ReefLink Database

Finance & Insurance
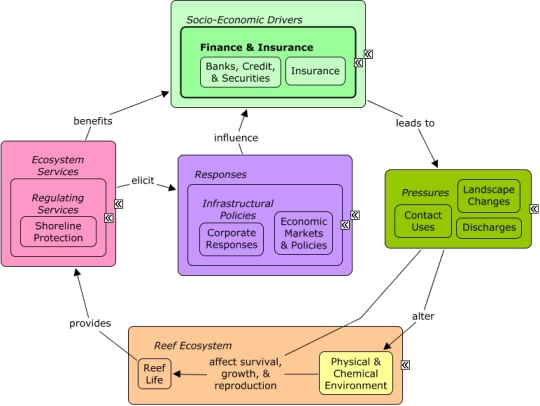
The Finance and Insurance sector is primarily involved in financial transactions and facilitating such financial transactions. This sector includes banks, credit unions, credit card companies, stock brokerages, investment funds, and insurance companies.
CMap
CMap Description
The Finance and Insurance sector can drive coastal development and contribute to landscape changes, including impervious surfaces, which alter rates of pollutant runoff, or to the need for physical changes to the coastline, such as shoreline armoring. Financial centers benefit from shoreline protection, particularly insurance companies, which are concerned with flood damage or erosion that put property and human lives at risk. Financial sectors also benefit indirectly from other ecosystem services that improve the well-being of sectors, such as tourism & recreation, which drive the overall economy. Corporate decisions and economic markets can influence how financial sectors distribute finances and set insurance rates.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011. Coastal Capital Literature Review: Economic Valuation of Coastal and Marine Resources in Jamaica. World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | 2011 | Jamaica | Review; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| 2011. Nonpoint Source Management Program 2010 Annual Report. Document # DEPLW-1205, Maine Department of Environmental Protection, Augusta, (Maine, USA). | 2011 | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Domestic Animal Waste; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Forestry; Housing; Impervious Surfaces; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Ban, NC; Adams, V; Pressey, RL; Hicks, J. 2011. Promise and problems for estimating management costs of marine protected areas. Conservation Letters 4:241-252. | 2011 | Global; Australia | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas |
| Biggs, D. 2011. Understanding Resilience in a Vulnerable Industry: the Case of Reef Tourism in Australia. Ecology and Society 16. | 2011 | Global; Australia | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Hannak, JS; Kompatscher, S; Stachowitsch, M; Herler, J. 2011. Snorkelling and trampling in shallow-water fringing reefs: Risk assessment and proposed management strategy. Journal of Environmental Management 92:2723-2733. | 2011 | Cuba; Egypt | Model; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Sediment; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling |
| Rouphael, AB; Abdulla, A; Said, Y. 2011. A framework for practical and rigorous impact monitoring by field managers of marine protected areas. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment 180:557-572. | 2011 | Australia; Egypt | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Pathogens |
| Ang, F. and S. Van Passel. 2010. The sustainable value approach: a clarifying and constructive comment. Ecological Economics 69:2303-2306. | 2010 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities | |
| Beharry-Borg, N. and R. Scarpa. 2010. Valuing quality changes in Caribbean coastal waters for heterogeneous beach visitors. Ecological Economics 69:1124-1139. | 2010 | South & Central America; Tobago; Caribbean | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Health Policies; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation |
| Bischof, B. G. 2010. Negotiating uncertainty Framing attitudes, prioritizing issues, and finding consensus in the coral reef environment management "crisis". Ocean and Coastal Management 53:597-614. | 2010 | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Mitigation | |
| Cognetti, G. and F. Maltagliati. 2010. Ecosystem service provision: an operational way for marine biodiversity conservation and management. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:1916-1923. | 2010 | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation | |
| Colton, M. A. and S. E. Swearer. 2010. A comparison of two survey methods: differences between underwater visual census and baited remote underwater video. Marine Ecology Progress Series 400:19-36. | 2010 | Australia | Model; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish |
| Fautin, D., P. Dalton, L. S. Incze, J. A. C. Leong, C. Pautzke, A. Rosenberg, P. Sandifer, G. Sedberry, J. W. Tunnell, I. Abbott, R. E. Brainard, M. Brodeur, L. G. Eldredge, M. Feldman, F. Moretzsohn, P. S. Vroom, M. Wainstein, and N. Wolff. 2010. An Overview of Marine Biodiversity in United States Waters. PLoS One 5:e11914. | 2010 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring; Lab Study | Banks, Credit, & Securities; CO2; Coastal Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Invasive Species; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing |
| Kirkby, C. A., R. Giudice-Granados, B. Day, K. Turner, L. M. Velarde- Andrade, A. Duenas-Duenas, J. C. Lara-Rivas, and D. W. Yu. 2010. The Market Triumph of Ecotourism: An Economic Investigation of the Private and Social Benefits of Competing Land Uses in the Peruvian Amazon. PLoS One 5:1-14. | 2010 | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Funding & Incentives; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Ransom, K. P. and S. C. Mangi. 2010. Valuing Recreational Benefits of Coral Reefs: The Case of Mombasa Marine National Park and Reserve, Kenya. Environmental Management 45:145-154. | 2010 | Kenya | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Sarkis, S., P. J. H. VanBeukering, and E. McKenzie, editors. 2010. TOTAL ECONOMIC VALUE OF BERMUDA�S CORAL REEFS: Valuation of Ecosystem Services. Department of Conservation Services, Bermuda. | 2010 | Bermuda | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Uyarra, M. C., J. A. Gill, and I. M. Cote. 2010. Charging for Nature: Marine Park Fees and Management from a User Perspective. Ambio 39:515-523. | 2010 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| van Beukering, P. J. H., S. Sarkis, E. McKenzie, S. Hess, L. Brander, M. Roelfsema, L. Looijenstijn-van der Putten, and T. Bervoets. 2010. Total Economic Value of Bermuda�s Coral Reefs Valuation of Ecosystem Services. | 2010 | Global; South & Central America; Bermuda; Caribbean | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Economic Markets & Policies; Fish; Monetary Valuation; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| van Beukering, P. J. H., S. Sarkis, E. McKenzie, S. Hess, L. Brander, M. Roelfsema, L. Looijenstijn-van der Putten, and T. Bervoets. 2010. Total economic value of bermuda�s coral reefs: valuation of ecosystem services. Van Beukering Consulting, Amsterdam, NL. | 2010 | Bermuda | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Wielgus, J., A. Balmford, T. B. Lewis, C. Mora, and L. R. Gerber. 2010. Coral reef quality and recreation fees in marine protected areas. Conservation Letters 3:38-44. | 2010 | Global; Cuba | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bruce Duguid. 2009. Fasten Your Seat Belt: Airlines and cap-and-trade. CTC764, Carbon Trust, United Kingdom. | 2009 | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Special Use Permitting | ||
| Butardo-Toribio, M. Z., P. M. Alino, and E. S. Guiang. 2009. Cost-Benefit Study of Marine Protected Areas: Implications on Financing and Institutional Needs. Philippine Agricultural Scientist 92:153-169. | 2009 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Fish; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Social Organizations |
| Caras, T. and Z. Pasternak. 2009. Long-term environmental impact of coral mining at the Wakatobi marine park, Indonesia. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:539-544. | 2009 | Indonesia | Algae; Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas; Octocoral; Skeletal Coral; Special Use Permitting; Stony Coral; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Cruz-Trinidad, A., R. C. Geronimo, and P. M. Alino. 2009. Development trajectories and impacts on coral reef use in Lingayen Gulf, Philippines. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:173-180. | 2009 | Philippines | Index or Indicator | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Housing; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Daily, G.C., S. Polasky, J. Goldstein, P.M. Kareiva, H.A. Mooney, L. Pejchar, T.H. Ricketts, J. Salzman, and R. Shallenberger. 2009. Ecosystem services in decision making: time to deliver. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:21-28. | 2009 | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Edwards, P. E. T. 2009. Sustainable financing for ocean and coastal management in Jamaica: The potential for revenues from tourist user fees. Marine Policy 33:376-385. | 2009 | Jamaica | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Greiner, R., L. Patterson, and O. Miller. 2009. Motivations, risk perceptions and adoption of conservation practices by farmers. Agricultural Systems 99:86-104. | 2009 | Australia | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Kareiva, P., editor. 2009. Special Issue of Frontiers in Ecology - focusing on ecosystem services. Issue 1, Volume 7, The Ecological Society of America. | 2009 | Global | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Fish; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Kroon, F. J. and J. Brodie. 2009. Catchment management and health of coastal ecosystems: synthesis and future research. Marine and Freshwater Research 60:1196-1200. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients |
| Leitao, F., M. N. Santos, K. Erzini, and C. C. Monteiro. 2009. Diplodus spp. assemblages on artificial reefs: Importance for near shore fisheries. Fisheries Management and Ecology 16:88-99. | 2009 | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Surface & Groundwater Flow | ||
| Maynard, J. A., J. E. Johnson, P. A. Marshall, C. M. Eakin, G. Goby, H. Schuttenberg, and C. M. Spillman. 2009. A Strategic Framework for Responding to Coral Bleaching Events in a Changing Climate. Environmental Management 11-Jan. | 2009 | Global; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Resource Use Management; Sea Temperatures |
| Muthiga, N. A. 2009. Evaluating the effectiveness of management of the Malindi-Watamu marine protected area complex in Kenya. Ocean and Coastal Management 52:417-423. | 2009 | Kenya; Tanzania; Seychelles | Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Marine Protected Areas |
| Parsons, D. M., M. A. Morrison, A. B. MacDiarmid, B. Stirling, P. Cleaver, I. W. G. Smith, and M. Butcher. 2009. Risks of shifting baselines highlighted by anecdotal accounts of New Zealand's snapper (Pagrus auratus) fishery. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 43:965-983. | 2009 | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish; Fishing Sector; Piscivorous Fish; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Reid-Grant, K. and M. G. Bhat. 2009. Financing marine protected areas in Jamaica: An exploratory study. Marine Policy 33:128-136. | 2009 | South & Central America; Jamaica; Caribbean | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Travel Services & Tour Operators |
