is accomplished. In some cases, Remediation (#281) may be preferable to more stringent effluent standards. The criteria include specific biochemical and ecological measures that would be good indicators of ecological health, including Biocriteria (#282). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biocriteria; Chemical Variables; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Provisioning Services; Toxics |
| Water Quality Management: Pet Waste Cleanup Ordinance & Education | In residential areas, pet waste can contributes to the large amount of nutrients and pathogens that enter the water through stormwater runoff. This is especially useful in regions such as Gu�nica, Puerto Rico where there are a lot of stray dogs. Education for pet-owners and possible ordinance would help decrease harmful pathogens reaching corals through stormwater runoff and reduce eutrophication. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Animal Waste Collection. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Clary, J., Leisenring, M., and Jeray, J. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Pollutant Category Summary: Fecal Indicator Bacteria. Wright Water Engineers. |
Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Domestic Animal Waste; Environmental Education & Outreach; Health; Health Policies; Invasive Species; Landscaping & Household Services; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Stormwater Management; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-Year Permits for Maintenance Dredging in Deepwater Ports; Deepwater Ports Maintenance Dredging and Disposal Manual, 62-045 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-45.001 Authority, Intent and Policy.
(1) This chapter is promulgated under the authority of Sections 403.061(26) and 403.816(1), F.S.
(2) It is the intent of this chapter to establish a permitting system for maintenance dredging in deep water commercial navigation
areas of the ports listed in Rule 62-45.020, F.A.C. This chapter incorporates standards and criteria which recognize the present most
beneficial use of these waters for deep water commercial navigation. Since the implementation of a comprehensive maintenance
dredging management plan is a major factor in determining the adequacy of a long-term maintenance dredging program, it is the
further intent of this chapter to give a position of prominence to such a plan within this permit system.
(3) It is the policy of the Department to provide a regulatory process which will enable the ports to conduct maintenance
dredging in an environmentally sound, expeditious and efficient manner.62-45.020 Scope.
(1) The permit system established by this chapter applies only to the ports of Ft. Pierce, Jacksonville, Miami, Palm Beach,
Panama City, Pensacola, Port Canaveral, Port Everglades, Port Manatee, Port St. Joe, St. Petersburg, and Tampa.
(2) The activities which may be included within a permit issued under this chapter are limited to maintenance dredging and
disposal of the maintenance dredged material.
(3) Applicants for permits under this chapter are limited to the port authorities or private interests using the port for deep water
commercial shipping and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The Department shall not issue separate permits to the port authority or
private interests and the U. S. Army Corps of Engineers when the responsibility of maintenance dredging or the disposal of the
maintenance dredged material from the port is shared by any of the parties. The permit, if issued, shall clearly specify the duties and
responsibilities of each party.
(4) A permit may be issued for any length of time up to 25 years. There shall be no more than one such permit for each of the
ports listed in subsection (1).
(5) The area within which work under this permit system may take place is limited to the federally maintained, port authority
maintained, or private interest maintained navigation channels, turning basins, or harbor berths associated with deep water
commercial navigation and associated dredged material disposal sites. Eligible port maintenance dredging areas are depicted on
NOS Charts Nos. 11491 (Port of Jacksonville), 11478 (Port Canaveral), 11475 (Fort Pierce Harbor), 11466 (Port of Palm Beach),
11468 (Port of Miami), 11470 (Port Everglades), 11413 (Tampa Bay, Northern Part), 11414 (Tampa Bay, Southern Part), 11393
(Port St. Joe), 11391 (Panama City), and 11383 (Port of Pensacola) on file with the Department and adopted here by reference.
Copies are available at cost upon request from the Office of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, MS
300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000. Application to Coral Reefs:Proper, environmentally sound, dredging and disposal of dredged material, as reviewed by permit processers, will limit the amount of sediment and nutrients released to open water. The process will be particularly applicable to coral reefs for the dredging and disposal of Miiami harbor. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| Air Pollution Control, 62-204 Florida Administrative Code (1996). | 62-204.100 Purpose and Scope.
(1) This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods.
(2) In addition, this chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassifiable with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have been adopted; further designates certain attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as air quality maintenance areas for particular pollutants; classifies all areas of the state as Class I, Class II, or Class III for determining which set of prevention of significant deterioration (PSD) increments apply; and designates all attainment and unclassifiable areas of the state as one or more PSD areas for determining which pollutant-specific PSD baseline dates apply. This chapter also sets forth procedures for redesignating and reclassifying areas as above.
