ReefLink Database

Biological Monitoring & Restoration
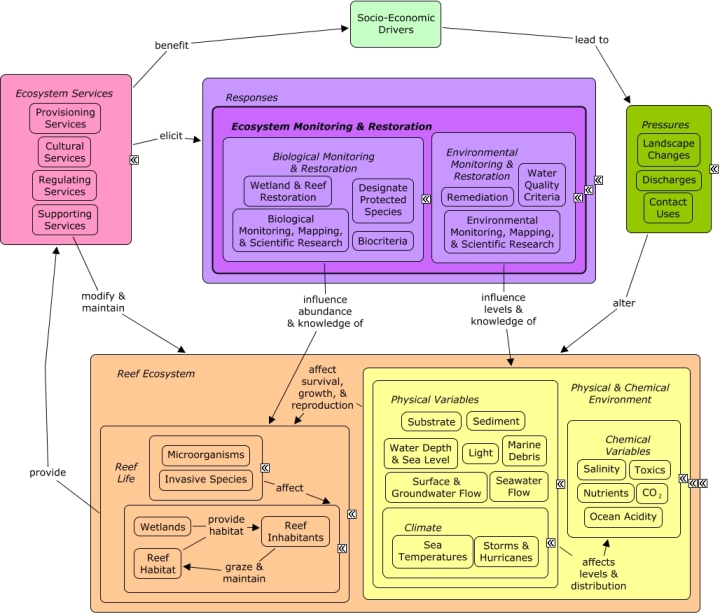
Biological monitoring is the use of a biological entity as a detector and its response as a measure to determine environmental conditions. Toxicity tests and ambient biological surveys are common biological monitoring methods. Biological restoration refers to responses to directly alter the condition of populations, communities, and habitat in the reef ecosystem through restoration activities, limits on degradation through biological criteria, or improving knowledge through monitoring, mapping, and scientific research.
CMap
CMap Description
A change in the provision of ecosystem services, or a desire to improve provision of ecosystem services, may elicit responses to directly alter the reef ecosystem. Wetland or reef restoration may include repairing damaged individuals, or replenishing degraded reefs or wetlands with nursery-grown individuals. Biological criteria described the desired biological condition. Additional responses may need to be enacted to ensure that biocriteria, once established, are achieved and maintained. Monitoring, mapping, and scientific research can be used to better understand changes in condition, bio-physical processes, and interactions among species, and how they may be impacted by various stressors or potential decisions. A healthy functioning reef ecosystem, beyond its existence or cultural value, is essential for a number of ecosystem goods and services, including shoreline protection, fishing, and recreational opportunities.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
More than 50 management options. Click here to load.
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abandoned Shipwreck Act of 1987, 43 United States Code §§ 2101-2106. | To establish title to certain abandoned shipwrecks. U. S. Government asserted three categories of abandoned shipwrecks; embedded in a State's submerged lands, embedded in corralline formations protected by a State on its submerged lands, located on a State's submerged lands and included or determined eligible for inclusion in the National Register of historic Places. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act requires, but is not limited to, development by NPS of guidelines for States and Federal agencies to develop appropriate and consistant policies to protect national resources and habitat areas, and to provide for public and private sector recovery consistant with historical values and environmental integrety. Corralline structures are specifically protected by the Act. Legislative Actions:Specific response will vary from Federal agency to Federal agency and State to State. Comments:The NPS published non-binding, advisory guidelines for States and Federal agencies to establish, review, revise, and implement programs to manage shipwrecks under their ownership or control. The guidance is entitled "Abondoned Shipwreck Act Guidelines." |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States; US State Waters |
Artificial Habitat; Coral; Designated Uses; Marine Protected Areas; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Amendment to the U.S. Caribbean Fishery Management Plans, Code of Federal Regulations § 600 and 622. | NMFS issues this final rule to implement a comprehensive amendment prepared by the Caribbean Fishery Management Council (Council) to amend its Reef Fish, Spiny Lobster, Queen Conch, and Coral Fishery Management Plans (FMPs). The comprehensive amendment is designed to ensure the FMPs are fully compliant with the provisions of the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (Magnuson-Stevens Act). This final rule redefines the fishery management units for the FMPs; establishes seasonal closures; imposes gear restrictions and requirements; revises requirements for marking pots and traps; and prohibits the filleting of fish at sea. In addition, the comprehensive amendment establishes biological reference points and stock status criteria; establishes rebuilding schedules and strategies to end overfishing and rebuild overfished stocks; provides for standardized collection of bycatch data; minimizes bycatch and bycatch mortality to the extent practicable; designates essential fish habitat (EFH) and EFH habitat areas of particular concern (HAPCs); and minimizes adverse impacts on such habitat to the extent practicable. The intended effect of this final rule is to achieve optimum yield in the fisheries and provide social and economic benefits associated with maintaining healthy stocks. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects coral reefs in the USVI and Puerto Rico from overfishing reef resources, specifically reef fish, lobster, and queen conch taking. It establishs seasonal closures, restrictions on the gear used, lists areas of specific biological reference points, and has a schedule and strategy for restocking fishery resources. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Recreational Fishing; Reef Inhabitants |
| Anadromous Fish Conservation Act of 1965, as amended, 16 United States Code § 757. | The Act is intended to conserve anadromous fish. It authorizes the Secretatries of Interior and Commerce to enter into cooperatve agreements with states and other non-federal interests for conservation, development and enhancement of anadromous fish and contribute up to fifty percent as the federal share of the cost of carrying out such agreements. Reclamation construction projects for water resource projects needed solely for such fish are also authorized. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Projects are for conservation, development, and enhancement on fisheries. Comments: |
Department of Interior/Department of Commerce Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Archaeological Resources Protection Act of 1979 as amended, 16 United States Code § 470. | To protect historic ruins, monuments, and objects of antiquity. Strenghtens and expands the protective provisions of the Antiquities Act of 1906 regarding archeological resources. It also revised the permitting process for conducting archeological research. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coastal Development; Cultural Policies; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Bald and Golden Eagle Protection Act of 1940, as amended, 16 United States Code § 668. | Protects Bald and Golden Eagles by prohibiting possession, sale or transport, alive or dead, or part, nest or egg, except as permitted by the Secretary of the Interior for scientific and exhibition purposes, or for religious purposes of Indians Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Fines of $100,000 per incividual, or $200,000 for organizations, or one year in prison, or both, can be utilized. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting |
| Chapter 2: Protection of indigenous, endangered and threatened fish, wildlife and plants, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates activities, including scientific research, that could affect indigenous species and species considered at risk (threatened) or endangered, establishes species of special concern and habitats that should be protected, requires permits for trimming mangroves Application to Coral Reefs:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Legislative Actions:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Chapter 7: Water pollution control, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | In coordination with EPA through Section 401 of the Clean Water Act, establishes controls for the discharge of wastewater and other pollutants to waters of the USVI, sets water quality standards. The Commissioner sets water quality standards applicable to he United States Virgin Islands to protect the public health and welfare and the present and future usa of such waters for public water supplies, propagation of fish, aquatic life and wildlife , recreational purposes and other legitamate uses. The standards are to be reviewed every three years. Application to Coral Reefs:Water of polluted quality is detrimental to propagation and survival of coral reef organisms. Setting appropriate water quality standards will play a major role in protecting coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Commissioner or any USVI resident can commence a civil action. Civil penalties for violators are not to exceed $50,000 per day. Any knowingly or negligently discharging polluants can be crimimnally punished with a fine of not less than $5,000 nor more than $75,000 per day of violation. A second conviction can be punishable up to a fine of $100,000, six years in jail, or both. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Biocriteria; Discharges; Health Policies; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies |
| Clean Water Act of 1974, 33 United States Code § 1252. | To restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the Nation's waters Application to Coral Reefs:The Act can be used to establish water quality standards for the disharge of pollutants into surface waters. Section 101 (3) stated that it will be the national policy that the discharge of toxic pollutants in toxic amounts will be prohibited. The legislation employs a variety of regulatory and nonregulatory tools to reduce direct pollutant discharges into waterways, finance wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The tools are employed to achieve the broad goal of restoring and maintaining the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters so they can support "the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish, and wildlife and recreation in and on the water." Legislative Actions:During the late 1980's, the program shifted from program-by-program, source by source, pollutant-by-pollutant approach to more holistic water-shed strategies. Under the watershed approach equal emphasis is placed on protecting healthy waters and restoring impaired waters. Also during the 1980's, voluntary programs for nonpoint runoff and regulatory programs for wet weather point sources began to be addressed. Comments:The Federal Water Pollution Contrl Act Amendments of 1972, PL 92-500, replaced the previous language of the Act entirely, including the Water Quality Act of 1965, the Clean Water Restoration Act of 1965, and the Water Quality Improvement Act of 1970, all of which had been amendments of the Water Pollution Control Act first passed in 1956. The 1977 amendments, PL 95-217, further amended PL 92-500. |
US Environmental Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States; US Territories |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Drinking Water Supply; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Hydrologic Management; Improved Technology; Mangroves; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sewage Treatment; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Coastal Zone Management Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1451-1456. | Preserve, protect, develop, and where possible, to restore or enhance the resources of the Nation's coastal zone for this and succeeding generations. Application to Coral Reefs:Protection of coastal areas can have an indirect influence on coral reef preservation and conservation by the use of environmentally sound construction and development by limiting runoff of contaminants and sediment that could have an adverse effect on inshore coral reefs if present. Legislative Actions:In addition, the Act authorized a national system of estuarine sanctuaries and the establishment of national field laboratories with a 50/50 cost-sharing grants with coastal states. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
City Planning; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Corporate Responses; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Hydrologic Management; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrients; Permitting & Zoning; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands |
| Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980, "Superfund", 42 United States Code §§ 9601-9675. | Provides Liability, compensation, cleanup, and emergency response for hazardous substances released into the environment. Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Political Pressure; Remediation; Waste Management Policies; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Coral Reef Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6401 (2000). | To preserve, sustain, and restore the condition of coral reef ecosystems, to promote the wise management and sustainable use of coral reef ecosystems, to benefit local communities and the Nation, to develop sound scientific information on the condition of coral reef ecosystems and threats to the ecosystems, to assist in the preservation of coral reefs by supporting and financing conservation programs including local and non-governmental programs, establish a formal mechanism for collecting and allocating monetary donations from the private sector to be used for coral reef conservation projects Application to Coral Reefs:Allowed the development of programs and projects, and provided financing for developing sound scientific data to preserve and restore coral reefs. Continued the Coral Reef Task Force and Coral Reef Initiative started under Executive Order 13089 (1998). Legislative Actions:Provided funding for matching grants, encouraged education and outreach, encouaged cooperative conservation and management through partnerships with other federal, state, regional and local partners including citizen groups. Comments:The Act is administrative, not regulatory. It established four major programs; (1) The National Coral Reef Action Strategy established goals for research, monitoring and conservation, (2, 3) The Coral Reef Conservation Program and Coral Reef Conservation Fund provided financial assistance for coral reef projects, (4) the National Program facilitated cooperative work between federal, state and regional efforts that work to improve coral reef ecosystems. The National Program also enhanced the public awareness of coral reefs through educational programs. The Act incorporated Executive Order 13,089 and provided coordinated funding activities through twelve federal agencies and seven states. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States; US Coral Reefs |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corporate Responses; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Food & Raw Materials; Funding & Incentives; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Public Administration; Remediation; Utilities |
| Domestic Wastewater Facilities, 62-600 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.021(2), Florida Statutes, as amended, the Florida Air and Water Pollution Control Act, established that no
wastes are to be discharged to any waters of the state without first being given the degree of treatment necessary to protect the
beneficial uses of such water. Toward this end, Sections 403.085 and 403.086, Florida Statutes, set forth requirements for the
treatment and reuse or disposal of domestic wastewater. Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, requires that any Department
planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be
developed as a rule. This chapter is promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of Sections 120.53(1), 120.55,
403.021, 403.051, 403.061, 403.062, 403.064, 403.085, 403.086, 403.087, 403.088, 403.0881, 403.101, 403.131, 403.161,
403.182, 403.859, and 403.918, Florida Statutes, concerning domestic wastewater facilities.