| Scheffer, M., J. Bascompte, W. A. Brock, V. Brovkin, S. R. Carpenter, V. Dakos, H. Held, E. H. van Nes, M. Rietkerk, and G. Sugihara. 2009. Early-warning signals for critical transitions. Nature 461:doi:10.1038/ture08227. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate | |
| Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. | 2009 | Southeast Asia; Europe | Review | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Incentives; Special Use Permitting; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Sukhdev, P., editor. 2009. The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity for policy makers: Responsing to the value of nature. Earthscan, Cambridge,(UK). | 2009 | Global; Europe; Germany; Norway | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities |
| Svensson, P., L. D. Rodwell, and M. J. Attrill. 2009. Privately Managed Marine Reserves as a mechanism for the conservation of coral reef ecosystems: A case study from Vietnam. Ambio 38:72-78. | 2009 | Global; Vietnam | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Tallis, H., R. Goldman, M. Uhl, and B. Brosi. 2009. Integrating conservation and development in the field: implementing ecosystem service projects. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 7:12�20. | 2009 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Cochard, R., S. L. Ranamukhaarachchi, G. P. Shivakoti, O. V. Shipin, P. J. Edwards, and K. T. Seeland. 2008. The 2004 tsunami in Aceh and Southern Thailand: A review on coastal ecosystems, wave hazards and vulnerability. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 10:3-40. | 2008 | Thailand | Review; Field Study & Monitoring; Model; Index or Indicator; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Infrastructure; Mangroves; Mitigation; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Daily, G. C. and P. A. Matson. 2008. Ecosystem services: from theory to implementation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 105:9455-9456. | 2008 | GIS & Maps | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives | |
| Gangai, J. W., R. Lenaburg, B. Batten, E. Drei-Horgan, N. Sheffner, D. Hamilton, M. Rezakhani, and P. Shrestha. 2008. Hurricane Flood Insurance study for the Hawaiian Islands. Pages 432-443 in Solutions to Coastal Disasters Congress 2008 - Proceedings of the Solutions to Coastal Disasters Congress 2008. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Model; GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Insurance; Military; Security Policies; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes |
| Lippmann, J. 2008. Review of scuba diving fatalities and decompression illness in Australia. Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine 38:71-78. | 2008 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Cuba | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Internet & Telecommunications; Tourism & Recreation |
| Pierre, S., S. Gaillard, N. Prevot-D'Alvise, J. Aubert, O. Rostaing-Capaillon, D. Leung-Tack, and J.-P. Grillasca. 2008. Grouper aquaculture: Asian success and Mediterranean trials. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18:297-308. | 2008 | Taiwan | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Monetary Valuation; Piscivorous Fish | |
| Teh, L. C. L., L. S. L. Teh, and F. C. Chung. 2008. A private management approach to coral reef conservation in Sabah, Malaysia. Biodiversity and Conservation 17:3061-3077. | 2008 | Malaysia | Field Study & Monitoring | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Hotel & Food Services; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. | 2008 | Global; South & Central America; Iran; Caribbean | Field Study & Monitoring; GIS & Maps | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Invasive Species; Irrigation; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies |
| Jordan, J. W. and S. L. Paulius. 2007. Lessons learned from Hurricane Katrina. Pages 43-58 in Forensic Engineering, Proceedings of the Congress. | 2007 | South & Central America; Mexico | Insurance; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes | |
| Mangi, S. C., C. M. Roberts, and L. D. Rodwell. 2007. Financial comparisons of fishing gear used in Kenya's coral reef lagoons. Ambio 36:671-676. | 2007 | Kenya | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 2007. National Artificial Reef Plan: Guidelines for Siting, Construction, Development, and Assessment of Artificial Reefs. US Department of Commerce. | 2007 | Field Study & Monitoring; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Military; Mitigation; Schools & Colleges | |
| Sumaila, U.R., William W. L. Cheung and Louise The. 2007. Rebuilding Hong Kong's marine fisheries: an evaluation of management options. FCRR 2007, Vol. 15(3), Fisheries Centre, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC. | 2007 | Columbia; China | Agriculture; Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Marine Protected Areas; Piscivorous Fish; Surface & Groundwater Flow | |