(3) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to identify the Florida State Implementation Plan (SIP) required by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51; to set forth the public notice and hearing requirements that the Department will adhere to for making SIP revisions; and to set forth the definitions, criteria, and procedures that the Department will use to review a federal agency�s general conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart W; and to adopt by reference an interagency memorandum of agreement that the Department will comply with to review any transportation conformity determination, made pursuant to 40 C.F.R. Part 51, Subpart T. The provisions to 40 C.F.R. 51.853 require that a federal agency make a general conformity determination for any federal agency action in a nonattainment or maintenance area, to ensure that such action is consistent with the SIP and that such federal conformity determination be reviewed by the affected state. The provisions of 40 C.F.R. 51.394 require that a transportation conformity determination be made for the adoption, acceptance, approval, or support of certain transportation plans, transportation improvement programs, and transportation projects in nonattainment and maintenance areas for transportation-related criteria pollutants to ensure that such actions are consistent with the SIP.
(4) Finally, this chapter adopts and incorporates by reference federal air pollution control regulations which are referenced in whole or in part throughout the Department�s air pollution control rules. Application to Coral Reefs:By reducing emmissions to air, particularly carbon dioxide, the pH of ocean waters will not be reduced and that is a direct benefit to coral reefs, since a reduction in pH is believed to be detrimental to corals. Legislative Actions:The Chapter designates all areas of the state as attainment, nonattainment, or unclassified with respect to each pollutant for which ambient air quality standards have benn adopted. Comments:This chapter establishes maximum allowable levels of pollutants in the ambient air, or ambient air quality standards, necessary to protect human health and public welfare. This chapter also establishes maximum allowable increases in ambient concentrations for subject pollutants to prevent significant deterioration of air quality in areas where ambient air quality standards are being met. It further specifies approved air quality monitoring and modeling methods. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Use Regulations; CO2; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Clean Air Act, 42 United States Code §§ 7400 et seq. | To ensure Americans have clean air to breath, and to protect the environment from air pollution. Regulates air emmissions from area, stationary and mobile sources. Charges federal land managers with direct responsibility to protect the "air quality and related values" of land under their control. The "related values" include fish and widlife and their habitats. The Clean Air Act is the law that defines EPA's responsibility for protecting and improving the nation's air quality and the stratospheric ozone layer. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act would decrease carbon dioxide emissions from sources in the United States, thereby making a contribution toward reducing ocean acidification, which is one of the problems contributing to coral reef decline. Legislative Actions:Response will differ from State to State because many Sates have been delegated to administer the Clean Air Act. However, States cannot have air quality standards less stringent then the federal standards. State air pollution agencies hold permit hearings and fines industries that violate air quality limits. States must develop state implementation plans that require approval by EPA. Comments:The 1990 amendments authorized the Acid Deposition Control Program, a program to control 189 toxic pollutants, established permit program requirements, expanded and modified the attainment of National Ambient Air Quality Standards, and expanded and modified enforcement authority. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Transportation Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Delegation of the Environmental Resource Program to Local Governments, 62-344 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) This chapter guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient,
streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental
resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments in accordance with the
provisions of Sections 373.103(8) and 373.441, F.S. This chapter also constitutes the Department�s authorization, in accordance with
Section 373.103(8), F.S., for delegations of the environmental resource permit program from the water management districts to local
governments provided that the procedures for delegation contained in this chapter are followed by the Districts. Delegations from
the Department and Districts shall be for the respective environmental resource permit program responsibilities of the Department
and the Suwannee River, St. Johns River, Southwest Florida and South Florida Water Management Districts, as set forth in
operating agreements listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C. Delegation agreements between the Department and local governments shall
be listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C., and delegation agreements between the Districts and local governments shall be listed in
Chapters 40B-1, 40C-1, 40D-1, and 40E-1, F.A.C.
(2) Nothing in this chapter shall preclude the Department, Districts, and local governments from entering into contracts or
interagency agreements as provided by law.
(3) Except as specifically provided in this chapter, nothing herein shall prevent a local government from adopting and
implementing an environmental regulatory program pursuant to its own authority.