- 442
(2) The requirements of this chapter represent the specific requirements of the Florida Department of Environmental Protection
and of Local Pollution Control Programs approved and established pursuant to Section 403.182, Florida Statutes, where such
authority has been delegated to those programs. It may be necessary for domestic wastewater facilities to conform with
requirements of other agencies, established via interagency agreements (e.g., for mosquito control); the absence of reference to
such arrangements in this chapter does not negate the need for compliance with those requirements.
(3) The purpose of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., is to provide minimum standards for the design of domestic wastewater facilities
and to establish minimum treatment and disinfection requirements for the operation of domestic wastewater facilities. All systems
shall be designed in accordance with sound engineering practice. Supported by moderating provisions, it is intended that Chapter
62-600, F.A.C., establish a framework whereby design flexibility and sound engineering practice can be used in developing
systems with which to manage domestic wastewater in an environmentally sound manner.
(4) As appropriate, Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., shall be used in conjunction with other Department rules relating to the design and
operation and maintenance of domestic wastewater facilities.
(5) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities
(including residuals management facilities).
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and modifications or expansions of existing facilities that
submit complete permit applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit complete applications for permit renewal after
July 1, 1991.
(6) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications on or before July 1, 1991, may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the time the permit was issued and with the conditions
of the existing construction or operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter.
(7) The standards and requirements of Part II of Chapter 62-600, F.A.C., and Rules 62-600.500 and 62-600.530, F.A.C., shall
be applicable to septic tank drainfield systems and other on-site waste treatment systems with subsurface disposal regulated by this
chapter. The reliability requirements of paragraph 62-600.400(1)(b), F.A.C., shall not apply to such septic tank drainfield systems
and other on-site waste treatment systems.
(8) The discharge limitation of subsection 62-600.510(4), F.A.C., shall not be applicable to facilities permitted on or before
January 1, 1982, that discharge into Class II waters or Class III waters which are subsequently reclassified as Class II waters.
(9) This chapter provides for exemptions, allowances for existing facilities and variations from standards and requirements.
Unless specifically provided otherwise, no wastewater permit shall be issued or renewed unless the permit applicant demonstrates
that the subject facility is in compliance with the applicable provisions of this chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting construction and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the processes for planning, design, construction, modification, or operating standards, criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Domestic Wastewater Treatment Plant monitoring, 62-601 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) Section 403.051(2)(a), Florida Statutes, as amended, part of the Florida
Air and Water Pollution Control Act, requires that any Department operating standards,
criteria, and requirements for wastewater facilities be developed as a rule. This rule is
promulgated to implement the provisions and requirements of the Act concerning
domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring.
(2) The purpose of Chapter 62-601, F.A.C., is to ensure that owners and
operators of domestic wastewater treatment facilities maintain accurate records and
submit reports required by this Chapter in a timely, accurate, cost-effective and uniform
manner.
(3) Standards and requirements in this chapter shall apply only to domestic
wastewater treatment, reuse, and disposal facilities (including residuals management
facilities). The standards and requirements are not applicable to facilities described in
Rules 62-600.120(1) and (2), F.A.C.
(a) Standards and requirements shall apply to all new facilities and
modifications or expansions of existing facilities that submit complete permit
applications to the Department after July 1, 1991.
(b) Standards and requirements shall apply to all existing facilities that submit
complete applications for permit renewal after July 1, 1991.
