ReefLink Database

Invasive Species
Invasive species are plants, animals, or other organisms that are foreign to a particular environment, and whose introduction may be detrimental when invasives compete with or consume native species. Invasive species in Caribbean reefs include lionfish, batfish, and tubastraea coral.
CMap
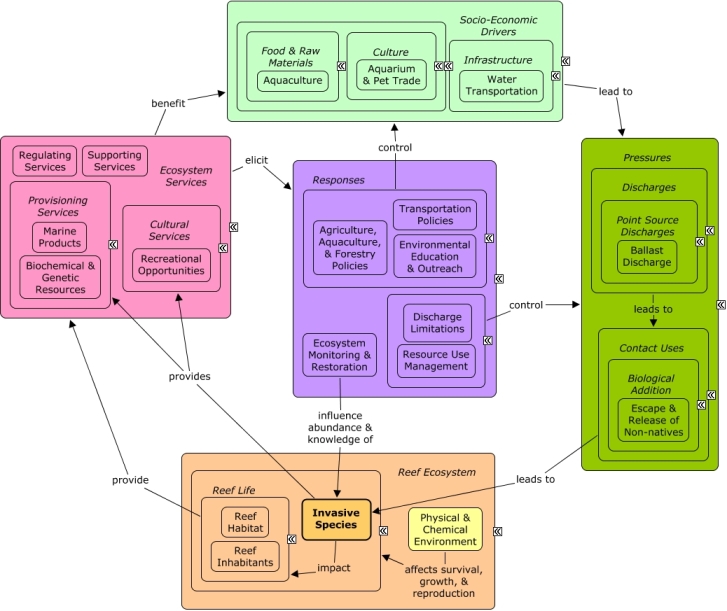
CMap Description
Invasive species may contribute to the diversity and aesthetic value of the reef, but often compete with or consume native species, and alter native communities. Collectors of exotic species, such as the aquarium and pet trade, or ballast water discharges from international ships may lead to the introduction of invasive species that compete with native species. Aquaculture facilities also pose a risk of accidentally releasing cultured species into wild populations. Monitoring and scientific research can be used to track invasive species and better understand their impact on native populations. Ballast discharges can be controlled through point-source regulations. Environmental education can be used to educate individuals against accidental or intentional introductions of exotic species. Remediation may be required to directly remove invasive species where they are severely impacting native species.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angawi, RF; Bavestrello, G; Calcinai, B; Dien, HA; Donnarumma, G; Tufano, MA; Paoletti, I; Grimaldi, E; Chianese, G; Fattorusso, E; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. 2011. Aurantoside J: a New Tetramic Acid Glycoside from Theonella swinhoei. Insights into the Antifungal Potential of Aurantosides. Marine Drugs 9:2809-2817. | 2011 | Indonesia | Invasive Species; Sponges | |
| Arias-Gonzalez, JE; Gonzalez-Gandara, C; Cabrera, JL; Christensen, V. 2011. Predicted impact of the invasive lionfish Pterois volitans on the food web of a Caribbean coral reef. Environmental Research 111:917-925. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean; Mexico | Model | Apex Fish Predators; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Barbour, AB; Allen, MS; Frazer, TK; Sherman, KD. 2011. Evaluating the Potential Efficacy of Invasive Lionfish (Pterois volitans) Removals. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Caribbean; Mexico | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species; Mangroves |
| Betancur-R, R; Hines, A; Acero, A; Orti, G; Wilbur, AE; Freshwater, DW. 2011. Reconstructing the lionfish invasion: insights into Greater Caribbean biogeography. Journal of Biogeography 38:1281-1293. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Bermuda; Caribbean | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Bonaldo, RM; Krajewski, JP; Bellwood, DR. 2011. Relative impact of parrotfish grazing scars on massive Porites corals at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef. Marine Ecology Progress Series 423:223-233. | 2011 | Australia | Algae; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral | |
| Coma, R; Serrano, E; Linares, C; Ribes, M; Diaz, D; Ballesteros, E. 2011. Sea Urchins Predation Facilitates Coral Invasion in a Marine Reserve. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | Algae; Invasive Species; Primary Production; Sea Urchins; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Darling, ES; Green, SJ; O'Leary, JK; Cote, IM. 2011. Indo-Pacific lionfish are larger and more abundant on invaded reefs: a comparison of Kenyan and Bahamian lionfish populations. Biological Invasions 13:2045-2051. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Kenya; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invasive Species |
| Donas, KP; Schonefeld, T; Schlabach, R; Torsello, G. 2011. Eccentric infrarenal aortic stenosis. Surgical and endovascular treatment. Chirurg 82:367-369. | 2011 | Invasive Species; Pathogens | ||
| Green, SJ; Akins, JL; Cote, IM. 2011. Foraging behaviour and prey consumption in the Indo-Pacific lionfish on Bahamian coral reefs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 433:159-167. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Bahamas; Caribbean | Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Gumovsky, AV; Ramadan, MM. 2011. Biology, immature and adult morphology, and molecular characterization of a new species of the genus Entedon (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) associated with the invasive pest Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae, Bruchinae) on Erythrina plants. Bulletin of Entomological Research 101:715-739. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Tanzania; Mozambique; China; South Africa | Invasive Species | |
| Hassan, HM; Elnagar, AY; Khanfar, MA; Sallam, AA; Mohammed, R; Shaala, LA; Youssef, DTA; Hifnawy, MS; El Sayed, KA. 2011. Design of semisynthetic analogues and 3D-QSAR study of eunicellin-based diterpenoids as prostate cancer migration and invasion inhibitors. European Journal Of Medicinal Chemistry 46:1122-1130. | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator | Invasive Species; Octocoral; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources | |
| Hixon, MA. 2011. 60 Years Of Coral Reef Fish Ecology: Past, Present, Future. Bulletin of Marine Science 87:727-765. | 2011 | Cuba | Model | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Hoeksema, BW; van der Land, J; van der Meij, SET; van Ofwegen, LP; Reijnen, BT; van Soest, RWM; de Voogd, NJ. 2011. Unforeseen importance of historical collections as baselines to determine biotic change of coral reefs: the Saba Bank case. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 32:135-141. | 2011 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Antilles; Indonesia; Caribbean | Climate; Invasive Species | |
| Hutchinson, JT; Langeland, KA; Meisenburg, M. 2011. Field Trials for Herbicide Control of Coral Ardisia (Ardisia crenata) in Natural Areas of North-Central Florida. Invasive Plant Science and Management 4:234-238. | 2011 | Florida | Field Study & Monitoring | Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Invasive Species |
| Ilves, KL; Kellogg, LL; Quattrini, AM; Chaplin, GW; Hertler, H; Lundberg, JG. 2011. Assessing 50-Year Change In Bahamian Reef Fish Assemblages: Evidence For Community Response To Recent Disturbance? Bulletin of Marine Science 87:567-588. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Bahamas; India; Caribbean | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Skeletal Coral | |
| Jud, ZR; Layman, CA; Lee, JA; Arrington, DA. 2011. Recent invasion of a Florida (USA) estuarine system by lionfish Pterois volitans/P. miles. Aquatic Biology 13:21-26. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Docks & Marinas; Fish; Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Lages, BG; Fleury, BG; Menegola, C; Creed, JC. 2011. Change in tropical rocky shore communities due to an alien coral invasion. Marine Ecology Progress Series 438:85-96. | 2011 | South & Central America; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Mexico | Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| Lapointe, BE; Bedford, BJ. 2011. Stormwater nutrient inputs favor growth of non-native macroalgae (Rhodophyta) on O'ahu, Hawaiian Islands. Harmful Algae 10:310-318. | 2011 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Discharges; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Lesser, MP; Slattery, M. 2011. Phase shift to algal dominated communities at mesophotic depths associated with lionfish (Pterois volitans) invasion on a Bahamian coral reef. Biological Invasions 13:1855-1868. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Caribbean | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Pathogens; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish; Sponges; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Meadows, A. 2011. Wildlife Conservation Education And International Programmes. Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences 21:305-316. | 2011 | Global | Review; Model | Collaboration & Partnering; Invasive Species; Mangroves |
| Meyer, AL; Dierking, J. 2011. Elevated size and body condition and altered feeding ecology of the grouper Cephalopholis argus in non-native habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 439:203-212. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Apex Fish Predators; Invasive Species; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Mumby, PJ; Harborne, AR; Brumbaugh, DR. 2011. Grouper as a Natural Biocontrol of Invasive Lionfish. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Munoz, RC; Currin, CA; Whitfield, PE. 2011. Diet of invasive lionfish on hard bottom reefs of the Southeast USA: insights from stomach contents and stable isotopes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 432:181-U494. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Cuba; Caribbean | Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. | 2011 | Aquaculture; Bivalves; Invasive Species; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Substrate | ||
| Sarac, TP. 2011. Influence and Critique of the ASTRAL and CORAL Trials. Seminars in Vascular Surgery 24:162-166. | 2011 | Invasive Species; Pathogens | ||
| Sutherland, WJ; Bardsley, S; Bennun, L; Clout, M; Cote, IM; Depledge, MH; Dicks, LV; Dobson, AP; Fellman, L; Fleishman, E; Gibbons, DW; Impey, AJ; Lawton, JH; Lickorish, F; Lindenmayer, DB; Lovejoy, TE; Mac Nally, R; Madgwick, J; Peck, LS; Pretty, J; Prio. 2011. Horizon scan of global conservation issues for 2011. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 26:10-16. | 2011 | Global | Review | Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Invasive Species; Pathogens; Schools & Colleges |