(4) It is an objective of the Department and Districts to protect the functions of entire ecological systems, as defined and
developed in the programs, rules and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is the intent of the Department and
Districts that any local government receiving delegation of all or a portion of the environmental resource program carry out that
program in a manner consistent with this objective. This paragraph shall not be construed or applied as additional permitting criteria
beyond those adopted by the reviewing agency or the local government. Application to Coral Reefs:In theory, delegating stormwater pond construction and wetland functional determinations, as well as most otrher issues related to stormwater and wetlands, to local government will produce more efficient permitting and oversight. Therefore, treated water that is discharged and reaches any ecosystem should contain less contamination than the same water if it had not treated. Legislative Actions: Comments:Guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient, streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Domestic Wastewater Facilities, 62-600 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.021(2), Florida Statutes, as amended, the Florida Air and Water Pollution Control Act, established that no
wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessary to protect the
beneficial uses of such water. Toward this end, Sections 403.085 and 403.086, Florida Statutes, set forth requirements for the
treatment and reuse or disposal of domestic wastewater. Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, requires that any Department
planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be
developed as a rule. This chapter is promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of Sections 120.53(1), 120.55,
403.021, 403.051, 403.061, 403.062, 403.064, 403.085, 403.086, 403.087, 403.088, 403.0881, 403.101, 403.131, 403.161,
403.182, 403.859, and 403.918, Florida Statutes, concerning domestic wastewater facilities.
- 442
(2) The requirements of this chapter represent the specific requirements of the Florida Department of Environmental Protection
and of Local Pollution Control Programs approved and established pursuant to Section 403.182, Florida Statutes, where such
authority has been delegated to those programs. It may be necessary for domestic wastewater facilities to conform with
requirements of other agencies, established via interagency agreements (e.g., for mosquito control); the absence of reference to
such arrangements in this chapter does not negate the need for compliance with those requirements.
(3) The purpose of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., is to provide minimum standards for the design of domestic wastewater facilities
and to establish minimum treatment and disinfection requirements for the operation of domestic wastewater facilities. All systems
shall be designed in accordance with sound engineering practice. Supported by moderating provisions, it is intended that Chapter
62-600, F.A.C., establish a framework whereby design flexibility and sound engineering practice can be used in developing
systems with which to manage domestic wastewater in an environmentally sound manner.
(4) As appropriate, Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., shall be used in conjunction with other Department rules relating to the design and
operation and maintenance of domestic wastewater facilities.
(5) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities
(including residuals management facilities).
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and modifications or expansions of existing facilities that
submit complete permit applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit complete applications for permit renewal after
July 1, 1991.
(6) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications on or before July 1, 1991, may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the time the permit was issued and with the conditions
of the existing construction or operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter.
(7) The standards and requirements of Part II of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., and Rules 62-600.500 and 62-600.530, F.A.C., shall
be applicable to septic tank drainfield systems and other on-site waste treatment systems with subsurface disposal regulated by this
chapter. The reliability requirements of paragraph 62-600.400(1)(b), F.A.C., shall not apply to such septic tank drainfield systems
and other on-site waste treatment systems.
(8) The discharge limitation of subsection 62-600.510(4), F.A.C., shall not be applicable to facilities permitted on or before
January 1, 1982, that discharge into Class II waters or Class III waters which are subsequently reclassified as Class II waters.
(9) This chapter provides for exemptions, allowances for existing facilities and variations from standards and requirements.
Unless specifically provided otherwise, no wastewater permit shall be issued or renewed unless the permit applicant demonstrates
that the subject facility is in compliance with the applicable provisions of this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting construction and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the processes for planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant monitoring, 62-601 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, as amended, part of the Florida
Air and Water Pollution Control Act, requires that any Department operating standards,
criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be developed as a rule. This rule is
promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of the Act concerning
domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring.
(2) The purpose of Chapter 62-601, F.A.C., is to ensure that owners and
operators of domestic wastewater treatment facilities maintain accurate records and
submit reports required by this Chapter in a timely, accurate, cost-effective and uniform
manner.
(3) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic
wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities (including residuals management
facilities). The standards and requirements are not applicable to facilities described in
Rules 62-600.120(1) and (2), F.A.C.
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and
modifications or expansions of existing facilities that submit complete permit
applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit
complete applications for permit renewal after July 1, 1991.
