ReefLink Database

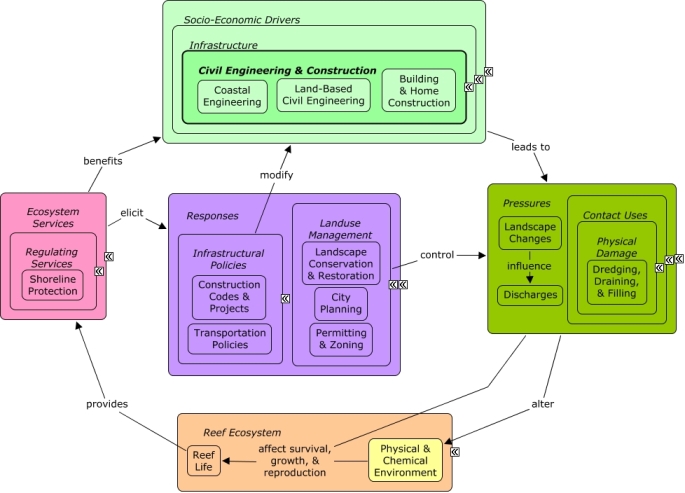
Civil Engineering & Construction
Civil Engineering and Construction specializes in the design and construction of infrastructure, including buildings and homes, roads, utility lines, and ports.
CMap
CMap Description
Civil engineering & construction create pressures primarily through activities related to the construction and maintenance of homes, buildings, roads, ports, harbors, and utility lines. Landscape changes, including devegetation, impervious surfaces, and soil disturbance can affect rates of pollutant runoff. In coastal areas, development may require shoreline armoring or dredging activities, which can directly impact coastal vegetation and alter patterns of water flow. Civil engineering & construction projects and the physical infrastructure they create benefit from shoreline protection, as well as indirectly from other ecosystem services that improve the well-being of sectors, such as tourism & recreation, which drive coastal development. City planning can reduce impacts of development through use of construction codes, permitting, and zoning. Landscape restoration, such as hydroseeding, may be used to reduce runoff along roads or other disturbed areas.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Hydroseeding High Risk Soils | Hydroseeding is a process that creates a slurry of seeds, water, and mulch. This slurry can be applied with the use of trucks, trailers, and even aircrafts. This method is particularly useful because it promotes quick germination and reduces erosion. It is especially beneficial to use this method where there is a vastness of bare soil due to clearing vegetation for roads, homes, and farming. Higher elevations are typically steeper and often experience heavy rainfall, and ultimately an extreme amount of erosion occurs if soil is bare. Erosion from the highlands can fill the reservoirs in the drainage basin with sediment. Using hydroseeding would increase vegetation and ultimately the stabilization of the soil. Also, increased vegetation through hydroseeding would help with infiltration rates because the roots would aerate the soil. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 1999. Temporary Seeding. NRCS Planning and Design Manual. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Reef Life; Sediment |
| Corporate Response: Develop Outreach with Shipping Businesses | This option requires the sanctuary to continue to alert shipping businesses about sanctuary regulations. Such regulations may include vessel waste discharge, ATBA, PSSA, etc. The targeted audiences will include importers, exporters, port authorities, commercial fishing companies, ship insurers. This information can be provided to the audience through NOAA nautical charts, trade publications, newsletters, trade shows, and direct mailings. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finance & Insurance; Infrastructural Policies; Insurance; Manufacturing & Trade; Ports & Harbors; Shipping, Storage, & Warehousing; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Damage Assessment, Documentation & Response: Respond to Natural Resource Injuries from Coastal Construction & Development | This involves assessing coral, seagrass, and hard bottom substrate that is impacted during coastal construction repair or alternation. If unacceptable damages are occurring this information will be useful in future permit decision making. If infringements have occurred, this information may be useful for compensatory mitigation and liability for restoration of those natural resources injured. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Ports & Harbors; Reef Habitat; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Special Use Permitting; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Develop Wayside Exhibits/Signs | Creating wayside exhibits is an easy way to inform the public about sanctuary resources, policies, and boundaries. Wayside exhibits can be signs displayed at popular fishing and recreation areas. Coordination and collaboration among local, state, and federal agencies is essential to ensure there is not duplication in efforts, over-signage, and that consistent information is provided. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Docks & Marinas; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management |
| Discharge Controls: Survey and Manage Household Chemical Use | This management option targets household indoor and outdoor chemical use (pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, cleaners, detergents, solvents, etc). Though these chemicals are typically used in small amounts, many make their way into the watershed because of improper use. Before designing a plan to manage these chemicals, data must be gathered from the local community through surveys. An ideal survey would gather information on what chemicals are being used, how they are used, and how they are disposed of. Enforcing proper use and disposal is very difficult, making a strong education program in response to findings from the study essential. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Culture; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Housing; Improved Technology; Landscaping & Household Services; Non-point Source Controls; Shelter; Textiles & Apparel; Toxics |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig Construction Regulations | The Minerals Management Service (MMS) has several requirements for leasing and permits for construction of new drilling rigs and platforms. Placement is very important so as to not interfere with other uses or the environment. These permits also cover exploratory structures for research and test sites. | Minerals Management Service. 2006. Leasing Oil and Natural Gas Resources. U.S. Department of the Interior. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Oil & Gas Rigs; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Develop Offshore Wind and Hydrokinetic Alternative Energies | Policies encouraging or authorizing construction of offshore facilities are evolving, and there are many sides to the issue of how to best manage them. Alternative energies are desirable and would reduce the dependence on fossil fuel resources. However, hydrokinetic technologies are just becoming viable, meaning long term impacts are still unknown. Facilitative policies reduce barriers for alternative energy development or increase barriers or costs for incumbent technologies. These include research and innovation policies, technology improvement subsidies, market based policies that internalize externalities, and regulatory changes that simplify the permitting process. | Energy Efficiency & Renewable Energy. 2009. Report to Congress on the Potential Environmental Effects of Marine and Hydrokinetic Energy Technologies. Department of Energy. Portman, M.E. 2010. Marine Renewable Energy Policy: Some US and International Perspectices Compared. Oceanography 23:98-105. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Construction Codes & Projects; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Funding & Incentives; Infrastructural Policies; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Seawater Flow; Utilities; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Utility Policies |
| Energy Policy & Development: Oil and Gas Rig End of Life | As oil production at a given offshore site decreases it becomes necessary to decommission the rigs that were drilling them. It is very expensive to dismantle and transport the rigs back to shore. One such well know case was Shell's Brent Spar 1995. Regulations on the end of life for oil rigs differ by country and even state within the US. The Minerals Management Service has a Rigs-to-Reefs program which supports and encourages the reuse of oil and gas structures for offshore artificial reef developments. If these structures are to be sunk as artificial reefs the normal permit requirements for artificial reefs still apply to ensure the structure will not interfere with navigation channels or degrade the environment. | Dauterive, L. 1999. Rigs-to reefs policy, progress, and perspective. Pages 313-318 in SPE/EPA Exploration & Production Environmental Conference. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Chemical Variables; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Services; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Littering; Manufacturing & Trade; Marine Debris; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Oil & Gas Industry; Permitting & Zoning; Petroleum Spills; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Provisioning Services; Solid Waste Disposal; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Management Planning | There are many aspects to properly managing forestry sites to reduce point source and non-point source pollutants. Forestry activities can degrade water quality with several types of pollutants and impacts, including: sediment, nutrients, forest chemicals like pesticides, organic debris from tree litter, increased water temperature and increased streamflow. The Forestry management plan and practices include, but are not limited to: pre-harvest planning, road construction and use, prescribed burning and fire management, brush management, timber harvest, regeneration, and application of forest chemicals. Wetlands Forest Management has additional best practices. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Biological Harvest; Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Streamside Management Areas | There are often surface waters, such as streams and lakes, within forestry areas that require special protection. This management option involves establishing and maintaining management areas (35 to 50 feet) around these surface waters to buffer against changes in temperature, increases in sediments and nutrients, and to provide bank stability. Canopy species in these areas also provide woody debris needed for instream channel structure and aquatic species habitat. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Runoff; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Primary Production; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waterborne Discharges; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Landuse Management: Household Landscaping Best Management Practices | Homeowners manipulate the visible features of the land surrounding their home through landscaping. This includes flora, fauna, and terrain. Best Management Practices (BMPs) for landscaping include selection of indigenous flora and fauna, landscape irrigation (sprinkler systems etc), stormwater runoff BMPs, reducing water use, integrated pest management, composting, and incorporation of permeable surfaces. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Addition; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Discharge Limitations; Environmental Education & Outreach; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Impervious Surfaces; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Sediment; Shelter; Supplemental Feeding; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges |
| Landuse Management: Mine Reclamation | Lands disturbed by mining must be reclaimed to their Approximate Original Contour (AOC). Mine operators must backfill, compact, and grade in order to restore the AOC of the land with all highwalls, spoil piles, and depressions eliminated. Spoil material is prone to erosion, and may carry various disturbed toxics into groundwater if not properly managed. Temporary roads and impervious surfaces may have also been constructed for mining purposes. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement. POSTMINING LAND USE: Exceptions to Approximate Original Contour Requirements for Mountaintop Removal Operations and steep Slope Mining Operations. Washington, DC. |
Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Mining; Mining Policies; Mitigation; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Valuation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Landuse Management: Temporary Road Planning and Construction | This management option involves minimizing sediment discharges from forestry and other temporary roads through their planning and construction. Since these roads are seasonal or temporary, less time and effort is normally invested in construction. Road construction has four main phases, clearing, leveling, construction and surfacing. Construction timing should be targeted to avoid sensitive spawning periods and during low stream flow at water passes. Road surface drainage shaping requires proper moisture content, surfacing, and grading. Drainage should be installed to reduce the volume and velocity of runoff water passing over sensitive areas. Methods for road surface drainage include: broad-based dip construction, pole culverts, ditch relief culverts, road outsloping and grading, ditch and turnout construction. Roadway runoff should be prevented from flowing directly into watercourses by using turnouts, wing ditches and dips. Brush barriers, silt fences, riprap and filter strips can be used to trap sediment in runoff water. Where roads cross streams it is important to guard against erosion, as such erosion may necessitate road repairs. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land & Air Transportation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Transportation; Transportation Policies |