| Feyrer, R., U. Kunzmann, and M. Weyand. 2006. Computer-assisted process simulation: A suitable instrument for process optimization in hospitals [Computerunterstutzte prozesssimulation: Ein beitrag zur prozessoptimierung im OP]. Zentralblatt fur Chirurgie 131:347-353. | 2006 | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Medical Centers | ||
| Lan, C.-H. and C.-Y. Hsui. 2006. Insight from complexity: A new approach to designing the deployment of artificial reef communities. Bulletin of Marine Science 78:21-28. | 2006 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Pomeroy, R. S., J. E. Parks, and C. M. Balboa. 2006. Farming the reef: Is aquaculture a solution for reducing fishing pressure on coral reefs? Marine Policy 30:111-130. | 2006 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Live Collection | |
| Capili, E. B., A. C. S. Ibay, and J. R. T. Villarin. 2005. Climate change impacts and adaptation on Philippine coasts. in Proceedings of MTS/IEEE OCEANS, 2005. | 2005 | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Fishing Sector; Pathogens; Plankton; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting | |
| Cho, L. 2005. Marine protected areas: A tool for integrated coastal management in Belize. Ocean and Coastal Management 48:932-947. | 2005 | South & Central America; Belize | Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Protected Areas |
| Chong, Jo. 2005. Protective values of mangrove and coral ecosystems: a review of methods and evidence. IUCN. | 2005 | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Mangroves; Nutrients; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Recreational Opportunities; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation | |
| Clua, E., B. Beliaeff, C. Chauvet, G. David, J. Ferraris, M. Kronen, M. Kulbicki, P. Labrosse, Y. Letourneur, D. Pelletier, O. Thebaud, and M. Leopold. 2005. Towards multidisciplinary indicator dashboards for coral reef fisheries management. Aquatic Living Resource 18:199-213. | 2005 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia | Field Study & Monitoring; Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation |
| McClanahan, T. R., S. Mwaguni, and N. A. Muthiga. 2005. Management of the Kenyan coast. Ocean and Coastal Management 48:901-931. | 2005 | Kenya | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Beaches & Nature Parks; Fishing Sector; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Pendleton, L. H. 2005. Understanding the potential economic impacts of sinking ships for SCUBA recreation. Marine Technology Society Journal 39:47-52. | 2005 | Australia; Cuba; Columbia; Europe | Review | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Monetary Valuation; Non-Monetary Valuation; Social Organizations; Tourism & Recreation |
| Tozzi, I. 2005. The miniate corals of sister Eufrasia Burlamacchi, founder of the monastery of San Domenico in Lucca [I corali miniati di suor Eufrasia Burlamacchi, fondatrice del monastero di San Domenico a Lucca]. Arte Cristiana 93:217-222. | 2005 | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Housing | |
| United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). 2005. Indonesia: preliminary damage and loss assessment, December 26, 2004 Natural Disaster. Technical Report. Consultative Group on Indonesia. | 2005 | Global; Indian Ocean; India; Indonesia | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fishing Sector; Housing; Infrastructure; Military; Mitigation; Skeletal Coral | |
| Uychiaoco, A. J., H. O. Arceo, S. J. Green, M. T. De La Cruz, P. A. Gaite, and P. M. Alino. 2005. Monitoring and evaluation of reef protected areas by local fishers in the Philippines: Tightening the adaptive management cycle. Biodiversity and Conservation 14:2775-2794. | 2005 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Fish; Social Organizations; Stony Coral |
| White, A. T., R.-L. Eisma-Osorio, and S. J. Green. 2005. Integrated coastal management and marine protected areas: Complementarity in the Philippines. Ocean and Coastal Management 48:948-971. | 2005 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Brown, E., E. Cox, P. Jokiel, K. u. Rodgers, W. Smith, B. Tissot, S. L. Coles, and J. Hultquist. 2004. Development of benthic sampling methods for the Coral Reef Assessment and Monitoring Program (CRAMP) in Hawaii. Pacific Science 58:145-158. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Monetary Valuation |
| Cokley, J. and C. Capel. 2004. Remote news delivery down under. Convergence 10:55-72. | 2004 | Australia | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities |
| Tongson, E. and M. Dygico. 2004. User fee system for marine ecotourism: The Tubbataha Reef experience. Coastal Management 32:17-23. | 2004 | Cuba; Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Marine Protected Areas; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Finkl, C. W. and R. H. Charlier. 2003. Sustainability of Subtropical Coastal Zones in Southeastern Florida: Challenges for Urbanized Coastal Environments Threatened by Development, Pollution, Water Supply, and Storm Hazards. Journal of Coastal Research 19:934-943. | 2003 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Cuba | Model | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Chemical Use Regulations; Discharges; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Remediation; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Water; Wetlands |
