ReefLink Database

Landscape Changes
Landscape Changes are alterations of the natural landscape through human activities, including coastal development, shoreline armoring, impervious surfaces, deforestation, or soil disturbance, which can alter water flow patterns and lead to pollutant runoff into coastal systems.
CMap
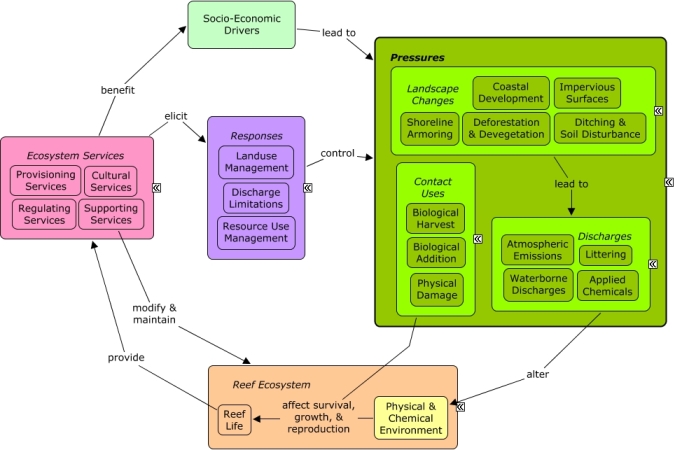
CMap Description
Landscape changes are driven by coastal development and the need for housing and infrastructure that depend on civil engineering and construction, as well as transportation projects. Economic growth in cultural sectors, such as tourism and recreation or fishing, may drive local population growth of residents or increase numbers of visitors. Landscape changes, including impervious surfaces, devegetation, shoreline armoring, dredging, or filling for construction of roads and buildings, can alter rates of pollutant runoff, directly impact coastal vegetation, and alter patterns of water flow. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that drive landscape changes also benefit from reef ecosystem services, including aesthetic value, seafood, and shoreline protection. Construction codes and regulations, transportation policies, agriculture policies, and landuse management through planning, permitting, and zoning can influence intensity and distribution of landscape changes. Dredging regulations can be used to limit impacts to coastal wetlands.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011. Coastal Capital Literature Review: Economic Valuation of Coastal and Marine Resources in Jamaica. World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Jamaica | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| 2011. Coastal Capital: Jamaica - The Economic Contribution of Jamaica�s Coral Reefs. World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Global; Jamaica | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Monetary Valuation; Ocean Acidity; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| 2011. Nonpoint Source Management Program 2010 Annual Report. Document # DEPLW-1205, Maine Department of Environmental Protection, Augusta, (Maine, USA). | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Housing; Impervious Surfaces; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Aburto-Oropeza, O; Erisman, B; Galland, GR; Mascarenas-Osorio, I; Sala, E; Ezcurra, E. 2011. Large Recovery of Fish Biomass in a No-Take Marine Reserve. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Mexico | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Baird, AH; Blakeway, DR; Hurley, TJ; Stoddart, JA. 2011. Seasonality of coral reproduction in the Dampier Archipelago, northern Western Australia. Marine Biology 158:275-285. | 2011 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Stony Coral |
| Burt, J; Bartholomew, A; Sale, PF. 2011. Benthic development on large-scale engineered reefs: A comparison of communities among breakwaters of different age and natural reefs. Ecological Engineering 37:191-198. | 2011 | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Bivalves; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Shoreline Protection; Sponges; Turf Algae | ||
| Figueiredo, J; Pereira, HM. 2011. Regime shifts in a socio-ecological model of farmland abandonment. Landscape Ecology 26:737-749. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Nutrients | |
| Kushner, B., P. Edwards, L. Burke, and E. Cooper. 2011. Coastal Capital: Jamaica - Coral Reefs, Beach Erosion and Impacts to Tourism in Jamaica. Working Paper, World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Jamaica | Model | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Monetary Valuation; Shoreline Protection; Social Organizations; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation |
| Mora, C; Aburto-Oropeza, O; Bocos, AA; Ayotte, PM; Banks, S; Bauman, AG; Beger, M; Bessudo, S; Booth, DJ; Brokovich, E; Brooks, A; Chabanet, P; Cinner, JE; Cortes, J; Cruz-Motta, JJ; Magana, AC; DeMartini, EE; Edgar, GJ; Feary, DA; Ferse, SCA; Friedlander. 2011. Global Human Footprint on the Linkage between Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning in Reef Fishes. PLoS Biology 9. | 2011 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fish |
| Nava, H; Ramirez-Herrera, MT. 2011. Government conservation policies on Mexican coastal areas: is "top-down" management working? Revista de Biologia Tropical 59:1487-1501. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Algae; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Non-Monetary Valuation; Recreational Opportunities; Sediment; Skeletal Coral |
| Navalgund, RR; Singh, RP. 2011. Climate Change Studies Using Space Based Observation. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing 39:281-295. | 2011 | Global; India | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Forestry; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Irrigation; Light; Salinity; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Oliver, L. M., J. C. Lehrter, and W. S. Fisher. 2011. Relating landscape development intensity to coral reef condition in the watersheds of St. Croix, US Virgin Islands. Marine Ecology Progress Series 427:293-302. | 2011 | US Virgin Islands | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Changes; Stony Coral |
| Oliver, LM; Lehrter, JC; Fisher, WS. 2011. Relating landscape development intensity to coral reef condition in the watersheds of St. Croix, US Virgin Islands. Marine Ecology Progress Series 427:293-302. | 2011 | US Virgin Islands | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Changes; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Riegl, BM; Purkis, SJ; Al-Cibahy, AS; Abdel-Moati, MA; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. 2011. Present Limits to Heat-Adaptability in Corals and Population-Level Responses to Climate Extremes. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model | Climate; Coastal Development; Ocean Acidity; Sea Temperatures; Stony Coral |
| Waite, R., E. Cooper, N. Zenny, and L. Burke. 2011. Coastal Capital: Jamaica - The Economic Value of Jamaica�s Coral Reef-Related Fisheries. Working Paper, World Resources Institute and The Nature Conservancy, Washington, D. C. (USA). | 2011 | Global; Jamaica | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Hotel & Food Services; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Ocean Acidity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Estes, J. A., M. T. Tinker, and J. L. Bodkin. 2010. Using Ecological Function to Develop Recovery Criteria for Depleted Species: Sea Otters and Kelp Forests in the Aleutian Archipelago. Conservation Biology 24:852-860. | 2010 | Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Sea Urchins | ||
| Fautin, D., P. Dalton, L. S. Incze, J. A. C. Leong, C. Pautzke, A. Rosenberg, P. Sandifer, G. Sedberry, J. W. Tunnell, I. Abbott, R. E. Brainard, M. Brodeur, L. G. Eldredge, M. Feldman, F. Moretzsohn, P. S. Vroom, M. Wainstein, and N. Wolff. 2010. An Overview of Marine Biodiversity in United States Waters. PLoS One 5:e11914. | 2010 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Banks, Credit, & Securities; CO2; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Foster, M. S. and D. R. Schiel. 2010. Loss of predators and the collapse of southern California kelp forests (?): Alternatives, explanations and generalizations. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 393:59-70. | 2010 | Review | Coastal Development; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Planktivorous Fish; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies | |
| Garcon, J. S., A. Grech, J. Moloney, and M. Hamann. 2010. Relative Exposure Index: an important factor in sea turtle nesting distribution. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:140-149. | 2010 | Australia | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Climate; Coastal Development; Sea Turtles |
| Harrison, P. A. 2010. Ecosystem services and biodiversity conservation: an introduction to the RUBICODE project. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2767-2772. | 2010 | Climate; Invasive Species; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Jones, K. B., E. T. Slonecker, M. S. Nash, A. C. Neale, T. G. Wade, and S. Hamann. 2010. Riparian habitat changes across the continental United States (1972-2003) and potential implications for sustaining ecosystem services. Landscape Ecology 1-15. | 2010 | Model; Remote Sensing | Agriculture; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Wetlands | |
| Lirman, D., A. Bowden-Kerby, S. Schopmeyer, B. Huntington, T. Thyberg, M. Gough, T. Gough, R. Gough, and Y. Gough. 2010. A window to the past: documenting the status of one of the last remaining 'megapopulations' of the threatened staghorn coral Acropora cervicornis in the Dominican Republic. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:773-781. | 2010 | South & Central America; Dominican Republic; Caribbean | Algae; Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Worms; Pathogens; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Murchie, K. J., E. Schwager, S. J. Cooke, A. J. Danylchuk, S. E. Danylchuk, T. L. Goldberg, C. D. Suski, and D. P. Philipp. 2010. Spatial ecology of juvenile lemon sharks (Negaprion brevirostris) in tidal creeks and coastal waters of Eleuthera, The Bahamas. Environmental Biology of Fishes 89:95-104. | 2010 | Bahamas | Field Study & Monitoring | Apex Fish Predators; Coastal Development; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Prouty, N. G., M. E. Field, J. D. Stock, S. D. Jupiter, and M. McCulloch. 2010. Coral Ba/Ca records of sediment input to the fringing reef of the southshore of Moloka'i, Hawai'i over the last several decades. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1822-1835. | 2010 | Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Sarkis, S., P. J. H. VanBeukering, and E. McKenzie, editors. 2010. TOTAL ECONOMIC VALUE OF BERMUDA�S CORAL REEFS: Valuation of Ecosystem Services. Department of Conservation Services, Bermuda. | 2010 | Bermuda | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Scharron, C. E. R. 2010. Sediment production from unpaved roads in a sub-tropical dry setting - Southwestern Puerto Rico. Catena 82:146-158. | 2010 | South & Central America; Puerto Rico; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Development; Mitigation; Sediment; Transportation Policies |
| Todd, P. A., X. Y. Ong, and L. M. Chou. 2010. Impacts of pollution on marine life in Southeast Asia. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:1063-1082. | 2010 | Global; Southeast Asia; Philippines | Review | Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Waterborne Discharges |
| van Beukering, P. J. H., S. Sarkis, E. McKenzie, S. Hess, L. Brander, M. Roelfsema, L. Looijenstijn-van der Putten, and T. Bervoets. 2010. Total Economic Value of Bermuda�s Coral Reefs Valuation of Ecosystem Services. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Bermuda; Caribbean | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Fish; Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Vandewalle, M., F. de Bello, M. P. Berg, T. Bolger, S. Doledec, F. Dubs, C. K. Feld, R. Harrington, P. A. Harrison, S. Lavorel, P. M. da Silva, M. Moretti, J. Niemela, P. Santos, T. Sattler, J. P. Sousa, M. T. Sykes, A. J. Vanbergen, and B. A. Woodcock. 2010. Functional traits as indicators of biodiversity response to land use changes across ecosystems and organisms. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2921-2947. | 2010 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Wielgus, J., E. Cooper, R. Torres, and L. Burke. 2010. Coastal capital: Dominican Republic. Case studies on the economic value of coastal ecosystems in the Dominican Republic. Washington, DC, World Resources Institute. | 2010 | Global; Dominican Republic | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Winfree, R. 2010. The conservation and restoration of wild bees. Pages 169-197 Year In Ecology And Conservation Biology 2010. | 2010 | Global | Agriculture; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Yang, R. Y., Y. C. Wu, H. H. Hwung, J. Y. Liou, and I. V. Shugan. 2010. Current countermeasure of beach erosion control and its application in Taiwan. Ocean and Coastal Management 53:552-561. | 2010 | Taiwan | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Infrastructure; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Yender, R. A. and J. Michel, editors. 2010. Oil Spills in Coral Reefs: Planning & Respoinse Considerations, Second Edition. U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Washington, D.C. | 2010 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Petroleum Spills | |
| Carilli, J. E., R. D. Norris, B. A. Black, S. M. Walsh, and M. McField. 2009. Local stressors reduce coral resilience to bleaching. PLoS One 4:e6324. | 2009 | Algae; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fleshy Macroalgae; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Sediment; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Chimetto, L. A., M. Brocchi, M. Gondo, C. C. Thompson, B. Gomez-Gil, and F. L. Thompson. 2009. Genomic diversity of vibrios associated with the Brazilian coral Mussismilia hispida and its sympatric zoanthids (Palythoa caribaeorum, Palythoa variabilis and Zoanthus solanderi). Journal of Applied Microbiology 106:1818-1826. | 2009 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Deforestation & Devegetation; Microorganisms | ||
| Cumberlidge, N., P. K. L. Ng, D. C. J. Yeo, C. Magalhaes, M. R. Campos, F. Alvarez, T. Naruse, S. R. Daniels, L. J. Esser, F. Y. K. Attipoe, F.-L. Clotilde-Ba, W. Darwall, A. McIvor, J. E. M. Baillie, B. Collen, and M. Ram. 2009. Freshwater crabs and the biodiversity crisis: Importance, threats, status, and conservation challenges. Biological Conservation 142:1665-1673. | 2009 | Global; Europe | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Stony Coral | |
| Cupido, R., S. Cocito, M. Barsanti, S. Sgorbini, A. Peirano, and G. Santangelo. 2009. Unexpected long-term population dynamics in a canopy-forming gorgonian coral following mass mortality. Marine Ecology Progress Series 394:195-200. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Octocoral; Sediment | |
| deGroot, R. S., R. Alkemade, L. Braat, L. Hein, and L. Willemen. 2009. Challenges in integrating the concept of ecosystem services and values in landscape planning, management and decision making. Ecological Complexity (inpress). | 2009 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Valuation | |
| Dung, L. D. 2009. Nha Trang Bay marine protected area, Vietnam: Initial trends in coral structure and some preliminary linkages between these trends and human activities (2002-2005). Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management 12:249-257. | 2009 | Vietnam | Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Hoeksema, B. W. and E. G. L. Koh. 2009. Depauperation Of The Mushroom Coral Fauna (Fungiidae) Of Singapore (1860S-2006) In Changing Reef Conditions. Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 91-101. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Deforestation & Devegetation; Stony Coral | |
| Hughes, A. O., J. M. Olley, J. C. Croke, and L. A. McKergow. 2009. Sediment source changes over the last 250 years in a dry-tropical catchment, central Queensland, Australia. Geomorphology 104:262-275. | 2009 | Australia; Europe | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Mitigation; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Lu, T., K. M. Ma, Y. X. Zhang, H. W. Ni, and B. J. Fu. 2009. Species Similarity - Distance Relationship In Wetlands: Effect Of Disturbance Intensity. Polish Journal Of Ecology 57:647-657. | 2009 | China | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Wetlands |
| Makarow, M., R. Ceulemans, and L. Horn. 2009. Science Policy Briefing: Impacts of Ocean Acidification. 37, European Science Foundation, France. | 2009 | Global; Europe | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Ocean Acidity |