| Wagner, D; Papastamatiou, YP; Kosaki, RK; Gleason, KA; McFall, GB; Boland, RC; Pyle, RL; Toonen, RJ. 2011. New Records of Commercially Valuable Black Corals (Cnidaria: Antipatharia) from the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands at Mesophotic Depths. Pacific Science 65:249-255. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Commercial Fisheries; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Invasive Species; Octocoral; Stony Coral | |
| Walker, SE; Parsons-Hubbard, K; Richardson-White, S; Brett, C; Powell, E. 2011. Alpha and beta diversity of encrusting foraminifera that recruit to long-term experiments along a carbonate platform-to-slope gradient: Paleoecological and paleoenvironmental implications. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 312:325-349. | 2011 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean; Mexico | Index or Indicator | Beaches & Nature Parks; Invasive Species; Ocean Acidity; Sediment; Substrate |
| Work, TM; Forsman, ZH; Szabo, Z; Lewis, TD; Aeby, GS; Toonen, RJ. 2011. Inter-Specific Coral Chimerism: Genetically Distinct Multicellular Structures Associated with Tissue Loss in Montipora capitata. PLoS One 6. | 2011 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species; Pathogens | |
| Ahrenholz, D. W. and J. A. Morris. 2010. Larval duration of the lionfish, Pterois volitans along the Bahamian Archipelago. Environmental Biology of Fishes 88:305-309. | 2010 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Caribbean | Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Banks, S. C., S. D. Ling, C. R. Johnson, M. P. Piggott, J. E. Williamson, and L. B. Beheregaray. 2010. Genetic structure of a recent climate change-driven range extension. Molecular Ecology 19:2011-2024. | 2010 | Global; Australia | Model | Climate; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Sea Temperatures; Sea Urchins |
| Barbour, A. B., M. L. Montgomery, A. A. Adamson, E. Diaz-Ferguson, and B. R. Silliman. 2010. Mangrove use by the invasive lionfish Pterois volitans. Marine Ecology Progress Series 401:291-294. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas | Complex Habitat & Resources; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves | |
| Breves-Ramos, A., A. O. R. Junqueira, H. P. Lavrado, S. H. G. Silva, and M. A. G. Ferreira-Silva. 2010. Population structure of the invasive bivalve Isognomon bicolor on rocky shores of Rio de Janeiro State (Brazil). Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 90:453-459. | 2010 | Bivalves; Invasive Species; Molluscs | ||
| Concepcion, G. T., S. E. Kahng, M. W. Crepeau, E. C. Franklin, S. L. Coles, and R. J. Toonen. 2010. Resolving natural ranges and marine invasions in a globally distributed octocoral (genus Carijoa). Marine Ecology Progress Series 401:113-127. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Pacific Ocean; Caribbean | Invasive Species; Octocoral; Ports & Harbors | |
| Cook, E. J., R. Shucksmith, H. Orr, G. V. Ashton, and J. Berge. 2010. Fatty acid composition as a dietary indicator of the invasive caprellid, Caprella mutica (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Marine Biology 157:19-27. | 2010 | Global; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Algae; Aquaculture; Artificial Habitat; Invasive Species |
| David, G. K., D. J. Marshall, and C. Riginos. 2010. Latitudinal variability in spatial genetic structure in the invasive ascidian, Styela plicata. Marine Biology 157:1955-1965. | 2010 | Australia | Invasive Species; Plankton; Sea Temperatures | |
| Fautin, D., P. Dalton, L. S. Incze, J. A. C. Leong, C. Pautzke, A. Rosenberg, P. Sandifer, G. Sedberry, J. W. Tunnell, I. Abbott, R. E. Brainard, M. Brodeur, L. G. Eldredge, M. Feldman, F. Moretzsohn, P. S. Vroom, M. Wainstein, and N. Wolff. 2010. An Overview of Marine Biodiversity in United States Waters. PLoS One 5:e11914. | 2010 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Banks, Credit, & Securities; CO2; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Goddard, J. H. R. and M. S. Love. 2010. Megabenthic Invertebrates On Shell Mounds Associated With Oil And Gas Platforms Off California. Bulletin of Marine Science 86:533-554. | 2010 | Anemones & Zooanthids; Echinoderms; Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Oil & Gas Rigs; Sea Urchins; Seastars | ||
| Harrison, P. A. 2010. Ecosystem services and biodiversity conservation: an introduction to the RUBICODE project. Biodiversity and Conservation 19:2767-2772. | 2010 | Climate; Invasive Species; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Hassan, H. M., M. A. Khanfar, A. Y. Elnagar, R. Mohammed, L. A. Shaala, D. T. A. Youssef, M. S. Hifnawy, and K. A. El Sayed. 2010. Pachycladins A-E, Prostate Cancer Invasion and Migration Inhibitory Eunicellin-Based Diterpenoids from the Red Sea Soft Coral Cladiella pachyclados. Journal of Natural Products 73:848-853. | 2010 | Invasive Species; Octocoral | ||
| Heiman, K. W. and F. Micheli. 2010. Non-native Ecosystem Engineer Alters Estuarine Communities. Integrative And Comparative Biology 50:226-236. | 2010 | Invasive Species; Marine Worms | ||
| Jenkins, A. P., S. D. Jupiter, I. Qauqau, and J. Atherton. 2010. The importance of ecosystem-based management for conserving aquatic migratory pathways on tropical high islands: a case study from Fiji. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20:224-238. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Fiji; Papua New Guinea | GIS & Maps | Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mangroves; Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Johnson, J. E. and D. J. Welch. 2010. Marine Fisheries Management in a Changing Climate: A Review of Vulnerability and Future Options. Reviews in Fisheries Science 18:106-124. | 2010 | Global | Review | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Ocean Acidity; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Lages, B. G., B. G. Fleury, A. C. Pinto, and J. C. Creed. 2010. Chemical defenses against generalist fish predators and fouling organisms in two invasive ahermatypic corals in the genus Tubastraea. Marine Ecology-an Evolutionary Perspective 31:473-482. | 2010 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| LaJeunesse, T. C., R. Smith, M. Walther, J. Pinzon, D. T. Pettay, M. McGinley, M. Aschaffenburg, P. Medina-Rosas, A. L. Cupul-Magana, A. L. Perez, H. Reyes-Bonilla, and M. E. Warner. 2010. Host-symbiont recombination versus natural selection in the response of coral-dinoflagellate symbioses to environmental disturbance. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 277:2925-2934. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Mexico | Anemones & Zooanthids; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| Lapointe, B. E. and B. J. Bedford. 2010. Ecology and nutrition of invasive Caulerpa brachypus f. parvifolia blooms on coral reefs off southeast Florida, USA. Harmful Algae 9:1-12. | 2010 | Florida; Bahamas | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Martin, L. B., W. A. Hopkins, L. D. Mydlarz, and J. R. Rohr. 2010. The effects of anthropogenic global changes on immune functions and disease resistance. Pages 129-148 Year In Ecology And Conservation Biology 2010. | 2010 | Global | Invasive Species; Pathogens; Toxics | |
| Neigel, J. E. 2010. Where are they now? The fates of two genetic lineages in an introduced Hawaiian reef fish. Molecular Ecology 19:1073-1074. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Piscivorous Fish; Plankton | |
| Niggl, W. and C. Wild. 2010. Spatial distribution of the upside-down jellyfish Cassiopea sp. within fringing coral reef environments of the Northern Red Sea: implications for its life cycle. Helgoland Marine Research 64:281-287. | 2010 | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator | Complex Habitat & Resources; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses | |
| Rubinoff, D., B. S. Holland, A. Shibata, R. H. Messing, and M. G. Wright. 2010. Rapid Invasion Despite Lack of Genetic Variation in the Erythrina Gall Wasp (Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim). Pacific Science 64:23-31. | 2010 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Japan; Samoa; Guam; China; Taiwan | Invasive Species | |
| Sheehy, D. J. and S. F. Vik. 2010. The role of constructed reefs in non-indigenous species introductions and range expansions. Ecological Engineering 36:1-11. | 2010 | South & Central America; Mexico | Review | Artificial Habitat; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Skeletal Coral |
| Steiner, S. C. C. and D. A. Willette. 2010. Distribution and size of benthic marine habitats in Dominica, Lesser Antilles. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:589-602. | 2010 | Antilles | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Ports & Harbors; Seagrasses |
| Steiner, S. C. C., K. J. Macfarlane, L. M. Price, and D. A. Willette. 2010. The distribution of seagrasses in Dominica, Lesser Antilles. Revista de Biologia Tropical 58:89-98. | 2010 | Antilles | Invasive Species; Seagrasses; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Wanless, R. M., S. Scott, W. H. H. Sauer, T. G. Andrew, J. P. Glass, B. Godfrey, C. Griffiths, and E. Yeld. 2010. Semi-submersible rigs: a vector transporting entire marine communities around the world. Biological Invasions 12:2573-2583. | 2010 | Fish; Invasive Species; Oil & Gas Rigs | ||
| Zabin, C. J., R. Obernolte, J. A. Mackie, J. Gentry, L. Harris, and J. Geller. 2010. A non-native bryozoan creates novel substrate on the mudflats in San Francisco Bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 412:129-139. | 2010 | Algae; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Substrate | ||