(4) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications
on or before July 1, 1991 may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the
time the permit was issued and with the conditions of the existing construction or
operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting monitoring requirements and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:to implement the provisions and requirements concerning domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Discharge Limitations; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Dredge and Fill Activities, 62-312 Florida Administrative Code. | This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department pursuant to Sections 403.91 through 403.929, F.S. Dredging or filling which is grandfathered by subsections 403.913(6), (8) and (9), F.S., is governed by Rules 62-312.150 and 62-312.160, F.A.C. The requirements of this part are in addition to and not in lieu of the water quality standards which are required by other portions of these sections. Except for the definitions contained in Rule 62-312.020, F.A.C., which shall also apply to activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., the provisions of this Part shall only apply to activities in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District and to activities grandfathered under Sections 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15) and (16), F.S.
Specific Authority 373.414(11)-(16), 373.4145, 403.805(1) FS. Law Implemented 373.409, 373.413, 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15), (16), 373.4145, 373.416, 373.418, 403.061, 403.813, 403.814 FS. History�New 12-10-84, Amended 8-7-85, Formerly 17-12.010, 17-312.010, Amended 10-3-95. Application to Coral Reefs:The permit reviewers will require BMP for dredge and fill activities. This will include siltation reduction methods that will keep sediment, nutrient and other contaminants from leaving the work site and getting into the water column and potentially reaching sensitive ecosysten, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department for dredge and fill activities. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Toxics |
| Emergency Wetlands Resources Act of 1986, 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote the conservations of wetlands for public benefit and to assist in the compliance with international obligations under various treaties and conventions for migratory birds. Application to Coral Reefs:Indirect application to protection of coral reefs through wetland functions of nutrient (particularly nitrogen) and sediment removal from land-based discharges prior to their entrance into open coastal waters. Legislative Actions:Authorizied the purchase of wetlands from the land and Water Conservation Fund monies. Required States to include wetlands in their Comprehensive Outdoor Recreation Plans. Comments:Secretary of Interior was required to establish a National Wetland Priority Conservation Plan to identify the locations and types of wetlands that should be priorities for state and federal acquisition. The Act established various fee schedules for entering national wildlife refuges. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Discharge Limitations; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction, 62-285 Florida Administrative Code. | Florida LEV Program. The Department of Environmental Protection (Department) adopts this rule to establish a Florida low emission vehicle (LEV) program that implements California motor vehicle emission standards pursuant to s. 177 of the Clean Air Act. This rule refers to many sections of chapter 1, division 3, title 13 of the California Code of Regulations (CCR), adopted and incorporated by reference at subsection 62-285.400(9), F.A.C. This rule also includes provisions specific to implementation in Florida. Application to Coral Reefs:Reducing greenhouse gases will contibute to a decrease in ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:To protect air quality, this rule applies to any heavy-duty diesel engine powered motor vehicle. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Climate Regulation; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Transportation Policies |
| Ground Water Permitting and Monitoring Requirements, 62-522 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Unless exempted by Rule 62-520.500, 62-520.510 or 62-520.520, F.A.C., no installation shall directly or indirectly
discharge into ground water any contaminant that causes a violation in the water quality standards and criteria for the receiving
ground water as established in Chapter 62-520, F.A.C., except within a zone of discharge established by permit or rule pursuant to
this chapter.
(2) Zones of discharge shall be allowed for projects or facilities that allow direct contact with ground water listed in paragraphs
(a) through (c) below, which provide beneficial discharges through wells to ground water as described in the cited rules.
(a) Projects designed to recharge aquifers with surface water of comparable quality, or projects designed to transfer water across
or between aquifers of comparable quality for the purpose of storage or conservation;
(b) Facilities permitted under Rule 62-610.466, F.A.C., for aquifer storage and recovery of reclaimed water, subsection 62-
610.560(3), F.A.C., for ground water recharge by injection of reclaimed water, or subsection 62-610.562(4), F.A.C., for creation of
salinity barrier systems by injection of reclaimed water; and
(c) Department-approved aquifer remediation projects that use Class V, Group 4, underground injection control wells as
described in paragraph 62-528.600(2)(d), F.A.C. A zone of discharge shall be allowed for primary standards for ground water for
closed-loop re-injection systems and for the prime constituents of the reagents used to remediate site contaminants, and for the
secondary standards for ground water, as specified in a Department-approved remedial action plan that addresses the duration and
size of the zone of discharge, and ground water monitoring requirements.
