ReefLink Database

Improved Technology
Improved technology refers to innovations in the production or distribution activities of factories, transportation, utilities, and other sectors that can lead to healthier, environmentally and economically improved practices that can save energy, resources, and money over time.
CMap
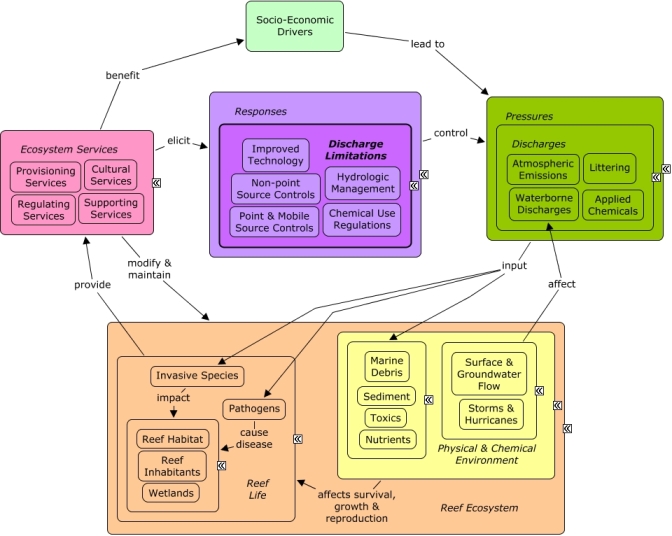
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to implement new or upgraded technology. Examples of environmental technologies range from recycling systems for waste water in industrial processes, to energy efficient car engines, to soil remediation techniques. They are basically any technology that, when compared to other similar technologies, does the same thing - but with less environmental impact. Many of these technologies have great potential to improve the environment, and, at the same time, contribute to economic growth and employment. Many of the same socio-economic sectors that create pollution benefit indirectly from goods and services provided by the reef, which provides recreational opportunities and contributes to the cultural identity of the local community and drives coastal development.Citations
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lapointe, B. E., R. Langton, B. J. Bedford, A. C. Potts, O. Day, and C. M. Hu. 2010. Land-based nutrient enrichment of the Buccoo Reef Complex and fringing coral reefs of Tobago, West Indies. Marine Pollution Bulletin 60:334-343. | 2010 | Tobago | Remote Sensing | Algae; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Plankton; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. | 2008 | Puerto Rico | Review; Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Improved Technology; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Protection; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Kelley Hart. 2006. The upper Neuse Clean Water Iniative Conservation Plan. | 2006 | US East Coast (NC, SC, GA) | GIS & Maps; Decision Support Frameworks & Tools | Agriculture; Drinking Water Supply; Improved Technology; Infrastructure; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Utilities Policies |
| Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. | 2005 | Improved Technology; Nutrients; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Barile, P. J. 2004. Evidence of anthropogenic nitrogen enrichment of the littoral waters of east central Florida. Journal of Coastal Research 20:1237-1245. | 2004 | Florida; US East Coast (NC, SC, GA); India | Index or Indicator | Algae; Discharges; Fleshy Macroalgae; Improved Technology; Marine Worms; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge |
| Kwong, J. and J. Kalani. 2004. Microtunnelling required for ocean outfall beneath coral reefs. Water and Wastewater International 19:12-Nov. | 2004 | US Pacific & Hawaii; Pacific Ocean | Construction Codes & Projects; Improved Technology; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge | |
| Robert Pitt and K. Dunkers. 1993. Lake Water Quality Improvements from Treatment of Stormwater Using the Flow Balancing Method, 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. Anaheim, CA. October 1993.; Detecting Water Quality Trends from Stormwater Discharge Reductions, Engineerin. in 66th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference. | 1993 | Global | Field Study & Monitoring | Agriculture; Algae; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Wastewater Discharge; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Herberts, J. C., M. K. Fries, and A. B. Archer. 1992. Barbados keeps beaches clean and traffic flowing. WATER QUALITY INTERNATIONAL 2:26-27. | 1992 | Beaches & Nature Parks; Improved Technology; Sewage Treatment; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge | ||
| Slocum, DE AN, RI CH AR D Berlandy, and RO BE RT Wardwell. 1986. Facilities Planning In The Caribbean A Case Study. Pages 1351-1357 in [No source information available]. | 1986 | South & Central America; Caribbean | Improved Technology; Sea Turtles; Sewage Treatment; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Bivalve Aquaculture Biofouling Control | These management options reduce, clean or remove biofouling organisms and other waste from bivalve production areas while minimizing environmental risk. Aquaculture shellfish production requires adequate food availability and water of dependable quantity and quality. Aquaculture operations and gear must have a minimal adverse impact on the surrounding water, plant, animal and human resources. Biofouling is detrimental to shellfish production, increasing exposure to pathogens, reducing the available food stuffs, and increasing organic loading. Only environmentally appropriate biofoul control methods should be used, and fouling organisms and algae should be disposed of appropriately to avoid local degradation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. |
Algae; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Improved Technology; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Octopus & Squid; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Snails & Conch; Supplemental Feeding |
| Discharge Controls: Survey and Manage Household Chemical Use | This management option targets household indoor and outdoor chemical use (pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, cleaners, detergents, solvents, etc). Though these chemicals are typically used in small amounts, many make their way into the watershed because of improper use. Before designing a plan to manage these chemicals, data must be gathered from the local community through surveys. An ideal survey would gather information on what chemicals are being used, how they are used, and how they are disposed of. Enforcing proper use and disposal is very difficult, making a strong education program in response to findings from the study essential. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Culture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Housing; Improved Technology; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Shelter; Textiles & Apparel; Toxics |