| Avila, E. and J. L. Carballo. 2009. A preliminary assessment of the invasiveness of the Indo-Pacific sponge Chalinula nematifera on coral communities from the tropical Eastern Pacific. Biological Invasions 11:257-264. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring | Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Sponges; Stony Coral |
| Belmaker, J., E. Brokovich, V. China, D. Golani, and M. Kifawi. 2009. Estimating the rate of biological introductions: Lessepsian fishes in the Mediterranean. Ecology 90:1134-1141. | 2009 | Model | Invasive Species | |
| Briggs, J. C. 2009. Atlantic coral reefs: the transplantation alternative. Biological Invasions 11:1845-1854. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species | |
| Bromage, E., L. Carpenter, S. Kaattari, and M. Patterson. 2009. Quantification of coral heat shock proteins from individual coral polyps. Marine Ecology Progress Series 376:123-132. | 2009 | Invasive Species; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Brudvig, L. A., E. I. Damschen, J. J. Tewksbury, N. M. Haddad, and D. J. Levey. 2009. Landscape connectivity promotes plant biodiversity spillover into non-target habitats. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106:9328-9332. | 2009 | Fishing Sector; Invasive Species | ||
| Bruschetti, M., C. Bazterrica, T. Luppi, and O. Iribarne. 2009. An invasive intertidal reef-forming polychaete affect habitat use and feeding behavior of migratory and locals birds in a SW Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 375:76-83. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring | Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Marine Worms; Sediment |
| Bulleri, F., L. Tamburello, and L. Benedetti-Cecchi. 2009. Loss of consumers alters the effects of resident assemblages on the local spread of an introduced macroalga. Oikos 118:269-279. | 2009 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Sea Urchins | ||
| Conklin, K. Y., A. Kurihara, and A. R. Sherwood. 2009. A molecular method for identification of the morphologically plastic invasive algal genera Eucheuma and Kappaphycus (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales) in Hawaii. Journal of Applied Phycology 9-Jan. | 2009 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Invasive Species |
| Dafforn, K. A., E. L. Johnston, and T. M. Glasby. 2009. Shallow moving structures promote marine invader dominance. Biofouling 25:277-287. | 2009 | Global | Invasive Species; Invertebrates | |
| Darling, J. A., A. Kuenzi, and A. M. Reitzel. 2009. Human-mediated transport determines the non-native distribution of the anemone Nematostella vectensis, a dispersal-limited estuarine invertebrate. Marine Ecology Progress Series 380:137-146. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Anemones & Zooanthids; Invasive Species | |
| Farrapeira, C. M. R. 2009. Barnacles (Crustacea: Cirripedia) of the estuarine and marine areas of the port of Recife (Pernambuco, Brazil). Cahiers de Biologie Marine 50:119-129. | 2009 | Invasive Species | ||
| Freshwater, D. W., A. Hines, S. Parham, A. Wilbur, M. Sabaoun, J. Woodhead, L. Akins, B. Purdy, P. E. Whitfield, and C. B. Paris. 2009. Mitochondrial control region sequence analyses indicate dispersal from the US East Coast as the source of the invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans in the Bahamas. Marine Biology 156:1213-1221. | 2009 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Indonesia; Philippines | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Garrone-Neto, D. and I. Sazima. 2009. The more stirring the better: cichlid fishes associate with foraging potamotrygonid rays. Neotropical Ichthyology 7:499-501. | 2009 | Invasive Species; Sediment; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Getter, K. L., D. B. Rowe, and B. M. Cregg. 2009. Solar radiation intensity influences extensive green roof plant communities. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening 8:269-281. | 2009 | Invasive Species; Light; Substrate | ||
| Hayden, T. A. and J. G. Miner. 2009. Rapid dispersal and establishment of a benthic Ponto-Caspian goby in Lake Erie: diel vertical migration of early juvenile round goby. Biological Invasions 11:1767-1776. | 2009 | Fish; Invasive Species; Molluscs; Plankton; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Hoffmann, B. D. and A. Kay. 2009. Pisonia grandis monocultures limit the spread of an invasive ant-a case of carbohydrate quality? Biological Invasions 11:1403-1410. | 2009 | Australia | Invasive Species | |
| Keller, B. D., D. F. Gleason, E. McLeod, C. M. Woodley, S. Airame, B. D. Causey, A. M. Friedlander, R. Grober-Dunsmore, J. E. Johnson, S. L. Miller, and R. S. Steneck. 2009. Climate Change, Coral Reef Ecosystems, and Management Options for Marine Protected Areas. Environmental Management 44:1069-1088. | 2009 | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Water Depth & Sea Level | ||
| Kingsford, R. T., J. E. M. Watson, C. J. Lundquist, O. Venter, L. Hughes, E. L. Johnston, J. Atherton, M. Gawel, D. A. Keith, B. G. Mackey, C. Morley, H. P. Possingham, B. Raynor, H. F. Recher, and K. A. Wilson. 2009. Major Conservation Policy Issues for Biodiversity in Oceania. Conservation Biology 23:834-840. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Micronesia | Review | Climate; Invasive Species; Pathogens |
| Kotiluoto, R., K. Ruokolainen, and M. Kettunen. 2009. Invasive Acacia auriculiformis Benth. in different habitats in Unguja, Zanzibar. African Journal of Ecology 47:77-86. | 2009 | Tanzania | Invasive Species | |
| Lajeunesse, T. C., W. Loh, and R. K. Trench. 2009. Do introduced endosymbiotic dinoflagellates 'take' to new hosts? Biological Invasions 11:995-1003. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| Larpov, K. A., N. J. Kogut, and J. J. Geibel. 2009. Estimating Fish Length From Vertical Morphometric Parameters. California Fish and Game 95:161-174. | 2009 | China | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species |
| Makarow, M., R. Ceulemans, and L. Horn. 2009. Science Policy Briefing: Impacts of Ocean Acidification. 37, European Science Foundation, France. | 2009 | Global; Europe | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; CO2; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Ocean Acidity |
| Messing, R. H., S. Noser, and J. Hunkeler. 2009. Using host plant relationships to help determine origins of the invasive Erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Biological Invasions 11:2233-2241. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Somalia; Mozambique; South Africa | Index or Indicator | Invasive Species |
| Morris, J. A. and J. L. Akins. 2009. Feeding ecology of invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans) in the Bahamian archipelago. Environmental Biology of Fishes 86:389-398. | 2009 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Index or Indicator | Fish; Invasive Species; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Naumann, M. S., W. Niggl, C. Laforsch, C. Glaser, and C. Wild. 2009. Coral surface area quantification-evaluation of established techniques by comparison with computer tomography. Coral Reefs 28:109-117. | 2009 | Invasive Species; Stony Coral | ||
| Nelson, S. G., E. P. Glenn, D. Moore, and B. Ambrose. 2009. Growth and Distribution of the Macroalgae Gracilaria salicornia and G-parvispora (Rhodophyta) Established from Aquaculture Introductions at Moloka'i, Hawai'i. Pacific Science 63:383-396. | 2009 | Algae; Aquaculture; Invasive Species; Nutrients | ||
| Phillips, J. A. 2009. Reproductive ecology of Caulerpa taxifolia (Caulerpaceae, Bryopsidales) in subtropical eastern Australia. European Journal of Phycology 44:81-88. | 2009 | Australia | Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species | |
| Riegl, B., A. Bruckner, S. L. Coles, P. Renaud, and R. E. Dodge. 2009. Coral Reefs Threats and Conservation in an Era of Global Change. Pages 136-186 Year In Ecology And Conservation Biology 2009. | 2009 | Global; Florida | Climate; CO2; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Riegl, B., A. Bruckner, S. L. Coles, P. Renaud, and R. E. Dodge. 2009. Coral reefs: threats and conservation in an era of global change. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1162:136-186. | 2009 | Global; Florida | Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Pathogens; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Rius, M., X. Turon, and D. J. Marshall. 2009. Non-lethal effects of an invasive species in the marine environment: the importance of early life-history stages. Oecologia 159:873-882. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Invasive Species; Invertebrates | |
| Sand, P. H. 2009. Diego Garcia: British-American legal black hole in the Indian ocean? Journal of Environmental Law 21:113-137. | 2009 | Global; Indian Ocean; Chagos Archipelago; India | Climate; Housing; Invasive Species; Military; Ocean Acidity | |
| Shertzer, K. W., E. H. Williams, and J. C. Taylor. 2009. Spatial structure and temporal patterns in a large marine ecosystem: Exploited reef fishes of the southeast United States. Fisheries Research 100:126-133. | 2009 | Florida | Climate; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Shucksmith, R., E. J. Cook, D. J. Hughes, and M. T. Burrows. 2009. Competition between the non-native amphipod Caprella mutica and two native species of caprellids Pseudoprotella phasma and Caprella linearis. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 89:1125-1132. | 2009 | Lab Study | Artificial Habitat; Invasive Species | |
| Stout, J. C. and C. L. Morales. 2009. Ecological impacts of invasive alien species on bees. Apidologie 40:388-409. | 2009 | Review | Invasive Species; Pathogens | |