(4) Domestic wastewater facilities that submit complete permit applications
on or before July 1, 1991 may:
(a) Continue to comply with the rule requirements that were in effect at the
time the permit was issued and with the conditions of the existing construction or
operation permit until the expiration of such permit, or
(b) Opt to comply with the requirements of this revised chapter. Application to Coral Reefs:Setting monitoring requirements and treatment water quality criteria for wastewater facilities will provide a system of less contaminated water being discharged to surface waters. The environmental impact of the wastewater will be less harmful to ecosystems. Legislative Actions: Comments:to implement the provisions and requirements concerning domestic wastewater treatment plant monitoring |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters |
Biocriteria; Building & Home Construction; Discharge Limitations; Manufacturing & Trade; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Sewage Treatment; Toxics; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Endangered Species Act of 1973, 16 United States Code §§ 1531-1544, 1361-1407. | To protect animal and plant species currently in danger of extinction (endangered) and those that may become endangered in the foreseeable future (threatened). Authorized the determination and listing of species as endangered and threatened; Prohibited unauthorized taking, possession, sale, and transport of endangered species; Provided authority to acquire land for the conservation of listed species, using land and water conservation funds; Authorized establishment of cooperative agreements and grants-in-aid to states that establish and maintain active and adequate programs for endangered and threatened wildlife and plants; Authorized the assessment of civil and criminal penalties for violating the act or regulations; and Authorized the payment of rewards to anyone furnishing information leading to arrest and conviction for any violation of the act. Application to Coral Reefs:Two species of coral are listed as threatened; elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata) and staghorn coral (Acropora cervicornis). They were placed on the list in 2006.Their habitat was listed as "critical habitat" in 2008. Legislative Actions:The Act provided for criminal and civil penalties dependent on the sections of the Act under which violations occured. Criminal penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $50,000 and not more than one year in prison. Civil penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $25,000. The Act provided for rewards to citizens that report violations leading to sucessful prosecution. The rewards are paid from the fine received. Comments:Listed species and critical habitats can be found in the Federal Register. The habitats for staghohn (73FR72210) and elkhorn (73FR72210) corals were declared critical in 2008. Since the entire coral reef is habitat for the species, critical designation could offer a method of protecting and conserving the reef. In this instance, by protecting individual species and their habitat, the entire reef is protected. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration /National Marine Fisheries Service/USFish and Wildlife Service (consultations with all federal agncies responsible for section 7(a)(1) compliance Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Coral; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Exec. Order No. 12962, Recreational Fisheries, 60 Federal Register (1995). | Federal agencies are directed to improve the quantity, function, sustainable productivity, and distribution of U.S. aquatic resources for increased recreational fishing opportunities in cooperation with states and tribes. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Exec. Order No. 13112, Invasive Species, 68 Federal Register 6183 (1990). | Federal agencies are directed to prevent the introduction of invasive species, detect and rapidly respond to control populations of such species in a cost effective and environmentalyy sound manner, accurately monitor invasive species, provide for restoration of native species and habitat conditions, conduct research to prevent introduction and to control invasive species, and promote public education on invasive species and the means to address them. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:No enforcement provisions. Federal agencies are encouraged to prevent the introduction, detect and respond to control, monitor, and conduct research of invasives. Secretary of Interior established an "Invasive Species Council" to address invasive species issues. Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Invasive Species; Political Pressure; Remediation |
| Exec. Order No. 13158, Marine Protected Areas, 65 Federal Register 34909 (2000). | This Executive Order is meant to help protect the significant natural and cultural resources within the marine environment for the benefit of present and future generations by strengthening and expanding the Nation�s system of marine protected areas. Application to Coral Reefs:Benefits to coral reefs within MPA's. Legislative Actions:One of the provisions of the Act requires that the Secretary develop a scientifically based, comprehensive system of MPA's representing diverse US marine ecosystems, and the Nation's natural and cultural resources. Comments: |
Department of Interior, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act of 1980, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | Required the Service to monitor non-game bird and fish species, identify species of management concerns, and implement conservation measures to preclude the need for listing under the Endangered Species Act. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Designate Protected Species; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Fish and Wildlife Service Act of 1956, 16 United States Code § 742. | Establishes a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on the commercial fishing industry but also includes the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment, and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife resources. Among other things, it authorizes the Secretary of the Interior to take such steps as may be required for the development, advancement, management, conservation, and protection of fish and wildlife resources, including, but not limited to, research, development of existing facilities, and acquisition by purchase or exchange of land and water or interests therein. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act is written for the support of commercial and recreational fisherpersons so that they enjoy the benefits of the Nation's fishery resources. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: |
Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Act of 1976, as amended through 1996,. | Provided for conservation and management of commercial and recreational fisheries in the US Exclusive Economic Zone (3-200 nautical miles offshore). Application to Coral Reefs:The Act recognized, and stated, that one of the greatest long-term threats to viable commercial and recreational fisheries is the continued loss of marine, esturaine, and other aquatic habitats, and that habitat considerations should receive increased attention for the conservation and management of fishery resources. Legislative Actions:The amended Act through 1996 created eight regional Fishery Management Councils and reguired foreign vessels to apply for permits to fish in US waters. The Councils develop Management plans for every fishery within their geographic region regarding guidelines for quota, bycatch caps and gear restrictions.. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: |
Biocriteria; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Resource Use Management; Responses |
| Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Reauthorization Act as amended through January 2007, Statutes at Large §§ 94-265. | National program for the conservation and management of fishery resources of the US to prevent overfishing, to rebuild overfished stocks, to facilitate the long-term protection of essential fish habitat, and to realize the full potential of the Nation's fishery resources. Application to Coral Reefs:Promote the protection of essential fish habitat in the review of projects conducted under federal permits, licenses, or other authorities that effct or have the potential to affect such habitats. The amendments of 2006 specifically require the protection of deep sea coral habitats. Legislative Actions:Requires government observers on board a certain number of fishing vessels. The Act provides for criminal and civil penalties dependent on the sections of the Act under which violations occured. Criminal penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $50,000 and not more than one year in prison. Civil penalties may be imposed including seizure, forfeiture, and condemnation of property. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Economic Markets & Policies; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972, 16 United States Code § 1361. | With certain exceptions, the Act establishes a mortiorium on the taking and importation of marine mammals, as well as products that are made from them. DOI is responsible for sea otter, walrus, polar bear, diugong and manatee. The DOC is responsible for Cretaceans and piniped other than the walrus. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The legislation mandated the use of an ecosystem-based management approach to marine resource management. The Marine Mammal Commission was established and has specific advisory and research duties. Required that government observers aboard some fishing vessels. Comments:The Act covers all species of marine mammals and plants, including anadromous fish, except for marine ammmals, birds, and highly migratory species, all of which are covered under other laws or treaties. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Designate Protected Species; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins |
| Marine Mammals, 50 Code of Federal Regulations. | The regulations prohibit the capture of marine mammals on land or sea in US waters and prohibits the improtation of any marine mammal product to the US (CFR 216.11-216.12) unless the person has a permit for scientific purposes (CFR 216.33-216.37). Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Political Pressure; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Whales & Dolphins |
| Marine Protection, Research, and Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 33 United States Code § 1401. | To regulate the dumping of all types of materials into ocean waters and to prevent or strictly limit the dumping into ocean waters of any material which would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities. To regulate (1) the transportation by any person of material from the United States and, in the case of United States vessels, aircraft, or agencies, the transportation of material from a location outside the United States, when in either case the transportation is for the purpose of dumping the material into ocean waters, and (2) the dumping of material transported by any person from a location outside the United States, if the dumping occurs in the territorial sea or the contiguous zone of the United States. Application to Coral Reefs:The Act has been historically used to regulate dumping of dredged materials and sewage sludge into the marine environment. The law intends to improve the conservation, understanding, management, and wise and sustainable use of marine resources, enhance public awareness, understanding, and appreciation of the marine environment, and to maintain for future generations the habitat, and ecologigal services, of the natural assemblage of living resources that inhabit those areas. Because permits are required, it can be assumed that dumping would not be allowed if the material would be dispersed into a sensitive habitat such as coral reefs. Legislative Actions:EPA may assess an administrative civil penalty up to $50,000 per person. Higher penalties can be assessed for dumping medical waste (up to $125,000). Each day in violation constitutes a separate offense. Continuing violations can suffer criminal penalties with fines and up to five years imprisionment possible. Comments:The Act has played a major role in regulating the disposal of dredged material into the ocean environment. However, medical and radioactive wastes, industrial wastes, as well as sewage sludge, are also regulated in the law. |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: US Territorial Waters; US Federal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biocriteria; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Marine Turtle Conservation Act of 2004, 16 United States Code § 6601. | The law was created to aid in the conservation of sea turtles and their nesting habitats in foreign countries by providing funds for the conservation of nesting areas, sea turtles in in their nesting habitats, and dealing with threats to sea turtle survival. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service/US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Designate Protected Species; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles |
| Migratory Bird Treaty Act, 16 United States Code § 715. | The Act established a Federal prohibition, unless permitted by regulations, to pursue, hunt, take, capture, kill, attempt to take, capture or kill, possess, offer for sale, sell, offer to purchase, purchase, deliver for shipment, ship, caused to be shipped, deliver for transport, carry, or cause to be carried by any means whatever, receive for shipment, transport or carriage, or export, at any time,or in any manner, any migratory bird, included in the terms of this Convention�for the protection of migratory birds�or any part, nest, or egg of such a bird. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Recent amendments to the Act increased the fine for misdemeanor convictions from $5000 to $15,000. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Designate Protected Species; Marine Birds; Resource Use Management |
| Mitigation Banking, 62-342 Florida Administrative Code. | (1) The Department recognizes that, in certain instances, adverse impacts of activities regulated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., can be offset through the utilization of mitigation credits from a permitted Mitigation Bank. This rule provides criteria for this mitigation alternative to complement existing mitigation criteria and requirements. This chapter is supplemental to and does not supersede any other criteria and requirements in rules promulgated under Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S.
(2) The Department intends that Mitigation Banks be used to minimize mitigation uncertainty associated with traditional mitigation practices and provide greater assurance of mitigation success. It is anticipated that the consolidation of multiple mitigation projects into larger contiguous areas will provide greater assurance that the mitigation will yield long-term, sustainable, regional ecological benefits. Mitigation Banks shall be consistent with Department endorsed watershed management objectives and emphasize restoration and enhancement of degraded ecosystems and the preservation of uplands and wetlands as intact ecosystems rather than alteration of landscapes to create wetlands. This is best accomplished through restoration of ecological communities that were historically present. The establishment and use of Mitigation Banks in or adjacent to areas of national, state, or regional ecological significance is encouraged, provided the area in which the Mitigation Bank is proposed to be located is determined appropriate for a Mitigation Bank and the Mitigation Bank meets all applicable permitting criteria.
(3) Nothing in this chapter shall affect the mitigation requirements set forth in any Mitigation Bank agreement or any permit issued under Chapter 84-79, Laws of Florida, or Part IV of Chapter 373, F.S., prior to February 2, 1994. If a permittee wishes to substantially modify a Mitigation Bank previously established by agreement or permit, the permittee must comply with this chapter. Additionally, some Mitigation Banks may be subject to the version of this section existing prior to July 1, 1996, under subsections 373.4136(9) and (10), F.S., and will not be affected by amendments adopted after that date. This chapter does not prohibit an applicant from proposing project-specific, pre-construction on-site or off-site mitigation, without establishing a Mitigation Bank. Application to Coral Reefs:Mitigation banking in coastal wetlands, as presented in the Chapter, can provide large areas of functioning wetlands. The wetlands can function as sediment and nutrient traps keeping sediment and nutrients from entering coastal waters and damaging marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments:Establishes the regulations and permitting requirements for mitigation banks. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US State Waters |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Docks & Marinas; Educational & Research Opportunities; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Ports & Harbors; Shoreline Armoring; Waste Management Policies |