| Ghina, F. 2003. Sustainable development in small island developing states: The case of the Maldvies. Environment, Development and Sustainability 5:139-165. | 2003 | Indian Ocean; Maldives; India | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Jordaan, J. T. 2003. Bord-and-pillar mining in inclined orebodies. Journal of The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 103:101-110. | 2003 | Banks, Credit, & Securities | ||
| Arin, T. and R. A. Kramer. 2002. Divers' willingness to pay to visit marine sanctuaries: An exploratory study. Ocean and Coastal Management 45:171-183. | 2002 | Philippines | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Monetary Valuation; Tourism & Recreation; Valuation |
| Barker, D. R. 2002. Biodiversity conservation in the wider Caribbean Region. Review of European Community and International Environmental Law 11:74-83. | 2002 | Global; South & Central America; Caribbean | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Mangroves; Seagrasses |
| Courtney, C. A., A. T. White, and E. Deguit. 2002. Building Philippine Local Government capacity for coastal resource management. Coastal Management 30:27-45. | 2002 | Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Resource Use Management | |
| Francis, J., A. Nilsson, and D. Waruinge. 2002. Marine protected areas in the Eastern African Region: How successful are they? Ambio 31:503-511. | 2002 | Kenya; Tanzania; Mozambique; Comoros; Madagascar; Seychelles; Mauritius | Review; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Corporate Responses; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Marine Protected Areas; Special Use Permitting |
| Spurgeon, J. 2002. Valuation of coral reefs: the next 10 years. WorldFish Center Economic Valuation and Policy Priorities for Sustainable Management of Coral Reefs. | 2002 | Index or Indicator; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Monetary Valuation; Resource Use Management; Valuation | |
| Van Heerden, G. M. J. 2002. A critical evaluation of the installation equipment of in-stope rock bolts and the effectiveness thereof in the Merensky stoping areas. Journal of The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy 102:87-92. | 2002 | South Africa | Banks, Credit, & Securities | |
| Whalley, J. and B. Zissimos. 2002. An internalisation-based World Environmental Organisation. World Economy 25:619-642. | 2002 | Global | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Manufacturing & Trade Policies | |
| White, A. T., C. A. Courtney, and A. Salamanca. 2002. Experience with marine protected area planning and management in the Philippines. Coastal Management 30:26-Jan. | 2002 | Philippines | Field Study & Monitoring; Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Fish; Marine Protected Areas |
| Mahon, R. and W. Hunte. 2001. Trap mesh selectivity and the management of reef fishes. Fish and Fisheries 2:356-375. | 2001 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Special Use Permitting |
| Mikkelsen, P. M. and J. Cracraft. 2001. Marine biodiversity and the need for systematic inventories. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:525-534. | 2001 | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Climate; Collaboration & Partnering; Echinoderms; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Worms; Molluscs; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges | |
| Naughton, J. and P. L. Jokiel. 2001. Coral reef mitigation and restoration techniques employed in the Pacific Islands: I. Overview. Pages 306-312 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Review | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Mitigation |
| Petersen, D. and R. Tollrian. 2001. Methods to enhance sexual recruitment for restoration of damaged reefs. Bulletin of Marine Science 69:989-1000. | 2001 | Florida | Lab Study | Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Sediment; Stony Coral |
| Salafsky, N., H. Cauley, G. Balachander, B. Cordes, J. Parks, C. Margoluis, S. Bhatt, C. Encarnacion, D. Russell, and R. Margoluis. 2001. A systematic test of an enterprise strategy for community-based biodiversity conservation. Conservation Biology 15:1585-1595. | 2001 | US Pacific & Hawaii | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Baticados, D. B. and R. F. Agbayani. 2000. Co-management in marine fisheries in Malalison Island, central Philippines. International Journal of Sustainable Development and World Ecology 7:343-355. | 2000 | Southeast Asia; Philippines | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector | |
| Debrot, A. O. and I. Nagelkerken. 2000. User perceptions on coastal resource state and management options in Curacao. Revista de Biologia Tropical 48:95-106. | 2000 | South & Central America; Antilles; Caribbean | Review; Index or Indicator | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Snails & Conch; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation |
| Gell, F. and M. Watson. 2000. UK overseas territories in the northeast Caribbean: Anguilla, British Virgin Islands, Montserrat. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 615-626. | 2000 | South & Central America; US Virgin Islands; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); Antilles; British Virgin Islands; Caribbean; United Kingdom | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Beaches & Nature Parks; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Special Use Permitting; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Gladstone, W. 2000. The ecological and social basis for management of a Red Sea marine-protected area. Ocean and Coastal Management 43:1015-1032. | 2000 | Saudi Arabia | Field Study & Monitoring | Algae; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Military; Seagrasses; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Tourism & Recreation |