| Strain, E. M. A. and C. R. Johnson. 2009. Competition between an invasive urchin and commercially fished abalone: Effect on body condition, reproduction and survivorship. Marine Ecology Progress Series 377:169-182. | 2009 | Australia | Algae; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species | |
| Vargas-Angel, B., L. S. Godwin, J. Asher, and R. E. Brainard. 2009. Invasive didemnid tunicate spreading across coral reefs at remote Swains Island, American SÄautmoa. Coral Reefs 28:53-53. | 2009 | Invasive Species; Tunicates | ||
| Vermeij, M. J. A., M. L. Dailer, and C. M. Smith. 2009. Nutrient enrichment promotes survival and dispersal of drifting fragments in an invasive tropical macroalga. Coral Reefs 7-Jan. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Vermeij, M. J. A., T. B. Smith, M. L. Dailer, and C. M. Smith. 2009. Release from native herbivores facilitates the persistence of invasive marine algae: a biogeographical comparison of the relative contribution of nutrients and herbivory to invasion success. Biological Invasions 11:1463-1474. | 2009 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Caribbean | Algae; Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Vignon, M. 2009. Biological introductions and parasites in coral reefs ecosystems: risk and consequences - Fish introduction into the Hawaiian archipelago. Cybium 33:192-192. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Wagner, D., S. E. Kahng, and R. J. Toonen. 2009. Observations on the life history and feeding ecology of a specialized nudibranch predator (Phyllodesmium poindimiei), with implications for biocontrol of an invasive octocoral (Carijoa riisei) in Hawaii. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 372:64-74. | 2009 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Octocoral; Sponges | |
| Wilson Freshwater, D., A. Hines, S. Parham, A. Wilbur, M. Sabaoun, J. Woodhead, L. Akins, B. Purdy, P. E. Whitfield, and C. B. Paris. 2009. Mitochondrial control region sequence analyses indicate dispersal from the US East Coast as the source of the invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans in the Bahamas. Marine Biology 156:1213-1221. | 2009 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Indonesia; Philippines | Model | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Wilson, S. B., G. W. Knox, K. L. Muller, R. Freyre, and Z. Deng. 2009. Seed Production and Viability of Eight Porterweed Selections Grown in Northern and Southern Florida. HortScience 44:1842-1849. | 2009 | Florida; Jamaica | Invasive Species | |
| Zajicek, P., S. Hardin, and C. Watson. 2009. A Florida marine ornamental pathway risk analysis. Reviews in Fisheries Science 17:156-169. | 2009 | Global; Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Review | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Fish; Invasive Species; Stony Coral; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Albins, M. A. and M. A. Hixon. 2008. Invasive Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans reduce recruitment of Atlantic coral-reef fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 367:233-238. | 2008 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Bahamas; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invasive Species |
| Briggs, J. C. 2008. Atlantic coral reefs: the transplantation alternative. Biological Invasions 10-Jan. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species | |
| Bruschetti, M., T. Luppi, E. Fanjul, A. Rosenthal, and O. Iribarne. 2008. Grazing effect of the invasive reef-forming polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus (Fauvel) on phytoplankton biomass in a SW Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 354:212-219. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Plankton; Primary Production; Seawater Flow | |
| Bulleri, F. and L. Benedetti-Cecchi. 2008. Facilitation of the introduced green alga Caulerpa racemosa by resident algal turfs: Experimental evaluation of underlying mechanisms. Marine Ecology Progress Series 364:77-86. | 2008 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Sediment | ||
| Burger, M. A. A., A. C. Barnes, and R. D. Adlard. 2008. Wildlife as reservoirs for parasites infecting commercial species: Host specificity and a redescription of Kudoa amamiensis from teleost fish in Australia. Journal of Fish Diseases 31:835-844. | 2008 | Australia; Japan | Aquaculture; Fish; Invasive Species; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Fleury, B. G., B. G. Lages, J. P. Barbosa, C. R. Kaiser, and A. C. Pinto. 2008. New hemiketal steroid from the introduced soft coral Chromonephthea braziliensis is a chemical defense against predatory fishes. Journal of Chemical Ecology 34:987-993. | 2008 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Octocoral | |
| Granek, E. F., E. M. P. Madin, M. A. Brown, W. Figueira, D. S. Cameron, Z. Hogan, G. Kristianson, P. De Villiers, J. E. Williams, J. Post, S. Zahn, and R. Arlinghaus. 2008. Engaging recreational fishers in management and conservation: Global case studies. Conservation Biology 22:1125-1134. | 2008 | Global; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hall-Spencer, J. M., R. Rodolfo-Metalpa, S. Martin, E. Ransome, M. Fine, S. M. Turner, S. J. Rowley, D. Tedesco, and M.-C. Buia. 2008. Volcanic carbon dioxide vents show ecosystem effects of ocean acidification. Nature 454:96-99. | 2008 | CO2; Invasive Species; Ocean Acidity; Sea Urchins; Stony Coral; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Kahng, S. E., Y. Benayahu, D. Wagner, and N. Rothe. 2008. Sexual reproduction in the invasive octocoral Carijoa riisei in Hawaii. Bulletin of Marine Science 82:17-Jan. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species; Octocoral | |
| Kruzic, P., A. Zuljevic, and V. Nikolic. 2008. The highly invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea poses a new threat to the banks of the coral Cladocora caespitosa in the Adriatic Sea. Coral Reefs 27:441. | 2008 | Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species | ||
| Laforsch, C., E. Christoph, C. Glaser, M. Naumann, C. Wild, and W. Niggl. 2008. A precise and non-destructive method to calculate the surface area in living scleractinian corals using X-ray computed tomography and 3D modeling. Coral Reefs 27:811-820. | 2008 | Model | Invasive Species; Stony Coral | |
| Medeiros, A. C., E. Vonallmen, M. Fukada, A. Samuelson, and T. Lau. 2008. Impact of the newly arrived seed-predating beetle Specularius impressithorax (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) in Hawai'i. Pacific Conservation Biology 14:12-Jul. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; China | Invasive Species; Ornamental Jewelry & Art | |
| Messing, R. H., S. Noser, and J. Hunkeler. 2008. Using host plant relationships to help determine origins of the invasive Erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Biological Invasions 9-Jan. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Somalia; Mozambique; South Africa | Index or Indicator | Invasive Species |
| New, T. R. 2008. Insect conservation on islands: Setting the scene and defining the needs. Journal of Insect Conservation 12:197-204. | 2008 | Climate; Invasive Species | ||
| Piola, R. F. and E. L. Johnston. 2008. The potential for translocation of marine species via small-scale disruptions to antifouling surfaces. Biofouling 24:145-155. | 2008 | Australia | Algae; Invasive Species; Marine Protected Areas | |
| Przeslawski, R., S. Ahyong, M. Byrne, G. Worheide, and P. Hutchings. 2008. Beyond corals and fish: The effects of climate change on noncoral benthic invertebrates of tropical reefs. Global Change Biology 14:2773-2795. | 2008 | South & Central America; Australia; Caribbean | Review | Climate; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Salinity; Sediment; Special Use Permitting |
| Radwan, M. M., S. P. Manly, K. A. El Sayed, V. B. Wali, P. W. Sylvester, B. Awate, G. Shah, and S. A. Ross. 2008. Sinulodurins A and B, antiproliferative and anti-invasive diterpenes from the soft coral Sinularia dura. Journal of Natural Products 71:1468-1471. | 2008 | Palau | Invasive Species; Octocoral | |
| Rosenthal, J. H. 2008. Renovascular hypertension - Drug or invasive therapy? [Renovaskulare hypertonie - Medikamentos oder invasiv therapieren?]. Nieren- und Hochdruckkrankheiten 37:158-163. | 2008 | Invasive Species | ||
| Santos, L. N., F. G. Araujo, and D. S. Brotto. 2008. Artificial structures as tools for fish habitat rehabilitation in a neotropical reservoir. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:896-908. | 2008 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species | |
| Stat, M. and R. D. Gates. 2008. Vectored introductions of marine endosymbiotic dinoflagellates into Hawaii. Biological Invasions 10:579-583. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Ballast Discharge; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Stony Coral | |
| Stimson, J. and E. Conklin. 2008. Potential reversal of a phase shift: The rapid decrease in the cover of the invasive green macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa Forssk. on coral reefs in Kane'ohe Bay, Oahu, Hawai'i. Coral Reefs 27:717-726. | 2008 | Algae; Invasive Species; Light; Skeletal Coral | ||
| Tepedino, V. J., B. A. Bradley, and T. L. Griswold. 2008. Might flowers of invasive plants increase native bee carrying capacity? Intimations from Capitol Reef National Park, Utah. Natural Areas Journal 28:44-50. | 2008 | Invasive Species | ||
| Water Environment Servicves. 2008. Three Creeks Restoration. | 2008 | Invasive Species; Littering; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands | ||