| National Environmental Policy Act of 1969, 42 United States Code §§ 4321-4377. | Requires analysis, public comment, and reporting for environmental impacts of federal actions. It stipulates the factors to be considered in environmental impact statements, and requires that federal agencies employ an interdisciplinary approach in related decision-making and develop means to ensure unqualified environmental values are given appropriate consideration, along with economic and technical considerations. Application to Coral Reefs:Requires an Environmental Assessment(EA), and potentially an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) if the project review finds there will be a significant impact. The EIS must detail the environmental impacts of the proposed action, unavoidable adverse environmental impacts, and alternatives to the proposed action. The resulting studies could protect sensitive environmental ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:The Act potentially could protect coral reefs if the proposed federal project could have a significant impact on the reef. Comments:The Act is completely procedural; it does not include specific regulations. The Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) was created by the Act. CEQ is part of the Executive Office of the President and one of the CEQ directives is to ensure that federal programs comply with NEPA. The puprose of the EIS is to disclose to the public and resource managers the probable long- and short-term impacts of the proposed project as well as consideration of less environmentally damaging alternatives to the recommended course of action. |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Energy Policy & Development; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Marine Debris; Microorganisms; Non-point Source Controls; Permitting & Zoning; Physical & Chemical Environment; Physical Variables; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Security; Socio-Economic Drivers; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972, 16 United States Code §§ 1431-1445. | Authorizes the Secretary of Commerce to designate and manage areas of the marine environment with special national significance due to their conservation, recreational, ecological, historical, scientific, cultural, archeological, educational, or esthetic qualities as National Marine Sanctuaries. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects marine resources, such as coral reefs, sunken historical vessels, or unique habitats. Legislative Actions:NOAA may impose civil penalties up tp $130,000 per day per violation. Criminal penalties were added in the 2000 amendments for interfering or resisting with any enforcement of the NMSA, or providing false information to the Secretary or any officer authorized to enforce NMSA. The 2000 amendments made it illegal to offer for sale, purchase, import, or export, any sanctuary resource and increased enforcement authority. Comments:There are 13 marine sanctuaries in the National Marine Sactuary System, six of which were created after 1990. Each sanctuary has a separarte staff and program in its local region. |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; CO2; Coastal Development; Commercial Fishing Boats; Coral; Corporate Responses; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Nutrients; Ocean Acidity; Oil & Gas Research & Exploration; Political Pressure; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| National Park Service General Partnership Authorities of 1970, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act supplemented and clarified the National Park Service's mandate with respect to the management of the National Park System. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Designated Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| National Park Service Organic Act of 1916, 16 United States Code § 1. | The Act was created to start the National Park Service within the Department of Interior for the purpose of promoting and regulating the use of federal areas such as national parks and monuments. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Created the National Park Service to be supervised by a Director. Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Construction Codes & Projects; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invasive Species; Landuse Management; Marine Protected Areas; Microorganisms; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Park Service, Department of Interior,. | To conserve the scenery, natural and historic objects, and wildlife of the National Parks; and to provide for the enjoyment of those resources in a sustainable manner. Regulations provide for the proper use, management, government, and protection of persons, property, and natural and cultural resources within areas under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Park Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Construction Codes & Projects; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designated Uses; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| National Wildlife Refuge System Administration Act of 1966, 16 United States Code § 66. | The Act defines the National Wildlife Refuge System and authorizes the Secretary of Interior to permit any use of a refuge provided such use is compatible with the major purpose for which the refuge was established. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Serice Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Construction Codes & Projects; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Landuse Management; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Political Pressure; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies |
| Neotropical Migratory Bird Conservation Act of 2000, 16 United States Code § 6101. | Established a matching grant program to fund projects that promote the conservation of neotropical migratory birds in the United States, Latin America, and the Caribbean. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act provided competitive grants in Latin America, the Carribean, and the United States for neotropical migratory birds that winter south of the border and summer in North America. The law encourages habitat protection, education, research, monitoring, and capacity building to provide for long-term protection of neotropical migratory birds. Comments:Over 800 species of birds are found in the United States and 500 migrate South of the border for the winter. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States; Latin America; Caribbean |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| North American Wetlands Conservation Act of 1989, 16 United States Code § 4411. | Provides funding and administrative direction for the implementation of the North American Waterfowl Management Plan and the Tripartite Agreement between Canada, the United States, and Mexico. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:A North American Wetlands Conservation Council was created to recommend projects to be funded under the Act to the Migratory Bird Conservation Commission. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Canada; Mexico |
Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Funding & Donations; Marine Birds; Public Administration |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Rules and Procedures for Coastal Construction and Excavation, 62B-033 Florida Administrative Code (2008). | (1) The beach and dune system is an integral part of the coastal system and represents one of the most valuable natural resources in Florida, providing protection to adjacent upland properties, recreational areas, and habitat for wildlife. A coastal construction control line (CCCL) is intended to define that portion of the beach and dune system which is subject to severe fluctuations caused by a 100-year storm surge, storm waves, or other forces such as wind, wave, or water level changes. These fluctuations are a necessary part of the natural functioning of the coastal system and are essential to post-storm recovery, long term stability, and the preservation of the beach and dune system. However, imprudent human activities can adversely interfere with these natural processes and alter the integrity and functioning of the beach and dune system. The control line and 50-foot setback call attention to the special hazards and impacts associated with the use of such property, but do not preclude all development or alteration of coastal property seaward of such lines.
(2) In order to demonstrate that construction is eligible for a permit, the applicant shall provide the Department with sufficient information pertaining to the proposed project to show that adverse and other impacts associated with the construction have been minimized and that the construction will not result in a significant adverse impact.
(3) After reviewing all information required pursuant to this rule chapter, the Department shall:
(a) Deny any application for an activity which either individually or cumulatively would result in a significant adverse impact including potential cumulative effects. In assessing the cumulative effects of a proposed activity, the Department shall consider the short-term and long-term impacts and the direct and indirect impacts the activity would cause in combination with existing structures in the area and any other similar activities already permitted or for which a permit application is pending within the same fixed coastal cell. The impact assessment shall include the anticipated effects of the construction on the coastal system and marine turtles. Each application shall be evaluated on its own merits in making a permit decision; therefore, a decision by the Department to grant a permit shall not constitute a commitment to permit additional similar construction within the same fixed coastal cell.
(b) Deny any application for an activity where the project has not met the Department�s siting and design criteria; has not minimized adverse and other impacts, including stormwater runoff; or has not provided mitigation of adverse impacts.