| Marine Zoning: Permitting Application & Award | This management approach is important because permits assure protection and conservation of coral resources from harmful activities and practices. Within sanctuary waters, special use permits (#157) can be used to allow scientists and others to conduct necessary work while following permitting regulations to reduce the impact of that work. General permits are often required for altering land-use, construction projects and certain discharges. To be eligible for a permit, the operator may be required to conduct impact assessments, institute best management practices and conduct monitoring of the project. Though permits are a necessary precaution, the process can be streamlined through ensuring clear submittal requirements, and reducing redundancy. Redundancy often occurs when multiple agencies must approve a permit, a single point of contact and standard, inter-agency protocols can reduce unnecessary redundancy. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Research Historical Hydrology | This activity involves a historical assessment of the hydrology of the surrounding water area around the sanctuary as it has affected water quality and biological communities within the sanctuary. It will clarify the role of freshwater inflows and water quality from local freshwater bodies. Also, this activity will examine the effects of structural modification and changes in quality, quantity, timing and distribution of freshwater releases from existing structures and will examine land-based practices affecting the water quality of runoff. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Physical Variables; Salinity; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Monitor Use Patterns on Artificial and Natural Reefs | This management option seeks to provide data for decisions concerning creating new artificial reefs. Use data is important because justification for artificial reefs extends from their ability to shift use pressures (diving, fishing, etc.) from natural reefs. Once an artificial reef is decided on there is much more data to collect and factors to consider when deciding where the artificial reef (#189). | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Defense; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Military; Museums, Amusement Parks, Historical Sites; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Valuation; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Vessel Grounding Regulations | In many areas, there are already regulations that target prop scarring to seagrasses and the seabed. Current boat grounding regulations should be evaluated to determine if additional regulations would be beneficial. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Development; Contact Uses; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Culture; Decision Support; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Physical Damage; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Dredging Regulations | Dredging is oftentimes prohibited with certain exceptions. Dredging regulation often falls under other controls over the alteration of the seabed, discharging or depositing materials. At times dredging is necessary for navigation or other activities, necessitating .permitting mechanisms for allowing otherwise prohibited activities. Revising the regulations to help eliminate negative dredge-and-fill activities within a certain distance of corals would be beneficial because it would help promote the reestablishment of sensitive benthic communities. Reservoirs may require periodic dredging to remove sediment that may have collected. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beach & Land Formation; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Mining; Mining Policies; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sand & Rock Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Substrate; Transportation; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Water Transportation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Develop Mobile Source Discharge Controls | Pollution discharge controls regulate where different types of discharges are allowed and what acceptable quantities released are. Typically discharge controls target point sources in the form of effluent pipes (#280), but discharges also occur from mobile sources such as boats and ships. There may need to be revisions on where depositing fish, fish parts, bait, cooling water, engine exhaust, deck wash, and effluent can be released. In many areas, these items are often excluded as prohibited, and they should possibly be included. Pollution discharge controls are different from Water Quality Standards (#22) which set acceptable environmental limits and leave it up to the manager to meet those criteria. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Chemical Variables; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Large Ships; Littering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Change Salvaging & Towing Practices | This option seeks to protect natural resources and reduce damage resulting from improper vessel salvage methods. In the past, salvage techniques have caused collateral damage when removing vessels grounded on the reef. These injuries often occur in the immediate area surrounding the grounded vessel but can be avoided with the use of proper salvage techniques developed with reef resources in mind. The principal causes of collateral injuries are dragging a vessel off the reef instead of floating it off; the use of steel towing cables that can drop on or drag across the substrate, impacting and dislodging resources (reef structure, corals, and sponges); and propwash and surge, generated by tugboat propellers, that displace sediment and dislodge organisms. To avoid or minimize collateral injuries, a reconnaissance survey should be conducted while the vessel is grounded to evaluate reef resources in the immediate area surrounding the vessel and determine an appropriate extraction route. Bunker fuel and cargo may need to be offloaded. Floating or buoyed towlines should be used instead of steel cables, and towing activities should be conducted at or near high tide to facilitate floating the vessel. Before and during the extraction, global positioning system (GPS) coordinates at the bow and stern of the vessel should be recorded to assist with future injury assessment. GPS tracking should be operating on the grounded vessel during egress from the site and on all salvage vessels or tugboats involved with the salvage operation. The outbound path for vessel extraction may also need to be buoyed, to help avoid or identify injuries that may occur during the salvage operation. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trampling; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| Resource Use Management: Marine Heritage Resource Protections | This management option involves protecting underwater items/sites that have historical, cultural, archaeological, or paleontological significance. This response advocates permits for action that may degrade the resource. This can be accomplished through creating an MHR field unit, monitoring MHR site degradation, and evaluating excavation and mitigation techniques. Field units can help conduct field research and coordinated, permitted research activities. Experts relating to archaeological research underwater can also be hired with additional funding. Through evaluation of excavation techniques, new technologies can be suggested such as: turbidity screens, sediment removal equipment, and seagrass restoration/relocation protocols to lead to less disturbance. Inventory and decision tools can also be used in the aid of Maritime Heritage Resource protection. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Services; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Mitigation; Physical Damage; Pipelines; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Valuation; Wetlands |
| Restoration: Restore Reef Habitat and Salvage Benthic Inhabitants Injured by Physical Damage | This management approach involves salvaging, maintenance, and re-stabilization or injured resources by management staff and private contractors in order to rescue and provide first aid following physical damage such as vessel groundings. This can be achieved using Reef Medics and other volunteer programs because these groups have experience with vessel navigation and operation, snorkeling, and SCUBA diving. Also, it allows for researchers to collect living coral material when relocation of such organisms is not possible. Salvage and re-stabilization is not limited to the living coral; octocorals, seagrasses, and the non-living framework may all be damaged of destabilized from groundings or other physical impacts. In addition to the habitat's structural integrity, it is important to re-establish aesthetics and ecological functionality. Funds from mitigation and case settlements should be used for this work, as long term costs of restoration and monitoring can be extensive. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Collier, C., Dodge, R., Gilliiam, Gracie, K., Gregg, L., Jaap, W., Mastry, M., and Poulos, N. 2007. Rapid Response and Restoration for coral reef injuries in the southeest Florida. Southeast Florida Coral Reef Initiative. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Coral; Cultural Policies; Cultural Services; Culture; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Octocoral; Physical Damage; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Skeletal Coral; Stony Coral; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Transportation; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that trap or filter impurities out of runoff water. These include but are not limited to, using swales, filter strips, oil/water separators, oil/grit separators, and sand filters. Often structural retrofitting is coupled with biological filters/controls to direct water as desired and to fully reap the benefits of both systems. Structural filters are often incorporated into retention/detention and infiltration systems as well. One disadvantage of structural filters is that they are often higher maintenance as sand and chambers fill and clog with pollutants over time. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Compost Filter System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Median Strip Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Montgomery County Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Off-Line Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Oil/Water Separators. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Organic Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Peat Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Perimeter Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Pocket Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Rockville Water Quality Inlet. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Sediment Basin (Water Quality Enhancement). Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Side-by-Side Infiltration Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Surface Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Sand Filter. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Underground Trench with Oil/Grit Chamber. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Under-the-Swale Infiltration Trench. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Quality Volume (WQV) Storage Tank. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. US EPA. EPA Filtration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Manufactured Products for Stormwater Inlets. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Alum Injection. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2005. Solid/liquid Waste Separation Facility. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of natural structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. These structures are typically characterized as retention ponds and incorporate natural vegetation such as grass. These ponds may be dry, or may drain into nearby wetlands. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Biological Stormwater Filtration | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementing engineering techniques that allow natural processes and plants to act as filters. Such techniques would include using grass parking and turf covered swales. Many of these techniques, such as reversed elevations for planted areas in parking lots, can demonstrate benefits both as natural filters and for the vegetation that are used since it eliminates the need to water them with irrigation systems. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Basic Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Bioretention System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Constructed Wetland. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Filter Strips. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Reversed Elevations System for Parking Lots and Planting Areas. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Riparian Forest Buffer. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Roadway Landscape Treatment System. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Biofiltration Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Pond Design. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Wet Swale. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Water Environment Research Foundation, American Society of Civil Engineers, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Federal Highway Administration, American Public Works Association, editor. 2008. Overview of Performance by BMP Category and Common Pollutant Type. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database [1999-2008]. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Golf Course Operations; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Sustained Reservoir Minimum Release of Minimum Baseflow to Sustain Aquatic Habitat | In some regions, even high intensity rivers (e.g. Rio Loco, Puerto Rico) are seasonal, drying for long enough to kill aquatic vegetation. Creating a constant baseflow would help sustain aquatic life and ultimately help to process nutrients. High intensity rivers are already prone to extreme channel erosion from the high flow rates, this erosion is even greater without any benthic biota to hold sediment on the river bottom. Restricting the release of reservoir water to that required to maintain aquatic biota would reduce the intensity of flow, stabilize the river bottom, create habitat and naturally process nutrients that could potentially contribute to eutrophication out on the coral reef. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Algae; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Pressures; Primary Production; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Regulating Services; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Retention/Detention | This method attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that retain runoff water for further treatment or controlled release. Water collection can be selective, targeting the first flush of water, which is typically the most polluted. Water retention has the additional benefit of later release at a place and time when the water is needed (e.g. for irrigation). Rainwater Collection Systems (#11) can be an important water resource in areas where freshwater is limited. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Detention Devices for Dry/Wet Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Dry Extended Detention Ponds. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2010. Stormwater Runoff Controls. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Water and Sediment Control Basin. CODE 638. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Water Volume Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Structural Stormwater Infiltration | This management option attempts to reduce the negative impacts of stormwater runoff through implementation of engineering structures that control the volume of surface water, facilitating faster absorption of the stormwater into the ground. Often these structures are able to infiltrate larger amounts of water faster while reducing exposure to surface sediments and pollutants. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. Combined Infiltration/Detention Basin. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/23/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Poresky, A., Clary, J., Strecker, E., and Earles, A. 2011. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database. Technical Summary: Volume Reduction. Geosyntec Consultants. US EPA. EPA Infiltration BMPs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. |
