ReefLink Database

Biological Harvest
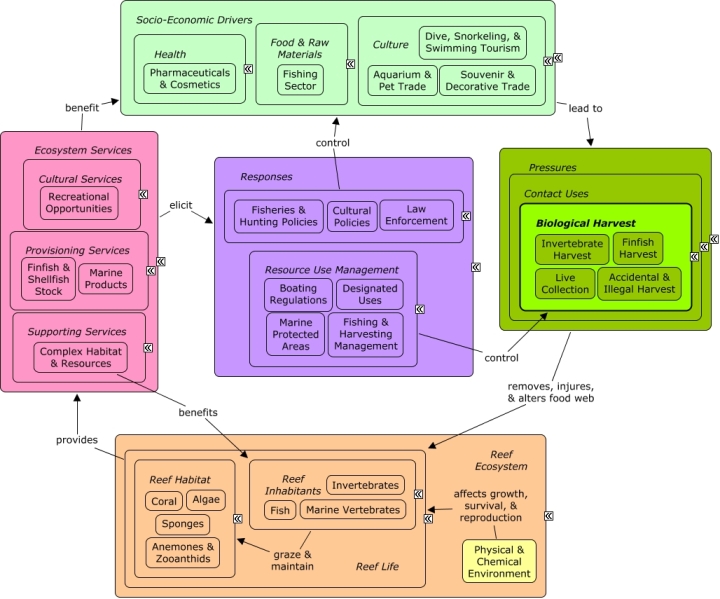
Biological Harvest is the collection of living things from the ecosystem for recreation, consumption, or sale of marine products. Harvest includes commercial and recreational fishing, invertebrate harvesting, live rock collection, accidental by-catch, and illegal harvest.
CMap
CMap Description
Harvesting of fish and invertebrates creates pressures on the reef ecosystem. Non-target species may be harvested or damaged during fishing activities. Overfishing of key species, particularly herbivores, can cause trophic cascades that increase the risk of algal overgrowth. The socio-economic sectors that create pressures on the reef ecosystem through harvesting are the same sectors that depend on the reef for recreational value, finfish and shellfish, and other marine products. These sectors also indirectly benefit from the complex structure formed by coral, seagrasses, and mangroves, which provide food and habitat for target fish and invertebrate species. Decision-makers can manage resources through fishing & harvesting policies that limit or direct fishing activities,;by designating protected areas orprotected species; or by increasing law enforcement to reduce illegal harvest.Citations
More than 50 citations. Click here to load.
| Citation | Year | Study Location | Study Type | Database Topics |
|---|
Management Options
| Management Option | Description | Sources | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture & Aquaculture: Bivalve Aquaculture Biofouling Control | These management options reduce, clean or remove biofouling organisms and other waste from bivalve production areas while minimizing environmental risk. Aquaculture shellfish production requires adequate food availability and water of dependable quantity and quality. Aquaculture operations and gear must have a minimal adverse impact on the surrounding water, plant, animal and human resources. Biofouling is detrimental to shellfish production, increasing exposure to pathogens, reducing the available food stuffs, and increasing organic loading. Only environmentally appropriate biofoul control methods should be used, and fouling organisms and algae should be disposed of appropriately to avoid local degradation. | Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. Conservation Practice Standard: Bivalve Aquaculture Gear and Biofouling Control. CODE 400, USDA. |
Algae; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Chemical Variables; Discharge Limitations; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Improved Technology; Invertebrate Harvest; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Non-point Source Controls; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Octopus & Squid; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Snails & Conch; Supplemental Feeding |
| Develop & Distribute Educational Materials: Establish VHF Radio Stations | The local sanctuary staff should work to secure a VHF radio station dedicated to provide information about local boating and water activities in multiple languages. Broadcast messages can include, but are not limited to information about regulations, navigation, resources, weather, and reef conditions. This will help prevent boaters, divers, and fishermen from negatively affecting the ecosystem. Assessments regarding cost and target audience areas must be conducted and external funding pursued to supplement the expense. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Create Alternative Livelihoods For Fishermen | Many fishermen rely on their catch as their family�s main source of income. When restrictions are placed on fishing it can be to the economic detriment of these fishermen. By creating alternative means of earning income for these fishermen, social and economic goals are accomplished while decreasing pressures on natural fish populations. These alternatives often come in the form of aquaculture, which helps to still meet the demand for fish. Another common alternative is tourism; fishermen can use their knowledge and equipment such as boats to accommodate tourism and recreational fishing. | All Islands Coral Reef Committee. Local Action Strategies. United States Coral Reef Task Force Accessed 6/13/2011. Sumaila, U.R., William W. L. Cheung and Louise The. 2007. Rebuilding Hong Kong's marine fisheries: an evaluation of management options. FCRR 2007, Vol. 15(3), Fisheries Centre, The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Cultural Policies; Culture; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Health; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Social Assistance; Tourism & Recreation |
| Economic Markets & Policy: Regulate International Trade of Reef Species | Many coral reef species are harvested internationally for a variety of markets including the aquarium trade, food, curios, jewelry and pharmaceuticals. The US is the largest importer for many of these markets. The US strictly limits extraction of stony coral and many reef species in its waters; but as a major importer and consumer of coral reef species, more actions can be taken to decrease the demand on international imports. Setting and enforcing regulations on what can be imported (such as Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species CITES) is one approach that has been taken. More information is needed, leaving room to collect trade data and assess the impacts of extraction techniques to find sustainable methods. Demand for species collected this way will be increased with greater transparency to consumers, which can be accomplished through certifications for environmentally cognoscente collectors and those using alternatives like aquaculture and coral farming. Continued participation in Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) and International Coral Reef Initiative (ICRI) is also beneficial. | U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. International Trade in Coral and Coral Reef Species: The Role of the United States. Report of the Trade Subgroup of the International Working Group to the U.S. Coral Reef Task Force, Washington, D.C. World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. U.S. Coral Reef Task Force. 2000. The National Action Plan to Conserve Coral Reefs. Washington, D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Corporate Responses; Cultural Policies; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Live Collection; Manufacturing & Trade; Manufacturing & Trade Policies; Marine Products; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Political Pressure; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Sponges; Stony Coral; Toxics; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Environmental Education: Deliver Non-Enforcement Resource Eductaion at the Resource Site | Voluntary compliance (#50) is the most desirable form of site protection. Lack of compliance often occurs unintentionally, due to a lack of knowledge and understanding. Law enforcement plays a role by ensuring rules are appropriately followed, but often the preventative component of this enforcement becomes secondary, especially on high use days/areas. Volunteers can assist by answering questions and talking to people recreating about the reef, reef resources, and how to appropriately recreate. Volunteers can watch to ensure people are acting appropriately, that boaters do not go too close to shallow reefs, and that groundings do not occur. Programs such as Team OCEAN have contributed over 15,000 hours to such activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Beaches & Nature Parks; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Culture; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Education & Information; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Invertebrate Harvest; Marine Debris; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Social Organizations; Sunscreen Use; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling |
| Evaluating Fishing Gear/Method Impacts: Conduct research on the ecological impacts on sanctuary preservation areas of baiting fishing and catch-and-release fishing by trolling | It is necessary to asses the ecological effects of catch�and-release fishing by trolling and bait-fishing in order to make informed decisions regarding their provisions in protected areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Coral; Culture; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Pressures; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Evaluating Fishing Gear/Method Impacts: Evaluate impacts of existing fishing gear and methods on habitats | Research is needed to investigate impact on habitat of commercial and recreation fishing gear and methods. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Coral; Culture; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Pressures; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Responses; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Socio-Economic Drivers; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Derelict Fishing Gear & Ghost Fishing | The term "ghost fishing" is used to describe the capture of marine organisms by lost or abandoned fishing gear. This is particularly a problem with gillnets, trammel nets and pots. Gear is usually lost because it becomes stuck on rough bottoms containing corals and stones, causing the buoy line to break during retrieval. Nets or pots may continue to fish for years, with captured fish and crustaceans dying and serving as attracting bait for more fish and organisms. Ghost fishing may therefore represent a serious problem in many areas, causing hidden fishing mortality over a long period of time. This management option co-insides with (#63) Respond to Natural Resource Injuries form Derelict Vessels. | Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Arthropods; Artificial Habitat; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Discharges; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Littering; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Debris; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Fishing & Harvesting Management: Research Low-impact Fishing Gear & Methods | Facilitating research to develop gear designs and fishing methods that minimize impacts is multifaceted. Ideal fishing gear is selective for the target species and sizes, with negligible direct or indirect impact on non-target species, sizes and habitats; but also efficient, giving quality, high catches at the lowest possible cost. Newly developed low-impact gear allows fishermen to fulfill their needs, providing food and income, while lessening the unintended environmental impact of those activities, like by-catch. Before an agency should promote new fishing gear or methods research is important to ensure there are no un-intended environmental tradeoffs. Biodegradable fishing line, modified traps, and buoy lines are examples of gear types that could be studied. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boat Movement; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Improved Technology; Invasive Species; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Debris; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Resource Use Management; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Forestry Policy: Forestry Management Planning | There are many aspects to properly managing forestry sites to reduce point source and non-point source pollutants. Forestry activities can degrade water quality with several types of pollutants and impacts, including: sediment, nutrients, forest chemicals like pesticides, organic debris from tree litter, increased water temperature and increased streamflow. The Forestry management plan and practices include, but are not limited to: pre-harvest planning, road construction and use, prescribed burning and fire management, brush management, timber harvest, regeneration, and application of forest chemicals. Wetlands Forest Management has additional best practices. | Environmental Protection Agency Office of Water. 1993. Guidance Specifying Management Measures For Sources Of Nonpoint Pollution In Coastal Waters. EPA/840/B-92/002, US EPA, Washington, DC. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011. National Handbook of Conservation Practices. U.S. Department of Agriculture. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Applied Chemicals; Biological Harvest; Chemical Use Regulations; Civil Engineering & Construction; Deforestation & Devegetation; Discharge Limitations; Ditching & Soil Disturbance; Fertilizer & Pesticide Use; Food & Raw Materials; Forestry; Landscape Changes; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Landuse Management; Manufacturing & Trade; Non-point Source Controls; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrients; Physical & Chemical Water Quality Criteria; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Regulating Services; Resource Use Management; Sediment; Supporting Services; Surface & Groundwater Flow; Toxics; Waterborne Discharges; Wetlands; Wood, Plastics, & Chemical Products |
| Marine Zoning: Permitting Application & Award | This management approach is important because permits assure protection and conservation of coral resources from harmful activities and practices. Within sanctuary waters, special use permits (#157) can be used to allow scientists and others to conduct necessary work while following permitting regulations to reduce the impact of that work. General permits are often required for altering land-use, construction projects and certain discharges. To be eligible for a permit, the operator may be required to conduct impact assessments, institute best management practices and conduct monitoring of the project. Though permits are a necessary precaution, the process can be streamlined through ensuring clear submittal requirements, and reducing redundancy. Redundancy often occurs when multiple agencies must approve a permit, a single point of contact and standard, inter-agency protocols can reduce unnecessary redundancy. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Building & Home Construction; Coastal Development; Collaboration & Partnering; Cultural Policies; Discharges; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Impervious Surfaces; Land-Based Civil Engineering; Landscape Changes; Landuse Management; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Point Source Discharges; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Security & Public Administration Policies; Special Use Permitting |
| Marine Zoning: Sanctuary Preservation Areas (SPAs) | This is a type of Marine Zoning used by the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS). SPAs focus on the protection of shallow, heavily used reefs where conflicts occur between user groups, and where concentrated visitor activity leads to resource degradation. They are designed to enhance the reproductive capabilities of renewable resources, protect areas critical for sustaining and protecting important marine species, and reduce user conflicts in high-use areas. This is accomplished through a prohibition of consumptive activities within these areas. They have been chosen based on the status of important habitat, the ability of a particular area to sustain and protect the habitat, the level of visitor use, and the degree of conflict between consumptive and non-consumptive users. The actual size and location of these zones have been determined by examination of user patterns, aerial photography, and ground-truthing of specific habitats. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Aquaculture; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Artisanal Fishing; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Coastal Development; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Landscape Changes; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Security; Small Boats; Souvenir & Decorative Trade; Supporting Services; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trampling; Travel Services & Tour Operators; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Special Use Areas | Special use areas are set aside for specific scientific or educational purposes. This is in order to encourage the recovery or restoration of injured or degraded resources. Also, the areas may be designated to facilitate access to, or use of, resources, and prevent other user conflicts. Special-use areas are achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts; and determining/establishing appropriate zones for high-impact or user-conflict activities. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Biomedical Research Policies; Complex Habitat & Resources; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Education & Information; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Health Policies; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Social Organizations; Special Use Permitting; Supporting Services; Wetland & Reef Restoration |