(3) Other discharges through wells or sinkholes that allow direct contact with class G-I, Class F-I, or Class G-II ground water
shall not be allowed a zone of discharge.
(4) Discharges that may cause an imminent hazard to the public or the environment through contamination of underground
supplies of drinking water or surface water affected by the ground water.
(5) Installations operated to render water fit for human consumption and which dispose non-hazardous concentrates from
membrane separation technologies, such as reverse osmosis, membrane softening, ultra-filtration, and electrodialysis, through land
application operations are exempt from obtaining a zone of discharge in order to discharge to ground water, provided the applicant
demonstrates that the receiving unconfined aquifer exhibits a natural background total dissolved solids concentration exceeding
1500 mg/L. Installations discharging to such aquifers shall not cause a violation of primary or secondary drinking water standards at
any private or public water supply well outside of the installation�s property boundary.
(6) It is the intent of the Department whenever possible to incorporate ground water discharge considerations into other
Department permits as appropriate, and not to require a separate permit for discharges to ground water. However, any published
notice of proposed agency action on an application for a permit shall contain notice, when appropriate, that ground water
considerations are being incorporated into such permits.
(7) The purpose of monitoring is to ensure that the permitting of zones of discharge, or exemptions therefrom, will not cause a
violation of ground water standards. Ground water monitoring is intended to allow predictions to be made of the movement and
composition of the discharge plume and compliance with applicable state ground water standards at the boundary of the zone of
discharge. Efforts shall be made to minimize the number and cost of monitoring wells, consistent with the ability to obtain useful
and reliable information.
(8) Existing installations discharging to Class G-II ground water are exempt from compliance with secondary standards outside
of a zone of discharge obtained by Department permit or rule except where compliance is required under Rule 62-520.520, F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:Groundwater flow will eventually bring the groundwater to an area where by intrusion it will enter waterbodies such as lakes, streams, estuaries, and the ocean. If the groundwater is contaminated, the contamination then enters the waterbody. The contaminants will affect the open water environment and degrade that system. Legislative Actions: Comments:Prohibits the discharge into ground water any contaminant that causes a violation in the water quality standards and criteria for the receiving ground water. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Sediment; Waste Management Policies |
| Identification of impaired surface waters, 62-303 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2002). | The Chapter established a methodology to identify surface waters of the state that will be included on the state's planning list of waters that will be assessed pursuant to subsections 403.067(2) and (3), Florida Statutes. It also establishes a methodology to identify impaired waters based on representative data that will be included on the state's verified list of impaired waters, for which the Department will calculate Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDLs), pursuant to subsection 403.067(4), F.S., and which will be submitted to the United States Environmental Protection Agency pursuant to paragraph 303(d)(1) of the Clean Water Act (CWA). Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Irrigation; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Microorganisms; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Marine Sanitation Devices (MSDs); Regulations to establish a No Discharge Zone (NDZ) for State waters within the boundary of the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary,Code of Federal Regulations § 40 CFR Part 140, 67 FR 35735. | US EPA established a no discharge zone within the boundaies of the FKNMS pursuant to section 312 (f) (4) (a) of the Clean Water Act. Application to Coral Reefs:Prohibition of waste discharges protects reefs system from eutrophication by the nutrients in waste (particularly nitrogen and phosphorus) as well as the debris and sediment in the waste. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Algae; Ballast Discharge; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Motor Vehicle Emissions Standards and Test Procedures, 62-242 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter pursuant to the Florida Clean Outdoor Air Law, Section
325.201, F.S., and in order to provide the Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles with the necessary rules, standards,
and criteria to administer the Florida Motor Vehicle Inspection Program.
(2) The Legislature has directed that in order to implement the Motor Vehicle Inspection Program, the Department of
Environmental Protection will set the standards and criteria listed below.
(a) Designation of program area (Section 325.204, F.S.).
(b) Emissions testing and inspection procedures (Section 325.206, F.S.).
(c) Inspection pass/fail criteria (Section 325.206, F.S.).
(d) Test equipment performance specifications (Sections 325.206, .212, and .213, F.S.).
(e) Definition of low emission adjustment (Section 325.209, F.S.).
(f) Inspection personnel training criteria (Section 325.213(1)(d), F.S.).