Applied Chemicals; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Stormwater Pollution Reduction Through Instituting Preventitive Best Management Practices | This method focuses on reducing the amount of harmful contaminants in stormwater runoff by establishing Best Management Practices that prevent the generation of the pollutant to begin with. These BMPs include educational programs, infrastructure improvements and agricultural BMPs. Examples of educational programs would be programs that educate the public on the importance of, and how to avoid depositing hazardous wastes, such as oil, into storm drains, or how to use landscape management controls to limit the chemical and debris that from enter stormwater runoff from their personal lawns. Infrastructure improvement could include the use of alternative turnarounds and street cleaning. Agricultural practices such as roofs and covers for pesticides and equipment, or use of bedding are both preventative stormwater practices. Some additional specific practices include: controlling fertilizer application, properly using and disposing of fertilizers, pesticides, motor oil, and other harmful chemicals, debris removal, exposure reduction, minimization of pollutants, parking lot cleaning, stormwater catch basin insert, eliminate curbs and gutters, green parking, green roofs, street design and patterns, bedding. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. US EPA. Alternative Turnarounds. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Eliminate Curbs and Gutters. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Parking. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Green Roofs. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. US EPA. Street Design and Patterns. National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Menu of BMPs Accessed 3/25/2011. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/25/2011. Irrigation Association. 2010. Turf and Landscape Irrigation Best Management Practices. |
Agriculture; Applied Chemicals; Chemical Use Regulations; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Environmental Education & Outreach; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Housing; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Mining; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Industry; Road Construction & Maintenance; Security & Public Administration Policies; Shelter; Solid Waste Disposal; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Toxics; Utilities; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Stormwater BMPs: Rainwater Collection Systems | Creating a rainwater collection system (either through policy change or the initiative of homeowners) would help in many ways. These systems would utilize water in an efficient manner. It would reduce the pressure of water as a finite resource. Water would be collected and utilized before it reaches the ground. Once rain falls to the ground, it picks up nutrients, chemicals, and pathogens on the ground and transports them in the form of runoff. Eventually this contaminated stormwater runoff enters water resources through the drainage basin. Collecting a considerable amount of water would prevent contamination of that water, and allow for it to be usable. Also, it would reduce the amount of water that is lost when it is contaminated as runoff. An overall reduced amount of stormwater runoff would reduce the amount of contaminants that would harm corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. Cisterns used for water harvesting. Urban BMP's - Water Runoff Management Accessed 3/18/2011. Leisenring, M., Clary, J., Stephenson, J., and Hobson, P. 2010. International Stormwater Best Management Practices (BMP) Database Pollutant Category Summary: Nutrients. Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Climate; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Energy Policies; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sediment; Shelter; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Utilities Policies; Waterborne Discharges |
| Water Quality Management: Treating Effluent Water Through Wetlands | Additional treatment of sewage is often a necessary management option because secondary treatment alone leaves 20,000 times more nutrients in the water than the safe limit for corals. High concentrations of nutrients in the water leads to eutrophication, and coral reefs are more sensitive to nutrient enrichment than any other coastal system. Wetlands are extremely successful at reducing nitrogen levels in water. Using natural wetlands or "living machines" to perform this task can actually be more cost effective than further sewage treatment. Each successive wetland treatment cell of the series can provide incredible levels of denitrification, and thus protect corals from nutrient enrichment. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2003. Waste Treatment Lagoon. CODE 359. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Primary Production; Security & Public Administration Policies; Sewage Treatment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Water Quality Management: Reduce Pollution & Discharges from Marinas & Live-Aboards | This management option strives to reduce and eliminate the discharge of wastewater and pollution within zones near corals. In many instances, "no-discharge" zones already exist and are simply poorly enforced. In other instances the discharge limits are not stringent enough. Successful regulation requires marinas to be equipped with the proper infrastructure to support transfer of wastewater from vessels to shore-side for treatment. This infrastructure includes: pump-out facilities and mobile pump-out services. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Cyanobacteria; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Health; Health Policies; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Pathogens; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Lagoon Restoration | Many times lagoons/wetlands are filled for urban development, agricultural development, etc. Lagoons/wetlands are a sink for nutrients, sediment, and contaminants. Wetlands close to reef watersheds can be huge contributors to reef health. This is because wetlands intercept surface-water runoff from higher, drier land and retain excess nutrients and pollutants. Also, lagoons are beneficial because they provide habitat for an array of wildlife. Overall, they can greatly reduce the amount nutrient-contaminated water that reaches corals. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2008. Chapter 13, Part 650. Wetland Restoration, Enhancement or Creation. Engineering Field Handbook. U.S. Depatrment of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Infrastructural Policies; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Manage Canal Water Quality | This management option addresses water quality issues that may arise from nearshore, confined areas, specifically dead-end canals. This management response does not focus on wastewater discharges into canals, but instead on the hydrologic structure and orientation of the canal itself. Physical problems with canal orientation can lead to such problems as low flushing and build-up of weed wrack. This is a problem because the build-up of weed wrack consumes oxygen and releases nutrients as it decays. When combined with low flushing and circulation, dead end canals have decreased oxygen concentrations, accelerated eutrophication, and accumulate organic materials, pollutants and sediment. To improve the current canal system, management can inventory and map canals to identify high risk hotspots and candidates for future canal restoration projects. Canals are typically constructed to best suit the water access needs of local homes and businesses. Preventing high risk canals from being constructed, or placing certain requirements on their construction through permitting is one way to reduce future problem spots. Some design strategies include: Construct non-linear canals without right-angles and flared inlets oriented to prevailing winds. Instead of dead-ends, canals should include a flow through water exchange system or install mechanical pumps. Canals should be as wide as possible in relation to depth and length. Canal depth should be uniform or progressively shallower away from the parent waterbody, with sloping banks (eliminate requirements for navigable depths to shoreline). Some canal improvement strategies include: Implement weed gates, air curtains, and aeration systems. Direct all stormwater and effluent away from canal systems. Reduce bulkheading and restore native vegetative buffers (#1). Promote diversity of substrates and habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Applied Chemicals; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Physical Damage; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Provisioning Services; Regulating Services; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Tourism & Recreation; Transportation; Transportation Policies; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Water; Water Depth & Sea Level; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Aquatic Organism Passage | This management action allows for upstream and downstream passage for fish and other aquatic organisms. The passage of these organisms is often restricted by barriers which must be modified, removed, or worked around with fishways. Sites should be evaluated for variations in discharge, tidal influence, hydraulics, geomorphic impacts, sediment transport and continuity, and organic debris movement. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Civil Engineering & Construction; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Water Resources |
| Waterway Management: Control River Volume Using Dams and Resevoirs | Constructing dams and creating reservoirs can have many affects, both positive and negative. Like smaller scale structural stormwater retention (#263), this management option retains groundwater for later controlled release. On this scale, the creation of a reservoir may require flooding of an area behind the dam that had other uses (e.g. agriculture). Proper vegetation can be used in and around the reservoir to incorporate biological filtration (#261). Slowing the release of water into rivers reduces the intensity of flow, reducing channel erosion. However, water should still be released consistently to allow for aquatic habitat to be maintained on the river bottom (#8). Lastly, with the correct infrastructure, a dam can be used as a sustainable hydroelectric energy source. | Morris, G.L., Fan, J. 1998. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and management of dams, reservoirs, and watersheds for sustainable use. Ver. 1.04 edition. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY. Environmental Protection Agency. 2007. National Management Measures to Control Nonpoint Source Pollution from Hydromodification. EPA 841-B-07-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC. |
Civil Engineering & Construction; Climate; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical Variables; Point Source Discharges; Storms & Hurricanes; Stormwater Management; Utilities; Utility Policies; Waste Management; Water; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Waterway Management: Collaborate with Projects Changing Water-Flow | Other organizations may be performing restorative freshwater projects (Everglades Restoration) or other flow altering projects (e.g. canals for small boats, agricultural irrigation etc) that affect the downstream marine management area (Florida Bay). Projects on the coast that involve hydrologic modifications (such as changing salinity) must be closely monitored in order to protect reef quality. Reefs are very sensitive systems and can only survive in a narrow salinity range. By taking an active role and monitoring freshwater flow projects, management staff can better ensure proper consideration of the impact on coastal marine environments. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan. 2010. Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan: 2009 System Status Report. |
Collaboration & Partnering; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Decision Support; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Salinity; Security & Public Administration Policies; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure | Canal and irrigation infrastructure typically includes concrete structures to control the flow of water. These low head dams, bulkheads, concrete footers, and other structures act as constricting forces in channels. This constriction leads to debris becoming lodged and thus changing the erosive forces. In turn, banks become destabilized. Channel erosion then increases along with bed scour and sediment transport. Removing these structures and making banks more gradual has the added benefit of allowing for riparian vegetation to be planted, which acts as a natural buffer. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Raw Materials; Hydrologic Management; Impervious Surfaces; Infrastructural Policies; Irrigation; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Non-point Source Controls; Physical Damage; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Substrate; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Waterway Management: Stream Bank Riparian Plantings | Planting native vegetation and trees in riparian zones helps to reduce erosion within channels. Such vegetation helps anchor the soil and sediment in place. Planting in riparian zones goes in hand with Remove Previous Canal and Irrigation Infrastructure (#274). This management option can be exercised in streams, canals used for boat passage, stormwater drainage ditches, or in agricultural irrigation channels. | Center for Watershed Protection. 2008. Guanica Bay watershed management plan. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture; Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Carbon Storage & Cycling; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Food & Energy Policies; Forestry; Hydrologic Management; Infrastructural Policies; Infrastructure; Irrigation; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Sediment; Stormwater Management; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Transportation; Utilities; Water; Water Resources; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-Year Permits for Maintenance Dredging in Deepwater Ports; Deepwater Ports Maintenance Dredging and Disposal Manual, 62-045 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-45.001 Authority, Intent and Policy.