| Marine Zoning: Existing Management Areas | The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary (FKNMS) uses this zoning category to identify areas that are managed by other agencies where restrictions already exist. These zones delineate the existing jurisdictional authority of other agencies (i.e., State parks, aquatic preserves, sanctuaries, and other restricted areas). Management of these areas within the Sanctuary may require additional regulations or restrictions to adequately protect resources. Any additional management measures will be developed and implemented in coordination with the agency having jurisdictional authority. Their function is not to establish another layer of bureaucracy, but to recognize established management areas and, at a minimum, to complement the existing management programs, ensuring cooperation and coordination with other agencies. Existing Management Areas will be maintained through revising GIS and NOAA charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation; Water Transportation |
| Marine Zoning: Wildlife Management Areas (WMAs) | Wildlife Management Areas include bird nesting, resting, or feeding areas, turtle nesting beaches, and other sensitive habitats including shallow flats that are important feeding areas for fish. These areas seek to provide protection for endangered/threatened species or their habitats while at the same time providing opportunity for public use. Wildlife Management Areas are achieved through placing and maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; implementing management responsibilities; adjusting existing zone boundaries if needed; evaluating allowable activities within the boundaries and make changes if needed; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; monitoring the effectiveness of current zones; and revising GIS and NOAA charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Beaches & Nature Parks; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Coastal Defense; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designate Protected Species; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Entertainment & Accommodation Services; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Landscape Conservation & Restoration; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Utilize Marine Protected Areas for Research and Monitoring | Research and monitoring of marine protected areas determine the degree to which the zones meet goals and objectives for protecting natural resources, as well as human-use patterns, attitudes and compliance. Once data is gathered from within the protected zone it can than be compared to comprable data from outside the protected zone, as a control. It is necessary to compile and review data on use patterns to determine where additional Special-Use Areas would be appropriate. Research in the protected area should be non-invasive. It is important to make the protected area available for external research as well. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Collaboration & Partnering; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Fish; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Landscape Changes; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Special Use Permitting; Wetlands |
| Marine Zoning: Ecological Reserves (ERs) | Ecological Reserves set aside areas with minimal human interference. These reserves aim to enhance and protect biodiversity through encompassing large, contiguous habitats. The goal of ecological reserves is to encourage spawning, nurseries, and residence areas that contribute to genetic protection of fish and marine life. Ecological Reserves can be achieved through a variety of methods such as: placing/maintaining buoys along zone boundaries; adjusting boundaries if necessary; evaluating allowable activities within zone boundaries; identifying potential areas that need additional zoning; reviewing the effectiveness of the zoning; and revising NOAA and GIS charts. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Coastal Defense; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Cruise Ships; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Oil & Gas Tankers; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Trampling; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Research Queen Conch Reproduction and Restoration | Inshore Queen Conch may be experiencing reproductive failure. Research on various snails in other parts of the world has shown that snails are susceptible to endocrine disruption caused by various anthropogenic contaminants. This activity will determine the cause of reproductive failure, possibly by endocrine disruption, of queen conch in reef areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Applied Chemicals; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Discharges; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring & Restoration; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing Sector; Invertebrates; Molluscs; Recreational Fishing; Reef Inhabitants; Snails & Conch; Waterborne Discharges |
| Monitor & Research: Biological Status and Trends Monitoring | This activity produces long-term comprehensive information on sanctuary-wide status and trends of biological resources. Data that could be collected on coral reef communities includes but is not limited to species abundance and density, biodiversity, benthic cover, coral condition, growth, recruitment, predation, and grazing. Mangroves and seagrasses should also be monitored. With adequate baseline data, changes in community structure and biocriteria can be identified and restoration or protection efforts can be taken. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Algae; Anemones & Zooanthids; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Aquarium Stock; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biocriteria; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Bivalves; Calcareous Macroalgae; Contact Uses; Coral; Coralline Algae; Cyanobacteria; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Invertebrates; Large Herbivorous Fish; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Products; Marine Vertebrates; Marine Worms; Microorganisms; Molluscs; Octocoral; Octopus & Squid; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Pathogens; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Primary Production; Provisioning Services; Resource Use Management; Sea Turtles; Sea Urchins; Seagrasses; Seastars; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tunicates; Wetlands; Whales & Dolphins |
| Monitor & Research: Survey and Collect Anecdotal Information | Anecdotal information is to be solicited from experts and amateur public participation through surveys and workshops. Persons of interest include fishermen, recreational divers, recreational dive facilities, salvors and other locals with knowledge of marine resources in the area. Information they provide can help identify marine cultural and natural resources and help update resource inventory. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Regulations; Coastal Engineering; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Cultural Policies; Cultural Protections; Cultural Services; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Products; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Responses; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Valuation; Water Transportation |
| Monitor & Research: Fisheries Sampling | Improved fisheries sampling programs require improving the spatial resolution of commercial and recreation fisheries-dependent and fisheries-independent sampling programs to provide statistics on catch and effort. Improved sampling can be achieved through evaluating and enhancing census programs by using smaller sampling areas. Also, fishery pre-recruitment monitoring efforts should be continued for long-term prediction of fishery stocks. Last, investigating life histories of fishery species needs to be conducted because it is currently a gap. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Security & Public Administration Policies; Small Herbivorous Fish |