| Nelson, W. A. 2009. Calcified macroalgae - critical to coastal ecosystems and vulnerable to change: a review. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:787-801. | 2009 | Global | Review | Agriculture; Algae; Aquaculture; CO2; Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Sediment |
| Obura, D. O. and G. Grimsditch. 2009. Resilience Assessment of Coral Reefs Rapid assessment protocol for coral reefs, focusing on coral bleaching and thermal stress. IUCN working group on Climate Change and Coral Reefs, IUCN, Gland, Switzerland. | 2009 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Algae; Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Sea Temperatures; Seagrasses; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Ramos, R., R. Cipriani, H. M. Guzman, and E. Garcia. 2009. Chronology of mercury enrichment factors in reef corals from western Venezuela. Marine Pollution Bulletin 58:222-229. | 2009 | Venezuela | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Non-point Source Runoff; Stony Coral; Toxics | |
| Sanchirico, J. N. and P. Mumby. 2009. Mapping ecosystem functions to the valuation of ecosystem services: Implications of species-habitat associations for coastal land-use decisions. Theoretical Ecology 2:67-77. | 2009 | Model; GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Valuation | |
| van der Meij, S. E. T., R. G. Moolenbeek, and B. W. Hoeksema. 2009. Decline of the Jakarta Bay molluscan fauna linked to human impact. Marine Pollution Bulletin 59:101-107. | 2009 | Java; Indonesia | Deforestation & Devegetation; Molluscs; Sediment; Substrate | |
| Waycott, M., C. M. Duarte, T. J. B. Carruthers, R. J. Orth, W. C. Dennison, S. Olyarnik, A. Calladine, J. W. Fourqurean, K. L. Heck, A. R. Hughes, G. A. Kendrick, W. J. Kenworthy, F. T. Short, and S. L. Williams. 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:12377-12381. | 2009 | Global | Climate; Coastal Development; Fish; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses | |
| Alongi, D. M. 2008. Mangrove forests: resilience, protection from tsunamis, and responses to global climate change. Estuarine and Coastal Marine Science 76:1-13. | 2008 | Global | Review; Model | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Mangroves; Nutrients; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Bouchon, C., P. Portillo, M. Louis, F. Mazeas, and Y. Bouchon-Navaro. 2008. Recent evolution of the coral reefs of Guadeloupe and Saint- Barthelemy Islands [evolution recente des recifs coralliens des îles de la Guadeloupe et de Saint-Barthelemy]. Revue d'Ecologie (La Terre et la Vie) 63:45-65. | 2008 | Antilles | Field Study & Monitoring | Chemical Use Regulations; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Fish; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Wastewater Discharge |
| Choate, A., J. Cohen, P. Groth, D. M. Theobald, B. Bierwagen, J. Thomas, and C. Pyke. 2008. Preliminary Steps towards Integrating Climate and Land Use: The Development of Land-Use Scenarios Consistent with Climate Change Emissions Storylines. Global Change Research Program, National Center for Environmental Assessment, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; EPA/600/R-08/076A, Washington DC. | 2008 | Global | Model; GIS & Maps | Climate; Housing; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Changes |
| Desalvo, M. K., C. R. Voolstra, S. Sunagawa, J. A. Schwarz, J. H. Stillman, M. A. Coffroth, A. M. Szmant, and M. Medina. 2008. Differential gene expression during thermal stress and bleaching in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata. Molecular Ecology 17:3952-3971. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Climate; Coastal Development; Stony Coral; Zooxanthellae | |
| Guest, J. R., P. A. Todd, E. Goh, B. Sivaloganathan, and K. P. Reddy. 2008. Can giant clam (Tridacna squamosa) populations be restored on Singapore's heavily impacted coral reefs? Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:570-579. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Light; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing | |
| Hughes, A. O., J. M. Olley, J. C. Croke, and L. A. Mckergow. 2008. Sediment sources in a dry-tropical catchment: central Queensland, Australia. IAHS-AISH Publication 351-358. | 2008 | Australia; Europe | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Mitigation; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jupiter, S. D. and G. S. Marion. 2008. Changes in forest area along stream networks in an agricultural catchment of the Great Barrier Reef lagoon. Environmental Management 42:66-79. | 2008 | Australia | GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Landscape Changes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Mora, C. 2008. A clear human footprint in the coral reefs of the Caribbean. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 275:767-773. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Agriculture; Algae; Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Mumby, P.J., A. Hastings. 2008. The impact of ecosystem connectivity on coral reef resilience. Journal of Applied Ecology 45:854-862. | 2008 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Mangroves; Small Herbivorous Fish; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Prouty, N. G., K. A. Hughen, and J. Carilli. 2008. Geochemical signature of land-based activities in Caribbean coral surface samples. Coral Reefs 27:727-742. | 2008 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Reitzel, A. M., J. C. Sullivan, N. Traylor-Knowles, and J. R. Finnerty. 2008. Genomic survey of candidate stress-response genes in the estuarine anemone Nematostella vectensis. Biological Bulletin 214:233-254. | 2008 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Anemones & Zooanthids; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Light; Nutrients; Pathogens; Salinity; Stony Coral | |
| Ryan, K. E., J. P. Walsh, D. R. Corbett, and A. Winter. 2008. A record of recent change in terrestrial sedimentation in a coral-reef environment, La Parguera, Puerto Rico: A response to coastal development? Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:1177-1183. | 2008 | Puerto Rico; Europe | Coastal Development; Sediment | |
| Smith, S. D. A., M. J. Rule, M. Harrison, and S. J. Dalton. 2008. Monitoring the sea change: Preliminary assessment of the conservation value of nearshore reefs, and existing impacts, in a high-growth, coastal region of subtropical eastern Australia. Marine Pollution Bulletin 56:525-534. | 2008 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Marine Debris; Molluscs |
| Cooper, J. A. G., D. A. Lewis, and O. H. Pilkey. 2007. Fetch-limited barrier islands: Overlooked coastal landforms. GSA Today 17:9-Apr. | 2007 | Global | Coastal Development; Mangroves; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Diaz, S., S. Lavorel, F. de Bello, F. Quetier, K. Grilgulis, and T. M. Robson. 2007. Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104:20684-20689. | 2007 | Global | Model | Landscape Changes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Fleitmann, D., R. B. Dunbar, M. McCulloch, M. Mudelsee, M. Vuille, T. R. McClanahan, J. E. Cole, and S. Eggins. 2007. East African soil erosion recorded in a 300 year old coral colony from Kenya. Geophysical Research Letters 34. | 2007 | Kenya | Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kleypas, J. A. and C. M. Eakin. 2007. Scientists' perceptions of threats to coral reefs: Results of a survey of coral reef researchers. Bulletin of Marine Science 80:419-436. | 2007 | Global; Japan | Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest | |
| McField, M. and P. Kramer. 2007. Healthy reefs for healthy people: A guide to indicators of reef health and social well-being in the Mesoamerican Reef region. 1-218. | 2007 | Global | Index or Indicator | Climate; Coastal Development; Tourism & Recreation |
| Mutchler, T., K. H. Dunton, A. Townsend-Small, S. Fredriksen, and M. K. Rasser. 2007. Isotopic and elemental indicators of nutrient sources and status of coastal habitats in the Caribbean Sea, Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 74:449-457. | 2007 | South & Central America; Caribbean; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Discharges; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge |
| Nuraini, S., E. C. Carballo, W. L. T. Van Densen, M. A. M. Machiels, H. J. Lindeboom, and L. A. J. Nagelkerke. 2007. Utilization of seagrass habitats by juvenile groupers and snappers in Banten Bay, Banten Province, Indonesia. Hydrobiologia 591:85-98. | 2007 | Indonesia | Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Piscivorous Fish; Seagrasses | |
| Petrat, L., L. Pettersson, P. Mumby, and P. Gaspar. 2007. Space for UNCBD and the due biodiversity project. European Space Agency, (Special Publication) ESA SP | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Landscape Changes; Mangroves |
| Ramos-Scharron, C. E. and L. H. MacDonald. 2007. Development and application of a GIS-based sediment budget model. Journal of Environmental Management 84:157-172. | 2007 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; Caribbean | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fish; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies |
| Rossi, S. and G. Tsounis. 2007. Temporal and spatial variation in protein, carbohydrate, and lipid levels in Corallium rubrum (Anthozoa, Octocorallia). Marine Biology 152:429-439. | 2007 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Deforestation & Devegetation; Octocoral | |
| Tupper, M. 2007. Identification of nursery habitats for commercially valuable humphead wrasse Cheilinus undulatus and large groupers (Pisces: Serranidae) in Palau. Marine Ecology Progress Series 332:189-199. | 2007 | Palau | Algae; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Wholesale & Retail Trade | |
| Chavez-Comparan, J. C. and R. Macias-Zamora. 2006. Structure of reef fish communities in the littoral of Colima, Mexico. Journal of Biological Sciences 6:65-75. | 2006 | South & Central America; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Waterborne Discharges |
| Fonseca E., A. C., H. K. Dean, and J. Cortes. 2006. Non-colonial coral macro-borers as indicators of coral reef status in the south Pacific of Costa Rica. Revista de Biologia Tropical 54:101-115. | 2006 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Costa Rica; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Bivalves; Deforestation & Devegetation; Marine Worms; Sediment |
| Frihy, O. E., A. N. Hassan, W. R. El Sayed, M. M. Iskander, and M. Y. Sherif. 2006. A review of methods for constructing coastal recreational facilities in Egypt (Red Sea). Ecological Engineering 27:12-Jan. | 2006 | Egypt | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Hotel & Food Services; Sediment; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hilbert, K. W. 2006. Land cover change within the Grand Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve: 1974-2001. Journal of Coastal Research 22:1552-1557. | 2006 | South & Central America; Mexico | Remote Sensing | Landscape Changes; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| McLeod, E. and R. V. Salm. 2006. Managing mangroves for resilience to climate change. The World Conservation Union, Gland, Switzerland. | 2006 | Climate; CO2; Coastal Development; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Nellemann, C. and E. Corcoran. 2006. Our precious coasts � Marine pollution, climate change and the resilience of coastal ecosystems. United Nations Environment Programme, GRID, Arendal, Norway. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Climate; CO2; Coastal Development; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Sediment; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Perkol-Finkel, S., G. Zilman, I. Sella, T. Miloh, and Y. Benayahu. 2006. Floating and fixed artificial habitats: Effects of substratum motion on benthic communities in a coral reef environment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 317:20-Sep. | 2006 | Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development | ||
| United Nations Environment Program - World Conservation Monitoring Center (UNEP-WCMC). 2006. In the front line: shoreline protection and other ecosystem services from mangroves and coral reefs. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge, UK. | 2006 | Global; South & Central America; Indian Ocean; India; Mexico | Climate; Coastal Development; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation | |
| Vanderstraete, T., R. Goossens, and T. K. Ghabour. 2006. The use of multi-temporal Landsat images for the change detection of the coastal zone near Hurghada, Egypt. International Journal of Remote Sensing 27:3645-3655. | 2006 | Egypt | Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Landscape Changes |
| Boulon, R., M. Chiappone, R. Halley, W. Jaap, B. Keller, B. Kruczynski, M. Miller, and C. Rogers. 2005. Atlantic Acropora Status Review. | 2005 | Global; South & Central America; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Jamaica; Belize; Caribbean; Mexico | Review | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Coastal Development; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Zooxanthellae |
| Cazes-Duvat, V. 2005. West Indies archipelagos coping with coastal erosion (Macarena, Seychelles and Maldives) [Les archipels de l'ouest de l'ocean Indien face à l'erosion cotiere (Mascareignes, Seychelles, Maldives)]. Annales de Geographie 114:342-361. | 2005 | Seychelles; Maldives | Hotel & Food Services; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Chabanet, P., M. Adjeroud, S. Andrefouet, Y.-M. Bozec, J. Ferraris, J.-A. Garcia-Charton, and M. Schrimm. 2005. Human-induced physical disturbances and their indicators on coral reef habitats: A multi-scale approach. Aquatic Living Resource 18:215-230. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation | |
| de Koning, J. and S. Thiesen. 2005. Aqua Solaris - An optimized small scale desalination system with 40 litres output per square meter based upon solar-thermal distillation. Desalination 182:503-509. | 2005 | Model | Deforestation & Devegetation; Energy Policy & Development; Pathogens | |
| Delgado, G. A., R. A. Glazer and D. Wetzel. 2005. The Effects of Water Quality on Embryogenesis and Larval Development of Queen Conch: Implications for Recruitment to and Coastal Development of the Florida Keys. South Florida Water Management District #OT050676. | 2005 | Florida | Coastal Development; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Snails & Conch | |
| Dimitrov, R. S. 2005. Precaution in global environmental politics. International Journal of Global Environmental Issues 5:96-113. | 2005 | Global | Deforestation & Devegetation | |
| Duvat, V. 2005. Coral reef coasts in small islands of the western Indian Ocean. Second part. Development and management [Les littoraux coralliens des petites îles de l'ouest de l'ocean Indien. Seconde partie. Amenagement et gestion]. Oceanis 31:195-341. | 2005 | Indian Ocean; India | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research |
| Friedlander, A., G. Aeby, E. Brown, A. Clark, S. Coles, S. Dollar, C. Hunter, P. Jokiel, J. Smith, B. Walsh, I. Williams, and W. Wiltse. 2005. The State of Coral Reef Ecosystems of the Main Hawaiian Islands. NOAA. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Coastal Development; Non-point Source Runoff | |
| Gayle, P. M. H., P. Wilson-Kelly, and S. Green. 2005. Transplantation of benthic species to mitigate impacts of coastal development in Jamaica. Revista de Biologia Tropical 53:105-115. | 2005 | Jamaica; Panama | Coastal Development; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Mitigation; Octocoral; Recreational Opportunities; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate | |
| Haynes, D., S. Carter, C. Gaus, J. Muller, and W. Dennison. 2005. Organochlorine and heavy metal concentrations in blubber and liver tissue collected from Queensland (Australia) dugong (Dugong dugon). Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:361-369. | 2005 | Australia | Coastal Development; Pathogens; Seagrasses; Toxics; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Kumaraguru, A. K., K. Jayakumar, J. J. Wilson, and C. M. Ramakritinan. 2005. Impact of the tsunami of 26 December 2004 on the coral reef environment of Gulf of Mannar and Palk Bay in the southeast coast of India. Current Science 89:1729-1741. | 2005 | India | Landscape Changes; Pathogens; Sediment | |
| Nott, J. and G. Hubbert. 2005. Comparisons between topographically surveyed debris lines and modelled inundation levels from severe tropical cyclones Vance and Chris, and their geomorphic impact on the sand coast. Australian Meteorological Magazine 54:187-196. | 2005 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Coastal Development; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Peterson, C. H. and M. J. Bishop. 2005. Assessing the environmental impacts of beach nourishment. Bioscience 55:887-896. | 2005 | Global | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Mitigation; Sea Turtles; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Petit, C. C. and J. J. Vandenabeele. 2005. Supporting coastal and lake applications with the help of remote sensing. Pages 2771-2774 in International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). | 2005 | Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Climate; Coastal Development; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Plankton; Sediment |
| Powell, B. and M. Martens. 2005. A review of acid sulfate soil impacts, actions and policies that impact on water quality in Great Barrier Reef catchments, including a case study on remediation at East Trinity. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:149-164. | 2005 | Australia | Review; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Cyanobacteria; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Fish; Microorganisms; Remediation; Wetlands |
| Schaffelke, B., J. Mellors, and N. C. Duke. 2005. Water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: Responses of mangrove, seagrass and macroalgal communities. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51:279-296. | 2005 | Australia | Algae; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Burke, L. and J. Maidens. 2004. Reefs at Risk in the Caribbean. World Resources Institute, Washington, D.C. | 2004 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Climate; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Pathogens; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation |
| Duval, M. A., D. N. Rader, K. C. Lindeman. 2004. Linking habitat protection and marine protected area programs to conserve coral reefs and associated back reef habitats. Bulletin of Marine Science 75:321-334. | 2004 | Field Study & Monitoring | Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting | |
| Eriksson, M. J. 2004. Formation and significance of a middle Silurian ravinement surface on Gotland, Sweden. Sedimentary Geology 170:163-175. | 2004 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment | ||
| Florida Department of Environmental Protection. 2004. Southeast Florida coral reef initiative: a local action strategy. | 2004 | Florida | Coastal Development; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest | |
| Goldberg, J. and C. Wilkinson. 2004. Status of Coral Reefs of the World: 2004. | 2004 | Global | Agriculture; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Seastars; Sediment | |
| Klosowska, B. B., S. R. Troelstra, J. E. Van Hinte, D. Beets, K. Van Der Borg, and A. F. M. De Jong. 2004. Late holocene environmental reconstruction of St. Michiel saline lagoon, Curacao (Dutch Antilles). Radiocarbon 46:765-774. | 2004 | Antilles; Europe | Agriculture; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; Deforestation & Devegetation; Non-point Source Runoff; Salinity; Sediment; Skeletal Coral | |
| Marschal, C., J. Garrabou, J. G. Harmelin, and M. Pichon. 2004. A new method for measuring growth and age in the precious red coral Corallium rubrum (L.). Coral Reefs 23:423-432. | 2004 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Octocoral | ||
| Mumby, P. J., A. J. Edwards, J. E. Arias-Gonzalez, K. C. Lindeman, P. G. Blackwell, A. Gall, M. I. Gorczynska, A. R. Harborne, C. L. Pescod., H. Renken, C. C. C. Wabnitz, and G. Llewenyn. 2004. Mangroves enhance the biomass of coral reef fish communities in the Caribbean. Nature 427:533-536. | 2004 | Global; South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Munday, P. L. 2004. Habitat loss, resource specialization, and extinction on coral reefs. Global Change Biology 10:1642-1647. | 2004 | Global; Papua New Guinea | Coastal Development; Nutrients; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Orpin, A. R., P. V. Ridd, S. Thomas, K. R. N. Anthony, P. Marshall, and J. Oliver. 2004. Natural turbidity variability and weather forecasts in risk management of anthropogenic sediment discharge near sensitive environments. Marine Pollution Bulletin 49:602-612. | 2004 | Australia | Coastal Development; Discharges; Sediment | |
| Pais, A., E. Azzurro, and L. A. Chessa. 2004. Distribution patterns of coastal fish assemblages associated with different rocky substrates in Asinara Island National Park (Sardinia, Italy). Italian Journal of Zoology 71:309-316. | 2004 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Substrate | ||
| Rodriguez, W. and I. C. Feller. 2004. Mangrove landscape characterization and change in Twin Cays, Belize using aerial photography and IKONOS satellite data. Atoll Research Bulletin 22-Jan. | 2004 | South & Central America; Belize; Caribbean | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Nutrients |
| Rolett, B. and J. Diamond. 2004. Environmental predictors of pre-European deforestation on Pacific islands. Nature 431:443-446. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Japan; Europe | Deforestation & Devegetation | |
| Sealey, K. S. 2004. Large-scale ecological impacts of development on tropical islands systems: Comparison of developed and undeveloped islands in the central Bahamas. Bulletin of Marine Science 75:295-320. | 2004 | Bahamas | Algae; Coastal Development; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Harris, L. E. 2003. Submerged reef structures for beach erosion control. Pages 1155-1163 in Coastal Structures 2003 - Proceedings of the Conference. | 2003 | Artificial Habitat; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection | ||
| Kramer, P. A. 2003. Synthesis of coral reef health indicators for the western Atlantic: Results of the AGRRA program (1997-2000). Atoll Research Bulletin Jan-57. | 2003 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Caribbean | Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Corallivorous Fish; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Pathogens; Piscivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral |
| Steiner, S. C. C. 2003. Stony corals and reefs of Dominica, lesser antilles. Atoll Research Bulletin 15-Jan. | 2003 | Antilles | Algae; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Hydrocoral; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Berkelmans, R., J. C. Hendee, P. A. Marshall, P. V. Ridd, A. R. Orpin, and D. Irvine. 2002. Automatic weather stations: Tools for managing and monitoring potential impacts to coral reefs. Marine Technology Society Journal 36:29-38. | 2002 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research | |
| Burke, L, L. Selig, and M. Spalding. 2002. Reefs at risk in southeast Asia. World Resources Institute, Washington, D.C. | 2002 | Southeast Asia | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Cesar, H., P. van Beukering, S. Pintz, and J. Dierking. 2002. Economic valuation of the coral reefs of Hawaii. Hawaii Coral Reefs Initiative, University of Hawaii, Hawaii, US. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Molluscs; Monetary Valuation; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Francis, J., A. Nilsson, and D. Waruinge. 2002. Marine protected areas in the Eastern African Region: How successful are they? Ambio 31:503-511. | 2002 | Kenya; Tanzania; Mozambique; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius | Review; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Corporate Responses; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Gagan, M. K., L. K. Ayliffe, B. N. Opdyke, D. Hopley, H. Scott-Gagan, and J. Cowley. 2002. Coral oxygen isotope evidence for recent groundwater fluxes to the Australian Great Barrier Reef. Geophysical Research Letters 29:43-1. | 2002 | Australia | Agriculture; Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Jackson, C. Rhett; Kolka, Randy. 2002. Forestry Best Management Practices And Their Effectiveness. in Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation. | 2002 | Chemical Use Regulations; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Scavia, D., J. C. Field, D. F. Boesch, R. W. Buddemeier, V. Burkett, D. R. Cayan, M. Fogarty, M. A. Harwell, R. W. Howarth, C. Mason, D. J. Reed, T. C. Royer, A. H. Sallenger, and J. G. Titus. 2002. Climate change impacts on U.S. coastal and marine ecosystems. Estuaries 25:149-164. | 2002 | Global | Review | Climate; CO2; Coastal Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Turgeon, D. D., R. G. Asch, B. D. Causey, R. E. Dodge, W. Jaap, K. Banks, J. Delaney, B. D. Keller, R. Speiler, C. A. Matos, J. R. Garcia, E. Diaz, D. Catanzaro, C. S. Rogers, Z. Hillis-Starr, R. Nemeth, M. Taylor, G. P. Schmahl, M. W. Miller, D. A. Gulko, J. E. Maragos, A. M. Friedlander, C. L. Hunter, R. S. Brainard, P. Craig, R. H. Richond, G. Davis, J. Starmer, M. Trianni, P. Houk, C. E. Birkeland, A. Edward, Y. Golbuu, J. Gutierrez, N. Idechong, G. Paulay, A. Tafileichig, and N. V. Velde. 2002. The state of coral reef ecosystems of the United States and Pacific Freely Associated States: 2002. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Ocean Service/National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD. | 2002 | Global; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Samoa; Guam | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Board, M.S. 2001. Vortechnics Treatment of Parking Lot Runoff, Thesis. | 2001 | Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff | ||
| Harborne, A. R., D. C. Afzal, and M. J. Andrews. 2001. Honduras: Caribbean Coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1221-1235. | 2001 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Johnson, M. E. and J. Ledesma-Vazquez. 2001. Pliocene-pleistocene rocky shorelines trace coastal development of Bahia Concepcion, gulf coast of Baja California Sur (Mexico). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 166:65-88. | 2001 | South & Central America; Mexico | Coastal Development; Echinoderms; Molluscs; Shoreline Protection; Stony Coral; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Lucey, P., T. J. Williams, J. L. Hinrichs, M. Winter, D. Steutel, and E. Winter. 2001. Three years of operation of AHI: The University of Hawaii's airborne hyperspectral imager. Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering 4369:112-120. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study | Ditching & Soil Disturbance |
| Muller-Parker, G. and J. Cortes. 2001. Spatial distribution of light and nutrients in some coral reefs of Costa Rica during January 1997. Revista de Biologia Tropical 49:251-263. | 2001 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Costa Rica; Pacific Ocean; Caribbean | Coastal Development; Nutrients; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Obura, D. O. 2001. Kenya. Marine Pollution Bulletin 42:1264-1278. | 2001 | Indian Ocean; Somalia; Kenya; India | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fish; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Salinity; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Agard, J. B. R. and J. F. Gobin. 2000. The Lesser Antilles, Trinidad and Tobago. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 627-641. | 2000 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Antilles; British Virgin Islands; St. Lucia; Trinidad; Tobago; Martinique; Venezuela; Guyana; Caribbean | Apex Fish Predators; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Deforestation & Devegetation; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Land & Air Transportation; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Chesney, E. J., D. M. Baltz, and R. G. Thomas. 2000. Louisiana estuarine and coastal fisheries and habitats: Perspectives from a fish's eye view. Ecological Applications 10:350-366. | 2000 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands |
| Comings, K.J., Booth, D.B., and R.R. Horner. 2000. Storm Water Pollutant Removal by Two Wet Ponds in Bellevue, Washington, April. Journal of Environmental Engineering | 2000 | Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Cotsapas, L., S. A. Zengel, and E. J. Barraza. 2000. El Salvador. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 545-558. | 2000 | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Petroleum Spills; Sediment; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Debrot, A. O. and J. Sybesma. 2000. The Dutch Antilles. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 595-614. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | GIS & Maps | Coastal Development; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Health Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Edinger, E. and D. R. Browne. 2000. Continental seas of western Indonesia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 381-404. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; China; Java; Indonesia | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Housing; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Harborne, A. R., M. D. McField, and E. K. Delaney. 2000. Belize. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 501-516. | 2000 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Light; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation |
| Johnson, A. K. L. and S. P. Ebert. 2000. Quantifying inputs of pesticides to the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park - A case study in the Herbert River catchment of North-East Queensland. Marine Pollution Bulletin 41:302-309. | 2000 | Australia | Agriculture; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Kumaraguru, A. K. 2000. Coral reefs in the Gulf of Mannar and the conservation strategies required. Ecology, Environment and Conservation 6:12-Jan. | 2000 | India | Coastal Development; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Leao, Z. M. A. N. and J. M. L. Dominguez. 2000. Tropical coast of Brazil. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 719-729. | 2000 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Infrastructure; Sediment |
| LeDrew Ellsworth, F., MI KE Wulder, and HE AT HE R Holden. 2000. Change detection of satellite imagery for reconnaissance of stressed tropical corals. Pages 2678-2680 in International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS). | 2000 | Fiji | Remote Sensing; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining Policies; Shoreline Armoring; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Souter, D. W. and O. Linden. 2000. The health and future of coral reef systems. Ocean and Coastal Management 43:657-688. | 2000 | Review | Biotechnology Research & Development; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Sea Temperatures; Seastars; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Vazquez, F., R. Rangel, A. M. Quintero-Marmol, J. Fernandez, E. Aguayo, A. Palacio, and V. K. Sharma. 2000. Southern Gulf of Mexico. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 467-482. | 2000 | South & Central America; Mexico | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Connell, S. D. and T. M. Glasby. 1999. Do urban structures influence local abundance and diversity of subtidal epibiota? A case study from Sydney Harbour, Australia. Marine Environmental Research 47:373-387. | 1999 | Australia | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Coralline Algae; Docks & Marinas; Shoreline Armoring | |