(3) The Department has set the vehicle in-use emission standards at levels that are achievable with proper operation and
maintenance of the various model year vehicles, if they have not been tampered with, and which will result in a significant reduction
in ozone-causing air pollutant emissions from automobiles and light duty trucks. It is the Department�s intent that eligibility for
emission control system performance warranty repairs of these vehicles be protected by reference to 40 CFR 85.2201 (Subpart W) �
Emission Control System Performance Warranty Short Tests.
(4) This chapter, and the Department of Highway Safety and Motor Vehicles rules it references, are intended as an integral part
of the Department�s program to achieve and maintain the National Ambient Air Quality Standards for ozone, carbon monoxide, and
particulate matter; and to control nuisance exhaust. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation and stanards for air emissions will contribute to lower greenhouse gasses and assist in combating ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Climate Regulation; CO2; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Land & Air Transportation; Nutrients; Transportation Policies |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Regulation of stormwater discharge, 62-25 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1988). | The discharge of untreated stormwater may reasonably be expected to be a source of pollution of waters of the state and is, therefore, subject to Department regulation. The Departmnet shall prevent pollution of waters of the state by discharges of stormwater, to ensure that the designated most beneficial uses of waters, as prescribed by Chapter 62-302, F.A.C., are protected. A permit under this chapter will be required only for new stormwater discharge facilities as defined herein. This provision shall not affect the Department's authority to require appropriate corrective action, pursuant to Sections 403.121-.161.F.S., whenever existing facilities cause or contribute to violations of state water quality standards. Stormwater discharges to groundwaters shall be regulated under the provisions of Chapters 62-520 and 62-522, F.A.C., and other applicable rules of the Department. The Department intends that, to the greatest extent practicable, the provisions of this chapter be delegated to either local governments or water management districts seeking such delegation. Application to Coral Reefs:Limiting the contaminants and their concentrations in stormwater discharge will reduce the contamination reaching various habitats, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Floridfa Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency, 62-016 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter implements the Florida Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency Act, providing for grants for renewable energy technologies and rebates for solar energy systems. This chapter also implements applications for corporate tax credits for renewable energy technologies provided for in Section 220.192, F.S.
Specific Authority 377.804(3), 377.806(7), 220.192(3) FS. Law Implemented 377.801, 377.802, 377.803, 377.804, 377.806, 220.192 FS. History � New 10-22-07. Application to Coral Reefs:The regulation could reduce greenhouse gas emissions from coal fired electric generating plants and thus reduce ocean acidification. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter implements the Florida Renewable Energy Technologies and Energy Efficiency Act, providing for grants for renewable energy technologies and rebates for solar energy systems. This chapter also implements applications for corporate tax credits for renewable energy technologies |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Small Community Wastewater Construction Grants Program, 62-505 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Florida�s Small Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program is
authorized by Sections 403.1835 and 403.1838, F.S. These statutes authorize the
Department to fund the planning, design, and construction of wastewater management
systems for qualifying small municipalities.
(2) This chapter sets forth the Department�s program management
procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance from the Small
Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program.
(3) Highest priority is given to projects that address the most serious risks to
public health, are necessary to achieve compliance, or assist systems most in need
based on an affordability index.
Specific Authority 403.1835(10) FS. Law Implemented 403.1835(3)(d), 403.1838 FS.
History � New 1-25-07. Application to Coral Reefs:Providing financial assistance to parties interested in building wastewater treatment palnts and best available standards for construction will result in higher treatment of wastewater prior to discharge to waters of the state. Less contaminated water will reach the marine environment where it would have the potential to adversely effect ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:sets forth the program management procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance from the Small Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Environmental Education & Outreach; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| State Revolving Fund Loan Program, 62-503 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Florida�s water pollution control revolving loan program is authorized by Section 403.1835, F.S. This statute establishes the Wastewater Treatment and Stormwater Management Revolving Loan Trust Fund, which meets federal requirements for a State Revolving Fund. The statute authorizes the Department to fund the planning, design, construction, and implementation of wastewater management systems and stormwater management systems. The Act also authorizes financial assistance for a wide range of services, equipment, and construction associated with nonpoint source pollution control. Project examples include brownfield remediation, wetland restoration, septic tank problem correction, best management practices (especially those for agricultural operations) for controlling leaching and runoff, animal waste management, boat discharge elimination, or other needs identified by the Department�s nonpoint source management program. National estuary program projects also may be eligible.