| Public Participation: Assist Seafood Watch | Assist Seafood Watch and other sustainable seafood consumption initiatives, in their efforts to educate the public and promote sustainable seafood. | The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. SeafoodWatch. 2005. Sustainable Seafood Business Practices. Monteray Bay. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Aquaculture; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Molluscs; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Sectors Filling Human Needs |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Consider Regulations for Catch & Release Trolling | This plan seeks to reduce or eliminate catch-and-release fishing in many fragile areas. First an assessment must be conducted to measure the effects of catch-and -release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Develop Mobile Source Discharge Controls | Pollution discharge controls regulate where different types of discharges are allowed and what acceptable quantities released are. Typically discharge controls target point sources in the form of effluent pipes (#280), but discharges also occur from mobile sources such as boats and ships. There may need to be revisions on where depositing fish, fish parts, bait, cooling water, engine exhaust, deck wash, and effluent can be released. In many areas, these items are often excluded as prohibited, and they should possibly be included. Pollution discharge controls are different from Water Quality Standards (#22) which set acceptable environmental limits and leave it up to the manager to meet those criteria. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Artisanal Fishing; Ballast Discharge; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Chemical Variables; Coastal Engineering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Discharge Limitations; Discharges; Docks & Marinas; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Large Ships; Littering; Oil & Gas Tankers; Physical Damage; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Point Source Discharges; Ports & Harbors; Recreational Fishing; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Wastewater Discharge; Water Transportation; Waterborne Discharges |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Ensure Consistency Among Fishing Regulations | Consistency will improve administrative and regulatory coordination between fisheries regulatory agencies. This involves using a protocol for drafting and revising fisheries regulations in order to implement a consistent set of regulations throughout the protected reef area. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Security; Security & Public Administration Policies; Security Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Activities Allowed in Existing Regulatory Zones | There are five different types of regulatory zones within the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary: Ecological Reserves, Sanctuary preservation Areas, Wildlife Management Areas, Existing Management Areas, and Special Use Areas. Each zone has a different set of prohibited or allowable activities. This type of diversity in zones allows for visitors to partake in the activity they desire, but in an area where the impact will be less severe. Allowable activities require periodic evaluation and may need to be changed or relocated to allow for recovery or to address other issues of concern. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Fishing Sector; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Tourism & Recreation |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Aquaculture/Mariculture Regulations | This will help determine if there is a need to establish mariculture operations regulations and proceed accordingly. This would help satisfy the commercial demand for fish while taking pressure off of the wild species. Such regulations should consider where, when and what species of mariculture are allowable. The environmental impact mariculture has can vary depending on current, depth and distance to land, making location and even season important. The species being cultured is also an important consideration, especially if they are non-native or different genetically from the local natural population as escapes may occur. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. NEPA. 1998. MARICULTURE DRAFT POLICY AND REGULATION NATURAL RESOURCES CONSERVATION AUTHORITY COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT DIVISION. National Environment & Planning agency. |
Agriculture, Aquaculture, & Forestry Policies; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Designated Uses; Domestic Animal Waste; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Food & Energy Policies; Food & Raw Materials; Invasive Species; Resource Use Management; Supplemental Feeding |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Bait Fishing and/or Catch & Release Trolling Regulations | This option seeks to reduce or eliminate bait fishing, and catch & release trolling in fragile areas. First assessments must be conducted to measure the effects of bait fishing and catch & release trolling. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Spearfishing Regulations | Spearfishing is already prohibited in ecological reserves, sanctuary preservation areas, management areas, and special-use areas. There are additional considerations to be made to see if restrictions need to be extended in high priority areas. There may also be need to be further scientific study on the impacts of spearfishing. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Culture; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Sectors Filling Human Needs; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Regulatory Review and Development: Evaluate Fishing Gear/Fishing Methods Regulations | In most regions there are already regulations that prohibit fishing methods that incorporate explosives, poisons, oil, and bleach. Further investigation may reveal additional methods, materials, or gear that should be prohibited as well. Regulations should aim to increase the use of low-impact gear (#194) in place of more destructive gear and methods. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Cochrane, K.L., editor. 2002. A Fishery Manager's Guidebook. Management Measures and their application. Fisheries Technical Paper 424, FAO, Rome. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Harvest; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Decision Support; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security & Public Administration Policies; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Regulations for Sponge Fisheries | Sponges play a vital role on reefs, providing structure, food and filtration. Depending on the method of removal, this process can be very destructive to other reef fauna and habitat. Research is needed to compare impacts of different sponge fishing methods in different areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boring Sponges; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Culture; Cyanobacteria; Educational & Research Opportunities; Encrusting Sponges; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Microorganisms; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Tube, Barrel, & Finger Sponges |
| Resource Use Management: Develop Live Collection Regulations | Live collection is often more destructive than capture of food fishes because of the destructive methods used to remove live fish and invertebrates from the reef habitat. These methods include use of cyanide and explosives. Current methods should be assessed and alternatives should be developed or collection prohibited. | World Resource Institute International Marinelife Alliance, editor. 1997. Sullied Seas. WRI, Washington D.C. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Contact Uses; Educational & Research Opportunities; Finfish Harvest; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Products; Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics Sources; Physical Damage; Resource Use Management; Scientific Research; Sponges; Toxics; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage; Wholesale & Retail Trade |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Catch Quotas | Quotas designate the Total Allowable Catch (TAC) allocated to an operating unit such as a country, a vessel, a company or an individual fisherman (individual quota) depending on the system of allocation. Quotas may or may not be transferable, inheritable, and tradable. While generally used to allocate total allowable catch, quotas could be used also to allocate fishing effort or biomass. | Seas At Risk. 2009. Moving Towards Low Impact Fisheries In Europe Policy Hurdles & Actions. |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boat Movement; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Raw Materials; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Snails & Conch; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Resource Use Management: Fisheries Management Enforcement | Marine protected areas and other types of coastal zone management areas have fisheries management policies that must be enforced in addition to the broader Statues, Regulation and Permit Requirements (#91). Illegal, unregulated and unreported (IUU) fishing is a major problem worldwide. Management area policies must be enforced to have an impact on the fisheries stock. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Commercial Fisheries; Decision Support; Designated Uses; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Live Collection; Marine Protected Areas; Mitigation; Permitting & Zoning; Physical Damage; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Security Policies; Special Use Permitting; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage | |
| Resource Use Management: Seasonal Fisheries and Harvesting | Finfish and shellfish stocks may be more or less susceptible to fishing pressures during certain times of the year. This may be due to seasonality of recruitment and/or changes in food/predation pressures. If fishing restrictions may be more successful if this seasonality is taken into consideration and fishing pressure adjusted accordingly. | Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Artisanal Fishing; Biochemical & Genetic Resources; Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Corallivorous Fish; Decision Support; Echinoderms; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fisheries & Hunting Policies; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Food & Energy Policies; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertivorous Fish; Large Herbivorous Fish; Live Collection; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Products; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Permitting & Zoning; Piscivorous Fish; Planktivorous Fish; Provisioning Services; Recreational Fishing; Small Herbivorous Fish; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Tourism & Recreation Policies | |
| Restoration: Removal of Invasive Algae | Benthic organisms on reefs maintain a delicate balance competing for space. In many areas, the competition between coral and algae has fallen out of balance due to confounding factors. Factors such as decreased herbivorous fish and invertebrates, and invasive algae species have allowed faster growing algae to take over many reefs, often growing into smothering mats that cover and kill coral. In Hawaii, there has been some success physically removing invasive algae such as Kappaphycus using underwater vacuums extended down from barges or volunteer events in shallower areas. | The Nature Conservancy. 2010.Two Million Pounds of Invasive Algae Removed From Maunalua Bay. (not cited) |
Algae; Aquaculture; Biological Addition; Biological Harvest; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Calcareous Macroalgae; Collaboration & Partnering; Coral; Coralline Algae; Decision Support; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Escape & Release of Non-natives; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Fleshy Macroalgae; Hydrocoral; Invasive Species; Large Herbivorous Fish; Octocoral; Reef Habitat; Skeletal Coral; Small Herbivorous Fish; Stony Coral; Turf Algae; Wetland & Reef Restoration; Zooxanthellae |
| Waterway Management: Mooring Buoy Management | Installing mooring buoys is encouraged in order to prevent damage to corals from anchors. Areas that experience a lot of traffic from recreation and fishing will experience damage from vessel groundings and boat gear. Mooring buoys help to minimize damage to corals and at the same time provide access to water resources. Mooring buoys protect as well as lower resource-use conflicts. Mooring buoy management is achieved through maintaining existing mooring buoys; assessing current buoy technology; reviewing visitor-use and boating data; developing sitting criteria; recommending new sites; conducting site assessments; installing additional buoys; and implementing vessel size limits in high-use and sensitive areas. | NOAA Marine Sanctuary Program. 2007. Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary revised management plan. National Ocean Service, Key West, FL. Altmeier, Bernie. FKNMS Mooring Buoy Mainenance. NOAA: FKNMS Mooring Buoy Manual Accessed 3/23/2011. The Coral Reef Alliance (CORAL) the Tour Opperators' Iniative (TOI) and The Center for Environmental Leadership in Business (CELB). 2003. A Practical Guide to Good Practice: Managing Environmental Impacts In The Marine Recreation Sector. |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Artisanal Fishing; Biological Harvest; Boating Activities; Boating Regulations; Contact Uses; Cultural Services; Designated Uses; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Physical Damage; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation; Water Resources; Water Transportation |
Laws
| Legal Citation | Purpose of Law | Management Organization | Database Topics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amendment to the U.S. Caribbean Fishery Management Plans, Code of Federal Regulations § 600 and 622. | NMFS issues this final rule to implement a comprehensive amendment prepared by the Caribbean Fishery Management Council (Council) to amend its Reef Fish, Spiny Lobster, Queen Conch, and Coral Fishery Management Plans (FMPs). The comprehensive amendment is designed to ensure the FMPs are fully compliant with the provisions of the Magnuson-Stevens Fishery Conservation and Management Act (Magnuson-Stevens Act). This final rule redefines the fishery management units for the FMPs; establishes seasonal closures; imposes gear restrictions and requirements; revises requirements for marking pots and traps; and prohibits the filleting of fish at sea. In addition, the comprehensive amendment establishes biological reference points and stock status criteria; establishes rebuilding schedules and strategies to end overfishing and rebuild overfished stocks; provides for standardized collection of bycatch data; minimizes bycatch and bycatch mortality to the extent practicable; designates essential fish habitat (EFH) and EFH habitat areas of particular concern (HAPCs); and minimizes adverse impacts on such habitat to the extent practicable. The intended effect of this final rule is to achieve optimum yield in the fisheries and provide social and economic benefits associated with maintaining healthy stocks. Application to Coral Reefs:Protects coral reefs in the USVI and Puerto Rico from overfishing reef resources, specifically reef fish, lobster, and queen conch taking. It establishs seasonal closures, restrictions on the gear used, lists areas of specific biological reference points, and has a schedule and strategy for restocking fishery resources. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fisheries; Ecosystem Monitoring & Restoration; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Recreational Fishing; Reef Inhabitants |
| Anadromous Fish Conservation Act of 1965, as amended, 16 United States Code § 757. | The Act is intended to conserve anadromous fish. It authorizes the Secretatries of Interior and Commerce to enter into cooperatve agreements with states and other non-federal interests for conservation, development and enhancement of anadromous fish and contribute up to fifty percent as the federal share of the cost of carrying out such agreements. Reclamation construction projects for water resource projects needed solely for such fish are also authorized. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:Projects are for conservation, development, and enhancement on fisheries. Comments: |
Department of Interior/Department of Commerce Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biocriteria; Collaboration & Partnering; Designate Protected Species; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, 18-18 Florida Administrative Code. | 18-18.001 Intent.
(1) The Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, the boundaries of which are fully described in Rule 18-18.002, F.A.C., was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations.
(2) These rules shall apply to all lands public and private within the boundaries of the preserve. However, privately owned uplands shall be excluded from these rules except as otherwise provided for herein.
(3) In promulgating and implementing these rules, it is the intent of the Department to construe the provisions of Sections 258.397 and 258.35 through 258.46, F.S., together and to apply the more stringent statutory provisions for the maintenance of the preserve.