(4) The Department shall issue a permit for construction which an applicant has shown to be clearly justified by demonstrating that all standards, guidelines, and other requirements set forth in the applicable provisions of Part I, Chapter 161, F.S., and this rule chapter are met, including the following:
(a) The construction will not result in removal or destruction of native vegetation which will either destabilize a frontal, primary, or significant dune or cause a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system due to increased erosion by wind or water;
(b) The construction will not result in removal or disturbance of in situ sandy soils of the beach and dune system to such a degree that a significant adverse impact to the beach and dune system would result from either reducing the existing ability of the system to resist erosion during a storm or lowering existing levels of storm protection to upland properties and structures;
(c) The construction will not direct discharges of water or other fluids in a seaward direction and in a manner that would result in significant adverse impacts. Forthe purposes of this rule section, construction shall be designed so as to minimize erosion induced surface water runoff within the beach and dune system and to prevent additional seaward or off-site discharges associated with a coastal storm event.
(d) The construction will not result in the net excavation of the in situ sandy soils seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback;
(e) The construction will not cause an increase in structure-induced scour of such magnitude during a storm that the structure-induced scour would result in a significant adverse impact;
(f) The construction will minimize the potential for wind and waterborne missiles during a storm;
(g) The activity will not interfere with public access, as defined in Section 161.021, F.S.; and
(h) The construction will not cause a significant adverse impact to marine turtles, or the coastal system.
(5) In order for a manmade frontal dune to be considered as a frontal dune defined under Section 161.053(6)(a)1., F.S., the manmade frontal dune shall be constructed to meet or exceed the protective value afforded by the natural frontal dune system in the immediate area of the subject shoreline. Prior to the issuance of a permit for a single-family dwelling meeting the criteria of Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., the manmade frontal dune must be maintained for a minimum of 12 months and be demonstrated to be as stable and sustainable as the natural frontal dune system.
(6) Sandy material excavated seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback shall be maintained on site seaward of the control line or 50-foot setback and be placed in the immediate area of construction unless otherwise specifically authorized by the Department.
(7) Swimming pools, wading pools, waterfalls, spas, or similar type water structures are expendable structures and shall be sited so that their failure does not have adverse impact on the beach and dune system, any adjoining major structures, or any coastal protection structure. Pools sited within close proximity to a significant dune shall be elevated either partially or totally above the original grade to minimize excavation and shall not cause a net loss of material from the immediate area of the pool. All pools shall be designed to minimize any permanent excavation seaward of the CCCL.
(8) Major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the beach and frontal dune to permit natural shoreline fluctuations, to preserve and protect beach and dune system stability, and to allow natural recovery to occur following storm-induced erosion. Where a rigid coastal structure exists, proposed major structures shall be located a sufficient distance landward of the rigid coastal structure to allow for future maintenance or repair of the rigid coastal structure. Although fishing piers shall be exempt from this provision, their foundation piles shall be located so as to allow for the maintenance and repair of any rigid coastal structure that is located in close proximity to the pier.(9) If in the immediate area a number of existing major structures have established a reasonably continuous and uniform construction line and if the existing structures have not been unduly affected by erosion, except where not allowed by the requirements of Section 161.053(6), F.S., and this rule chapter, the Department shall issue a permit for the construction of a similar structure up to that line.
(10) In considering applications for single-family dwellings proposed to be located seaward of the 30-year erosion projection pursuant to Section 161.053(6), F.S., the Department shall require structures to meet criteria in Section 161.053(6)(c), F.S., and all other siting and design criteria established in this rule chapter.
(11) In considering project impacts to native salt-tolerant vegetation, the Department shall evaluate the type and extent of native salt-tolerant vegetation, the degree and extent of disturbance by invasive nuisance species and mechanical and other activities, the protective value to adjacent structures and natural plant communities, the protective value to the beach and dune system, and the impacts to marine turtle nesting and hatchlings. The Department shall restrict activities that lower the protective value of natural and intact beach and dune, coastal strand, and maritime hammock plant communities. Activities that result in the removal of protective root systems or reduce the vegetation�s sand trapping and stabilizing properties of salt tolerant vegetation are considered to lower its protective value. Construction shall be located, where practicable, in previously disturbed areas or areas with non-native vegetation in lieu of areas of native plant communities when the placement does not increase adverse impact to the beach and dune system. Planting of invasive nuisance plants, such as those listed in the Florida Exotic Pest Plant Council�s 2005 List of Invasive Species � Categories I and II, will not be authorized if the planting will result in removal or destruction of existing dune-stabilizing native vegetation or if the planting is to occur on or seaward of the dune system. A copy of this list is available on the Internet at www.fleppc.org; or can be obtained by writing to the Department of Environmental Protection, Bureau of Beaches and Coastal Systems, 3900 Commonwealth Boulevard, Mail Station 300, Tallahassee, Florida 32399-3000; or by telephoning (850) 488-7708. Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction and the remediation of construction impacts shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect native salt-tolerant vegetation and native plant communities. A construction fence, a designated location for construction access or storage of equipment and materials, and a restoration plan shall be required if necessary for protection of existing native salt-tolerant vegetation during construction.