| Discharge Controls: Point Source Effluent Toxicity Standards | Effluent Toxicity is considered the aggregate toxic effect to aquatic organisms from all pollutants contained in a facility's wastewater (effluent). It is one part of the Water Quality Standards (#22) that prohibits the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts. Numerical criteria can be adopted from the Clean Water Act of based on scientifically-defensible methods. In addition to setting this numerical criteria, enforcement of the standards requires inspection programs and monitoring. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Chemical Variables; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Improved Technology; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Discharge Controls: Air Filtration & Scrubbing | The management option reduces emissions of air contaminants from structures through interception and/or collection. These filters and scrubbers can be implemented on ventilation emitting particulate matter, volatile organic compounds, ammonia, odorous sulfur compounds, methane or other greenhouse gasses. There are many alternative filters and scrubbers depending on the ventilation system and the characteristics of the emissions. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Atmospheric Emissions; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Chemical Variables; Climate Regulation; CO2; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Manufacturing & Trade; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ocean Acidity; Regulating Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Energy Efficiency Initiatives | Energy efficiency is one of the lowest cost strategies for reducing greenhouse gases. Energy efficiency is also one of the few options that actually reduce user costs as well, since using less energy should reduce energy bills. Energy efficiency can be promoted across the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. In the US, the ENERGY STAR program has served as a trusted source of information to help consumers and organizations throughout the nation adopt energy-efficient products and practices. Other ways to incentivize energy improvements include subsidizing (e.g. tax exemption) or issuing lower interest loans for investments in energy use reduction technologies and infrastructure (e.g. more efficient heating/cooling systems). | Environmental Protection Agency. ENERGY STAR and Other Climate Protection Partnerships. 2009 Annual Report. US EPA. |
Atmospheric Emissions; City Planning; Climate Regulation; CO2; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Oil & Gas Industry; Shelter; Utilities; Utility Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Change Salvaging & Towing Practices | This option seeks to protect natural resources and reduce damage resulting from improper vessel salvage methods. In the past, salvage techniques have caused collateral damage when removing vessels grounded on the reef. These injuries often occur in the immediate area surrounding the grounded vessel but can be avoided with the use of proper salvage techniques developed with reef resources in mind. The principal causes of collateral injuries are dragging a vessel off the reef instead of floating it off; the use of steel towing cables that can drop on or drag across the substrate, impacting and dislodging resources (reef structure, corals, and sponges); and propwash and surge, generated by tugboat propellers, that displace sediment and dislodge organisms. To avoid or minimize collateral injuries, a reconnaissance survey should be conducted while the vessel is grounded to evaluate reef resources in the immediate area surrounding the vessel and determine an appropriate extraction route. Bunker fuel and cargo may need to be offloaded. Floating or buoyed towlines should be used instead of steel cables, and towing activities should be conducted at or near high tide to facilitate floating the vessel. Before and during the extraction, global positioning system (GPS) coordinates at the bow and stern of the vessel should be recorded to assist with future injury assessment. GPS tracking should be operating on the grounded vessel during egress from the site and on all salvage vessels or tugboats involved with the salvage operation. The outbound path for vessel extraction may also need to be buoyed, to help avoid or identify injuries that may occur during the salvage operation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Wastewater Management System Standards | This management option involves reducing the amount of pollutants entering groundwater by enforcing existing standards. Inspection and compliance programs for cesspits, Onsite Sewage Treatment and Disposal Systems (OSTDS) and septic tanks are necessary to do this. Municipal sewage treatment plants have a variety of means to meet these standards, including improving management of current treatment systems or upgrading treatment systems with newer technology. Some of these technologies include: Continuous-Flow, Suspended-Growth Aerobic Systems (CFSGAS), Fixed-film, Sequencing batch reactor systems, Stabilization ponds, FWS constructed wetlands, and other aquatic systems (#2), Enhanced nutrient removal: phosphorus & nitrogen, Recirculating sand/media filters and Land treatment systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Center for Watershed Protection. 2004. Illicit Discharge Detection and Elimination. US EPA. US Environmental Protection Agency. 2002. Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual. EPA/625/R-00/008, US EPA. |