(1) This chapter is promulgated under the authority of Sections 403.061(26) and 403.816(1), F.S.
(2) It is the intent of this chapter to establish a permitting system for maintenance dredging in deep water commercial navigation
areas of the ports listed in Rule 62-45.020, F.A.C. This chapter incorporates standards and criteria which recognize the present most
beneficial use of these waters for deep water commercial navigation. Since the implementation of a comprehensive maintenance
dredging management plan is a major factor in determining the adequacy of a long-term maintenance dredging program, it is the
further intent of this chapter to give a position of prominence to such a plan within this permit system.
(3) It is the policy of the Department to provide a regulatory process which will enable the ports to conduct maintenance
dredging in an environmentally sound, expeditious and efficient manner.62-45.020 Scope.
(1) The permit system established by this chapter applies only to the ports of Ft. Pierce, Jacksonville, Miami, Palm Beach,
Panama City, Pensacola, Port Canaveral, Port Everglades, Port Manatee, Port St. Joe, St. Petersburg, and Tampa.
(2) The activities which may be included within a permit issued under this chapter are limited to maintenance dredging and
disposal of the maintenance dredged material.
(3) Applicants for permits under this chapter are limited to the port authorities or private interests using the port for deep water
commercial shipping and the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. The Department shall not issue separate permits to the port authority or
private interests and the U. S. Army Corps of Engineers when the responsibility of maintenance dredging or the disposal of the
maintenance dredged material from the port is shared by any of the parties. The permit, if issued, shall clearly specify the duties and
responsibilities of each party.
(4) A permit may be issued for any length of time up to 25 years. There shall be no more than one such permit for each of the
ports listed in subsection (1).
(5) The area within which work under this permit system may take place is limited to the federally maintained, port authority
maintained, or private interest maintained navigation channels, turning basins, or harbor berths associated with deep water
commercial navigation and associated dredged material disposal sites. Eligible port maintenance dredging areas are depicted on
NOS Charts Nos. 11491 (Port of Jacksonville), 11478 (Port Canaveral), 11475 (Fort Pierce Harbor), 11466 (Port of Palm Beach),
11468 (Port of Miami), 11470 (Port Everglades), 11413 (Tampa Bay, Northern Part), 11414 (Tampa Bay, Southern Part), 11393
(Port St. Joe), 11391 (Panama City), and 11383 (Port of Pensacola) on file with the Department and adopted here by reference.
Copies are available at cost upon request from the Office of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, MS
300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000. Application to Coral Reefs:Proper, environmentally sound, dredging and disposal of dredged material, as reviewed by permit processers, will limit the amount of sediment and nutrients released to open water. The process will be particularly applicable to coral reefs for the dredging and disposal of Miiami harbor. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment |
| Administrative fines for damaging State Lands of products thereof, 18-14 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-14.003 Violations.
It shall be a violation of this rule for any person or the agent of any person to knowingly refuse to comply with any provision of
Chapter 253, F.S., willfully violate any provision of Chapter 253, F.S., or to willfully damage state land (the ownership or
boundaries of which have been established by the state) or products thereof, by doing any of the following:
(1) Fill, excavate, or dredge, including prop dredging in a manner which produces a defined channel, on state land without the
lease, license, easement or other form of consent required by the Board.
(2) Remove, in violation of state or federal law, any product from state land without written approval or specific exemption
from the Board or Department.
(3) Discharge contaminants, wastes, effluents, sewage or any other pollutant as defined in Chapter 376 or Chapter 403, F.S.,
on, under or over state land; when such discharge is in violation of Chapter 403 or conditions of a permit issued pursuant to that
chapter, or conditions of a lease or easement issued pursuant to Chapter 253, F.S.
- 37
(4) Maintain, place or build permanent or temporary structures, including, but not limited to, additions to existing structures;
all structures whose use is not water-dependent; sanitary septic systems; fences, docks and pilings; houses; oil rigs; and utility
installations on or over state land without consent or authority from the Board or Department.
(5) Place garbage, refuse, or debris on or over state land without approval by the Board or Department.