(2) The federal Water Pollution Control Act, as amended, commonly called the Clean Water Act, authorizes federal appropriations for grants to the Department to capitalize the State Revolving Fund. The Act requires that the state contribute matching funds of 20% to qualify for federal capitalization grants. The State Revolving Fund must be operated in perpetuity by the Department.
(3) This rule sets forth the Department�s program management procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance.
Specific Authority 403.1835(5)(a) FS. Law Implemented 403.1835 FS. History - New 7-29-04. Application to Coral Reefs:Providing financial assistance to parties interested in building wastewater treatment palnts and best available standards for construction will result in higher treatment of wastewater prior to discharge to waters of the state. Less contaminated water will reach the marine environment where it would have the potential to adversely effect ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the Wastewater Treatment and Stormwater Management Revolving Loan Trust Fund to fund the planning, design, construction, and implementation of wastewater management systems and stormwater management systems and to provide financial assistance for a wide range of services, equipment, and construction associated with nonpoint source pollution control. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Environmental Education & Outreach; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Stationary Sources - Emission Standards, 62-296 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department of Environmental Protection adopts this chapter to establish emission limiting standards and compliance requirements for stationary sources of air pollutant emissions.
(2) The chapter includes emission limitations for specific categories of facilities and emissions units, and it establishes reasonably available control technology requirements. Where work practice standards, including requirements for specific types of pollution control equipment, are provided for in this chapter, such standards shall be of the same force and effect as emission limiting standards. The emission limiting and work practice standards of Rule 62-296.320, F.A.C., and Rules 62-296.401 through 62-296.480, F.A.C., are applicable statewide. The reasonably available control technology requirements are established for specific areas of the state as set forth in Rules 62-296.500, 62-296.600, and 62-296.700, F.A.C.
(3) A facility or emissions unit subject to any standard or requirement of 40 CFR. Part 60, 61, 63 or 65, adopted and incorporated by reference at Rule 62-204.800, F.A.C., shall comply with such standard or requirement. Nothing in this chapter shall relieve a facility or emissions unit from complying with such standard or requirement, provided, however, that where a facility or emissions unit is subject to a standard established in this chapter, such standard shall also apply.
(4) Words and phrases used in this chapter, unless clearly indicated otherwise, are defined at Rule 62-210.200, F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:Controlling air emission pollutants can assist in controlling ocean acid acidification and the damaging effect of ocean water acidification on coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:To protect air quality, the chapter includes emission limitations for specific categories of facilities and emissions units, and it establishes reasonably available control technology requirements. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Atmospheric Emissions; Chemical Use Regulations; Climate Regulation; CO2; Corporate Responses; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Total maximum daily loads, 62-304 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | The Chapter establishes Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), and their allocations, for waters that have been verified to be impaired by a pollutant pursuant to Chapter 62-303. F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Envitonmental Protection Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Biomedical Research Policies; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Impervious Surfaces; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Water quality based effluent limitations, 62-650 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To implement the provisions of Section 403.051, 403.085 through 403.088 concerning the development of effluent limitations for wastewater facilities. Application to Coral Reefs:The Florida Air and Water Pollution Act establishes that no wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessay to protect the beneficial uses of such water. Requiring treatment of industrial and domestic waste water indirectly protects adjoining ecosystem, such as reefs, by limiting the pollutant that reach these other systems. Legislative Actions:The Department shall not issue a permit for a discharge to waters of the state, unless the Department has established an efflent limit for those pollutants in the discharge that are present in quantities or concentrations which can be reasonably expected to cause or contribute, directly or indirectly, to a violation of any water quality standard established in rule 62-302. The effluent limit may be a technology based effluent limit (TBEL), a water quality based effluent limit (WQBEL) determined by a Level 1 process, or where applicable, a WQBEL determined by a Level 2 process. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Domestic Animal Waste; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Wetland applications, 62-611 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To provide qualitative and quantitative design criteria discharge limits, permitting requirements, and monitoring requirements for wetlands, man-made and natural, receiving domestic wastewater. Application to Coral Reefs:Because wetlands act as buffers and remove nutrients from contaminated water, in many case the nutrients will not reach the estuarine and marine environments and potentially have an adverse effect on coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative in nature and specific pollutant limits and monitoring requirements are specified in individual permits Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Education & Outreach; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