Chemical Variables; City Planning; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Control River Volume Using Dams and Resevoirs | Constructing dams and creating reservoirs can have many affects, both positive and negative. Like smaller scale structural stormwater retention (#263), this management option retains groundwater for later controlled release. On this scale, the creation of a reservoir may require flooding of an area behind the dam that had other uses (e.g. agriculture). Proper vegetation can be used in and around the reservoir to incorporate biological filtration (#261). Slowing the release of water into rivers reduces the intensity of flow, reducing channel erosion. However, water should still be released consistently to allow for aquatic habitat to be maintained on the river bottom (#8). Lastly, with the correct infrastructure, a dam can be used as a sustainable hydroelectric energy source. | Morris, G.L., Fan, J. 1998. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. Ver. 1.04 edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY. Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean Air Act, 42 United States Code §§ 7400 et seq. | To ensure Americans have clean air to breath, and to protect the environment from air pollution. Regulates air emmissions from area, stationary and mobile sources. Charges federal land managers with direct responsibility to protect the "air quality and related values" of land under their control. The "related values" include fish and widlife and their habitats. The Clean Air Act is the law that defines EPA's responsibility for protecting and improving the nation's air quality and the stratospheric ozone layer. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act would decrease carbon dioxide emissions from sources in the United States, thereby making a contribution toward reducing ocean acidification, which is one of the problems contributing to coral reef decline. Legislative Actions:Response will differ from State to State because many Sates have been delegated to administer the Clean Air Act. However, States cannot have air quality standards less stringent then the federal standards. State air pollution agencies hold permit hearings and fines industries that violate air quality limits. States must develop state implementation plans that require approval by EPA. Comments:The 1990 amendments authorized the Acid Deposition Control Program, a program to control 189 toxic pollutants, established permit program requirements, expanded and modified the attainment of National Ambient Air Quality Standards, and expanded and modified enforcement authority. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; CO2; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Improved Technology; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Non-Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Transportation Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, "Superfund", 42 United States Code §§ 9601-9675. | Provides Liability, compensation, cleanup, and emergency response for hazardous substances released into the environment. Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Remediation; Waste Management Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Lacey Act, 16 United States Code §§ 3372 et seq. | The Act provides that it is unlawful for any person to import, export, transport, sell, receive, acquire, or purchase any fish or wildlifeor plant taken, possessed, transported, or sold in violation of any law, treaty, or regulation of the United States or in violation of any Indian tribal law whether in interstate or foreign commerce. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act makes possession, selling, transporting, importing, exporting, receiving, acquiring, and purchasing illegal under specific cases. Corals would be included. Legislative Actions:Civil Penalties up to $10,000 per each violation or maximum criminal sanctions of $20,000 in fines and/or up to five years imprisonment. All plants and animals taken in violation of the Act are subject to forfeiture as well as all vessels, vehicles, aircraft, and other equipment used to aid in the importing, exporting, transporting, selling, receiving, acquiring, or purchasing of fish and wildlife or plants in a criminal violation for which a felony conviction is obtained where the owner should have known of the illegal transgression. Comments: |
US Department of Agriculture/Us Border Patrol Jurisdiction: United States |
Aquarium Stock; Coral; Improved Technology; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Transportation Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986, 42 United States Code §§ 9601 et seq. | Reautorized CERCLA Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA/SARA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions:The amended Act stressed the importance of permanent and innovative treatment technologies, required Superfund actions to consider the standards and requirements found in other State and Federal environmental laws, provided new enforcement authorities and settlement tools. Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Waste Management Policies |