| Corsi, S.R., Breb, S.R., R.T. Bannerman and R.e. Pitt. 1999. Evaluation of the Multi-chambered Treatment Train, a Retrofit Water Quality Management Practice, USGS Open File Report 99-270, Middleton, WI. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Glasby, T. M. and S. D. Connell. 1999. Urban structures as marine habitats. Ambio 28:595-598. | 1999 | Docks & Marinas; Shoreline Armoring | ||
| Kunzmann, A. 1999. Korallen, Fischer und Touristen. Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 51:25-32. | 1999 | Global; Philippines | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Wright, J. and D. Morton. 1999. Promoting erosion control in the Virgin Islands. Pages 8-May in Investing in the protection of our environment. Proceedings of conference 30, Nashville, 1999. (International Erosion Control Association). | 1999 | US Virgin Islands | Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Housing; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Cortes, J., A. C. Fonseca, M. Barrantes, and P. Denyer. 1998. Type, distribution, and origin of sediments of the Gandoca-Manzanillo National Wildlife Refuge, Limon, Costa Rica. Revista de Biologia Tropical 46:251-256. | 1998 | South & Central America; Costa Rica; Caribbean | Beaches & Nature Parks; Deforestation & Devegetation; Molluscs; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Fondo, E. N. and E. E. Martens. 1998. Effects of mangrove deforestation on macrofaunal densities, Gazi Bay, Kenya. Mangroves and Salt Marshes 2:75-83. | 1998 | Kenya | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Franklin, H. 1998. Coral culturing and temporal recruitment patterns in Zanzibar, Tanzania. Ambio 27:651-655. | 1998 | Tanzania | Coastal Development | |
| Fuchs, A. and U. Radtke. 1998. Ecological problems on the carribean island of Barbados [Okologische probleme auf der karibischen insel Barbados]. Geographische Rundschau 50:706-713. | 1998 | Cuba | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water | |
| Gibson, J., M. McField, and S. Wells. 1998. Coral reef management in Belize: An approach through integrated coastal zone management. Ocean and Coastal Management 39:229-244. | 1998 | South & Central America; Belize | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Permitting & Zoning; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Pitt, R.; Robertson, B.; and Field, R. 1998. Innovative Multi-Chambered Stormwater Control Device for Critical Source Areas. Proc. Adv. in Urban Wet Weather Pollut. Reduction , Cleveland, Ohio, WEF (CP3805), 141. | 1998 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Discharges; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation Policies | |
| Poole, A. and A. Robertson. 1998. Pleistocene fanglomerate deposition related to uplift of the Troodos ophiolite, Cyprus. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program: Scientific Results 160:545-568. | 1998 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Worheide, G. 1998. The reef cave dwelling ultraconservative coralline demosponge Astrosclera willeyana Lister 1900 from the Indo-Pacific. Facies 38:Jan-88. | 1998 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Calcium Carbonate Deposition; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Microorganisms; Special Use Permitting; Sponges; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Barry, G. A. and G. E. Rayment. 1997. Heavy metals and nutrients in soils and sediments of Raine Island, Great Barrier Reef. Pages 281-285 in Land Contamination and Reclamation. | 1997 | Australia; Papua New Guinea | Agriculture; Landscape Changes; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Foster, G. and L. Carter. 1997. Mud sedimentation on the continental shelf at an accretionary margin - Poverty Bay, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics 40:157-173. | 1997 | Europe | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Komatsu, T. 1997. Long-term changes in the Zostera bed area in the Seto Inland Sea (Japan), especially along the coast of the Okayama Prefecture. Oceanologica Acta 20:209-216. | 1997 | Japan | Review | Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development; Nutrients |
| Kricher, J. 1997. A Neotropical companion: an introduction to the animals, plants and ecosystems of the New World tropics. Second edition. A Neotropical companion: an introduction to the animals, plants and ecosystems of the New World tropics. Second edition. | 1997 | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Pitt, R., Robertson, B. Barron, P., Ayyoubi, A. and S. Clark . 1997. Stormwater Treatment At Critical Areas Vol. 1: The Multi-Chambered Treatment Train (MCTT), USEPA Cooperative Agreement No. CR 819573 . | 1997 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Verstappen, H. TH . 1997. The effect of climatic change on southeast Asian geomorphology. Journal of Quaternary Science 12:413-418. | 1997 | Southeast Asia | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Coastal Development; Sediment |
| World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. | 1997 | Global; Tanzania; Maldives; Fiji; Papua New Guinea; Southeast Asia; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Germany | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Health Policies; Live Collection; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Cecich, V., L. Gonzales, A. Hoisaeter, J. Williams, and K. Reddy. 1996. Use of shredded tires as lightweight backfill material for retaining structures. Waste Management and Research 14:433-451. | 1996 | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Civil Engineering & Construction; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies | |
| Dubinsky, Z. and N. Stambler. 1996. Marine pollution and coral reefs. Global Change Biology 2:511-526. | 1996 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Nutrients; Plankton; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Harris Lee, E., J. Mostkoff Benjamin, and GE RA LD Zadikoff. 1996. Artificial reefs: from waste to resources. Pages 754-759 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1996 | Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Housing; Shoreline Armoring; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Sammarco, P. W. 1996. Comments on coral reef regeneration, bioerosion, biogeography, and chemical ecology: Future directions. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 200:135-168. | 1996 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Review | Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Nutrients; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Sediment |
| Shulman, M. J. and D. R. Robertson. 1996. Changes in the coral reefs of San Bias, Caribbean Panama: 1983 to 1990. Coral Reefs 15:231-236. | 1996 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sea Urchins; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Boon John, D., JE FF RE Y Claassen, and F. Pieters Renaldo. 1995. Environmentally responsive artificial beach design, Curacao, Netherlands antilles. Pages 17-18 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Antilles | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Hotel & Food Services; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Brown, K., R. K. Turner, H. Hameed, and I. Bateman. 1995. Tourism and sustainability in environmentally fragile areas: case studies from the Maldives and Nepal. Working Paper - Centre for Social & Economic Research on the Global Environment. | 1995 | Global; Maldives | Deforestation & Devegetation; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Chen, K. M. 1995. Disappearance of ALS from Guam: Implications for exogenous causes. Pages 1549-1553 in Clinical Neurology. | 1995 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Cuba; Guam | Deforestation & Devegetation; Drinking Water Supply; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Housing; Military; Pathogens; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water | |
| Korotky, A. M., N. G. Razjigaeva, L. A. Ganzey, V. G. Volkov, T. A. Grebennikova, V. B. Bazarova, and N. N. Kovalukh. 1995. Late Pleistocene-Holocene coastal development of islands off Vietnam. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences 11:301-308. | 1995 | Vietnam | Coastal Development; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Pollnac Richard, B. and W. McManus John. 1995. Human factors in a coral reef database. Pages 100-101 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1995 | Global | Index or Indicator | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Cultural Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Natural Gas & Electric Power |
| Basiago, A. D. 1994. Sustainable development in tropical forest ecosystems. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 1:34-40. | 1994 | South & Central America; Thailand; Papua New Guinea; Mexico | Model | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Forestry |
| Cocks, K. D. and B. H. Walker. 1994. Contribution of \sustainability' criteria to social perceptions of land use options". Land Degradation & Rehabilitation 5:143-151. | 1994 | Australia | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning | |
| Gomez, E. D., P. M. Alino, H. T. Yap, and W. Y. Licuanan. 1994. A review of the status of Philippine reefs. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:62-68. | 1994 | Review; Index or Indicator | Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Sediment | |
| Huber, M. E. 1994. An assessment of the status of the coral reefs of Papua New Guinea. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:69-73. | 1994 | Global; Papua New Guinea | Agriculture; Commercial Fisheries; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Forestry; Mangroves; Nutrients; Sediment | |
| Leao, Z. M. A. N., M. D. Telles, R. Sforza, H. A. Bulhoes, and R. K. P. Kikuchi. 1994. Impact of tourism development on the coral reefs of the Abrolhos area, Brazil. Pages 254-260 in Proceedings of the colloquium on global aspects of coral reefs, Miami, 1993. | 1994 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Pitt, R. and R. Creel. 1994. Evaluating Detention Pond Performance with Computer Modeling Verification. | 1994 | Model | Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Runoff; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Abeykoon, A. T. 1993. Population, environment and sustainable development. Sri Lanka journal of social sciences 16:57-64. | 1993 | Sri Lanka | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Mining Policies | |
| Budd, A. F., K. O. Mann, and H. M. Guzman. 1993. Environmental interpretation using insoluble residues within reef coral skeletons: problems, pitfalls, and preliminary results. Coral Reefs 12:31-42. | 1993 | South & Central America; Panama; Caribbean | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Chavez, ER NE ST O and JO HN Tunnell. 1993. Needs for management and conservation of the southern Gulf of Mexico. Pages 2040-2053 in Coastal Zone: Proceedings of the Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management. | 1993 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Petroleum Spills; Piscivorous Fish; Sea Turtles; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation |
| Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. | 1993 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Docks & Marinas; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Jones, G. W. 1993. Population, environment and sustainable development in Indonesia. Majalah Demografi Indonesia 20:20-Jan. | 1993 | Java; Indonesia | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fishing Sector; Land & Air Transportation | |
| Maul, G. A. 1993. Implications of future climate on the ecosystems and socio-economic structure in the marine and coastal regions of the intra-Americas sea. Pages 28-Mar Climatic change in the intra-Americas sea. | 1993 | Global; South & Central America; Bahamas; Bermuda; Caribbean; Mexico | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks; Climate; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands |
| Davis Jr, R. A., A. C. Hine, and E. A. Shinn. 1992. Holocene coastal development on the Florida peninsula. Pages 193-212 Quaternary coasts of the United States. | 1992 | Florida | Coastal Development; Mangroves; Sediment | |
| Dawson Shepherd, A. R., R. M. Warwick, K. R. Clarke, and B. E. Brown. 1992. An analysis of fish community responses to coral mining in the Maldives. Environmental Biology of Fishes 33:367-380. | 1992 | Maldives | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish | |
| Fautin, D. G., D. J. Futuyma, and F. C. James. 1992. Annual review of ecology and systematics. Volume 23. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics | 1992 | Global | Review; Model | Landscape Changes |
| Guzman, H. M. and C. E. Jimenez. 1992. Contamination of coral reefs by heavy metals along the Caribbean coast of Central America (Costa Rica and Panama). Marine Pollution Bulletin 24:554-561. | 1992 | South & Central America; Costa Rica; Panama; Caribbean | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Petroleum Spills; Sediment; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Imbach, A. 1992. 500 years after Columbus. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 1:18. | 1992 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Nicaragua; Costa Rica; Panama | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Stafford-Smith, M.G. 1992. Mortality of the hard coral Leptoria phrygia under persistent sediment influx. Pages 289-99 in Proceedings of the 7th International Coral Reef Symposium. | 1992 | Coastal Development; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Sediment; Stony Coral | ||
| Weerakkody, U. 1992. The Holocene coasts of Sri Lanka. Geographical Journal 158:300-306. | 1992 | Sri Lanka | Coastal Development; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Sandner, G. and B. Ratter. 1991. Topographical problem areas in the delimitation of maritime boundaries and their political relevance: Case studies from the Western Caribbean. Ocean and Shoreline Management 15:289-308. | 1991 | South & Central America; Honduras; Nicaragua; Costa Rica; Caribbean | Coastal Development; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Sullivan, P. K. and V. Dayananda. 1991. Engineering management considerations in coastal development. Page 1430 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1991 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Beaches & Nature Parks; Chemical Use Regulations; Coastal Development; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrients | |
| Watanabe, J. M. and C. Harrold. 1991. Destructive grazing by sea urchins Strongylocentrotus spp. in a central California kelp forest: potential roles of recruitment, depth, and predation. Marine Ecology Progress Series 71:125-141. | 1991 | Algae; Deforestation & Devegetation; Invertebrates; Pathogens; Sea Urchins | ||
| Uda, TA KA AK I. 1990. Damages caused by storm surges in Maldives. NIST Special Publication 796:431-433. | 1990 | Indian Ocean; Maldives; India | Coastal Development; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Soekarno, R. 1989. Comparative studies on the status of Indonesian coral reefs. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 23:215-222. | 1989 | Indonesia | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Fish |
| Van Vliet Lanoe, B. 1989. Coast lines. Reports in honour of Andre Guilcher. Second meeting of the Groupe Francais de Geomorphologie, Caen, November 1988 [Les littoraux. Journees en l'honneur d'Andre Guilcher. Second forum du Groupe Francais de Geomorphologie, Caen, Novembre 1988]. Bulletin - Centre de Geomorphologie du CNRS, Caen 36. | 1989 | France | Coastal Development; Sediment | |