(4) The preserve shall be administered and managed in accordance with the following goals:
(a) To preserve, protect, and enhance Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay by reasonable regulation of human activity within the preserve through the development and implementation of a comprehensive management program;
(b) To protect and enhance the waters of the preserve so that the public may continue to enjoy the traditional recreational uses of those waters such as swimming, boating and fishing;
(c) To coordinate with federal, state, and local agencies to aid in carrying out the intent of the legislature in creating the preserve;
(d) To use applicable federal, state, and local management programs, which are compatible with the intent and provisions of the Act and these rules, to assist in managing the preserve;
(e) To encourage activities that protect or enhance the biological and aesthetic values of the preserve, including but not limited to the modification of existing manmade conditions towards their natural condition, when reviewing applications or developing and implementing management plans for the preserve;
(f) To preserve and promote indigenous life forms and habitats including but not limited to sponges, soft corals, hard corals, seagrasses, mangroves, mud flats, marine reptiles, game and non-game fish species, marine mammals, tropical marine invertebrates, birds and shellfish;
(g) To acquire additional title interests in land wherever such acquisitions would serve to protect or enhance the biological or aesthetic values of the preserve. Application to Coral Reefs:Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve protection of water quality will contribute to a lowering of contaminants leaving the preserve on tides and thus limiting the contaminants that reach off-shore ecosystems including the FKNMS and the reef system within the sanctuary. Legislative Actions: Comments:This chapter establishes the rules to protect the Biscayne Bay Aquatic Preserve, which was established for the purpose of preserving and enhancing Biscayne Bay and all natural waterways tidally connected to the bay in an essentially natural condition so that its biological and aesthetic values may endure for the enjoyment of future generations. |
Florida State Department of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: Designated Marine Areas |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boat Movement; Coastal Development; Docks & Marinas; Dredging Regulations; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Hydrologic Management; Landuse Management; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Marine Debris; Nutrients; Point Source Discharges; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Seawater Flow; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Small Boats; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Chapter 1: Wildlife including protected areas, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates hunting, including for migratory birds, wildlife restoration, establishes and regulates wildlife and marine sactuaries and game preserves. Application to Coral Reefs:The coral reefs of the US Virgin Islands are within the boundaries off the marine sanctuaries and therefore have the same protection that marine sanctuaries have. Special licenses are required for scientific investigation and for collectors. In wildlife and marine sanctuaries, except under proper permit, taking or posessing any bird, fish, or other wildlife is illegal. Discharge of a firearm or release of arrows (spearfishing) in wildlife or marine sanctuaries is illegal. No form of waste can be thrown, placed or deposited in a wildlife or marine sanctuary. Legislative Actions:The Commissioner or any USVI resident can commence a civil action. Civil penalties for violators are not to exceed $50,000 per day. Any knowingly or negligently discharging polluants can be crimimnally punished with a fine of not less than $5,000 nor more Comments:Commissioner of Planning and Natural Resources can designate and establish wildlife and marine sanctuaries, and accept monitary and animal donations from the United States. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Arthropods; Bivalves; Complex Habitat & Resources; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Fish; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Marine Vertebrates; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Wetlands |
| Chapter 2: Protection of indigenous, endangered and threatened fish, wildlife and plants, 12 Virgin Islands Code. | Regulates activities, including scientific research, that could affect indigenous species and species considered at risk (threatened) or endangered, establishes species of special concern and habitats that should be protected, requires permits for trimming mangroves Application to Coral Reefs:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Legislative Actions:It is illegal to take or posses "live rock" which is defined as dead or live coral. It is illegaal to cut all three species of mangrove trees. Forbidding the takeing of coral directly protects coral species. Not cutting mangraoves will aid in sediment control and the removal of nutrients that could enter coral reef areas. The Commission can designate habitats for listed threatened or endangered species. Comments: |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Aquarium & Pet Trade; Aquarium Stock; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Ornamental Jewelry & Art; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals, 73 Federal Register § 6895 (2008). | To make it unlawful, to import or export the species into or from the US, to take the species within the US or territorial seas of the US, to take the species upon the high seas, to possess, sell, deliver, carry, transport, or ship by any means whatsoever the species taken in violation, to deliver, receive, carry, transport, or ship in interstate or foreign commerce, by any means whatsoever and in the course of a commercial activity the species, to sell or offer for sale in interstate or foreign commerce the species, to violate any regulation pertaining to the species. Application to Coral Reefs:The deignation of Acropa palmeta and Acropa cervicornis as threathened species will allow the species advantages in recovery. The designation protects the reef habitat because the species must have the reef to reproduce and grow. Legislative Actions:Section 11 of the ESA provides civil and criminal penalties for a violation of the ESA. Comments: |
NOAA Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Virgin Islands; Puerto Rico |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Recreational Opportunities; Skeletal Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Endangered and Threatened Species; Critical Habitat for Threatened Elkhorn and Staghorn Corals; Final Rule, 73 Federal Register § 72210. | We, the National Marine
Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final
rule designating critical habitat for
elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and
staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which
we listed as threatened under the
Endangered Species Act of 1973, as
amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four
specific areas are designated: the Florida
area, which comprises approximately
1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of
marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area,
which comprises approximately 1,383
square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine
habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area,
which comprises approximately 121
square miles (313 sq km) of marine
habitat; and the St. Croix area, which
comprises approximately 126 square
miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We
are excluding one military site,
comprising approximately 5.5 square
miles (14.3 sq km), because of national