| Hardman-Mountford, N. J., K. A. Koranteng, and A. R. G. Price. 2000. The Gulf of Guinea Large Marine Ecosystem. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 773-796. | 2000 | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Fish; Fishing Sector; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Runoff; Salinity; Solid Waste Disposal; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Whales & Dolphins | ||
| Labrosse, P., R. Fichez, R. Farman, and T. Adams. 2000. New Caledonia. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 723-736. | 2000 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; New Caledonia; Europe; France | Agriculture; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Sea Turtles; Special Use Permitting; Valuation | |
| Vazquez, F., R. Rangel, A. M. Quintero-Marmol, J. Fernandez, E. Aguayo, A. Palacio, and V. K. Sharma. 2000. Southern Gulf of Mexico. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 1 467-482. | 2000 | South & Central America; Mexico | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Deforestation & Devegetation; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Seagrasses; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wetlands | |
| Vuki, V. C., S. Appana, M. R. Naqasima, and M. Vuki. 2000. Vanuatu. Seas at the millennium - an environmental evaluation - Volume 2 737-749. | 2000 | Vanuatu | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Beaches & Nature Parks; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Forestry; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies |
| Waldman, M. and Y. Shevah. 2000. Biological diversity - An overview. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 123:299-310. | 2000 | Global | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Beecham, B. 1999. 'Reef jet' and 'Oceania' - debis finances two different designs to service dive cruise markets. Work Boat World 18:53-54. | 1999 | Australia | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products | |
| Hinrichsen, D. 1999. Reefs at risk. Defenders 74:15-Jun. | 1999 | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Storms & Hurricanes | ||
| Windevoxhel, N. J., J. J. Rodriguez, and E. J. Lahmann. 1999. Situation of integrated coastal zone management in Central America: Experiences of the IUCN wetlands and coastal zone conservation program. Ocean and Coastal Management 42:257-282. | 1999 | South & Central America | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Mangroves; Tourism & Recreation; Wetlands | |
| Bortone, S. A. 1998. Resolving the attraction-production dilemma in artificial reef research: Some Yeas and Nays. Fisheries 23:10-Jun. | 1998 | Model | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector | |
| Chichilnisky, G. and G. Heal. 1998. Economic returns from the biosphere. Nature 391:629-630. | 1998 | China | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Monetary Valuation; Special Use Permitting | |
| Gibson, J., M. McField, and S. Wells. 1998. Coral reef management in Belize: An approach through integrated coastal zone management. Ocean and Coastal Management 39:229-244. | 1998 | South & Central America; Belize | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Finfish Harvest; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Permitting & Zoning; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Kasprzak, R. A. 1998. Use of oil and gas platforms as habitat in Louisiana's artificial reef program. Gulf of Mexico Science 16:37-45. | 1998 | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Defense; Corporate Responses; Finfish Harvest; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Rigs; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting; Utility Policies | ||
| Lewis, AL AN. 1998. National Marine Aquarium, Plymouth. 32:22-23. | 1998 | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Docks & Marinas | ||
| Makoloweka, S. and K. Shurcliff. 1997. Silencing the dynamite fishers. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 6:24-25. | 1997 | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Housing; Resource Use Management | |
| Wells, S. 1997. Protecting a marine wonderland. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 6:14-16. | 1997 | South & Central America; Belize | Banks, Credit, & Securities | |
| White, A. T., V. Barker, and G. Tantrigama. 1997. Using integrated coastal management and economics to conserve coastal tourism resources in sri lanka. Ambio 26:335-344. | 1997 | Sri Lanka | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Beaches & Nature Parks; Tourism & Recreation | |
| World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. | 1997 | Global; Tanzania; Maldives; Fiji; Papua New Guinea; Southeast Asia; Vietnam; Indonesia; Philippines; Germany | Lab Study; GIS & Maps | Apex Fish Predators; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Health Policies; Live Collection; Mangroves; Non-point Source Runoff; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Hooten, A. J. and M. E. Hatziolos. 1995. Sustainable financing mechanisms for coral reef conservation. Proceedings of a workshop, Washington, DC, June 1995. in Sustainable financing mechanisms for coral reef conservation. Proceedings of a workshop, Washington, DC, June 1995. | 1995 | Global | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Marine Protected Areas | |