| Weijerman, M., R. Most, K. Wong, and S. Beavers. 2008. Attempt to control the invasive red alga Acanthophora spicifera (Rhodophyta: Ceramiales) in a Hawaiian Fishpond: An assessment of removal techiques and management options. Pacific Science 62:517-532. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Fish; Invasive Species; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Work, T.M., G. S. Aeby, J. E. Maragos. 2008. Phase shift from a coral to a corallimorph-dominated reef associated with a shipwreck on Palmyra atoll. PLoS One 3:e2989. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean; Palmyra Atoll | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species | |
| World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Iran; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Zhu, P., Q. Li, and G. Wang. 2008. Unique microbial signatures of the alien Hawaiian marine sponge Suberites zeteki. Microbial Ecology 55:406-414. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Cyanobacteria; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Sponges | |
| Beuck, L., A. Vertino, E. Stepina, M. Karolczak, and O. Pfannkuche. 2007. Skeletal response of Lophelia pertusa (Scleractinia) to bioeroding sponge infestation visualised with micro-computed tomography. Facies 53:157-176. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Boring Sponges; Invasive Species; Sponges; Stony Coral | |
| Bianchi, C. N. 2007. Biodiversity issues for the forthcoming tropical Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 580:21-Jul. | 2007 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Algae; Climate; Invasive Species | |
| Coles, S. L. and H. Bolick. 2007. Invasive introduced sponge Mycale grandis overgrows reef corals in Kane'ohe Bay, O'ahu, Hawai'i. Coral Reefs 26:911. | 2007 | Invasive Species; Sponges | ||
| Creed, J. C. and A. F. De Paula. 2007. Substratum preference during recruitment of two invasive alien corals onto shallow-subtidal tropical rocky shores. Marine Ecology Progress Series 330:101-111. | 2007 | Invasive Species; Stony Coral | ||
| Glasby, T. M., S. D. Connell, M. G. Holloway, and C. L. Hewitt. 2007. Nonindigenous biota on artificial structures: Could habitat creation facilitate biological invasions? Marine Biology 151:887-895. | 2007 | Docks & Marinas; Invasive Species | ||
| Hoare, J. M., S. Pledger, N. J. Nelson, and C. H. Daugherty. 2007. Avoiding aliens: Behavioural plasticity in habitat use enables large, nocturnal geckos to survive Pacific rat invasions. Biological Conservation 136:510-519. | 2007 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species | |
| Janssen, J., J. E. Marsden, C. R. Bronte, D. J. Jude, S. P. Sitar, and F. W. Goetz. 2007. Challenges to deep-water reproduction by lake trout: Pertinence to restoration in Lake Michigan. Journal of Great Lakes Research 33:59-74. | 2007 | Cuba | Invasive Species; Plankton; Primary Production | |
| Johnson, C. E. and T. L. Goulet. 2007. A comparison of photographic analyses used to quantify zooxanthella density and pigment concentrations in Cnidarians. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 353:287-295. | 2007 | Global | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Anemones & Zooanthids; Invasive Species; Zooxanthellae |
| Kahng, S. E. and C. D. Kelley. 2007. Vertical zonation of megabenthic taxa on a deep photosynthetic reef (50-140 m) in the Au'au Channel, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 26:679-687. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Calcareous Macroalgae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Octocoral | |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service, editor. 2007. Native Plants for Coastal Dune Restoration: What, When, and How for Florida. US Department of Agriculture. | 2007 | Florida; Puerto Rico; Australia; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Shoreline Protection | |
| O'Doherty, D. C. and A. R. Sherwood. 2007. Genetic population structure of the Hawaiian alien invasive seaweed Acanthophora spicifera (Rhodophyta) as revealed by DNA sequencing and ISSR analyses. Pacific Science 61:223-233. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Invasive Species | |
| Page, H. M., J. E. Dugan, D. M. Schroeder, M. M. Nishimoto, M. S. Love, and J. C. Hoesterey. 2007. Trophic links and condition of a temperate reef fish: Comparisons among offshore oil platform and natural reef habitats. Marine Ecology Progress Series 344:245-256. | 2007 | Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Oil & Gas Rigs | ||
| Pickering, T. D., P. Skelton, and R. J. Sulu. 2007. Intentional introductions of commercially harvested alien seaweeds. Botanica Marina 50:338-350. | 2007 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Aquaculture; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Relini, G., M. Relini, G. Palandri, S. Merello, and E. Beccornia. 2007. History, ecology and trends for artificial reefs of the Ligurian sea, Italy. Hydrobiologia 580:193-217. | 2007 | Algae; Artificial Habitat; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fleshy Macroalgae; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | ||
| Stimson, J., T. Cunha, and J. Philippoff. 2007. Food preferences and related behavior of the browsing sea urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Linnaeus) and its potential for use as a biological control agent. Marine Biology 151:1761-1772. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Invasive Species; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Wagner, D., S. E. Kahng, and R. J. Toonen. 2007. New report of nudibranch predators of the invasive octocoral Carijoa riisei in the Main Hawaiian Islands. Coral Reefs 26:411. | 2007 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Invasive Species; Octocoral | |
| Bolton, T. F. and W. M. Graham. 2006. Jellyfish on the rocks: Bioinvasion threat of the international trade in aquarium live rock. Biological Invasions 8:651-653. | 2006 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Invasive Species | |
| Coles, S. L., F. L. M. Kandel, P. A. Reath, K. Longenecker, and L. G. Eldredge. 2006. Rapid assessment of nonindigenous marine species on coral reefs in the main Hawaiian islands. Pacific Science 60:483-507. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Lab Study; Model | Algae; Invasive Species; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Davenport, J. and J. L. Davenport. 2006. The impact of tourism and personal leisure transport on coastal environments: A review. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 67:280-292. | 2006 | Cuba | Review | Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Regulations; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Hotel & Food Services; Infrastructure; Invasive Species; Land & Air Transportation; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling |
| Erickson, A. A., V. J. Paul, K. L. Van Alstyne, and L. M. Kwiatkowski. 2006. Palatability of macroalgae that use different types of chemical defenses. Journal of Chemical Ecology 32:1883-1895. | 2006 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Sea Urchins | ||
| Lages, B. G., B. G. Fleury, C. E. L. Ferreira, and R. C. Pereira. 2006. Chemical defense of an exotic coral as invasion strategy. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 328:127-135. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Fish; Invasive Species; Octocoral |
| Lapointe, B. E., B. J. Bedford, and R. Baumberger. 2006. Hurricanes Frances and Jeanne remove blooms of the invasive green alga Caulerpa brachypus forma parvifolia (Harvey) cribb from coral reefs off northern Palm Beach County, Florida. Estuaries and Coasts 29:966-971. | 2006 | Florida; France | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Lewis, J. B. 2006. Biology and Ecology of the Hydrocoral Millepora on Coral Reefs. Advances in Marine Biology 50:Jan-55. | 2006 | Algae; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Corallivorous Fish; Fish; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Pathogens; Petroleum Spills; Plankton; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes; Zooxanthellae | ||
| Li, H.-M., H. Xiao, H. Peng, H.-X. Han, and D.-Y. Xue. 2006. Potential global range expansion of a new invasive species, the erythrina gall wasp, Quadrastichus erythrinae Kim (insecta: Hymenoptera: Eulophidae). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology 54:229-234. | 2006 | Global; South & Central America | Climate; Invasive Species | |
| Obenat, S., E. Spivak, and J. M. Orensanz. 2006. Reproductive biology of the invasive reef-forming serpulid, Ficopomatus enigmaticus, in the Mar Chiquita coastal lagoon, Argentina. Invertebrate Reproduction and Development 49:263-271. | 2006 | Invasive Species; Marine Worms | ||
| Obenat, S., E. Spivak, and L. Garrido. 2006. Life history and reproductive biology of the invasive amphipod Melita palmata (Amphipoda: Melitidae) in the Mar Chiquita coastal lagoon, Argentina. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 86:1381-1387. | 2006 | Invasive Species | ||
| Page, H. M., J. E. Dugan, C. S. Culver, and J. C. Hoesterey. 2006. Exotic invertebrate species on offshore oil platforms. Marine Ecology Progress Series 325:101-107. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Anemones & Zooanthids; Artificial Habitat; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Oil & Gas Rigs | |
| Raniello, R., M. Lorenti, C. Brunet, and M. C. Buia. 2006. Photoacclimation of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea to depth and daylight patterns and a putative new role for siphonaxanthin. Marine Ecology 27:20-30. | 2006 | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Light | ||