(6) Any other willful act that causes damage to state land, or products thereof, when such activity occurs without the required
approval by the Board or Department. Application to Coral Reefs:Controlling and limiting excavation and dredging, as well as discharge of contaminants, wastes, sewage, and other pollutants will assist in keeping sediment and pollutants from reaching the coral reefs and causing degradation of reef organisms.. Legislative Actions: Comments:Administrative Fines for Damaging State Lands or Products Thereof |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Petroleum Spills; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Substrate; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Amendment to the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations revising the boundary of the northernmost area to be avoided off the coast of Florida, Federal Register § Volume 65, Number226 (2000). | NOAA, in conjunction with the US Coast Guard, proposed to revise the northernmost area to be avoided (ATBA) off the coast of the Florida Keys. The change was expected to increaase maritime safety and to avoid harm to the marine environment and its resources. Application to Coral Reefs:The amendments directly protect coral reefs because the change of the nothernmost area presented in the regulation as Area To Be Avoided resulted in large vessels not entering the area that had been the site of large vessel groundings. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in conjunction with the US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Boat Movement; Civil Engineering & Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Cruise Ships; Fish; Large Ships; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Reef Inhabitants; Transportation Policies; Water Transportation |
| American Antiquities Act of 1906, 16 United States Code §§ 431-433. | The Act provides penalties for unauthorized collection, excavation, or destruction of historic or prehistoric ruins, monuments, or objects of antiquity on lands owned or controlled by the United States. It authorized that areas of extrodinary geographical, historical , aesthetic value can be designated national monuments. Application to Coral Reefs:Has been used by Presidential Proclamation in 2001 to expand or create two national monuments; the Virgin Islands Coral Reef Monument and the Buck Island Reef National Monument. The monuments include coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Docks & Marinas; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management |
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 10: Open shorelines, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | The seashore has always provided recreation, meditation, and physical therapy to the residents of the USVI. The shoreline provides access to the sea and a way of life for fisherman.The law requires that the public be given access to shorelines of the USVI for use and enjoyment. Application to Coral Reefs:The limitation on barriers, obstructions, and retraints to beach access will have a minor role in protecting coral reefs because sedimentation that would have been associated with that minor construction will not occur. Legislative Actions:No person, firm, corporation, association or other legal entity shall create, erect, maintain, or construct any obstruction, barrier, or restraint of any nature whatsoever upon, across or within the shorelines of the USVI as defined in this section, which would interfere with the right of the public individually and collectively. to use and enjoy any shoreline. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Mangroves; Marine Vertebrates; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses |
| Chapter 13: Environmental protection, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Establishes an environmental protection program for land development to prevent soil erosion and for the conservation of beaches, shorelines, and the coastal zone of USVI. Rules and Regulations were to prevent improper development of land and harmful environmental changes. Application to Coral Reefs:The Earth Change Plan review will indicate any adverse environmental impacts, including those that could effect coral reefs such as sedimentation. Legislative Actions:The law requires an "Earth Change Plan" from the Department of Planning and Natural Resources before any land can be cleared, graded, filled, or otherwise disturbed. Violation from the approved Earth Change Plan is punishable by a fine of $200 per day per violation. Violation of other portions of the Chapter is punishable by $5,000 fine or one year imprisionment per violation. Development in the first tierof the coastal zone requires a coastal zone permit. Comments:Chapter 13 includes comprehensive erosion and sediment control measures applicable to public and private developments including construction and maintenance of streets and roads. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Coastal Development; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management; Shoreline Armoring |
| Chapter 21: Virgin Islands coastal zone management, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Protect, maintain, preserve and, where feasible, enhance and restore, the overall quality of the environment in the coastal zone, the natural and man-made resources therein, and the scenic and historic resources of the coastal zone for he benefit of residents of and visitors of the USVI Application to Coral Reefs:The Legislature stated coastal zone protection will conserve ecologically significant resource areas for their contribution to marine productivity and value as wildlife habitats, and preserve the function and integrity of reefs, marine meadows, salt ponds, mangroves and other significant natural areas. The legislation will also maintain or increase coastal water quality through control of erosion, sedimentation, runoff, siltation and sewage discharge. Legislative Actions:Any violation of the chapter will be grounds for revocation or suspension of coastal zone permit and an order to cease and desist. Any person who violates any provision of the chapter shall be subject to a civil fine not to exceed $10,000 per day. Exemplary damages may be assessed at the discretion of the court. Comments:Section 908 of the law shows Coastal Zone Boundaries. Section 909 shows areas of special concern. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging Regulations; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring |
| Chapter 3: Trees and vegetation next to waterways, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Establishes buffer zone for protecting natural watercourses from vegetation clearing. The buffer zone either 30 feet from the center of the natural watercourse, or 25 feet from its edge, whichever is greater. Application to Coral Reefs:Assists in erosion control and can protect reefs from harmful sedimentation, if the stream or river sediment is capable of reaching the coral reef. Vegetation along river and stream banks will remove nutrients and assist in preventing eutrophocation of waters that can reach coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Enforcement is by conservation officers with assistance from local police when required. Penalties are fines of not more than $100, or 180 days in jail, or both Comments:Permits can be obtained if the purpose of clearing is for development. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landscaping & Household Services; Landuse Management; Resource Use Management; Shoreline Protection; Wetlands |
| Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 (CBRA), 16 United States Code §§ 3501 et seq. | Promote more appropriate use and conservation of coastal barriers along the Atlantic, Gulf and Great Lakes coastlines. Minimize the loss of human life; reduce wasteful expenditures on shoreline development; minimize damage to wildlife, marine life, and other natural services, and establish a coastal barrier resources system. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restrict most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals. |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coral; Funding & Incentives; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Runoff; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Wetlands |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, as amended through 2004,. | A voluntary national program to encourage coastal states to develop and implement coastal zone management plans and requires that "any federal activity within or outside of the coastal zone that affects any land or water use or natural resource of the coastal zone" shall be "consistent to the maximum extent practicable with the enforceable policies" of a state's coastal zone management plan. The law includes an Enhancement Grants program for protecting, restoring, or enhancing existing coastal wetlands or creating new coastal wetlands. It also establishes the National Estuarine Research Reserve System, guidelines for estuarine research, and financial assistance for land acquisition. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:The 1985 amendments (PL 99-272) established the National Estuarine Reserve Research System a State-Federal process for designating national reserves and guidelines for estuarine research.The 1990 amendments (PL 101-508) established new Enhancement Grants for eight specific areas, including protecting, restoring or enhancing existing coastal wetlands or creating new coastal wetlands and assessing the cumulative effects of coastal development on coastal wetlands and fishery resource. Also, the 1990 statute established a new Coastal Nonpoint Source Pollution Control Program. The 1998 and 2004 (PL 105-383 and PL 108-456) established a program for the prevention and control of harmful algal blooms and hypoxia, and included authorization for a representative of the Department of Interior to assess the economic and ecological impacts of algal blooms and hypoxia. Comments:If implemented, the programs for economic, ecological and control of harmful algal blooms and hypoxia would be useful for coral reef issues. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Economic Markets & Policies; Infrastructural Policies; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow |
| Conceptual Agency Review, 62-029 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter is limited in application to dredge and fill permit applications for projects in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District which, pursuant to Section 373.4145, F.S., are to be reviewed and processed under the rules authorized and adopted under Sections 403.91-.929, F.S. (1984 Supp.), as amended.
(1) The purpose of this rule is to establish those procedures applicable to review of requests for conceptual agency review pursuant to Section 380.06(9), F.S., for projects that undergo development of regional impact review (DRIs).
(2) Conceptual agency review is a licensing action and approval or denial shall constitute final agency action.
(3) Under this rule, applicants who must obtain construction or operation permits for potential sources of water pollution or for dredging and filling activities may apply for conceptual agency review of certain aspects of a proposed development, including the location, densities, intensity of use, character and major design features. Application to Coral Reefs:Limited to projects in Northwest Florida. Legislative Actions:The legislation applies only to dredge and fill projects in the area of the Northwest Florida Water Mkanagement District. Comments:The purpose of this rule is to establish those procedures for dredge and fill permit applications for projects in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District that require conceptual agency review of certain aspects of a proposed development, including the location, densities, intensity of use, character and major design features. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Delegation of the Environmental Resource Program to Local Governments, 62-344 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) This chapter guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient,
streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental
resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments in accordance with the
provisions of Sections 373.103(8) and 373.441, F.S. This chapter also constitutes the Department�s authorization, in accordance with
Section 373.103(8), F.S., for delegations of the environmental resource permit program from the water management districts to local
governments provided that the procedures for delegation contained in this chapter are followed by the Districts. Delegations from
the Department and Districts shall be for the respective environmental resource permit program responsibilities of the Department
and the Suwannee River, St. Johns River, Southwest Florida and South Florida Water Management Districts, as set forth in
operating agreements listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C. Delegation agreements between the Department and local governments shall
be listed in Chapter 62-113, F.A.C., and delegation agreements between the Districts and local governments shall be listed in
Chapters 40B-1, 40C-1, 40D-1, and 40E-1, F.A.C.
(2) Nothing in this chapter shall preclude the Department, Districts, and local governments from entering into contracts or
interagency agreements as provided by law.
(3) Except as specifically provided in this chapter, nothing herein shall prevent a local government from adopting and
implementing an environmental regulatory program pursuant to its own authority.
(4) It is an objective of the Department and Districts to protect the functions of entire ecological systems, as defined and
developed in the programs, rules and plans of the Department and water management districts. It is the intent of the Department and
Districts that any local government receiving delegation of all or a portion of the environmental resource program carry out that
program in a manner consistent with this objective. This paragraph shall not be construed or applied as additional permitting criteria
beyond those adopted by the reviewing agency or the local government. Application to Coral Reefs:In theory, delegating stormwater pond construction and wetland functional determinations, as well as most otrher issues related to stormwater and wetlands, to local government will produce more efficient permitting and oversight. Therefore, treated water that is discharged and reaches any ecosystem should contain less contamination than the same water if it had not treated. Legislative Actions: Comments:Guides the participation of counties, municipalities and local pollution control programs in an efficient, streamlined permitting system by setting forth the procedures and requirements for delegations of all or a part of the environmental resource permit program from the Department and water management districts to local governments |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Delineation of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters, 62-340 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2000). | The Rule's intent is to provide a unified statewide methodology for the delineation of the extent of wetlands to satisfy the mandate of Section 373.421, F. S. Application to Coral Reefs:Preservation of wetlands will allow them to continue to function as buffers for sediment and contaminant control keeping them from reaching estuarine and marine waters and eventually habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Rule is administrative and methodological for delineation purposes. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Drinking Water Supply; Energy Policy & Development; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Invertebrates; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Domestic Wastewater Facilities, 62-600 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.021(2), Florida Statutes, as amended, the Florida Air and Water Pollution Control Act, established that no
wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessary to protect the
beneficial uses of such water. Toward this end, Sections 403.085 and 403.086, Florida Statutes, set forth requirements for the
treatment and reuse or disposal of domestic wastewater. Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, requires that any Department
planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be
developed as a rule. This chapter is promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of Sections 120.53(1), 120.55,
403.021, 403.051, 403.061, 403.062, 403.064, 403.085, 403.086, 403.087, 403.088, 403.0881, 403.101, 403.131, 403.161,
403.182, 403.859, and 403.918, Florida Statutes, concerning domestic wastewater facilities.
- 442
(2) The requirements of this chapter represent the specific requirements of the Florida Department of Environmental Protection
and of Local Pollution Control Programs approved and established pursuant to Section 403.182, Florida Statutes, where such
authority has been delegated to those programs. It may be necessary for domestic wastewater facilities to conform with
requirements of other agencies, established via interagency agreements (e.g., for mosquito control); the absence of reference to
such arrangements in this chapter does not negate the need for compliance with those requirements.