| Allen, K. C. and D. L. Dineley. 1988. Mid-Devonian to mid-Permian floral and faunal regions and provinces. Pages 531-548 Caledonian-Appalachian orogen. | 1988 | Europe | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment | |
| Foster, M. S. and D. R. Schiel. 1988. Kelp communities and sea otters: keystone species or just another brick in the wall? Pages 92-115 The community ecology of sea otters. | 1988 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sea Urchins | |
| McManus, J. W. 1988. Coral reefs of the ASEAN Region: status and management. Ambio 17:189-193. | 1988 | Southeast Asia | Field Study & Monitoring | City Planning; Deforestation & Devegetation; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Sediment; Special Use Permitting |
| Myers, N. 1988. Environmental degradation and some economic consequences in the Philippines. Environmental Conservation 15:205-214. | 1988 | Global; Philippines | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fishing Sector | |
| Cambers, G. 1987. A programme for beach erosion control in Barbados, West Indies. Pages ChiOceanPress-1987 in IN: 1987 PROC. COASTAL & PORT ENGINEERING IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES, SECOND INT. CONF., (BEIJING, CHINA: SEP. 7-11, 1987). | 1987 | South & Central America; China; Caribbean | Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Cortes N., J. and M. J. Risk. 1985. A reef under siltation stress: Cahuita, Costa Rica. Bulletin of Marine Science 36:339-356. | 1985 | Costa Rica | Deforestation & Devegetation; Sediment; Stony Coral | |
| Ebeling, A. W. and D. R. Laur. 1985. The influence of plant cover on surfperch abundance at an offshore temperate reef. Environmental Biology of Fishes 12:169-179. | 1985 | Deforestation & Devegetation; Fish; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Fulford, E. T. 1985. Reef type breakwaters for shoreline stabilization. Pages Am.Soc.Civ.Engrs.-1985 in IN: COASTAL ZONE'85, PROC. FOURTH SYMP. ON COASTAL & OCEAN MANAGEMENT, (BALTIMORE, U.S.A.: JUL. 30-AUG. 2, 1985), O.T. MAGOON. | 1985 | Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection | ||
| Lal, P. N. 1984. Environmental implications of coastal development in Fiji. Ambio 13:316-321. | 1984 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Fiji | Agriculture; Coastal Development; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bakus, G. J. 1983. The selection and management of coral reef preserves. Ocean Management 8:305-316. | 1983 | Field Study & Monitoring | Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bannerman, R.; Baun, K.; Bohn, M.; Hughes, P.; Graczyk, D. 1983. Nationwide Urban Runoff Program, Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Evaluation of Urban Nonpoint Source Pollution Management in Milwaukee County, Wisconsin. Volume 2. Feasibility and Application of Urban Nonpoint Source Pollution. | 1983 | Field Study & Monitoring | Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges | |
| Finn, D. 1983. Land use and abuse in the East African region. Ambio 12:296-301. | 1983 | Agriculture; Beaches & Nature Parks; Deforestation & Devegetation; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Goforth, GF; Diniz, EV; Rauhut, JB. 1983. Stormwater hydrological characteristics of porous and conventional paving systems., NTIS, SPRINGFIELD, VA (USA), 1983., 302 pp. | 1983 | Review | Impervious Surfaces; Littering; Non-point Source Runoff; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Finn, D. P. 1982. Soil loss in developing countries and its relationship to marine resources: examples from East Africa. in [No source information available]. | 1982 | Agriculture; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Gourlay, M. R. and P. G. Flood. 1981. Impact of coastal engineering works upon a coral cay: Heron Island. Pages 159-163 in IN: CONF. ON ENVIRONMENTAL ENGNG. 1981, PREPRINTS, (TOWNSVILLE, AUSTRALIA: JUL. 8-10, 1981), BARTON, AUSTRALIA, INST. ENGRS. | 1981 | Australia | Review | Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering |
| Spadoni, RI CH AR D and TH OM AS Campbell. 1980. Coral Reef Protection During Beach Restoration In Florida. Pages 152-159 in Proceedings of SOUTHEASTCON Region 3 Conference. | 1980 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Beaches & Nature Parks; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection |
| Fairbridge, R. W. 1976. Effects of Holocene climatic change on some tropical geomorphic processes. Quaternary Research 6:529-556. | 1976 | Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Carlton, J. M. 1974. Land-building and stabilization by mangroves. Environmental Conservation 1:285-294. | 1974 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Housing; Mangroves; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Substrate |
| SHIER, DE. 1969. Vermetid Reefs And Coastal Development In The Ten Thousand Islands, Southwest Florida. Geol Soc Amer Bull 80:485-507. | 1969 | Florida | Coastal Development; Sediment; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Anon,. Colloque International Sur L'Exploitation Des Oceans, 2Nd, 1974, Volume 1: Politiques De Developpement Oceanique, Volume 2: Mise En Valeur Industrielle Des Plateaux Continentaux, Volume 3: Systemes Des Mesures Pour L'Analyse Et La Prevision De L'Environne. in [No source information available]. | Index or Indicator; Remote Sensing | Artificial Habitat; Coastal Development; Fishing Sector; Microorganisms; Pipelines; Salinity; Shoreline Protection; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Tissier, M. L., editor. The DPSIR Framework Technical assistance to SMAP III ICZM Projects: A tool for integrated modelling and analysis in coastal zones. | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Landscape Changes | ||
| van der Meij, S. E. T., R. G. Moolenbeek, and B. W. Hoeksema. Decline of the Jakarta Bay molluscan fauna linked to human impact. Marine Pollution Bulletin | Java; Indonesia | Deforestation & Devegetation; Molluscs; Sediment; Substrate |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Hydroseeding High Risk Soils | Hydroseeding is a process that creates a slurry of seeds, water, and mulch. This slurry can be applied with the use of trucks, trailers, and even aircrafts. This method is particularly useful because it promotes quick germination and reduces erosion. It is especially beneficial to use this method where there is a vastness of bare soil due to clearing vegetation for roads, homes, and farming. Higher elevations are typically steeper and often experience heavy rainfall, and ultimately an extreme amount of erosion occurs if soil is bare. Erosion from the highlands can fill the reservoirs in the drainage basin with sediment. Using hydroseeding would increase vegetation and ultimately the stabilization of the soil. Also, increased vegetation through hydroseeding would help with infiltration rates because the roots would aerate the soil. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 1999. Temporary Seeding. NRCS Planning and Design Manual. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Reef Life; Sediment |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Change Agricultural Cover Crop Practices | Cover crop outreach entails changing agricultural practices in an area to leave vegetation and cover on the soil while growing other crops (e.g. Coffee). Agricultural practices that encourage leaving soil bare are extremely susceptible to erosion (e.g. sun grown Coffee). Cover crop methods and shade-grown crops (e.g. shade-grown Coffee) would reduce the large amount of sediment that is eroding, particularly from high elevations, and ultimately will reduce the amount of sediment that reaches the coral reefs. Options to encourage transition to cover crop practices include outreach to raise awareness of benefits and cost share programs to help farmers with the burden of the extra expense. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Conservation Cover. CODE 327. US Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Responses; Sediment |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Contour Farming | Contour Farming involves sloping land in such a way that field preparation, planting and cultivating are done on the contour. This includes following established grades of terraces or diversions. During heavy rains the crop rows formed slow water runoff reducing erosion and water runoff of non-point source pollutants such as agricultural herbicides and fertilizers. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Fertilizer Application Management | This agricultural best management practice involves the development, implementation and periodic update of nutrient management plans. Nutrient management plans are used to efficiently apply nutrients at appropriate rates so as to still achieve desired crop yields. There are several important measures and considerations that must be taken before developing the nutrient plan. Farm and field maps, yield expectations, nutrient resources, and geologic field limitations are all important. Some crops fix nitrogen, such as legumes, and have a nitrogen credit that must be factored. Field limitations include shallow aquifers, nearby surface water, sinkholes, and highly erodible soils. If the nutrients to be applied aren�t commercial they must be assessed to determine the nutrient value and the rate of availability of the nutrients. The nutrient plan�s timing and application methods should use the limiting nutrient concept and avoid applications to frozen soil and during periods of leaching or runoff. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Jokela, Bill, Peter Kleinman, John Peters, and Ann Wolf,. 2011. Manure Spreader Calibration & Manure Testing. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Grazing Land Management | This management option protects range, pasture and other types of grazing lands for agricultural animals. Special actions should be taken to protect sensitive areas such as streams, wetlands and estuaries if livestock is to have access to these areas. Grazing management practices can be categorized into four types, vegetative stabilization, grazing management systems, access limitations and alternative water supplies. Vegetative stabilization involves reestablishing the vegetative cover on ranges after it has been removed by grazing to reduce erosion rates. Grazing management systems typically reduce the time livestock spend in each pasture to increase the quantity and quality of vegetation in those pastures. Grazing frequency, timing, duration, area allocation, and livestock distribution kind, class, distribution and stocking rates should all be considered in the management system to ensure adequate pasture rehabilitation. Access limitations, such as fencing and stream crossings are used to herd and control livestock movement. Physical disturbance from livestock can increase erosion, so crossings and watering access points should be hardened. Alternative water supplies are an alternative to more sensitive water sources that may be vulnerable to erosion and discharges from grazing areas. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Sediment; Waterborne Discharges |
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Sodic Soil Management | In coastal agriculture it is important to manage and reduce accumulations of salts on the soil surface and down to the crop rooting depth. Saline seep often occurs in crop areas where the water table is very shallow. Irrigation management or drainage improvements may be necessary. Another option may be subsoiling, where internal soil drainage is restricted by layers of contrasting permeability and soil moisture levels are low enough to allow shattering and mixing of soil layers. Vegetative measures include planting deep rooted crops such as wheatgrass and alfalfa. Soil amendments can be used to treat sodium, displacing it with calcium depending on the specific chemistry of the soil. Though crop yield does not directly impact coral reefs, ground water restoration projects may change the raise the water table, making sodic soil management important. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Raw Materials; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Salinity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Local Businesses | Information should be provided to business along the water so that employees will be aware of environmentally sensitive business practices. This can be achieved through informative brochures, and distributing other educational materials. These interactions can also be used to inform businesses of opportunities for voluntary certifications (#104). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Infrastructural Policies; Manufacturing & Trade; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Coastal Construction & Development | This involves assessing coral, seagrass, and hard bottom substrate that is impacted during coastal construction repair or alternation. If unacceptable damages are occurring this information will be useful in future permit decision making. If infringements have occurred, this information may be useful for compensatory mitigation and liability for restoration of those natural resources injured. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Ports & Harbors; Reef Habitat; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Special Use Permitting; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Data Management & Decision Tools: Develop a Geographic Information System Incorporating Satellite and Aerial Images | This option involves the acquisition of high-resolution, low altitude photos of management areas and grounding hotspots. These photos can then be used for baseline documentation for natural resource litigation, research, and management decisions. If these images are to be incorporated into larger geodatabase, such as that proposed in # 166, a standardized protocol should be developed in advance, as suggested in management option #166. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Ecosystem Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Discharge Controls: Carbon Sequestration | Carbon sequestration is the process through which practices remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. The term "sink" is also used to describe agricultural and forestry lands that absorb CO2, the major global warming gas emitted by human activities. Agricultural and forestry practices can also release CO2 and other greenhouse gases to the atmosphere. In the ocean, phytoplankton are another major carbon sink. | Houghton, R.A. 2002. Magnitude, distribution and causes of terrestrial carbon sinks and some implications for policy. Climate Policy 2:71-88. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Algae; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Forestry; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Plankton; Political Pressure; Solid Waste Disposal |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Streamside Management Areas | There are often surface waters, such as streams and lakes, within forestry areas that require special protection. This management option involves establishing and maintaining management areas (35 to 50 feet) around these surface waters to buffer against changes in temperature, increases in sediments and nutrients, and to provide bank stability. Canopy species in these areas also provide woody debris needed for instream channel structure and aquatic species habitat. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Management Planning | There are many aspects to properly managing forestry sites to reduce point source and non-point source pollutants. Forestry activities can degrade water quality with several types of pollutants and impacts, including: sediment, nutrients, forest chemicals like pesticides, organic debris from tree litter, increased water temperature and increased streamflow. The Forestry management plan and practices include, but are not limited to: pre-harvest planning, road construction and use, prescribed burning and fire management, brush management, timber harvest, regeneration, and application of forest chemicals. Wetlands Forest Management has additional best practices. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Biological Harvest; Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Injury Prevention: Foster Reef Resilience | Resilience relates to how well the reef ecosystem is able to maintain key functions and processes while under abnormal pressure or stress. Two ways of supporting coral reef resilience are: incorporating known resilient areas into management design and by implementing strategies to either reinstate or protect factors that contribute to resilience, such as good environmental conditions, biological diversity, and connectivity. | Marshall, P. and H. Schuttenberg. 2006. A reef manager's guide to coral bleaching. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Contact Uses; Coral; Decision Support; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Pressures; Resource Use Management |