| Ritchie, K. B. 2006. Regulation of microbial populations by coral surface mucus and mucus-associated bacteria. Marine Ecology Progress Series 322:14-Jan. | 2006 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Invasive Species; Pathogens; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral | |
| Roseman, E. F., W. W. Taylor, D. B. Hayes, A. L. Jones, and J. T. Francis. 2006. Predation on walleye eggs by fish on reefs in western Lake Erie. Journal of Great Lakes Research 32:415-423. | 2006 | Cuba | Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Ruiz-Carus, R., R. E. Matheson Jr., D. E. Roberts Jr., and P. E. Whitfield. 2006. The western Pacific red lionfish, Pterois volitans (Scorpaenidae), in Florida: Evidence for reproduction and parasitism in the first exotic marine fish established in state waters. Biological Conservation 128:384-390. | 2006 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fish; Invasive Species |
| Chapman, M. G., J. People, and D. Blockley. 2005. Intertidal assemblages associated with natural corallina turf and invasive mussel beds. Biodiversity and Conservation 14:1761-1776. | 2005 | Algae; Invasive Species | ||
| Conklin, E. J. and J. E. Smith. 2005. Abundance and spread of the invasive red algae, Kappaphycus spp., in Kane'ohe Bay, Hawai'i and an experimental assessment of management options. Biological Invasions 7:1029-1039. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Sea Urchins; Small Herbivorous Fish | |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, M. M. Littler, and D. S. Littler. 2005. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: II. Cross-shelf discrimination of nitrogen sources indicates widespread assimilation of sewage nitrogen. Harmful Algae 4:1106-1122. | 2005 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Lapointe, B. E., P. J. Barile, M. M. Littler, D. S. Littler, B. J. Bedford, and C. Gasque. 2005. Macroalgal blooms on southeast Florida coral reefs: I. Nutrient stoichiometry of the invasive green alga Codium isthmocladum in the wider Caribbean indicates nutrient enrichment. Harmful Algae 4:1092-1105. | 2005 | South & Central America; Florida; Caribbean | Algae; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species; Nutrients | |
| Meister, H. S., D. M. Wyanski, J. K. Loefer, S. W. Ross, A. M. Quattrini, and K. J. Sulak. 2005. Further evidence for the invasion and establishment of Pterois volitans (Teleostei: Scorpaenidae) along the Atlantic Coast of the United States. Southeastern Naturalist 4:193-206. | 2005 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Paula, A. F. and J. C. Creed. 2005. Spatial distribution and abundance of nonindigenous coral genus Tubastraea (Cnidaria, Scleractinia) around Ilha Grande, Brazil. Brazilian journal of biology = Revista brasleira de biologia 65:661-673. | 2005 | Invasive Species; Oil & Gas Rigs; Stony Coral | ||
| Work, T. M. and R. A. Rameyer. 2005. Coral Reefs 24:384-390. | 2005 | Samoa; American Samoa | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Zooxanthellae |
| Andrefouet, S., M. Zubia, and C. Payri. 2004. Mapping and biomass estimation of the invasive brown algae Turbinaria ornata (Turner) J. Agardh and Sargassum mangarevense (Grunow) Setchell on heterogeneous Tahitian coral reefs using 4-meter resolution IKONOS satellite data. Coral Reefs 23:26-38. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Pacific Ocean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps; Remote Sensing | Algae; Biotechnology Research & Development; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Seagrasses |
| Avasthi, A. 2004. Releasing Nemo proves a disaster for native fish. New Scientist 183:13. | 2004 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Ballast Discharge; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species | ||
| Bryan, S. E., A. Cook, J. P. Evans, P. W. Colls, M. G. Wells, M. G. Lawrence, J. S. Jell, A. Greig, and R. Leslie. 2004. Pumice rafting and faunal dispersion during 2001-2002 in the Southwest Pacific: Record of a dacitic submarine explosive eruption from Tonga. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 227:135-154. | 2004 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Fiji; Tonga | Model | Algae; Beaches & Nature Parks; Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Stony Coral; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Buddemeier, R. W., J. A. Kleypas, and R. B. Aronson. 2004. Coral reefs & global climate change: potential contributions of climate change to stresses on coral reef ecosystems. | 2004 | Global | Climate; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Pathogens; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Goldberg, J. and C. Wilkinson. 2004. Status of Coral Reefs of the World: 2004. | 2004 | Global | Agriculture; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Seastars; Sediment | |
| Meusnier, I., M. Valero, J. L. Olsen, and W. T. Stam. 2004. Analysis of rDNA ITS1 indels in Caulerpa taxifolia (Chlorophyta) supports a derived, incipient species status for the invasive strain. European Journal of Phycology 39:83-92. | 2004 | Australia; New Caledonia | GIS & Maps | Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species |
| Salgado-Barragan, J., N. Mendez, and A. Toledano-Granados. 2004. Ficopomatus miamiensis (Polychaeta: Serpulidae) and Styela canopus (Ascidiacea: Styelidae), non-native species in Urias estuary, SE Gulf of California, Mexico. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 45:167-173. | 2004 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Panama; Mexico | Ballast Discharge; Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Worms | |
| Schwindt, E., C. G. De Francesco, and O. O. Iribarne. 2004. Individual and reef growth of the invasive reef-building polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus in a south-western Atlantic coastal lagoon. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 84:987-993. | 2004 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Salinity | |
| Schwindt, E., O. O. Iribarne, and F. I. Isla. 2004. Physical effects of an invading reef-building polychaete on an Argentinean estuarine environment. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 59:109-120. | 2004 | Invasive Species; Marine Worms; Seawater Flow; Sediment | ||
| Semmens, B. X., E. R. Buhle, A. K. Salomon, and C. V. Pattengill-Semmens. 2004. A hotspot of non-native marine fishes: Evidence for the aquarium trade as an invasion pathway. Marine Ecology Progress Series 266:239-244. | 2004 | Florida | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Ballast Discharge; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fish; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Social Organizations | |
| Smith, J. E., C. L. Hunter, E. J. Conklin, R. Most, T. Sauvage, C. Squair, and C. M. Smith. 2004. Ecology of the invasive red alga Gracilaria salicornia (Rhodophyta) on O'ahu, Hawai'i. Pacific Science 58:325-343. | 2004 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Algae; Aquaculture; Invasive Species; Salinity; Social Organizations | |
| Stedman, L. 2004. A Unanimous Vote of confidence? Pages 31-32 Water 21. | 2004 | Global | Ballast Discharge; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Invasive Species; Light; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Davidson, K., M. Hamnett, and C. Minato. 2003. The first four years: Hawaii Coral Reef Initiative Research Program. | 2003 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Finfish Harvest; Fish; Invasive Species; Monetary Valuation; Nutrients |
| Kairo, M., B. Ali, O. Cheesman, K. Haysom, and S. Murphy. 2003. Invasive species threats in the caribbean region. CAB International. | 2003 | South & Central America; Antilles; Cuba; Caribbean | Review | Invasive Species; Special Use Permitting |
| Wabnitz, C., M. Taylor, E. Green, and T. Razak. 2003. From Ocean to Aquarium. UNEP-WCMC, Cambridge, UK. | 2003 | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Fish; Invasive Species | ||
| Williams, J. C., G. V. Byrd, and N. B. Konyukhov. 2003. Whiskered Auklets Aethia pygmaea, foxes, humans and how to right a wrong. Marine Ornithology 31:175-180. | 2003 | Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Plankton; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Coles, S. L. and L. G. Eldredge. 2002. Nonindigenous species introductions on Coral Reefs: A need for information. Pacific Science 56:191-209. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Algae; Fishing Sector; Invasive Species |
| Hutchings, P. A., R. W. Hilliard, and S. L. Coles. 2002. Species introductions and potential for marine pest invasions into tropical marine communities, with special reference to the Indo-Pacific. Pacific Science 56:223-233. | 2002 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Panama; Papua New Guinea; Indonesia; Philippines; Caribbean | Ballast Discharge; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Large Ships; Military; Pathogens; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Small Boats | |
| Lambert, G. 2002. Nonindigenous Ascidians in tropical waters. Pacific Science 56:291-298. | 2002 | South & Central America; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Palau; Guam; Caribbean; Mexico | Field Study & Monitoring | Ballast Discharge; Coastal Defense; Docks & Marinas; Invasive Species; Military; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Rigs; Plankton; Ports & Harbors; Salinity |