(3) The purpose of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., is to provide minimum standards for the design of domestic wastewater facilities
and to establish minimum treatment and disinfection requirements for the operation of domestic wastewater facilities. All systems
shall be designed in accordance with sound engineering practice. Supported by moderating provisions, it is intended that Chapter
62-600, F.A.C., establish a framework whereby design flexibility and sound engineering practice can be used in developing
systems with which to manage domestic wastewater in an environmentally sound manner.
(4) As appropriate, Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., shall be used in conjunction with other Department rules relating to the design and
operation and maintenance of domestic wastewater facilities.
(5) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities
(including residuals management facilities).
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and modifications or expansions of existing facilities that
submit complete permit applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit complete applications for permit renewal after
July 1, 1991.
(6) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications on or before July 1, 1991, may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the time the permit was issued and with the conditions
of the existing construction or operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter.
(7) The standards and requirements of Part II of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., and Rules 62-600.500 and 62-600.530, F.A.C., shall
be applicable to septic tank drainfield systems and other on-site waste treatment systems with subsurface disposal regulated by this
chapter. The reliability requirements of paragraph 62-600.400(1)(b), F.A.C., shall not apply to such septic tank drainfield systems
and other on-site waste treatment systems.
(8) The discharge limitation of subsection 62-600.510(4), F.A.C., shall not be applicable to facilities permitted on or before
January 1, 1982, that discharge into Class II waters or Class III waters which are subsequently reclassified as Class II waters.
(9) This chapter provides for exemptions, allowances for existing facilities and variations from standards and requirements.
Unless specifically provided otherwise, no wastewater permit shall be issued or renewed unless the permit applicant demonstrates
that the subject facility is in compliance with the applicable provisions of this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting construction and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the processes for planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant monitoring, 62-601 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, as amended, part of the Florida
Air and Water Pollution Control Act, requires that any Department operating standards,
criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be developed as a rule. This rule is
promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of the Act concerning
domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring.
(2) The purpose of Chapter 62-601, F.A.C., is to ensure that owners and
operators of domestic wastewater treatment facilities maintain accurate records and
submit reports required by this Chapter in a timely, accurate, cost-effective and uniform
manner.
(3) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic
wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities (including residuals management
facilities). The standards and requirements are not applicable to facilities described in
Rules 62-600.120(1) and (2), F.A.C.
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and
modifications or expansions of existing facilities that submit complete permit
applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit
complete applications for permit renewal after July 1, 1991.
(4) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications
on or before July 1, 1991 may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the
time the permit was issued and with the conditions of the existing construction or
operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting monitoring requirements and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:to implement the provisions and requirements concerning domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Discharge Limitations; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Dredge and Fill Activities, 62-312 Florida Administrative Code. | This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department pursuant to Sections 403.91 through 403.929, F.S. Dredging or filling which is grandfathered by subsections 403.913(6), (8) and (9), F.S., is governed by Rules 62-312.150 and 62-312.160, F.A.C. The requirements of this part are in addition to and not in lieu of the water quality standards which are required by other portions of these sections. Except for the definitions contained in Rule 62-312.020, F.A.C., which shall also apply to activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., the provisions of this Part shall only apply to activities in the geographical territory of the Northwest Florida Water Management District and to activities grandfathered under Sections 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15) and (16), F.S.
Specific Authority 373.414(11)-(16), 373.4145, 403.805(1) FS. Law Implemented 373.409, 373.413, 373.414(9), (11), (12)(a), (13), (14), (15), (16), 373.4145, 373.416, 373.418, 403.061, 403.813, 403.814 FS. History�New 12-10-84, Amended 8-7-85, Formerly 17-12.010, 17-312.010, Amended 10-3-95. Application to Coral Reefs:The permit reviewers will require BMP for dredge and fill activities. This will include siltation reduction methods that will keep sediment, nutrient and other contaminants from leaving the work site and getting into the water column and potentially reaching sensitive ecosysten, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:This part provides the requirements and procedures for obtaining permits and jurisdictional declaratory statements from the Department for dredge and fill activities. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Large Ships; Nutrients; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Ports & Harbors; Sediment; Toxics |
| Electric Power Siting, 62-017 Florida Administrative Code. | 62-17.011 General.
(1) The purpose of Part I is to implement the provisions of the Florida Electrical Power Plant Siting Act, Sections 403.501 - 403.518, F.S., as amended.
(2) The department promulgates Part I pursuant to the charge of the legislature to provide efficient, centralized review of the needs for increased electrical power generation and the effects of generation-related activities on human health and the environment and ecology of the lands and waters within the state.
(3) This Part addresses applications for certification of:
(a) A new site for a steam or solar electrical power plant;
(b) The construction and operation of additional steam or solar electrical generating units to be located at sites which have been previously certified for an ultimate site capacity; and
(c) An existing power plant site which had or had applied for permits prior to the effective date of the Act.
Specific Authority 403.504(1), 403.517(1)(a), FS. Law Implemented 403.504(2)(3)(5), 403.517, 403.5175, FS. History - New 5-7-74, Amended 12-27-77, Formerly 17-17.01, Amended 5-9-83, Formerly 17-17.011, Amended 2-1-99. Application to Coral Reefs: To provide efficient, centralized review of the needs for increased electrical power generation and the effects of generation-related activities on human health and the environment and ecology of the lands and waters within the state. (3) This Part addresses applications for certification of: (a) A new site for a steam or solar electrical power plant; Legislative Actions: Comments:To provide efficient, centralized review of the needs for increased electrical power generation and the effects of generation-related activities on human health and the environment and ecology of the lands and waters within the state. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: |
Building & Home Construction; Carbon Storage & Cycling; Climate Regulation; Energy Policy & Development; Natural Gas & Electric Power; Point & Mobile Source Controls |
| Environmental resource permitting procedures, 62-343 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2003). | The rule provides the procedural requirements for processing environmental resource permits and obtaining formal determinations of the landward extent of wetlands and surface waters. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring permits for projects related to environmental resources will indirectly protect environmental habitats. The permits are related to stormwater managemnt systems including discharges to wetlands. The permit conditions can limit toxics, nutrients and sediment that would be discharged to the environment if the rule were not in place. Legislative Actions:The rule is procedural and does not have fines or penalties. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Permitting & Zoning; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands |
| Environmental Resource Permitting, 62-330 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2005). | Under the Chapter, DEP exercises its independent authority under Part IV, Chapter 373, F.S., to regulate surface water management systems, including activities in, on or over wetlands or other surface waters. The term "surface water management system" or "system" include stormwater mangement systems, dams, impoundments, reservoirs, appurtenant works, or works, or any combination thereof, and includes dredging and filling. "Dredging" means excavation, by any means, in surface waters or wetlands Application to Coral Reefs:Regulating stormwater management systems, dams, reservoirs and dredging will contribute to controlling contaminates from entering estuarine and marine environments and protect ecosystems including coral reefs., Legislative Actions:Individual permits will contain the conditions for environmental protection. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
City Planning; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Estuaries Protection Act of 1968, 16 United States Code §§ 1221-1226. | Authorizes the Secretary of Interior in cooperation with other federal agencies and the states, to study and inventory estuaries of the united states, including land and water of the Great Lakes, and to determine whether such areas should be acquired for protection. The Secretary is also requied to encourage state and local governments to consider the importance of estuaries in their planning activities relative to federal natural resources grants. Application to Coral Reefs:Established the congressional policy on the values of wetlands and the need to conserve their natural resources. Protection of wetlands provide coral reefs with an indirect benefit as the wetland serves the functions of nutrient removal and sediment containment Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Secretary of Interior in conjunction with other federal agencies and States Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Seagrasses; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Exec. Order No. 11988, Management of Flood Prone Areas, 42 Federal Register 2691 (1977). | This order requires all federal agencies to take action and avoid to the extent possible, adverse impacts over the short and long term associated with the occupation and modification of flood prone areas and to avoid direct or indirect aid to the development of flood prone areas whenever there is a viable alternative. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Landuse Management; Public Administration |
| Florida Aquatic Preserves, 18-20 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-20.001 Intent.
(1) All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency.