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Landuse Management: Mine Reclamation | Lands disturbed by mining must be reclaimed to their Approximate Original Contour (AOC). Mine operators must backfill, compact, and grade in order to restore the AOC of the land with all highwalls, spoil piles, and depressions eliminated. Spoil material is prone to erosion, and may carry various disturbed toxics into groundwater if not properly managed. Temporary roads and impervious surfaces may have also been constructed for mining purposes. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement. POSTMINING LAND USE: Exceptions to Approximate Original Contour Requirements for Mountaintop Removal Operations and steep Slope Mining Operations. Washington, DC. |
Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Valuation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Landuse Management: Household Landscaping Best Management Practices | Homeowners manipulate the visible features of the land surrounding their home through landscaping. This includes flora, fauna, and terrain. Best Management Practices (BMPs) for landscaping include selection of indigenous flora and fauna, landscape irrigation (sprinkler systems etc), stormwater runoff BMPs, reducing water use, integrated pest management, composting, and incorporation of permeable surfaces. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Addition; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shelter; Supplemental Feeding; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Marine Zoning: Permitting Application & Award | This management approach is important because permits assure protection and conservation of coral resources from harmful activities and practices. Within sanctuary waters, special use permits (#157) can be used to allow scientists and others to conduct necessary work while following permitting regulations to reduce the impact of that work. General permits are often required for altering land-use, construction projects and certain discharges. To be eligible for a permit, the operator may be required to conduct impact assessments, institute best management practices and conduct monitoring of the project. Though permits are a necessary precaution, the process can be streamlined through ensuring clear submittal requirements, and reducing redundancy. Redundancy often occurs when multiple agencies must approve a permit, a single point of contact and standard, inter-agency protocols can reduce unnecessary redundancy. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Marine Zoning: Utilize Marine Protected Areas for Research and Monitoring | Research and monitoring of marine protected areas determine the degree to which the zones meet goals and objectives for protecting natural resources, as well as human-use patterns, attitudes and compliance. Once data is gathered from within the protected zone it can than be compared to comprable data from outside the protected zone, as a control. It is necessary to compile and review data on use patterns to determine where additional Special-Use Areas would be appropriate. Research in the protected area should be non-invasive. It is important to make the protected area available for external research as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Research and Monitor Wetlands | This management option involves monitoring and research of mangroves, both for biotic and abiotic factors. Some biotic factors include disease, species, invasive species, abundance, age and leaf litter. Important abiotic factors include sedimentation rates, types and causes of turbidity, and soil chemistry. The activity would document changes to the extent of mangrove vegetation by using historical aerial photography and other records. Wetland nutrient and contaminant processing productivity depends on maintaining a balance and not exceeding thresholds. There remain many unknowns in wetland restoration as to optimal capacity and how to achieve this. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Primary Production; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Develop Innovative Monitoring Tools | This management option calls for identifying and evaluating monitoring tools and methodologies used to detect pollutants and identify cause-and-effect relationships among water quality and biological resources. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Chemical Variables; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Scientific Research; Toxics |
| Monitor & Research: Research Historical Hydrology | This activity involves a historical assessment of the hydrology of the surrounding water area around the sanctuary as it has affected water quality and biological communities within the sanctuary. It will clarify the role of freshwater inflows and water quality from local freshwater bodies. Also, this activity will examine the effects of structural modification and changes in quality, quantity, timing and distribution of freshwater releases from existing structures and will examine land-based practices affecting the water quality of runoff. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Physical Variables; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Adaptive Management | By definition, adaptive management is a structured management approach that links science to decision-making, thereby improving the probability of restoration success. It provides an efficient process to address risk and uncertainty inherent within ecosystem restoration by encouraging flexible plans and designs. Monitoring (#) is an important component of adaptive management. The affect of different restoration alternatives can be seen using monitoring data, and compared against other environmental variables to determine what the best future actions are based on results of previous projects. | CERP Committee. 2006. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan Adaptive Management Strategy. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Physical Variables; Public Administration; Regulating Services; Remediation; Scientific Research; Supporting Services |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Channel & Reef Navigation Markers | This option would evaluate the need for proper marking to ensure better navigation. There are many types of markers, including buoys, charts, beacons, and GPS mapping. Such markers can also be used to advocate prohibition on vessel speeds greater than idle speed in areas designated as idle-speed only/no-wake and around shallow reef locations. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Beach & Land Formation; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Transportation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Restoration: Land Reclamation Integrating Landslide Treatments | This management option is exercised to prevent down slope movement of earthen materials, including natural soils, and spoil/waste from mining or forestry activities. Extreme caution and planning must be exercised before permitting any personnel, equipment or other machinery into the slide area. An experienced engineer should analyze the stability of the site both before and after alterations are made to evaluate stability. Water Control: sources of water that enter the area can be controlled to keep the material dry, as it is typically more stable when dry. Loading Control: where appropriate, consider removing excess material from upper portions of the slide area to reduce slide mass. Slope Reduction: where practice, use grading to reduce the slope of the slide area. Increasing Internal Strength: consider the impact of removing and recompacting of material at designed levels of moisture and with biotechnical slope stabilization practices. External Restraints: external restraints can be used where slope movements must be limited due to surrounding valued improvements (e.g. structures), where manipulation of the material may not achieve desired improvements. External restraints must be designed to prevent overturning, sliding at or below the base, and bearing failure of the foundation. Vegetative Treatment: deep rooted grasses and shrubs with proven performance in soil bioengineering applications can be planted using selected soil bioengineering or biotechnical slope stabilization techniques appropriate to the site. Transpiration and infiltration should be considered when choosing vegetation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Forestry; Infrastructure; Insurance; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment |
| Restoration: Land Reclamation Integrating Toxic Discharge Controls | This option aims to eliminate unsightly residues, reduce erosion and control acid or otherwise toxic aqueous discharges from abandoned coal mines, coalmine waste or other types of land change. For toxic mine drainage, preventative actions include mine sealing, infiltration control, day lighting, and neutralization with alkaline material such as hydrated lime. Which action to take relies heavily on groundwater and runoff in the region of the mine. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Aquaculture; Coal Mining; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Ocean Acidity; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Restoration: Beach Renourishment and Nourishment | Beaches are subject to natural accretion and erosion. Tourism is often best supported by wide, accessible, public sandy beaches. Beaches can be restored to counteract natural erosion by transporting large quantities of sand onto the beach. This sand often comes from nearby dredging. Caution should be used when restoring long sections of beaches, as often the area above the mean high tide line is littoral, or privately owned, and restoration of these beaches can impact these property rights, see "Stop the Beach Renourishment, Inc. v. Florida Department of Environmental Protection (2010) U.S. Supreme Court decision." Beach protection or nourishment offers an alternative to this often expensive and abrupt type of renourishment, nourishment involves practices which encourage coastal accretion and discourage erosional forces. See "Florida's Beach and Shore Preservation Act" for some restrictions on this. | NOAA Coastal Services Center. Beach Nourishment: A Guide for Local Government Officials. Coastal Services Center Accessed 6/17/2011. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Culture; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Recreational Opportunities; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation |
| Restoration: Beach Vegatation Restoration | Natural beaches are often host to important costal dune ecosystems. Due to tourism, much of the vegetation that comprises these dune ecosystems may be compromised. The natural vegetation provides an important ecosystem service, with roots providing deep stabilization against physical damage and removal of that sand. Without such vegetation sand and dunes can be completely washed away during hurricanes and other surge events. The dunes themselves offer some protection to nearby inland infrastructure during these same storm events. When the beach past the dunes is for public access it is beneficial to build raised walk-overs over the dune vegetation. This prevents trampling, which leads to dune blowouts. | Natural Resources Conservation Service, editor. 2007. Native Plants for Coastal Dune Restoration: What, When, and How for Florida. US Department of Agriculture. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Culture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Invasive Species; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Physical Damage; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. Water collection can be selective, targeting the first flush of water, which is typically the most polluted. Water retention has the additional benefit of later release at a place and time when the water is needed (e.g. for irrigation). Rainwater Collection Systems (#11) can be an important water resource in areas where freshwater is limited. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Detention Devices for Dry/Wet Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Water and Sediment Control Basin. CODE 638. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Volume Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Infiltration | This management option attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that control the volume of surface water, facilitating faster absorption of the stormwater into the ground. Often these structures are able to infiltrate larger amounts of water faster while reducing exposure to surface sediments and pollutants. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. US EPA. EPA Infiltration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Rainwater Collection Systems | Creating a rainwater collection system (either through policy change or the initiative of homeowners) would help in many ways. These systems would utilize water in an efficient manner. It would reduce the pressure of water as a finite resource. Water would be collected and utilized before it reaches the ground. Once rain falls to the ground, it picks up nutrients, chemicals, and pathogens on the ground and transports them in the form of runoff. Eventually this contaminated stormwater runoff enters water resources through the drainage basin. Collecting a considerable amount of water would prevent contamination of that water, and allow for it to be usable. Also, it would reduce the amount of water that is lost when it is contaminated as runoff. An overall reduced amount of stormwater runoff would reduce the amount of contaminants that would harm corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Cisterns used for water harvesting. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shelter; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Sustained Reservoir Minimum Release of Minimum Baseflow to Sustain Aquatic Habitat | In some regions, even high intensity rivers (e.g. Rio Loco, Puerto Rico) are seasonal, drying for long enough to kill aquatic vegetation. Creating a constant baseflow would help sustain aquatic life and ultimately help to process nutrients. High intensity rivers are already prone to extreme channel erosion from the high flow rates, this erosion is even greater without any benthic biota to hold sediment on the river bottom. Restricting the release of reservoir water to that required to maintain aquatic biota would reduce the intensity of flow, stabilize the river bottom, create habitat and naturally process nutrients that could potentially contribute to eutrophication out on the coral reef. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Algae; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of natural structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. These structures are typically characterized as retention ponds and incorporate natural vegetation such as grass. These ponds may be dry, or may drain into nearby wetlands. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Transportation Policy: Dust Control Application | This action is taken to control dust from unpaved roads and other surfaces, which is generated by traffic and/or wind. Some dust control products (palliatives) for application include: water, hydroscopic palliatives, adhesive, petroleum emulsion, polymer emulsion, clay additive, and bituminous. There are specific considerations for application of each, including seasons and when to use which. For example, hygroscopic palliatives (control dust by absorbing water from the air) shall not be used in arid and semi-arid environments. Calcium chloride and magnesium chloride shall not be used in locations where the daily summertime relative humidity averages below 30%. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land & Air Transportation; Mining; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Water Quality Management: Treating Effluent Water Through Wetlands | Additional treatment of sewage is often a necessary management option because secondary treatment alone leaves 20,000 times more nutrients in the water than the safe limit for corals. High concentrations of nutrients in the water leads to eutrophication, and coral reefs are more sensitive to nutrient enrichment than any other coastal system. Wetlands are extremely successful at reducing nitrogen levels in water. Using natural wetlands or "living machines" to perform this task can actually be more cost effective than further sewage treatment. Each successive wetland treatment cell of the series can provide incredible levels of denitrification, and thus protect corals from nutrient enrichment. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2003. Waste Treatment Lagoon. CODE 359. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Aquatic Organism Passage | This management action allows for upstream and downstream passage for fish and other aquatic organisms. The passage of these organisms is often restricted by barriers which must be modified, removed, or worked around with fishways. Sites should be evaluated for variations in discharge, tidal influence, hydraulics, geomorphic impacts, sediment transport and continuity, and organic debris movement. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Water Resources |
| Waterway Management: Boat Access Plan | An optimal boat access strategy involves conducting a survey of all public and private boat access points throughout the area. Once entry and exit sites are identified, channel markings can be placed accordingly. An effective strategy must also consider boat access needs, location, and intensity of use. This will help to efficiently mark the waterways so that there can be a reduction in damage to reefs, seagrasses and wetlands. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Culture; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Changes; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Lagoon Restoration | Many times lagoons/wetlands are filled for urban development, agricultural development, etc. Lagoons/wetlands are a sink for nutrients, sediment, and contaminants. Wetlands close to reef watersheds can be huge contributors to reef health. This is because wetlands intercept surface-water runoff from higher, drier land and retain excess nutrients and pollutants. Also, lagoons are beneficial because they provide habitat for an array of wildlife. Overall, they can greatly reduce the amount nutrient-contaminated water that reaches corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Chapter 13, Part 650. Wetland Restoration, Enhancement or Creation. Engineering Field Handbook. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Collaborate with Projects Changing Water-Flow | Other organizations may be performing restorative freshwater projects (Everglades Restoration) or other flow altering projects (e.g. canals for small boats, agricultural irrigation etc) that affect the downstream marine management area (Florida Bay). Projects on the coast that involve hydrologic modifications (such as changing salinity) must be closely monitored in order to protect reef quality. Reefs are very sensitive systems and can only survive in a narrow salinity range. By taking an active role and monitoring freshwater flow projects, management staff can better ensure proper consideration of the impact on coastal marine environments. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan. 2010. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan: 2009 System Status Report. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Salinity; Security & Public Administration Policies; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| American Antiquities Act of 1906, 16 United States Code §§ 431-433. | The Act provides penalties for unauthorized collection, excavation, or destruction of historic or prehistoric ruins, monuments, or objects of antiquity on lands owned or controlled by the United States. It authorized that areas of extrodinary geographical, historical , aesthetic value can be designated national monuments. Application to Coral Reefs:Has been used by Presidential Proclamation in 2001 to expand or create two national monuments; the Virgin Islands Coral Reef Monument and the Buck Island Reef National Monument. The monuments include coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Docks & Marinas; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management |
| Archaeological Resources Protection Act of 1979 as amended, 16 United States Code § 470. | To protect historic ruins, monuments, and objects of antiquity. Strenghtens and expands the protective provisions of the Antiquities Act of 1906 regarding archeological resources. It also revised the permitting process for conducting archeological research. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 10: Open shorelines, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | The seashore has always provided recreation, meditation, and physical therapy to the residents of the USVI. The shoreline provides access to the sea and a way of life for fisherman.The law requires that the public be given access to shorelines of the USVI for use and enjoyment. Application to Coral Reefs:The limitation on barriers, obstructions, and retraints to beach access will have a minor role in protecting coral reefs because sedimentation that would have been associated with that minor construction will not occur. Legislative Actions:No person, firm, corporation, association or other legal entity shall create, erect, maintain, or construct any obstruction, barrier, or restraint of any nature whatsoever upon, across or within the shorelines of the USVI as defined in this section, which would interfere with the right of the public individually and collectively. to use and enjoy any shoreline. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Mangroves; Marine Vertebrates; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses |
| Chapter 13: Environmental protection, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Establishes an environmental protection program for land development to prevent soil erosion and for the conservation of beaches, shorelines, and the coastal zone of USVI. Rules and Regulations were to prevent improper development of land and harmful environmental changes. Application to Coral Reefs:The Earth Change Plan review will indicate any adverse environmental impacts, including those that could effect coral reefs such as sedimentation. Legislative Actions:The law requires an "Earth Change Plan" from the Department of Planning and Natural Resources before any land can be cleared, graded, filled, or otherwise disturbed. Violation from the approved Earth Change Plan is punishable by a fine of $200 per day per violation. Violation of other portions of the Chapter is punishable by $5,000 fine or one year imprisionment per violation. Development in the first tierof the coastal zone requires a coastal zone permit. Comments:Chapter 13 includes comprehensive erosion and sediment control measures applicable to public and private developments including construction and maintenance of streets and roads. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management; Shoreline Armoring |
| Chapter 21: Virgin Islands coastal zone management, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Protect, maintain, preserve and, where feasible, enhance and restore, the overall quality of the environment in the coastal zone, the natural and man-made resources therein, and the scenic and historic resources of the coastal zone for he benefit of residents of and visitors of the USVI Application to Coral Reefs:The Legislature stated coastal zone protection will conserve ecologically significant resource areas for their contribution to marine productivity and value as wildlife habitats, and preserve the function and integrity of reefs, marine meadows, salt ponds, mangroves and other significant natural areas. The legislation will also maintain or increase coastal water quality through control of erosion, sedimentation, runoff, siltation and sewage discharge. Legislative Actions:Any violation of the chapter will be grounds for revocation or suspension of coastal zone permit and an order to cease and desist. Any person who violates any provision of the chapter shall be subject to a civil fine not to exceed $10,000 per day. Exemplary damages may be assessed at the discretion of the court. Comments:Section 908 of the law shows Coastal Zone Boundaries. Section 909 shows areas of special concern. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging Regulations; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring |
| Chapter 3: Trees and vegetation next to waterways, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Establishes buffer zone for protecting natural watercourses from vegetation clearing. The buffer zone either 30 feet from the center of the natural watercourse, or 25 feet from its edge, whichever is greater. Application to Coral Reefs:Assists in erosion control and can protect reefs from harmful sedimentation, if the stream or river sediment is capable of reaching the coral reef. Vegetation along river and stream banks will remove nutrients and assist in preventing eutrophocation of waters that can reach coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Enforcement is by conservation officers with assistance from local police when required. Penalties are fines of not more than $100, or 180 days in jail, or both Comments:Permits can be obtained if the purpose of clearing is for development. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management; Shoreline Protection; Wetlands |
| Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 (CBRA), 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote more appropriate use and conservation of coastal barriers along the Atlantic, Gulf and Great Lakes coastlines. Minimize the loss of human life; reduce wasteful expenditures on shoreline development; minimize damage to wildlife, marine life, and other natural services, and establish a coastal barrier resources system. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restrict most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coral; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Wetlands |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, as amended through 2004,. | A voluntary national program to encourage coastal states to develop and implement coastal zone management plans and requires that "any federal activity within or outside of the coastal zone that affects any land or water use or natural resource of the coastal zone" shall be "consistent to the maximum extent practicable with the enforceable policies" of a state's coastal zone management plan. The law includes an Enhancement Grants program for protecting, restoring, or enhancing existing coastal wetlands or creating new coastal wetlands. It also establishes the National Estuarine Research Reserve System, guidelines for estuarine research, and financial assistance for land acquisition. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:The 1985 amendments (PL 99-272) established the National Estuarine Reserve Research System a State-Federal process for designating national reserves and guidelines for estuarine research.The 1990 amendments (PL 101-508) established new Enhancement Grants for eight specific areas, including protecting, restoring or enhancing existing coastal wetlands or creating new coastal wetlands and assessing the cumulative effects of coastal development on coastal wetlands and fishery resource. Also, the 1990 statute established a new Coastal Nonpoint Source Pollution Control Program. The 1998 and 2004 (PL 105-383 and PL 108-456) established a program for the prevention and control of harmful algal blooms and hypoxia, and included authorization for a representative of the Department of Interior to assess the economic and ecological impacts of algal blooms and hypoxia. Comments:If implemented, the programs for economic, ecological and control of harmful algal blooms and hypoxia would be useful for coral reef issues. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Economic Markets & Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Delineation of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters, 62-340 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2000). | The Rule's intent is to provide a unified statewide methodology for the delineation of the extent of wetlands to satisfy the mandate of Section 373.421, F. S. Application to Coral Reefs:Preservation of wetlands will allow them to continue to function as buffers for sediment and contaminant control keeping them from reaching estuarine and marine waters and eventually habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative and methodological for delineation purposes. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Energy Policy & Development; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Estuaries Protection Act of 1968, 16 United States Code §§ 1221-1226. | Authorizes the Secretary of Interior in cooperation with other federal agencies and the states, to study and inventory estuaries of the united states, including land and water of the Great Lakes, and to determine whether such areas should be acquired for protection. The Secretary is also requied to encourage state and local governments to consider the importance of estuaries in their planning activities relative to federal natural resources grants. Application to Coral Reefs:Established the congressional policy on the values of wetlands and the need to conserve their natural resources. Protection of wetlands provide coral reefs with an indirect benefit as the wetland serves the functions of nutrient removal and sediment containment Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Secretary of Interior in conjunction with other federal agencies and States Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Seagrasses; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Exec. Order No. 11988, Management of Flood Prone Areas, 42 Federal Register 2691 (1977). | This order requires all federal agencies to take action and avoid to the extent possible, adverse impacts over the short and long term associated with the occupation and modification of flood prone areas and to avoid direct or indirect aid to the development of flood prone areas whenever there is a viable alternative. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Landuse Management; Public Administration |
| Florida Aquatic Preserves, 18-20 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-20.001 Intent.