| Levin, P. S., J. A. Coyer, R. Petrik, and T. P. Good. 2002. Community-wide effects of nonindigenous species on temperate rocky reefs. Ecology 83:3182-3193. | 2002 | England | Field Study & Monitoring | Invasive Species |
| Luppi, T. A. and C. C. Bas. 2002. The role of the invasive polychaete Ficopomatus enigmaticus Fauvel 1923 (Polychaeta: Serpulidae) reefs in the recruitment of Cyrtograpus angulatus Dana 1851 (Brachyura: Grapsidae), in the Mar Chiquita coastal lagoon, Argentina [Rol de los arrecifes del po. Ciencias Marinas 28:319-330. | 2002 | Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms | ||
| Paulay, G., L. Kirkendale, G. Lambert, and C. Meyer. 2002. Anthropogenic biotic interchange in a coral reef ecosystem: A case study from Guam. Pacific Science 56:403-422. | 2002 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Micronesia; Guam | Ballast Discharge; Complex Habitat & Resources; Docks & Marinas; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Invasive Species; Military; Ports & Harbors; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Perrings, C. 2002. Biological invasions in aquatic systems: The economic problem. Bulletin of Marine Science 70:541-552. | 2002 | Model | Invasive Species; Pathogens | |
| Poff, N. L., M. M. Brinson, and J. W. Day. 2002. Aquatic ecosystems & global climate change. | 2002 | Global | Model | Algae; Climate; CO2; Fish; Invasive Species; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Scavia, D., J. C. Field, D. F. Boesch, R. W. Buddemeier, V. Burkett, D. R. Cayan, M. Fogarty, M. A. Harwell, R. W. Howarth, C. Mason, D. J. Reed, T. C. Royer, A. H. Sallenger, and J. G. Titus. 2002. Climate change impacts on U.S. coastal and marine ecosystems. Estuaries 25:149-164. | 2002 | Global | Review | Climate; CO2; Coastal Development; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Sea Temperatures; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Depth & Sea Level; Wetlands |
| Turgeon, D. D., R. G. Asch, B. D. Causey, R. E. Dodge, W. Jaap, K. Banks, J. Delaney, B. D. Keller, R. Speiler, C. A. Matos, J. R. Garcia, E. Diaz, D. Catanzaro, C. S. Rogers, Z. Hillis-Starr, R. Nemeth, M. Taylor, G. P. Schmahl, M. W. Miller, D. A. Gulko, J. E. Maragos, A. M. Friedlander, C. L. Hunter, R. S. Brainard, P. Craig, R. H. Richond, G. Davis, J. Starmer, M. Trianni, P. Houk, C. E. Birkeland, A. Edward, Y. Golbuu, J. Gutierrez, N. Idechong, G. Paulay, A. Tafileichig, and N. V. Velde. 2002. The state of coral reef ecosystems of the United States and Pacific Freely Associated States: 2002. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Ocean Service/National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science, Silver Spring, MD. | 2002 | Global; Florida; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico; US Pacific & Hawaii; Samoa; Guam | Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Climate; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Pathogens; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Whitfield, P. E., T. Gardner, S. P. Vives, M. R. Gilligan, W. R. Courtenay Jr., G. C. Ray, and J. A. Hare. 2002. Biological invasion of the Indo-Pacific lionfish Pterois volitans along the Atlantic coast of North America. Marine Ecology Progress Series 235:289-297. | 2002 | Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Atlantic Ocean; Bermuda | Ballast Discharge; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fish; Invasive Species | |
| Withgott, J. 2002. Invasive species: California tries to rub out the monster of the lagoon. Science 295:2201-2202. | 2002 | Global | Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species | |
| Karhuketo, T. S. and H. J. Puhakka. 2001. Endoscope-guided round window fistula repair. Otology and Neurotology 22:869-873. | 2001 | Australia; Cuba | Review | Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Invasive Species |
| Nlyibigira, E. I. and Z. S. Abdallah. 2001. Distribution and abundance, in maize and sorghum, of lepidopteran stemborers and associated indigenous parasitoids in zanzibar. Insect Science and its Application 21:335-346. | 2001 | Fiji | Invasive Species; Special Use Permitting | |
| Schwindt, E., A. Bortolus, and O. O. Iribarne. 2001. Invasion of a reef-builder polychaete: Direct and indirect impacts on the native benthic community structure. Biological Invasions 3:137-149. | 2001 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | Algae; Bivalves; Invasive Species; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Worms; Sediment | |
| Stimson, J., S. T. Larned, and E. Conklin. 2001. Effects of herbivory, nutrient levels, and introduced algae on the distribution and abundance of the invasive macroalga Dictyosphaeria cavernosa in Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii. Coral Reefs 19:343-357. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Algae; Discharges; Fish; Invasive Species; Nutrients; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Talbot, F. and C. Wilkinson. 2001. Coral reefs, mangroves and seagrasses: a sourcebook for managers. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville (Australia). | 2001 | Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Climate; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Forestry; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation |
| Maragos, J. E. 2000. Hawaiian Islands (U.S.A.). Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 791-812. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Golf Course Operations; Hotel & Food Services; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Military; Pathogens; Recreational Fishing; Scientific Research; Sea Turtles; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Noss, R. F. 2000. High-risk ecosystems as foci for considering biodiversity and ecological integrity in ecological risk assessments. Environmental Science and Policy 3:321-332. | 2000 | Review | Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species | |
| Rao, D. V. S. and F. Al-Yamani. 2000. The Arabian Gulf. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 16-Jan. | 2000 | Indian Ocean; India | Dam Construction & Maintenance; Fish; Invasive Species; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Plankton; Scientific Research; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Walker, D. I. 2000. The Western Australian region. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 691-704. | 2000 | Australia | Invasive Species; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Seagrasses | |
| Haynes, J. M., T. W. Stewart, and G. E. Cook. 1999. Benthic macroinvertebrate communities in southwestern Lake Ontario following invasion of Dreissena: Continuing change. Journal of Great Lakes Research 25:828-838. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Artificial Habitat; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Invertebrates | |
| Smith, C. M. and L. J. Walters. 1999. Fragmentation as a strategy for Caulerpa species: Fates of fragments and implications for management of an invasive weed. Marine Ecology 20:307-319. | 1999 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Aquaculture; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Seagrasses | |
| Stiger, V. and C. E. Payri. 1999. Spatial and seasonal variations in the biological characteristics of two invasive brown algae, turbinaria ornata (turner) j. agardh and sargassum mangarevense (grunow) setchell (sargassaceae, fucales) spreading on the reefs of tahiti (french polynesia). Botanica Marina 42:295-306. | 1999 | Algae; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species | ||
| Mckinney M.L. 1998. Is marine biodiversity at less risk? Evidence and implications. Diversity and Distributions 4:3-8. | 1998 | Invasive Species | ||
| Davis, A. R., D. E. Roberts, and S. P. Cummins. 1997. Rapid invasion of a sponge-dominated deep-reef by Caulerpa scalpelliformis (Chlorophyta) in Botany Bay, New South Wales. Austral Ecology 22:146-150. | 1997 | Model | Complex Habitat & Resources; Fleshy Macroalgae; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Sponges | |
| Fukuda, T. 1996. What does the red-tiled roof mean? The conservation movement in the historic district of Taketomi Island, Okinawa. Geographical Review of Japan, Series A 69:727-743. | 1996 | Japan | Building & Home Construction; Cultural Protections; Housing; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Military; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Smith, J. M. B. 1996. Notes on coral-trees (Erythrina) in Australia with particular reference to E. crista-galli L. in New South Wales. Australian Geographical Studies 34:225-236. | 1996 | South & Central America; Australia | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Beaches & Nature Parks; Invasive Species | |
| Zann, L. P. 1996. The state of the Marine Environment Report for Australia (SOMER): Process, findings and perspectives. Ocean and Coastal Management 33:63-86. | 1996 | Global; Australia | Invasive Species; Littering; Mangroves; Nutrients; Seagrasses; Seastars; Sediment; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Fookes, E. 1995. Development and eustatic control of an Upper Jurassic reef complex (Saint Germain-de-Joux, Eastern France). Facies 33:129-149. | 1995 | France | Invasive Species; Sediment; Skeletal Coral; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Matthews, W. S., A. E. van Wyk, and G. J. Bredenkamp. 1993. Endemic flora of the north-eastern Transvaal Escarpment, South Africa. Biological Conservation 63:83-94. | 1993 | South Africa | Forestry; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Substrate | |
| Fosberg, F. R. 1992. Vegetation of the Society Islands. Pacific Science 46:232-250. | 1992 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Europe | Forestry; Invasive Species; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics | |
| Lubbock, H. R. and N. V. C. Polunin. 1975. Conservation and the tropical marine aquarium trade. Environmental Conservation 2:229-232. | 1975 | South & Central America; Florida; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Kenya; Mauritius; Sri Lanka; Thailand; Saudi Arabia; Japan; Indonesia; Philippines; Taiwan; Caribbean; France; Germany | Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Complex Habitat & Resources; Invasive Species |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Marine Zoning: Utilize Marine Protected Areas for Research and Monitoring | Research and monitoring of marine protected areas determine the degree to which the zones meet goals and objectives for protecting natural resources, as well as human-use patterns, attitudes and compliance. Once data is gathered from within the protected zone it can than be compared to comprable data from outside the protected zone, as a control. It is necessary to compile and review data on use patterns to determine where additional Special-Use Areas would be appropriate. Research in the protected area should be non-invasive. It is important to make the protected area available for external research as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Research and Monitor Wetlands | This management option involves monitoring and research of mangroves, both for biotic and abiotic factors. Some biotic factors include disease, species, invasive species, abundance, age and leaf litter. Important abiotic factors include sedimentation rates, types and causes of turbidity, and soil chemistry. The activity would document changes to the extent of mangrove vegetation by using historical aerial photography and other records. Wetland nutrient and contaminant processing productivity depends on maintaining a balance and not exceeding thresholds. There remain many unknowns in wetland restoration as to optimal capacity and how to achieve this. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; Complex Habitat & Resources; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Variables; Primary Production; Regulating Services; Scientific Research; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Exotic Species Regulations | The release of exotic species is already prohibited in many areas. Often these regulations do not consider exotic species released in ballast water. Regulations on discharge of ship ballast water containing exotic or non-indigenous species is therefore an area for regulatory improvement. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Biological Addition; Boating Regulations; Discharge Limitations; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Invasive Species; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Aquaculture/Mariculture Regulations | This will help determine if there is a need to establish mariculture operations regulations and proceed accordingly. This would help satisfy the commercial demand for fish while taking pressure off of the wild species. Such regulations should consider where, when and what species of mariculture are allowable. The environmental impact mariculture has can vary depending on current, depth and distance to land, making location and even season important. The species being cultured is also an important consideration, especially if they are non-native or different genetically from the local natural population as escapes may occur. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. NEPA. 1998. MARICULTURE DRAFT POLICY AND REGULATION NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION AUTHORITY COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT DIVISION. National Environment & Planning agency. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Designated Uses; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invasive Species; Resource Use Management; Supplemental Feeding |
| Resource Use Management: Prevent Introduction of Invasive Species | Preventing the introduction of invasive species involves public awareness of the invasive species, minimizing modes and prone areas for invasion, and detecting small populations for early eradication. Some common modes of terrestrial transportation include livestock and domestic animals, mowing equipment, and firewood. Clean equipment before transport to a new location. Remove soil from plants, and plant bare-root. Use high grade seed and weed free livestock feeds. Reduce opportunities for invasive plants by keeping native plant populations strong and healthy and seeding in cover crops to reduce barren soil. | Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Ballast Discharge; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Invasive Species; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Manufacturing & Trade; Transportation; Water Transportation | |
| Restoration: Removal of Invasive Algae | Benthic organisms on reefs maintain a delicate balance competing for space. In many areas, the competition between coral and algae has fallen out of balance due to confounding factors. Factors such as decreased herbivorous fish and invertebrates, and invasive algae species have allowed faster growing algae to take over many reefs, often growing into smothering mats that cover and kill coral. In Hawaii, there has been some success physically removing invasive algae such as Kappaphycus using underwater vacuums extended down from barges or volunteer events in shallower areas. | The Nature Conservancy. 2010.Two Million Pounds of Invasive Algae Removed From Maunalua Bay. (not cited) |
Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcareous Macroalgae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Coralline Algae; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Reef Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Zooxanthellae |
| Restoration: Beach Vegatation Restoration | Natural beaches are often host to important costal dune ecosystems. Due to tourism, much of the vegetation that comprises these dune ecosystems may be compromised. The natural vegetation provides an important ecosystem service, with roots providing deep stabilization against physical damage and removal of that sand. Without such vegetation sand and dunes can be completely washed away during hurricanes and other surge events. The dunes themselves offer some protection to nearby inland infrastructure during these same storm events. When the beach past the dunes is for public access it is beneficial to build raised walk-overs over the dune vegetation. This prevents trampling, which leads to dune blowouts. | Natural Resources Conservation Service, editor. 2007. Native Plants for Coastal Dune Restoration: What, When, and How for Florida. US Department of Agriculture. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Culture; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Invasive Species; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Physical Damage; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling |
| Water Quality Management: Pet Waste Cleanup Ordinance & Education | In residential areas, pet waste can contributes to the large amount of nutrients and pathogens that enter the water through stormwater runoff. This is especially useful in regions such as Gu�nica, Puerto Rico where there are a lot of stray dogs. Education for pet-owners and possible ordinance would help decrease harmful pathogens reaching corals through stormwater runoff and reduce eutrophication. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Animal Waste Collection. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Clary, J., Leisenring, M., and Jeray, J. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Pollutant Category Summary: Fecal Indicator Bacteria. Wright Water Engineers. |
Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Domestic Animal Waste; Environmental Education & Outreach; Health; Health Policies; Invasive Species; Landscaping & Household Services; Microorganisms; Nutrients; Pathogens; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Stormwater Management; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Water; Water Resources; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exec. Order No. 13112, Invasive Species, 68 Federal Register 6183 (1990). | Federal agencies are directed to prevent the introduction of invasive species, detect and rapidly respond to control populations of such species in a cost effective and environmentalyy sound manner, accurately monitor invasive species, provide for restoration of native species and habitat conditions, conduct research to prevent introduction and to control invasive species, and promote public education on invasive species and the means to address them. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:No enforcement provisions. Federal agencies are encouraged to prevent the introduction, detect and respond to control, monitor, and conduct research of invasives. Secretary of Interior established an "Invasive Species Council" to address invasive species issues. Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Invasive Species; Political Pressure; Remediation |
| National Park Service Organic Act of 1916, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act was created to start the National Park Service within the Department of Interior for the purpose of promoting and regulating the use of federal areas such as national parks and monuments. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Created the National Park Service to be supervised by a Director. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invasive Species; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