(2) Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(3) The preserves shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals: (a) To preserve, protect, and enhance these exceptional areas of sovereignty submerged lands by reasonable regulation of
human activity within the preserves through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program; (b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserves so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating, and fishing; (c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the Legislature in creating the preserves; (d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the act and these rules, and to assist in managing the preserves; (e) To encourage the protection, enhancement or restoration of the biological, aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions toward their natural condition, and discourage
activities which would degrade the aesthetic, biological, or scientific values, or the quality, or utility of a preserve, when reviewing applications, or when developing and implementing management plans for the preserves; (f) To preserve, promote, and utilize indigenous life forms and habitats, including but not limited to: sponges, soft coral, hard corals, submerged grasses, mangroves, salt water marshes, fresh water marshes, mud flats, estuarine, aquatic, and marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, estuarine, aquatic and marine invertebrates, estuarine, aquatic and marine mammals, birds, shellfish and mollusks; (g) To acquire additional title interests in lands wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological,
aesthetic, or scientific values of the preserves; (h) To maintain those beneficial hydrologic and biologic functions, the benefits of which accrue to the public at large. (4) Nothing in these rules shall serve to eliminate or alter the requirements or authority of other governmental agencies, including counties and municipalities, to protect or enhance the preserves provided that such requirements or authority are not inconsistent with the act and this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:By maintaining coastal aquatic preserves in their natural condition, mangrove forests, wetlands and submerged aquatic vegetation will perform the functions of being sediment traps and removing some contaminants such as nutrients. Therefore, they will not reach marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Aquatic preserves which are described in Part II of Chapter 258, Florida Statutes, were established for the purpose of being preserved in an essentially natural or existing condition so that their aesthetic, biological and scientific values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. All sovereignty lands within a preserve shall be managed primarily for the maintenance of essentially natural conditions, the propagation of fish and wildlife, and public recreation, including hunting and fishing where deemed appropriate by the Board, and the managing agency. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Waste Management Policies |
| General permit for activities seaward of the coastal construction control line, 62B-34 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2010). | To implement the provisions of Section 161.053(19) F. S. providing General Permits for activities performed seaward of the Coastal Construction Control line. Persons wishing to use one or more of the General Permits as set forth in Part II of this rule chapter shall be subject to the notice provisions of subsection 62B-34.030(4) F. A. C. before any activity is conducted as authorized herein.The general conditions provided pursuant to Section 62-B34-0.50, F. A. C. , shall apply to all of the General Permits issued under this rule chapter. Strict compliance with all of the terms, conditions, requirements, limitations, and restrictions applicable to a desired General Permit under this rule chapter is required to qualify for such a permit. Application to Coral Reefs:The rule requires erosion control BMP. Therefore, sediment from construction will not enter the marine environment and damage coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Civil fines are applicable for work done that was not authorized in the permit. Comments: |
Florida Departrment of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring |
| Joint Coastal Permits and Concurrent Processing of Proprietary Authorizations, 62B-049 Florida Administrative Code. | This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. In the event that there is a conflict between the procedural requirements of this chapter and other procedural rules promulgated pursuant to the referenced statutes, then this chapter shall govern. The standards and criteria for issuance of joint coastal permits include the criteria for environmental resource or wetland resource permits pursuant to Chapter 62-312, F.A.C., and the rules adopted under Chapter 62-330, F.A.C., the coastal construction criteria pursuant to Chapter 62B-41, F.A.C., and any specific criteria for issuance of a joint coastal permit listed in this chapter. The criteria for the associated proprietary authorizations are found in Chapters 18-18, 18-20, 18-21, F.A.C.
Specific Authority 161.055, 373.427 FS. Law Implemented 161.041, 161.055, 373.427 FS. History�New 10-12-95, Amended 2-19-98, 5-17-07. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring a permit with regulatory review of the construction project, in a joint review of wetland and submerged land issues, will assist in minimizing potential adverse environmental impacts from the work and such potential detrimental portions of the project (e.g. sedimentation) will not enter the marine environment resulting in ecosystem damage. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter implements the provisions of Section 161.055, F.S., by combining the regulatory requirements of the coastal construction program (Section 161.041, F.S.) with the environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit program (Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.) to establish the joint coastal permit program. Activities that would have required both a coastal construction permit and an environmental resource (or wetland resource) permit, are now authorized by a single joint coastal permit. In addition, this chapter provides for concurrent review of any activity requiring a joint coastal permit that also requires a proprietary authorization for use of sovereign submerged lands owned by the Board of Trustees of the Internal Improvement Trust Fund. This chapter also establishes procedures for processing applications for joint coastal permits and the linked proprietary authorizations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Mangroves; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection |
| Mangrove Trimming and Preservation Act, 403.9321-403.9333 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | It is the intent of the Legislature to protect and preserve mangrove resources valuable to our environmentand economy from unregulated removal, defoliation, and destruction. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection and preservation of wetland systems, including mangroves, allow the systems to act as buffers to remove nutrients and sediment that could reach coral reefs and cause damage. Legislative Actions:Permits are required prior to any trimming. A Professional Mangrove Trimmer must be present when work is being performed. Penalties can include restoration and/or mitigation. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Birds; Non-Monetary Valuation; Nutrients; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Shoreline Protection |
| Marine Turtle Conservation Act of 2004, 16 United States Code § 6601. | The law was created to aid in the conservation of sea turtles and their nesting habitats in foreign countries by providing funds for the conservation of nesting areas, sea turtles in in their nesting habitats, and dealing with threats to sea turtle survival. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Designate Protected Species; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles |
| Mitigation Banking, 62-342 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department recognizes that, in certain instances, adverse impacts of activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., can be offset through the utilization of mitigation credits from a permitted Mitigation Bank. This rule provides criteria for this mitigation alternative to complement existing mitigation criteria and requirements. This chapter is supplemental to and does not supersede any other criteria and requirements in rules promulgated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.
(2) The Department intends that Mitigation Banks be used to minimize mitigation uncertainty associated with traditional mitigation practices and provide greater assurance of mitigation success. It is anticipated that the consolidation of multiple mitigation projects into larger contiguous areas will provide greater assurance that the mitigation will yield long-term, sustainable, regional ecological benefits. Mitigation Banks shall be consistent with Department endorsed watershed management objectives and emphasize restoration and enhancement of degraded ecosystems and the preservation of uplands and wetlands as intact ecosystems rather than alteration of landscapes to create wetlands. This is best accomplished through restoration of ecological communities that were historically present. The establishment and use of Mitigation Banks in or adjacent to areas of national, state, or regional ecological significance is encouraged, provided the area in which the Mitigation Bank is proposed to be located is determined appropriate for a Mitigation Bank and the Mitigation Bank meets all applicable permitting criteria.
(3) Nothing in this chapter shall affect the mitigation requirements set forth in any Mitigation Bank agreement or any permit issued under Chapter 84-79, Laws of Florida, or Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., prior to February 2, 1994. If a permittee wishes to substantially modify a Mitigation Bank previously established by agreement or permit, the permittee must comply with this chapter. Additionally, some Mitigation Banks may be subject to the version of this section existing prior to July 1, 1996, under subsections 373.4136(9) and (10), F.S., and will not be affected by amendments adopted after that date. This chapter does not prohibit an applicant from proposing project-specific, pre-construction on-site or off-site mitigation, without establishing a Mitigation Bank. Application to Coral Reefs:Mitigation banking in coastal wetlands, as presented in the Chapter, can provide large areas of functioning wetlands. The wetlands can function as sediment and nutrient traps keeping sediment and nutrients from entering coastal waters and damaging marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the regulations and permitting requirements for mitigation banks. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Shoreline Armoring; Waste Management Policies |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969 as amended through 1982,. | Declared a national policy that will encourage productive and enjoyable harmony between man and his environment : promote efforts that will prevent or eliminate damage to the environment and biosphere: stimulate the health and welfare of resources important to the Nation and establish a Council on Environmental Quality. Application to Coral Reefs:Re-athorizes NEPA of 1969. Provides additional funding. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The amendments did not add regulations to the Act |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Atmospheric Emissions; Chemical Variables; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Educational & Research Opportunities; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Infrastructural Policies; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Mining; Oil & Gas Industry; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Toxics; Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulation of stormwater discharge, 62-25 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1988). | The discharge of untreated stormwater may reasonably be expected to be a source of pollution of waters of the state and is, therefore, subject to Department regulation. The Departmnet shall prevent pollution of waters of the state by discharges of stormwater, to ensure that the designated most beneficial uses of waters, as prescribed by Chapter 62-302, F.A.C., are protected. A permit under this chapter will be required only for new stormwater discharge facilities as defined herein. This provision shall not affect the Department's authority to require appropriate corrective action, pursuant to Sections 403.121-.161.F.S., whenever existing facilities cause or contribute to violations of state water quality standards. Stormwater discharges to groundwaters shall be regulated under the provisions of Chapters 62-520 and 62-522, F.A.C., and other applicable rules of the Department. The Department intends that, to the greatest extent practicable, the provisions of this chapter be delegated to either local governments or water management districts seeking such delegation. Application to Coral Reefs:Limiting the contaminants and their concentrations in stormwater discharge will reduce the contamination reaching various habitats, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Floridfa Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Landuse Management; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Sediment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899, 33 United States Code § 1252. | This law prohibits the discharge of any type of refuse matter in U.S. waters without permission (section 13). In addition, the excavation, fill, or alteration of the course, condition, or capacity of any port, channel, river, or other areas within the limits of this law is prohibited. This law prohibits the construction or alteration of a structure in wetlands of the U.S. (sections 9 and 10). Construction in wetlands and waters of the U.S. requires a permit from the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Application to Coral Reefs:Under section 10, excavation or fill within navigable waters requires approval of the Chief of Engineers and concerns about contaminated sediments with dredge and fill projects in navigable waters is addressed within the permitting process. Indirect protection of coral reefs is offered by the Act and its prohibition of dumping refuse into navigable waters and the process of anaylzing sediment in proposed dredge and fill operations. Legislative Actions:Violations of the law are punished under section 309 of the Clean Water Act and section 205 of National Fishing Enhancement Act. Fines imposed for violation will not be less than $10,000 per violation or more than $25,000 per violation. Comments:Many states, including Florida, require additional permits for constuction of docks, piers, wharfs, jetties and other structures in navigable waters and wetlands in addition to the Corps of Engineers permit. Authority to issue permits for discharge of refuse matter under section 13 was modified by the amendments to Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1972 and established the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System Permit process. The Act was initially established to protect interstate commerce in navigable waters. The permit review process involves factors including economics, aethetics, general envitonmental concerns, historical values, water quality, and fish and wildlife impact before project approval is granted. |
US Army Corps of Engineers (COE), and US Coast Guard Jurisdiction: United States |
Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Landuse Management; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Rules and Procedures for Application for Coastal Construction Permits, 62B-041 Florida Administrative Code. | No coastal construction shall be conducted without a permit issued by the Department under this chapter, unless it is determined that the coastal construction does not fall within the requirements of section 161.041, F.S., or unless the interior tidal water body is exempted by the Department pursuant to subsection 161.041(1), F.S. Application to Coral Reefs:Requiring a permit with regulatory review of the construction project will assist in minimizing potential adverse environmental impacts from the work and such potential detrimental portions of the project (e.g. sedimentation) will not enter the marine environment resulting in ecosystem damage. Legislative Actions: Comments:No coastal construction shall be conducted without a permit issued by the Department under this chapter, unless it is determined that the coastal construction does not fall within the requirements of section 161.041, F.S., or unless the interior tidal water body is exempted by the Department pursuant to subsection 161.041(1), F.S. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the Coastal Barrier Resources Act of 1982 include (1) Coastal Barrier Improvement Act of 1990, (2) Coastal Barrier Resources Reauthorization Act of 2000, (3) Coastal Barriers Resources Reauthorization Act of 2005,. | (1) Added additional areas along the Great Lakes, Puerto Rico, the Florida Keys and the Virgin Islands and established "Otherwise Protected Areas OPAs); (2) amended the guidelines for making recommendations regarding additions to the CBRS and reqired a pilot digital mapping project; (3) reauthorized CBRA and required the submission of the final digital mapping pilot project. Application to Coral Reefs:Development of coastal barrier islands can cause sedimentation, through runoff and construction activities, that could reach inshore coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Restricted most federal expenditures and financial assistance that encourage development including federal flood insurance. Comments:Recognized coastal barriers as essential habitat for many fish, water fowl and other aquatic animals |
U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Development; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Forestry; Mangroves; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Shoreline Protection |
| Small Community Wastewater Construction Grants Program, 62-505 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Florida�s Small Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program is
authorized by Sections 403.1835 and 403.1838, F.S. These statutes authorize the
Department to fund the planning, design, and construction of wastewater management
systems for qualifying small municipalities.