security impacts. Application to Coral Reefs:The law protects coral habitat for elkhorn and staghorn coral which strenghtens their protection in the FKNMS, Puerto Rico, and US Virgin Islands. Legislative Actions: Comments:the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), issue a final rule designating critical habitat for elkhorn (Acropora palmata) and staghorn (A. cervicornis) corals, which we listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act of 1973, as amended (ESA), on May 9, 2006. Four specific areas are designated: the Florida area, which comprises approximately 1,329 square miles (3,442 sq km) of marine habitat; the Puerto Rico area, which comprises approximately 1,383 square miles (3,582 sq km) of marine habitat; the St. John/St. Thomas area, which comprises approximately 121 square miles (313 sq km) of marine habitat; and the St. Croix area, which comprises approximately 126 square miles (326 sq km) of marine habitat. We are excluding one military site, comprising approximately 5.5 square miles (14.3 sq km), because of national security impacts. |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; US Territories; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas; US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Recreational Fishing; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Estuaries and Clean Waters Act of 2000, 33 United States Code §§ 2901 et seq. | Creates a federal interagency council that includes the Director of the Fish and Wildlife Service, the Secretary of Army for Civil Works, the Secretary of Agriculture, the Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency, and the Administrator of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. The council is charged with developing a national estuary habitat restoration strategy and providing grants to entities to restore and protect estuary habitat to promote the strategy. Application to Coral Reefs:Protecting water quality in estuaries will help mitigate the impacts of water pollution which inturn would help mitigate ocean acidification. Legislative Actions:The Act authorized the formation of the Estuary Habitat Restoration Council that was responsible for developing a National Habitat Restoration Strategy. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service, US Army Corps of Engineers, Department of Agriculture, US Environmental Protection Agency, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: United States |
Ballast Discharge; Building & Home Construction; Collaboration & Partnering; Dredging, Draining, & Filling; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Forestry; Funding & Donations; Mangroves; Marine Birds; Mining; Non-point Source Runoff; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Nutrients; Remediation; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Sewage Treatment; Solid Waste Disposal; Waste Management; Waste Management Policies; Wastewater Discharge |
| Exec. Order No. 12962, Recreational Fisheries, 60 Federal Register (1995). | Federal agencies are directed to improve the quantity, function, sustainable productivity, and distribution of U.S. aquatic resources for increased recreational fishing opportunities in cooperation with states and tribes. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Funding & Donations; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Act of 1956, as amended, 16 United States Code § 742. | Established a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on commercial fishing industry but also with a direction to administer the Act with regard to the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments:The 1998 amendments promoted voluteer programs and community partnerships for the benefit of national wildlife refuges. |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Bivalves; Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Economic Markets & Policies; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Donations; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Political Pressure; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Snails & Conch; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Fish and Wildlife Conservation Act of 1980, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | Required the Service to monitor non-game bird and fish species, identify species of management concerns, and implement conservation measures to preclude the need for listing under the Endangered Species Act. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Designate Protected Species; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Funding & Incentives; Marine Birds; Marine Protected Areas; Public Administration; Resource Use Management |
| Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act, 16 United States Code §§ 2901-2911. | To provide financial and technical assistance to the states for development, revision and implementation of conservation plans and programs for nongame fish and wildlife, and to encourage federal agencies to utilize their statutory and administrative authority to conserve and to promote the conservation of nongame fish and wildlife and their habitats. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions: Comments: |
Federal Agencies Jurisdiction: United States |
Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Funding & Incentives; Microorganisms; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration |
| Fish and Wildlife Service Act of 1956, 16 United States Code § 742. | Establishes a comprehensive national fish, shellfish, and wildlife resources policy with emphasis on the commercial fishing industry but also includes the inherent right of every citizen and resident to fish for pleasure, enjoyment, and betterment, and to maintain and increase public opportunities for recreational use of fish and wildlife resources. Among other things, it authorizes the Secretary of the Interior to take such steps as may be required for the development, advancement, management, conservation, and protection of fish and wildlife resources, including, but not limited to, research, development of existing facilities, and acquisition by purchase or exchange of land and water or interests therein. Application to Coral Reefs: Legislative Actions:The Act is written for the support of commercial and recreational fisherpersons so that they enjoy the benefits of the Nation's fishery resources. Comments: |
US Fish and Wildlife Service Jurisdiction: |
Commercial Fisheries; Designate Protected Species; Environmental Education & Outreach; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Public Administration; Recreational Fishing; Resource Use Management; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations, Federal Register § Volume 66, Number 11 (2001). | NOAA established the Tortugas Ecological Reserve (a no-take zone) in the Tortugas region (Tortugas or region) of the Florida Keys to protect significant coral resources and to protect an area that serves as a source of biodiversity for the Sanctuary as well as for the southwest shelf of Florida. Establishment of the Reserve included expansion of the Sanctuary boundary to ensure that the Reserve protects sensitive coral habitats lying outside the existing boundary of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Regulation protects significant coral resources and many marine species by providing a no-take zone. Legislative Actions:The regulation increased the no-take zones to 24 areas. Fishing is prohibited in Tortugas north for areas that are within State waters. Diving is prohibited in Tortugas south. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Jurisdiction: US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Biological Harvest; Bivalves; Boating Activities; Commercial Fisheries; Coral; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Lobster, Crab, & Shrimp; Marine Protected Areas; Molluscs; Octopus & Squid; Recreational Fishing; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Sea Urchins; Seastars; Snails & Conch; Sponges; Stony Coral; Tourism & Recreation; Trawling & Fishing Gear Damage |
| Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary Regulations; Final Rule, Code of Federal Regulations § Parts 922, 929, 937 (1997). | NOAA developed the comprehensive Final Management Plan for the FKNMS and issued the Plan on January 30, 1997. Congress and the Governer of Florida were provided a 45-day period to provide certification of unacceptable regulations that needed amendments. NOAA incorporated the certified changes provided and issued the final regulations and management plan for the Sanctuary that went into effect with the publication of the final rule, including waters within the State of Florida in the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the third largest barrier coral reef in the world. Included in the FKNMS are the Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 square nautical miles of coral reefs. The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive. The Act protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, further protecting coral, mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act requires the preparation of a comprehensive management plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:The final rule codifies the Act and further defines boundaries of the Sanctuary as well as providing a list of species protected in the Sanctuary. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric and Administration Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Territorial Waters; State Coastal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Ballast Discharge; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Boating Regulations; Collaboration & Partnering; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Cultural Protections; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Invertebrates; Large Ships; Live Collection; Mangroves; Marine Debris; Nutrient & Contaminant Processing; Oil & Gas Tankers; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Inhabitants; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Sediment; Shoreline Protection; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Transportation Policies; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| Magnuson-Stevens Fisheries Conservation and Management Reauthorization Act as amended through January 2007, Statutes at Large §§ 94-265. | National program for the conservation and management of fishery resources of the US to prevent overfishing, to rebuild overfished stocks, to facilitate the long-term protection of essential fish habitat, and to realize the full potential of the Nation's fishery resources. Application to Coral Reefs:Promote the protection of essential fish habitat in the review of projects conducted under federal permits, licenses, or other authorities that effct or have the potential to affect such habitats. The amendments of 2006 specifically require the protection of deep sea coral habitats. Legislative Actions:Requires government observers on board a certain number of fishing vessels. The Act provides for criminal and civil penalties dependent on the sections of the Act under which violations occured. Criminal penalties may be imposed up to a maximum of $50,000 and not more than one year in prison. Civil penalties may be imposed including seizure, forfeiture, and condemnation of property. Comments: |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration/National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: United States |
Apex Fish Predators; Biological Monitoring & Restoration; Commercial Fisheries; Commercial Fishing Boats; Complex Habitat & Resources; Economic Markets & Policies; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Fishing Sector; Marine Protected Areas |
| Proclamation No. 7392, The Buck Island Reef National Park, 66 Federal Register 7335-7336 (2001). | 18,000 acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:The Proclamation expanded the original momument thus protecting additional coral reefs within the monument boundaries. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Commercial Fishing Boats; Cruise Ships; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Fishing; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Proclamation No. 7399, Establishment of Virgin Islands Coral Reef National monument, 66 Federal Register 7364 (2001). | Designated 12,000 marine acres in the US Virgin Islands Application to Coral Reefs:Monuments include coral reefs thereby providing the coral reefs within the monument bondaries the same protection as the designated monument areas. Legislative Actions: Comments:Together, Proclamation 7399 and 7392 designated a total of 30,843 marine acres in the United States Virgin Isalnds as monuments. |
US Virgin Islands, Department of Planning and Natural Resources, Division of Environmental Protection Jurisdiction: US Virgin Islands |
Building & Home Construction; Commercial Fishing Boats; Designate Protected Species; Dive, Snorkeling, & Swimming Tourism; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fishing Sector; Invertebrate Harvest; Mangroves; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Resource Use Management; Road Construction & Maintenance; Seagrasses; Small Boats; Tourism & Recreation Policies |
| Sikes Act of 1960, 16 United States Code § 670. | Promote effectual planning, development, maintenance, and coordination of wildlife, fish, and game conservation and rehabilitation in military reservations. Application to Coral Reefs:The Integrated Natural Resources Management Plan (INRMP) required by the Sikes Act integrate many different aspects of natural resource management including endangered species, fisheries, wetlands and environmental contaminants. Protection of wetlands and regulation of the discharge of environmental contaminants on military installations can indirectly protect coral reefs by decreasing runoff to nearshore waters. Legislative Actions:DoD must develop and implement Integrated Natural Resources Management Plans (INRMP) for nearly 380 military installations across the US. The development of the INRMP is a voluntary, cooperative effort between participating agencies. Comments:The preparation of the INRMP between DoD, USFWS and State FWS ensures proper consideration of fish, wildlife and habitat needs. The amendments also require the control of invasive species, migratory birds, and law enforcement issues. |
Department of Defense/Department of Interior (US Fish and Wildlife Service)/State Fish and Wildlife Agencies Jurisdiction: US Military Installments |
Biological Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Environmental Monitoring, Mapping, & Scientific Research; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Finfish Harvest; Invasive Species; Marine Birds; Non-point Source Controls; Point & Mobile Source Controls; Public Administration; Resource Use Management; Waste Management Policies; Wetlands |
| The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary and Protection Act, Public Law 101-605 (H.R. 5909 United States Code (1990). | To protect the resources of the area delineated in section 5(b) of the Act, to educate and interpret for the public regarding the Florida Keys marine environment, and to manage such human uses of the Sanctuary consistent with the Act. Nothing in the Act is intended to restrict activities that do not cause adverse effects to the resources or property of the Sanctuary or that do not pose harm to the users of the Sanctuary. Application to Coral Reefs:The Sanctuary sets aside the coral reef system that is the thrid largest coral reef barrier in the world. Included in the FKNMS are Key Largo Marine Sanctuary containing 103 square nautical miles of coral reefs and Looe Key National Marine Sanctuary containing 5.32 squared nautical miles of coral reefs.The Act protects the reefs from anchoring directly into the coral formation and taking coral dead or alive in the Sanctuary. From Miami to the Marquesas Keys there are over 6000 patch reefs. The Act also protects mangrove islands and submerged aquatic vegetation, both potential buffers for the reef system against eutrophication and sediment deposition. The Act prohibits oil and hydrocarbon exploration, mining or altering the seabed, restricts large shipping traffic, and restricts the discharge of pollutants, futher protecting mangroves, and submerged aquatic vegetation. Legislative Actions:The Act required the preparation of a comprehensive mangement plan and implementing regulations to protect Sanctuary resources. Comments:Large vessel groundings on coral reefs in the Florida Keys was a major driver for the designation of the Sanctuary. In 1989, there were three groundings of large commercial vessels on the coral reef tract within an eighteen day period. |
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration as lead agency and Florida Department of Environmental Protection, Florida Fish and Wildlife Commission, and Monroe County as Co-Trustees Jurisdiction: US Coral Reefs; US Federal Waters; US State Waters; Designated Marine Areas |
Anchoring & Vessel Grounding; Ballast Discharge; Boating Regulations; Complex Habitat & Resources; Coral; Economic Markets & Policies; Educational & Research Opportunities; Environmental Education & Outreach; Existence Value & Sense of Place; Finfish Harvest; Fish; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Invertebrate Harvest; Large Ships; Marine Debris; Marine Protected Areas; Recreational Opportunities; Reef Habitat; Reef Inhabitants; Reef Life; Shoreline Protection; Substrate; Tourism & Recreation Policies; Water Transportation |
| The Sustainable Fisheries Act, 23 §§ 104-297 (1996). | To amend the Magnuson Fisheries Conservation and Management Act to authorize appropriations, to provide for sustainable fisheries, and for other purposes. Application to Coral Reefs:The law recogonizes that direct and indirect habitat losses have resulted in a diminshed capacity to support existing fish levels. Habitat considerations should receive increased attention for conservation and management of fishery resources in the United States. Therefore, the Act encourages, though not indirectly, the protection of coral reefs. Legislative Actions: Comments: |
National Marine Fisheries Service Jurisdiction: US Federal Waters |
Accidental & Illegal Harvest; Apex Fish Predators; Commercial Fisheries; Economic Markets & Policies; Finfish & Shellfish Stock; Fishing & Harvesting Management; Mangroves; Seagrasses |