| United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). 1995. Collection of Tourism Expenditure Statistics. Technical Manual No. 2. | 1995 | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| Worthington, D. G., A. J. Fowler, and P. J. Doherty. 1995. Determining the most efficient method of age determination for estimating the age structure of a fish population. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 52:2320-2326. | 1995 | Australia | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish | |
| Ingram, G. B. 1994. Institutional obstacles to conservation: Fergusson Island, Papua New Guinea. Pacific Affairs 67:26-45. | 1994 | Papua New Guinea | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Forestry; Landscape Conservation & Restoration | |
| Zann, L. P. 1994. The status of coral reefs in South Western Pacific Islands. Marine Pollution Bulletin 29:52-61. | 1994 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Fiji; Tonga; Samoa | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Nutrients; Seastars; Sediment | |
| Imbach, A. 1992. 500 years after Columbus. People & the planet / IPPF, UNFPA, IUCN 1:18. | 1992 | South & Central America; Belize; Honduras; Nicaragua; Costa Rica; Panama | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Deforestation & Devegetation; Finfish Harvest; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Pernetta, J. C. 1992. Impacts of climate change and sea level rise on small island states. Global Environmental Change 2:19-31. | 1992 | Global; US Pacific & Hawaii; Australia; Maldives | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Mitchell, B. A. and J. R. Barborak. 1991. Developing coastal park systems in the tropics: planning in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Coastal Management 19:113-134. | 1991 | Global; Turks and Caicos | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Marine Birds; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Whales & Dolphins | |
| Hinrichsen, D. 1989. Coping with pollution in Indonesia. Earthwatch 35:8-Jun. | 1989 | Indonesia | Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Sediment; Special Use Permitting; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Preu, C. 1989. Problems of recent morphodynamics of the Sri Lankan coast [Zur problematik der rezenten morphodynamik an den kusten Sri Lankas]. Erdkundliches Wissen 97:23-42. | 1989 | Sri Lanka | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation | |
| Bell, ME LV IN. 1986. Needs Of Marine Artificial Reef Programs In The United States: A State Manager'S Viewpoint. Pages 552-555 in Oceans Conference Record (IEEE). | 1986 | Artificial Habitat; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Finfish Harvest; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation | ||
| [No author name available]. 1985. Another port for Florida? PORT DEV. INT3:-22. | 1985 | Florida | Agriculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fish; Forestry | |
| Madrid, A. P. 1985. Deep-water hydrocarbon exploration in the Philippines. Energy 10:493-504. | 1985 | Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| Madrid Apollo, P. 1983. Deep-Water Hydrocarbon Exploration In The Philippines. Energy 10:493-504. | 1983 | Philippines | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Funding & Incentives; Water Depth & Sea Level | |
| WEEKS STEVE, G. 1982. Small-Diameter Concentric Tubing Extends Economic Life Of High Water/Sour Gas Edwards Producers. JPT J PET TECHNOL. | 1982 | Field Study & Monitoring | Banks, Credit, & Securities | |
| Dale, G. 1978. Money-in-the-bank: a model for coral reef fish coexistence. Environmental Biology of Fishes 3:103-108. | 1978 | Model | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Fish | |
| Campo, P. C. and T. R. Villanueva. Improving the Triple Bottom line Returns from Small-scale Forestry. | Model; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Collaboration & Partnering; Forestry; Housing; Resource Use Management | ||
| Summary of Economic Valuation Studies and their Policy Relevance for Jamaica. World Resource Institute, Washington, D.C. (USA). | Jamaica | Review | Banks, Credit, & Securities; Monetary Valuation; Valuation |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Phase Out Unwanted Subsidies | Subsidies are often offered to promote certain types of growth and development. At a later time, with changing priorities, it may be determined that these types of growth and development are no longer optimal. For example, sun grown coffee, was subsidized in Guancia Bay, PR, as it was expected to have higher future market demand. However, it requires clearing large tracts of land on steep, extremely erodible clay soils. This leads to high volumes of erosion because there is no vegetation to anchor the soil in place. Now these subsidies are promoting sun grown coffee even though shade grown is better for the land and reefs because it reduces erosion, extreme runoff, and adds vegetation to the land. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Banks, Credit, & Securities; City Planning; Corporate Responses; Decision Support; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Landuse Management; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies |
| Corporate Response: Standardized Environmental Certifications and Labels | Product labeling initiatives are based on the premise that product information represented by or contained on the label is otherwise not readily available (or apparent) and is of value in consumer purchase decisions. For example, warning labels highlight product safety and toxic exposure hazards and advise consumers on ways to minimize risks. Likewise, a number of environmental certification programs (ECPs) identify products' environmental burdens and/or set standards for products' environmental attributes. Properly designed environmental labeling efforts can change consumer and manufacturer attitudes and behaviors, thus reducing environmental burdens. The specific metrics used to measure environmental label effectiveness include: 1) consumer awareness of labels, 2) consumer acceptance of labels (credibility and understanding), 3) changes in consumer behavior, 4) changes in manufacturer behavior, and 5) improvement of end goals, such as environmental quality. | Malcohn, E., Bentham Paulos, Andrew Stoeckle, Herbert Han-Pu Wang, and Julie Lynch. Determinants of Effectiveness for Environmental Certification and Labeling Programs. EPA-742-R-94-001, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Climate; CO2; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Forestry; Health; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Birds; Medical Care; Medical Centers; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Resource Use Management; Toxics; Transportation; Utilities; Whales & Dolphins; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Corporate Response: Invest & Co-finance Projects | Investing and co-financing projects that aim to conserve or restore habitats can be an effective means to preserving reef habitats as well as establishing positive working relationships between organizations. Investing in private sector projects will promote desired businesses and business practices, reducing barriers to entry and competitiveness as compared to traditional businesses and business practices to counterbalance advantages from undesired externalities. | World Bank Group. 2008. Biodiversity, Climate Change, and Adaptation. Nature based solutions from the world bank portfolio. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, Washington, DC. |
Aquarium Stock; Banks, Credit, & Securities; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biomedical Research Policies; Collaboration & Partnering; Corporate Responses; Economic Markets & Policies; Finance & Insurance; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Donations; Funding & Incentives; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Shipping Businesses | This option requires the sanctuary to continue to alert shipping businesses about sanctuary regulations. Such regulations may include vessel waste discharge, ATBA, PSSA, etc. The targeted audiences will include importers, exporters, port authorities, commercial fishing companies, ship insurers. This information can be provided to the audience through NOAA nautical charts, trade publications, newsletters, trade shows, and direct mailings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finance & Insurance; Infrastructural Policies; Insurance; Manufacturing & Trade; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Restoration: Land Reclamation Integrating Landslide Treatments | This management option is exercised to prevent down slope movement of earthen materials, including natural soils, and spoil/waste from mining or forestry activities. Extreme caution and planning must be exercised before permitting any personnel, equipment or other machinery into the slide area. An experienced engineer should analyze the stability of the site both before and after alterations are made to evaluate stability. Water Control: sources of water that enter the area can be controlled to keep the material dry, as it is typically more stable when dry. Loading Control: where appropriate, consider removing excess material from upper portions of the slide area to reduce slide mass. Slope Reduction: where practice, use grading to reduce the slope of the slide area. Increasing Internal Strength: consider the impact of removing and recompacting of material at designed levels of moisture and with biotechnical slope stabilization practices. External Restraints: external restraints can be used where slope movements must be limited due to surrounding valued improvements (e.g. structures), where manipulation of the material may not achieve desired improvements. External restraints must be designed to prevent overturning, sliding at or below the base, and bearing failure of the foundation. Vegetative Treatment: deep rooted grasses and shrubs with proven performance in soil bioengineering applications can be planted using selected soil bioengineering or biotechnical slope stabilization techniques appropriate to the site. Transpiration and infiltration should be considered when choosing vegetation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Forestry; Infrastructure; Insurance; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Runoff; Sediment |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|