(2) This chapter sets forth the Department�s program management
procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance from the Small
Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program.
(3) Highest priority is given to projects that address the most serious risks to
public health, are necessary to achieve compliance, or assist systems most in need
based on an affordability index.
Specific Authority 403.1835(10) FS. Law Implemented 403.1835(3)(d), 403.1838 FS.
History � New 1-25-07. Application to Coral Reefs:Providing financial assistance to parties interested in building wastewater treatment palnts and best available standards for construction will result in higher treatment of wastewater prior to discharge to waters of the state. Less contaminated water will reach the marine environment where it would have the potential to adversely effect ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:sets forth the program management procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance from the Small Community Wastewater Facilities Grants Program. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Environmental Education & Outreach; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Sovereign submerged lands management, 18-21 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | To manage, protect, and enhance sovereignty lands so that the public may continue to enjoy traditional uses, including, but not limited to, navigation, fishing and swimming, public drinking water supply, shellfish harvesting, public recreation, and fish and wildlife propagation and management. Application to Coral Reefs:Permitting activities on submerged lands owned by Florida will improve water quality which will indirectly protect reef systems. Legislative Actions:These rules are to implement the administration and management responsibilities of the board and department regarding sovereign submerged lands. Responsibility for environmental permitting of activities and water quality protection on sovereign lands is vested with the Department of Environmental Protection. These rules are considered cumulative. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Beach & Land Formation; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fisheries; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Energy Policy & Development; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| State Revolving Fund Loan Program, 62-503 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Florida�s water pollution control revolving loan program is authorized by Section 403.1835, F.S. This statute establishes the Wastewater Treatment and Stormwater Management Revolving Loan Trust Fund, which meets federal requirements for a State Revolving Fund. The statute authorizes the Department to fund the planning, design, construction, and implementation of wastewater management systems and stormwater management systems. The Act also authorizes financial assistance for a wide range of services, equipment, and construction associated with nonpoint source pollution control. Project examples include brownfield remediation, wetland restoration, septic tank problem correction, best management practices (especially those for agricultural operations) for controlling leaching and runoff, animal waste management, boat discharge elimination, or other needs identified by the Department�s nonpoint source management program. National estuary program projects also may be eligible.
(2) The federal Water Pollution Control Act, as amended, commonly called the Clean Water Act, authorizes federal appropriations for grants to the Department to capitalize the State Revolving Fund. The Act requires that the state contribute matching funds of 20% to qualify for federal capitalization grants. The State Revolving Fund must be operated in perpetuity by the Department.
(3) This rule sets forth the Department�s program management procedures and the requirements for obtaining financial assistance.
Specific Authority 403.1835(5)(a) FS. Law Implemented 403.1835 FS. History - New 7-29-04. Application to Coral Reefs:Providing financial assistance to parties interested in building wastewater treatment palnts and best available standards for construction will result in higher treatment of wastewater prior to discharge to waters of the state. Less contaminated water will reach the marine environment where it would have the potential to adversely effect ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the Wastewater Treatment and Stormwater Management Revolving Loan Trust Fund to fund the planning, design, construction, and implementation of wastewater management systems and stormwater management systems and to provide financial assistance for a wide range of services, equipment, and construction associated with nonpoint source pollution control. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Building & Home Construction; Environmental Education & Outreach; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface water quality standards in table format, 62.302.500 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | This section of Chapter 62-302 presents the water quality standards in a tabular format for each class of waters of the State. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Chemical Variables; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Docks & Marinas; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Permitting & Zoning; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface waters of the State, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-301 (1996). | It is the intent of this Chapter to define the landward externt of surface waters of the state. Te findings, declarations, and intentfor this Chapter are the same as those for Chapter 62-302 F. A. C. Application to Coral Reefs:By defining the landward extent of surface waters of the State using dominant plant species, the guidance in the Chapter will include wetlands and transitional zones on many occasions. Through the protection of these areas, filtration of sediment and nutrients will be maintained and two of the harmful parameters for coral reefs will be reduced. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is a guidance document and does not contain penalties. The Chapter provides a list of plant species for use with the guidance as well as the methods of calculating the areas of state waters. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Arthropods; Ballast Discharge; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biotechnology Research & Development; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Invertebrates; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Petroleum Spills; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wastewater Discharge; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| The DPNR states that wetlands in the Virgin Islands are covered by the Clean water Act and the Endangered and Indigenous Species Act of 1990 (Title 12, Chapter 2, US Virgin Island Code,. | To protect wetlands and wetland species from degradation, loss as a result of dredging and filling. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of wetlands assists in controlling sedimentation and nutrient runoff from terrstrial locations, thus protecting coral reefs that are influenced by terrestrial sources. Legislative Actions: Comments:The wetlands portion of the USVI Division of Environmental Protection website was under construction at the time of this atlas preparation. However, it appears that DEP works with the USACE and USEPA on matters related to wetlands. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Construction Codes & Projects; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Shoreline Armoring; Wetlands |
| Uniform Mitigation Assessment Method, Florida Administrative Code Annotated §§ Chapter 62-345 (2005). | Establishes a methodology that provides a standard procedure for assessing the functions provided by wetlands and other surface waters, the amount that those functions are reduced by a proposed impact, and the amount of mitigation necessary to offset that loss. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting wetlands provides wetland areas that can act as buffers against nutrients, pollutants and contaminants from reaching habitats including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Chapter is administrative and provides methods to assess wetland value and appropriate mitigation to offset impact. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Building & Home Construction; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Forestry; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Wetlands |
| Water quality based effluent limitations, 62-650 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (1996). | To implement the provisions of Section 403.051, 403.085 through 403.088 concerning the development of effluent limitations for wastewater facilities. Application to Coral Reefs:The Florida Air and Water Pollution Act establishes that no wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessay to protect the beneficial uses of such water. Requiring treatment of industrial and domestic waste water indirectly protects adjoining ecosystem, such as reefs, by limiting the pollutant that reach these other systems. Legislative Actions:The Department shall not issue a permit for a discharge to waters of the state, unless the Department has established an efflent limit for those pollutants in the discharge that are present in quantities or concentrations which can be reasonably expected to cause or contribute, directly or indirectly, to a violation of any water quality standard established in rule 62-302. The effluent limit may be a technology based effluent limit (TBEL), a water quality based effluent limit (WQBEL) determined by a Level 1 process, or where applicable, a WQBEL determined by a Level 2 process. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Building & Home Construction; Cleaner & Solvent Use; Coal Mining; Construction Codes & Projects; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Domestic Animal Waste; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Food, Beverage, & Tobacco Products; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Mineral, Rock, & Metal Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Road Construction & Maintenance; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Utility Line Construction & Maintenance; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Waterborne Discharges; Wholesale & Retail Trade; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