(12) Special conditions relative to the nature, timing, and sequence of construction shall be placed on permitted activities when necessary to protect marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. In marine turtle nesting areas, all forms of lighting shall be shielded or otherwise designed so as not to disturb marine turtles. Tinted glass or similar light control measures shall be used for windows and doors which are visible from the nesting areas of the beach. The Department shall suspend any permitted construction when the permittee has not provided the required protection for marine turtles and their nests and nesting habitat. Application to Coral Reefs:Regulation of coastal construction through permit review and modification will protect coastal ecosystems from degradation and loss and in doing so protects other marine ecosystems including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Chapter 62B-33 Florida Administrative Code, provides the design and siting requirements that must be met to obtain a coastal construction control line permit.Approval or denial of a permit application is based upon a review of the potential impacts to the beach dune system, adjacentproperties, native salt resistant vegetation, and marine turtles. Comments:The Coastal Construction Control Line (CCCL) is an essential element of Florida's coastal management program. It provides protection for Florida's beaches and dunes while assuring reasonable use of private property. Recognizing the value of the state's beaches, the Florida legislature initiated the Coastal Construction Contorl Line Program to protect the coastal system from improperly sited and designed structures which can destabilize or destroy the beach and dune system. Once destabilized, the valuable natural resources are lost, as are its important values for recreation, upland property protection and environmental habitat. Adoption of a coastal construction line establishes an area of jurisdiction in which special siting and design criteria are applied for construction and related activities.These standards may be more stringent than those already applied in the rest of the coastal building zone because of the greater forces expected to occur in the more seaward zone of the beach during a storm event. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Beach & Land Formation; Building & Home Construction; City Planning; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Construction Codes & Projects; Cruise Ships; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Pipelines; Ports & Harbors; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Shoreline Armoring; Shoreline Protection; Storms & Hurricanes; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Depth & Sea Level |
| Significant amendments to the National Marine Sanctuaries Act of 1972. Amendments of 1980 were PL 96-332, 1984 were PL98-498, 1988 were Title II of PL 100-627, 1992 were PL 102-587, 1996 were PL 104-283 and for 2000 were PL106-513,. | Title III of the Marine Protection, Reseach and Sanctuaries Act was amended to create the National Marine Sanctuaries Program. The amendments of 1980 mandated the terms of designation to include the geographic area included within the sanctuary and the characteristics of the area that give it conservation, recreational, ecological, or esthetic value, and the types of activities that would be subject to regulation to protect those characteristics. The 1984 amendments required a Resource Assessment Report documenting present and potential use of the area. 1998 amendments established a special use permit for commercial operations, added a section that a vessel or person causing damage to the resources of a sanctuary would be liable for both response and cleanup costs as well as damages for any sanctuary resource destroyed. Amendments of 1992 provided that Title III may be cited as 'The National Marine Sanctuaries Act." Also, federal agencies had to be consistent with the National Environmental Policy Act in commenting on proposed designations. Application to Coral Reefs:Strenghtened the protectinon of marine sanctuaries and their resources. Some specific purposes of the Act that add to coral reef protection include; to identify and designate national marine sanctuaries of the marine environment, to maintain the natural b Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Oceanic Aatmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Construction Codes & Projects; Coral; Cruise Ships; Deforestation & Devegetation; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Large Ships; Mangroves; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act of 1986, 42 United States Code §§ 9601 et seq. | Reautorized CERCLA Application to Coral Reefs:If a hazardous waste is spilled or discaharge illegally at or near a coral reef, the CERCLA/SARA could be used for rapid response and cleanup of the spill or discharge. Legislative Actions:The amended Act stressed the importance of permanent and innovative treatment technologies, required Superfund actions to consider the standards and requirements found in other State and Federal environmental laws, provided new enforcement authorities and settlement tools. Comments: |
United States Environmntal Protection Agency Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Improved Technology; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Political Pressure; Remediation; Security & Public Administration Policies; Waste Management Policies |
| Surface water quality standards, 62-302 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2008). | The Chapter establishes the minimum concentrations of contamination that are allowable to protect the designated uses of a waterbody. Designated uses include public drinking water supplies, propagation of fish and wildlife, agricultural, recreation, industrial, and navigation. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting surface waters by limiting the concentration of pollutants that can be present will control the concentrations of those pollutants that will reach estuarine and marine environments, thus protecting the associated ecosystems, including coral reefs. Legislative Actions:Penalties are not presented in the Rule. Specific requirements and penalties are addrressed in individual permits. The Rule relies heavily on biocriteria including acute toxicity, chronic toxicity, Shannon-Weaver Diversity Index. Section 400 presents the classes of Florida waters; Class I potable water supplies, Class II shellfish propagation or harvesting, Class III recreation, propagation and maintenance of a healthy, well-balanced population of fish and wildlife, Class IV agricultural water supplies, Class V navigation, utility and industrial use. Comments: |
Florida Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biocriteria; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Civil Engineering & Construction; Coastal Development; Commercial Fisheries; Complex Habitat & Resources; Dam Construction & Maintenance; Deforestation & Devegetation; Designate Protected Species; Discharge Limitations; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Drinking Water Supply; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Impervious Surfaces; Invertebrates; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Pipelines; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Toxics; Waste Management Policies |
| Total maximum daily loads, 62-304 Florida Administrative Code Annotated (2006). | The Chapter establishes Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs), and their allocations, for waters that have been verified to be impaired by a pollutant pursuant to Chapter 62-303. F.A.C. Application to Coral Reefs:By regulating the amount of pollutants that will be allowed to be discharged into major waterbodies of the state, the amount of pollutants reaching estuarine and then marine environments, and eventually coral reefs, will assist in protecting the reefs and other habitats. Legislative Actions:The planning list of impaired water bodies has been completed. Data on each water bodies has been collected. DEP is in the process of calculating TMDLs for each water body. Comments: |
Florida Department of Envitonmental Protection Jurisdiction: United States; State Coastal Waters |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Ballast Discharge; Biomedical Research Policies; Coastal Development; Deforestation & Devegetation; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Dredging Regulations; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Impervious Surfaces; Irrigation; Landuse Management; Metals, Electronics, & Machinery Products; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point Source Discharges; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Shoreline Armoring; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