(1) All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency.
(2) Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(3) The preserves shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals: (a) To preserve, protect, and enhance these exceptional areas of sovereignty submerged lands by reasonable regulation of
human activity within the preserves through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program; (b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserves so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating, and fishing; (c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the Legislature in creating the preserves; (d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the act and these rules, and to assist in managing the preserves; (e) To encourage the protection, enhancement or restoration of the biological, aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions toward their natural condition, and discourage
activities which would degrade the aesthetic, biological, or scientific values, or the quality, or utility of a preserve, when reviewing applications, or when developing and implementing management plans for the preserves; (f) To preserve, promote, and utilize indigenous life forms and habitats, including but not limited to: sponges, soft coral, hard corals, submerged grasses, mangroves, salt water marshes, fresh water marshes, mud flats, estuarine, aquatic, and marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, estuarine, aquatic and marine invertebrates, estuarine, aquatic and marine mammals, birds, shellfish and mollusks; (g) To acquire additional title interests in lands wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological,
aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves; (h) To maintain those beneficial hydrologic and biologic functions, the benefits of which accrue to the public at large. (4) Nothing in these rules shall serve to eliminate or alter the requirements or authority of other governmental agencies, including counties and municipalities, to protect or enhance the preserves provided that such requirements or authority are not inconsistent with the act and this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:By maintaining coastal aquatic preserves in their natural condition, mangrove forests, wetlands and submerged aquatic vegetation will perform the functions of being sediment traps and removing some contaminants such as nutrients. Therefore, they will not reach marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Waste Management Policies |
| General permit for activities seaward of the coastal construction control line, 62B-34 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2010). | To implement the provisions of Section 161.053(19) F. S. providing General Permits for activities performed seaward of the Coastal Construction Control line. Persons wishing to use one or more of the General Permits as set forth in Part II of this rule chapter shall be subject to the notice provisions of subsection 62B-34.030(4) F. A. C. before any activity is conducted as authorized herein.The general conditions provided pursuant to Section 62-B34-0.50, F. A. C. , shall apply to all of the General Permits issued under this rule chapter. Strict compliance with all of the terms, conditions, requirements, limitations, and restrictions applicable to a desired General Permit under this rule chapter is required to qualify for such a permit. Application to Coral Reefs:The rule requires erosion control BMP. Therefore, sediment from construction will not enter the marine environment and damage coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Civil fines are applicable for work done that was not authorized in the permit. Comments: |
Florida Departrment of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring |
| Joint Coastal Permits and Concurrent Processing of Proprietary Authorizations, 62B-049 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. In the event that there is a conflict between the procedural requirements of this chapter and other procedural rules promulgated pursuant to the referenced statutes, then this chapter shall govern. The standards and criteria for issuance of joint coastal permits include the criteria for environmental resource or wetland resource permits pursuant to Chapter 62-312, F.A.C., and the rules adopted under Chapter 62-330, F.A.C., the coastal construction criteria pursuant to Chapter 62B-41, F.A.C., and any specific criteria for issuance of a joint coastal permit listed in this chapter. The criteria for the associated proprietary authorizations are found in Chapters 18-18, 18-20, 18-21, F.A.C.
Specific Authority 161.055, 373.427 FS. Law Implemented 161.041, 161.055, 373.427 FS. History�New 10-12-95, Amended 2-19-98, 5-17-07. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring a permit with regulatory review of the construction project, in a joint review of wetland and submerged land issues, will assist in minimizing potential adverse environmental impacts from the work and such potential detrimental portions of the project (e.g. sedimentation) will not enter the marine environment resulting in ecosystem damage. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection |
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Marine Turtle Conservation Act of 2004, 16 United States Code § 6601. | The law was created to aid in the conservation of sea turtles and their nesting habitats in foreign countries by providing funds for the conservation of nesting areas, sea turtles in in their nesting habitats, and dealing with threats to sea turtle survival. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Designate Protected Species; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles |
| Mitigation Banking, 62-342 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department recognizes that, in certain instances, adverse impacts of activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., can be offset through the utilization of mitigation credits from a permitted Mitigation Bank. This rule provides criteria for this mitigation alternative to complement existing mitigation criteria and requirements. This chapter is supplemental to and does not supersede any other criteria and requirements in rules promulgated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.
(2) The Department intends that Mitigation Banks be used to minimize mitigation uncertainty associated with traditional mitigation practices and provide greater assurance of mitigation success. It is anticipated that the consolidation of multiple mitigation projects into larger contiguous areas will provide greater assurance that the mitigation will yield long-term, sustainable, regional ecological benefits. Mitigation Banks shall be consistent with Department endorsed watershed management objectives and emphasize restoration and enhancement of degraded ecosystems and the preservation of uplands and wetlands as intact ecosystems rather than alteration of landscapes to create wetlands. This is best accomplished through restoration of ecological communities that were historically present. The establishment and use of Mitigation Banks in or adjacent to areas of national, state, or regional ecological significance is encouraged, provided the area in which the Mitigation Bank is proposed to be located is determined appropriate for a Mitigation Bank and the Mitigation Bank meets all applicable permitting criteria.
(3) Nothing in this chapter shall affect the mitigation requirements set forth in any Mitigation Bank agreement or any permit issued under Chapter 84-79, Laws of Florida, or Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., prior to February 2, 1994. If a permittee wishes to substantially modify a Mitigation Bank previously established by agreement or permit, the permittee must comply with this chapter. Additionally, some Mitigation Banks may be subject to the version of this section existing prior to July 1, 1996, under subsections 373.4136(9) and (10), F.S., and will not be affected by amendments adopted after that date. This chapter does not prohibit an applicant from proposing project-specific, pre-construction on-site or off-site mitigation, without establishing a Mitigation Bank. Application to Coral Reefs:Mitigation banking in coastal wetlands, as presented in the Chapter, can provide large areas of functioning wetlands. The wetlands can function as sediment and nutrient traps keeping sediment and nutrients from entering coastal waters and damaging marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the regulations and permitting requirements for mitigation banks. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Shoreline Armoring; Waste Management Policies |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Regulation of stormwater discharge, 62-25 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1988). | The discharge of untreated stormwater may reasonably be expected to be a source of pollution of waters of the state and is, therefore, subject to Department regulation. The Departmnet shall prevent pollution of waters of the state by discharges of stormwater, to ensure that the designated most beneficial uses of waters, as prescribed by Chapter 62-302, F.A.C., are protected. A permit under this chapter will be required only for new stormwater discharge facilities as defined herein. This provision shall not affect the Department's authority to require appropriate corrective action, pursuant to Sections 403.121-.161.F.S., whenever existing facilities cause or contribute to violations of state water quality standards. Stormwater discharges to groundwaters shall be regulated under the provisions of Chapters 62-520 and 62-522, F.A.C., and other applicable rules of the Department. The Department intends that, to the greatest extent practicable, the provisions of this chapter be delegated to either local governments or water management districts seeking such delegation. Application to Coral Reefs:Limiting the contaminants and their concentrations in stormwater discharge will reduce the contamination reaching various habitats, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Floridfa Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Revised Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Management Plan §§ Public Law 101-605 (HR 5909, Public Law (2007). | The document is a report on the results of NOAA's five year review of strategies and activities detailed in the 1996 Final Management Plan and Environmental Impact Statement for the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The plan specifically addresses preserving and enhancing Sanctuary resources including four national wildlife refuges, six state parks, three state aquatic preserves, Key Largo Marine Sanctuary, Looe Key Marine Sanctuary and a total of 2,900 square nautical miles of coastal waters and numerous coral reefs. The sanctuary ecosystems are facing specific threats including direct human impacts such as vessel groundidngs, pollution and overfishing. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration with the Florida Department of Environmental Protection and the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission as Co-trustees Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Seastars; Sediment; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899, 33 United States Code § 1252. | This law prohibits the discharge of any type of refuse matter in U.S. waters without permission (section 13). In addition, the excavation, fill, or alteration of the course, condition, or capacity of any port, channel, river, or other areas within the limits of this law is prohibited. This law prohibits the construction or alteration of a structure in wetlands of the U.S. (sections 9 and 10). Construction in wetlands and waters of the U.S. requires a permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Application to Coral Reefs:Under section 10, excavation or fill within navigable waters requires approval of the Chief of Engineers and concerns about contaminated sediments with dredge and fill projects in navigable waters is addressed within the permitting process. Indirect protection of coral reefs is offered by the Act and its prohibition of dumping refuse into navigable waters and the process of anaylzing sediment in proposed dredge and fill operations. Legislative Actions:Violations of the law are punished under section 309 of the Clean Water Act and section 205 of National Fishing Enhancement Act. Fines imposed for violation will not be less than $10,000 per violation or more than $25,000 per violation. Comments:Many states, including Florida, require additional permits for constuction of docks, piers, wharfs, jetties and other structures in navigable waters and wetlands in addition to the Corps of Engineers permit. Authority to issue permits for discharge of refuse matter under section 13 was modified by the amendments to Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972 and established the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Permit process. The Act was initially established to protect interstate commerce in navigable waters. The permit review process involves factors including economics, aethetics, general envitonmental concerns, historical values, water quality, and fish and wildlife impact before project approval is granted. |
US Army Corps of Engineers (COE), and US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: United States |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Rules and Procedures for Application for Coastal Construction Permits, 62B-041 Florida Administrative Code. | No coastal construction shall be conducted without a permit issued by the Department under this chapter, unless it is determined that the coastal construction does not fall within the requirements of section 161.041, F.S., or unless the interior tidal water body is exempted by the Department pursuant to subsection 161.041(1), F.S. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring a permit with regulatory review of the construction project will assist in minimizing potential adverse environmental impacts from the work and such potential detrimental portions of the project (e.g. sedimentation) will not enter the marine environment resulting in ecosystem damage. Legislative Actions: Comments:No coastal construction shall be conducted without a permit issued by the Department under this chapter, unless it is determined that the coastal construction does not fall within the requirements of section 161.041, F.S., or unless the interior tidal water body is exempted by the Department pursuant to subsection 161.041(1), F.S. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 include (1) Coastal Barrier Improvement Act of 1990, (2) Coastal Barrier Resources Reauthorization Act of 2000, (3) Coastal Barriers Resources Reauthorization Act of 2005,. | (1) Added additional areas along the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, the Florida Keys and the Virgin Islands and established "Otherwise Protected Areas OPAs); (2) amended the guidelines for making recommendations regarding additions to the CBRS and reqired a pilot digital mapping project; (3) reauthorized CBRA and required the submission of the final digital mapping pilot project. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restricted most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Forestry; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Surface water quality standards in table format, 62.302.500 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | This section of Chapter 62-302 presents the water quality standards in a tabular format for each class of waters of the State. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| The DPNR states that wetlands in the Virgin Islands are covered by the Clean water Act and the Endangered and Indigenous Species Act of 1990 (Title 12, Chapter 2, US Virgin Island Code,. | To protect wetlands and wetland species from degradation, loss as a result of dredging and filling. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of wetlands assists in controlling sedimentation and nutrient runoff from terrstrial locations, thus protecting coral reefs that are influenced by terrestrial sources. Legislative Actions: Comments:The wetlands portion of the USVI Division of Environmental Protection website was under construction at the time of this atlas preparation. However, it appears that DEP works with the USACE and USEPA on matters related to wetlands. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Wetlands |
| Total maximum daily loads, 62-304 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | The Chapter establishes Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), and their allocations, for waters that have been verified to be impaired by a pollutant pursuant to Chapter 62-303. F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Envitonmental Protection Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Biomedical Research Policies; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Impervious Surfaces; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Uniform Mitigation Assessment Method, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-345 (2005). | Establishes a methodology that provides a standard procedure for assessing the functions provided by wetlands and other surface waters, the amount that those functions are reduced by a proposed impact, and the amount of mitigation necessary to offset that loss. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting wetlands provides wetland areas that can act as buffers against nutrients, pollutants and contaminants from reaching habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is administrative and provides methods to assess wetland value and appropriate mitigation to offset impact. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
