ReefLink Database

Housing
Housing is a subsector of the Shelter Sector. It includes specialty trade construction of single family and multi-unit housing, household products, household retail, and real estate businesses (realtors, appraisers, etc).
CMap
CMap Description
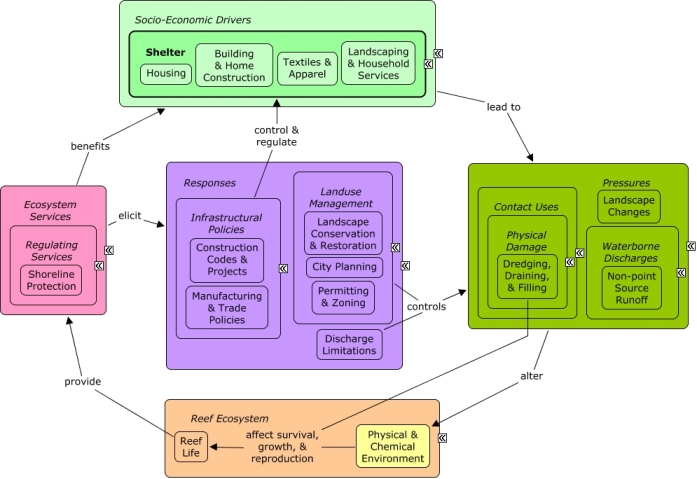
The Shelter Sector creates pressures primarily through activities related to the construction and maintenance of homes and buildings. Landscape changes, including devegetation and soil disturbance can affect rates of non-point source runoff. Maintenance of homes and buildings may also include application of chemicals, such as fertilizers and pesticides, which can run off into coastal waters, altering the levels of sediment, toxics, and nutrients within the physical & chemical environment. In coastal areas, development may require shoreline armoring or dredging activities, which can directly impact coastal vegetation and alter patterns of water flow. Homes and buildings benefit from shoreline protection, as well as indirectly from other ecosystem services that improve the well-being of sectors, such as tourism & recreation, which drive coastal development. City planning can reduce impacts of development by encouraging smart growth or low-impact development, or through use of construction codes, permitting, and zoning. Landscape restoration, such as hydroseeding, may be used to restore areas of significant vegetation loss.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge Controls: Survey and Manage Household Chemical Use | This management option targets household indoor and outdoor chemical use (pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, cleaners, detergents, solvents, etc). Though these chemicals are typically used in small amounts, many make their way into the watershed because of improper use. Before designing a plan to manage these chemicals, data must be gathered from the local community through surveys. An ideal survey would gather information on what chemicals are being used, how they are used, and how they are disposed of. Enforcing proper use and disposal is very difficult, making a strong education program in response to findings from the study essential. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Culture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Housing; Improved Technology; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Shelter; Textiles & Apparel; Toxics |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Energy Efficiency Initiatives | Energy efficiency is one of the lowest cost strategies for reducing greenhouse gases. Energy efficiency is also one of the few options that actually reduce user costs as well, since using less energy should reduce energy bills. Energy efficiency can be promoted across the residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. In the US, the ENERGY STAR program has served as a trusted source of information to help consumers and organizations throughout the nation adopt energy-efficient products and practices. Other ways to incentivize energy improvements include subsidizing (e.g. tax exemption) or issuing lower interest loans for investments in energy use reduction technologies and infrastructure (e.g. more efficient heating/cooling systems). | Environmental Protection Agency. ENERGY STAR and Other Climate Protection Partnerships. 2009 Annual Report. US EPA. |
Atmospheric Emissions; City Planning; Climate Regulation; CO2; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Funding & Incentives; Greenhouse Gas Emissions; Housing; Improved Technology; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Oil & Gas Industry; Shelter; Utilities; Utility Policies; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|
